New Graphical Methods and Test Statistics for Testing Composite Normality
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Review of Relevant Material
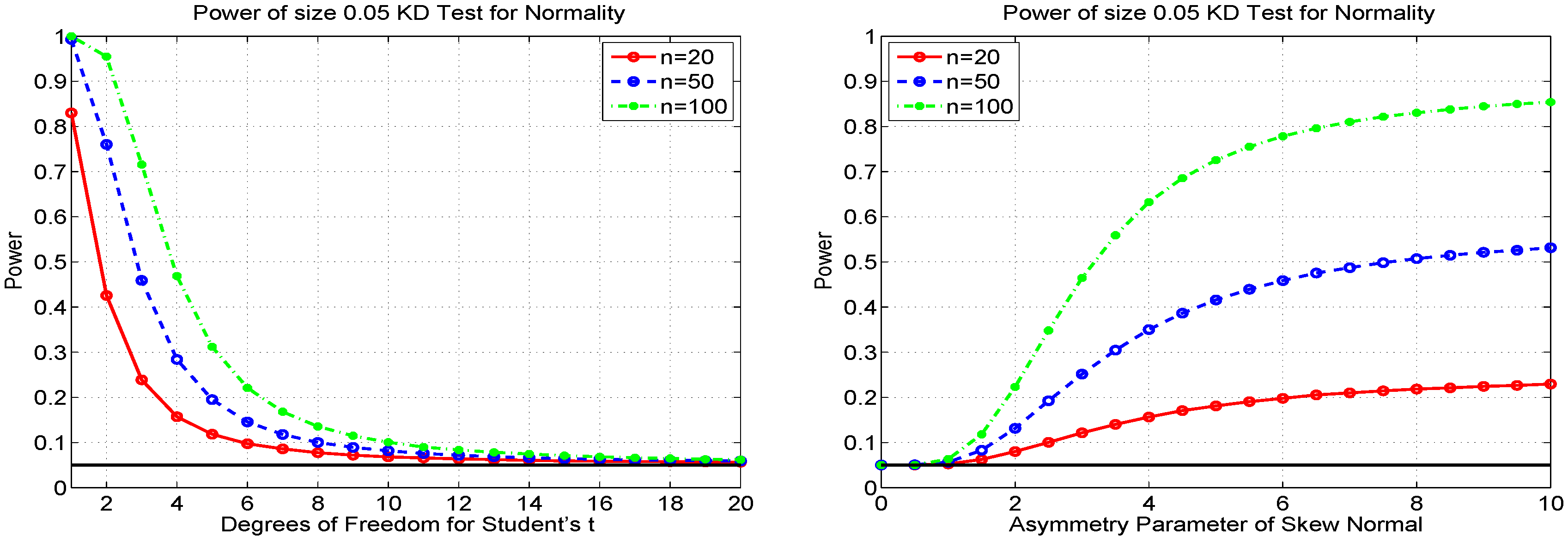
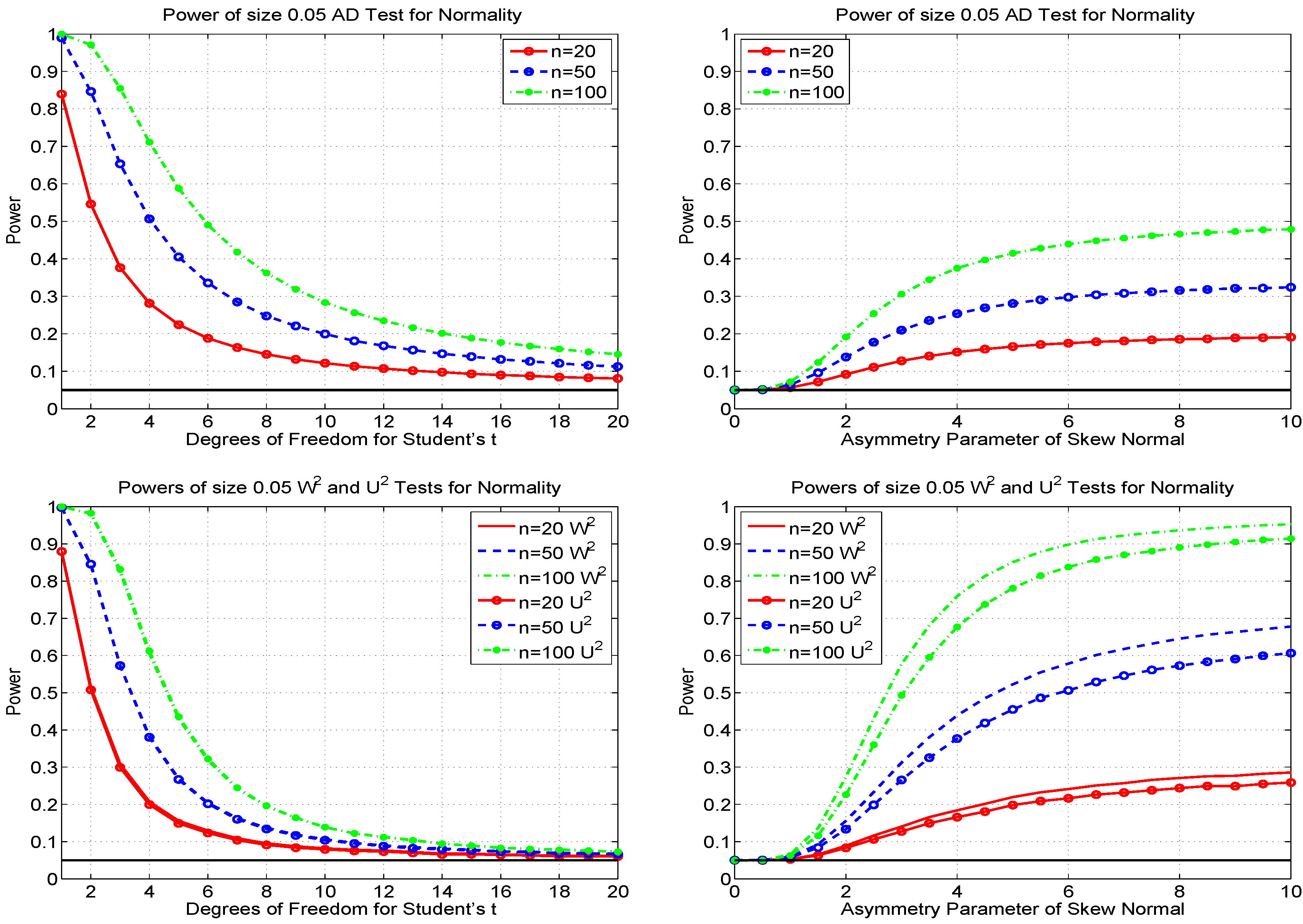
3. Null Bands
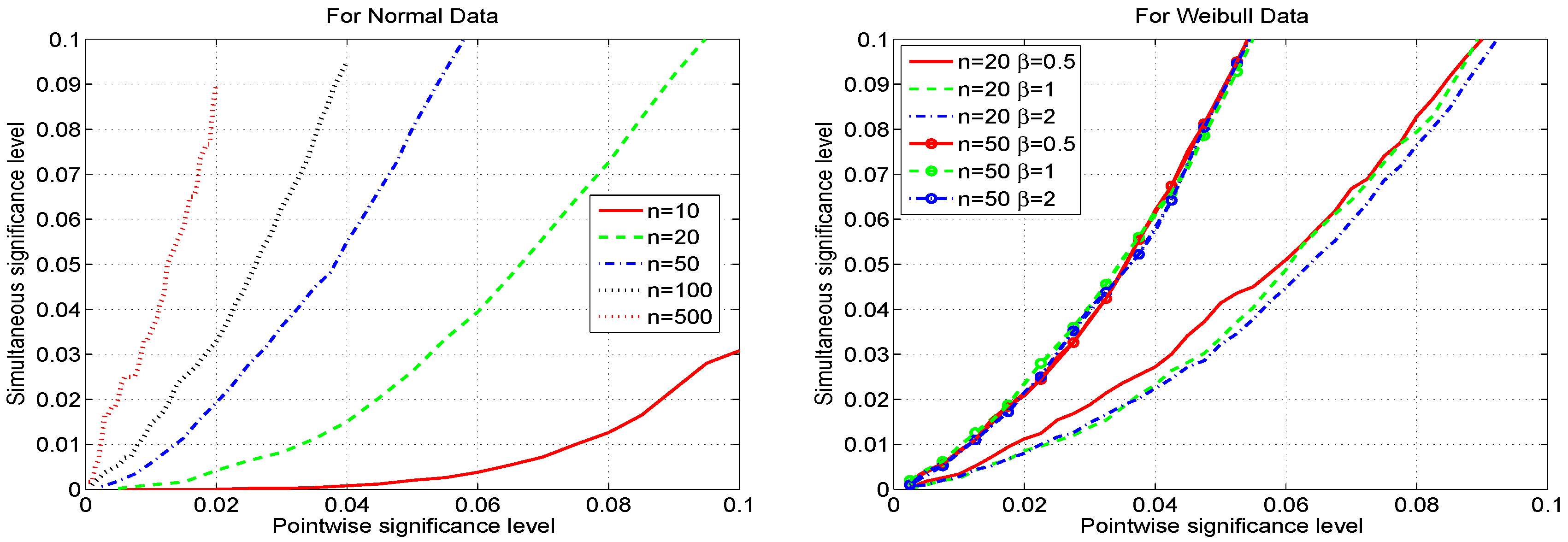
3.1. Mapping Pointwise and Simultaneous Significance Levels
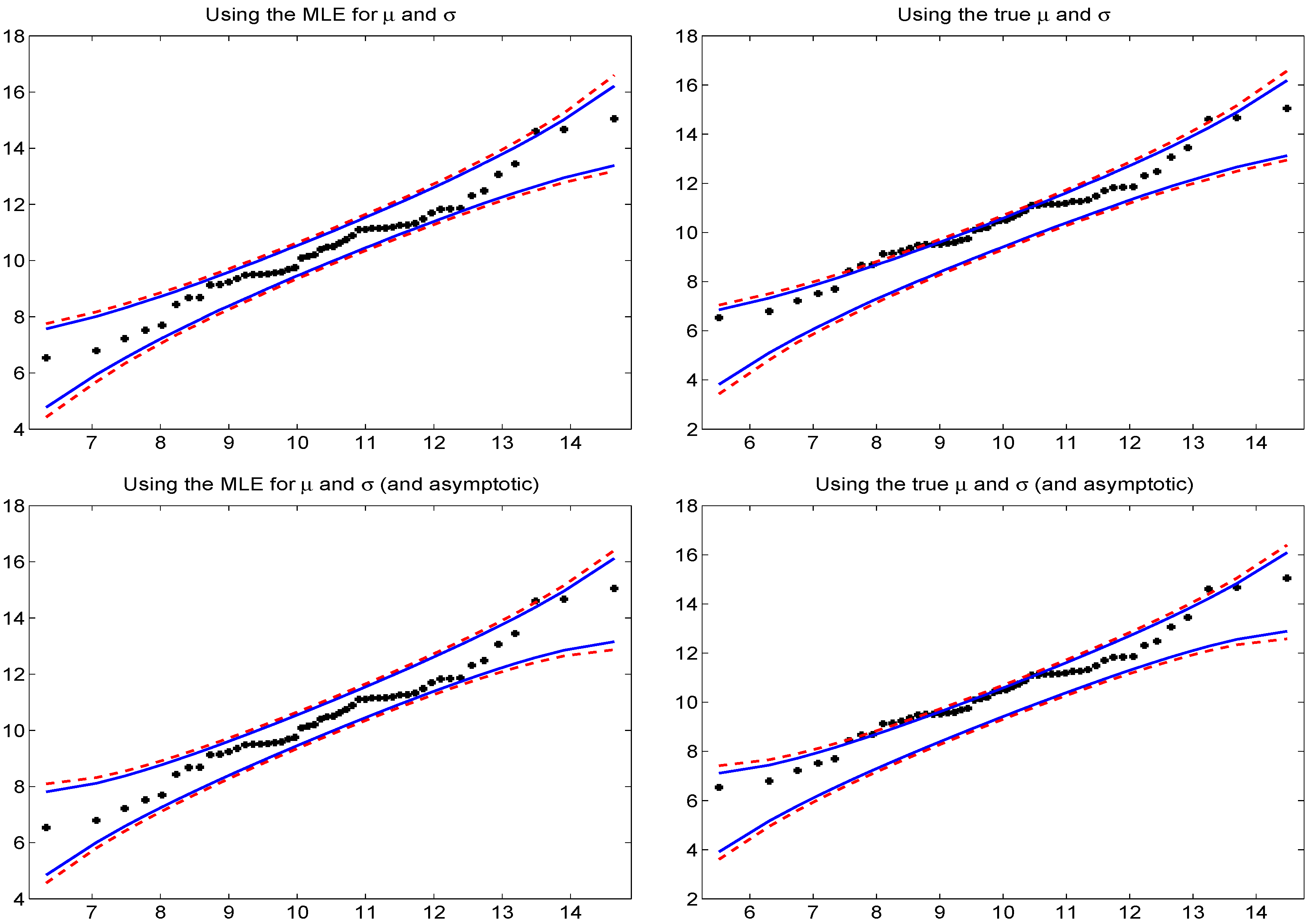
3.2. Q-Q Test
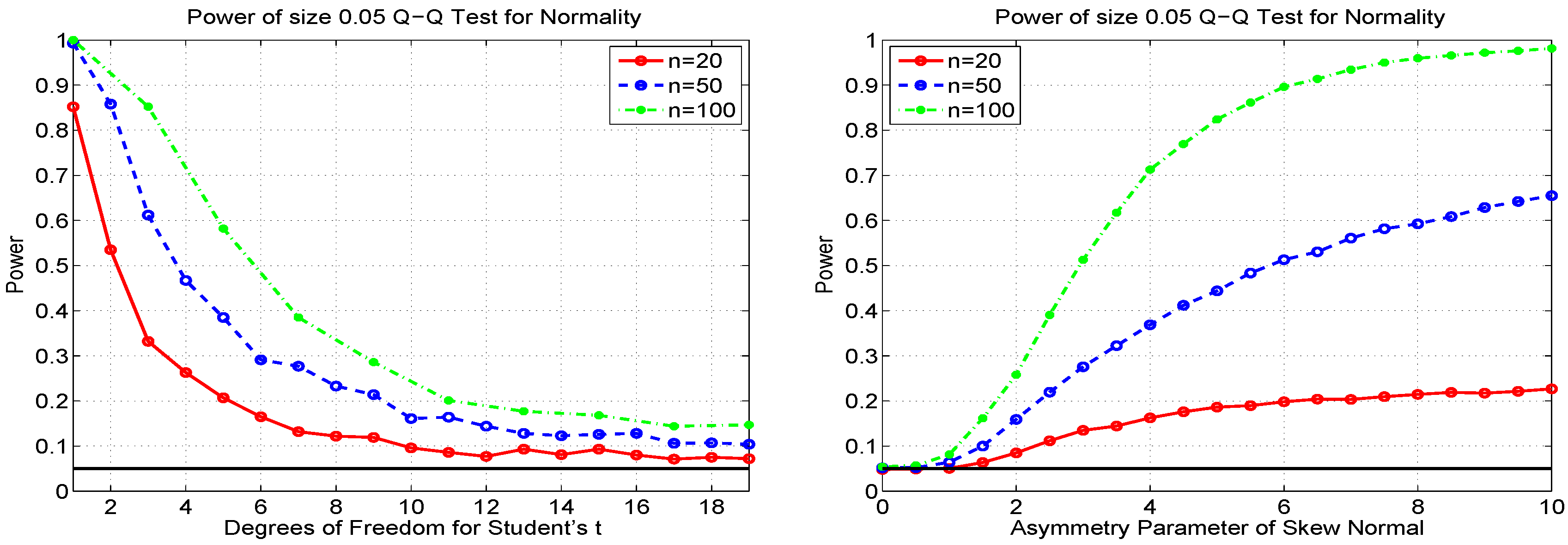
4. Further P-P and Q-Q Type Plots
4.1. (Horizontal) Stabilized P-P Plots
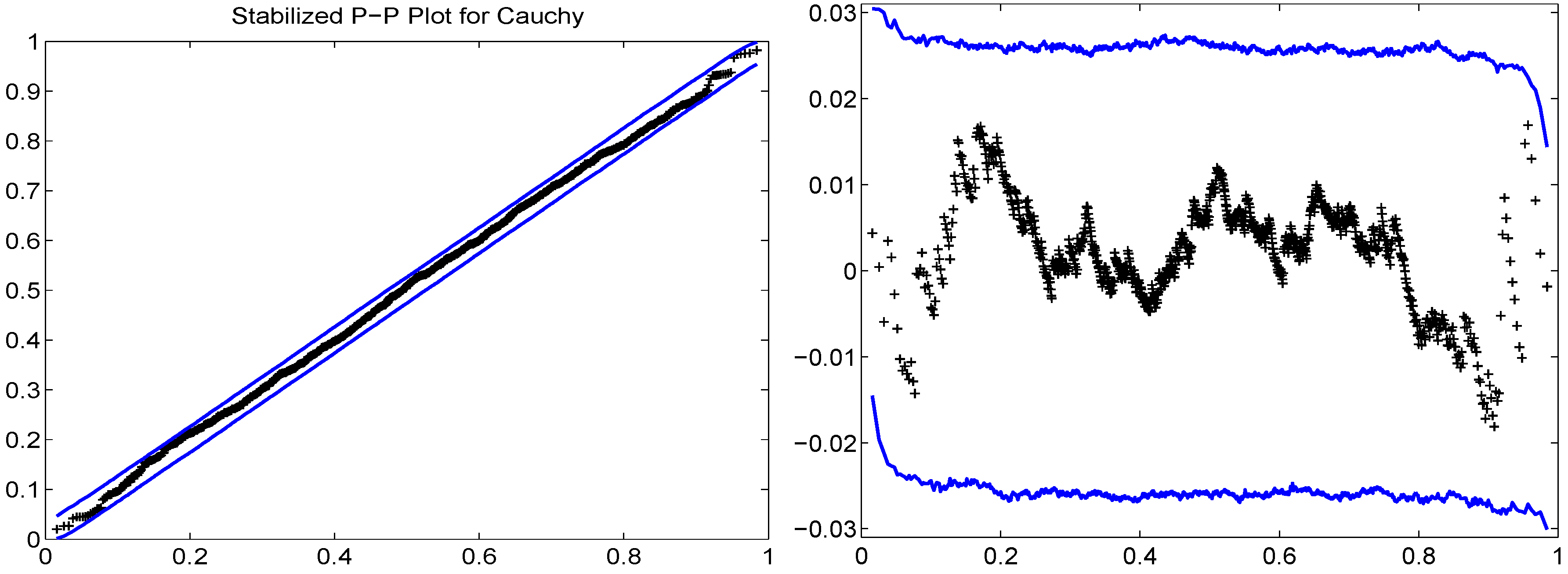

4.2. Modified S-P (MSP) Plots
| n \ coef | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | ||||
| 50 | ||||
| 100 |
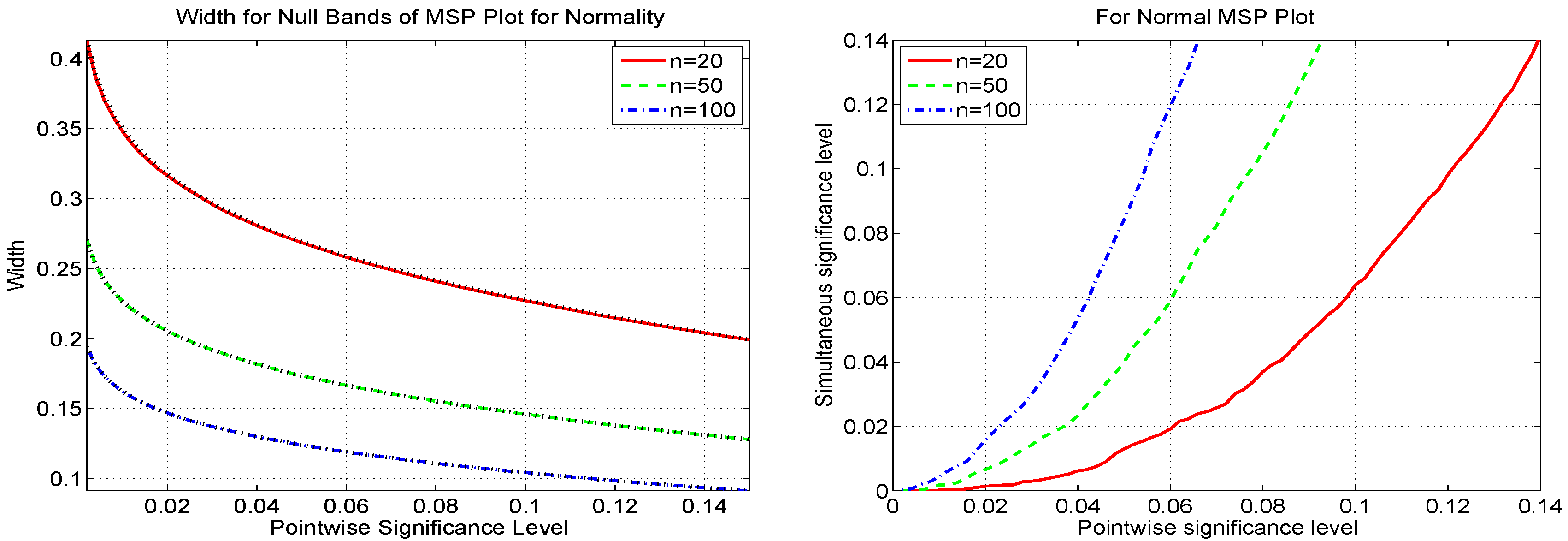
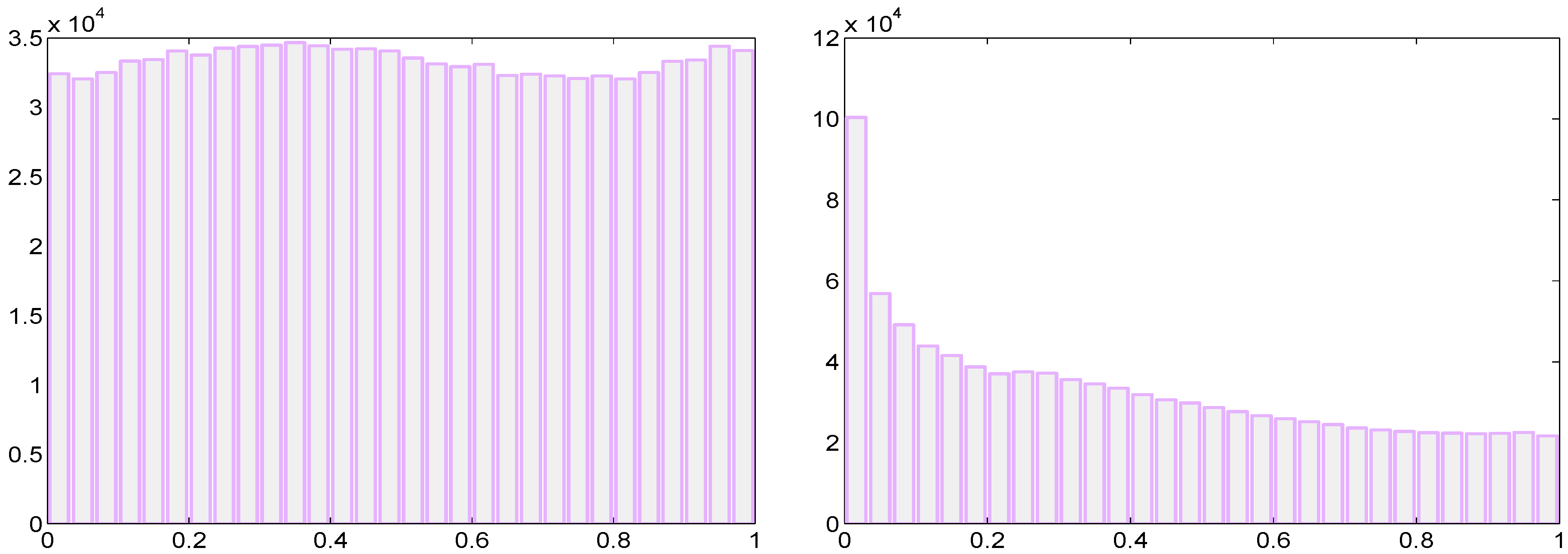
4.3. MSP Test for Normality
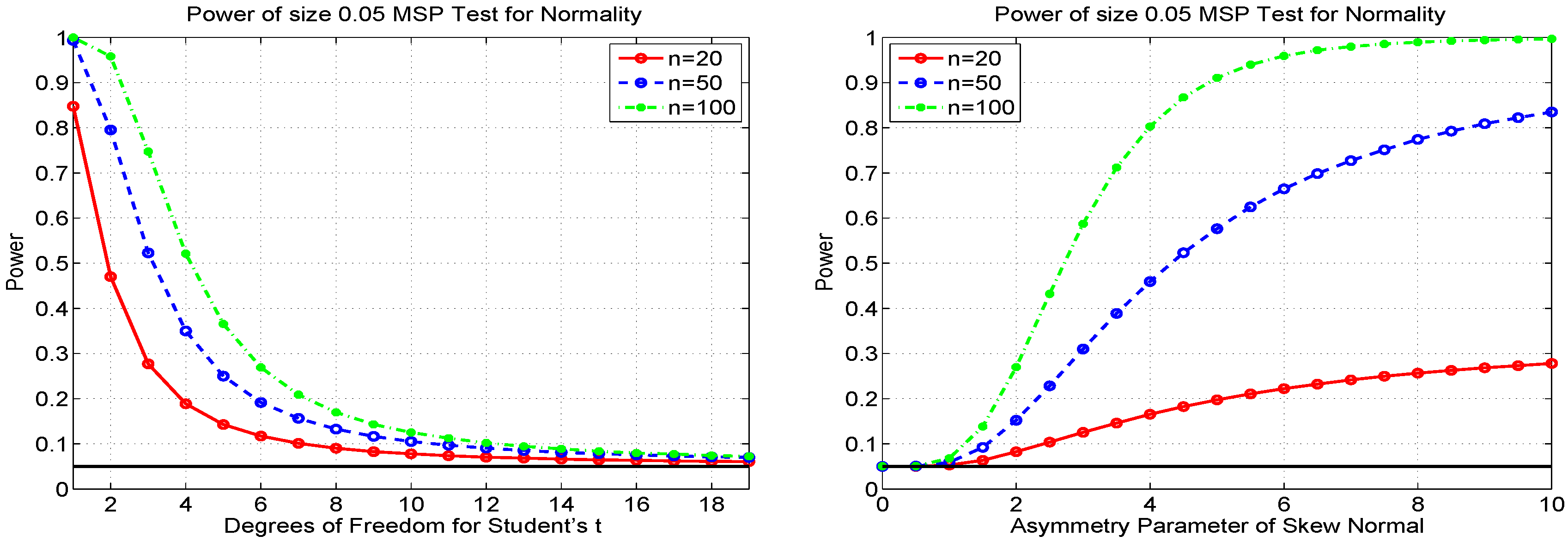
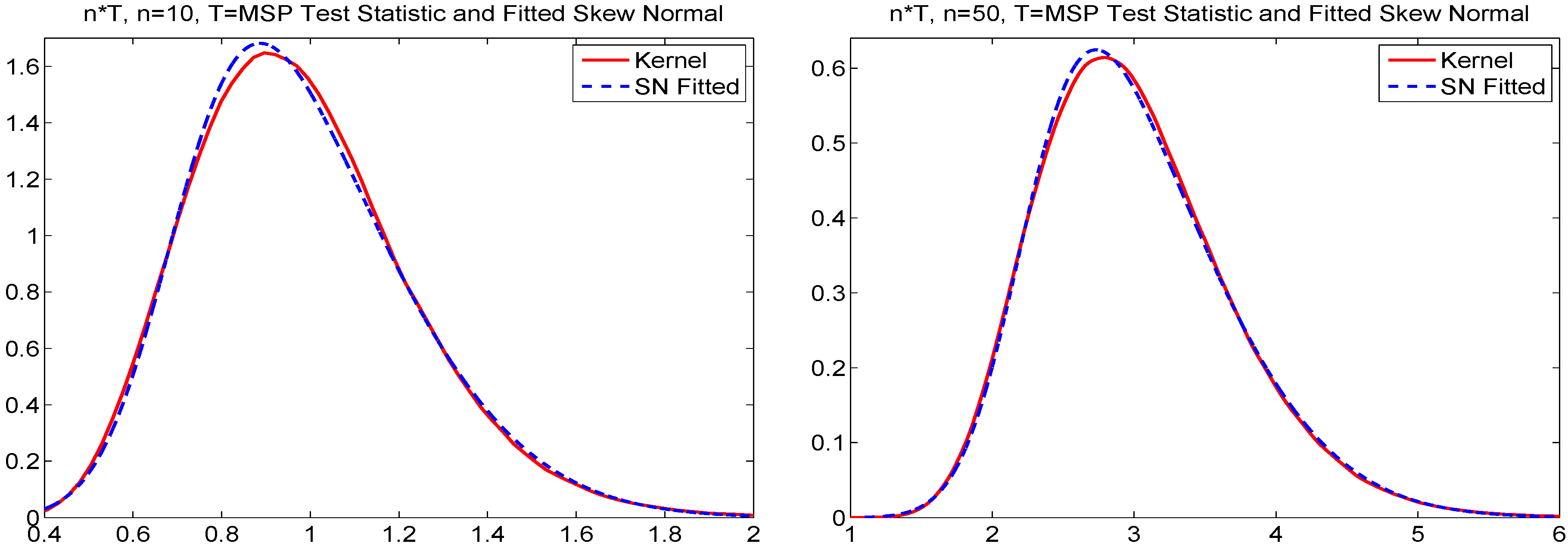
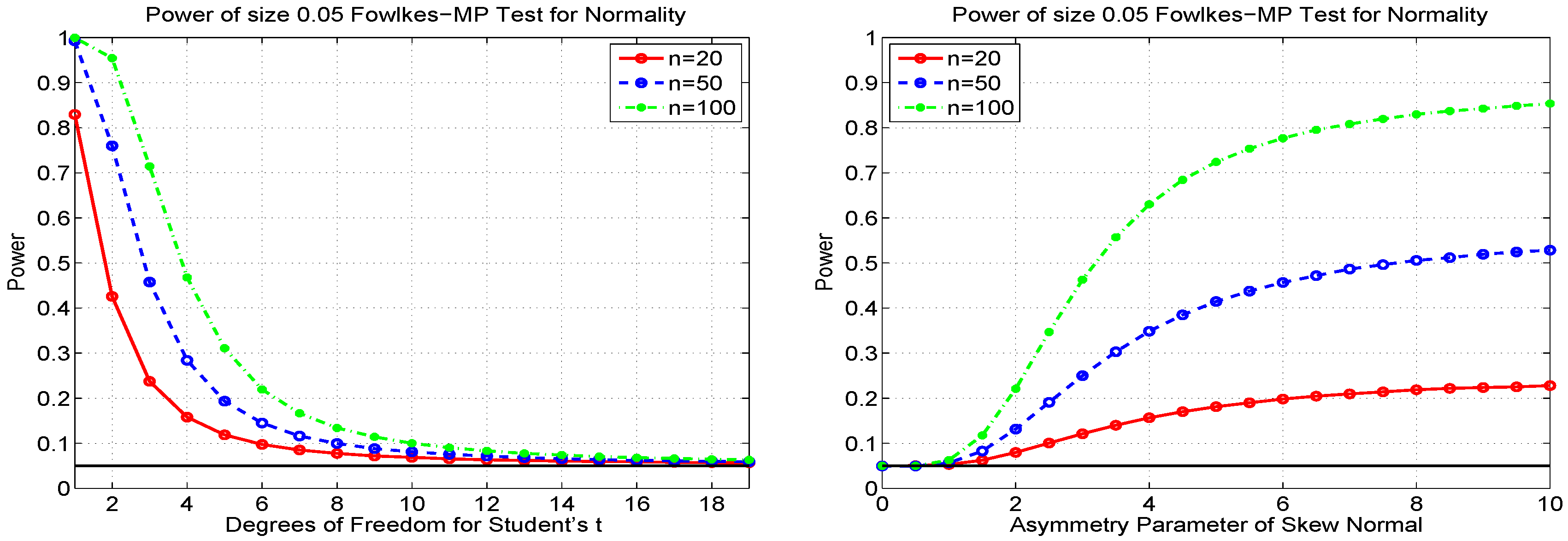
4.4. Modified Percentile (Fowlkes-MP) Plots

4.5. Power Comparisons Against Two-Component Mixed Normal Alternative
| Model \ Test | n | KD | AD | MSP | F–MP | JB | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. 0 (Normal) | 100 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.050 |
| No. 1 (Finance) | 100 | 0.799 | 0.712 | 0.916 | 0.924 | 0.799 | 0.798 | 0.890 | 0.635 |
| No. 2 (Equal Means) | 100 | 0.198 | 0.322 | 0.298 | 0.309 | 0.216 | 0.197 | 0.417 | 0.127 |
| No. 3 (Equal Vars) | 100 | 0.303 | 0.001 | 0.400 | 0.439 | 0.250 | 0.302 | 0.039 | 0.191 |
| No. 0 (Normal) | 200 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.050 |
| No. 1 (Finance) | 200 | 0.983 | 0.881 | 0.997 | 0.998 | 0.973 | 0.983 | 0.994 | 0.940 |
| No. 2 (Equal Means) | 200 | 0.358 | 0.430 | 0.523 | 0.545 | 0.328 | 0.358 | 0.642 | 0.225 |
| No. 3 (Equal Vars) | 200 | 0.593 | 0.000 | 0.756 | 0.789 | 0.492 | 0.594 | 0.428 | 0.394 |
5. Further Tests for Composite Normality
5.1. Jarque-Bera Test


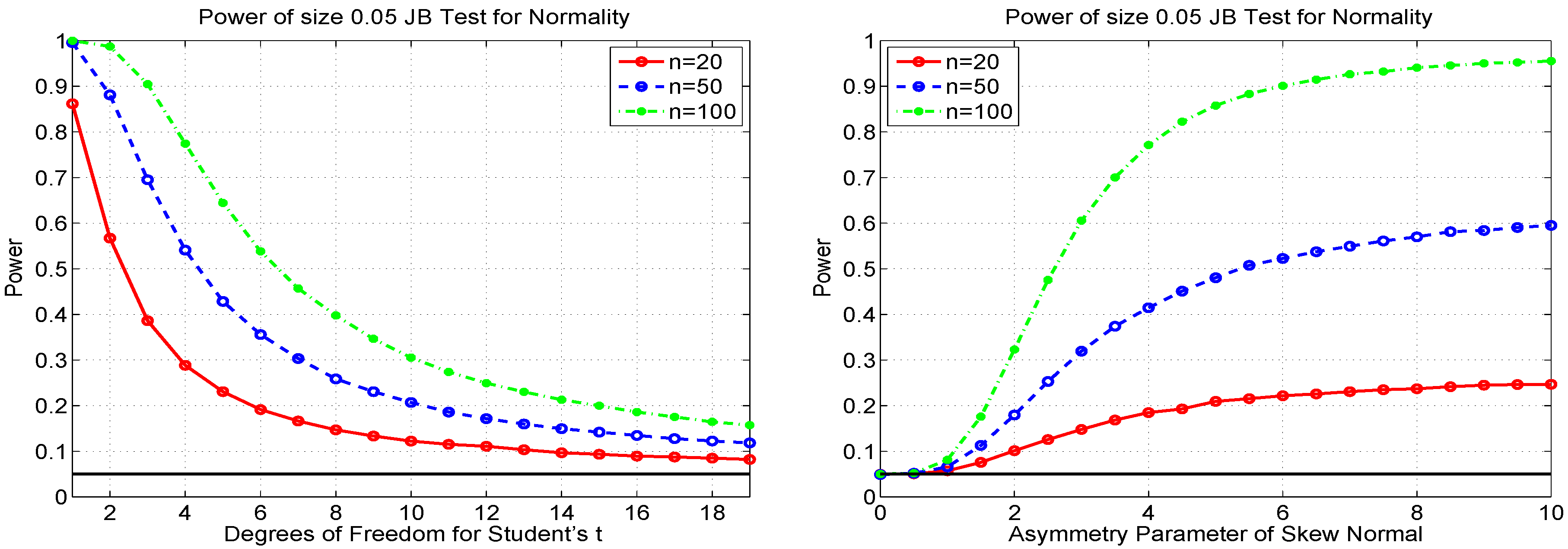
5.2. Ghosh Graphical Test

5.3. Information-Theoretic Distribution Test
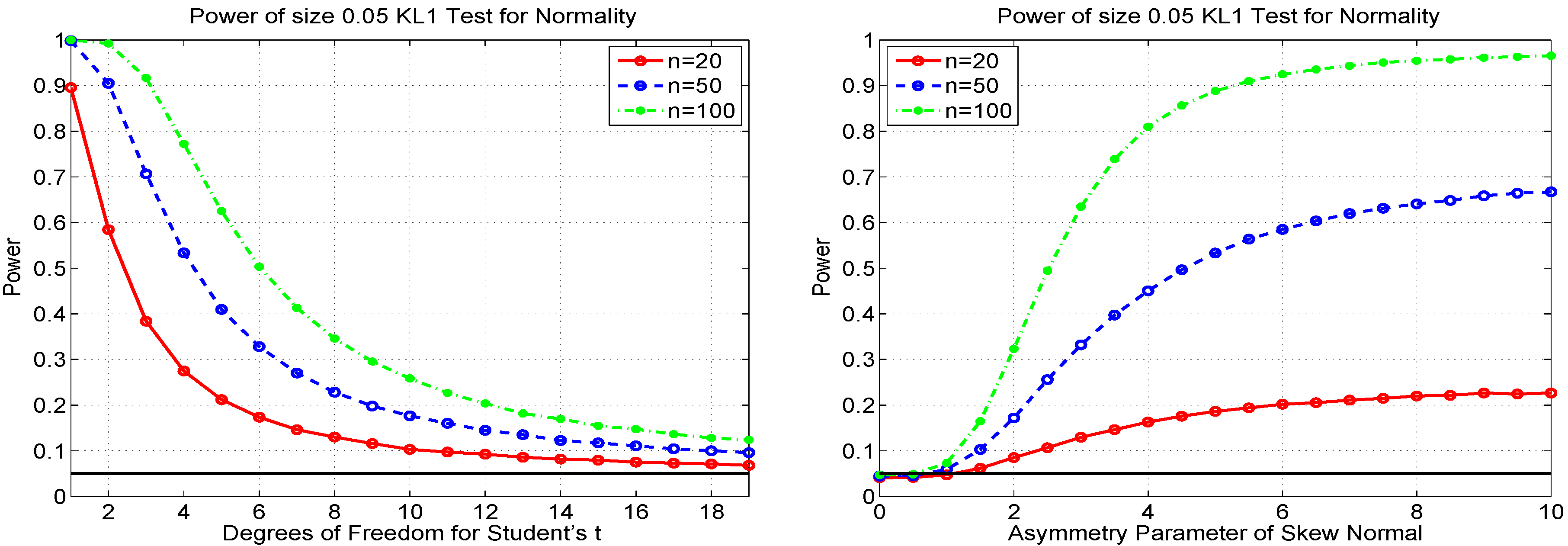
6. Combining Tests and Power Envelopes
6.1. Combining Tests
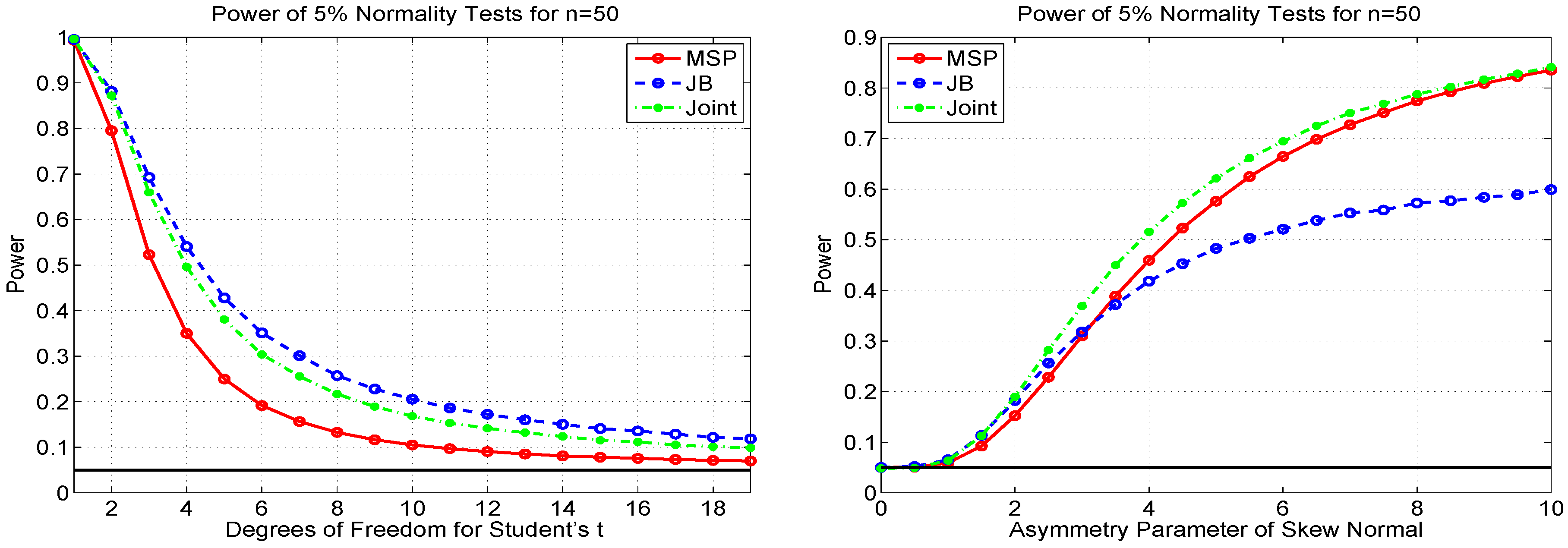
6.2. Power Comparisons for Testing Composite Normality
6.3. Most Powerful Tests and Power Envelopes
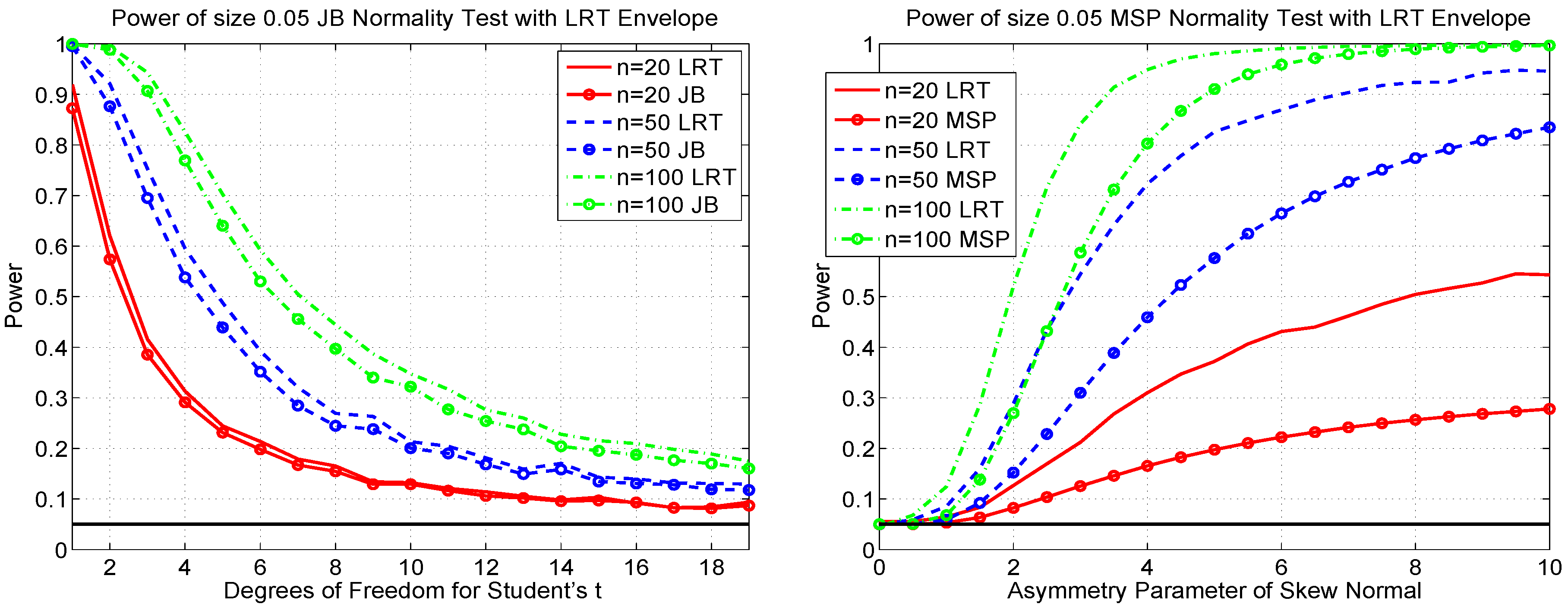
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- M.S. Paolella, and P. Polak. “ALRIGHT: Asymmetric LaRge-scale (I)GARCH with Hetero-Tails.” Int. Rev. Econ. Financ., 2015, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M.S. Paolella, and P. Polak. “COMFORT: A Common Market Factor Non-Gaussian Returns Model.” J. Econ. 187 (2015): 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. Krause, M.S. Paolella, P. Polak, and University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland. “SIMBACO: Simulation-Based Method for Portfolio Optimization for Copula Models.” 2015, to be submitted for publication. [Google Scholar]
- R.W. Butler, J. Näf, M.S. Paolella, P. Polak, and University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland. “Getting out of the COMFORT Zone: The MEXI Distribution for Asset Returns.” 2015, to be submitted for publication. [Google Scholar]
- A. Buja, and W. Rolke. Calibration for Simultaneity: (Re)Sampling Methods for Simultaneous Inference with Applications to Function Estimation and Functional Data. Philadelphia, PA, USA: The Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- J.H.J. Einmahl, and I.W. McKeague. “Confidence Tubes for Multiple Quantile Plots via Empirical Likelihood.” Ann. Stat. 27 (1999): 1348–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A.C. Davison, and D.V. Hinkley. Bootstrap Methods and Their Application. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- S. Aldor-Noiman, L.D. Brown, A. Buja, W. Rolke, and R.A. Stine. “The Power to See: A New Graphical Test of Normality.” Am. Stat. 67 (2013): 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Aldor-Noiman, L.D. Brown, A. Buja, W. Rolke, and R.A. Stine. “Correction to: The power to See: A New Graphical Test of Normality.” Am. Stat. 68 (2014): 318. [Google Scholar]
- L. Dümbgen, and J.A. Wellner. “Confidence Bands for a Distribution Function: A New Look at the Law of the Iterated Logarithm.” 2014. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1402.2918 (accessed on 28 January 2015).
- W.A. Rosenkrantz. “Confidence Bands for Quantile Functions: A Parametric and Graphic Alternative for Testing Goodness of Fit.” Am. Stat. 54 (2000): 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- W.F. Webber. “Comment on Rosenkrantz (2000). In Letters to the Editor.” Am. Stat. 55 (2001): 171–172. [Google Scholar]
- E.B. Fowlkes. “Some Methods for Studying the Mixture of Two Normal (Lognormal) Distributions.” J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 74 (1979): 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J.R. Michael. “The Stabilized Probability Plot.” Biometrika 70 (1983): 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Ghosh. “A New Graphical Tool to Detect Non-Normality.” J. R. Stat. Soc. 58 (1996): 691–702. [Google Scholar]
- T. Stengos, and X. Wu. “Information-Theoretic Distribution Test with Application to Normality.” Econom. Rev. 29 (2010): 307–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G. Blom. Statistical Estimates and Transformed Beta Variables. New York, NY, USA: John Wiley & Sons, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- T. Anderson, and D. Darling. “Asymptotic Theory of Certain “Goodness of Fit” Criteria Based on Stochastic Processes.” Ann. Math. Stat. 23 (1952): 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T. Anderson, and D. Darling. “A Test of Goodness of Fit.” J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 49 (1954): 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. Durbin. Distribution Theory for Tests Based on Sample Distribution Function. CBMS-NSF Regional Conference Series in Applied Mathematics; Philadelphia, PA, USA: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- A. Azzalini. “A Class of Distributions Which Includes the Normal Ones.” Scand. J. Stat. 12 (1985): 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- N.T. Gridgeman. “A Comparison of Two Methods of Analysis of Mixtures of Normal Distributions.” Technometrics 12 (1970): 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H.C. Thode. Testing for Normality. New York, NY, USA: Marcel Dekker, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- L.D. Brown. “In-Season Prediction of Batting Averages: A Field Test of Empirical Bayes and Hierarchical Bayes Methodologies.” Ann. Appl. Stat. 2 (2008): 113–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K. Roeder. “A Graphical Technique for Determining the Number of Components in A Mixture of Normals.” J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 89 (1994): 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C.M. Jarque, and A.K. Bera. “Efficient Tests for Normality, Homoskedasticity and Serial Independence of Regression Residuals.” Econ. Lett. 6 (1980): 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. D’Agostino, and E.S. Pearson. “Testing for Departures from Normality. Empirical Results for Distribution of b2 and .” Biometrika 60 (1973): 613–622. [Google Scholar]
- K.O. Bowman, and L.R. Shenton. “Omnibus Test Contours for Departures from Normality Based on and b2.” Biometrika 62 (1975): 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A. Takemura, M. Akimichi, and S. Kuriki. “Skewness and Kurtosis as Locally Best Invariant Tests of Normality.” 2006. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/math.ST/0608499 (accessed on 28 January 2015).
- M.S. Paolella. Intermediate Probability: A Computational Approach. New York, NY, USA: Wiley-Interscience, 2007. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paolella, M.S. New Graphical Methods and Test Statistics for Testing Composite Normality. Econometrics 2015, 3, 532-560. https://doi.org/10.3390/econometrics3030532
Paolella MS. New Graphical Methods and Test Statistics for Testing Composite Normality. Econometrics. 2015; 3(3):532-560. https://doi.org/10.3390/econometrics3030532
Chicago/Turabian StylePaolella, Marc S. 2015. "New Graphical Methods and Test Statistics for Testing Composite Normality" Econometrics 3, no. 3: 532-560. https://doi.org/10.3390/econometrics3030532
APA StylePaolella, M. S. (2015). New Graphical Methods and Test Statistics for Testing Composite Normality. Econometrics, 3(3), 532-560. https://doi.org/10.3390/econometrics3030532





