Periods and Amplitudes of Southern Pine Beetle Infestations under Climate Change
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Estimating the Relationship between SPB Infestation Risk and Climatic and Other Factors
2.1.1. Generalized Linear Model with a Fractional Response Variable
2.1.2. Empirical Model and Data
2.2. Projecting Climate Change Impacts on SPB Infestations
2.3. Analyzing the Cyclical Patterns of SPB Infestations
3. Results
3.1. Estimated Relationship between SPB Infestation Risk and Climatic and Other Factors
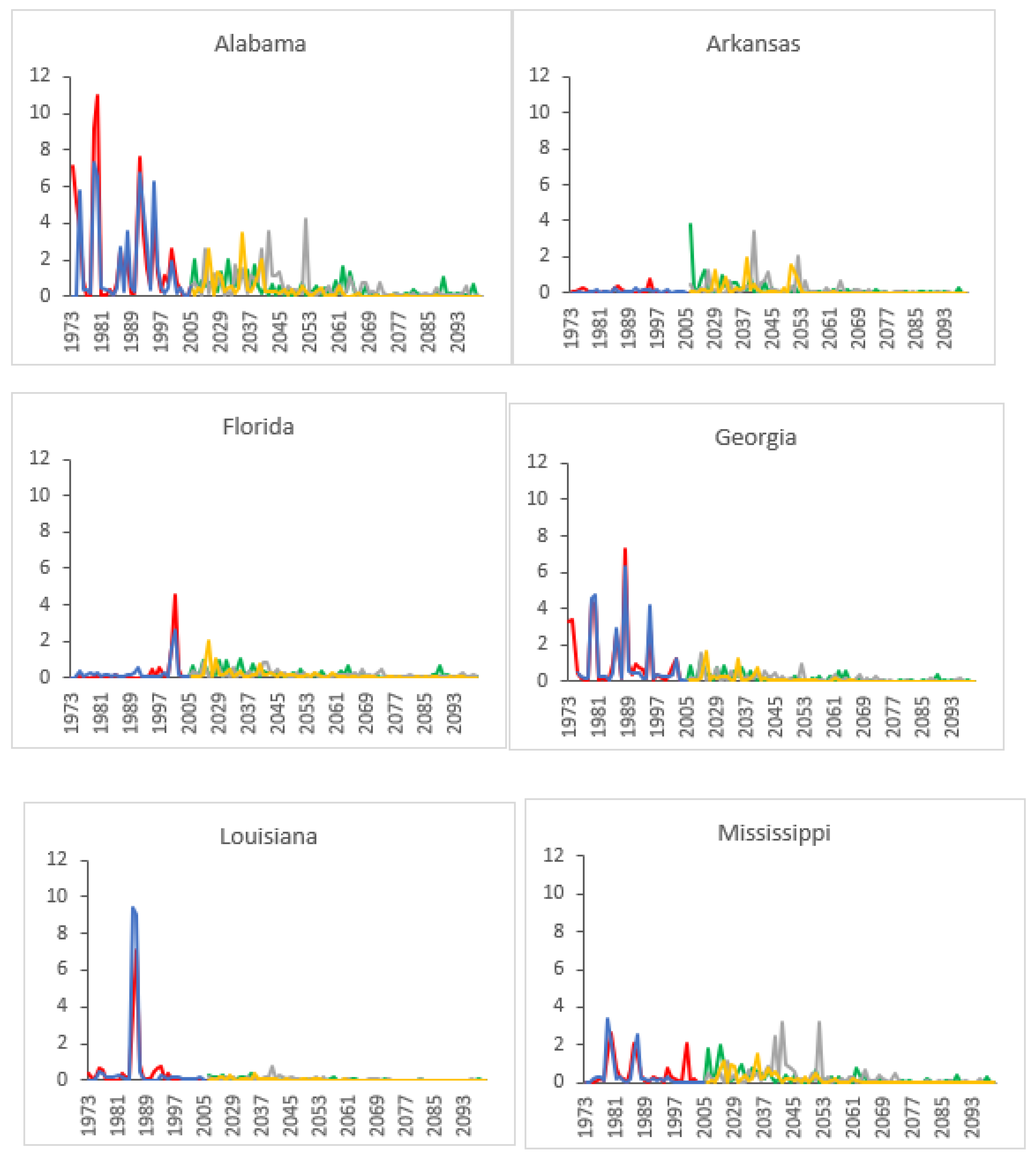
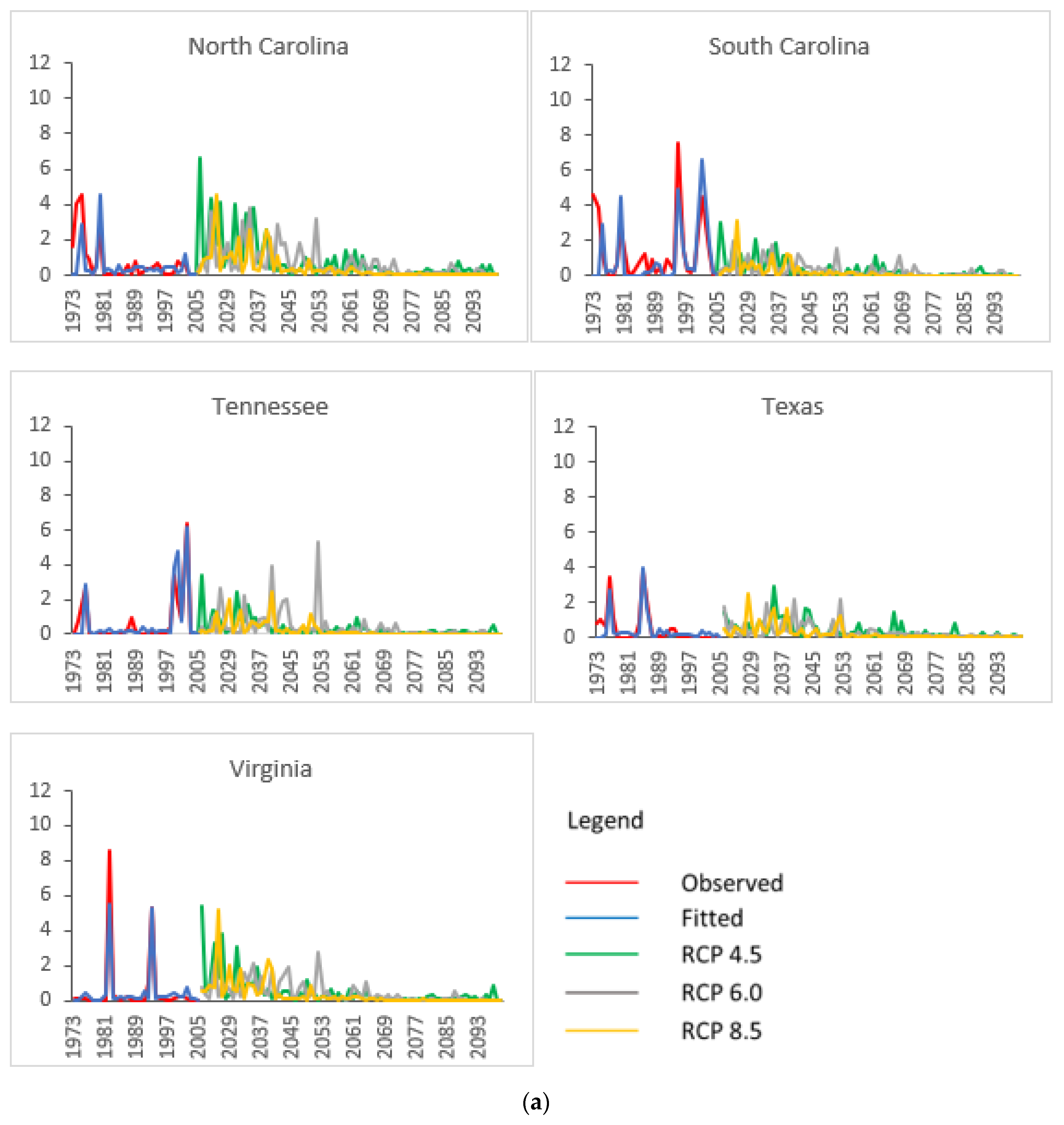
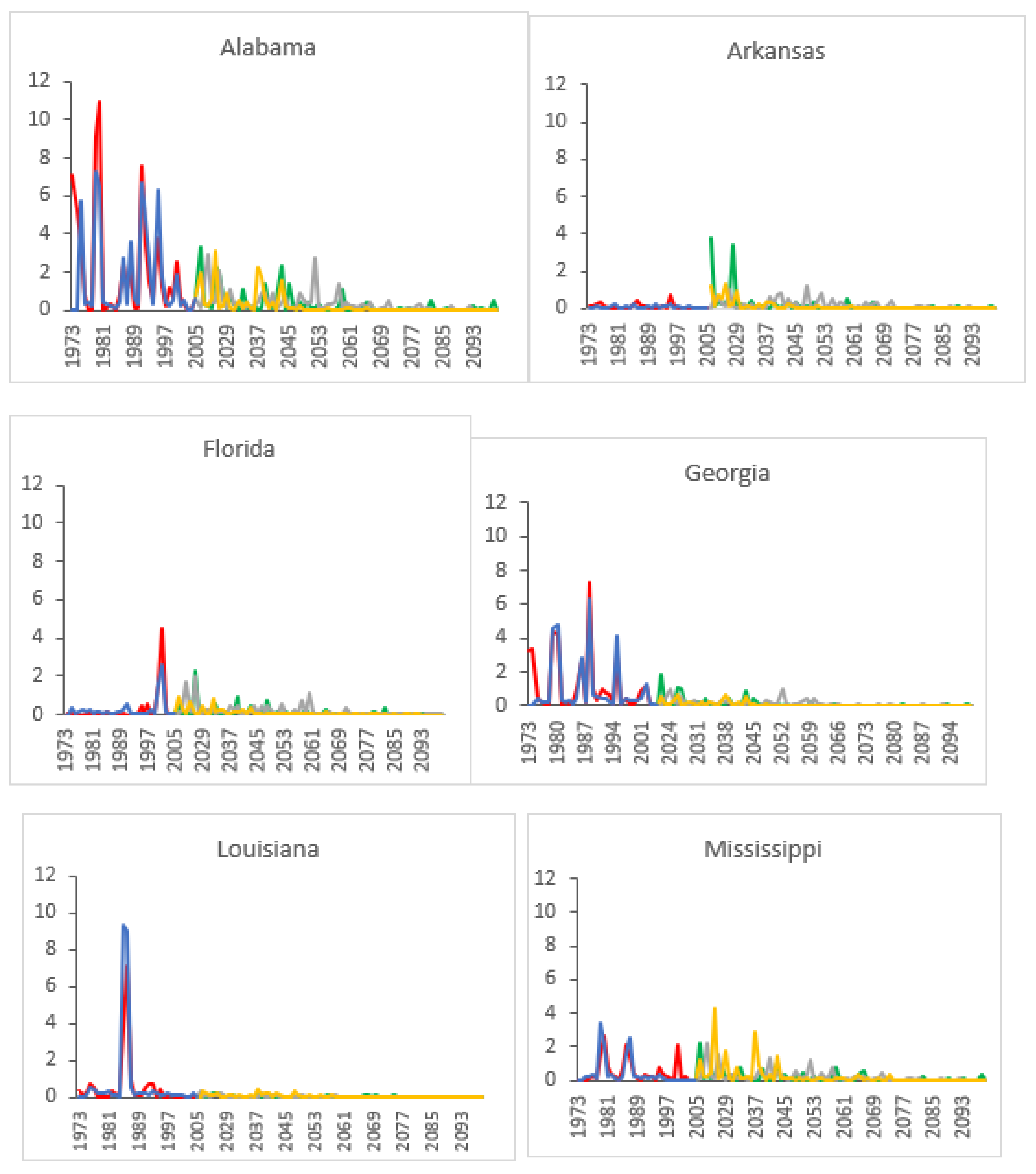
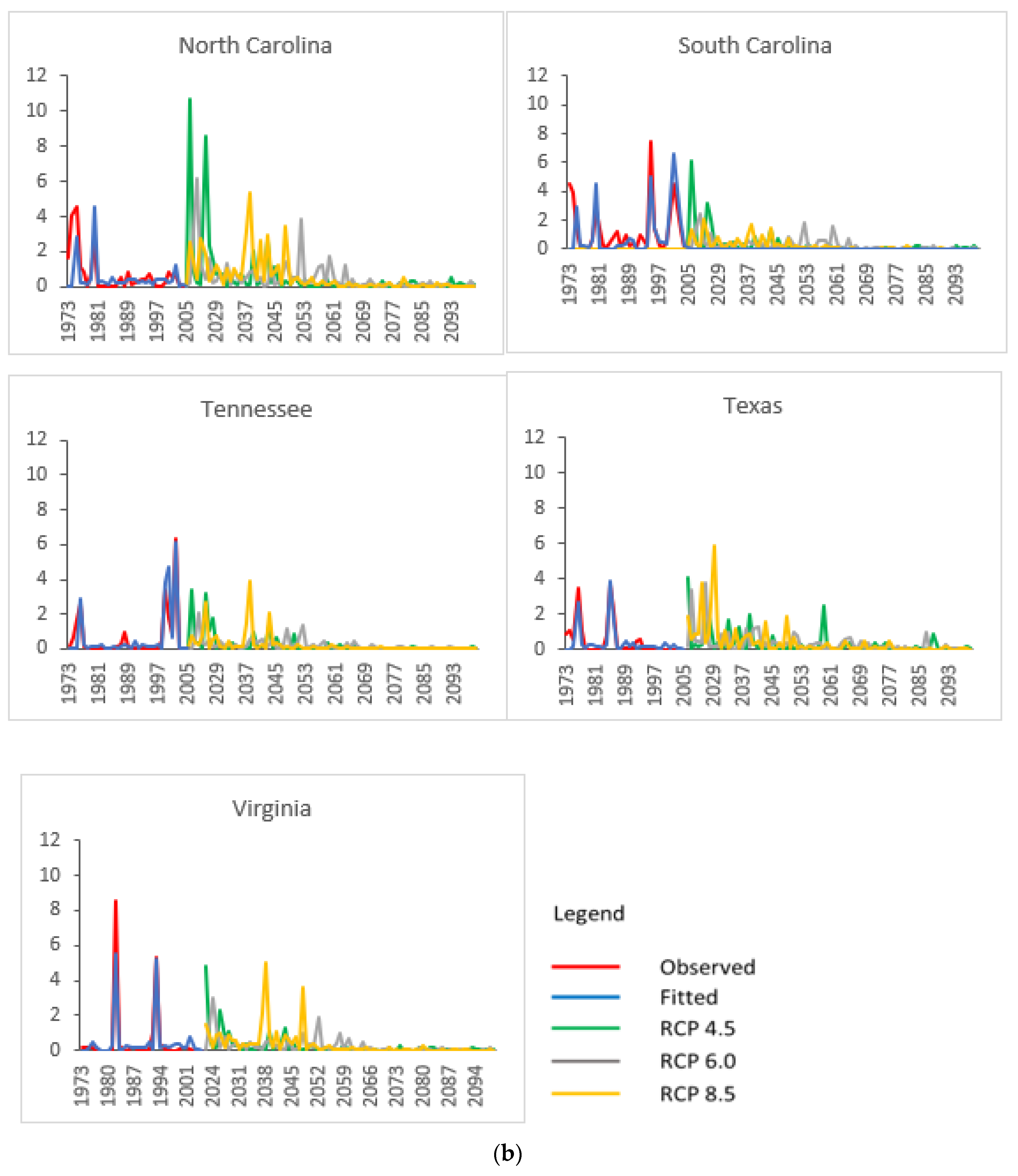
3.2. Projected SPB Infestation Risk under Climate Change
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Billings, R.; Clarke, S.R.; Mendoza, V.E.; Cabrera, P.C.; Figueroa, B.M.; Campos, J.R.; Baeza, G. Bark beetle outbreaks and fire: A devastating combination for Central America’s pine forests. Unasylva 2004, 55, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Coulson, R.N.; Klepzig, K.D. Southern Pine Beetle II; USDA Forest Service Southern Research Station: Asheville, NC, USA, 2011.
- Pye, J.M.; Holmes, T.P.; Prestemon, J.P.; Wear, D.N. Economic impacts of the southern pine beetle. In Southern Pine Beetle II; Coulson, R.N., Klepzig, K.D., Eds.; USDA Forest Service Southern Research Station: Asheville, NC, USA, 2011; pp. 213–222. [Google Scholar]
- Krist, K.J., Jr.; Ellenwood, J.R.; Woods, M.E.; McMahan, A.J.; Cowardin, J.P.; Ryerson, D.E.; Sapio, F.J.; Zweifler, M.O.; Romero, S.A. 2013–2023 National Insect and Disease Forest Risk Assessment; USDA Forest Service: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2014.
- Payne, T.L. Life history and habits. In The Southern Pine Beetle; Thatcher, R.C., Searcy, J.L., Coster, J.E., Hertel, G., Eds.; USDA Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1980; pp. 7–28. [Google Scholar]
- Flamm, R.O.; Coulson, R.N.; Payne, T.L. The southern pine beetle. In Dynamics of Forest Insect Populations: Patterns, Causes, Implications; Berryman, A.A., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 531–553. [Google Scholar]
- Salinas-Moreno, Y.; Mendoza, M.G.; Barrios, M.A.; Cisneros, R.; Macías-Sámano, J.; Zúñiga, G. Areography of the genus Dendroctonus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae) in Mexico. J. Biogeogr. 2004, 31, 1163–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.R.; Riggins, J.J.; Stephen, F.M. Forest management and southern pine beetle outbreaks: A historical perspective. For. Sci. 2016, 62, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, K.J.; Aoki, C.F.; Arango-Velez, A.; Cancelliere, J.; D’Amato, A.W.; DiGirolomo, M.F.; Rabaglia, R.J. Expansion of southern pine beetle into northeastern forests: Management and impact of a primary bark beetle in a new region. J. For. 2018, 116, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.E.; Heath, L.S.; Skog, K.E.; Birdsey, R.A. Methods for Calculating Forest Ecosystem and Harvested Carbon with Standard Estimates for Forest Types of the United States; USDA Forest Service Northeastern Research Station: Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2005.
- Wear, D.; Greis, J. The Southern Forest Futures Project: Summary Report; USDA Forest Service Southern Research Station: Asheville, NC, USA, 2012.
- FAOSTAT. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/FO (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- Birdsey, R.A. Carbon Storage and Accumulation in United States Forest Ecosystems; USDA Forest Service Northeastern Forest Experiment Station: Radnor, PA, USA, 1992.
- Loeffler, D.; Anderson, N.; Stockmann, K.; Skog, K.; Healey, S.; Jones, J.; Morrison, J.; Young, J. Estimates of Carbon Stored in Harvested Wood Products from United States Forest Service Southern Region, 1911–2012; USDA Forest Service Rocky Mountain Research Station: Missoula, MT, USA, 2014; Unpublished report.
- USDA Forest Service. Baseline Estimates of Carbon Stocks in Forests and Harvested Wood Products for National Forest System Units: Southern Region; USDA Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2015.
- Hicke, J.A.; Meddens, A.J.H.; Allen, C.D.; Kolden, C.A. Carbon stocks of trees killed by bark beetles and wildfire in the western United States. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 035032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, D.E.; Ewers, B.E.; Pendall, E. Impact of mountain pine beetle induced mortality on forest carbon and water fluxes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 105004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNulty, S.; Lorio, P., Jr.; Ayres, M.P.; Reeve, J. Predictions of southern pine beetle populations using a forest ecosystem model. In The Productivity and Sustainability of Southern Forest Ecosystems in Changing Environment; Mickler, R., Fox, S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 617–634. [Google Scholar]
- Ayres, M.P.; Lombardero, M.J. Assessing the consequences of global change for forest disturbance from herbivores and pathogens. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 262, 263–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.W.; Liebhold, A.M. Climate change and the outbreak ranges of two North American bark beetles. Agric. For. Entomol. 2002, 4, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J. Risk and damage of southern pine beetle outbreaks under global climate change. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 191, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffa, K.F.; Aukema, B.H.; Bentz, B.J.; Carroll, A.L.; Hicke, J.A.; Turner, M.G.; Romme, W.H. Cross-scale drivers of natural disturbances prone to anthropogenic amplification: The dynamics of bark beetle eruptions. Bioscience 2008, 58, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesk, C.; Cofel, E.; D’Amato, A.W.; Dodds, K.; Horton, R. Threats to North American forests from southern pine beetle with warming winters. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, J. Comovement and cyclical patterns of southern pine beetle outbreaks. In Environmental Modeling: New Research; Findley, P.N., Ed.; Nova Science: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Birt, A. Regional population dynamics. In Southern Pine Beetle II; Coulson, R.N., Klepzig, K.D., Eds.; USDA Forest Service Southern Research Station: Asheville, NC, USA, 2011; pp. 109–128. [Google Scholar]
- Weed, A.S.; Ayres, M.P.; Liebhold, A.M.; Billings, R. Spatio-temporal dynamics of a tree-killing beetle and its predator. Ecography 2016, 39, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, J.A.; Weed, A.S.; Aoki, C.F.; Sullivan, B.T.; Ayres, M.P. Temperature affects phenological synchrony in a tree killing bark beetle. Oecologia 2018, 188, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gara, R.I. Studies on the attack behavior of the southern pine beetle. I. The spreading and collapse of outbreaks. Contrib. Boyce Thompson Inst. 1967, 23, 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- Turchin, P.; Lorio, P., Jr.; Taylor, A.; Billings, R. Why do populations of southern pine beetle (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) fluctuate? Environ. Entomol. 1991, 20, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hain, F.P.; Duehl, A.J.; Gardner, M.J.; Payne, T.L. Natural history of the southern pine beetle. In Southern Pine Beetle II; Coulson, R.N., Klepzig, K.D., Eds.; USDA Forest Service Southern Research Station: Asheville, NC, USA, 2011; pp. 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Martinson, S.J.; Ylioja, T.; Sullivan, B.T.; Billings, R.; Ayres, M.P. Alternate attractors in the population dynamics of a tree-killing bark beetle. Popul. Ecol. 2013, 55, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.R.; Nowak, J.T. Forest Insect and Disease Leaflet 49; USDA Forest Service Pacific Northwest Research Station: Portland, OR, USA, 2009.
- Gagne, J.; Coulson, R.; Foltz, J.; Wagner, T.; Edson, L. Attack and survival of Dendroctonus frontalis in relation to weather during three years in east Texas. Environ. Entomol. 1980, 9, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungerer, M.J.; Ayres, M.P.; Lombardero, M.J. Climate and the northern distribution limits of Dendroctonus frontalis Zimmermann (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). J. Biogeogr. 1999, 26, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, J.A. Temperature extremes as a factor in the ecology of the southern pine beetle. J. For. 1933, 31, 329–336. [Google Scholar]
- King, E. Rainfall and epidemics of the southern pine beetle. Environ. Entomol. 1972, 1, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkstein, L. The Effect of Climate upon Outbreaks of the Southern Pine Beetle; Publications in Climatology; C.W. Thornthwaite Associates: Dublin, OH, USA, 1974; Volume 27, pp. 1–65. [Google Scholar]
- Kalkstein, L. Effects of climatic stress upon outbreaks of the southern pine beetle. Environ. Entomol. 1976, 5, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trân, J.K.; Ylioja, T.; Billings, R.; Régnière, J.; Ayres, M.P. Impact of minimum winter temperatures on the population dynamics of Dendroctonus frontalis. Ecol. Appl. 2007, 17, 882–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thatcher, R.C.; Pickard, L.S. Seasonal variations in activity of the southern pine beetle in east Texas. J. Econ. Entomol. 1964, 57, 840–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.B.; Miles, P.D.; Perry, C.H.; Pugh, S.A. Forest Resources of the United States, 2007; USDA Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Pye, J.M.; Price, T.S.; Clarke, S.R.; Huggett, R.J., Jr. A History of Southern Pine Beetle Outbreaks in the Southeastern United States through 2004. Available online: https://www.srs.fs.usda.gov/econ/data/spb-withheld/ (accessed on 21 January 2015).
- McNab, W.H.; Cleland, D.T.; Freeouf, J.A.; Keys, J.E., Jr.; Nowacki, G.J.; Carpenter, C.A. Description of Ecological Subregions: Sections of the Conterminous United States; USDA Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- Bailey, R.G. Description of the Ecoregions of the United States; USDA Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1980.
- Papke, L.E.; Wooldridge, J.M. Econometric methods for fractional response variables with an application to 401(k) plan participation rates. J. Appl. Econom. 1996, 11, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin, J.W.; Hilbe, J. Generalized Linear Models and Extensions, 2nd ed.; Stata Press: College Station, TX, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Papke, L.E.; Wooldridge, J.M. Panel data methods for fractional response variables with an application to test pass rates. J. Econom. 2008, 145, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate Data Online. Available online: https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/cdo-web/ (accessed on 15 January 2015).
- BCSD-CMIP5 Climate Monthly Projections, Downscaled CMIP3 and CMIP5 Climate and Hydrology Projections. Available online: https://gdo-dcp.ucllnl.org/downscaled_cmip_projections/dcpInterface.html#Projections:%20Complete%20Archives (accessed on 6 March 2015).
- Donner, L.J.; Wyman, B.; Hemler, R.S.; Horowitz, L.; Ming, Y.; Zhao, M.; Golaz, J.-C.; Ginoux, P.; Lin, S.-J.; Schwarzkopf, M.D.; et al. The dynamical core, physical parameterizations, and basic simulation characteristics of the atmospheric component AM3 of the GFDL Global Coupled Model CM3. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 3484–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Hughes, J.K.; Bellouin, N.; Hardiman, S.C.; Jones, G.S.; Knight, J.; Liddicoat, S.; O’connor, F.M.; Andres, R.J.; Bell, C.; et al. The HadGEM2-ES implementation of CMIP5 centennial simulations. Geosci. Model Dev. 2011, 4, 543–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flato, G.; Marotzke, J.; Abiodun, B.; Braconnot, P.; Chou, S.C.; Collins, W.; Cox, P.; Driouech, F.; Emori, S.; Eyring, V.; et al. Evaluation of climate models. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- van Vuuren, D.P.; Edmonds, J.; Kainuma, M.; Riahi, K.; Thomson, A.; Hibbard, K.; Hurtt, G.C.; Kram, T.; Krey, V.; Lamarque, J.-F.; et al. The representative concentration pathways: An overview. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett, M.S. Periodogram analysis and continuous spectra. Biometrics 1950, 37, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, M.S. An Introduction to Stochastic Processes with Specifical References to Method and Applications, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Hodrick, R.J.; Prescott, E.C. Postwar US business cycles: An empirical investigation. J. Money Credit Bank. 1997, 29, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodrick, R.J. An Exploration of Trend-Cycle Decomposition Methodologies in Simulated Data; NBER Working Paper 26750; National Bureau of Economic Research: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ravn, M.O.; Uhlig, H. On adjusting the Hodrick-Prescott filter for the frequency of observations. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2002, 84, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGCRP. Climate Science Special Report: Fourth National Climate Assessment, Volume I; Wuebbles, D.J., Fahey, D.W., Hibbard, K.A., Dokken, D.J., Stewart, B.C., Maycock, T.K., Eds.; US Global Change Research Program: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- McClelland, W.T.; Hain, F.P. Survival of declining Dendroctonus frontalis populations during a severe and nonsevere winter. Environ. Entomol. 1979, 8, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardero, M.J.; Ayres, M.P.; Ayres, B.D.; Reeve, J.D. Cold tolerance of four species of bark beetle (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) in North America. Environ. Entomol. 2000, 29, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Billings, R. Mechanical control of southern pine beetle infestations. In Southern Pine Beetle II; Coulson, R.N., Klepzig, K.D., Eds.; USDA Forest Service Southern Research Station: Asheville, NC, USA, 2011; pp. 399–414. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo, J.A.; Sullivan, B.T.; Myers, S.W.; Ayres, M.P. Are southern pine forests becoming too warm for the southern pine beetle? Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 315, 108813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaro, C.; Nowak, J.T.; Elledge, A. Why have southern pine beetle outbreaks declined in the southeastern US. with the expansion of intensive pine silviculture? A brief review of hypotheses. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 391, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, G. Major Forest Insect and Disease Conditions in the United States: 2014 Update; USDA Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
| Independent Variable | Estimated Coefficient | Standard Error | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| USVt (unsalvaged timber in the current year) | 0.1032 | 0.0091 | 0.000 |
| lnSPTt (log average spring temperature in the current year) | 0.0154 | 0.0052 | 0.003 |
| lnFLTt (log average fall temperature in the current year) | −0.0141 | 0.0053 | 0.008 |
| lnSPPt−1 (log spring total precipitation one year ago) | −0.0010 | 0.0004 | 0.006 |
| lnWNPt−1 (log winter total precipitation one year ago) | −0.0011 | 0.0003 | 0.000 |
| lnMinWNTt−1 (log winter min temperature one year ago) | 0.0047 | 0.0017 | 0.007 |
| lnSPTt−2 (log average spring temperature two years ago) | −0.0096 | 0.0049 | 0.049 |
| lnSMTt−2 (log average summer temperature two years ago) | 0.0218 | 0.0100 | 0.030 |
| State | Historical (1973–2004) | HadGEM2-ES | GFDL-CM3 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCP 4.5 | RCP 6.0 | RCP 8.5 | RCP 4.5 | RCP 6.0 | RCP 8.5 | |||||||||
| A | P | A | P | A | P | A | P | A | P | A | P | A | P | |
| AL | 1.584 | 6.67 | 0.393 | 2.35 | 0.640 | 4.35 | 0.460 | 2.44 | 0.495 | 3.57 | 0.466 | 3.85 | 0.014 | 3.26 |
| AR | 0.086 | 4.55 | 0.406 | 4.35 | 0.409 | 5.56 | 0.285 | 3.53 | 0.467 | 2.50 | 0.211 | 2.94 | 0.001 | 3.53 |
| FL | 0.462 | 5.26 | 0.194 | 2.30 | 0.170 | 2.60 | 0.226 | 3.89 | 0.249 | 3.39 | 0.273 | 3.85 | 0.003 | 3.85 |
| GA | 1.002 | 8.33 | 0.193 | 2.38 | 0.200 | 2.60 | 0.199 | 2.44 | 0.227 | 3.52 | 0.161 | 3.92 | 0.011 | 3.23 |
| LA | 1.242 | 7.69 | 0.061 | 2.90 | 0.079 | 2.60 | 0.050 | 2.33 | 0.034 | 3.52 | 0.038 | 2.51 | 0.000 | 3.23 |
| MS | 0.408 | 6.67 | 0.302 | 4.55 | 0.481 | 2.60 | 0.220 | 2.44 | 0.272 | 3.57 | 0.305 | 2.56 | 0.004 | 3.13 |
| NC | 0.578 | 6.45 | 0.933 | 3.57 | 0.680 | 2.60 | 0.586 | 2.44 | 1.286 | 2.88 | 0.788 | 3.92 | 0.017 | 3.23 |
| SC | 0.963 | 5.26 | 0.441 | 2.36 | 0.346 | 2.60 | 0.359 | 2.44 | 0.683 | 4.08 | 0.382 | 3.91 | 0.009 | 3.26 |
| TN | 0.758 | 4.55 | 0.440 | 4.55 | 0.718 | 2.58 | 0.343 | 2.44 | 0.475 | 4.93 | 0.278 | 3.03 | 0.006 | 3.57 |
| TX | 0.503 | 8.00 | 0.411 | 3.57 | 0.404 | 3.27 | 0.335 | 3.33 | 0.526 | 3.57 | 0.510 | 2.99 | 0.132 | 3.39 |
| VA | 0.955 | 5.41 | 0.732 | 4.55 | 0.461 | 4.85 | 0.602 | 7.69 | 0.528 | 2.90 | 0.388 | 3.01 | 0.007 | 3.36 |
| Regional average | 0.776 | 6.26 | 0.410 | 3.40 | 0.417 | 3.29 | 0.333 | 3.22 | 0.477 | 3.49 | 0.345 | 3.32 | 0.019 | 3.37 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, H.; Gan, J. Periods and Amplitudes of Southern Pine Beetle Infestations under Climate Change. Climate 2022, 10, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10090126
An H, Gan J. Periods and Amplitudes of Southern Pine Beetle Infestations under Climate Change. Climate. 2022; 10(9):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10090126
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Hyunjin, and Jianbang Gan. 2022. "Periods and Amplitudes of Southern Pine Beetle Infestations under Climate Change" Climate 10, no. 9: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10090126
APA StyleAn, H., & Gan, J. (2022). Periods and Amplitudes of Southern Pine Beetle Infestations under Climate Change. Climate, 10(9), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10090126






