Permutation Entropy and Information Recovery in Nonlinear Dynamic Economic Time Series
Abstract
1. Introduction
The 1000-point collapse of the Dow Jones Industrial Average on 6 May 2010 “… was a small indicator of how complex and chaotic, in the formal sense, these systems have become …” Ben Bernanke, Interview with the International Herald Tribune, 17 May 2010
Looking Ahead
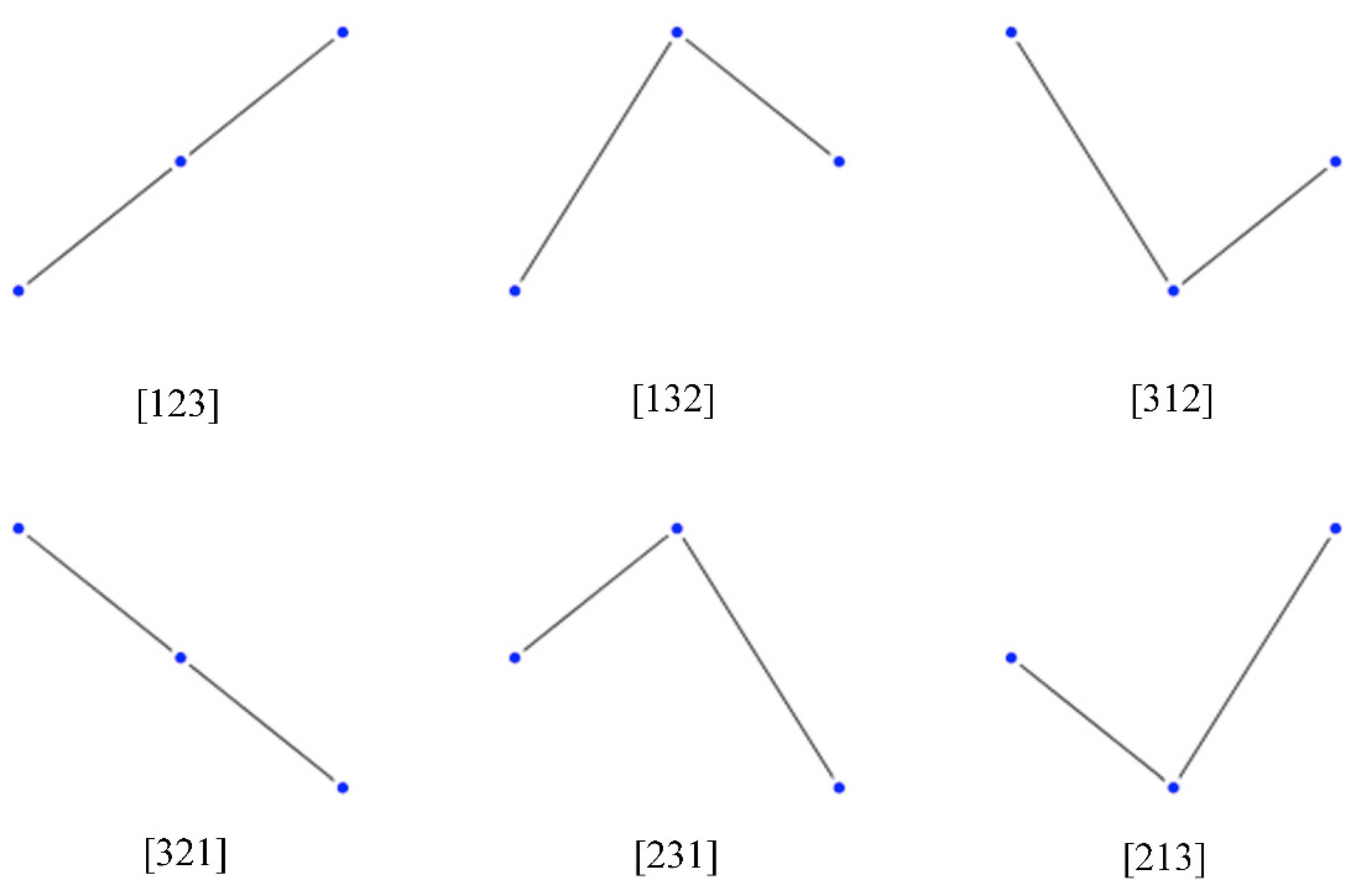
2. Permutation Entropy and Ordinal Patterns
3. Information Theoretic Estimation and Inference Base
The Cressie–Read Family of Power Divergence Measures and the PE metric
4. Estimation and Empirical Applications
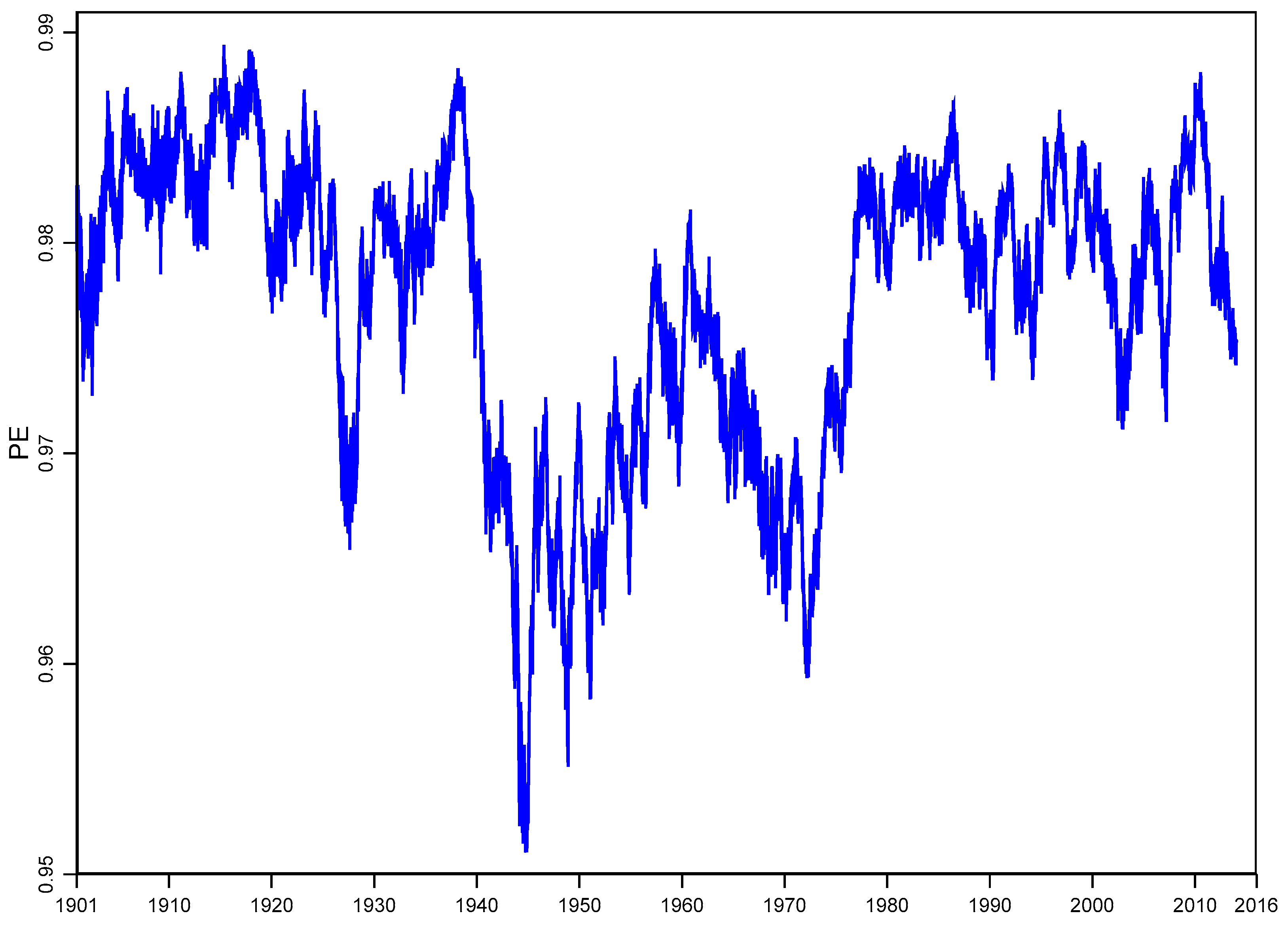
4.1. PE Information Recovery Estimation
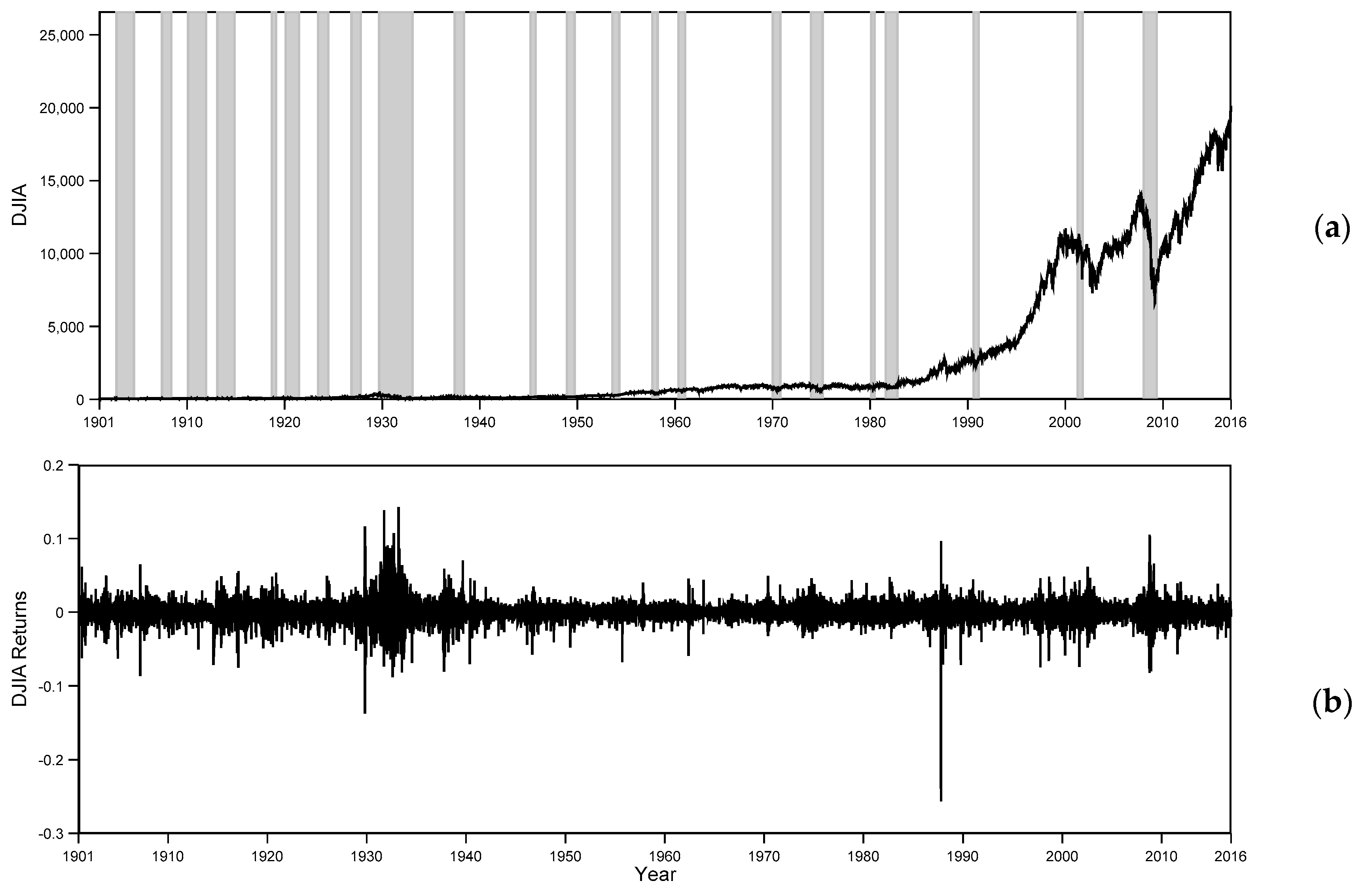
4.2. Analysis of the Full DJIA Time Series: 1901–2016
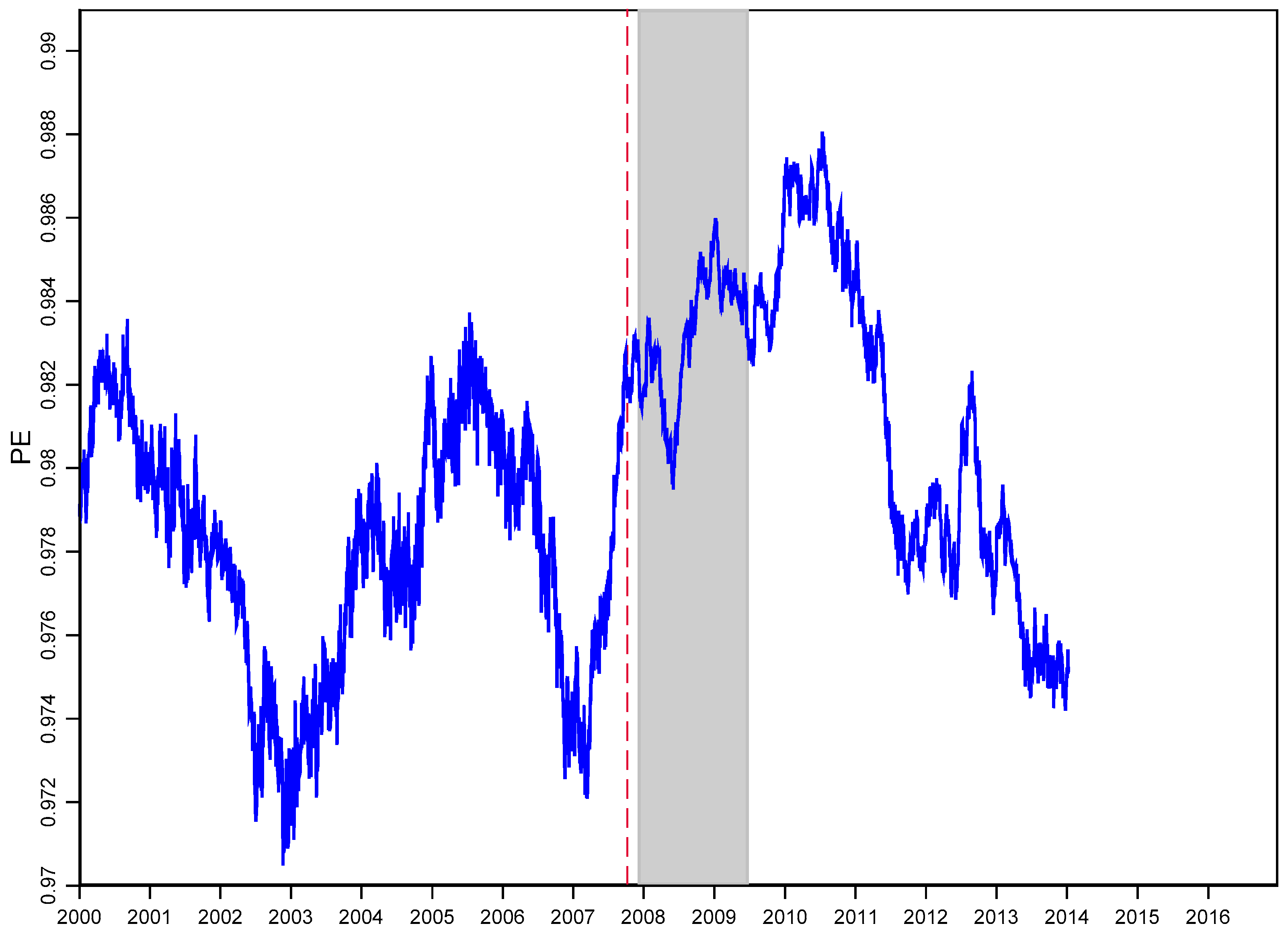
4.3 Rolling Window Analysis
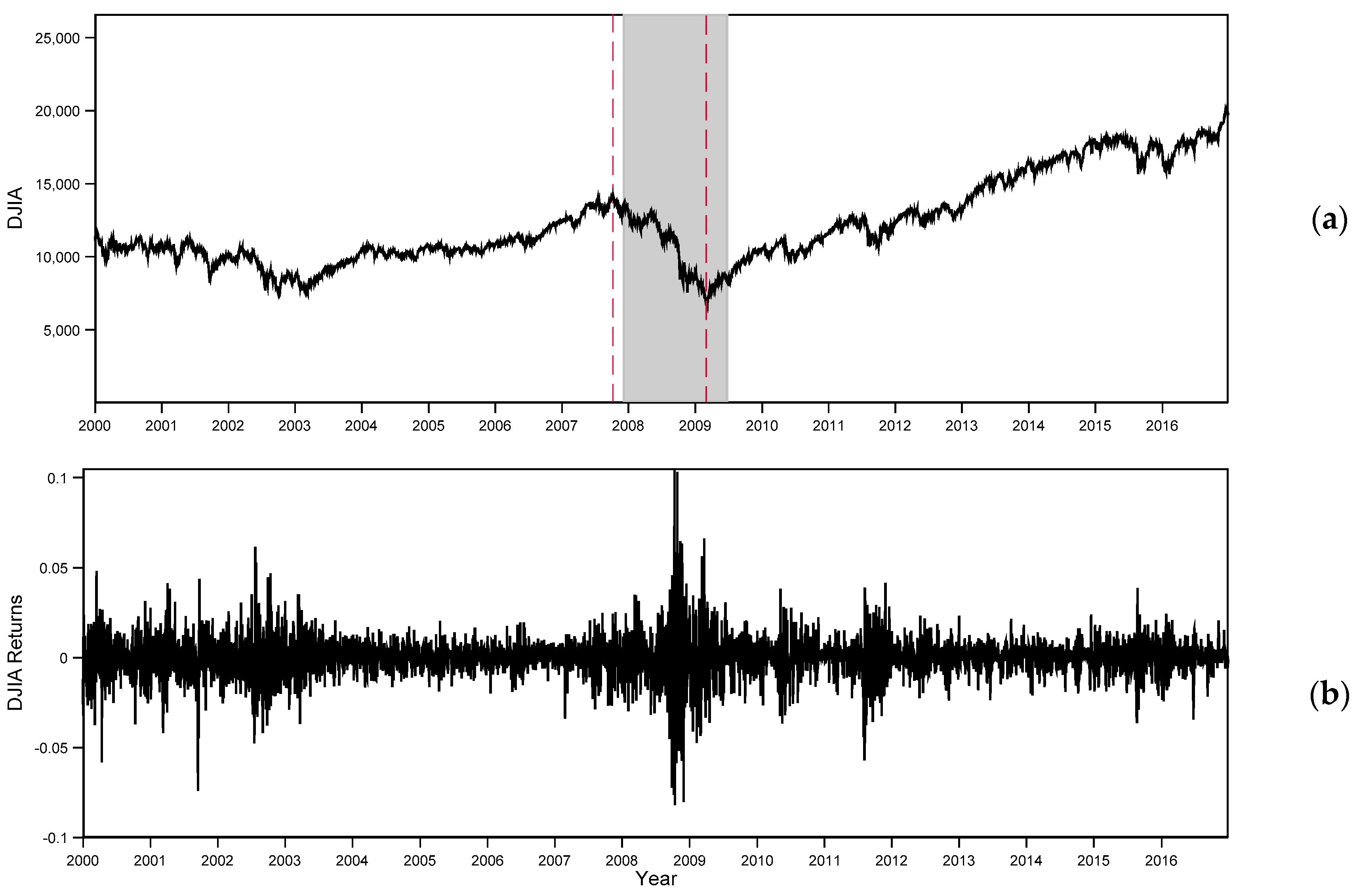
4.4. Post-World War II Analysis
4.5. Rolling Window Analysis
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
| Time Period | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permutation | 1901–2016 | 2000–2016 | ||
| Count | Relative Freq. | Count | Relative Freq. | |
| 1259 | 0.04 | 118 | 0.028 | |
| 1369 | 0.043 | 154 | 0.036 | |
| 1108 | 0.035 | 164 | 0.038 | |
| 1388 | 0.044 | 187 | 0.044 | |
| 1167 | 0.037 | 202 | 0.047 | |
| 1407 | 0.045 | 197 | 0.046 | |
| 1456 | 0.046 | 154 | 0.036 | |
| 1357 | 0.043 | 188 | 0.044 | |
| 1136 | 0.036 | 172 | 0.04 | |
| 1176 | 0.037 | 143 | 0.033 | |
| 1095 | 0.035 | 179 | 0.042 | |
| 1460 | 0.046 | 184 | 0.043 | |
| 1332 | 0.043 | 171 | 0.04 | |
| 1265 | 0.04 | 225 | 0.053 | |
| 1459 | 0.046 | 223 | 0.052 | |
| 1077 | 0.034 | 195 | 0.046 | |
| 1177 | 0.037 | 162 | 0.038 | |
| 1538 | 0.049 | 186 | 0.043 | |
| 1145 | 0.036 | 158 | 0.037 | |
| 1151 | 0.037 | 181 | 0.042 | |
| 1452 | 0.046 | 203 | 0.047 | |
| 1305 | 0.041 | 174 | 0.041 | |
| 1494 | 0.047 | 141 | 0.033 | |
| 1719 | 0.055 | 218 | 0.051 | |
| Total | 31,492 | 1 | 4279 | 1 |
Appendix C
| PE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period | T | D = 4 | D = 5 | D = 6 |
| 1901–2016 | 31,495 | 0.998 | 0.997 | 0.995 |
| 2000–2016 | 4282 | 0.997 | 0.994 | 0.983 |
| 2007–2009 | 755 | 0.992 | 0.975 | 0.91 |
Appendix D. Computational Implications
References
- Alvarez-Ramirez, Jose, and Eduardo Rodríguez. 2011. Long-term recurrence patterns in the late 2000 economic crisis: Evidences from entropy analysis of the Dow Jones index. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 78: 1332–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigó, José María, Samuel Zambrano, and Miguel AF Sanjuán. 2010. Detecting Determinism in Time Series with Ordinal Patterns: A Comparative Study. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos 20: 2915–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandt, Christoph. 2005. Ordinal time series analysis. Ecological Modelling 182: 229–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandt, Christoph. 2016. Permutation Entropy and Order Patterns in Long Time Series. In Time Series Analysis and Forecasting, Contributions to Statistics. Edited by Ignacio Rojas and Hector Pomares. Cham: Springer, pp. 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- Bandt, Christoph, and Bernd Pompe. 2002. Permutation Entropy: A natural Complexity Measure for Time Series. Physics Review Letters 88: 174102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandt, Chstoph, and Faten Shiha. 2007. Order Patterns in Time Series. Journal of Time Series Analysis 28: 646–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandt, Christoph, Gerhard Keller, and Bernd Pompe. 2002. Entropy of interval maps via permutations. Nonlinearity 15: 1595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bariviera, Aurelio, Angelo Plastino, and George Judge. 2018. Spurious Seasonality Detection: A Non-Parametric Test Proposal. Econometrics 6: 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, William Arnold, Apostolos Serletis, and Demitre Serletis. 2012. Nonlinear and Complex Dynamics in Economics. Working Paper Series in Theoretical and Applied Economics 201238. Lawrence: University of Kansas. [Google Scholar]
- Barsky, Robert B., and J. Bradford de Long. 1993. Why Does the Stock Market Fluctuate? The Quarterly Journal of Economics 108: 291–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canovas, Jose S., and Antonio Guillamon. 2009. Permutations and time series analysis. Chaos 19: 043103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Yinhe, Wen-wen Tung, J. B. Gao, Vladimir A. Protopopescu, and Lee M. Hively. 2004. Detecting dynamical changes in time series using the permutation entropy. Physical Review E 70: 046217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, Susan B., Scott Sigmund Gartner, Michael R. Haines, Alan L. Olmstead, Richard Sutch, and Gavin Wright. 2006. Historical Statistics of the United States. New York: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Clower, Erica, and Miguel Henry. 2019. PENTROPY: GAUSS Module to Compute Permutation Entropy Point Estimates of a Time Series. Statistical Software Components G00016, Boston College Department of Economics. Available online: https://ideas.repec.org/c/boc/bocode/g00016.html (accessed on 29 January 2019).
- Cressie, Noel, and Timothy RC Read. 1984. Multinomial Goodness–of–Fit Tests. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B 46: 440–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, Richard H., and Bruce Mizrach. 1994. Complex Economic Dynamics, Volume I: An Introduction to Dynamical Systems and Market Mechanisms. Cambridge: MIT Press. [Google Scholar]
- Eckmann, Jean-Pierre, and David Ruelle. 1985. Ergodic theory of chaos and strange attractors. Reviews of Modern Physics 57: 617–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, Amos, George G. Judge, and Douglas Miller. 1996. Maximum Entropy Econometrics. New York: John Wiley & Sons. [Google Scholar]
- Gorban, Alexander N., Pavel A. Gorban, and George Judge. 2010. Entropy: The Markov Ordering Approach. Entropy 12: 1145–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groth, Andreas. 2005. Visualization of coupling in time series by order recurrence plots. Physical Review E 72: 046220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, Miguel, Ron C. Mittelhammer, and John B. Loomis. 2018. An information theoretic approach to estimating willingness to pay for river recreation site attributes. Water Resource Economics 21: 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Yunfei, Feiyan Liu, Jianbo Gao, Changxiu Cheng, and Changqing Song. 2017. Characterizing Complexity Changes in Chinese Stock Markets by Permutation Entropy. Entropy 19: 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, George. 2016. Some Comments on the Current State of Econometrics. The Annual Review of Resource Economics 8: 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, George G., and Ron C. Mittelhammer. 2012a. An Information Theoretic Approach to Econometrics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Judge, George G., and Ron C. Mittelhammer. 2012b. Implications of the Cressie—Read Family of Additive Divergences for Information Recovery. Entropy 14: 2427–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juselius, Katarina, and Søren Johansen. 2006. Chapter 16. Extracting information from the data: A European view on empirical macro. In Post Walrasian Macroeconomics: Beyond the Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium Model. Edited by David Colander. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Kantz, Holger, and Thomas Schreiber. 2004. Nonlinear Time Series Analysis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, K., and M. Sinn. 2005. Ordinal of time series. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 356: 114–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, Andres M., Maria Teresa Martin, Angelo Plastino, and George Judge. 2012. On Extracting Probability Distribution Information from Time Series. Entropy 14: 1829–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBaron, Blake, and Leigh Tesfatsion. 2008. Modeling Macroeconomies as Open-Ended Dynamic Systems of Interacting Agents. American Economic Review: Papers & Proceedings 98: 246–50. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Daeyup. 2012. Permutation Entropies (PEs) of International Short-Term Interest Rates and Interest Rate Spreads Before the Financial Crisis of 2007–2009. Working Paper. Seoul: Bank of Korea. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, Andrew Wen-Chuan. 2008. Efficient market hypothesis. In The New Pagrave Dictionary of Economics. Edited by Steven N. Durlauf and Lawrence E. Blume. New York: Palgrave McMillan. [Google Scholar]
- Matilla-García, Mariano. 2007. A non-parametric test for independence based on symbolic dynamics. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control 31: 3889–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilla-García, Mariano, and Manuel Ruiz Marín. 2008. A Non-parametric test Using permutation Entropy. Journal of Econometrics 144: 139–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilla-García, Mariano, and Manuel Ruiz Marín. 2009. Detection of non-linear structure in time series. Economic Letters 105: 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilla-García, Mariano, and Manuel Ruiz Marín. 2010. A New Test for Chaos and Determinism based on Symbolic Dynamics. Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization 76: 600–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensi, Walid, Makram Beljid, and Shunsuke Managi. 2014. Structural breaks and the time-varying levels of weak-form efficiency in crude oil markets: Evidence from the Hurst exponent and Shannon entropy methods. International Economics 140: 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelhammer, Ron C., and George Judge. 2011. A Family of Empirical Likelihood Functions and Estimators for the Binary Response Model. Journal of Econometrics 164: 207–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, Marston, and Gustav A. Hedlund. 1938. Symbolic Dynamics. American Journal of Mathematics 60: 815–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, Steven M. 1991. Approximate entropy as a measure of system complexity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 88: 2297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, Timothy R. C., and Noel A.C. Cressie. 1988. Goodness–of–Fit Statistics for Discrete Multivariate Data. New York: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, Haroldo V., Max Jauregui, Luciano Zunino, and Ervin K. Lenzi. 2017. Characterizing time series via complexity-entropy curves. Physical Review E 95: 062106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedl, Maik, Andreas Müller, and Niels Wessel. 2013. Practical considerations of permutation entropy. The European Physical Journal, Special Topics 222: 249–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosser, J. Barkley, Jr. 1999. On the Complexities of Complex Economic Dynamics. Journal of Economic Perspectives 13: 169–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schittenkopf, Christian, Peter Tiňo, and Georg Dorffner. 2002. The benefit of information reduction for trading strategies. Applied Economics 34: 917–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensoy, Ahmet, Frank J. Fabozzi, and Veysel Eraslan. 2017. Predictability dynamics of emerging sovereign CDS markets. Economics Letters 161: 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serletis, Apostolos. 2016. Introduction to Macroeconomic Dynamics Special Issue on Complexity in Economic Systems. Macroeconomic Dynamics 20: 461–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, Claude Elwood. 1948. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell System Technical Journal 27: 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staniek, Matthäus, and Klaus Lehnertz. 2007. Parameter Selection for Permutation Entropy Measurements. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos 17: 3729–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiglitz, Joseph. 2018. Where modern macroeconomics went wrong. Oxford Review of Economic Policy 34: 70–106. [Google Scholar]
- Stutzer, Michael J. 1980. Chaotic dynamics and bifurcation in a macro model. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control 2: 353–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Aman. 1996. Entropy, divergence and distance measures with econometric applications. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference 49: 137–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin, Massimiliano. 2008. Forbidden patterns in financial time series. Chaos 18: 013119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanin, Massimiliano, Luciano Zunino, Osvaldo A. Rosso, and David Papo. 2012. Permutation Entropy and Its Main Biomedical and Econophysics Applications: A Review. Entropy 14: 1553–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, Luciano, Massimiliano Zanin, Benjamin M. Tabak, Darío G. Pérez, and Osvaldo A. Rosso. 2009. Forbidden patterns, permutation entropy and stock inefficiency. Physica A 388: 2854–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, Luciano, Massimiliano Zanin, Benjamin M. Tabak, Darío G. Pérez, and Osvaldo A. Rosso. 2010a. Complexity-entropy causality plane: A useful approach to quantify the stock market inefficiency. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 389: 1891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, Luciano, Miguel C. Soriano, Ingo Fischer, Osvaldo A. Rosso, and Claudio R. Mirasso. 2010b. Permutation-information-theory approach to unveil delay dynamics from time-series analysis. Physical Review E 82: 046212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Henry, M.; Judge, G. Permutation Entropy and Information Recovery in Nonlinear Dynamic Economic Time Series. Econometrics 2019, 7, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/econometrics7010010
Henry M, Judge G. Permutation Entropy and Information Recovery in Nonlinear Dynamic Economic Time Series. Econometrics. 2019; 7(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/econometrics7010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleHenry, Miguel, and George Judge. 2019. "Permutation Entropy and Information Recovery in Nonlinear Dynamic Economic Time Series" Econometrics 7, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/econometrics7010010
APA StyleHenry, M., & Judge, G. (2019). Permutation Entropy and Information Recovery in Nonlinear Dynamic Economic Time Series. Econometrics, 7(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/econometrics7010010




