Phosphorus Nutrient Management through Synchronization of Application Methods and Rates in Wheat and Maize Crops
Abstract
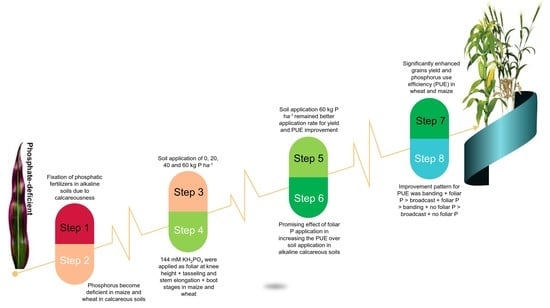
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Plant Height
2.2. Number of Grains (Maize and Wheat) Ear−1/Spike−1
2.3. Thousand Grain Weight (g)
2.4. Biological Yield (t ha−1)
2.5. Grain Yield
2.6. Harvest Index (%)
2.7. Phosphorus Use Efficiency (PUE)
2.8. Nitrogen in Maize and Wheat Leaves
2.9. Phosphorus in Maize and Wheat Leaves
2.10. Potassium in Maize and Wheat Leaves
2.11. Postharvest Soil NPK
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Set Up
4.2. Agronomic Parameters
4.3. Plant Analysis
4.4. Soil Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- General Assembly. United Nations Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. 2015. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/post2015/transformingourworld (accessed on 9 October 2020).
- Stubenrauch, J.; Garske, B.; Ekardt, F. Sustainable land use, soil protection and phosphorus management from a cross-national perspective. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, H.; Fatima, R.; Sharma, A.; Mathur, S. Enhancement of applicability of rock phosphate in alkaline soils by organic compost. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 113, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimpour, S.; Khavazi, K.; Nadian, H.; Besharati, H.; Miransari, M. Enhancing phosphorous availability to canola (Brassica napus L.) using P solubilizing and sulfur oxidizing bacteria. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2010, 4, 330–334. [Google Scholar]
- Adeyemi, O.; Keshavarz-Afshar, R.; Jahanzad, E.; Battaglia, M.L.; Luo, Y.; Sadeghpour, A. Effect of Wheat Cover Crop and Split Nitrogen Application on Corn Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketterings, Q.; Czymmek, K. Removal of Phosphorus by Field Crops; Agronomy Fact Sheet Series; Fact Sheet #28; Nutrient Management Spear Program, Cornell University: Ithaca, NY, USA; Available online: http://nmsp.cals.cornell.edu/publications/factsheets/factsheet28.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2020).
- Qureshi, M.A.; Ahmad, Z.A.; Akhtar, N.; Iqbal, A.; Mujeeb, F.; Shakir, M.A. Role of phosphate solubilizing bacteria (PSB) in enhancing P availability and promoting cotton growth. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2012, 22, 204–210. [Google Scholar]
- Halajnia, A.; Haghnia, G.H.; Fotovat, A.; Khorasani, R. Phosphorus fractions in calcareous soils amended with P fertilizer and cattle manure. Geoderma 2009, 150, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Uexküll, H.R.; Mutert, E. Global extent, development and economic impact of acid soils. Plant Soil 1995, 171, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieleski, R.L. Phosphate Pools, Phosphate Transport, and Phosphate Availability. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 1973, 24, 225–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Bucio, J.; De la Vega, O.M.; Guevara-García, A.; Herrera-Estrella, L. Enhanced phosphorus uptake in transgenic tobacco plants that overproduce citrate. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meena, R.S.; Kumar, S.; Datta, R.; Lal, R.; Vijayakumar, V.; Brtnicky, M.; Sharma, M.P.; Yadav, G.S.; Jhariya, M.K.; Jangir, C.K. Impact of agrochemicals on soil microbiota and management: A review. Land 2020, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brtnicky, M.; Dokulilova, T.; Holatko, J.; Pecina, V.; Kintl, A.; Latal, O.; Vyhnanek, T.; Prichystalova, J.; Datta, R. Long-Term Effects of Biochar-Based Organic Amendments on Soil Microbial Parameters. Agronomy 2019, 9, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaei, A.; Lakzian, A.; Datta, R.; Haghnia, G.; Astaraei, A.; Rasouli-Sadaghiani, M.; Ceccherini, M.T. Impact of chlortetracycline and sulfapyridine antibiotics on soil enzyme activities. Int. Agrophys. 2017, 31, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaei, A.; Lakzian, A.; Haghnia, G.; Astaraei, A.; Rasouli-Sadaghiani, M.; Ceccherini, M.T.; Datta, R. Assessment of some cultural experimental methods to study the effects of antibiotics on microbial activities in a soil: An incubation study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danish, S.; Younis, U.; Akhtar, N.; Ameer, A.; Ijaz, M.; Nasreen, S.; Huma, F.; Sharif, S.; Ehsanullah, M. Phosphorus solubilizing bacteria and rice straw biochar consequence on maize pigments synthesis. Int. J. Biosci. 2015, 5, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Younis, U.; Danish, S.; Shah, M.H.R.; Malik, S.A. Nutrient shifts modeling in Spinacea oleracea L. and Trigonella corniculata L. in contaminated soil amended with biochar. Int. J. Biosci. 2014, 5, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Danish, S.; Zafar-ul-Hye, M. Co-application of ACC-deaminase producing PGPR and timber-waste biochar improves pigments formation, growth and yield of wheat under drought stress. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, H.; Ahmed, N.; Mubashir, M.; Danish, S. Chemical production of acidified activated carbon and its influences on soil fertility comparative to thermo-pyrolyzed biochar. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar-ul-Hye, M.; Tahzeeb-ul-Hassan, M.; Abid, M.; Fahad, S.; Brtnicky, M.; Dokulilova, T.; Datta, R.; Danish, S. Potential role of compost mixed biochar with rhizobacteria in mitigating lead toxicity in spinach. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 69183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izhar Shafi, M.; Adnan, M.; Fahad, S.; Wahid, F.; Khan, A.; Yue, Z.; Danish, S.; Zafar-ul-Hye, M.; Brtnicky, M.; Datta, R. Application of Single Superphosphate with Humic Acid Improves the Growth, Yield and Phosphorus Uptake of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in Calcareous Soil. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Fahad, S.; Zamin, M.; Shah, S.; Mian, I.A.; Danish, S.; Zafar-Ul-hye, M.; Battaglia, M.L.; Naz, R.M.M.; Saeed, B.; et al. Coupling phosphate-solubilizing bacteria with phosphorus supplements improve maize phosphorus acquisition and growth under lime induced salinity stress. Plants 2020, 9, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, F.; Silberbush, M. Response of maize to foliar vs. soil application of nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium fertilizers. J. Plant Nutr. 2002, 25, 2333–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, F.; Ahmad, I.; Bakhsh, A.; Kiran, S.; Danish, S.; Ullah, H. Effect of Foliar Application of Boron with Calcium and Potassium on Quality and Yield of Mango cv. Summer Bahisht (SB) Chaunsa. Open Agric. 2019, 4, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, S.; Kiran, S.; Fahad, S.; Ahmad, N.; Ali, M.A.; Tahir, F.A.; Rasheed, M.K.; Shahzad, K.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; et al. Alleviation of chromium toxicity in maize by Fe fortification and chromium tolerant ACC deaminase producing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 185, 109706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fageria, N.K.; Filho, M.P.B.; Moreira, A.; Guimarães, C.M. Foliar fertilization of crop plants. J. Plant. Nutr. 2009, 32, 1044–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halo, B. Effect of foliar application of phosphorus salt on yellowing of wheat seedlings. J. Res. Assam Agric. Univ. 1980, 1, 108–109. [Google Scholar]
- Silberstein, O.; Wittwer, S.H. Foliar application of phosphatic nutrients to vegetable crops. In Proceedings of the American Society for Horticultural Science; American Society for Horticultural Science: College Park, MD, USA, 1951; Volume 58, pp. 179–190. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, R.C. Foliar fertilization improves nutrient use efficiency. Fluid J. 2003, 11, 22–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.S.; Sutradhar, A.; Edano, M.L.; Edwards, J.T.; Girma, K. Response of winter wheat grain yield and phosphorus uptake to foliar phosphite fertilization. Int. J. Agron. 2014, 2014, 801626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Benbella, M.; Paulsen, G.M. Efficacy of treatments for delaying senescence of wheat leaves: II. Senescence and grain yield under field conditions. Agron. J. 1998, 90, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girma, K.; Martin, K.L.; Freeman, K.W.; Mosali, J.; Teal, R.K.; Raun, W.R.; Moges, S.M.; Arnall, D.B. Determination of optimum rate and growth stage for foliar-applied phosphorus in corn. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2007, 38, 1137–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosali, J.; Desta, K.; Teal, R.K.; Freeman, K.W.; Martin, K.L.; Lawles, J.W.; Raun, W.R. Effect of foliar application of phosphorus on winter wheat grain yield, phosphorus uptake, and use efficiency. J. Plant Nutr. 2006, 29, 2147–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Chohan, M.A.; Ali, S.; Gul, R.; Khan, S. Response of wheat to foliar application of nutrients. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2006, 1, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wahid, F.; Sharif, M.; Fahad, S.; Adnan, M.; Khan, I.A.; Aksoy, E.; Ali, A.; Sultan, T.; Alam, M.; Saeed, M.; et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi improve the growth and phosphorus uptake of mung bean plants fertilized with composted rock phosphate fed dung in alkaline soil environment. J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 42, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, F.; Fahad, S.; Danish, S.; Adnan, M.; Yue, Z.; Saud, S.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Brtnicky, M.; Hammerschmiedt, T.; Datta, R. Sustainable management with mycorrhizae and phosphate solubilizing bacteria for enhanced phosphorus uptake in calcareous soils. Agriculture 2020, 10, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singaram, P.; Kothandaraman, G.V. Studies on residual, direct and cumulative effect of phosphorus sources on the availability, content and uptake of phosphorus and yield of maize. Madras Agric. J. 1994, 81, 425–429. [Google Scholar]
- Soylu, S.; Sade, B.; Topal, A.; Akgün, N.; Gezgin, S.; Hakki, E.E.; Babaoǧlu, M. Responses of irrigated durum and bread wheat cultivars to boron application in a low boron calcareous soil. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2005, 29, 275–286. [Google Scholar]
- Kenbaev, B.; Sade, B. Response of field-grown barley cultivars grown on zinc-deficient soil to zinc application. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2002, 33, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.P.; Sharma, U.C. Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus on the yield and severity of turcicum blight of maize in Nagaland. Indian Phytopathol. 1991, 44, 383–385. [Google Scholar]
- Maqsood, M.; Abid, A.M.; Iqbal, A.; Hussain, M.I. Effect of variable rate of nitrogen and phosphorus on growth and yield of maize (golden). Online J. Biol. Sci. 2001, 1, 19–20. [Google Scholar]
- Arain, A.S.; Alam, S.M.; Tunio, A.K.G. Performance of maize genotypes under varying NP-fertilizer environments. Sarhad J. Agric. 1989, 5, 623–626. [Google Scholar]
- Gooding, M.J.; Davies, W.P. Foliar urea fertilization of cereals: A review. Fertil. Res. 1992, 32, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, J.; Mosluh, K.I. Erefects of urea spray on wheat in Iraq. Exp. Agric. 1981, 17, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fareed, M.K. Effect of Varying Fertilizer Rate and Plant Stand Density on Growth and Yield of Spring Maize. Mastes’s Thesis, University of Agriculture Faisalabad, Faisalabad, Pakistan, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.Z.; Rehman, N.; Khan, M.A. Micronutrients status of Bannu basen soils. Sarhad J. Agric. 2006, 22, 150–157. [Google Scholar]
- Yasir, A.M.; Khalil, S.K.; Jan, M.T.; Khan, A.Z. Phenology, growth, and grain yield of maize as influenced by foliar applied urea at different growth stages. J. Plant Nutr. 2010, 33, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Alston, A.M. Effects of soil water content and foliar fertilization with nitrogen and phosphorus in late season on the yield and composition of wheat. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1979, 30, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Ghosh, P.K.; Ghosh, S.; De, T.K.; Maiti, T.K. Role of heavy metal resistant Ochrobactrum sp. and Bacillus spp. strains in bioremediation of a rice cultivar and their PGPR like activities. J. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, R. The effects of integrated application of micronutrient on wheat in low organic carbon conditions of alkaline soils of western Iran. In Proceedings of the 18th World Congress of Soil Science, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 9–15 July 2006; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Hamayun, M.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, A.L.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Ahmad, N.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, I.J. Effect of foliar and soil application of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium on yield components of lentil. Pak. J. Bot. 2011, 43, 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Reuter, D.J.; Dyson, C.B.; Elliott, D.E.; Lewis, D.C.; Rudd, C.L. An Appraisal of Soil Phosphorus Testing Data for Crops and Pastures in South Australia. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 1995, 35, 979–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, K.H.; Nagy, R.; Gao, L.L.; Smith, S.E.; Bucher, M.; Smith, F.A.; Jakobsen, I. Physiological and molecular evidence for Pi uptake via the symbiotic pathway in a reduced mycorrhizal colonization mutant in tomato associated with a compatible fungus. New Phytol. 2005, 168, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, H. Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1995; ISBN 9780124735422. [Google Scholar]
- Zameer Khan, M.; Muhammad, S.; Naeem, M.A.; Akhtar, E.; Khalid, M. Response of some wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) varieties to foliar application of N & K under rainfed conditions. Pak. J. Bot. 2006, 38, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Rafiullah; Khan, M.J.; Muhammad, D. Foliar application of phosphorus to enhance phosphorus utilization and crop growth: A hydroponic study. Sarhad J. Agric. 2018, 34, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Marfo, T.D.; Datta, R.; Vranová, V.; Ekielski, A. Ecotone Dynamics and Stability from Soil Perspective: Forest-Agriculture Land Transition. Agriculture 2019, 9, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.S.; Datta, R.; Pathan, S.I.; Lal, R.; Meena, R.S.; Babu, S.; Das, A.; Bhowmik, S.N.; Datta, M.; Saha, P.; et al. Effects of conservation tillage and nutrient management practices on soil fertility and productivity of rice (Oryza sativa L.)-rice system in North eastern region of India. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfo, T.D.; Datta, R.; Pathan, S.I.; Vranová, V. Ecotone dynamics and stability from soil scientific point of view. Diversity 2019, 11, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, C.; Wang, K.; Liu, J.; Lu, J.; Xu, K. Rational phosphorus application facilitates the sustainability of the wheat/maize/soybean relay strip intercropping system. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.P. Methods of Soil Analysis Part 3: Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Page, A.L., Helmke, P.A., Loeppert, R.H., Soltanpour, P.N., Tabatabai, M.A., Johnston, C.T., Sumner, M.E., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 869–919. [Google Scholar]
- Benton, J.J.; Wolf, B., Jr.; Mills, H.A. Mills Plant Analysis Handbook: A Practical Sampling, Preparation, Analysis, and Interpretation Guide, 1st ed.; Micro-Macro Publishing Inc.: Athens, GA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, M. Chapter 37: Nitrogen-Total. Methods Soil Anal. Part 3 Chem. Methods-SSSA B Ser. 1996, 5, 1085–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Soltanpour, P.N. Determination of Nutrient Availability and Elemental Toxicity by AB-DTPA Soil Test and ICPS. In Advances in Soil Science; Stewart, B.A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; Volume 16, pp. 165–190. [Google Scholar]
- Walkley, A. An Examination of Methods for Determining Organic Carbon and Nitrogen in Soils. J. Agric. Sci. 1935, 25, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total Carbon, Organic Carbon, and Organic Matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Page, A.L., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 916–1010, Part 2. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, G.W. Soil pH and soil acidity. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 3: Chemical Methods; John Wiley & Sons: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; Volume 5, pp. 475–490. [Google Scholar]
- Soltanpour, P.N.; Schwab, A.P. A new soil test for simultaneous extraction of macroand micro-nutrients in alkaline soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1977, 8, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, R.G.; Torrie, J.H.; Dickey, D.A. Principles and Procedures of Statistics: A Biometrical Approach, 3rd ed.; McGraw Hill Book International Co.: Singapore, 1997. [Google Scholar]
| Foliar P | Methods | P Levels (kg ha−1) | Mean | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | |||
| Maize | ||||||
| No Foliar spray | - | 197 | 211 | 214 | 216 | 210 b |
| Foliar P | - | 205 | 213 | 219 | 221 | 215 a |
| - | BC | 200 | 209 | 215 | 218 | 211 b |
| - | BD | 202 | 215 | 219 | 219 | 214 a |
| Year I | - | 198 | 210 | 214 | 216 | 210 NS |
| Year II | - | 204 | 214 | 219 | 222 | 215 |
| Mean | 201 d | 212 c | 217 b | 219 a | ||
| Wheat | ||||||
| No Foliar spray | - | 78 | 82 | 86 | 90 | 84 b |
| Foliar P | - | 87 | 91 | 93 | 96 | 92 a |
| - | BC | 80 | 84 | 88 | 91 | 86 b |
| - | BD | 85 | 89 | 90 | 95 | 90 a |
| Year I | - | 82 | 85 | 88 | 92 | 87 NS |
| Year II | - | 83 | 88 | 90 | 94 | 89 |
| Mean | 82 d | 87 c | 89 b | 93 a | ||
| Foliar P | Methods | P Levels (kg ha−1) | Mean | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | |||
| Maize Crop | ||||||
| No Foliar | - | 338 | 366 | 392 | 405 | 375 b |
| Foliar P | - | 357 | 413 | 422 | 436 | 407 a |
| - | BC | 343 | 379 | 394 | 416 | 383 b |
| - | BD | 352 | 400 | 421 | 426 | 399 a |
| Year I | - | 343 | 387 | 406 | 426 | 390 |
| Year II | - | 352 | 393 | 408 | 415 | 392 |
| Mean | 348 d | 390 c | 407 b | 421 a | ||
| Wheat Crop | ||||||
| No Foliar | - | 45 | 51 | 52 | 54 | 51 b |
| Foliar P | - | 49 | 54 | 56 | 58 | 54 a |
| - | BC | 46 | 51 | 53 | 54 | 51 b |
| - | BD | 48 | 54 | 55 | 57 | 53 a |
| Year I | - | 45 | 50 | 51 | 53 | 50 |
| Year II | - | 49 | 55 | 57 | 58 | 55 |
| Mean | 47 d | 52 c | 54 b | 56 a | ||
| Foliar P | Methods | P Levels (kg ha−1) | Mean | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | |||
| Maize | ||||||
| No Foliar spray | - | 221 | 242 | 244 | 263 | 243 b |
| Foliar P | - | 232 | 262 | 273 | 282 | 262 a |
| - | BC | 222 | 248 | 258 | 265 | 248 b |
| - | BD | 231 | 256 | 260 | 280 | 257 a |
| Year I | - | 220 | 244 | 254 | 268 | 246 |
| Year II | - | 232 | 260 | 264 | 278 | 258 |
| Mean | 226 d | 252 c | 259 b | 273 a | ||
| Wheat | ||||||
| No Foliar spray | - | 41 | 43 | 45 | 48 | 44 b |
| Foliar P | - | 45 | 46 | 49 | 51 | 48 a |
| - | BC | 43 | 44 | 46 | 47 | 45 b |
| - | BD | 43 | 45 | 48 | 51 | 47 a |
| Year I | - | 42 | 44 | 46 | 47 | 45 |
| Year II | - | 44 | 46 | 48 | 51 | 47 |
| Mean | 43 d | 45 c | 47 b | 49 a | ||
| Foliar P | Methods | P Levels (kg ha−1) | Mean | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | |||
| Maize Crop | ||||||
| No Foliar | - | 9.00 | 10.76 | 11.38 | 11.58 | 10.68 b |
| Foliar P | - | 10.18 | 11.52 | 11.78 | 11.91 | 11.35 a |
| - | BC | 9.56 | 10.86 | 11.44 | 11.66 | 10.88 b |
| - | BD | 9.62 | 11.41 | 11.72 | 11.83 | 11.14 a |
| Year I | - | 9.61 | 11.09 | 11.59 | 11.73 | 11.01 NS |
| Year II | - | 9.57 | 11.18 | 11.56 | 11.76 | 11.02 |
| Mean | 9.59 d | 11.14 c | 11.58 b | 11.75 a | ||
| Wheat Crop | ||||||
| No Foliar | - | 7.25 | 8.40 | 8.88 | 9.10 | 8.41 b |
| Foliar P | - | 8.22 | 8.94 | 9.20 | 9.40 | 8.94 a |
| - | BC | 7.67 | 8.49 | 8.85 | 9.15 | 8.54 b |
| - | BD | 7.80 | 8.86 | 9.24 | 9.35 | 8.81 a |
| Year I | - | 7.77 | 8.66 | 9.03 | 9.31 | 8.69 NS |
| Year II | - | 7.70 | 8.68 | 9.05 | 9.20 | 8.66 |
| Mean | 7.74 d | 8.67 c | 9.04 b | 9.25 a | ||
| Foliar P | Methods | P Levels (kg ha−1) | Mean | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | |||
| Maize | ||||||
| No Foliar spray | - | 3.16 | 4.24 | 4.57 | 4.71 | 4.17 b |
| Foliar P | - | 3.72 | 4.50 | 4.82 | 4.88 | 4.48 a |
| - | BC | 3.42 | 4.27 | 4.62 | 4.72 | 4.26 b |
| - | BD | 3.46 | 4.47 | 4.77 | 4.87 | 4.39 a |
| Year I | - | 3.42 | 4.38 | 4.67 | 4.75 | 4.31 NS |
| Year II | - | 3.47 | 4.36 | 4.71 | 4.84 | 4.34 |
| Mean | 3.44 d | 4.37 c | 4.69 b | 4.79 a | ||
| Wheat | ||||||
| No Foliar spray | - | 2.57 | 3.51 | 3.66 | 3.95 | 3.42 b |
| Foliar P | - | 3.21 | 3.88 | 4.11 | 4.30 | 3.88 a |
| - | BC | 2.90 | 3.55 | 3.76 | 4.04 | 3.56 b |
| - | BD | 2.88 | 3.83 | 4.01 | 4.22 | 3.73 a |
| Year I | - | 2.92 | 3.76 | 3.88 | 4.11 | 3.67 NS |
| Year II | - | 2.86 | 3.62 | 3.89 | 4.14 | 3.63 |
| Mean | 2.89 d | 3.69 c | 3.88 b | 4.13 a | ||
| Foliar P | Methods | P Levels (kg ha−1) | Mean | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | |||
| Maize | ||||||
| No Foliar spray | - | 36 | 38 | 40 | 40 | 39 ab |
| Foliar P | - | 36 | 39 | 42 | 42 | 40 a |
| - | BC | 36 | 38 | 40 | 41 | 39 a |
| - | BD | 36 | 39 | 41 | 41 | 39 a |
| Year I | - | 37 | 40 | 41 | 41 | 40 |
| Year II | - | 35 | 38 | 41 | 41 | 39 |
| Mean | 36 d | 39 c | 41 ab | 41a | ||
| Wheat | ||||||
| No Foliar spray | - | 41 | 42 | 42 | 46 | 43 b |
| Foliar P | - | 43 | 45 | 47 | 51 | 47 a |
| - | BC | 42 | 43 | 43 | 47 | 44 b |
| - | BD | 43 | 45 | 47 | 50 | 46 a |
| Year I | - | 42 | 44 | 44 | 49 | 45 |
| Year II | - | 43 | 43 | 46 | 48 | 45 |
| Mean | 42 d | 44 c | 45 b | 49 a | ||
| Foliar P | Methods | P Levels (kg ha−1) | Mean | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | |||
| Maize | ||||||
| No Foliar spray | - | - | 54.3 | 35.3 | 25.9 | 38.5 |
| Foliar P | - | 283.2 | 61.0 | 39.5 | 27.7 | 102.8 |
| - | BC | - | 53.3 | 35.8 | 25.8 | 38.3 |
| - | BD | - | 62.0 | 39.0 | 27.8 | 42.9 |
| Year I | - | 277.6 | 59.0 | 37.4 | 26.4 | 100.1 |
| Year II | - | 288.8 | 56.3 | 37.4 | 27.2 | 102.4 |
| Mean | 283.2 | 57.6 | 37.4 | 26.8 | ||
| Wheat | ||||||
| No Foliar spray | - | - | 47.0 | 27.3 | 23.1 | 32.5 |
| Foliar P | - | 322.5 | 59.7 | 36.7 | 27.9 | 111.7 |
| - | BC | - | 43.1 | 27.3 | 22.9 | 31.1 |
| - | BD | - | 63.6 | 36.7 | 28.2 | 42.8 |
| Year I | - | 336.5 | 55.8 | 31.5 | 25.0 | 112.2 |
| Year II | - | 308.5 | 50.9 | 32.6 | 26.1 | 104.5 |
| Mean | 322.5 | 53.3 | 32.0 | 25.5 | ||
| Foliar P | Methods | P Levels (kg ha−1) | Mean | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | |||
| Maize | ||||||
| No Foliar spray | - | 1.38 | 1.49 | 1.92 | 2.11 | 1.73 b |
| Foliar P | - | 1.91 | 2.24 | 2.33 | 2.46 | 2.23 a |
| - | BC | 1.58 | 1.80 | 2.07 | 2.23 | 1.92 b |
| - | BD | 1.71 | 1.93 | 2.19 | 2.34 | 2.04 a |
| Year I | - | 1.68 | 1.83 | 2.04 | 2.22 | 1.94 |
| Year II | - | 1.60 | 1.90 | 2.21 | 2.35 | 2.02 |
| Mean | 1.64 d | 1.87 c | 2.13 b | 2.28 a | ||
| Wheat | ||||||
| No Foliar spray | - | 1.43 | 1.61 | 1.92 | 2.05 | 1.75 b |
| Foliar P | - | 1.65 | 1.97 | 2.18 | 2.25 | 2.01 a |
| - | BC | 1.49 | 1.72 | 1.98 | 2.08 | 1.82 b |
| - | BD | 1.59 | 1.86 | 2.12 | 2.22 | 1.95 a |
| Year I | - | 1.58 | 1.79 | 2.05 | 2.14 | 1.89 |
| Year II | - | 1.49 | 1.79 | 2.05 | 2.16 | 1.87 |
| Mean | 1.54 d | 1.79 c | 2.05 b | 2.15 a | ||
| Foliar P | Methods | P Levels (kg ha−1) | Mean | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | |||
| Maize | ||||||
| No Foliar spray | - | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.17 b |
| Foliar P | - | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.22 a |
| - | BC | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.19 b |
| - | BD | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.21 a |
| Year I | - | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.19 |
| Year II | - | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.20 |
| Mean | 0.16 d | 0.19 c | 0.21 b | 0.23 a | ||
| Wheat | ||||||
| No Foliar spray | - | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.13 b |
| Foliar P | - | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.16 a |
| - | BC | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.14 b |
| - | BD | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.15 a |
| Year I | - | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.14 |
| Year II | - | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.14 |
| Mean | 0.12 d | 0.14 c | 0.15 b | 0.16 a | ||
| Foliar P | Methods | P Levels (kg ha−1) | Mean | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | |||
| Maize | ||||||
| No Foliar spray | - | 2.77 | 3.09 | 3.42 | 3.68 | 3.24 b |
| Foliar P | - | 3.02 | 3.52 | 3.80 | 3.98 | 3.58 a |
| - | BC | 2.80 | 3.26 | 3.56 | 3.81 | 3.36 b |
| - | BD | 2.99 | 3.34 | 3.67 | 3.85 | 3.46 a |
| Year I | - | 2.71 | 3.22 | 3.47 | 3.69 | 3.27 |
| Year II | - | 3.07 | 3.38 | 3.76 | 3.96 | 3.54 |
| Mean | 2.89 d | 3.30 c | 3.61 b | 3.83 a | 13.64 | |
| Wheat | ||||||
| No Foliar spray | - | 2.7 | 3.2 | 3.4 | 3.5 | 3.2 b |
| Foliar P | - | 3.2 | 3.5 | 3.8 | 3.9 | 3.6 a |
| - | BC | 2.9 | 3.3 | 3.5 | 3.7 | 3.3 b |
| - | BD | 3.1 | 3.4 | 3.7 | 3.8 | 3.5 a |
| Year I | - | 2.9 | 3.3 | 3.5 | 3.7 | 3.4 |
| Year II | - | 3.1 | 3.4 | 3.6 | 3.8 | 3.5 |
| Mean | 3.0 d | 3.4 c | 3.6 b | 3.7 a | ||
| Foliar P | Method | P Levels (kg ha−1) | Mean | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | |||
| Year I | ||||||
| 0 | BC | 0.70 | 0.89 | 1.01 | 1.05 | 0.9 |
| 0 | BD | 0.75 | 0.90 | 0.93 | 1.03 | 0.9 |
| 144 mM | BC | 0.85 | 1.02 | 1.25 | 1.35 | 1.1 |
| 144 mM | BD | 0.93 | 1.09 | 1.31 | 1.40 | 1.2 |
| Year II | ||||||
| 0 | BC | 0.88 | 0.95 | 1.03 | 1.09 | 1.0 |
| 0 | BD | 0.81 | 0.85 | 0.95 | 0.89 | 0.9 |
| 144 mM | BC | 0.96 | 1.08 | 1.23 | 1.37 | 1.2 |
| 144 mM | BD | 0.98 | 1.11 | 1.28 | 1.36 | 1.2 |
| Average Across Methods | ||||||
| No Foliar spray | - | 0.79 | 0.89 | 0.98 | 1.02 | 0.92 b |
| Foliar P | - | 0.93 | 1.07 | 1.27 | 1.37 | 1.16 a |
| - | BC | 0.85 | 0.98 | 1.13 | 1.22 | 1.04 a |
| - | BD | 0.87 | 0.99 | 1.12 | 1.17 | 1.04 a |
| Year I | - | 0.81 | 0.97 | 1.12 | 1.21 | 1.03 |
| Year II | - | 0.91 | 1.00 | 1.12 | 1.18 | 1.05 |
| Mean | 0.86 d | 0.98 c | 1.12 b | 1.19 a | ||
| Foliar P | Method | P Levels (kg ha−1) | Mean | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | |||
| Year I | ||||||
| 0 | BC | 1.37 | 1.65 | 2.13 | 2.45 | 1.90 |
| 0 | BD | 1.72 | 2.07 | 2.40 | 2.81 | 2.25 |
| 144 mM | BC | 2.24 | 2.74 | 3.02 | 3.33 | 2.83 |
| 144 mM | BD | 2.55 | 3.02 | 3.41 | 3.73 | 3.17 |
| Year II | ||||||
| 0 | BC | 1.49 | 1.81 | 2.33 | 2.60 | 2.05 |
| 0 | BD | 1.80 | 2.26 | 2.57 | 3.01 | 2.41 |
| 144 mM | BC | 2.35 | 2.81 | 3.20 | 3.42 | 2.94 |
| 144 mM | BD | 2.74 | 3.34 | 3.57 | 3.86 | 3.38 |
| Average Across Methods | ||||||
| No Foliar spray | - | 1.59 | 1.94 | 2.35 | 2.72 | 2.15 b |
| Foliar P | - | 2.47 | 2.97 | 3.30 | 3.58 | 3.08 a |
| - | BC | 1.86 | 2.25 | 2.67 | 2.95 | 2.43 b |
| - | BD | 2.20 | 2.67 | 2.99 | 3.35 | 2.80 a |
| Year I | - | 1.97 | 2.37 | 2.74 | 3.08 | 2.54 |
| Year II | - | 2.09 | 2.55 | 2.92 | 3.22 | 2.70 |
| Mean | 2.03 d | 2.46 c | 2.83 b | 3.15 a | ||
| Foliar P | Method | P Levels (kg ha−1) | Mean | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | |||
| Year I | ||||||
| 0 | BC | 89 | 96 | 105 | 134 | 105.8 |
| 0 | BD | 99 | 109 | 120 | 132 | 114.9 |
| 144 mM | BC | 111 | 127 | 134 | 138 | 127.3 |
| 144 mM | BD | 122 | 135 | 140 | 143 | 134.8 |
| Year II | ||||||
| 0 | BC | 92 | 106 | 110 | 140 | 111.8 |
| 0 | BD | 105 | 113 | 117 | 138 | 118.1 |
| 144 mM | BC | 110 | 131 | 141 | 149 | 132.5 |
| 144 mM | BD | 124 | 140 | 145 | 153 | 140.3 |
| Average Across Methods | ||||||
| No Foliar spray | - | 96 | 106 | 113 | 136 | 113 b |
| Foliar P | - | 117 | 133 | 140 | 146 | 134 a |
| - | BC | 100 | 115 | 122 | 140 | 119 b |
| - | BD | 112 | 124 | 130 | 141 | 127 a |
| Year I | - | 105 | 117 | 124 | 137 | 121 |
| Year II | - | 108 | 122 | 128 | 145 | 126 |
| Mean | 106 d | 120 c | 126 b | 141 a | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rafiullah; Khan, M.J.; Muhammad, D.; Fahad, S.; Adnan, M.; Wahid, F.; Alamri, S.; Khan, F.; Dawar, K.M.; Irshad, I.; et al. Phosphorus Nutrient Management through Synchronization of Application Methods and Rates in Wheat and Maize Crops. Plants 2020, 9, 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101389
Rafiullah, Khan MJ, Muhammad D, Fahad S, Adnan M, Wahid F, Alamri S, Khan F, Dawar KM, Irshad I, et al. Phosphorus Nutrient Management through Synchronization of Application Methods and Rates in Wheat and Maize Crops. Plants. 2020; 9(10):1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101389
Chicago/Turabian StyleRafiullah, Muhammad Jamal Khan, Dost Muhammad, Shah Fahad, Muhammad Adnan, Fazli Wahid, Saud Alamri, Farmanullah Khan, Khadim Muhammad Dawar, Inam Irshad, and et al. 2020. "Phosphorus Nutrient Management through Synchronization of Application Methods and Rates in Wheat and Maize Crops" Plants 9, no. 10: 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101389
APA StyleRafiullah, Khan, M. J., Muhammad, D., Fahad, S., Adnan, M., Wahid, F., Alamri, S., Khan, F., Dawar, K. M., Irshad, I., Danish, S., Arif, M., Amanullah, Saud, S., Khan, B., Mian, I. A., Datta, R., Zarei, T., Shah, A. A., ... Siddiqui, M. H. (2020). Phosphorus Nutrient Management through Synchronization of Application Methods and Rates in Wheat and Maize Crops. Plants, 9(10), 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101389