Modeling the Contribution of Aerosols to Fog Evolution through Their Influence on Solar Radiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
- In Section 2, the solar radiative model is briefly presented and equations are given in the appendices.
- 2.
- In Section 3, the solar scheme is used and compared to the LH74 scheme for a one-dimensional simulation of a fog event during the ParisFog campaign at SIRTA. The role of aerosols on the heating of atmospheric layers is investigated for clear sky and foggy sky.
- 3.
- In Section 4, sensitivity tests are conducted in order to evaluate the impact of different parametrizations including the presence of aerosols before fog formation, BC in cloud droplets and cloud fraction during and after fog development.
2. The Layer-Dependent Scheme for Solar Radiation in Code_Saturne
3. The ParisFog Experiment
3.1. Observations and Simulation Conditions
- Vertical profiles of wind, temperature and humidity by radiosondes at 12, 21 (UTC) on the 18 of February and 0000, 0300, 0600, 1000 (UTC) on the 19 of February.
- Near surface measurements on a 30 m mast of: temperature, humidity, wind and turbulence by sonic anemometers, long wave and solar radiative fluxes.
- Surface measurements at 2 m of: temperature, humidity, visibility, and radiative fluxes.
- Fog droplet number with an optical particle counter (OPC) Pallas Wallas 2000.
- Ceilometer measurements to estimate the fog/stratus layer depth/elevation.
- Aerosols size distribution with a Scanning Mobility Particle Size (SMPS), an optical particle counter (OPC Grimm 1.109), and filter sampling to determine their chemical composition.
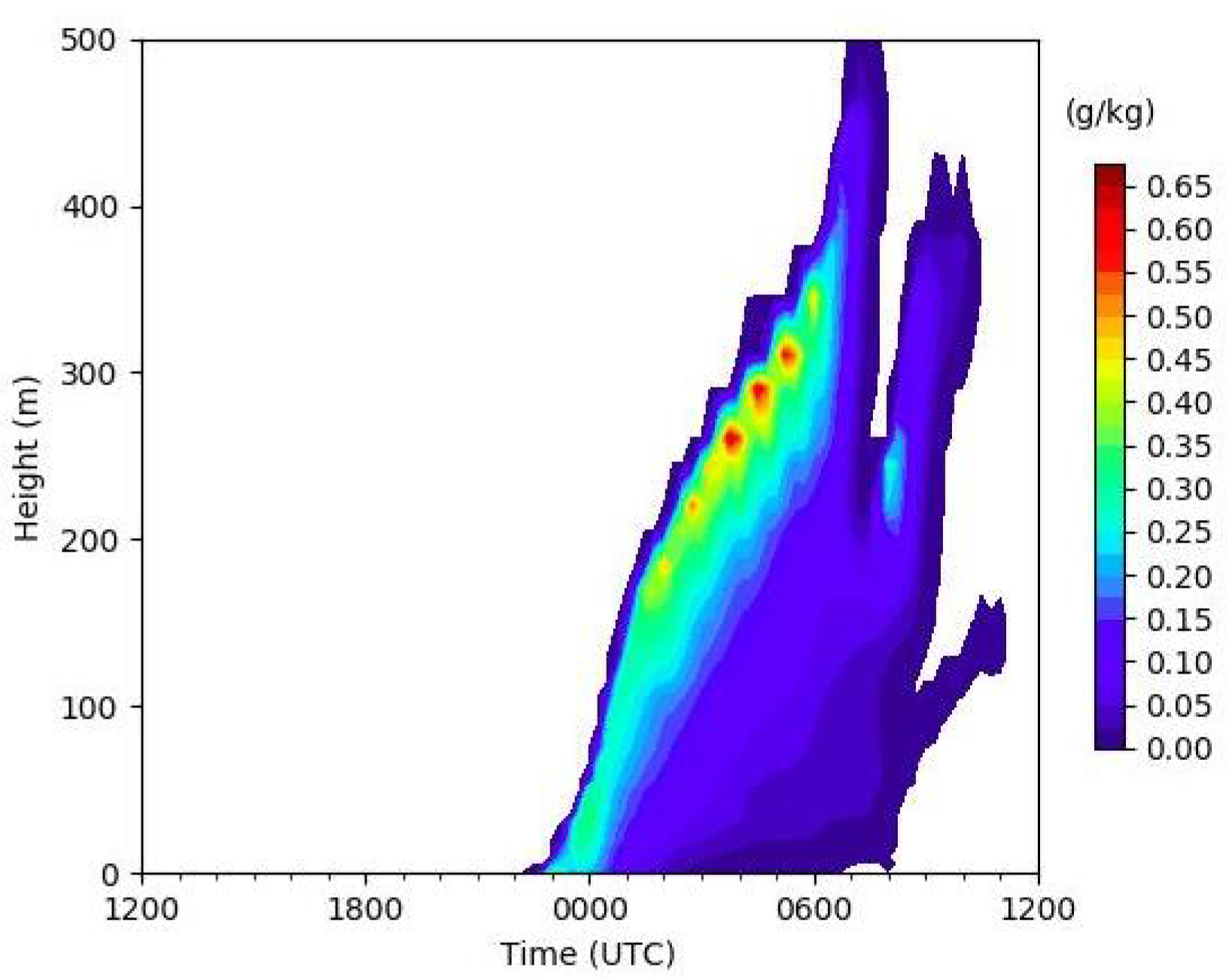
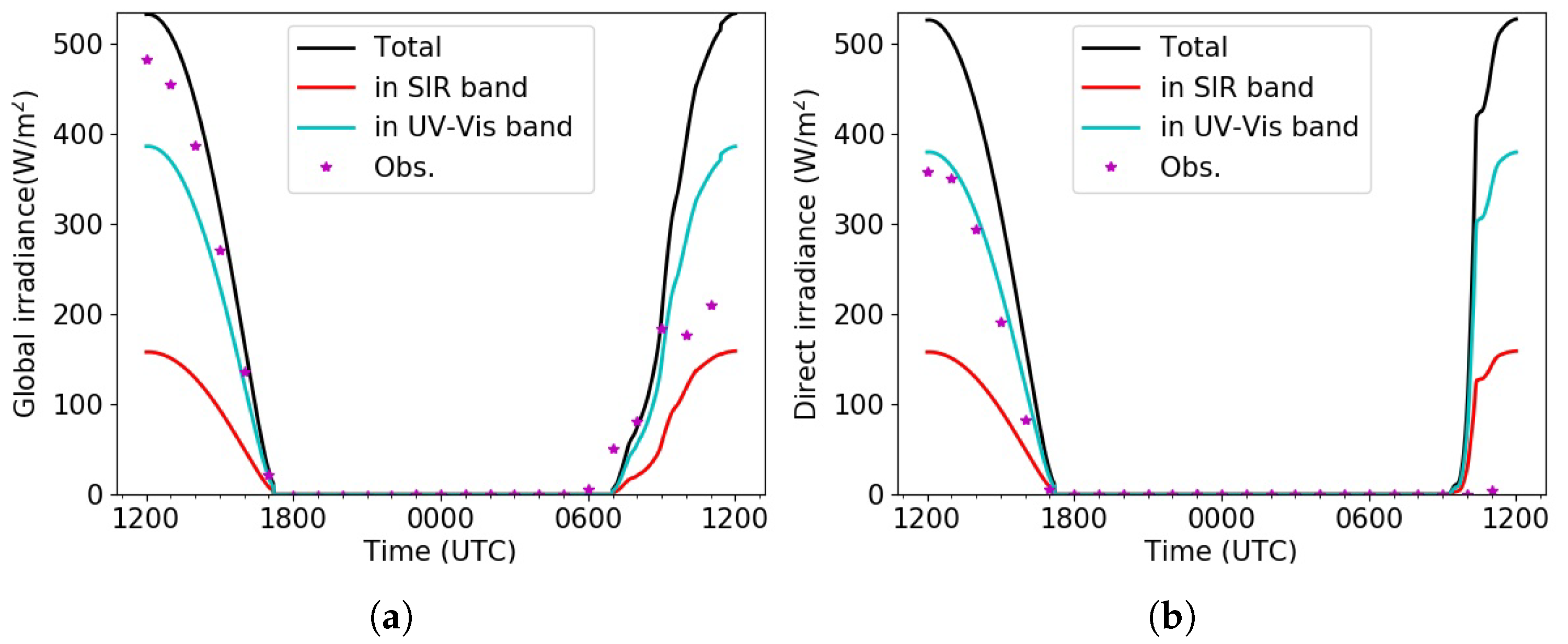
3.2. Fog-Event Simulation
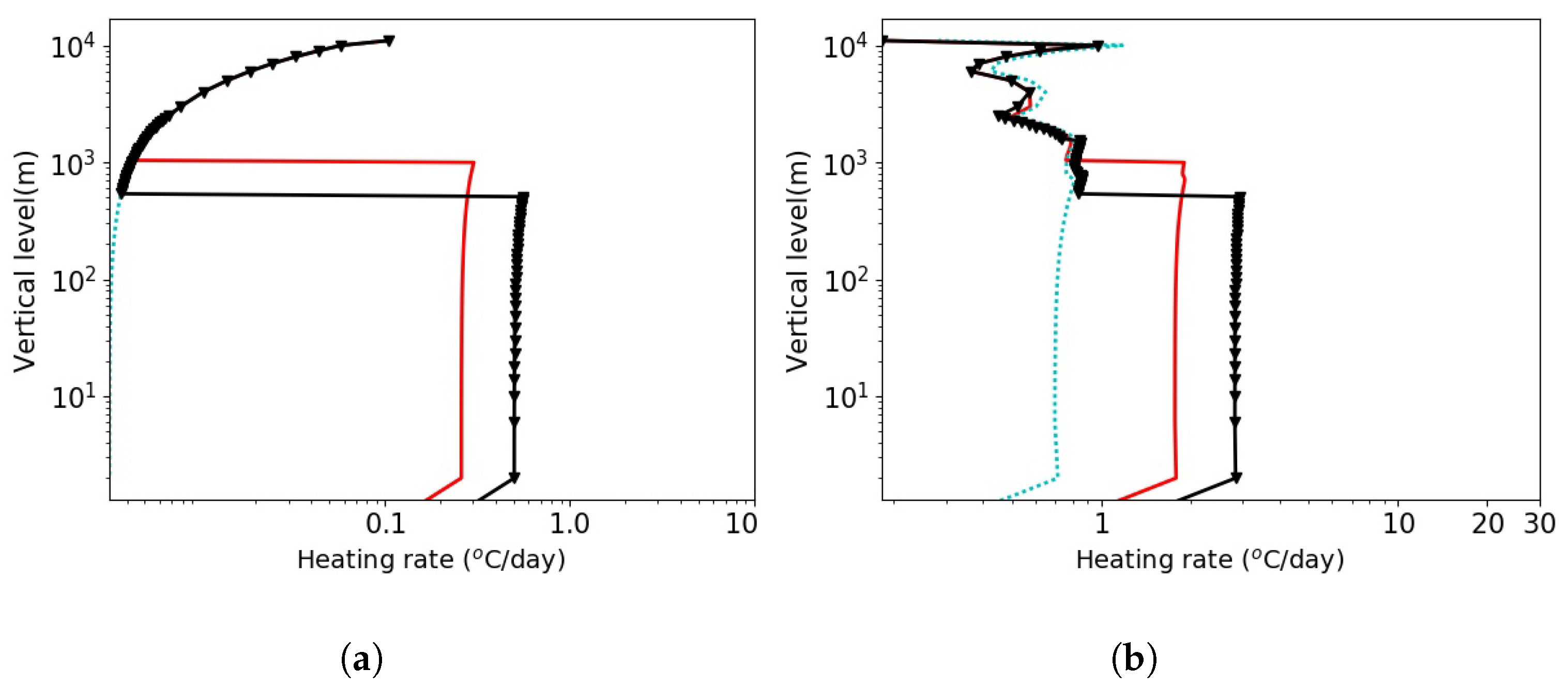
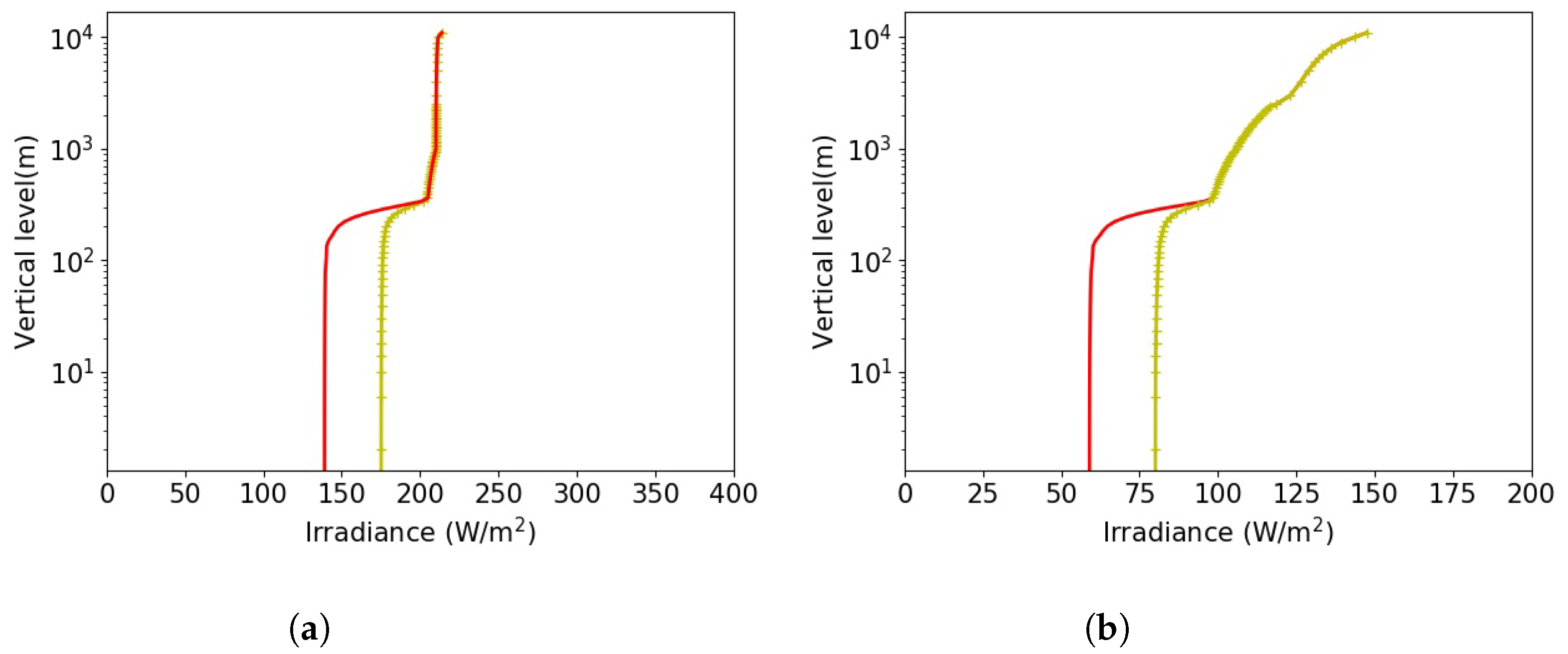
3.3. Sensitivity Tests on Aerosols
3.4. Sensitivity Tests on the Fog Evolution
3.4.1. Sensitivity to Interstitial Aerosols
3.4.2. Sensitivity to Effective Radius of Cloud Droplet
3.4.3. Sensitivity to BC Concentration
3.4.4. Sensitivity to the Treatment of Partial Cloudiness
3.4.5. Simplified Parametrization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Optical Characteristics of Aerosols and Clouds
Appendix B. Estimation of Solar Radiation
Appendix B.1. Solar Radiation in the SIR Band
| k, n ∈ [1, 8] | 4 × 10 | 2 × 10 | 0.0035 | 0.0377 | 0.195 | 0.94 | 4.46 | 19 |
| p(k) | 0.6470 | 0.0698 | 0.1443 | 0.0584 | 0.0335 | 0.0225 | 0.0158 | 0.0087 |
Appendix B.2. Solar Radiation in the UV-Vis Band
Appendix B.3. Total Solar Radiation
References
- Rap, A.; Scott, C.E.; Spracklen, D.V.; Bellouin, N.; Forster, P.M.; Carslaw, K.S.; Schmidt, A.; Mann, G. Natural aerosol direct and indirect radiative effects. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 3297–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartelet, K.; Legorgeu, C.; Lugon, L.; Maanane, Y.; Musson-Genon, L. Representation of aerosol optical properties using a chemistry transport model to improve solar irradiance modelling. Sol. Energy 2018, 176, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohard, J.; Pinty, J.; Bedos, C. Extending Twomey’s Analytical Estimate of Nucleated Cloud Droplet Concentrations from CCN Spectra. J. Atmos. Sci. 1998, 55, 3348–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenes, A.; Seinfeld, J. Parameterization of cloud droplet formation in global climate models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.T.; Wang, W.C.; Chen, J.P. A modeling study of aerosol impacts on cloud microphysics and radiative properties. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2007, 133, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Razzak, H.; Ghan, S.; Rivera-Carpio, C. A parameterization of aerosol activation: 1. Single aerosol type. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 6123–6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasahara, M.; Hôller, R.; Tohno, S.; Onishi, Y.; Ma, C. Application of PIXE technique to studies on global warming/cooling effect on atmospheric aerosol. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B. Beam Interact. Mater. Atmos. 2002, 189, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, T.; Richter, R.; Liu, W.; Caillol, S. Fighting global warming by climate engineering: Is the Earth radiation management and the solar radiation management any option for fighting climate change? Renew. Syst. Energy Rev. 2014, 31, 792–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhen, Z.; Mi, Z.; Sun, H.; Yang, G. Solar irradiance feature extraction and support vector machines based weather status pattern recognition model for short time photovoltaic power forecasting. Energy Build. 2015, 86, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambezidis, H.; Psiloglou, B.; Karagiannis, D.; Dumka, U.; Kaskaoutis, D. Recent improvements of the meteorological radiation model for solar irradiance estimates under all-sky conditions. Renew. Energy 2016, 93, 142–158. [Google Scholar]
- Gueymard, C.A.; Ruiz-Arias, J.A. Validation of direct normal irradiance predictions under arid conditions: A review of radiative models and their turbidity-dependent performance. Renew. Syst. Energy Rev. 2015, 45, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psiloglou, B.E.; Santamouris, M.; Asimakopoulos, D.N. Atmospheric Broadband Model for Computation of Solar Radiation at the Earth’s Surface. Application to Mediterranean Climate. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2000, 157, 829–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, P.A.; Hacker, J.P.; Dudhia, J.; Haupt, S.E.; Ruiz-Arias, J.A.; Gueymard, C.A.; Thompson, G.; Eidhammer, T.; Deng, A. WRF-Solar: Description and Clear-Sky Assessment of an Augmented NWP Model for Solar Power Prediction. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2015, 97, 1249–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartelet, K.; Debry, E.; Fahey, K.; Roustan, Y.; Tombette, M.; Sportisse, B. Simulation of aerosols and gas-phase species over Europe with the Polyphemus system: Part I—Model-to-data comparison for 2001. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 6116–6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcrette, J.J.; Boucher, O.; Jones, L.; Bechtold, D.S.P.; Beljaars, A.; Benedetti, A.; Bonet, A.; Kaiser, J.W.; Razinger, M.; Schulz, M.; et al. Aerosol analysis and forecast in the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Integrated Forecast System:Forward modeling. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Asmar, L.; Musson Genon, L.; Eric, D.; Dupont, J.C.; Sartelet, K. Improvement of solar irradiance modelling during cloudy sky days using measurements. Sol. Energy 2021, 230, 1175–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, K. An Introduction to Atmospheric Radiation, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Millbrae, CA, USA, 2002; Volume 84. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, M.; Koepke, P.; Schult, T. Optical Properties of Aerosols and Clouds: The Software Package OPAC. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 1998, 79, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhao, D.; Zeng, C.; Li, J.; Lu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhu, B. Atmospheric heating rate due to black carbon aerosols: Uncertainties and impact factors. Atmos. Res. 2020, 240, 104891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Razzak, H.; Ghan, S. A parameterization of aerosol activation: 2. Multiple aerosol types. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 6837–6844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chýlek, P.; Lesins, G.B.; Videen, G.; Wong, J.G.D.; Pinnick, R.G.; Ngo, D.; Klett, J.D. Black carbon and absorption of solar radiation by clouds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 105, 6837–6844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.C.; Penner, J.E.; Prospero, J.M.; Grant, K.E.; Rau, G.H.; Kawamoto, K. Cloud susceptibility and the first aerosol indirect forcing: Sensitivity to black carbon and aerosol concentrations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, AAC 10-1–AAC 10-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandu, I.; Tulet, P.; Brenguier, J.L. Parameterization of the cloud droplet single scattering albedo based on aerosol chemical composition for LES modelling of boundary layer clouds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motos, G.; Schmale, J.; Corbin, J.C.; Zanatta, M.; Baltensperger, U.; Gysel-Beer, M. Droplet activation behaviour of atmospheric black carbon particles in fog as a function of their size and mixing state. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 2183–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcrette, J.J.; Jakob, C. The Response of the ECMWF Model to Changes in the Cloud Overlap Assumption. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2000, 128, 1707–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, B.; Geleyn, J.F. A Comprehensive Radiation Scheme for Numerical Weather Prediction Models with Potential Applications in Climate Simulations. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1992, 120, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, R.; Bozzo, A. ECRAD: A New Radiation Scheme for the IFS; Technical Memorandum; ECMWF: Reading, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Curry, J. Cloud overlap statistics. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1989, 94, 9925–9935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Musson-Genon, L.; Dupont, E.; Milliez, M.; Carissimo, B. On the Influence of a Simple Microphysics Parametrization on Radiation Fog Modelling: A Case Study During ParisFog. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2014, 151, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeffelin, M.; Bergot, T.; Elias, T.; Tardif, R.; Carrer, D.; Chazette, P.; Colomb, M.; Drobinski, P.; Dupont, E.; Dupont, J.C.; et al. PARISFOG: Shedding New Light on Fog Physical Processes. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2010, 91, 767–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacis, A.A.; Hansen, J. A Parameterization for the Absorption of Solar Radiation in the Earth’s Atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 1974, 31, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.; Klemp, J.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.; Barker, D.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.Y.; Duda, M. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Version 3; Technical Report; University Corporation for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2008; p. 1002 KB. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psiloglou, B.E.; Kambezidis, H.D. Performance of the meteorological radiation model during the solar eclipse of 29 March 2006. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 6047–6059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musson-Genon, L.; Dupont, E.; Wendum, D. Reconstruction of the surface-layer vertical structure from measurements of wind, temperature and humidity at two levels. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2007, 124, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzereau, E.; Musson-Genon, L.; Carissimo, B. On the Definition of the Cloud Water Content Fluctuations and Its Effects on the Computation of a Second-Order Liquid Water Correlation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 64, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musson-Genon, L. Comparison of Different Simple Turbulence Closures with a One-Dimensional Boundary Layer Model. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1995, 123, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guimet, V.; Laurence, D. A Linearised Turbulent Production in the K-ε Model for Engineering Applications; Elsevier Science Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2002; pp. 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangognio, J. Impact des Aérosols Sur le Cycle de vie du Brouillard: De L’observation à la Modélisation. Thesis. 2009. Available online: https://www.umr-cnrm.fr/IMG/pdf/these_jerome.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Zieger, P.; Fierz-Schmidhauser, R.; Gysel, M.; Ström, J.; Henne, S.; Yttri, K.E.; Baltensperger, U.; Weingartner, E. Effects of relative humidity on aerosol light scattering in the Arctic. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 3875–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, G.L. The Parameterization of Radiation for Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Models. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1984, 112, 826–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.P.; Gleeson, E.; Rontu, L. Radiation sensitivity tests of the HARMONIE 37h1 NWP model. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 1433–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, S.C.; Stamnes, K.; Jayaweera, K. Radiative Energy Budget in the Cloudy and Hazy Arctic. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 1002–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, M.D. A Solar Radiation Model for Use in Climate Studies. J. Atmos. Sci. 1992, 49, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Wiscombe, W. The Delta-Eddington Approximation for Radiative Flux Transfer. J. Atmos. Sci. 1976, 33, 2452–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meador, W.E.; Weaver, W.R. Two-Stream Approximations to Radiative Transfer in Planetary Atmospheres: A Unified Description of Existing Methods and a New Improvement. J. Atmos. Sci. 1980, 37, 630–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddington, A.S. On the radiative equilibrium of the stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1916, 77, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasten, F.; Young, A.T. Revised optical air mass tables and approximation formula. Appl. Opt. 1989, 28, 4735–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morcrette, J.J.; Fouquart, Y. The Overlapping of Cloud Layers in Shortwave Radiation Parameterizations. J. Atmos. Sci. 1986, 43, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Clear Sky | Cloudy Sky | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MBE | RMSE | MBE | |
| Global | 19 | 5 | 59 | 17 |
| Direct | 21 | −7 | 50 | −18 |
| Mode 1 | Mode 2 | Mode 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N (cm) | 8700 | 8300 | 1000 |
| R (m) | 0.0165 | 0.055 | 0.4 |
| 1.57 | 1.59 | 1.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Asmar, L.; Musson-Genon, L.; Dupont, E.; Ferrand, M.; Sartelet, K. Modeling the Contribution of Aerosols to Fog Evolution through Their Influence on Solar Radiation. Climate 2022, 10, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10050061
Al Asmar L, Musson-Genon L, Dupont E, Ferrand M, Sartelet K. Modeling the Contribution of Aerosols to Fog Evolution through Their Influence on Solar Radiation. Climate. 2022; 10(5):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10050061
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Asmar, Lea, Luc Musson-Genon, Eric Dupont, Martin Ferrand, and Karine Sartelet. 2022. "Modeling the Contribution of Aerosols to Fog Evolution through Their Influence on Solar Radiation" Climate 10, no. 5: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10050061
APA StyleAl Asmar, L., Musson-Genon, L., Dupont, E., Ferrand, M., & Sartelet, K. (2022). Modeling the Contribution of Aerosols to Fog Evolution through Their Influence on Solar Radiation. Climate, 10(5), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10050061







