Evaluating the Growth Performance of Nile and Red Tilapia and Its Influence on Morphological Growth and Yield of Intercropped Wheat and Sugar Beet Under a Biosaline Integrated Aquaculture–Agriculture System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Fish Growth
2.2. Growth Parameters of Wheat
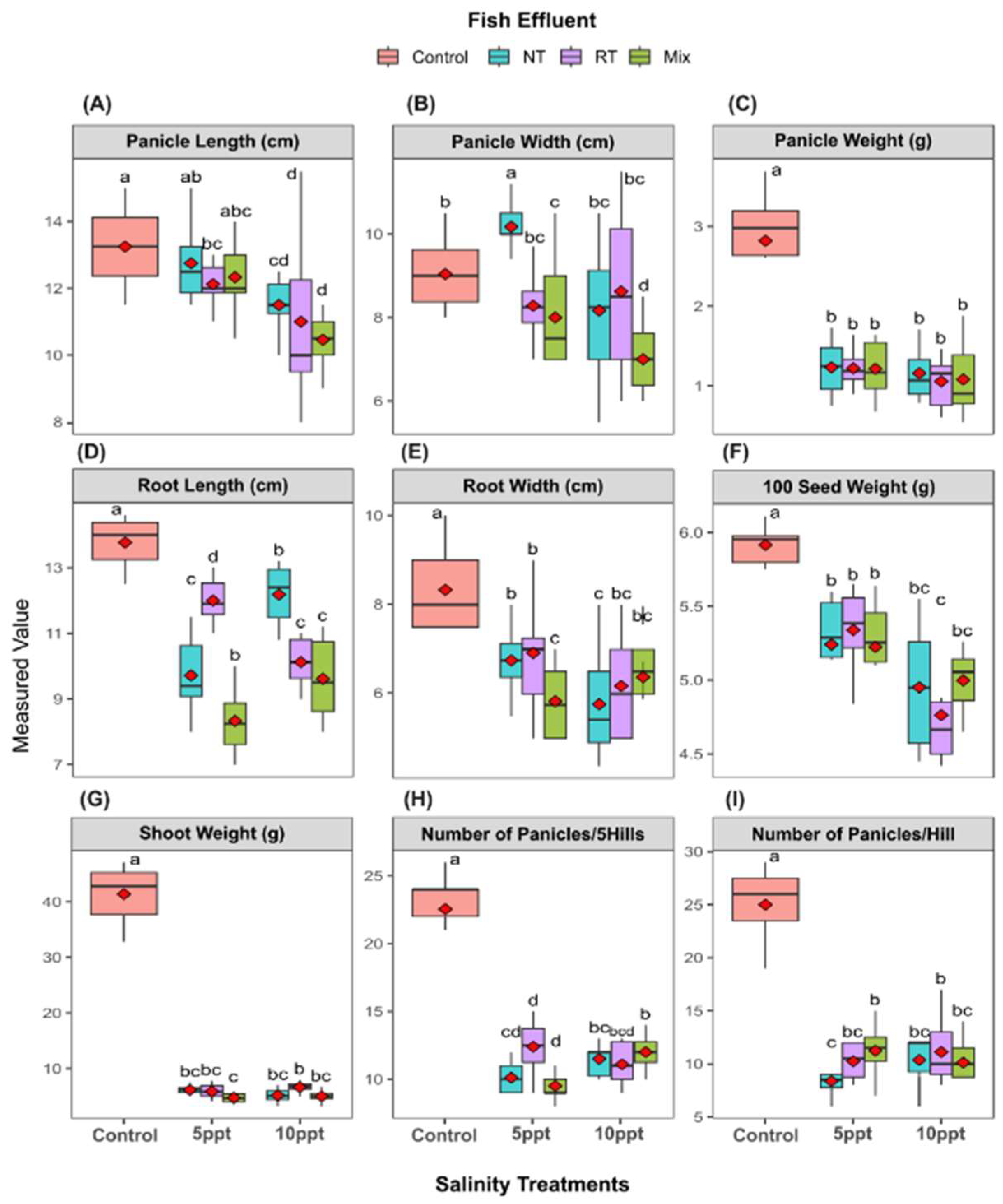
2.3. Yield Traits and Responses in Wheat
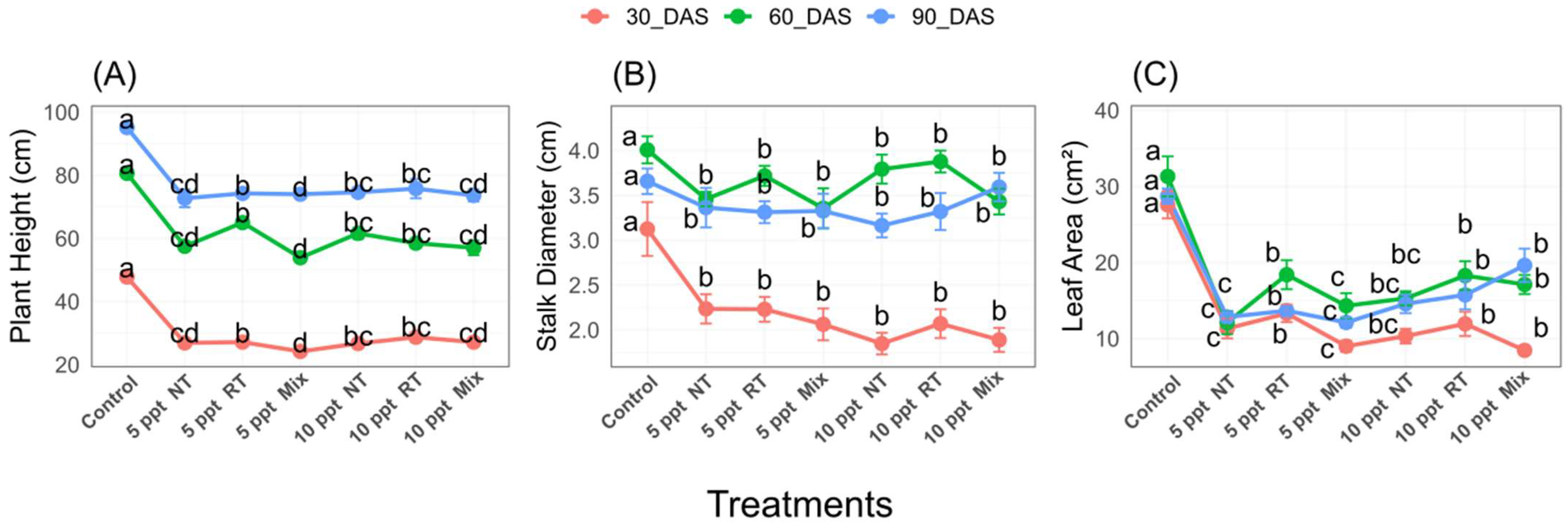
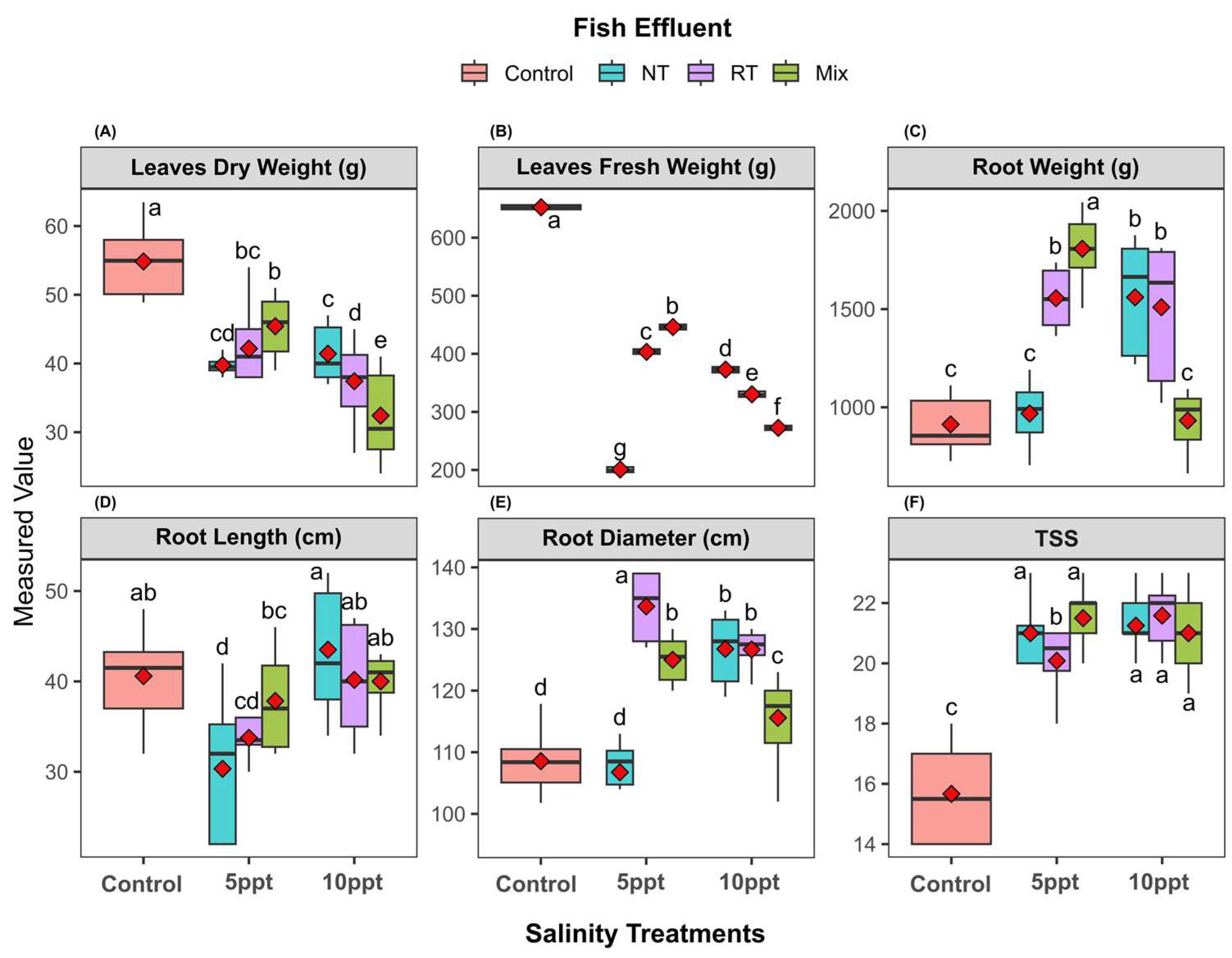
2.4. Morphological Parameters of Sugar Beet at Different Stages
2.5. Yield Traits of Sugar Beet
2.6. Principal Component Analysis for Both Wheat and Sugar Beet
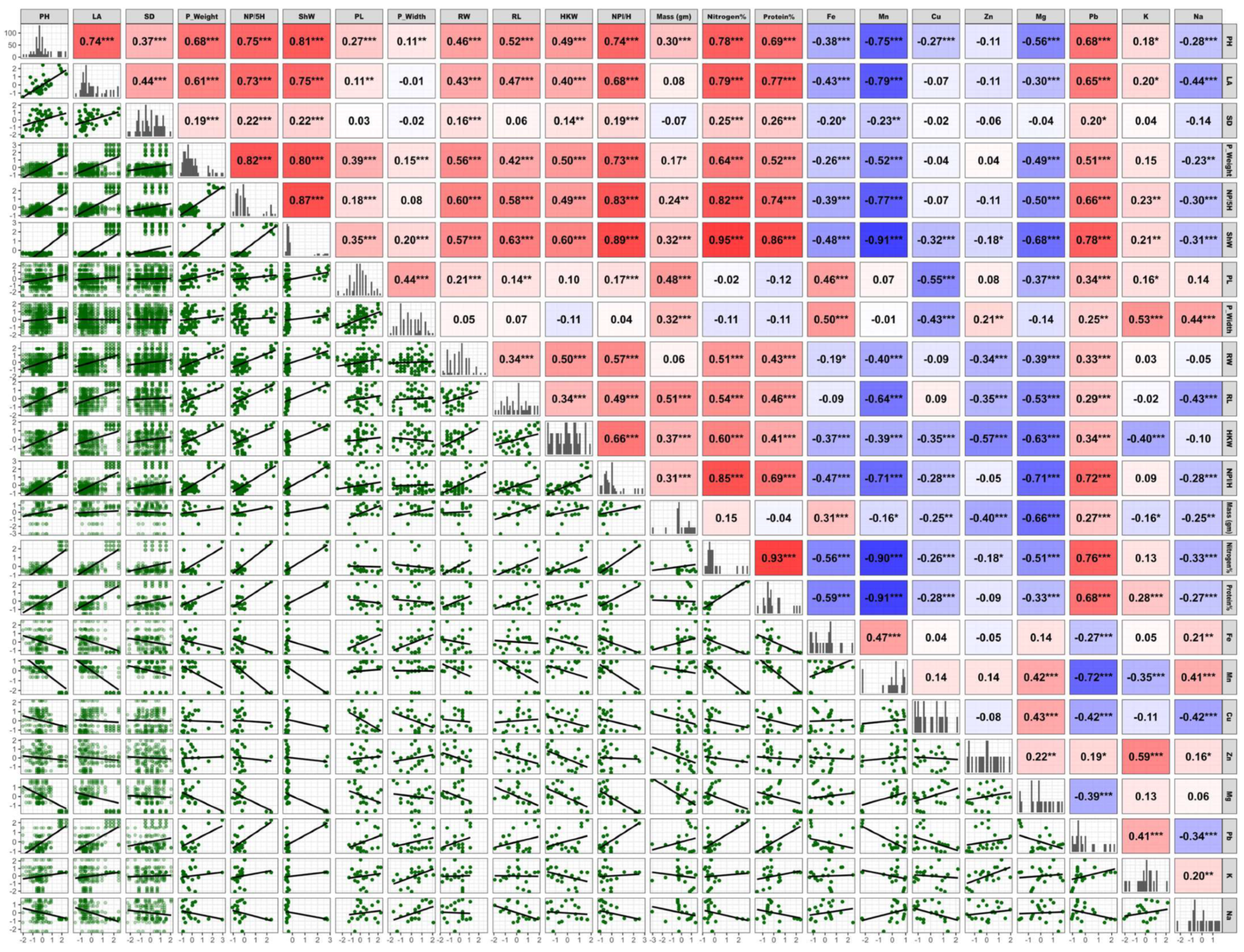
2.7. Correlation Analysis Between Wheat Traits Under Different Treatments
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Site Description
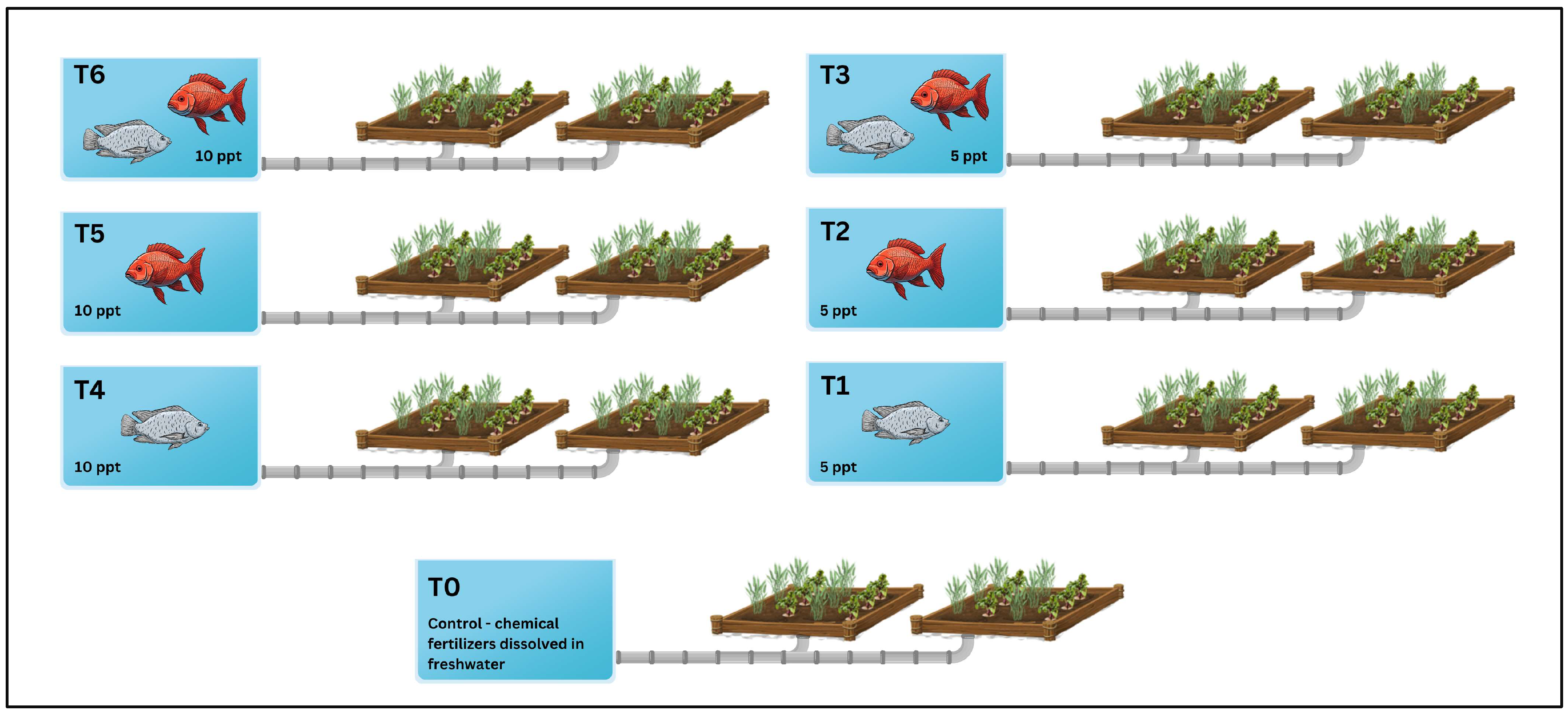
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Agronomical Procedures
4.4. Trait Measurement
4.5. Nutrient Composition of Forage Biomass
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corwin, D.L. Climate change impacts on soil salinity in agricultural areas. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 72, 842–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, S.N.; Arnell, N.W. A global assessment of the impact of climate change on water scarcity. Clim. Change 2016, 134, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, N. Sea-level rise caused by climate change and its implications for society. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2013, 89, 281–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Ma, X.; Wan, P.; Liu, L. Plant salt-tolerance mechanism: A review. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rerhou, B.; Mosseddaq, F.; Naimi, M.; Moughli, L.; Ezzahiri, B.; Bel-Lahbib, S.; Namr, K.I.; Mokrini, F. Compost Applications Improve Soil Fertility, Sugar Beet Performances, and Decrease Sclerotium rolfsii Sacc. Survival Under Saline Irrigation in a Semi-Arid Climate. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 586–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Marschner, P.; Cao, W.; Zuo, C.; Qin, W. Influence of salinity and water content on soil microorganisms. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2015, 3, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, Y.; Li, Y.; Nie, L. Regulation of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline (2-AP) biosynthesis and grain quality in fragrant rice under salt stress. Field Crops Res. 2025, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, R.; Sarkar, B.; Jat, H.S.; Sharma, P.C.; Bolan, N.S. Soil salinity under climate change: Challenges for sustainable agriculture and food security. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, P.; Kumar, R. Soil salinity: A serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Hossain, M.; Huq, M.; Wheeler, D. Climate change and soil salinity: The case of coastal Bangladesh. AMBIO 2015, 44, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, M.D.; Yadav, R.K.; Narjary, B.; Yadav, G.; Jat, H.S.; Sheoran, P.; Meena, M.K.; Antil, R.S.; Meena, B.L.; Singh, H.V.; et al. Municipal solid waste (MSW): Strategies to improve salt affected soil sustainability: A review. Waste Manag. 2019, 84, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fageria, N.K.; Gheyi, H.R.; Moreira, A. Nutrient bioavailability in salt affected soils. J. Plant Nutr. 2011, 34, 945–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimera, F.; Mugwanya, M.; Dawood, M.; Sewilam, H. Growth response of kale (Brassica oleracea) and Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) under saline aqua-sandponics-vegeculture system. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimera, F.; Mugwanya, M.; Ahmed, W.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Sewilam, H. Optimizing growth and yield of striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) and quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) in a biosaline integrated aquaculture–agriculture systems. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Ward, J.D.; Saint, C.P. Can integrated aquaculture-agriculture (IAA) produce “more crop per drop”? Food Secur. 2014, 6, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasimuna, O.J.; Maulu, S.; Nawanzi, K.; Lundu, B.; Mphande, J.; Phiri, C.J.; Kikamba, E.; Siankwilimba, E.; Siavwapa, S.; Chibesa, M. Integrated agriculture-aquaculture as an alternative to improving small-scale fish production in Zambia. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1161121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinkela, P.M.; Mutiaka, B.K.; Dochain, D.; Rollin, X.; Mafwila, J.; Bindelle, J. Smallholders’ practices of integrated agriculture aquaculture system in peri-urban and rural areas in Sub Saharan Africa. Tropicultura 2018, 37, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Global predictions of primary soil salinization under changing climate in the 21st century. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Quillérou, E.; Nangia, V.; Murtaza, G.; Singh, M.; Thomas, R.; Drechsel, P.; Noble, A. Economics of salt-induced land degradation and restoration. Nat. Resour. Forum 2014, 38, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panta, S.; Flowers, T.; Lane, P.; Doyle, R.; Haros, G.; Shabala, S. Halophyte agriculture: Success stories. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 107, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, T.J.; Colmer, T.D. Salinity tolerance in halophytes. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 945–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekka, C.; Petropoulos, G.P.; Triantakonstantis, D.; Detsikas, S.E.; Chalkias, C. Exploring the spatial patterns of soil salinity and organic carbon in agricultural areas of Lesvos Island, Greece, using geoinformation technologies. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO/ICLARM/IIRR. Integrated Agriculture–Aquaculture: A Primer. No. 407. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/items/f56e803b-3d6d-4615-a9f2-c1e3a7dcda61 (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Mugwanya, M.; Kimera, F.; Madkour, K.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Sewilam, H. Influence of salinity on the biometric traits of striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) and barley (Hordeum vulgare) cultivated under an integrated aquaculture-agriculture system. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, L.A.; Abu-Hashim, M.; Shaghaleh, H.; Elsadek, E.; Hamad, A.A.A.; Hamoud, Y.A. A Comprehensive Review of the Multiple Uses of Water in Aquaculture-Integrated Agriculture Based on International and National Experiences. Water 2023, 15, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, L.A.; Shaghaleh, H.; El-Kassar, G.M.; Abu-Hashim, M.; Elsadek, E.A.; Hamoud, Y.A. Aquaponics: A Sustainable Path to Food Sovereignty and Enhanced Water Use Efficiency. Water 2023, 15, 4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifedayo, O.O.; Adewale, F.O.; Thomas, A.O. Comparative study on growth and economic performances of Nile Tilapia, oreochromis niloticus reared under different culture enclosures in Akure, Nigeria. Aquac. Stud. 2020, 20, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Leithy, A.A.A.; Hemeda, S.A.; El Naby, W.S.H.A.; El Nahas, A.F.; Hassan, S.A.H.; Awad, S.T.; El-Deeb, S.I.; Helmy, Z.A. Optimum salinity for Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) growth and mRNA transcripts of ion-regulation, inflammatory, stress- and immune-related genes. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 45, 1217–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.H.; Jiang, D.L.; Huang, Y.; Li, B.J.; Chen, C.H.; Lin, H.R.; Xia, J.H. Identifying a Major QTL Associated with Salinity Tolerance in Nile Tilapia Using QTL-Seq. Mar. Biotechnol. 2018, 20, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr-Eldahan, S.; Shreadah, M.A.; Maher, A.M.; Ali, T.E.-S.; Nabil-Adam, A. New vaccination approach using formalin-killed Streptococcus pyogenes vaccine on the liver of Oreochromis niloticus fingerlings. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, M.M.; Leungnaruemitchai, A.; Suebsong, W.; Somjai, D.; Nimnual, K.; Abdurahman, L.; Nganing, K. A comparative growth performance and survival of different genetic strains of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and Red tilapia (Oreochromis spp.) in a floating net cage culture farming in the Cirata Lake, West Java, Indonesia. Thai J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 54, 280–293. [Google Scholar]
- Nassar, S.A.; Hassan, A.G.A.; Badran, M.F.; Abdel-Rahim, M.M. Effects of salinity level on growth performance, feed utilization, and chromatic deformity of the hybrid Red tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus x O. mossambicus. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2021, 25, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavilli, H.; Yolcu, S.; Skorupa, M.; Aciksoz, S.B.; Asif, M. Salt and drought stress-mitigating approaches in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) to improve its performance and yield. Planta 2023, 258, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, H.-A.A.; Mekki, B.; El-Sadek, M.E.; El Lateef, E.E. Effect of L-Ornithine application on improving drought tolerance in sugar beet plants. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, J.; Uddin, J.; Hossain, M.A.; Henry, R.; Begum, M.K.; Sohel, A.T.; Mou, M.A.; Ahn, J.; Cheong, E.J.; Lim, Y.-S. Exogenous putrescine attenuates the negative impact of drought stress by modulating physio-biochemical traits and gene expression in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrović, M.; Janakiev, T.; Grbić, M.L.; Unković, N.; Stević, T.; Vukićević, S.; Dimkić, I. Insights into Endophytic and Rhizospheric Bacteria of Five Sugar Beet Hybrids in Terms of Their Diversity, Plant-Growth Promoting, and Biocontrol Properties. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 87, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayyab, M.; Wakeel, A.; Mubarak, M.U.; Artyszak, A.; Ali, S.; Hakki, E.E.; Mahmood, K.; Song, B.; Ishfaq, M. Sugar Beet Cultivation in the Tropics and Subtropics: Challenges and Opportunities. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erenstein, O.; Jaleta, M.; Mottaleb, K.A.; Sonder, K.; Donovan, J.; Braun, H.-J. Global Trends in Wheat Production, Consumption and Trade. In Wheat Improvement: Food Security in a Changing Climate; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL Sabagh, A.; Islam, M.S.; Skalicky, M.; Singh, K.; Hossain, M.A.; Hossain, A.; Mahboob, W.; Iqbal, M.A.; Ratnasekera, D.; Singhal, R.K.; et al. Salinity Stress in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in the Changing Climate: Adaptation and Management Strategies. Front. Agron. 2021, 3, 661932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Day, D.A.; Fricke, W.; Watt, M.; Arsova, B.; Barkla, B.J.; Bose, J.; Byrt, C.S.; Chen, Z.; Foster, K.J.; et al. Energy costs of salt tolerance in crop plants. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1072–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhan, D.K.; Phong, L.T.; Verdegem, M.J.; Duong, L.T.; Bosma, R.H.; Little, D.C. Integrated freshwater aquaculture, crop and livestock production in the Mekong delta, Vietnam: Determinants and the role of the pond. Agric. Syst. 2007, 94, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzby, K.M.; Lin, L.-S. Scaling aquaponic systems: Balancing plant uptake with fish output. Aquac. Eng. 2014, 63, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Gewaily, M.; Sewilam, H. Combined effects of water salinity and ammonia exposure on the antioxidative status, serum biochemistry, and immunity of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 49, 1461–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariyanto, D.; Muslikhin, M. Performance of red tilapia in three different levels of salinity. Indones. Aquac. J. 2011, 6, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angadi, P. The physiological adaptations during salinity stress in Tilapia fish: A review. Acta Èntomol. Zool. 2024, 5, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djiba, P.K.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y. Correlation between metabolic rate and salinity tolerance and metabolic response to salinity in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Animals 2021, 11, 3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kombat, E.O.; Zhao, J.; Abakari, G.; Owusu-Afriyie, G.; Birteeb, P.T.; Alhassan, E.H. Metabolic cost of acute and chronic exposure of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) to different levels of salinity. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 6152–6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.; Madkour, K.; Mugwanya, M.; Kimera, F.; Sewilam, H. Growth performances, body composition, and blood variables of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) juveniles grown in a recirculating aquaculture system under different water salinity levels. J. Appl. Aquac. 2023, 36, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrhman, A.M.; Sharawy, Z.Z.; Goda, A.M.A.S.; Slater, M.R.J. Adaptability of the nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus juveniles to water salinity by controlling dietary sodium chloride levels. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2020, 24, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zaeem, S.Y. Production of salinity tolerant tilapia through interspecific hybridization between Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and red tilapia (Oreochromis sp.). Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 7, 2955–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.F.M. Tilapia culture in salt water: Environmental requirements, nutritional implications and economic potentials. Av. En Nutr. Acuicola 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gadallah, M.A.; Milad, S.I.; Mabrook, Y.M.; Mabrook, Y.M.; Abo Yossef, A.Y.; Ma, G. Evaluation of some Egyptian bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) cultivars under salinity stress. Alex. Sci. Exch. J. 2017, 38, 259–270. [Google Scholar]
- Arif, Y.; Singh, P.; Siddiqui, H.; Bajguz, A.; Hayat, S. Salinity induced physiological and biochemical changes in plants: An omic approach towards salt stress tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 156, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassar, R.M.A.; Kamel, H.A.; Ghoniem, A.E.; Alarcón, J.J.; Sekara, A.; Ulrichs, C.; Abdelhamid, M.T. Physiological and anatomical mechanisms in wheat to cope with salt stress induced by seawater. Plants 2020, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, N.; El Naggar, G. Water quality, fish production and economics of nile tilapia, oreochromis niloticus, and african catfish, clarias gariepinus, monoculture and polycultures. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2010, 41, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, M.; Pakniyat, H. Evaluation of wheat cultivars under salinity stress based on some agronomic and physiological traits. J. Agric. Soc. Sci 2008, 4, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnasamy, K.; Bell, R.; Ma, Q. Wheat responses to sodium vary with potassium use efficiency of cultivars. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Mawly, S.E.; Zanouny, I. Response of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) to potassium application and irrigation with saline water. Ass. Univ. Bull. Environ. Res. 2004, 7, 123–136. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Geng, G.; Wang, Y. Salt Tolerance in Sugar Beet: From Impact Analysis to Adaptive Mechanisms and Future Research. Plants 2024, 13, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.-Q.; Liang, N.; Feng, R.-J.; Zhang, J.-J. Evaluation of salinity tolerance in seedlings of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) cultivars using proline, soluble sugars and cation accumulation criteria. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2013, 35, 2665–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ievinsh, G.; Andersone-Ozola, U.; Jēkabsone, A. Similar Responses of Relatively Salt-Tolerant Plants to Na and K during Chloride Salinity: Comparison of Growth, Water Content and Ion Accumulation. Life 2022, 12, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; ElSayed, A.I.; Moore, M.; Dietz, K.-J. Redox and reactive oxygen species network in acclimation for salinity tolerance in sugar beet. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 1283–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, K.; Mondal, S.; Gorai, S.; Singh, A.P.; Kumari, A.; Ghosh, T.; Roy, A.; Hembram, S.; Gaikwad, D.J.; Mondal, S.; et al. Impacts of salinity stress on crop plants: Improving salt tolerance through genetic and molecular dissection. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1241736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwaly, S.; Nasr, H.; Ahmed, K.; Fathi, M. Multifaceted stress response in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fingerlings: Integrative analysis of salinity, ammonia, and stocking density effects on growth, physiology, and gene expression. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 51, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isayenkov, S.V.; Maathuis, F.J.M. Plant Salinity Stress: Many Unanswered Questions Remain. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Fujita, M. Plant Responses and Tolerance to Salt Stress: Physiological and Molecular Interventions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, E.; Motamedi-Tehrani, J.; Peyghan, R. Effect of Short-Term Stress and Interaction of Salinity and Ammonia-N Levels, Associated With Food Deprivation on Fatty Acid Profile and Body Composition in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac. Nutr. 2025, 2025, 8840365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqib, M.; Akhtar, J.; Abbas, G.; Nasim, M. Salinity and drought interaction in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is affected by the genotype and plant growth stage. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2013, 35, 2761–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Iqbal, M.; Hashim, M.M. Impact of Sowing Dates on the Yield and Quality of Sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) cv. California-KWS: Sowing dates effects on sugar beet. Proc. Pak. Acad. Sci. B Life Environ. Sci. 2020, 57, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- GitHub-Myaseen208/Agricolae: Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research. Available online: https://github.com/myaseen208/agricolae (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Gómez-Rubio, V. ggplot2—Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis (2nd Edition). J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 77, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, J.W.; Green, W.A.; Schloerke, B.; Crowley, J.; Cook, D.; Hofmann, H.; Wickham, H. The Generalized Pairs Plot. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2013, 22, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatments | Fish | IW a (g/fish) | FW (g/fish) | WG (g/fish) | FI (g/fish) | FCR | SGR (%/day) | SR% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 ppt | Nile Tilapia | 8.68 a ± 0.01 | 160.34 e ± 0.05 | 151.66 e ± 0.04 | 224.53 c ± 0.08 | 1.48 a | 1.38 c ± 0.02 | 89 a |
| Red Tilapia | 8.88 a ± 0.02 | 161.51 c ± 0.08 | 152.63 c ± 0.09 | 232.05 a ± 0.1 | 1.52 a | 1.37 c ± 0.01 | 86 a | |
| Mix | 8.52 a ± 0.012 | 160.55 d ± 0.08 | 152.03 d ± 0.09 | 220.93 d ± 0.05 | 1.45 a | 1.39 bc ± 0.01 | 91 a | |
| 10 ppt | Nile Tilapia | 8.66 a ± 0.02 | 144.39 f ± 0.05 | 135.73 f ± 0.06 | 212.53 f ± 0.05 | 1.57 a | 1.33 d ± 0.01 | 94 a |
| Red Tilapia | 8.74 a ± 0.04 | 174.52 a ± 0.1 | 165.78 a ± 0.06 | 227.56 b ± 0.05 | 1.37 a | 1.42 a ± 0.01 | 88 a | |
| Mix | 8.76 a ± 0.03 | 171.57 b ± 0.1 | 162.81 b ± 0.07 | 214.63 e ± 0.1 | 1.32 a | 1.41 ab ± 0.01 | 94 a |
| Treatment | Fish | 30 DAS | 45 DAS | 75 DAS | 105 DAS | 135 DAS | 165 DAS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Fertilizer | 24 cd ± 0.49 | 35 c ± 0.36 | 47.67 a ± 0.75 | 48.79 a ± 0.86 | 51.25 a ± 0.61 | 53.42 a ± 0.74 |
| 5 ppt | Nile Tilapia | 23.04 d ± 0.49 | 30.25 d ± 0.51 | 35.08 c ± 0.78 | 36.18 c ± 0.79 | 37.21 e ± 0.85 | 37.79 d ± 0.48 |
| Red Tilapia | 28.5 a ± 0.75 | 38.67 ab ± 1.12 | 44.5 ab ± 0.15 | 48.58 a ± 0.14 | 50.6 ab ± 0.51 | 51 ab ± 0.95 | |
| Mix | 25.92 bc ± 0.5 | 40.42 a ± 0.54 | 46.5 a ± 0.86 | 47.33 a ± 0.77 | 47.75 bc ± 0.76 | 49.67 b ± 0.72 | |
| 10 ppt | Nile Tilapia | 27 ab ± 0.33 | 35.63 c ± 0.44 | 41.83 b ± 0.66 | 45.67 ab ± 0.81 | 46.5 cd ± 0.8 | 49.54 b ± 0.83 |
| Red Tilapia | 23.67 d ± 0.33 | 35.67 c ± 0.45 | 45.17 a ± 0.86 | 46.92 a ± 0.85 | 47.67 bc ± 0.45 | 48.71 b ± 0.84 | |
| Mix | 24.47 cd ± 0.29 | 36.92 bc ± 0.43 | 41.42 b ± 0.87 | 42.88 b ± 0.8 | 43.68 d ± 0.85 | 45.33 c ± 0.77 |
| Treatment | Fish | 30 DAS | 45 DAS | 75 DAS | 105 DAS | 135 DAS | 165 DAS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Fertilizer | 6.83 b ± 0.32 | 10.33 a ± 0.48 | 15.17 bc ± 0.53 | 18 b ± 0.65 | 20.67 bc ± 0.51 | 36.75 ab ± 0.71 |
| 5 ppt | Nile Tilapia | 7.17 ab ± 0.32 | 9.58 a ± 0.47 | 13.92 c ± 0.54 | 17.83 b ± 0.77 | 19.67 c ± 0.72 | 30.67 d ± 0.28 |
| Red Tilapia | 7.5 ab ± 0.38 | 10 a ± 0.48 | 16.75 ab ± 0.65 | 18.75 ab ± 0.22 | 20.83 bc ± 0.37 | 32.33 d ± 0.68 | |
| Mix | 8.42 a ± 0.31 | 9.5 a ± 0.47 | 15.75 abc ± 0.71 | 20.33 ab ± 0.41 | 23.17 ab ± 0.53 | 34.25 c ± 0.84 | |
| 10 ppt | Nile Tilapia | 7.83 ab ± 0.27 | 10 a ± 0.28 | 16.5 ab ± 0.51 | 21.25 a ± 0.71 | 24.58 a ± 0.82 | 38.33 a ± 0.59 |
| Red Tilapia | 7.75 ab ± 0.3 | 10.5 a ± 0.54 | 17.67 a ± 0.58 | 19.17 ab ± 0.63 | 21.92 abc ± 0.61 | 38.58 a ± 0.66 | |
| Mix | 8.33 a ± 0.36 | 10.33 a ± 0.33 | 15.75 abc ± 0.51 | 20.67 a ± 0.76 | 21.67 bc ± 0.73 | 36.17 b ± 0.8 |
| Growing Season | Air Temp. (°C) | Relative Humidity (%) | Short Wave Solar Radiation (W/m2) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Total Sun Hours/Day | ETo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sep-23 | 27.94 | 68.73 | 253.75 | 1.59 | 11.38 | 9.55 |
| Oct-23 | 23.83 | 77.37 | 183.16 | 1.45 | 10.46 | 6.22 |
| Nov-23 | 20.65 | 74.21 | 144.76 | 1.45 | 9.61 | 4.64 |
| Dec-23 | 16.45 | 74.03 | 118.61 | 1.40 | 9.13 | 3.27 |
| Jan-24 | 14.20 | 69.08 | 132.60 | 1.17 | 9.34 | 3.47 |
| Feb-24 | 14.00 | 74.14 | 170.13 | 1.53 | 10.07 | 4.59 |
| Mar-24 | 17.40 | 64.88 | 221.54 | 1.56 | 10.99 | 6.70 |
| Apr-24 | 22.24 | 65.32 | 274.04 | 1.77 | 11.88 | 9.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madkour, K.; Kimera, F.; Mugwanya, M.; Eissa, R.A.; Nasr-Eldahan, S.; Aref, K.; Ahmed, W.; Farouk, E.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Abdelmaksoud, Y.; et al. Evaluating the Growth Performance of Nile and Red Tilapia and Its Influence on Morphological Growth and Yield of Intercropped Wheat and Sugar Beet Under a Biosaline Integrated Aquaculture–Agriculture System. Plants 2025, 14, 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091346
Madkour K, Kimera F, Mugwanya M, Eissa RA, Nasr-Eldahan S, Aref K, Ahmed W, Farouk E, Dawood MAO, Abdelmaksoud Y, et al. Evaluating the Growth Performance of Nile and Red Tilapia and Its Influence on Morphological Growth and Yield of Intercropped Wheat and Sugar Beet Under a Biosaline Integrated Aquaculture–Agriculture System. Plants. 2025; 14(9):1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091346
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadkour, Khaled, Fahad Kimera, Muziri Mugwanya, Rafat A. Eissa, Sameh Nasr-Eldahan, Kholoud Aref, Walaa Ahmed, Eman Farouk, Mahmoud A. O. Dawood, Yasmine Abdelmaksoud, and et al. 2025. "Evaluating the Growth Performance of Nile and Red Tilapia and Its Influence on Morphological Growth and Yield of Intercropped Wheat and Sugar Beet Under a Biosaline Integrated Aquaculture–Agriculture System" Plants 14, no. 9: 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091346
APA StyleMadkour, K., Kimera, F., Mugwanya, M., Eissa, R. A., Nasr-Eldahan, S., Aref, K., Ahmed, W., Farouk, E., Dawood, M. A. O., Abdelmaksoud, Y., Abdelkader, M. F., & Sewilam, H. (2025). Evaluating the Growth Performance of Nile and Red Tilapia and Its Influence on Morphological Growth and Yield of Intercropped Wheat and Sugar Beet Under a Biosaline Integrated Aquaculture–Agriculture System. Plants, 14(9), 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091346







