Abstract
Bone loss and osteoporosis is a serious health problem worldwide. The impact of osteoporosis is far greater than many other serious health problems, such as breast and prostate cancers. Statistically, one in three women and one in five men over 50 years of age will experience osteoporotic fractures in their life. In this paper, the design and development of a portable IoT-based sensing system for early detection of bone loss have been presented. The CTx-I biomarker was measured in serum samples as a marker of bone resorption. A planar interdigital sensor was used to evaluate the changes in impedance by any variation in the level of CTx-I. Artificial antibodies were used to introduce selectivity to the sensor for CTx-I molecule. Artificial antibodies for CTx-I molecules were created using molecular imprinted polymer (MIP) technique in order to increase the stability of the system and reduce the production cost and complexity of the assay procedure. Real serum samples collected from sheep blood were tested and the result validation was done by using an ELISA kit. The PoC device was able to detect CTx-I concentration as low as 0.09 ng/mL. It exhibited an excellent linear behavior in the range of 0.1–2.5 ng/mL, which covers the normal reference ranges required for bone loss detection. Future possibilities to develop a smart toilet for simultaneous measurement of different bone turnover biomarkers was also discussed.
1. Introduction
Osteoporosis is a disease that reduces the quality and quantity of bones, making them weak and more likely to fracture [1]. Osteoporosis can affect men and women, but women are at greater risk of developing it. This disease is rather a more serious problem for the postmenopausal women and elderly people [2].
Bone is a metabolically active tissue that is continuously being remodeled throughout an individual’s lifetime, first being broken down (bone resorption) and then being rebuilt (bone formation) [3]. During childhood and teenage years, formation occurs faster than resorption; as a result, bones become heavier, larger and denser. This condition will continue until peak bone mass (maximum bone density and strength) is reached around age 30, and during 30–45, the bone condition will be relatively stable. After that, bone resorption begins to overpass bone formation. For women, bone loss is quickest in the first few years after menopause. The modelling and remodeling process of bone directly influences bone’s mechanical structure and its strength. Under normal conditions, bone formation and bone resorption are tightly coupled to each other in order to provide a balance in skeletal metabolism. Usually, osteoporosis occurs when bone formation and bone resorption are uncoupled, and the process of bone resorption happens at a higher rate than bone formation. Figure 1 shows the difference of bones between a healthy person and an osteoporotic patient.
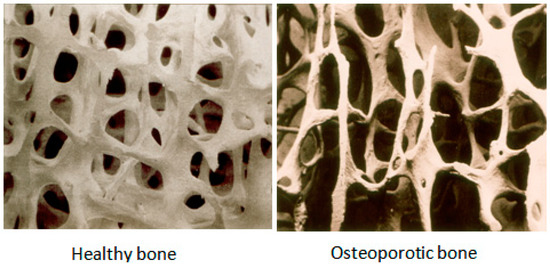
Figure 1.
Depicting healthy bone and osteoporotic bone [7].
Research on biochemical markers of bone turnover has significantly improved in the last few years [4]. Among the several markers of bone resorption, measurements of the urinary excretion of N-terminal and C-terminal cross-linked telopeptides and serum C-terminal cross-linked telopeptides are the most sensitive and accurate [5].
Type I Collagen is the main structural protein of bones that forms approximately 90% of the organic bone matrix. Type I collagen is broken down during the process of bone resorption, and C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (CTx-I) is released into the circulation. So, it can be considered as an excellent prognostic biomarker that can be used for the measurement of bone resorption and can give information about the rate of bone loss [6]. If the concentration of CTx-I exceeds the reference range (0.04–0.63 ng/mL in serum) it can be considered as an indication of bone loss occurrence [4].
2. Current Methodologies
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is the most accurate way and the gold standard technique to diagnose osteoporosis by measuring the bone mineral density (BMD) osteoporosis [8]. DXA scan (Figure 2) uses dual X-ray beams at two photon energies to measure BMD. Dense bones allow less of the X-ray beams to pass through them.
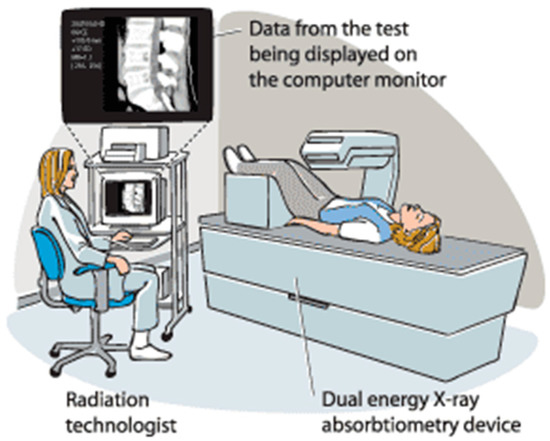
Figure 2.
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) [9].
The amount of X-ray beams that are blocked by bone and soft tissue is compared to each other. This test can diagnose osteoporosis and monitor the improvement of bone density during a treatment.
Since bone density changes very slowly, BMD studies are needed to be of longer duration up to 2–3 years [10], whereas changes in biochemical markers of bone turnover can be evident after only a few weeks. Therefore, detection and quantification of biochemical markers in conjunction with the measurement of bone density can aid in monitoring disease and the response to treatment [11].
Most of the available techniques for the detection of biochemical markers of bone turnover are based on enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). ELISA is able to detect very low concentrations of antigens or antibodies in a biological fluid through a colour variation. In the ELISA method enzyme-labeled antigens and antibodies are used for the detection of target molecules. Alkaline phosphatase and glucose oxidase are the most commonly used enzymes [12,13]. ELISA has been widely used in peptide and protein detection [14]. The wells of a 96-well microtiter plate are coated with the antigen. The antigen binds to a specific antibody, which is then identified by the secondary enzyme-linked antibody. A chromogenic substrate is used to change the colour in the existence of antigen. Lastly, the measurement is performed using a spectrophotometer. Figure 3 shows a general procedure of ELISA technique.
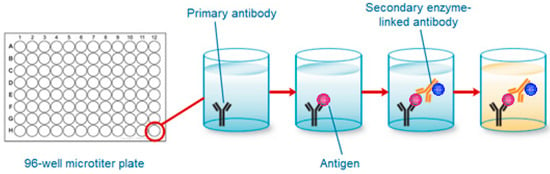
Figure 3.
General procedure of ELISA technique.
In spite of the great sensitivity and selectivity, the use of such techniques has huge limitations because of the high equipment cost and the labour involved. ELISA-based assays are expensive and time consuming. Moreover, they require laboratory environment and technical expertise. Devices that can utilize the antigen-antibody based methods together with low-cost sensors for point-of-care (PoC) testing looks to be an excellent replacement for ELISA-based immunoassays [4,15,16].
3. Interdigital Sensor Based Measurement
Interdigital sensors are structured in a finger-like pattern operating in the principle of parallel plate capacitors. The advantages of using these sensors lie in the uniformity of the electric field along with non-destructive, in situ, and single side access to the material under test. When a time dependent voltage signal is provided as an input to the sensor, the electric field lines bulge from one electrode to another of opposite polarity as a result of the planar structure of the material. A novel MEMS-based senor with specified dimensions was fabricated to employ interdigitated sensing and used to detect CTx-I molecules. The penetration depth of the electric field lines was varied with the variation of the number of sensing electrodes between the excitation electrodes of the sensors. The characteristics of the switching electric field passing through the test sample were studied to analyze the information about the properties of the test sample [17].
Etching and photolithography techniques were used to fabricate the interdigital sensors used in this work. A total 36 sensors were designed on a four-inch silicon wafer. The gold electrodes with 500 nm thickness were patterned on the silicon substrate using the sputtering method. Each sensor has a dimension of 10 × 10 mm2 including a sensing area of 2.5 × 2.5 mm2 [18]. Figure 4 shows a silicon sensor with a 1-5-25 configuration that includes five sensing electrodes between two excitation electrodes with 25 µm spacing between the consecutive electrodes. The average penetration depth of electric field for deionized water was calculated to be 212.5 µm [19].
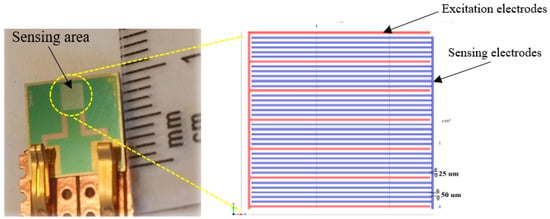
Figure 4.
Planar interdigital sensor with multi-sensing electrode configuration.
3.1. Synthesis of Artificial Antibodies for CTx-I and Functionalization of the Sensor
In order to introduce selectivity to the sensor, the sensing area will be coated by artificial antibodies. The coating materials to detect CTx-I will be created by molecular imprinted polymer (MIP) technology. Molecular imprinting is an inexpensive and relatively inexpensive technique that allows the creation of artificial recognition sites in synthetic polymers. Figure 5 shows the general principle of molecular imprinting technology. A template molecule (T) is mixed with the functional monomers (M) and then a cross-linker (CL) forms a self-assembled complex (1); The polymerization of the resulting system produces a highly cross-linked structure including imprinted sites (2); Finally, template molecules are extracted from the polymer matrix living cavities that can selectively recognize and bind the target molecule (3) [20]. MIPs have considerable potential for applications in the areas of clinical analysis, medical diagnostics, environmental monitoring, and drug delivery. Molecular imprinting technology allows the creation of synthetic receptors with binding constants comparable to natural receptors, but capable of withstanding much harsher conditions such as high temperature, pressure, extreme pH, and organic solvents compared to proteins and nucleic acids. These materials are also less expensive to synthesize and can be manufactured in large quantities with good reproducibility [21]. Artificial antibodies are appropriate alternatives to natural antibodies and biological receptors.
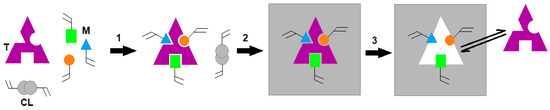
Figure 5.
General principle of molecular imprinting technology.
The most popular synthetic strategies to produce MIPs are bulk polymerization and precipitation polymerization. In this work, precipitation polymerization technique was employed to create the artificial antibodies for CTx-I on polymer microspheres [22]. For the traditional MIP preparation method (bulk polymerization), the polymers in the form of bulk need to be crushed, ground, and sieved to produce polymer particles with a desired size. Therefore, large quantities of analyte recognition sites are wasted during these time-consuming processes. Compared with bulk polymers, spherical MIPs are easily prepared by different polymerization techniques such as precipitation polymerization.
MIP was prepared using precipitation polymerization method reported in our previous paper [23]. Methacrylic acid (MAA) as the monomer, 2,2-azoisobutronitrile (AIBN) as the initiator and ethylene glycol methacrylate (EGDMA) as the cross-linker were procured for Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MI, USA) and CTx-I peptide as the template was synthesised by LifeTein (Somerset, NJ, USA). A mixture was prepared by mixing the template, functional monomer and cross-linker in the accetonitlile solvent. The initiator was then added to the solution and kept in a hot-water bath (60 °C) to start the polymerization process. The polymer was formed after 20 h. In the next stage, the template molecules were removed from the polymer using the soxhlet extraction technique with a mixture of methanol/acetic acid 50/50 (v/v) for 24 h, leaving recognition sites which are complementary with the CTx-I molecule. The extraction of the target molecule was validated by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) testing of the eluent remained from the soxhlet extraction. After that, static adsorption and uptake kinetics of CTx-I to MIP were assessed by using HPLC to determine the saturation level of MIP and the adsorption time required by MIP to capture the CTx-I available in the sample. The detailed procedure of MIP creation has been explained in our earlier work [24].
The PTL-MM01 dip-coater was utilized to coat the sensing area with the MIP-based artificial antibodies. A coating suspension was prepared by mixing the MIP with the acrylic lacquer. The sensor was dipped in the coating suspension and withdrawn after 5 s with a speed of 100 mm/s and was dried at room temperature for 2 h.
3.2. Development of a Microcontroller-Based System for Impedance Monitoring
In order to offer a portable PoC device for bone loss monitoring, a microcontroller-based system was developed to measure the level of CTx-1 in serum and data transfer data to an Internet of Things (IoT)-based cloud server. The data can then be provided to the medical practitioner using the IoT technology and a detailed investigation can initiate for early detection and treatment.
An AD5933 [25] impedance analyzer was used to collect the impedance information which was generated due to different CTx-1 concentrations. I2C protocol [26] was used to collect the impedance data from the coated sensor. A battery was used to supply power to the microcontroller. Eventually, the measured CTx-1 concentration was transferred to an IoT-based cloud server in order to provide the data to a practitioner for further assessment and investigation. An ADG849 switch was used to calibrate the system before every measurement. The microcontroller collects the impedance data from the impedance analyzer and uses the standard calibration graph to calculate the CTx-1 concentration. The circuit diagram of the proposed PoC device is shown in Figure 6.
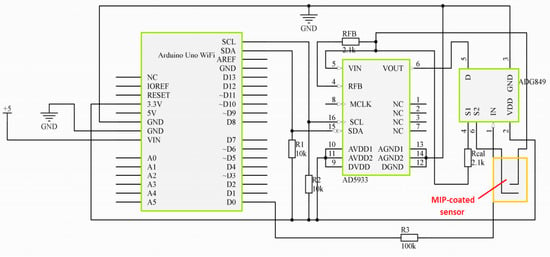
Figure 6.
Circuit diagram of the proposed point of care device.
The microcontroller board contains an integrated WiFi, which helps to connect the PoC device with a gateway to transfer the data to a remote server. Thingspeak [27] is a free IoT-based cloud server that was used to store the data. This cloud server is accessible from any location, which helps the health care provider to monitor the real-time data for early detection of bone loss. The Arduino ciao [28] library was used to transfer the CTx-I concentrations to the designated private channel in Thingspeak.
3.3. Development of the Calibration Curve and Real Sample Measurement
The calibration experiments were carried out by testing five known-concentration samples (0.1, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, and 2.5 ppb). The samples were prepared by dissolving the CTx-I peptide in deionized water. A 50 µL measure of the sample was pipetted on the MIP-coated surface, after seven minutes the surface was rinsed and the measurement was done using the developed PoC device. 320 Hz was considered as the optimum frequency as it was suggested by the commercial impedance analyzer HIOKI 3536 [23]. Figure 7 shows the calibration curve of the PoC device. Every measurement was done five times and the mean value was used to plot the calibration standard curve (Table 1). The coating layer was regenerated after completing each measurement by immersing the sensor in 1% HCL in distilled water [4].
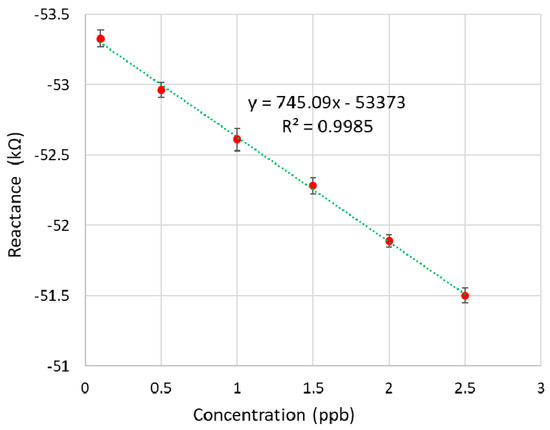
Figure 7.
Calibration curve of the PoC system.

Table 1.
The mean value of reactance and standard deviation for different concentrations of CTx-I.
The sensor provides its values of resistance and reactance at normal condition. The impedance values changes when the sample contains contamination. The reactance corresponding to zero concentration is the normal value of reactance of the sensor.
Unknown real serum samples collected from sheep blood were tested using the developed sensing system to measure the concentration of CTx-1. The results were validated using a serum CrossLaps® ELISA kit. Figure 8 shows a comparison between the PoC results and the ELISA results. The real-time data from the developed device is shown in Figure 9. The graph is developed to show the capability of the developed sensing system to transfer the measured data to the IoT-based cloud server at frequent intervals. As changes in CTx-I levels are evident after almost three weeks, the intervals between the real measurements should be at least three weeks.
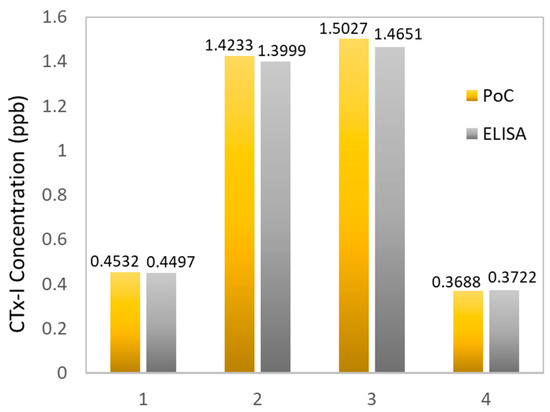
Figure 8.
Comparison between the results collected from the PoC device and the standard ELISA.
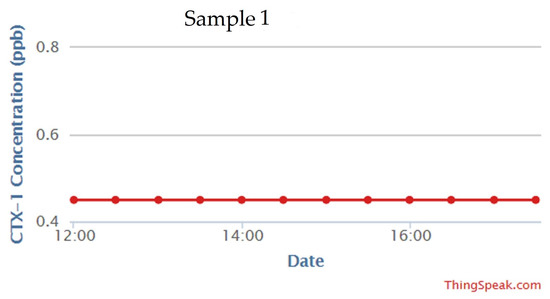
Figure 9.
Real time data of CTx-I from the developed PoC device.
3.4. Future Possibilities
The developed system uses the blood serum as the test sample. In spite of the excellent performance of the proposed PoC device, use of blood sampling is being extremely unpopular for continuous monitoring, as blood sampling is not possible and acceptable for most people who are going to use this device at home. Therefore, development of a PoC device which can use urine as the test sample would be highly desirable. A smart toilet can be developed by attaching a PoC urine testing device to toilet. The bone loss monitoring can be done automatically and without human interaction. The data collected from each measurement would be transmitted wirelessly to the health care center for further actions.
Urinary CTx-I is considered as a normalized ratio to urinary creatinine in order to adjust the variations in urine flowrate. Therefore, CTx-I and creatinine should be measured from the same aliquot. Once the concentration of creatinine is determined in the urine sample, the concentration of CTx-I should be corrected with the creatinine level, using the equation [29]:
Special memory sites for creatinine can be synthesized using molecular imprinting technology [30,31]. Creatinine is a polar molecule, so improved interaction could be expected with MIPs synthesized from highly hydrophobic monomers like methacrylic acid (MAA). Therefore, in order to prepare the creatinine-selective MIP, MAA can be used as the monomer, EGDMA as the cross-linker, and creatinine as the template molecule. Precipitation polymerization method can be used to make the imprinted polymer in the form of microspheres. The synthesized MIP will be immobilized on the sensing surface using a self-assembled monolayer, such as acrylic resin.
However, recent literatures claimed that single biomarker measurement is not enough for detection of bone loss or monitoring a treatment procedure, advising that simultaneous measurement of multiple bone turnover markers could be beneficial [32]. Recently, multiplex PoC devices have been developed for the diagnosis of different diseases [33,34,35]. Urinary calcium (Ca2+) is another biomarker of bone resorption. A simultaneous measurement of CTx-I, creatinine, and calcium in urine can give an accurate and reliable information about the rate of bone loss.
Calcium-imprinted polymers can be prepared using ion imprinted polymers (IIPs) by solidification of polymers in the presence of calcium ions as the template. IIPs have been increasingly developed during the last 20 years, on the principle of MIPs. Ion imprinting technology is a useful approach to synthesize artificial materials as biomimetic antibodies that can recognize any target ions [36]. A Ca2+ selective polymer can be synthesized by precipitation polymerization using calcium ions as the template, itaconic acid (ITA) as the functional monomer, EGDMA as the cross-linker, and 2,2-azoisobutronitrile (AIBN) as the initiator. Figure 10 represents the schematic of the method of Ca2+-IIP and the related recognition mechanism [37].
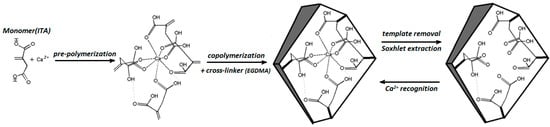
Figure 10.
Schematic representation of Ca+2-IIP method.
A multiplex assay can be developed by designing a sensor array for better and quicker measurement of calcium, CTx-I, and creatinine biomarkers. The developed device could be attached to toilet for automatic sampling of urine. The simultaneous measurement of calcium, CTx-I and creatinine will be done and the measured values would be transferred to the medical practitioner for further investigation. The graphical illustration of the future sensing system is shown in Figure 11.
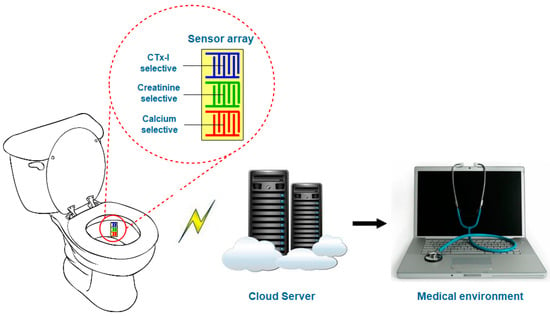
Figure 11.
Schematic diagram of the possible smart toilet for continuous monitoring of bone loss.
The smart toilet provides the regular real-time monitoring of different biochemical markers in urine without human interaction. This device can indicate the early stages of osteoporosis so that the treatment can be started earlier when it is most effective, without waiting for a long time, identified by a DXA scan. The DXA scan can be used for an extra precautionary measurement.
4. Conclusions
An IoT-based portable sensing device for measuring the serum CTx-I molecule was developed. The artificial antibodies prepared by molecular imprinting technology were used to introduce selectivity of CTx-I to a planar interdigital sensor. The developed PoC device is able to measure the concentration of CTx-I in serum and transfer the measured data to an IoT-based cloud server. The transferred data will be delivered to a medical practitioner for further analysis and investigation. The After developing the calibration curve using known-concentration samples, four unknown-concentration sheep serum samples were tested using the proposed device, which are then compared with ELISA-based measurement. The proposed PoC device exhibited a linear behavior in the range of 0.1 ng/mL to 2.5 ng/mL, which is good enough for bone loss detection. The results obtained from the developed device are in good agreement with ELISA results. However, design and development of a smart toilet could be more beneficial as a PoC device. The initial investigations and the results are based on laboratory data and serum has been available for test sample. The sensor can be also used for the detection of CTx-I from blood. However, that may not be too attractive, so urine is considered as the future possibility. In this case, portable system is extremely important to be installed at the toilet, and data can be uploaded to the cloud for remote monitoring.
Author Contributions
Nasrin Afsarimanesh conceived, designed and performed the experiments; Nasrin Afsarimanesh analyzed the data; Md Eshrat E Alahi contributed in the design and development of microcontroller-based system; Nasrin Afsarimanesh wrote the paper. Subhas Chandra Mukhopadhyay and Marlena Kruger supervised the project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rachner, T.D.; Khosla, S.; Hofbauer, L.C. Osteoporosis: Now and the future. Lancet 2011, 377, 1276–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oden, A.; McCloskey, E.; Kanis, J.; Harvey, N.; Johansson, H. Burden of high fracture probability worldwide: Secular increases 2010–2040. Osteoporos. Int. 2015, 26, 2243–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibel, M.J.; Robins, S.P.; Bilezikian, J.P. Dynamics of Bone and Cartilage Metabolism: Principles and Clinical Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Afsarimanesh, N.; Zia, A.I.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Kruger, M.; Yu, P.-L.; Kosel, J.; Kovacs, Z. Smart sensing system for the prognostic monitoring of bone health. Sensors 2016, 16, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afsarimanesh, N.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Marlena, K. Biosensors for the measurement of C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (CTX-I). J. Osteoporos. Phys. Act. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; MacFarlane, G.; Srivastava, V.; Mohan, S.; Baylink, D. A new monoclonal antibody ELISA for detection and characterization of C-telopeptide fragments of type I collagen in urine. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2001, 69, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osteoporosis in RA. Available online: https://www.nras.org.uk/osteoporosis-in-ra (accessed on 23 February 2018).
- Kanis, J.A.; Melton, L.J.; Christiansen, C.; Johnston, C.C.; Khaltaev, N. The diagnosis of osteoporosis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1994, 9, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bone Mineral Density Scan. Available online: http://www.medbroadcast.com/procedure/getprocedure/bone-mineral-density-scan (accessed on 23 February 2018).
- Schuit, S.; Van der Klift, M.; Weel, A.; De Laet, C.; Burger, H.; Seeman, E.; Hofman, A.; Uitterlinden, A.; Van Leeuwen, J.; Pols, H. Fracture incidence and association with bone mineral density in elderly men and women: The rotterdam study. Bone 2004, 34, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastell, R.; Barton, I.; Hannon, R.; Chines, A.; Garnero, P.; Delmas, P. Relationship of early changes in bone resorption to the reduction in fracture risk with risedronate. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2003, 18, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, S. A short history, principles, and types of ELISA, and our laboratory experience with peptide/protein analyses using ELISA. Peptides 2015, 72, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lequin, R.M. Enzyme immunoassay (eia)/enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 2415–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engvall, E. The ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, M.; Patil, M.; Epur, R.; Yun, Y.; Shanov, V.; Schulz, M.; Heineman, W.R.; Datta, M.K.; Kumta, P.N. Gold-coated carbon nanotube electrode arrays: Immunosensors for impedimetric detection of bone biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, Y.-H.; Bhattacharya, A.; Watts, N.B.; Schulz, M.J. A label-free electronic biosensor for detection of bone turnover markers. Sensors 2009, 9, 7957–7969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamishev, A.V.; Sundara-Rajan, K.; Fumin, Y.; Yanqing, D.; Zahn, M. Interdigital sensors and transducers. Proc. IEEE 2004, 92, 808–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Yu, P.-L. Novel Sensors for Food Inspection: Modelling, Fabrication and Experimentation; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zia, A.I.; Rahman, M.S.A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Yu, P.-L.; Al-Bahadly, I.H.; Gooneratne, C.P.; Kosel, J.; Liao, T.-S. Technique for rapid detection of phthalates in water and beverages. J. Food Eng. 2013, 116, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, K.; Linares, A.V.; Bompart, M.; Bui, B.T.S. Molecularly imprinted polymers. In Molecular Imprinting; Haupt, K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Whitcombe, M.J.; Kirsch, N.; Nicholls, I.A. Molecular imprinting science and technology: A survey of the literature for the years 2004–2011. J. Mol. Recognit. 2014, 27, 297–401. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rechichi, A.; Cristallini, C.; Vitale, U.; Ciardelli, G.; Barbani, N.; Vozzi, G.; Giusti, P. New biomedical devices with selective peptide recognition properties. Part 1: Characterization and cytotoxicity of molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2007, 11, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afsarimanesh, N.; Alahi, M.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Kruger, M.; Yu, P.-L. Development of molecular imprinted polymer interdigital sensor for C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen. In Proceedings of the 2016 10th International Conference on Sensing Technology (ICST), Nanjing, China, 11–13 November 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Afsarimanesh, N.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Kruger, M. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical biosensor for bone loss detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devices, A. AD5933: Impedance Analyzer. Available online: http://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/AD5933.pdf (accessed on 4 September 2017).
- Mankar, J.; Darode, C.; Trivedi, K.; Kanoje, M.; Shahare, P. Review of I2C protocol. Int. J. 2014, 2, 474–479. [Google Scholar]
- Thingspeak. Available online: https://thingspeak.com/ (accessed on 26 August 2017).
- Website, A. Ciao. Available online: https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/Ciao (accessed on 26 August 2017).
- Urine Cartilaps. Available online: http://peramed.com/peramed/docs/AC-10F1_EN.pdf (accessed on 23 February 2018).
- Khadro, B.; Betatache, A.; Sanglar, C.; Bonhommé, A.; Errachid, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIP) based electrochemical sensor for detection of urea and creatinine. Sens. Lett. 2011, 9, 2261–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Tsai, T.-C.; Thomas, J.L.; Lin, H.-Y. Recognition of creatinine by poly (ethylene-co-vinylalcohol) molecular imprinting membrane. Desalination 2008, 234, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashayar, P.; Aghaei Meybodi, H.; Amoabediny, G.; Larijani, B. Biochemical markers of bone turnover and their role in osteoporosis diagnosis: A narrative review. Recent Pat. Endocr. Metab. Immune Drug Discov. 2015, 9, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petra, S.; Gerald, A. Multiplexed point-of-care testing-xpoct. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 728–742. [Google Scholar]
- Piraino, F.; Volpetti, F.; Watson, C.; Maerkl, S.J. A digital–analog microfluidic platform for patient-centric multiplexed biomarker diagnostics of ultralow volume samples. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 1699–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piraino, F. Diagnostic Devices with Microfluidics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Branger, C.; Meouche, W.; Margaillan, A. Recent advances on ion-imprinted polymers. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 859–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, T.; Shamkhali, A.N.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Joo, S.W. A Ca2+ selective membrane electrode based on calcium-imprinted polymeric nanoparticles. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 8479–8487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).