Innovative RNAi Strategies and Tactics to Tackle Plum Pox Virus (PPV) Genome in Prunus domestica-Plum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Transformed Plums and Molecular Characterization
2.2. Resistance Studies
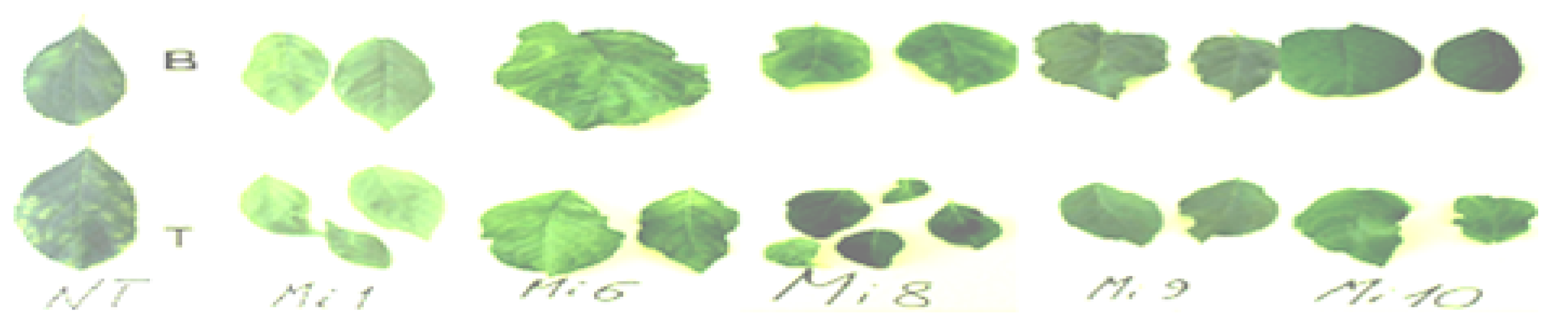
2.2.1. Behavior of Different Plum Clones
2.2.2. Phenotypes of the AmisiCPRNA Plums
2.2.3. Behavior of the amiCPRNA Plums
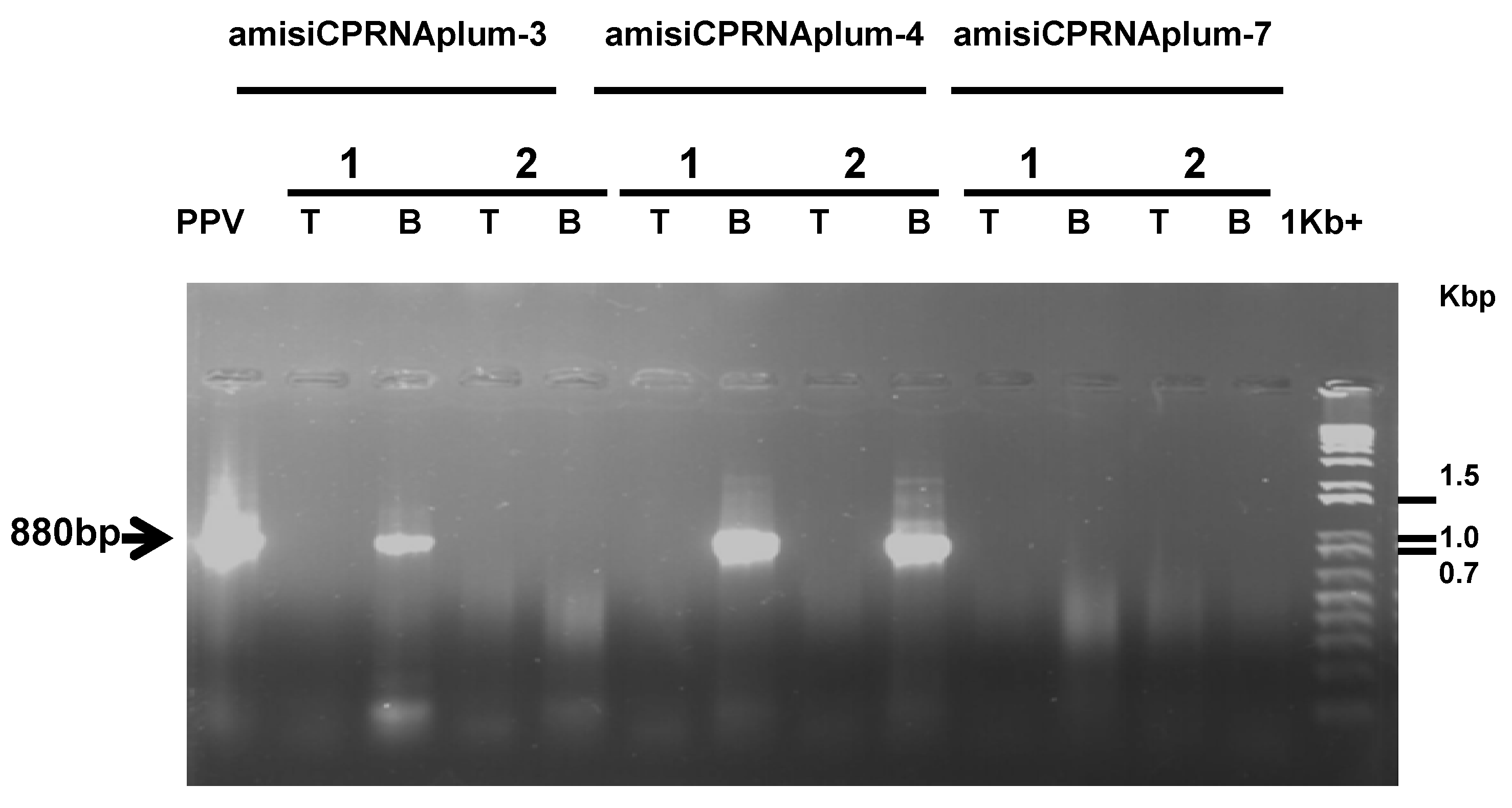
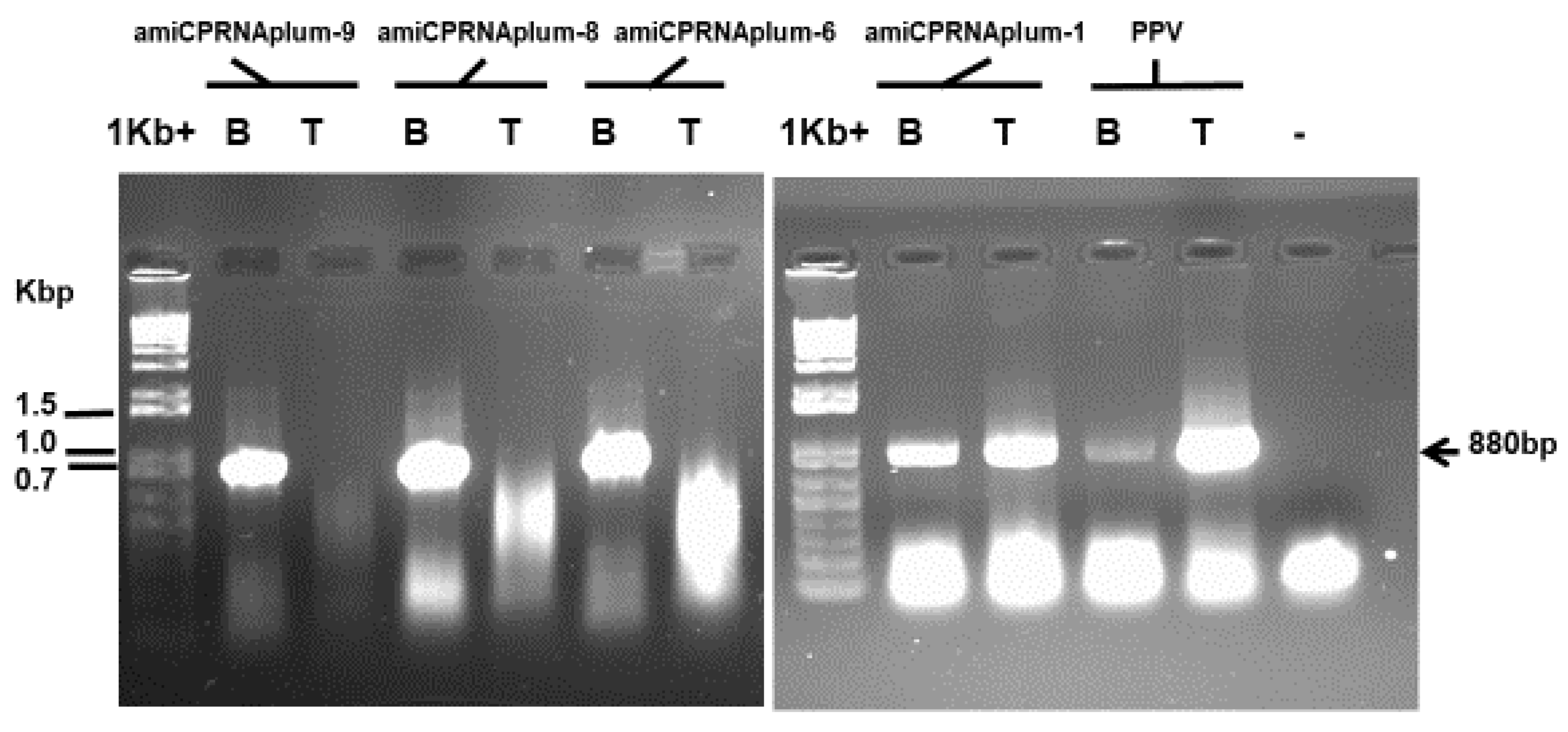
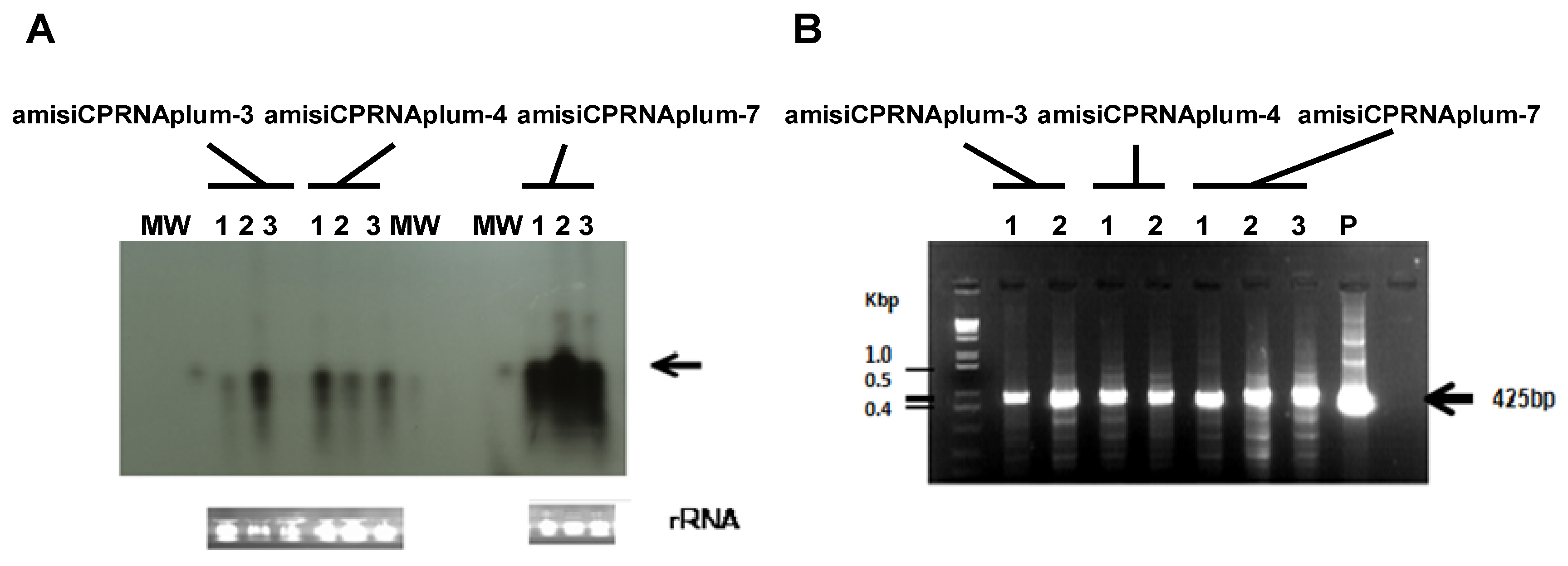
2.3. Down-Regulation of the PPV Genome Replication by RNAi Silencing
2.4. RNAi Technology for Protecting Perennial Plants
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Gene Constructs
4.2. Plant Transformation and Selection
4.3. Molecular Analysis of Plants
4.4. Challenging Assays and Symptomatology
4.5. Serological and Molecular Analyses
4.6. Down Regulation Studies
4.7. DNA Methylation
4.8. RNAi Detection
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviations | Full Name |
| AGO | argaunote protein |
| Ami | artificial miRNA |
| cDNA | complementary DNA |
| CP | capsid protein |
| DAS-ELISA | Double Antibody Sandwich- enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| dCTP | desoxyribonucleotide cytidine phosphate |
| DNA | desoxyribonucleic acid |
| EDTA | ethylene diamine tetra-acetate |
| FWD | forward |
| HS | HoneySweet |
| ihRP | intron hairpin RNA plasmid |
| NGS | next generation sequencing |
| Nib | nuclear inclusion b |
| NT | non-transformed |
| OD | optical density |
| PAGE | polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| PNRSV | Prunus necrotic ringspot virus |
| PPV | Plum pox virus |
| RdDM | RNA directed DNA methylation |
| RDR6 | RNA polymerase DNA dependent 6 |
| REV | reverse |
| RISC | RNAi inducing silencing complex |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| RNAi | RNA interfering |
| rRNA | ribosomal RNA |
| RT | reverse transcriptase |
| SiRNA | small interfering RNA |
| tasiRNA | trans-acting siRNA |
| TBE | tris borate EDTA |
| TuMV | Turnip mosaic virus |
| TYMV | Turnip yellow mosaic virus |
References
- Garcia, J.A.; Glasa, M.; Cambra, M.; Candresse, T. Plum pox virus and sharka: A model 436 potyvirus and a major disease. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2014, 15, 226–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba, M.; Hadidi, A.; Candresse, T.; Cambra, M. Plum pox virus. In Virus and Virus-Like Diseases of Pome and Stone Fruit; Hadidi, A., Barba, M., Candresse, T., Jelkmann, W., Eds.; American Phytopathological Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2011; pp. 185–197. [Google Scholar]
- Neumüller, M.; Hartmann, W. The phenotypically quantitative nature of hypersensitivity of European plum (Prunus domestica L.) against the Plum pox virus and its description using the hypersensitivity index. Hortic. Sci. 2008, 35, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, J.; Jarosova, J. Susceptibility of plum trees cv. ‘Jojo’ to a Czech isolate of Plum pox virus strain D. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 34, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsalves, D. Transgenic Papaya: A Case Study on the Theoretical and Practical Application of Virus Resistance. In Plant Biotechnology 2002 and Beyond, Proceedings of the 10th IAPTC&B Congress, Orlando, FL, USA, 23–28 June 2002; Vasil, I.K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003; pp. 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ravelonandro, M.; Scorza, R.; Bachelier, J.C.; Labonne, G.; Levy, L.; Damsteegt, V.; Callahan, A.M.; Dunez, J. Resistance of transgenic Prunus domestica to Plum pox virus infection. Plant Dis. 1997, 81, 1231–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scorza, R.; Callahan, A.; Dardick, C.; Ravelonandro, M.; Polak, J.; Malinowski, T.; Zagrai, I.; Cambra, M.; Kamenova, I. Genetic engineering of Plum pox virus resistance: ‘HoneySweet’ plum—From concept to product. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2013, 115, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorza, R.; Ravelonandro, M.; Callahan, A.; Zagrai, I.; Polak, J.; Malinowski, T.; Cambra, M.; Levy, L.; Damsteegt, V.; Krska, B.; et al. HoneySweet’(C5), The first genetically engineered Plum pox virus–resistant Plum (Prunus domestica L.) Cultivar. Hortscience 2016, 51, 601–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baulcombe, D. RNA silencing in plants. Nature 2004, 431, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotti, M.; dos Santos, E.A.; Cagliari, D.; Christiaens, O.; Taning, C.N.T.; Smagghe, G. RNA interference technology in crop protection against arthropod pests, pathogens and nematodes. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.W.; Lin, S.S.; Reyes, J.L.; Chen, K.C.; Wu, H.W.; Yeh, S.D.; Chua, N.H. Expression of artificial microRNAs in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana confers virus resistance. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Z.; Zhu, C.X.; Guo, X. Highly efficient virus resistance mediated by artificial microRNAs that target the suppressor of PVX and PVY in plants. Plant Biol. (Stuttg) 2011, 13, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J. Artificial trans-acting small interfering RNA: A tool for plant biology study and crop improvements. Planta 2014, 239, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonell, A.; Carrington, J.C.; Daròs, D.A. Fast-forward generation of effective artificial small RNAs for enhanced antiviral defense in plants. RNA Dis. 2016, 3, e1130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; San Leon, D.; Mesel, F.; Garcia, J.A.; Simon-Mateo, C. Assorted Processing of Synthetic Trans-Acting siRNAs and Its Activity in Antiviral Resistance. PLoS ONE. 2015, 10, e0132281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonell, A.; Fahlgren, N.; Mitchell, S.; Cox, K.L.; Reilly, K.C.; Mockler, T.C. Highly specific gene silencing in a monocot species by artificial microRNAs derived from chimeric MIRNA precursors. Plant J. 2015, 82, 1061–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, S.; Zhou, X.; Xia, J.; Chellapan, P.; Zhang, X.; Jin, H.; Zhou, X. Multiple distinct small RNAs originate from the same microRNA precursors. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravelonandro, M.; Scorza, R.; Hily, J.M.; Briard, P. The efficiency of RNA interference for conferring stable resistance to plum pox virus. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2014, 118, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravelonandro, M.; Briard, P.; Hily, J.M.; Scorza, R. RNAi to silence the plum pox virus genome. Acta Hortic. 2013, 974, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hily, J.M.; Ravelonandro, M.; Damsteegt, V.; Bassett, C.; Petri, C.; Liu, Z.; Scorza, R. Plum pox virus coat protein gene intron-hairpin-RNA (ihpRNA) constructs provide resistance to plum pox virus in Nicotiana benthamiana and Prunus domestica. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2007, 132, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofacker, I.L.; Stadler, P.F. Memory efficient folding algorithms for circular RNA secondary structures. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1172–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravelonandro, M.; Monsion, M.; Teycheney, P.Y.; Delbos, R.; Dunez, J. Construction of a chimeric viral gene expressing Plum pox virus coat protein. Gene 1992, 120, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, C.; Hily, J.M.; Vann, C.; Dardick, C.; Scorza, R. A high-throughput transformation system allows the regeneration of marker-free plum plants (Prunus domestica). Ann. Appl. Biol. 2011, 159, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Dardick, C.; Kundu, J.K. RNAi-Mediated resistance against viruses in perennial fruit plants. Plants 2019, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, F.J.; Pang, S.Z.; Tricoli, D.M.; Gonsalves, D. Evidence that resistance in squash mosaic comovirus coat protein-transgenic plants is affected by plant developmental stage and enhanced by combination of transgenes from different lines. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 2299–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, J.K.; Briard, P.; Hily, J.M.; Ravelonandro, M.; Scorza, R. Role of the 26nt siRNA in the resistance of transgenic Prunus domestica graft inoculated with plum pox virus. Virus Genes 2008, 36, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, T.; Cambra, M.; Capote, N.; Zawadzka, B.; Gorris, M.T.; Scorza, R.; Ravelonandro, M. Field trials of plum clones transformed with the Plum pox virus coat protein (PPV-cp) gene. Plant Dis. 2006, 90, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagrai, I.; Ravelonandro, M.; Gaboreanu, I.; Ferencz, B.; Scorza, R.; Zagrai, L.; Kelemen, B.; Pamfil, D.; Popescu, O. Transgenic plums expressing the plum pox virus (PPV) coat protein gene do not assist the development of PPV recombinants under field conditions. J. Plant Pathol. 2011, 93, 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- Ilardi, V.; Di Nicola-Negri, E. Genetically engineered resistance to Plum pox virus infection in herbaceous and stone fruit hosts. GM Crop. 2011, 2, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, C.A.; De Francesco, A.; Pena, E.J.; Costa, N.; Plata, M.I.; Sendin, L.; Castagnaro, A.P.; García, M.L. Resistance to citrus psorosis virus in transgenic sweet orange plants is triggered by coat protein-RNA silencing. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 151, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carthew, R.W.; Sontheimer, E.J. Origins and mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 642–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blevins, T.; Rajeswaran, R.; Shivaprasad, P.V.; Beknazariants, D.; Si-Ammour, A.; Park, H.S.; Vazquez, F.; Robertson, D.; Meins, F., Jr.; Hohn, T.; et al. Four plant dicers mediate viral small RNA biogenesis and DNA virus induced silencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 6233–6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottwein, E.; Cullen, B.R. Viral and cellular microRNAs as determinants of viral pathogenesis and immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, L.E.; Overdijk, J.R.; van Damme, M. Small RNA molecules and their role in plant disease. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 154, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossowski, S.; Schwab, R.; Weigel, D. Gene silencing in plants using artificial microRNAs and other small RNAs. Plant J. 2008, 53, 674–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumberger, N.; Baulcombe, D.C. Arabidopsis Argonaute1 is an RNA slicer that selectively recruits microRNAs and short interfering RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 102, 11928–11933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Laia, T.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Yuana, C.; Jina, Z.; Lia, H.; Yua, Z.; Qina, C.; Törc, M.; et al. Mini review: Revisiting mobile RNA silencing in plants. Plant Sci. 2019, 278, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; Wu, Q.; Ito, T.; Cillo, F.; Li, W.X.; Chen, X.; Yu, J.L.; Ding, S.W. RNAi-mediated viral immunity requires amplification of virus-derived siRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Ye, J.; Fang, R. Artificial microRNA-mediated virus resistance in plants. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 6690–6699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.; Zhang, Q.; Yasir, M.; Li, F. Small RNA based genetic engineering for plant viral resistance: Application in crop protection. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Moreno, M.J.; Hernández, J.A.; Diaz-Vivancos, P. Sharka: How do plants respond to Plum pox virus infection? J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baulcombe, D.C.; Dean, C. Epigenetic Regulation in Plant Responses to the Environment. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a019471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalakouras, A.; Moser, M.; Zwiebell, M.; Krczal, G.; Hell, R.; Wassenegger, M. A hairpin RNA construct residing in an intron efficiently triggered RNA-directed DNA methylation in tobacco. Plant J. 2009, 60, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahlgren, N.; Montgomery, T.A.; Howell, M.D.; Allen, E.; Dvorak, S.K.; Alexander, A.L.; Carrington, J.C. Regulation of AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR3 by TAS3 ta-siRNA affects developmental timing and patterning in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scorza, R.; Callahan, A.; Levy, L.; Damsteegt, V.; Webb, K.; Ravelonandro, M. Posttranscriptional gene silencing in plum pox virus resistant transgenic European plum containing the Plum pox potyvirus coat protein gene. Trans. Res. 2001, 10, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Kohalmi, S.E.; Svircev, A.; Wang, A.; Sanfacon, H.; Tian, L. Silencing of the host factor eIF(iso)4E gene confers plum pox virus resistance in plum. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e50627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Almodóvar, R.C.; Clemente-Moreno, M.J.; Díaz-Vivancos, P.; Petri, C.; Rubio, M.; Padilla, I.M.G.; Ilardi, P.V.; Burgos, L. Greenhouse evaluation confirms in vitro sharka resistance of genetically engineered h-UTR/P1 plum plants. Plant Cell Tissue Organ 2015, 120, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorova, T.; Mikhailov, R.; Pushin, A.; Miroshnichenko, D.; Dolgov, S. Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation of Russian Commercial Plum cv. “Startovaya” (Prunus domestica L.) With Virus-Derived Hairpin RNA Construct Confers Durable Resistance to PPV Infection in Mature Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesley, S.V.; Helliwell, C.A.; Smith, N.A.; Wang, M.B.; Rouse, D.T.; Liu, Q.; Gooding, P.S.; Singh, S.P.; Abbott, D.; Stoutjesdijk, P.A.; et al. Construct design for efficient, effective and high-throughput gene silencing in plants. Plant J. 2001, 27, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Horikoshi, T.; Katsuyama, H.; Handa, T.; Takayanagi, K. A simple and efficient DNA extraction method for plants, especially woody plants. Plant Tissue Cult. Biotechnol. 1998, 4, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Scorza, R.; Ravelonandro, M.; Callahan, A.M.; Cordts, J.M.; Fuchs, M.; Dunez, J.; Gonsalves, D. Transgenic plum (Prunus domestica L.) express the plum pox virus coat protein gene. Plant Cell Rep. 1994, 14, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, G.C.; Adams, A.N. Characteristics of the microplate method of Enzyme-Linked-ImmunoSorbent-Assay for the detection of plant viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1977, 34, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetzel, T.; Candresse, T.; Ravelonandro, M.; Dunez, J. A polymerase chain reaction assays adapted to plum pox virus detection. J. Virol. Methods 1991, 33, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hily, J.M.; Scorza, R.; Webb, R.; Ravelonandro, M. Accumulation of the long class of siRNA is associated with resistance to Plum pox virus in transgenic woody perennial plum tree. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2005, 8, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Primers | Sequences | Cistron Sources Experiments |
|---|---|---|
| 5FWDCP | AAGCTGAYGAAAGRGAGGACGAG | PPV CP detection 32P Probe |
| 3REVCP | CTACACTCCCCTCACACCGAGGAA | PPV CP detection 32P Probe |
| 80Nib | TTGGGTTCTTGAACAAGCACC | Nib PPV detection |
| 340FWD | CAACTCAAACGCGCTAGTCAAC | CP Methylation |
| 660REV | ATACGCTTCAGCCACGTTACTG | CP Methylation PPV detection |
| miRNA157 | GTGCTCTCCTACTTCTGT | amiRNA detection 32P probe |
| miRNA159 | TAGAGCTTCCCTTCAATCCT | amiRNA detection 32P probe |
| miRNA171 | ATCTGATGAACCTGCCAAT | amiRNA detection 32P probe |
| miRNA marker | AAATCTCAACCAGCCACTGCT | Molecular weight marker Probe |
| amiCPRNA-PLUMS | |||||||
| CLONES | 2 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 15 |
| 1st CYCLE | 4/10 | 5/10 | 3/4 | 3/4 | 4/10 | 3/4 | 4/6 |
| 4TH CYCLE | 4/4 | 5/5 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 4/4 | 3/3 | 4/4 |
| amisiCPRNA-PLUMS | |||||||
| CLONES | 2 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 10 | |
| 1st CYCLE | 4/4 | 1/4 | 2/3 | 6/6 | 0/4 | 4/7 | |
| 4TH CYCLE | 4/4 | 1/4 | 1/3 | 6/6 | 0/4 | 4/4 | |
| Clones | Bottom | Tip |
|---|---|---|
| amiCPRNA-plum1 | +++ | 1.23 |
| amiCPRNA-plum6 | +++ | 0.55 |
| amiCPRNA-plum8 | +++ | 0.23 |
| amiCPRNA-plum9 | +++ | 0.0 |
| amiCPRNA-plum10 | +++ | 0.23 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ravelonandro, M.; Scorza, R.; Briard, P. Innovative RNAi Strategies and Tactics to Tackle Plum Pox Virus (PPV) Genome in Prunus domestica-Plum. Plants 2019, 8, 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8120565
Ravelonandro M, Scorza R, Briard P. Innovative RNAi Strategies and Tactics to Tackle Plum Pox Virus (PPV) Genome in Prunus domestica-Plum. Plants. 2019; 8(12):565. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8120565
Chicago/Turabian StyleRavelonandro, Michel, Ralph Scorza, and Pascal Briard. 2019. "Innovative RNAi Strategies and Tactics to Tackle Plum Pox Virus (PPV) Genome in Prunus domestica-Plum" Plants 8, no. 12: 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8120565
APA StyleRavelonandro, M., Scorza, R., & Briard, P. (2019). Innovative RNAi Strategies and Tactics to Tackle Plum Pox Virus (PPV) Genome in Prunus domestica-Plum. Plants, 8(12), 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8120565





