Functional Improvement of Human Cardiotrophin 1 Produced in Tobacco Chloroplasts by Co-Expression with Plastid Thioredoxin m
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
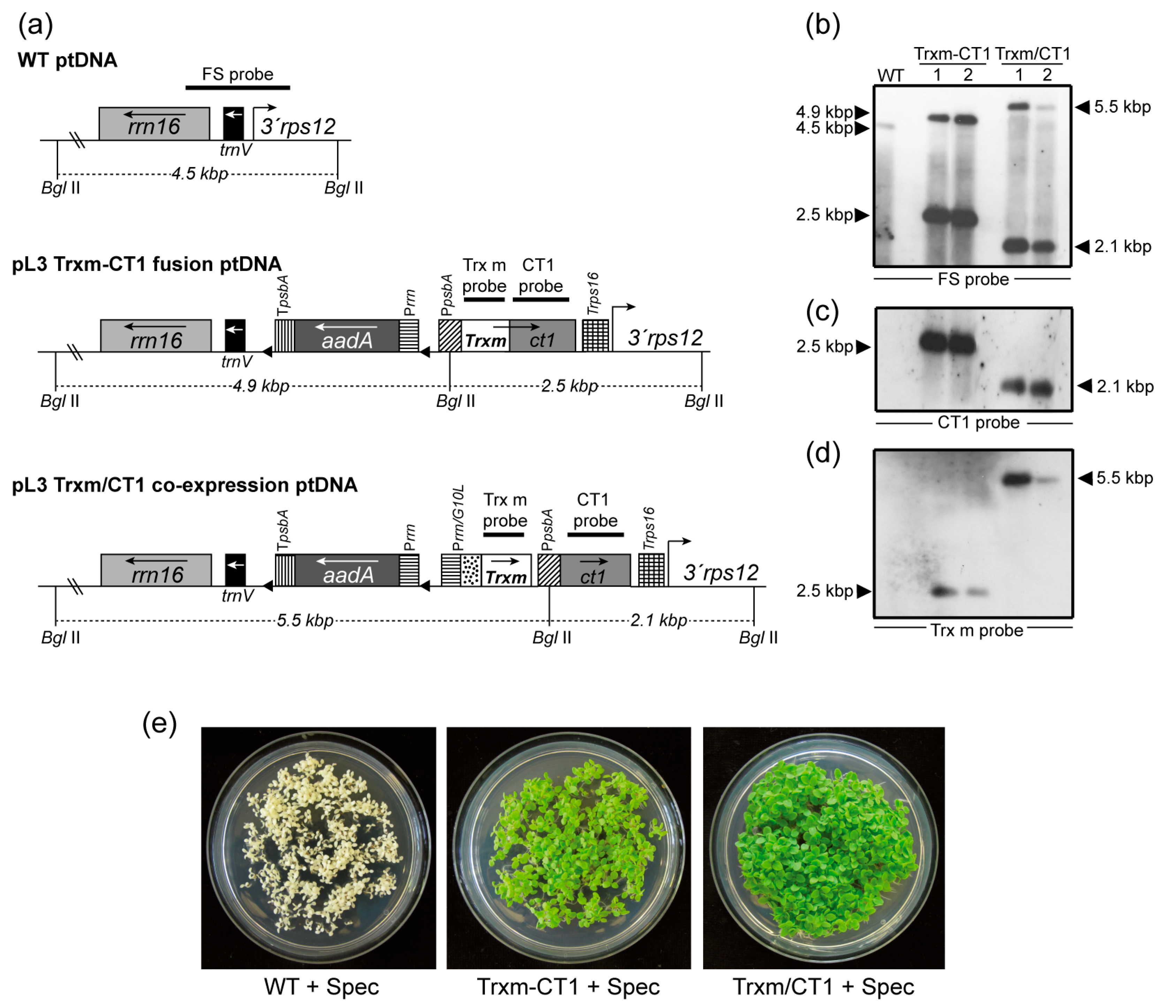
2.1. Generation of Transplastomic Tobacco Plants Expressing Human CT1 Fused or Co-Expressed with Trx m
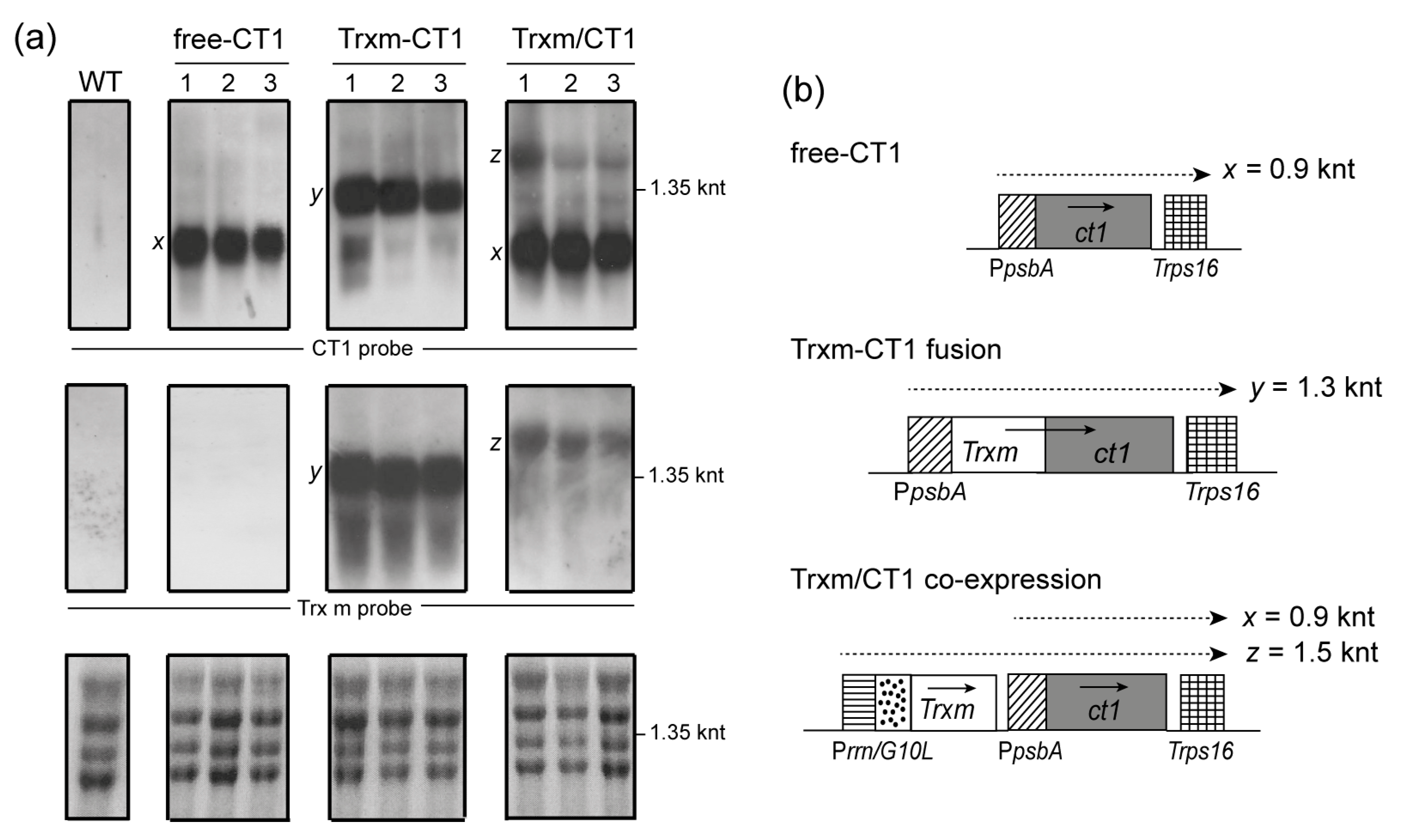
2.2. Expression Levels of Human CT1 Fused or Co-Expressed with Trx m in Tobacco Chloroplasts
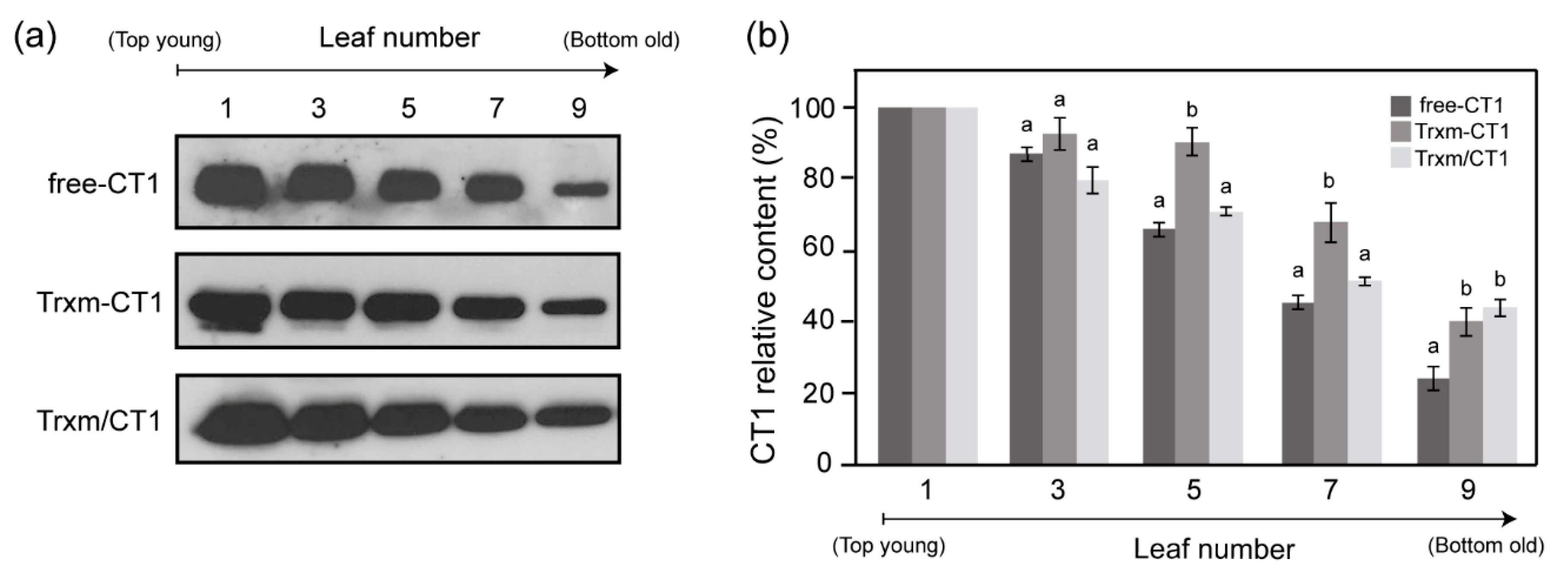
2.3. Stability of Human CT1 Expressed in Tobacco Chloroplasts
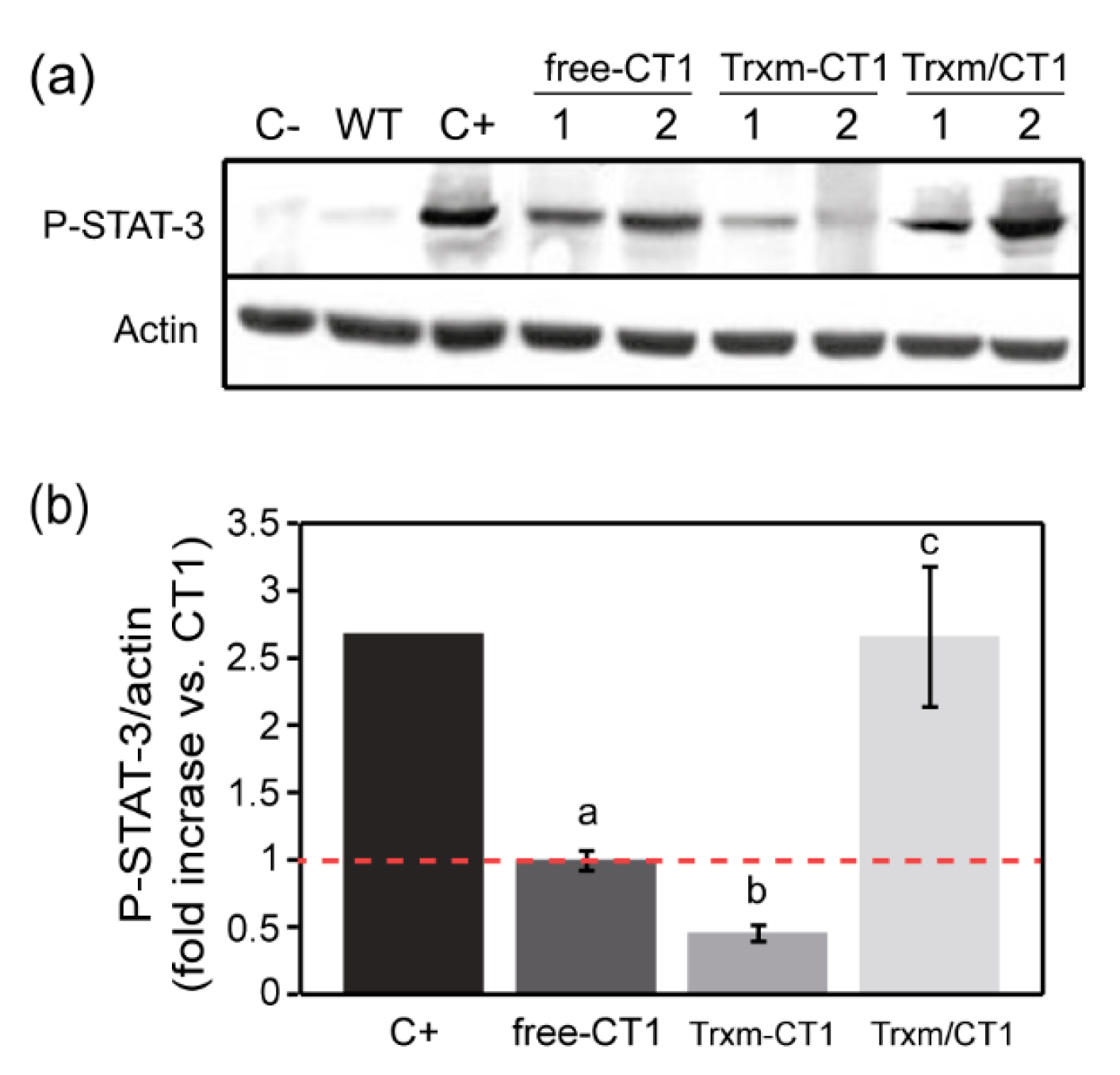
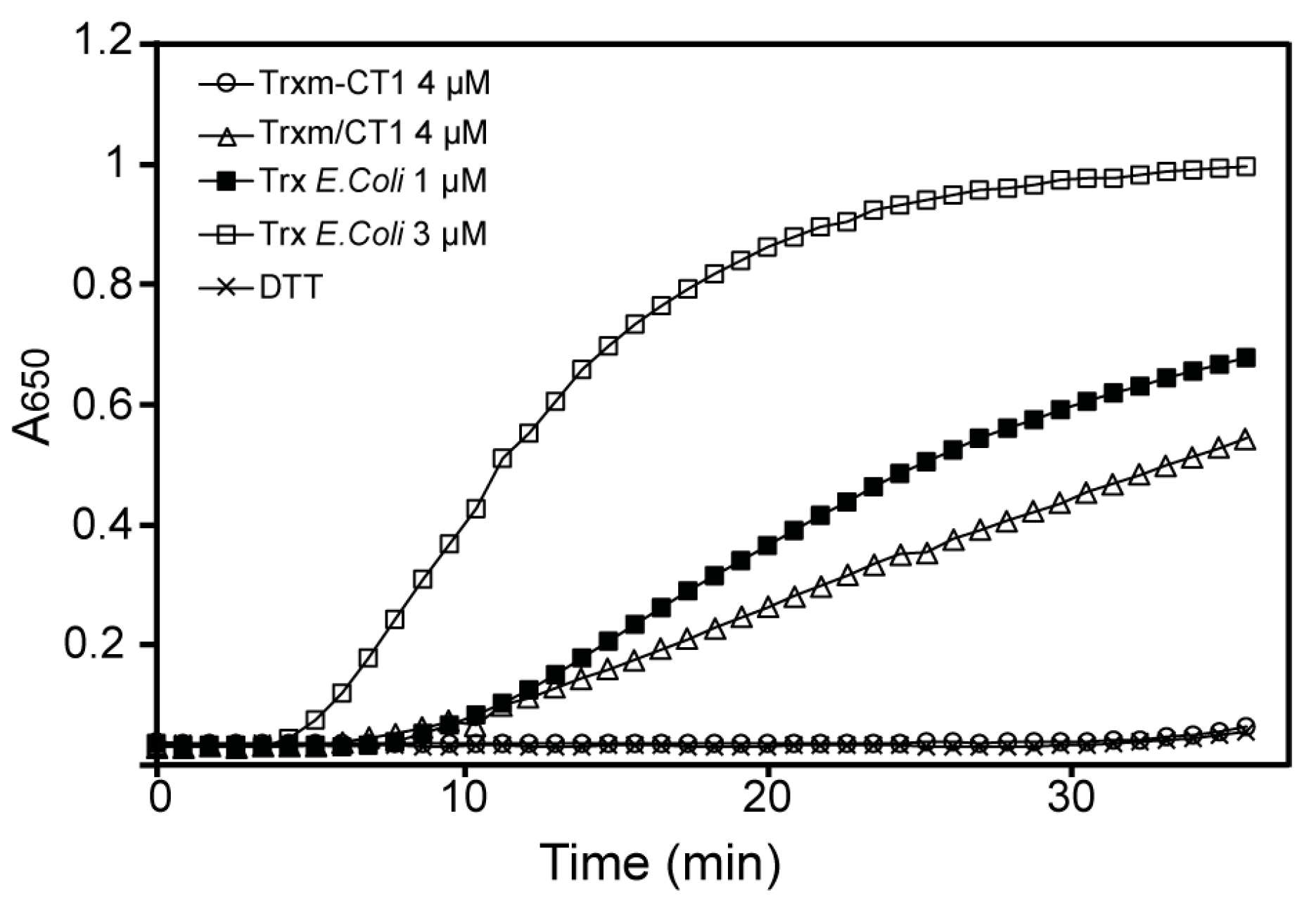
2.4. Fusion and Co-Expression of Chloroplast-Expressed CT1 with Trx m Modulates the Protein’s Function
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Generation of Plastid Transformation Vectors
4.2. Bombardment and Regeneration of Chloroplast Transgenic Plants
4.3. Southern and Northern-Blot Analysis
4.4. Western-Blot Analysis
4.5. Bioactivity Analysis of Recombinant CT1
4.6. Trx m Protein Purification
4.7. Insulin Reduction Assay
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alireza, T.; Nader, R.E. Molecular Farming in Plants. In Plants for Future; Intech Open: London, UK, 2015; pp. 25–41. [Google Scholar]
- Buyel, J.F. Plant molecular farming—Integration and exploitation of side streams to achieve sustainable biomanufacturing. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 1893. [Google Scholar]
- Adem, M.; Beyene, D.; Feyissa, T. Recent achievements obtained by chloroplast transformation. Plant Methods 2017, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, N.; Michoux, F.; Lössl, A.G.; Nixon, P.J. Challenges and perspectives in commercializing plastid transformation technology. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 5945–5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oey, M.; Lohse, M.; Kreikemeyer, B.; Bock, R. Exhaustion of the chloroplast protein synthesis capacity by massive expression of a highly stable protein antibiotic. Plant J. 2009, 57, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castiglia, D.; Sannino, L.; Marcolongo, L.; Ionata, E.; Tamburino, R.; De Stradis, A.; Cobucci-Ponzano, B.; Moracci, M.; La Cara, F.; Scotti, N. High-level expression of thermostable cellulolytic enzymes in tobacco transplastomic plants and their use in hydrolysis of an industrially pretreated Arundo donax L. biomass. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azhagiri, A.K.; Maliga, P. Exceptional paternal inheritance of plastids in Arabidopsis suggests that low-frequency leakage of plastids via pollen may be universal in plants. Plant J. 2007, 52, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davoodi-Semiromi, A.; Samson, N.; Daniel, H. The green vaccine: A global strategy to combat infectious and autoimmune diseases. Hum. Vaccin. 2009, 5, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Vargas, T.; Ruiz, O.N.; Daniell, H. Characterization of heterologous multigene operons in transgenic chloroplasts. Transcription, processing, and translation. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 1746–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.; Samson, N.P.; Koya, V.; Daniell, H. A protocol for expression of foreign genes in chloroplasts. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 739–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniell, H.; Chebolu, S.; Kumar, S.; Singleton, M.; Falconer, R. Chloroplast-derived vaccine antigens and other therapeutic proteins. Vaccine 2005, 23, 1779–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennica, D.; King, K.L.; Shaw, K.J.; Luis, E.; Rullamas, J.; Luoh, S.M.; Darbonne, W.C.; Knutzon, D.S.; Yen, R.; Chien, K.R.; et al. Expression cloning of cardiotrophin 1, a cytokine that induces cardiac myocyte hypertrophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Yoldi, M.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J.; Bustos, M. Cardiotrophin-1: A multifaceted cytokine. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farran, I.; Río-Manterola, F.; Íñiguez, M.; Gárate, S.; Prieto, J.; Mingo-Castel, A.M. High-density seedling expression system for the production of bioactive human cardiotrophin-1, a potential therapeutic cytokine, in transgenic tobacco chloroplasts. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2008, 6, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, Y.; Buchanan, B.B.; Vignols, F.; Reichheld, J.-P. Thioredoxins and glutaredoxins: Unifying elements in redox biology. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2009, 43, 335–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, C.; Lillig, C.H.; Holmgren, A. Thioredoxins and glutaredoxins as facilitators of protein folding. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2008, 1783, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, R.; Malki, A.; Hölgren, A.; Richarme, G. Chaperone properties of Escherichia coli thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. Biochem. J. 2003, 371, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Jung, Y.J.; Lee, J.R.; Lee, Y.M.; Jang, H.H.; Lee, S.S.; Park, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Moon, J.C.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Heat-shock and redox-dependent functional switching of an h-type Arabidopsis thioredoxin from a disulfide reductase to a molecular chaperone. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Barrio, R.; Fernández-San Millán, A.; Carballeda, J.; Corral-Martínez, P.; Seguí-Simarro, J.M.; Farran, I. Chaperone-like properties of tobacco plastid thioredoxins f and m. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasukawa, T.; Kanei-Ishii, C.; Maekawa, T.; Fujimoto, J.; Yamamoto, T.; Ishii, S. Increase of solubility of foreign proteins in Escherichia coli by coproduction of the bacterial thioredoxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 25328–25331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-Z.; Gong, Z.-W.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.-M.; Zhu, H.-Q.; Wang, W.-B.; Du, Y.; Wang, S.; Yu, W.-Y.; Sun, Z.-W. Co-expression of tetanus toxin fragment C in Escherichia coli with thioredoxin and its evaluation as an effective subunit vaccine candidate. Vaccine 2011, 29, 5978–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, P.; de Lorenzo, V.; Fernández, L.A. Thioredoxin Fusions Increase Folding of Single Chain Fv Antibodies in the Cytoplasm of Escherichia coli: Evidence that Chaperone Activity is the Prime Effect of Thioredoxin. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 357, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, C.L.; Britton, Z.T.; Robinson, A.S. Recombinant protein expression and purification: A comprehensive review of affinity tags and microbial applications. Biotechnol. J. 2012, 7, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaVallie, E.R.; Lu, Z.; Diblasio-Smith, E.A.; Collins-Racie, L.A.; McCoy, J.M. Thioredoxin as a fusion partner for production of soluble recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 2000, 326, 322–340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, J.; Ståhl, S.; Lundeberg, J.; Uhlén, M.; Nygren, P.Å. Affinity Fusion Strategies for Detection, Purification, and Immobilization of Recombinant Proteins. Protein Expr. Purif. 1997, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, Y.; Belin, C.; Delorme-Hinoux, V.; Reichheld, J.-P.; Riondet, C. Thioredoxin and glutaredoxin systems in plants: Molecular mechanisms, crosstalks, and functional significance. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 17, 1124–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, V.; Lamkemeyer, P.; Miginiac-Maslow, M.; Hirasawa, M.; Knaff, D.B.; Dietz, K.-J.; Issakidis-Bourguet, E. Characterization of plastidial thioredoxins from Arabidopsis belonging to the new y-type. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 4088–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsova, B.; Hoja, U.; Wimmelbacher, M.; Greiner, E.; Üstün, S.; Melzer, M.; Petersen, K.; Lein, W.; Börnke, F. Plastidial thioredoxin z interacts with two fructokinase-like proteins in a thiol-dependent manner: Evidence for an essential role in chloroplast development in Arabidopsis and Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Cell Online 2010, 22, 1498–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, B.B. Role of Light in the Regulation of Chloroplast Enzymes. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 1980, 31, 341–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neira, J.L.; González, C.; Toiron, C.; De Prat-Gay, G.; Rico, M. Three-dimensional solution structure and stability of thioredoxin m from spinach. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 15246–15256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancelin, J.-M.; Guilhaudis, L.; Krimm, I.; Blackledge, M.J.; Marion, D.; Jacquot, J.P. NMR structures of thioredoxin m from the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 2000, 41, 334–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katti, S.K.; LeMaster, D.M.; Eklund, H. Crystal structure of thioredoxin from Escherichia coli at 1.68 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 212, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Barrio, R.; Fernández-San Millán, A.; Corral-Martínez, P.; Seguí-Simarro, J.M.; Farran, I. Tobacco plastidial thioredoxins as modulators of recombinant protein production in transgenic chloroplasts. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011, 9, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, A.; Hervás-Stubbs, S.; Daniell, H.; Mingo-Castel, A.M.; Veramendi, J. High-yield expression of a viral peptide animal vaccine in transgenic tobacco chloroplasts. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2004, 2, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, H.; Maliga, P. Sequences downstream of the translation initiation codon are important determinants of translation efficiency in chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iamtham, S.; Day, A. Removal of antibiotic resistance genes from transgenic tobacco plastids. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 1172–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniell, H. Transformation and Foreign Gene Expression in Plants Mediated by Microprojectile Bombardment. Methods Mol. Biol. 1997, 62, 463–489. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holmgren, A. Thioredoxin catalyzes the reduction of insulin disulfides by dithiothreitol and dihydrolipoamide. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 9627–9632. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maliga, P.; Bock, R. Plastid biotechnology: Food, fuel, and medicine for the 21st century. Plant Physiol. 2011, 155, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marchis, F.; Pompa, A.; Bellucci, M. Plastid proteostasis and heterologous protein accumulation in transplastomic plants. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marco, A. Strategies for successful recombinant expression of disulfide bond-dependent proteins in Escherichia coli. Microb. Cell Fact. 2009, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Duan, H.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, T.; Tao, H.; Zhang, Z. The role of thioredoxin and disulfide isomerase in the expression of the snake venom thrombin-like enzyme calobin in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3). Protein Expr. Purif. 2004, 38, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farran, I.; McCarthy-Suárez, I.; Río-Manterola, F.; Mansilla, C.; Lasarte, J.J.; Mingo-Castel, Á.M. The vaccine adjuvant extra domain A from fibronectin retains its proinflammatory properties when expressed in tobacco chloroplasts. Planta 2010, 231, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leelavathi, S.; Reddy, V.S. Chloroplast expression of His-tagged GUS-fusions: A general strategy to overproduce and purify foreign proteins using transplastomic plants as bioreactors. Mol. Breed. 2003, 11, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzi, P.; Scotti, N.; Alagna, F.; Tornesello, M.L.; Pompa, A.; Vitale, A.; De Stradis, A.; Monti, L.; Grillo, S.; Buonaguro, F.M.; et al. Translational fusion of chloroplast-expressed human papillomavirus type 16 L1 capsid protein enhances antigen accumulation in transplastomic tobacco. Transgenic Res. 2008, 17, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scotti, N.; Alagna, F.; Ferraiolo, E.; Formisano, G.; Sannino, L.; Buonaguro, L.; De Stradis, A.; Vitale, A.; Monti, L.; Grillo, S.; et al. High-level expression of the HIV-1 Pr55gag polyprotein in transgenic tobacco chloroplasts. Planta 2009, 229, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staub, J.M.; Garcia, B.; Graves, J.; Hajdukiewicz, P.T.J.; Hunter, P.; Nehra, N.; Paradkar, V.; Schlittler, M.; Carroll, J.A.; Spatola, L.; et al. High-yield production of a human therapeutic protein in tobacco chloroplasts. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.N.; Hajdukiewicz, P.T.J.; Broyles, D.; Rodriguez, D.; Xu, C.W.; Nehra, N.; Staub, J.M. Plastid-expressed 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase genes provide high level glyphosate tolerance in tobacco. Plant J. 2001, 25, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Badillo-Corona, J.A.; Karcher, D.; Gonzalez-Rabade, N.; Piepenburg, K.; Borchers, A.M.I.; Maloney, A.P.; Kavanagh, T.A.; Gray, J.C.; Bock, R. High-level expression of human immunodeficiency virus antigens from the tobacco and tomato plastid genomes. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2008, 6, 897–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch-Machint, I.; Newell, C.A.; Hibberd, J.M.; Gray, J.C. Accumulation of rotavirus VP6 protein in chloroplasts of transplastomic tobacco is limited by protein stability. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2004, 2, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, M.S.; Klaas, M.; Gonzalez-Rabade, N.; Poage, M.; Badillo-Corona, J.A.; Zhou, F.; Karcher, D.; Bock, R.; Gray, J.C.; Dix, P.J. Plastid transformation of high-biomass tobacco variety Maryland Mammoth for production of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 antigen. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2008, 6, 914–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, W. Protein Degradation Machineries in Plastids. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 599–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaire, S.D.; Michelet, L.; Zaffagnini, M.; Massot, V.; Issakidis-Bourguet, E. Thioredoxins in chloroplasts. Curr. Genet. 2007, 51, 343–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.B.; Li, B.; Jin, S.; Daniell, H. Expression and characterization of antimicrobial peptides Retrocyclin-101 and Protegrin-1 in chloroplasts to control viral and bacterial infections. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011, 9, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lentz, E.M.; Segretin, M.E.; Morgenfeld, M.M.; Wirth, S.A.; Dus Santos, M.J.; Mozgovoj, M.V.; Wigdorovitz, A.; Bravo-Almonacid, F.F. High expression level of a foot and mouth disease virus epitope in tobacco transplastomic plants. Planta 2010, 231, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schürmann, P.; Buchanan, B.B. The ferredoxin/thioredoxin system of oxygenic photosynthesis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 1235–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, V.; Issakidis-Bourguet, E.; Marchand, C.; Hirasawa, M.; Lancelin, J.-M.; Knaff, D.B.; Miginiac-Maslow, M. The Arabidopsis plastidial thioredoxins. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 23747–23752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira Dos Santos, C.; Laugier, E.; Tarrago, L.; Massot, V.; Issakidis-Bourguet, E.; Rouhier, N.; Rey, P. Specificity of thioredoxins and glutaredoxins as electron donors to two distinct classes of Arabidopsis plastidial methionine sulfoxide reductases B. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 4371–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, P.; Sanz-Barrio, R.; Innocenti, G.; Ksas, B.; Courteille, A.; Rumeau, D.; Issakidis-Bourguet, E.; Farran, I. Overexpression of plastidial thioredoxins f and m differentially alters photosynthetic activity and response to oxidative stress in tobacco plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmer, Y.; Koller, A.; del Val, G.; Manieri, W.; Schürmann, P.; Buchanan, B.B. Proteomics gives insight into the regulatory function of chloroplast thioredoxins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montrichard, F.; Alkhalfioui, F.; Yano, H.; Vensel, W.H.; Hurkman, W.J.; Buchanan, B.B. Thioredoxin targets in plants: The first 30 years. J. Proteomics 2009, 72, 452–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpe, K. Overview of tag protein fusions: From molecular and biochemical fundamentals to commercial systems. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 60, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Filutowicz, M. Hexahistidine (His6)-tag dependent protein dimerization: A cautionary tale. Acta Biochim. Pol. 1999, 46, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bøe, C.A.; Garcia, I.; Pai, C.C.; Sharom, J.R.; Skjølberg, H.C.; Boye, E.; Kearsey, S.; MacNeill, S.A.; Tyers, M.D.; Grallert, B. Rapid regulation of protein activity in fission yeast. BMC Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, T.; Amiram, M.; Dagher, S.; Trabbic-Carlson, K.; Shamji, M.F.; Setton, L.A.; Chilkoti, A. Fusion order controls expression level and activity of elastin-like polypeptide fusion proteins. Protein Sci. 2009, 18, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.L.; Yao, X.Q.; Xue, C.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, X.H.; Liu, Z.M. Increasing the homogeneity, stability and activity of human serum albumin and interferon-α2b fusion protein by linker engineering. Protein Expr. Purif. 2008, 61, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Yu, J.; Chong, D.K.X.; Hough, J.; Engen, P.C.; Langridge, W.H.R. A plant-based cholera toxin B subunit–insulin fusion protein protects against the development of autoimmune diabetes. Nat. Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaVallie, E.R.; Rehemtulla, A.; Racie, L.A.; DiBlasio, E.A.; Ferenz, C.; Grant, K.L.; Light, A.; McCoy, J.M. Cloning and functional expression of a cDNA encoding the catalytic subunit of bovine enterokinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 23311–23317. [Google Scholar]
- Parks, T.D.; Leuther, K.K.; Howard, E.D.; Johnston, S.A.; Dougherty, W.G. Release of Proteins and Peptides from Fusion Proteins Using a Recombinant Plant Virus Proteinase. Anal. Biochem. 1994, 216, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sul, I.; Korban, S. A highly efficient method for isolating genomic DNA from plant tissues. Plant Tissue Cult. Biotechnol. 1996, 2, 113–116. [Google Scholar]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ancín, M.; Sanz-Barrio, R.; Santamaría, E.; Fernández-San Millán, A.; Larraya, L.; Veramendi, J.; Farran, I. Functional Improvement of Human Cardiotrophin 1 Produced in Tobacco Chloroplasts by Co-Expression with Plastid Thioredoxin m. Plants 2020, 9, 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9020183
Ancín M, Sanz-Barrio R, Santamaría E, Fernández-San Millán A, Larraya L, Veramendi J, Farran I. Functional Improvement of Human Cardiotrophin 1 Produced in Tobacco Chloroplasts by Co-Expression with Plastid Thioredoxin m. Plants. 2020; 9(2):183. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9020183
Chicago/Turabian StyleAncín, María, Ruth Sanz-Barrio, Eva Santamaría, Alicia Fernández-San Millán, Luis Larraya, Jon Veramendi, and Inmaculada Farran. 2020. "Functional Improvement of Human Cardiotrophin 1 Produced in Tobacco Chloroplasts by Co-Expression with Plastid Thioredoxin m" Plants 9, no. 2: 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9020183
APA StyleAncín, M., Sanz-Barrio, R., Santamaría, E., Fernández-San Millán, A., Larraya, L., Veramendi, J., & Farran, I. (2020). Functional Improvement of Human Cardiotrophin 1 Produced in Tobacco Chloroplasts by Co-Expression with Plastid Thioredoxin m. Plants, 9(2), 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9020183




