Phylogenetic and Comparative Analyses of Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Chinese Viburnum and Sambucus (Adoxaceae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
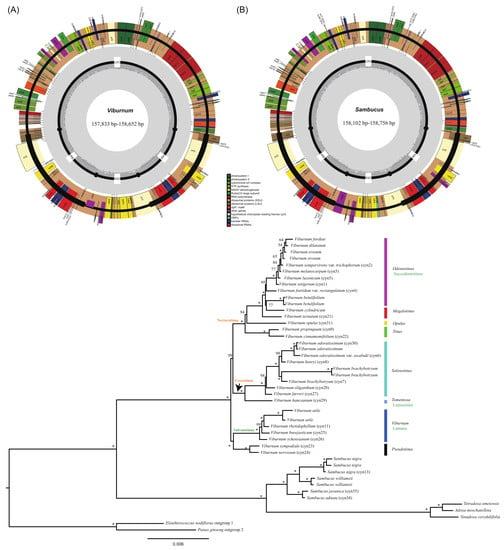
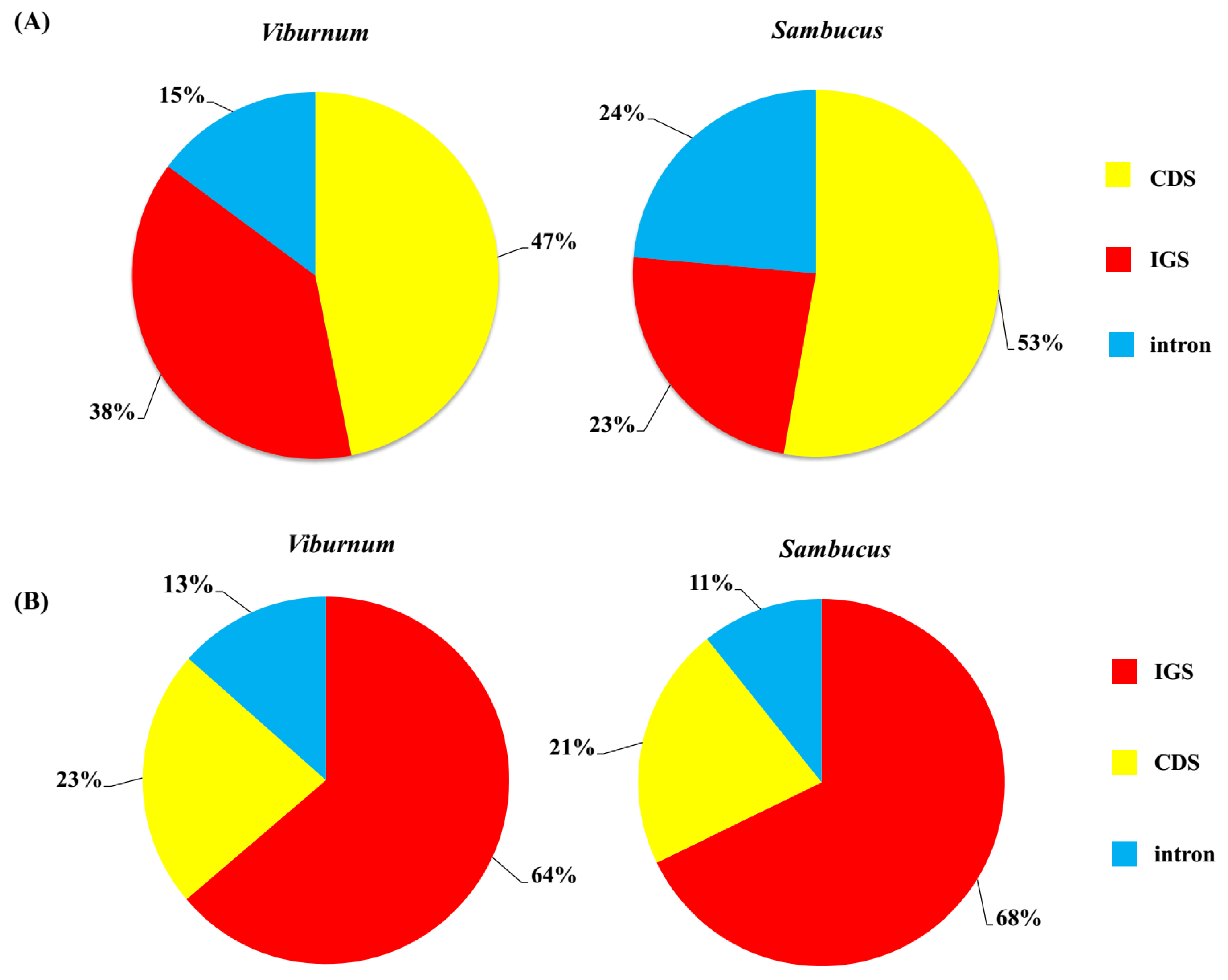
2.1. Chloroplast Genome Assembly and Features
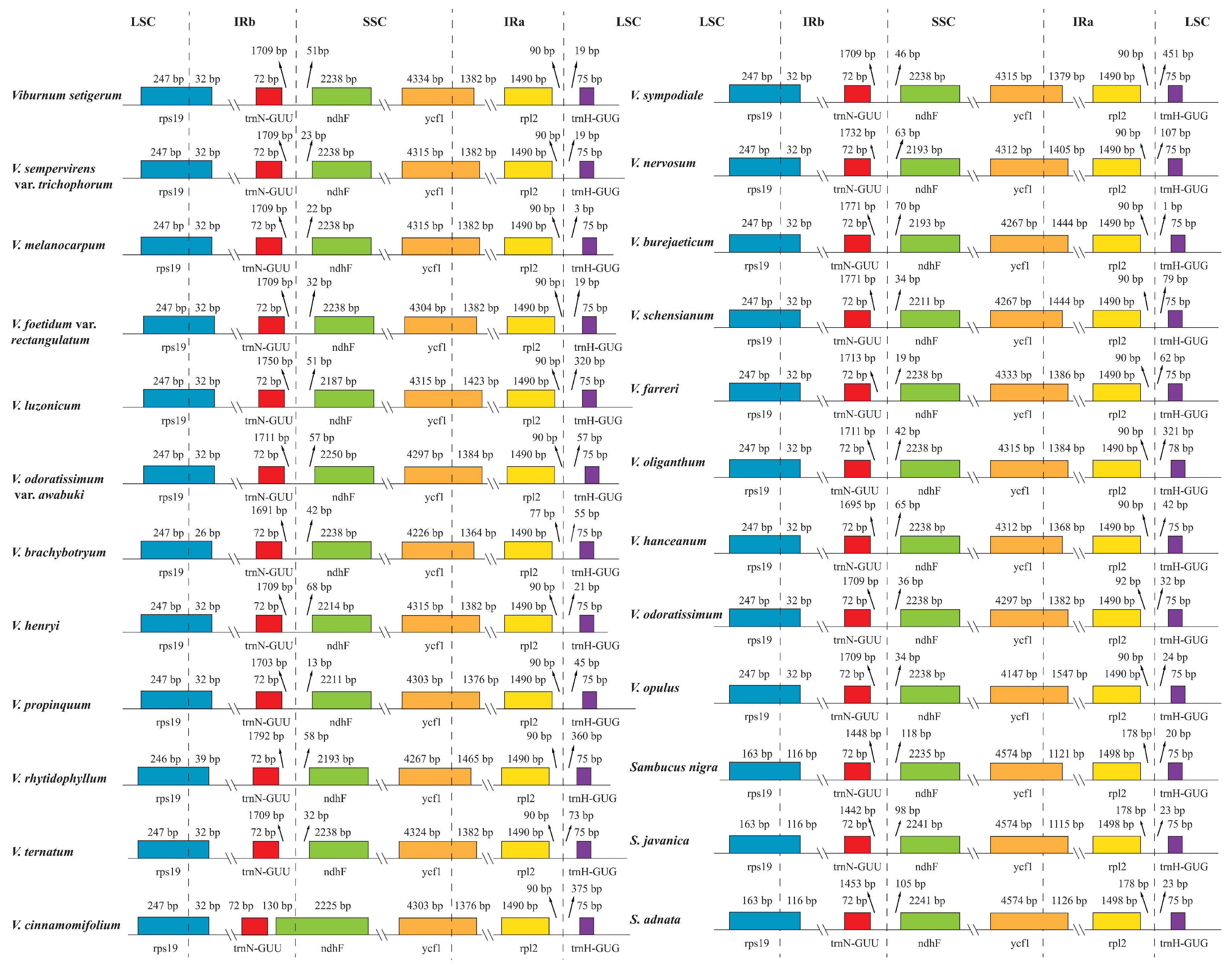
2.2. Expansion and Contraction of the Inverted Repeat Regions
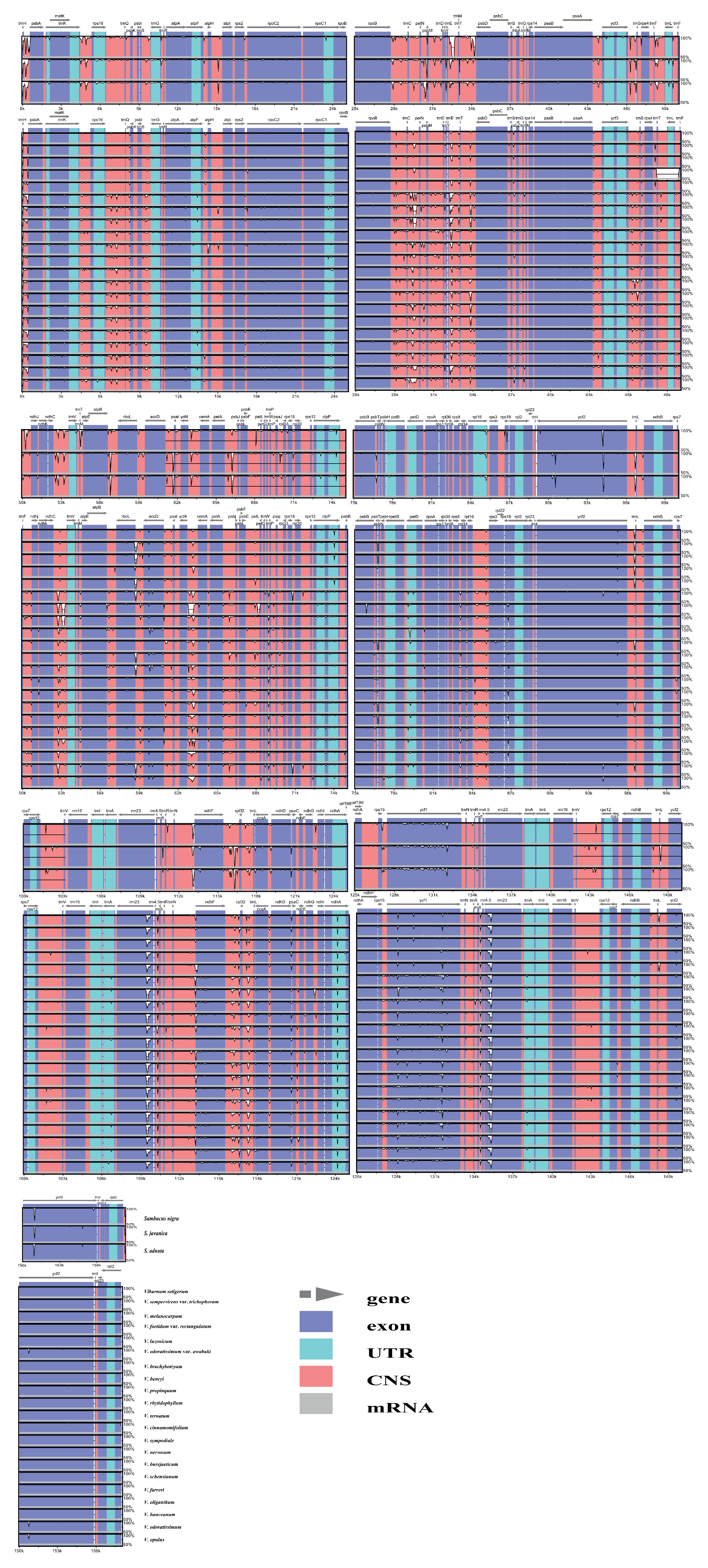
2.3. Sequence Divergence Analysis
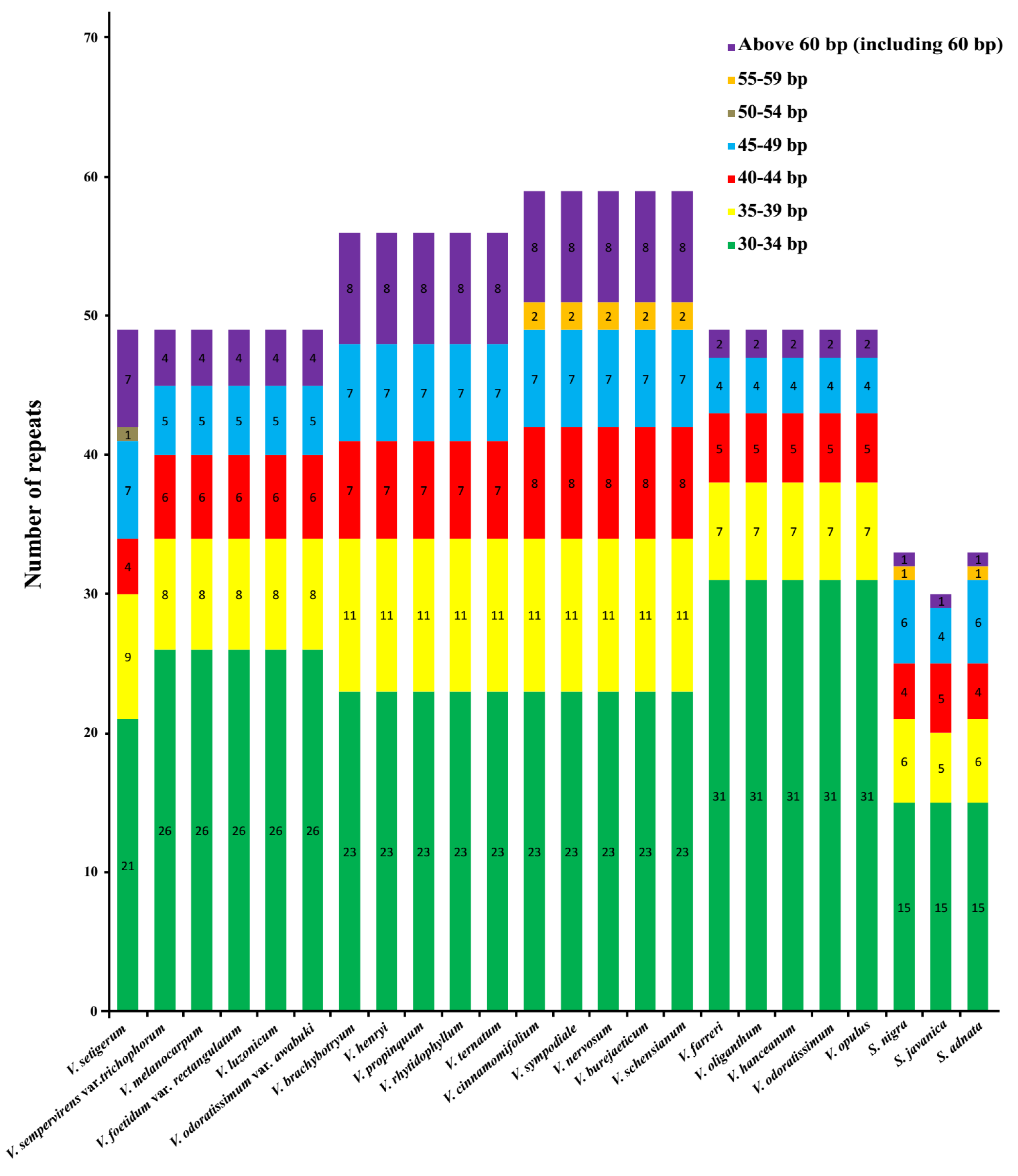
2.4. Characterization of Repeat Sequences and SSR Polymorphisms
2.5. Phylogenetic Relationships
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection, Sequencing and Assembly
3.2. Whole Chloroplast Genome Annotation and Comparison
3.3. Identification of Repeat Sequences and SSRs
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- The Angiosperm Phylogeny Group. An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG IV. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2016, 181, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.E.; Malecot, V. Viburnum. In Flora of China, Lentibulariaceae Through Dipsacaceae; Wu, Z.Y., Raven, P.H., Hong, D.Y., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China; Missouri Botanical Garden Press: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2011; Volume 19, pp. 570–611. [Google Scholar]
- Dirr, M.A. Viburnums: Flowering Shrubs for Every Season; Timber Press, Inc.: Portland, OR, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rehder, A. The Viburnums of Eastern Asia. In Trees and Shrubs; Part, II; Sargent, C.S., Ed.; Houghton Mifflin: Boston, MA, USA, 1908; Volume II, pp. 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson, D.H.; Hara, H. A Revision of Caprifoliaceae of Japan with Reference to Allied Plants in other Districts and the Adoxaceae; Academia Scientific Books, Inc.: Tokyo, Japan, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue, M. A preliminary analysis of phylogenetic relationships in Viburnum (Caprifoliaceae s.1.). Syst. Bot. 1983, 8, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, J.H. The genus Viburnum (Caprifoliaceae) in Malaysia. Reinwardtia 1951, 1, 107–170. [Google Scholar]
- Killip, E.P.; Smith, A.C. The south American species of Viburnum. Bull. Torrey Bot. Club 1931, 57, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoghue, M. The Phylogenetic Relationships of Viburnum. In Advances in Cladistics; Platnick, N., Funk, V., Eds.; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; Volume 2, pp. 143–166. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson, T.; Donoghue, M.J. Phylogenetic relationships of Sambucus and Adoxa (Adoxoideae, Adoxaceae) based on nuclear ribosomal ITS sequences and preliminary morphological data. Syst. Bot. 1997, 22, 555–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.Y.; Gao, A.; Gong, J.; Xia, L.; Jia, X.; Li, N.; Hou, X.Y.; Lu, F.; Ni, S.F. Overview of Pharmaceutical Research on Sambucus L. Ningxia J. Agric. For. Sci. Tech. 2011, 52, 59–60. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.B.; Wu, Y.; Yang, J.; Shahzad, K.; Li, Z.H. Comparative chloroplast genomics of Dipsacales species: Insights into sequence variation, adaptive evolution, and phylogenetic relationships. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oersted, A.S. Til belysning af slaegten Viburnum. Vidensk. Medd. Naturhist. Foren. Kjobenhavn 1861, 13, 267–305. [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue, M.J.; Baldwin, B.G.; Li, J.; Winkworth, R.C. Viburnum phylogeny based on chloroplast trnK intron and nuclear ribosomal ITS DNA sequences. Syst. Bot. 2004, 29, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkworth, R.C.; Donoghue, M.J. Viburnum phylogeny: Evidence from the duplicated nuclear gene GBSSI. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2004, 33, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkworth, R.C.; Donoghue, M.J. Viburnum phylogeny based on combined molecular data: Implications for taxonomy and biogeography. Am. J. Bot. 2005, 92, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, W.L.; Donoghue, M.J. Dissolution of Viburnum section Megalotinus (Adoxaceae) of Southeast Asia and its implications for morphological evolution and biogeography. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2011, 172, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, W.L.; Donoghue, M.J. Barcoding success as a function of phylogenetic relatedness in Viburnum, a clade of woody angiosperms. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, W.L.; Arakaki, M.; Sweeney, P.W.; Edwards, E.J.; Donoghue, M.J. A chloroplast tree for Viburnum (Adoxaceae) and its implications for phylogenetic classification and character evolution. Am. J. Bot. 2014, 101, 1029–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.B.; Yang, S.X.; Li, H.T.; Yang, J.; Li, D.Z. Comparative Chloroplast Genomes of Camellia Species. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yao, X.; Tan, Y.H.; Gan, Y.; Corlett, R.T. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of the avocado: Gene organization, comparative analysis, and phylogenetic relationships with other Lauraceae. Can. J. For. Res. 2016, 46, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, C.; Zhao, X.; Chen, S.; Qu, G. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Betula platyphylla: Gene organization, RNA editing, and comparative and phylogenetic analyses. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, J.; Huo, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yuan, Z. The complete chloroplast genomes of Punica granatum and a comparison with other species in Lythraceae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.B.; Han, E.K.; Choi, H.J.; Lee, J.H. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Viburnum japonicum (Adoxaceae), an evergreen broad-leaved shrub. Mitochondrial DNA Part B Resour. 2018, 3, 458–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.L.; Dong, H.J.; Landrein, S.; Zhao, F.; Yu, W.B.; Soltis, D.E.; Soltis, P.S.; Backlund, A.; Wang, H.F.; Li, D.Z.; et al. Revisiting the phylogeny of Dipsacales: New insights from phylogenomic analyses of complete plastomic sequences. J. Syst. Evol. 2020, 58, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.X.; Liu, H.; Moore, M.J.; Landrein, S.; Liu, B.; Zhu, Z.X.; Wang, H.F. Plastid phylogenomic insights into the evolution of the Caprifoliaceae s.l. (Dipsacales). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2020, 142, 106641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.H.; Tang, P.; Li, Z.Z.; Li, D.W.; Liu, Y.F.; Huang, H.W. The first complete chloroplast genome sequences in Actinidiaceae: Genome structure and comparative analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.S.; Park, K.T.; Park, S. The chloroplast genome of Symplocarpus renifolius: A comparison of chloroplast genome structure in Araceae. Genes 2017, 8, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Liu, J.; Luo, L.; Wei, X.; Zhang, J.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Xiao, P. Complete chloroplast genome sequences of Schisandra chinensis: Genome structure, comparative analysis, and phylogenetic relationship of basal angiosperms. Sci. China Life Sci. 2017, 60, 1286–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalier-Smith, T. Chloroplast evolution: Secondary symbiogenesis and multiple losses. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, R62–R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Lv, S.; Zhang, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, L.; Biradar, S.S.; Tan, X.; Wan, F.; Weining, S. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of a major invasive species, crofton weed (Ageratina adenophora). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.H.; Zhang, J.J.; Yao, X.H.; Huang, H.W. Chloroplast microsatellite markers in Liriodendron tulipifera (Magnoliaceae) and cross-species amplification in L. chinense. Am. J. Bot. 2011, 98, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Xu, C.; Cheng, T.; Lin, K.; Zhou, S. Sequencing angiosperm plastid genomes made easy: A complete set of universal primers and a case study on the phylogeny of Saxifragales. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Li, Q.; Hu, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, S. The complete Amomum kravanh chloroplast genome sequence and phylogenetic analysis of the Commelinids. Molecules 2017, 22, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.Q.; Yap, Z.Y.; Li, P.; Comes, H.P.; Qiu, Y.X. Plastome organization, genome-based phylogeny and evolution of plastid genes in Podophylloideae (Berberidaceae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 127, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, B.G.; Sanderson, M.J.; Porter, J.M.; Wojciechowski, M.F.; Campbell, C.S.; Donoghue, M.J. The ITS region of nuclear ribosomal DNA: A valuable source of evidence on angiosperm phylogeny. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1995, 82, 247–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronn, R.; Liston, A.; Parks, M.; Gernandt, D.S.; Shen, R.; Mockler, T. Multiplex sequencing of plant chloroplast genomes using Solexa sequencing-by-synthesis technology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, e122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyman, S.K.; Jansen, R.K.; Boore, J.L. Automatic annotation of organellar genomes with DOGMA. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 3252–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schattner, P.; Brooks, A.N.; Lowe, T.M. The tRNAscan-SE, snoscan and snoGPS web servers for the detection of tRNAs and snoRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohse, M.; Drechsel, O.; Kahlau, S.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW-a suite of tools for generating physical maps of plastid and mitochondrial genomes and visualizing expression data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. Reputer: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES science gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In Proceedings of the Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
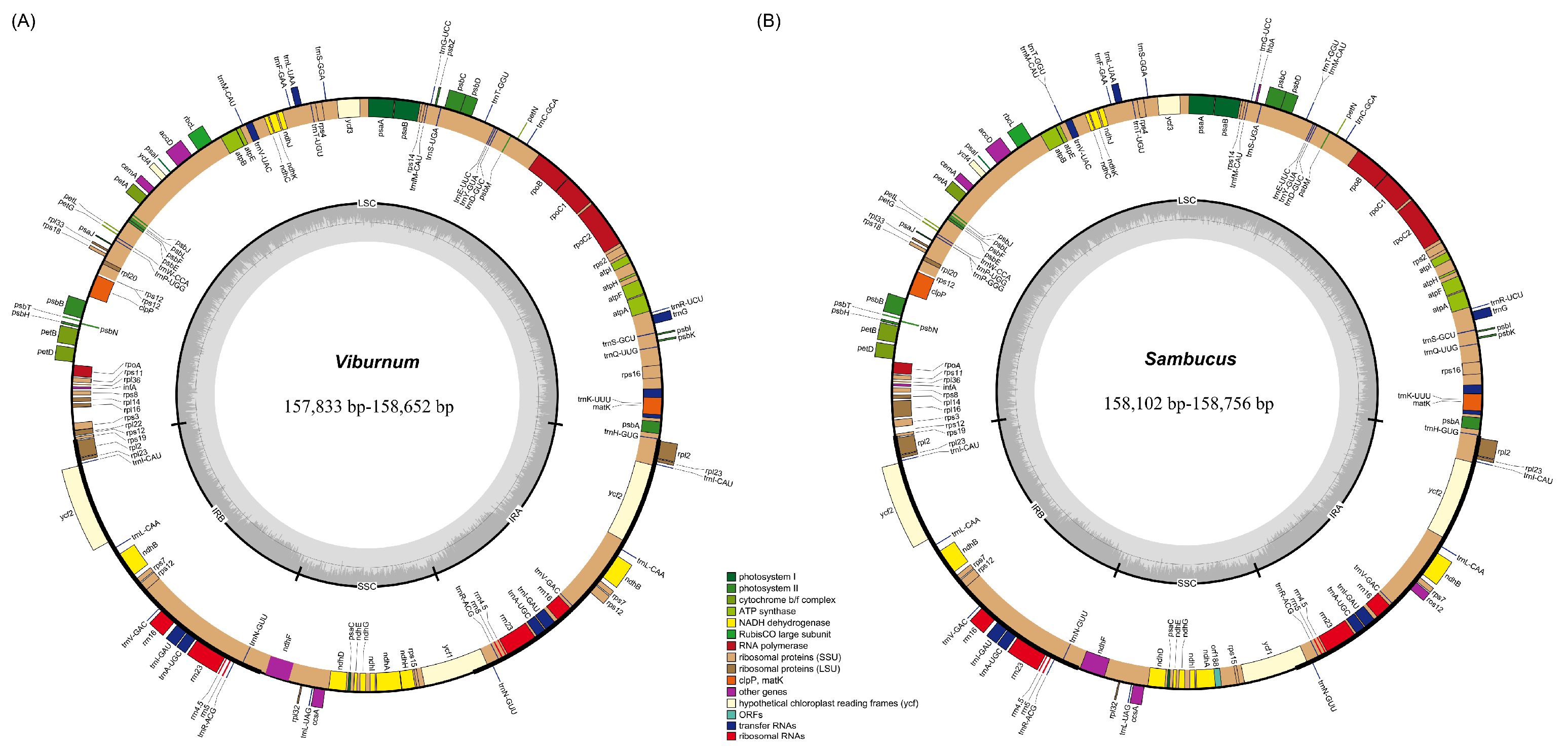

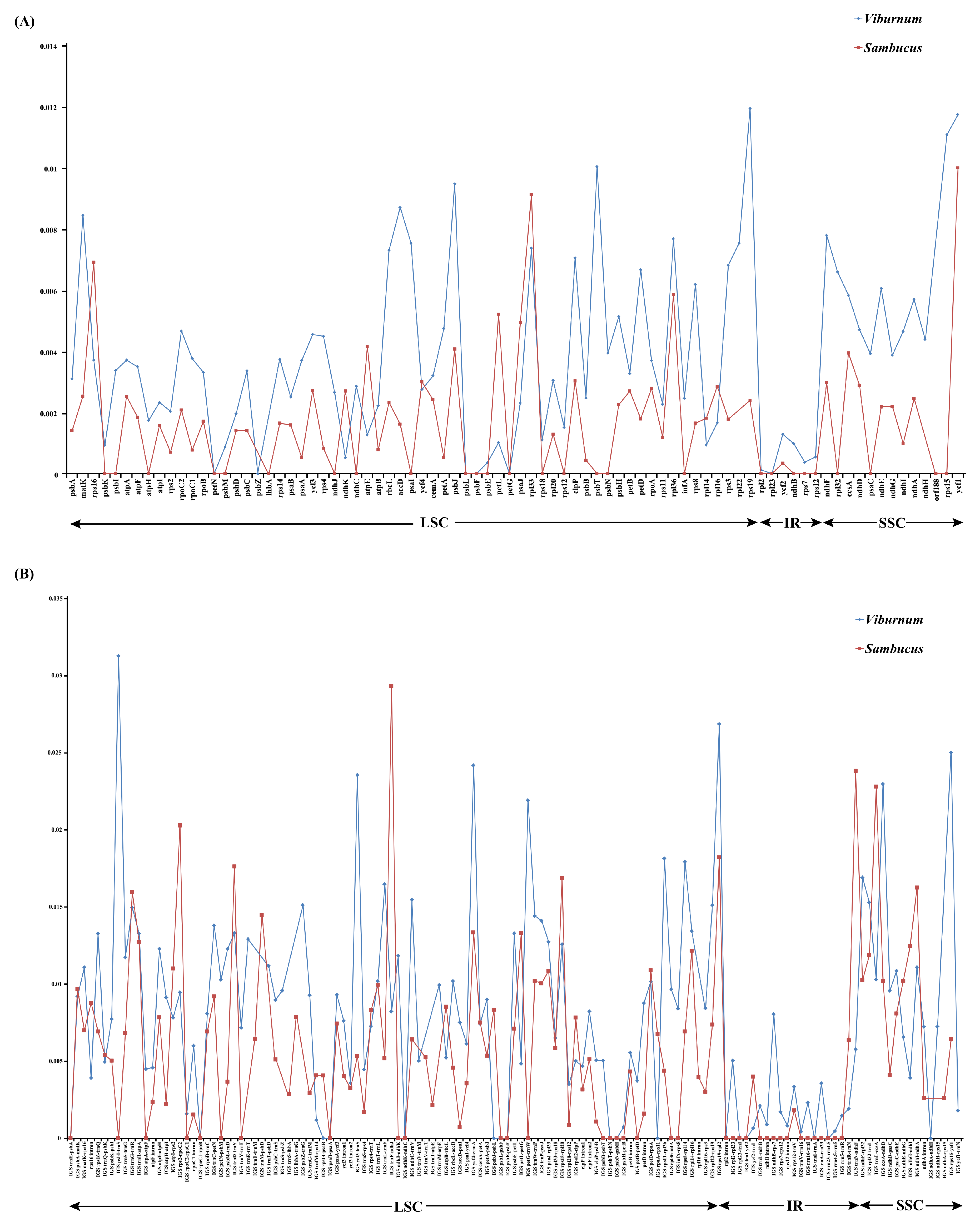
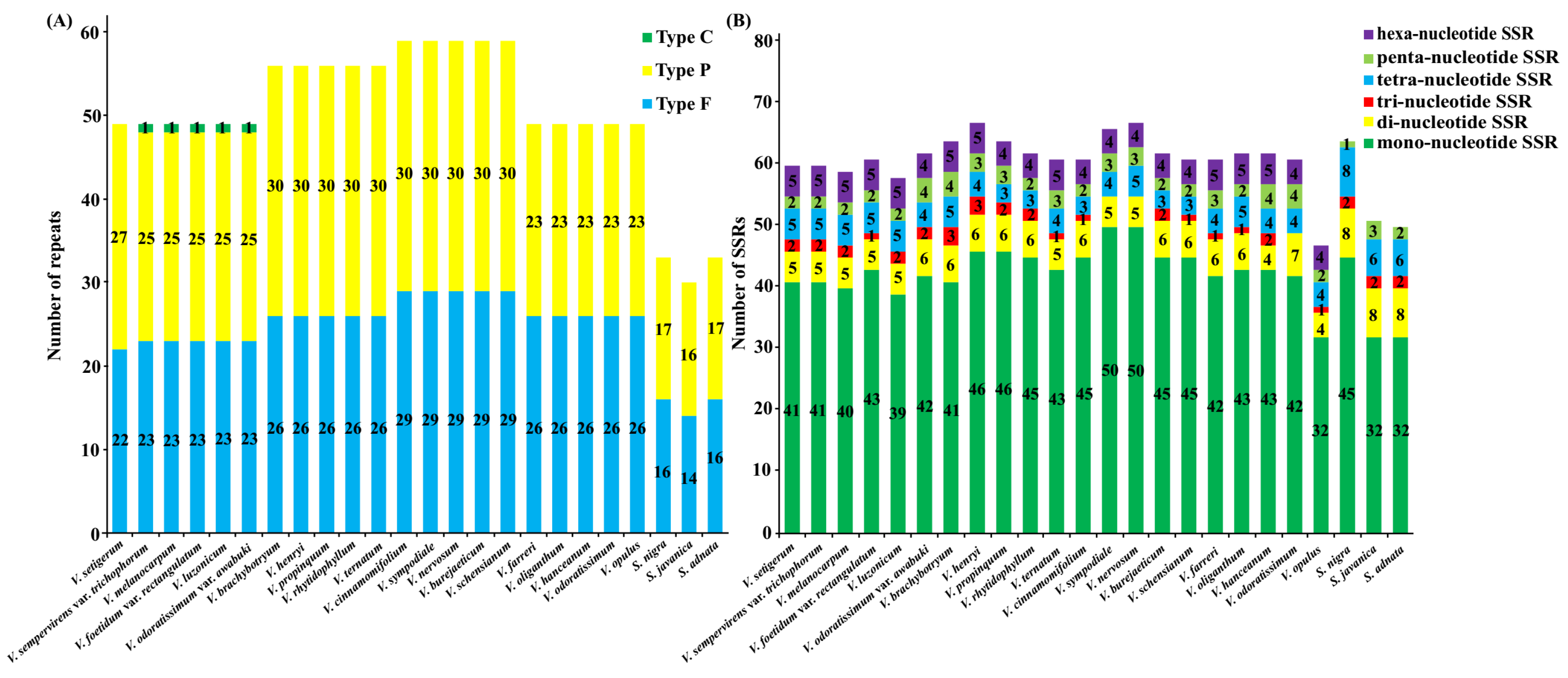
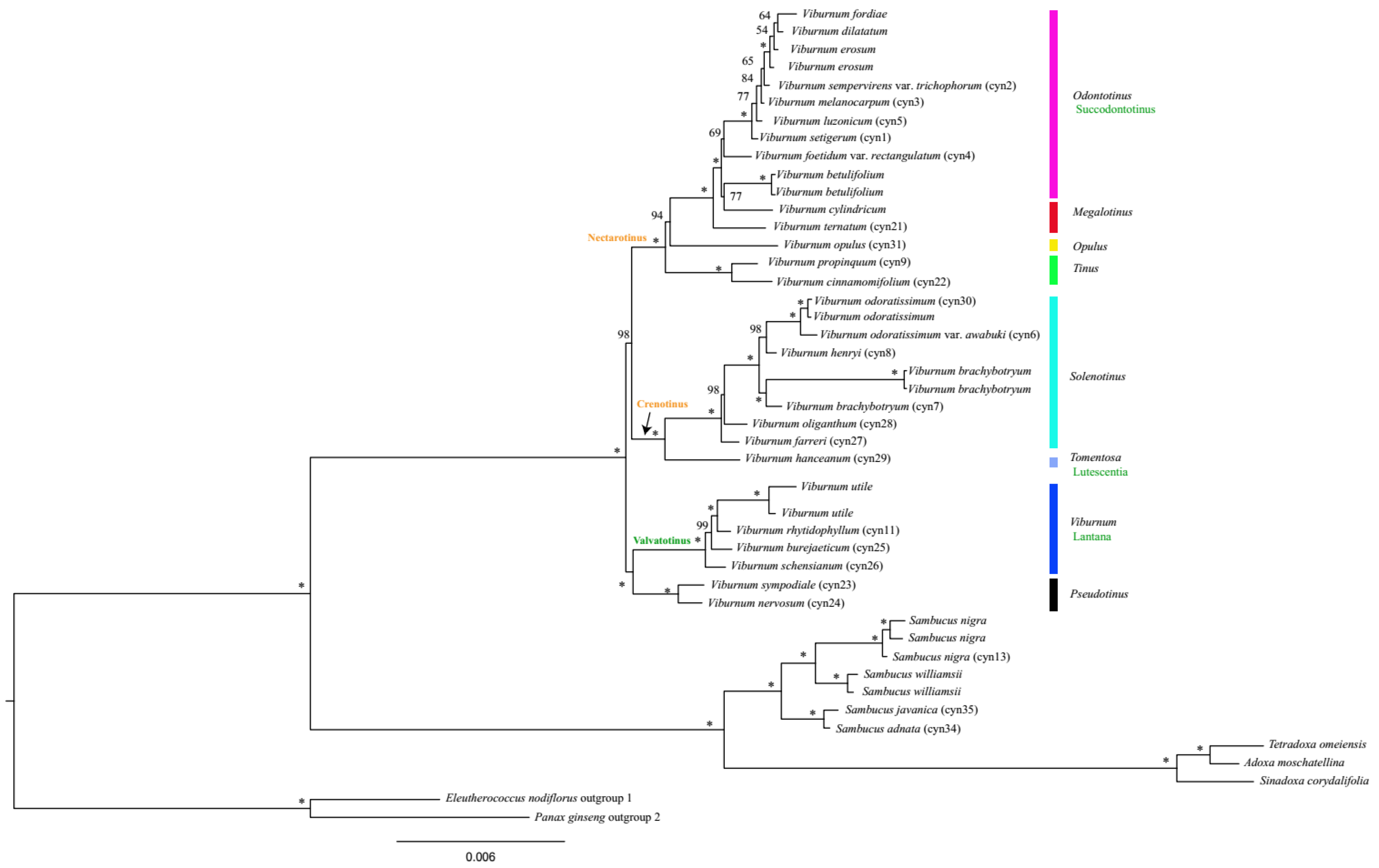
| Species | Genome Size (bp) | LSC Length (bp) | SSC Length (bp) | IR Length (bp) | Total GC Content (%) | Number of Genes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | CDS | rRNAs | tRNAs | ||||||
| V. setigerum | 158,306 | 86,763 | 18,539 | 26,502 | 38.1% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. sempervirens var. trichophorum | 158,184 | 86,710 | 18,472 | 26,501 | 38.1% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. melanocarpum | 158,196 | 86,695 | 18,497 | 26,502 | 38.1% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. foetidum var. rectangulatum | 158,230 | 86,835 | 18,431 | 26,482 | 38.1% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. luzonicum | 158,652 | 87,892 | 17,674 | 26,543 | 38.1% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. odoratissimum var. awabuki | 158,126 | 86,718 | 18,438 | 26,485 | 38.1% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. brachybotryum | 157,833 | 86,809 | 18,268 | 26,378 | 38.1% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. henryi | 157,862 | 86,430 | 18,452 | 26,490 | 38.1% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. propinquum | 157,987 | 86,839 | 18,350 | 26,399 | 38.1% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. rhytidophyllum | 158,520 | 87,054 | 18,338 | 26,564 | 38.1% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. ternatum | 158,344 | 87,109 | 18,407 | 26,414 | 38.1% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. cinnamomifolium | 158,347 | 87,210 | 18,347 | 26,395 | 38.1% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. sympodiale | 158,238 | 87,118 | 18,330 | 26,395 | 38.0% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. nervosum | 157,890 | 86,715 | 18,341 | 26,417 | 38.0% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. burejaeticum | 157,913 | 86,669 | 18,274 | 26,485 | 38.1% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. schensianum | 157,924 | 86,681 | 18,289 | 26,477 | 38.1% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. farreri | 158,046 | 86,809 | 18,401 | 26,418 | 38.1% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. oliganthum | 158,309 | 87,038 | 18,453 | 26,409 | 38.1% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. hanceanum | 158,195 | 86,815 | 18,436 | 26,472 | 38.1% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. odoratissimum | 158,020 | 86,653 | 18,419 | 26,474 | 38.1% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| V. opulus | 158,520 | 87,114 | 18,456 | 26,475 | 38.2% | 130 | 85 (6) | 8 (4) | 37 (7) |
| S. nigra | 158,102 | 86,518 | 18,978 | 26,303 | 38.0% | 132 | 84 (6) | 8 (4) | 40 (7) |
| S. javanica | 158,624 | 87,226 | 18,854 | 26,272 | 38.0% | 132 | 84 (6) | 8 (4) | 40 (7) |
| S. adnata | 158,756 | 87,328 | 18,862 | 26,283 | 38.0% | 132 | 84 (6) | 8 (4) | 40 (7) |
| Gene Group | Gene Name |
|---|---|
| Ribosomal RNAs | rrn16(×2), rrn23(×2), rrn4.5(×2), rrn5(×2) |
| Transfer RNAs | trnH-GUG, trnK-UUUa, trnQ-UUG, trnS-GCU, trnGa, trnR-UCU |
| trnC-GCA, trnD-GUC, trnY-GUA, trnE-UUC, trnT-GGU | |
| trnS-UGA, trnG-UCC, trnfM-CAU, trnS-GGA, trnT-UGU | |
| trnL-UAAa, trnF-GAA, trnV-UACa, trnM-CAU, trnW-CCA | |
| trnP-UGG, trnl-CAU(×2), trnL-CAA(×2), trnV-GAC(×2) | |
| trnl-GAUa(×2), trnA-UGCa(×2), trnR-ACG(×2), trnN-GUU(×2) | |
| trnL-UAG, trnM-CAUx, trnT-GGUx, trnP-GGGx | |
| Photosystem I | psaB, psaA, psal, psaJ, psaC |
| Photosystem II | psbA, psbK, psbl, psbM, psbD, psbC, psbZz, psbB, psbT, |
| psbL, psbF, psbE, psbH, psbN, psbJ | |
| Cytochrome | petN, petA, petL, petG, petBa, petDa |
| ATP synthase | atpA, atpFa, atpH, atpl, atpE, atpB |
| Rubisco | rbcL |
| NADH dehydrogenease | ndhJ, ndhK, ndhC, ndhBa(×2), ndhD, ndhE, ndhG |
| ndhl, ndhAa, ndhHz | |
| Ribosomal proteins (large units) | rpl33, rpl20, rpl36, rpl14, rpl16, rpl16a, rpl22z, rpl2a(×2), |
| rpl23(×2), rpl32 | |
| Ribosomal proteins (small units) | rps16a, rps2, rps14, rps4, rps18, rps12b (×2), rps11, rps8, |
| rps7(×2), rps15, rps3, rps19 | |
| RNA polymerase | rpoC2, rpoC1a, rpoB, rpoA |
| Miscellaneous proteins & ATP-dependent protease subunit P | matK, clpPb |
| Other genes | accD, cemA, infA, ccsA, orf188x, lhbAx |
| Hypothetical proteins & Conserved reading frame | ycf3b, ycf4, ycf2(×2), ycf1Ψ |
| Viburnum | Pi | Sambucus | Pi |
|---|---|---|---|
| noncoding regions | |||
| rps15-ycf1 | 0.02502 | trnF-ndhJ | 0.02934 |
| ycf4-cemA | 0.02419 | trnN-ndhF | 0.02384 |
| ycf3-trnS | 0.02356 | rps2-rpoC2 | 0.02029 |
| ccsA-ndhD | 0.02298 | rps18-rpl20 | 0.01687 |
| rps8-rpl14 | 0.01794 | trnG-trnR | 0.01596 |
| ndhF-rpl32 | 0.01691 | trnM-psbD | 0.01446 |
| trnL-trnF | 0.01647 | ycf4-cemA | 0.01335 |
| ndhC-trnV | 0.01548 | ndhG-ndhI | 0.01247 |
| rpl32-trnL | 0.01529 | rpl32-trnL | 0.01188 |
| psbZ-trnG | 0.01512 | atpI-rps2 | 0.01101 |
| coding regions | |||
| rps19 | 0.01193 | ycf1 | 0.00999 |
| ycf1 | 0.01173 | rpl33 | 0.00912 |
| rps15 | 0.01107 | rps16 | 0.00691 |
| accD | 0.00870 | atpE | 0.00415 |
| matK | 0.00844 | ccsA | 0.00394 |
| ndhF | 0.00779 | clpP | 0.00303 |
| rpl22 | 0.00753 | ycf4 | 0.00300 |
| rpl33 | 0.00737 | ndhF | 0.00298 |
| rbcL | 0.00730 | ndhD | 0.00288 |
| clpP | 0.00705 | rpl16 | 0.00285 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ran, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, C.; Cao, Y. Phylogenetic and Comparative Analyses of Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Chinese Viburnum and Sambucus (Adoxaceae). Plants 2020, 9, 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9091143
Ran H, Liu Y, Wu C, Cao Y. Phylogenetic and Comparative Analyses of Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Chinese Viburnum and Sambucus (Adoxaceae). Plants. 2020; 9(9):1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9091143
Chicago/Turabian StyleRan, Hang, Yanyan Liu, Cui Wu, and Yanan Cao. 2020. "Phylogenetic and Comparative Analyses of Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Chinese Viburnum and Sambucus (Adoxaceae)" Plants 9, no. 9: 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9091143
APA StyleRan, H., Liu, Y., Wu, C., & Cao, Y. (2020). Phylogenetic and Comparative Analyses of Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Chinese Viburnum and Sambucus (Adoxaceae). Plants, 9(9), 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9091143