Generation of Transgenic Self-Incompatible Arabidopsis thaliana Shows a Genus-Specific Preference for Self-Incompatibility Genes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
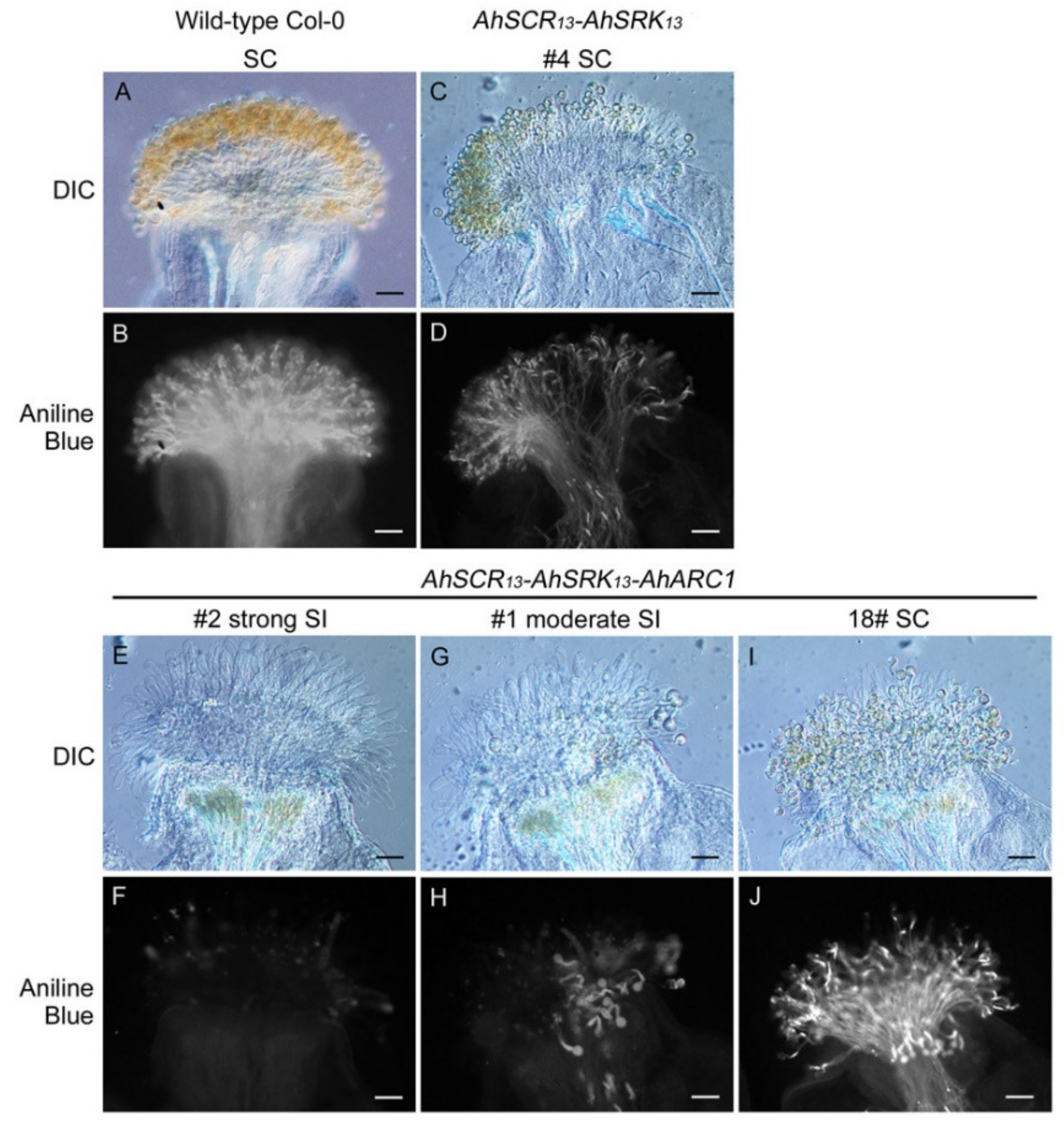
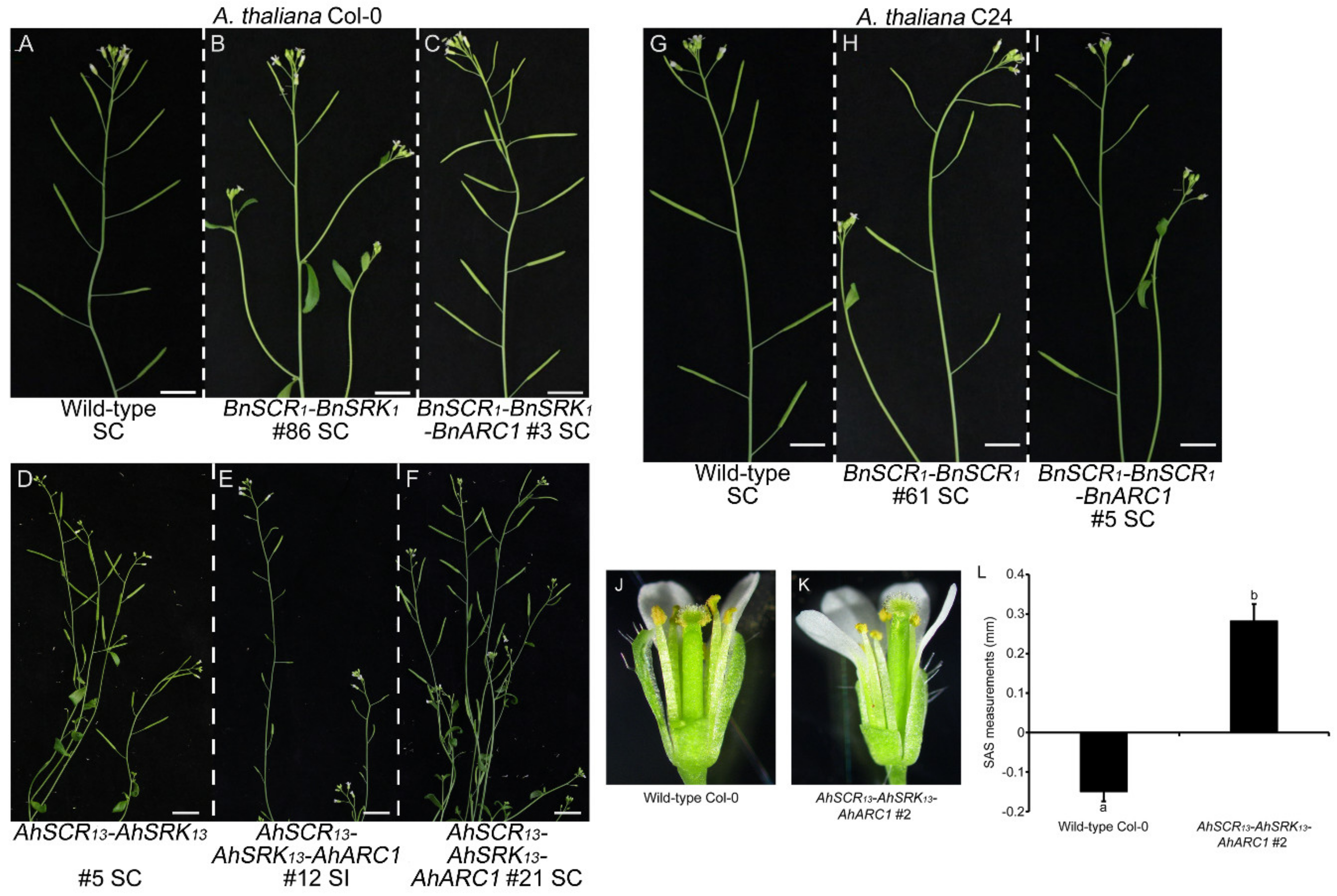
2.1. Reconstruction of ARC1-Mediated Self-Incompatibility in A. thaliana Col-0 using A. halleri Self-Incompatibility Genes
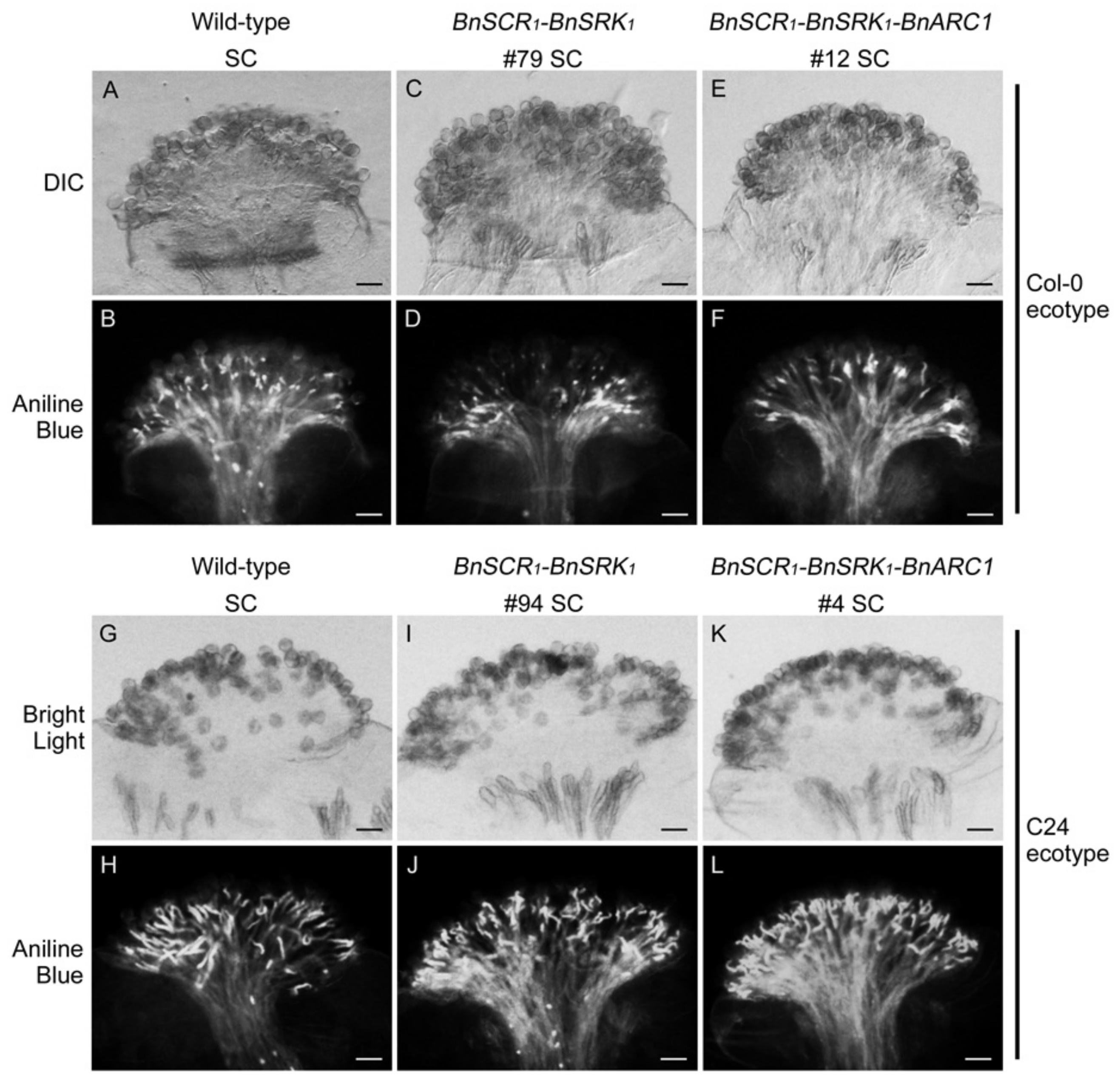
2.2. Self-Incompatibility Related Genes of B. napus are Not Sufficient to Restore Self-Incompatibility in both A. thaliana Col-0 and C24 Ecotypes
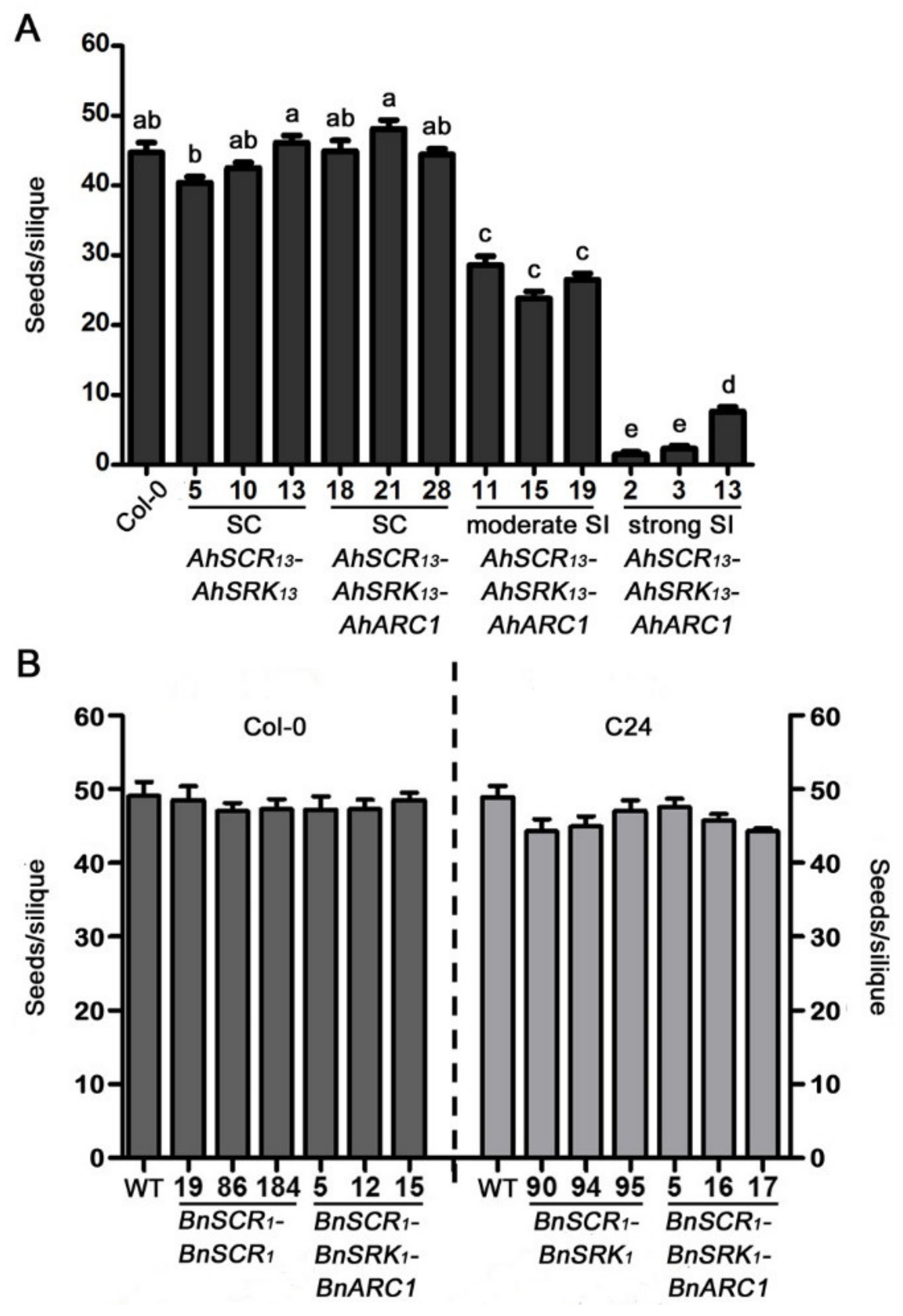
2.3. Seed Production is Significantly Reduced in Col-0 Lines Expressing AhSCR13-AhSRK13-AhARC1
2.4. The Expression Levels of the SCR-SRK-ARC1 Transgenes are Not Associated with the Intensity of Self-Incompatibility Response in A. thaliana
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Vector Construction and Plant Transformation
4.3. Pollination Assays
4.4. Quantitative RT-PCR Assays
4.5. Accession Numbers
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franklin-Tong, V.E.; Holdaway-Clarke, T.L.; Straatman, K.R.; Kunkel, J.G.; Hepler, P.K. Involvement of extracellular calcium influx in the self-incompatibility response of Papaver rhoeas. Plant J. 2002, 29, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin-Tong, N.V.; Franklin, F.C.H. Gametophytic self-incompatibility inhibits pollen tube growth using different mechanisms. Trends Plant Sci. 2003, 8, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, T.H.; Tsukamoto, T. The molecular and genetic bases of S-RNase-based self-incompatibility. Plant Cell 2004, 16, S72–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, S.; Isogai, A. Self-incompatibility in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2005, 56, 467–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrallah, J.B.; Nasrallah, M.E. Pollen-stigma signaling in the sporophytic self-incompatibility response. Plant Cell 1993, 5, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luu, D.T.; Marty-Mazars, D.; Trick, M.; Dumas, C.; Heizmann, P. Pollen-stigma adhesion in Brassica spp involves SLG and SLR1 glycoproteins. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giranton, J.L.; Dumas, C.; Cock, J.M.; Gaude, T. The integral membrane S-locus receptor kinase of Brassica has serine/threonine kinase activity in a membranous environment and spontaneously forms oligomers in planta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 3759–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasaki, T.; Hatakeyama, K.; Suzuki, G.; Watanabe, M.; Isogai, A.; Hinata, K. The S receptor kinase determines self-incompatibility in Brassica stigma. Nature 2000, 403, 913–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.F.; Stone, S.L.; Christie, L.N.; Sulaman, W.; Nazarian, K.A.; Burnett, L.A.; Arnoldo, M.A.; Rothstein, S.J.; Goring, D.R. Expression of the S receptor kinase in self-compatible Brassica napus cv. Westar leads to the allele-specific rejection of self-incompatible Brassica napus pollen. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2001, 265, 552–559. [Google Scholar]
- Schopfer, C.R.; Nasrallah, M.E.; Nasrallah, J.B. The male determinant of self-incompatibility in Brassica. Science 1999, 286, 1697–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, G.; Kai, N.; Hirose, T.; Fukui, K.; Nishio, T.; Takayama, S.; Isogai, A.; Watanabe, M.; Hinata, K. Genomic organization of the S locus: Identification and characterization of genes in SLG/SRK region of S9 haplotype of Brassica campestris (syn Rapa). Genetics 1999, 153, 391–400. [Google Scholar]
- Shiba, H.; Iwano, M.; Entani, T.; Ishimoto, K.; Shimosato, H.; Che, F.S.; Satta, Y.; Ito, A.; Takada, Y.; Watanabe, M.; et al. The dominance of alleles controlling self-incompatibility in Brassica pollen is regulated at the RNA level. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachroo, A.; Schopfer, C.R.; Nasrallah, M.E.; Nasrallah, J.B. Allele-specific receptor-ligand interactions in Brassica self-incompatibility. Science 2001, 293, 1824–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, S.; Shimosato, H.; Shiba, H.; Funato, M.; Che, F.S.; Watanabe, M.; Iwano, M.; Isogai, A. Direct ligand-receptor complex interaction controls Brassica self-incompatibility. Nature 2001, 413, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doucet, J.; Lee, H.K.; Goring, D.R. Pollen acceptance or rejection: A tale of two pathways. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goring, D.R. Exocyst, exosomes, and autophagy in the regulation of Brassicaceae pollen-stigma interactions. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 69, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murase, K.; Shiba, H.; Iwano, M.; Che, F.S.; Watanabe, M.; Isogai, A.; Takayama, S. A membrane-anchored protein kinase involved in Brassica self-incompatibility signaling. Science 2004, 303, 1516–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Yang, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, Z.; Khan, F.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, G.; Tu, J.; Shen, J.; Yi, B.; et al. Functional analysis of M-locus protein kinase revealed a novel regulatory mechanism of self-incompatibility in Brassica napus L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakita, M.; Murase, K.; Iwano, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Watanabe, M.; Shiba, H.; Isogai, A.; Takayama, S. Two distinct forms of M-locus protein kinase localize to the plasma membrane and interact directly with S-locus receptor kinase to transduce self-incompatibility signaling in Brassica rapa. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 3961–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakita, M.; Shimosato, H.; Murase, K.; Isogai, A.; Takayama, S. Direct interaction between S-locus receptor kinase and M-locus protein kinase involved in Brassica self-incompatibility signaling. Plant Biotechnol. 2007, 24, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, M.S.; Matias, D.D.; Fernandes-Carvalho, E.; Mazzurco, M.; Gu, T.; Rothstein, S.J.; Goring, D.R. Two members of the thioridoxin-h family interact with the kinase domain of a Brassica S locus receptor kinase. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gu, T.; Mazzurco, M.; Sulaman, W.; Matias, D.D.; Goring, D.R. Binding of an arm repeat protein to the kinase domain of the S-locus receptor kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrillac, D.; Cock, J.M.; Dumas, C.; Gaude, T. The S-locus receptor kinase is inhibited by thioredoxins and activated by pollen coat proteins. Nature 2001, 410, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, S.L.; Arnoldo, M.; Goring, D.R. A breakdown of Brassica self-incompatibility in ARC1 antisense transgenic plants. Science 1999, 286, 1729–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, S.L.; Anderson, E.M.; Mullen, R.T.; Goring, D.R. ARC1 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase and promotes the ubiquitination of proteins during the rejection of self-incompatible Brassica pollen. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 885–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, M.A.; Chong, Y.T.; Haasen, K.E.; Aldea-Brydges, M.G.; Stone, S.L.; Goring, D.R. Cellular pathways regulating responses to compatible and self-incompatible pollen in Brassica and Arabidopsis stigmas intersect at Exo70A1,a putative component of the exocyst complex. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 2655–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, S.; Jamshed, M.; Samuel, M.A. Degradation of glyoxalase I in Brassica napus stigma leads to self-incompatibility response. Nat. Plants 2015, 1, 15185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusaba, M.; Dwyer, K.; Hendershot, J.; Vrebalov, J.; Nasrallah, J.B.; Nasrallah, M.E. Self-incompatibility in the genus Arabidopsis: Characterization of the S locus in the outcrossing A. lyrata and its autogamous relative A. thaliana. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schierup, M.H.; Mable, B.K.; Awadalla, P.; Charlesworth, D. Identification and characterization of a polymorphic receptor kinase gene linked to the self-incompatibility locus of Arabidopsis lyrata. Genetics 2001, 158, 387–399. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Toomajian, C.; Sherman-Broyles, S.; Plagnol, V.; Guo, Y.L.; Hu, T.T.; Clark, R.M.; Nasrallah, J.B.; Weigel, D.; Nordborg, M. The evolution of selfing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 2007, 317, 1070–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchimatsu, T.; Suwabe, K.; Shimizu-Inatsugi, R.; Isokawa, S.; Pavlidis, P.; Städler, T.; Suzuki, G.; Takayama, S.; Watanabe, M.; Shimizu, K.K. Evolution of self-compatibility in Arabidopsis by a mutation in the male specificity gene. Nature 2010, 464, 1342–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.L.; Zhao, X.; Lanz, C.; Weigel, D. Evolution of the S-locus region in Arabidopsis relatives. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrallah, M.E.; Liu, P.; Sherman-Broyles, S.; Boggs, N.A.; Nasrallah, J.B. Natural variation in expression of self-incompatibility in Arabidopsis thaliana: Implications for the evolution of selfing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16070–16074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman-Broyles, S.; Boggs, N.; Farkas, A.; Liu, P.; Vrebalov, J.; Nasrallah, M.E.; Nasrallah, J.B. S locus genes and the evolution of self-fertility in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggs, N.A.; Nasrallah, J.B.; Nasrallah, M.E. Independent S-locus mutations caused self-fertility in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggs, N.A.; Dwyer, K.G.; Shah, P.; McCulloch, A.A.; Bechsgaard, J.; Schierup, M.H.; Nasrallah, M.E.; Nasrallah, J.B. Expression of distinct self-incompatibility specificities in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 2009, 182, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, A.C.; Liu, P.; Nasrallah, J.B. A transgenic self-incompatible Arabidopsis thaliana model for evolutionary and mechanistic studies of crucifer self-incompatibility. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.M.; Brugiere, N.; Cui, Y.; Goring, D.; Rothstein, S. Transformation of Arabidopsis with a Brassica SLG/SRK region and ARC1 gene is not sufficient to transfer the self-incompatibility phenotype. Mol. General Genet. MGG 2000, 263, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrallah, M.E.; Liu, P.; Nasrallah, J.B. Generation of self-incompatible Arabidopsis thaliana by transfer of two S locus genes from A. lyrata. Science 2002, 297, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwano, M.; Ito, K.; Fujii, S.; Kakita, M.; Asano-Shimosato, H.; Igarashi, M.; Kaothien-Nakayama, P.; Entani, T.; Kanatani, A.; Takehisa, M.; et al. Calcium signalling mediates self-incompatibility response in the Brassicaceae. Nat Plants 2015, 1, 15128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, E.; Meheust, R.; Soucaze, M.; Goubet, P.M.; Gallina, S.; Poux, C.; Fobis-Loisy, I.; Guillon, E.; Gaude, T.; Sarazin, A.; et al. Dominance hierarchy arising from the evolution of a complex small RNA regulatory network. Science 2014, 346, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitashiba, H.; Liu, P.; Nishio, T.; Nasrallah, J.B.; Nasrallah, M.E. Functional test of Brassica self-incompatibility modifiers in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18173–18178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indriolo, E.; Safavian, D.; Goring, D.R. The ARC1 E3 ligase promotes two different self-pollen avoidance traits in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 1525–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, S.; Odashima, M.; Fujimoto, R.; Sato, Y.; Kitashiba, H.; Nishio, T. Self-compatibility in Brassica napus is caused by independent mutations in S-locus genes. Plant J. 2007, 50, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tochigi, T.; Udagawa, H.; Li, F.; Kitashiba, H.; Nishio, T. The self-compatibility mechanism in Brassica napus L. is applicable to F1 hybrid breeding. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 123, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.B.; Zhou, G.L.; Ma, C.Z.; Zhai, W.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wu, M.; Yue, Y.; Duan, Z.; et al. Helitron-like transposons contributed to the mating system transition from out-crossing to self-fertilizing in polyploid Brassica napus L. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goubet, P.M.; Berges, H.; Bellec, A.; Prat, E.; Helmstetter, N.; Mangenot, S.; Gallina, S.; Holl, A.C.; Fobis-Loisy, I.; Vekemans, X.; et al. Contrasted patterns of molecular evolution in dominant and recessive self-incompatibility haplotypes in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Widmer, A. Herkogamy and its effects on mating patterns in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.Q.; Wang, Z.X.; Zhang, H.Y.; Hu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, M.; Dun, X.; Yi, B.; Wen, J.; Ma, C.; et al. Altered transcription and neofunctionalization of duplicated genes rescue the harmful effects of a chimeric gene in Brassica napus. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 2060–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.K.; Shimizu-Inatsugi, R.; Tsuchimatsu, T.; Purugganan, M.D. Independent origins of self-compatibility in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchimatsu, T.; Goubet, P.M.; Gallina, S.; Holl, A.C.; Fobis-Loisy, I.; Bergès, H.; Marande, W.; Prat, E.; Meng, D.; Long, Q.; et al. Patterns of polymorphism at the self-incompatibility locus in 1083 Arabidopsis thaliana genomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 1878–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantikanjana, T.; Rizvi, N.; Nasrallah, M.E.; Nasrallah, J.B. A dual role for the s-locus receptor kinase in self-incompatibility and pistil development revealed by an Arabidopsis rdr6 mutation. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 2642–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indriolo, E.; Goring, D.R. Yeast two-hybrid interactions between Arabidopsis lyrata S Receptor Kinase and the ARC1 E3 ligase. Plant Signal. Behav. 2016, 11, e1188233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Koch, M.A.; Haubold, B.; Mitchell-Olds, T. Comparative evolutionary analysis of chalcone synthase and alcohol dehydrogenase loci in Arabidopsis, Arabis, and related genera Brassicaceae. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 1483–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.I.; Lauga, B.; Charlesworth, D. Rates and patterns of molecular evolution in inbred and outbred Arabidopsis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 1407–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beilstein, M.A.; Nagalingum, N.S.; Clements, M.D.; Manchester, S.R.; Mathews, S. Dated molecular phylogenies indicate a Miocene origin for Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18724–18728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossowski, S.; Schneeberger, K.; Lucas-Lledo, J.I.; Warthmann, N.; Clark, R.M.; Shaw, R.G.; Weigel, D.; Lynch, M. The rate and molecular spectrum of spontaneous mutations in Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 2010, 327, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.T.; Pattyn, P.; Bakker, E.G.; Cao, J.; Cheng, J.F.; Clark, R.M.; Fahlgren, N.; Fawcett, J.A.; Grimwood, J.; Gundlach, H.; et al. The Arabidopsis lyrata genome sequence and the basis of rapid genome size change. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechsgaard, J.S.; Castric, V.; Charlesworth, D.; Vekemans, X.; Schierup, M.H. The transition to self-compatibility in Arabidopsis thaliana and evolution within S-haplotypes over 10 Myr. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, K.G.; Berger, M.T.; Ahmed, R.; Hritzo, M.K.; McCulloch, A.A.; Price, M.J.; Serniak, N.J.; Walsh, L.T.; Nasrallah, J.B.; Nasrallah, M.E. Molecular characterization and evolution of self-incompatibility genes in Arabidopsis thaliana: The case of the Sc haplotype. Genetics 2013, 193, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavian, D.; Goring, D.R. Secretory activity is rapidly induced in stigmatic papillae by compatible pollen, but inhibited for self-incompatible pollen in the Brassicaceae. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachowiec, J.; Queitsch, C.; Kliebenstein, D.J. Molecular mechanisms governing differential robustness of development and environmental responses in plants. Ann. Bot. 2016, 117, 795–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Schnable, J.C. Functional divergence between subgenomes and gene pairs after whole genome duplications. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajdukiewicz, P.; Svab, Z.; Maliga, P. The small, versatile pPZP family of Agrobacterium binary vectors for plant transformation. Plant Mol. Biol. 1994, 25, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutu, C.; Brandle, J.; Brown, D.; Brown, K.; Miki, B.; Simmonds, J.; Hegedus, D.D. pORE: A modular binary vector series suited for both monocot and dicot plant transformation. Transgenic Res. 2007, 16, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, E.; Levesque-Lemay, M.; Schneiderman, D.; Albani, D.; Schernthaner, J.; Routly, E.; Robert, L.S. Characterization of a gene highly expressed in the Brassica napus pistil that encodes a novel proline-rich protein. Sex. Plant Reprod. 2005, 17, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fobis-Loisy, I.; Chambrier, P.; Gaude, T. Genetic transformation of Arabidopsis lyrata: Specific expression of the green fluorescent protein GFP in pistil tissues. Plant Cell Rep. 2007, 26, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, S.J.; Bent, A.F. Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998, 16, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Self-Incompatible | Total No. T1 Plants Tested | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transgenes | Strongly | Moderately | Self-Compatible | |
| AhSCR13-AhSRK13 | 0 | 0 | 30 | 30 |
| AhSCR13-AhSRK13-AhARC1 | 4 | 16 | 14 | 34 |
| BnSCR1-BnSRK1 | 0 | 0 | 21 | 21 |
| BnSCR1-BnSRK1-BnARC1 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 12 |
| Transgenes | Self-Incompatible | Self-Compatible | Total No. T1 Plants Tested |
|---|---|---|---|
| BnSCR1-BnSRK1 | 0 | 13 | 13 |
| BnSCR1-BnSRK1-BnARC1 | 0 | 9 | 9 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Zhou, G.; Goring, D.R.; Liang, X.; Macgregor, S.; Dai, C.; Wen, J.; Yi, B.; Shen, J.; Tu, J.; et al. Generation of Transgenic Self-Incompatible Arabidopsis thaliana Shows a Genus-Specific Preference for Self-Incompatibility Genes. Plants 2019, 8, 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8120570
Zhang T, Zhou G, Goring DR, Liang X, Macgregor S, Dai C, Wen J, Yi B, Shen J, Tu J, et al. Generation of Transgenic Self-Incompatible Arabidopsis thaliana Shows a Genus-Specific Preference for Self-Incompatibility Genes. Plants. 2019; 8(12):570. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8120570
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Tong, Guilong Zhou, Daphne R. Goring, Xiaomei Liang, Stuart Macgregor, Cheng Dai, Jing Wen, Bin Yi, Jinxiong Shen, Jinxing Tu, and et al. 2019. "Generation of Transgenic Self-Incompatible Arabidopsis thaliana Shows a Genus-Specific Preference for Self-Incompatibility Genes" Plants 8, no. 12: 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8120570
APA StyleZhang, T., Zhou, G., Goring, D. R., Liang, X., Macgregor, S., Dai, C., Wen, J., Yi, B., Shen, J., Tu, J., Fu, T., & Ma, C. (2019). Generation of Transgenic Self-Incompatible Arabidopsis thaliana Shows a Genus-Specific Preference for Self-Incompatibility Genes. Plants, 8(12), 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8120570





