Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Litsea cubeba Essential Oil Against Salmonella typhimurium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chemical Composition Analysis of LCEO
2.2. Antibacterial Activity of LCEO
2.2.1. Inhibition Zone Analysis
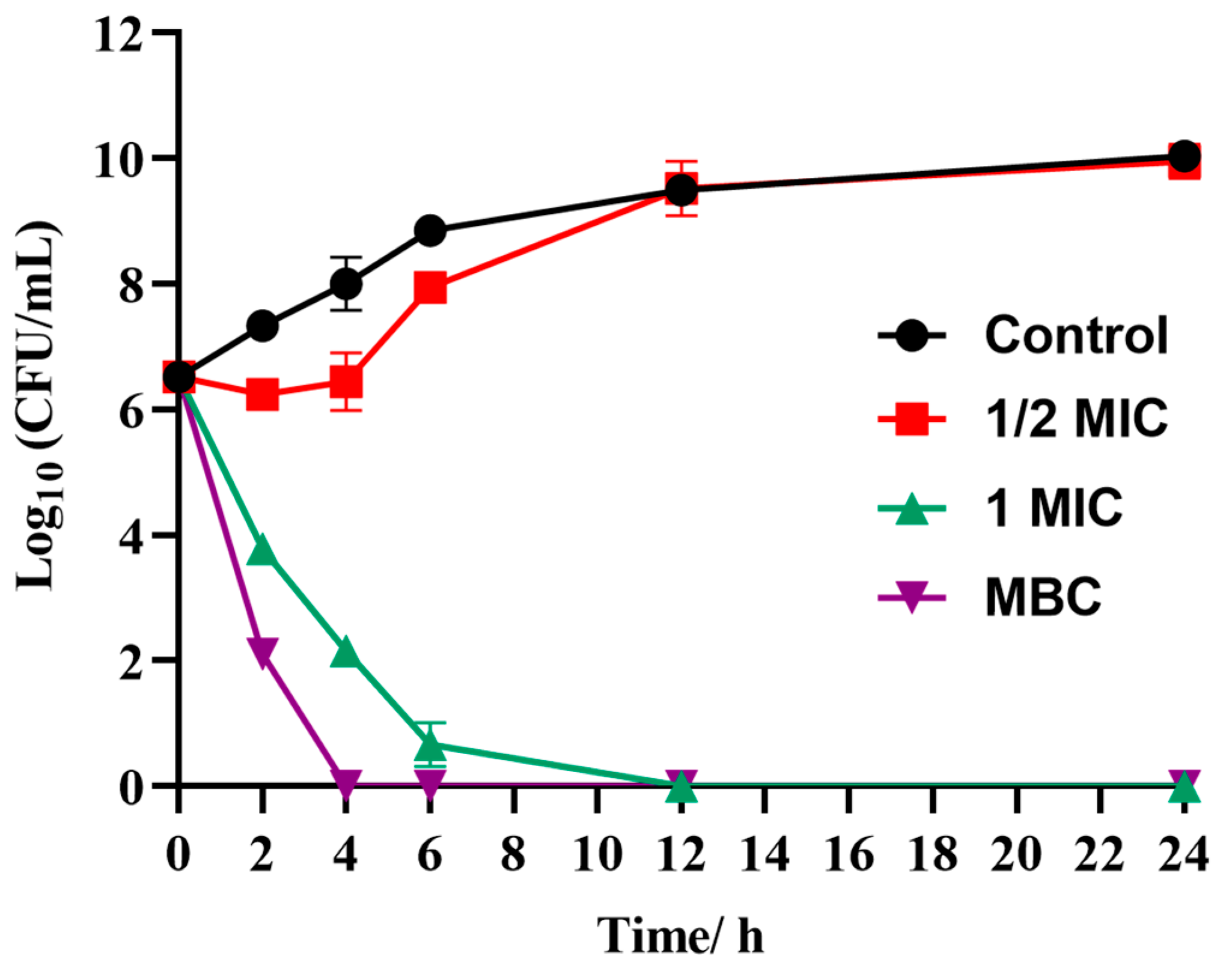
2.2.2. Time-Killing Curves
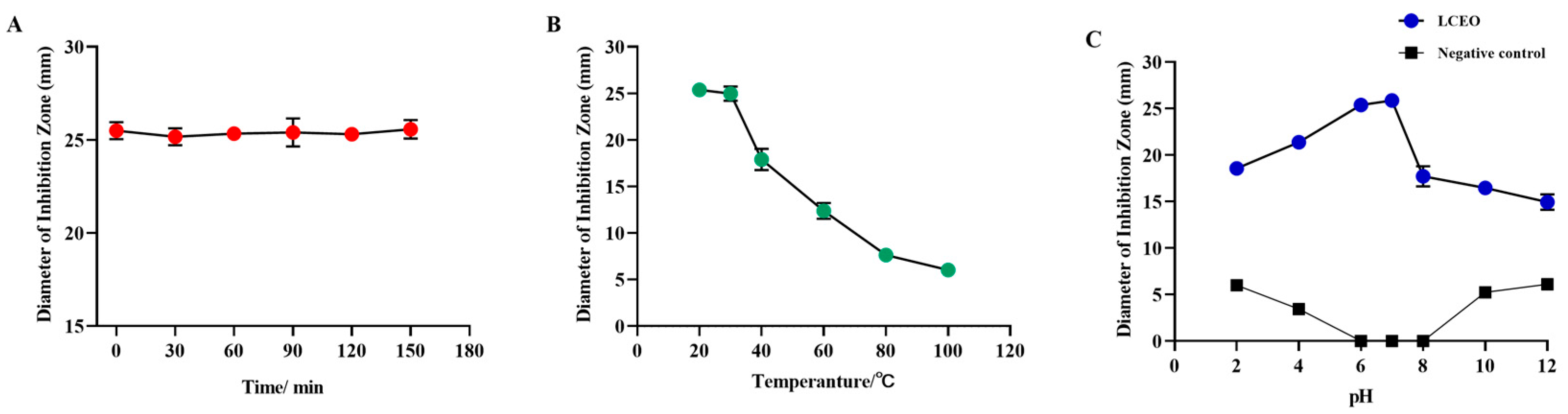
2.3. Effects of Environmental Factors on the Bacteriostatic Stability of LCEO
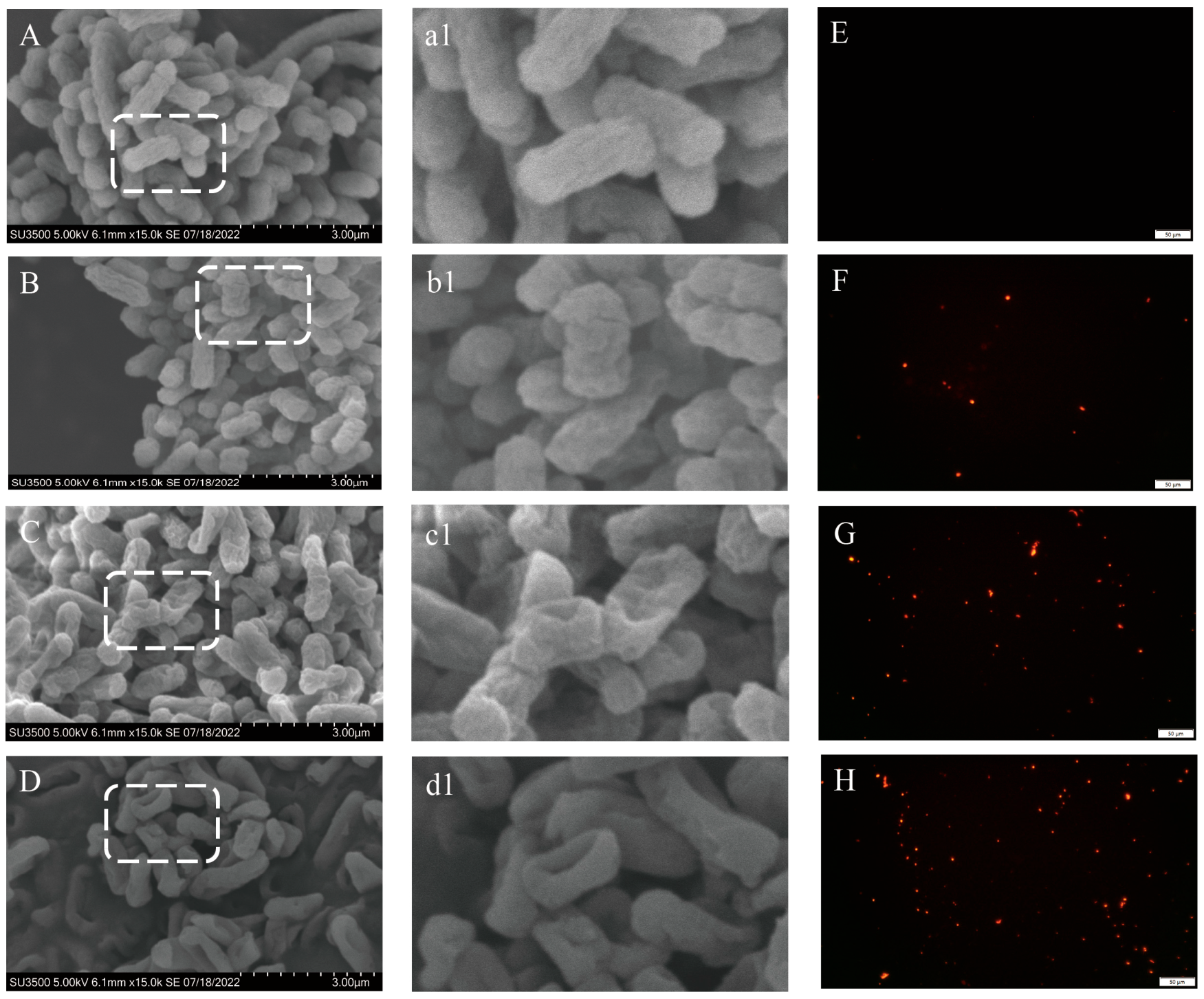
2.4. Effect of LCEO on Morphology and Membrane Permeability of S.Tm
2.5. Antibacterial Mechanism of LCEO
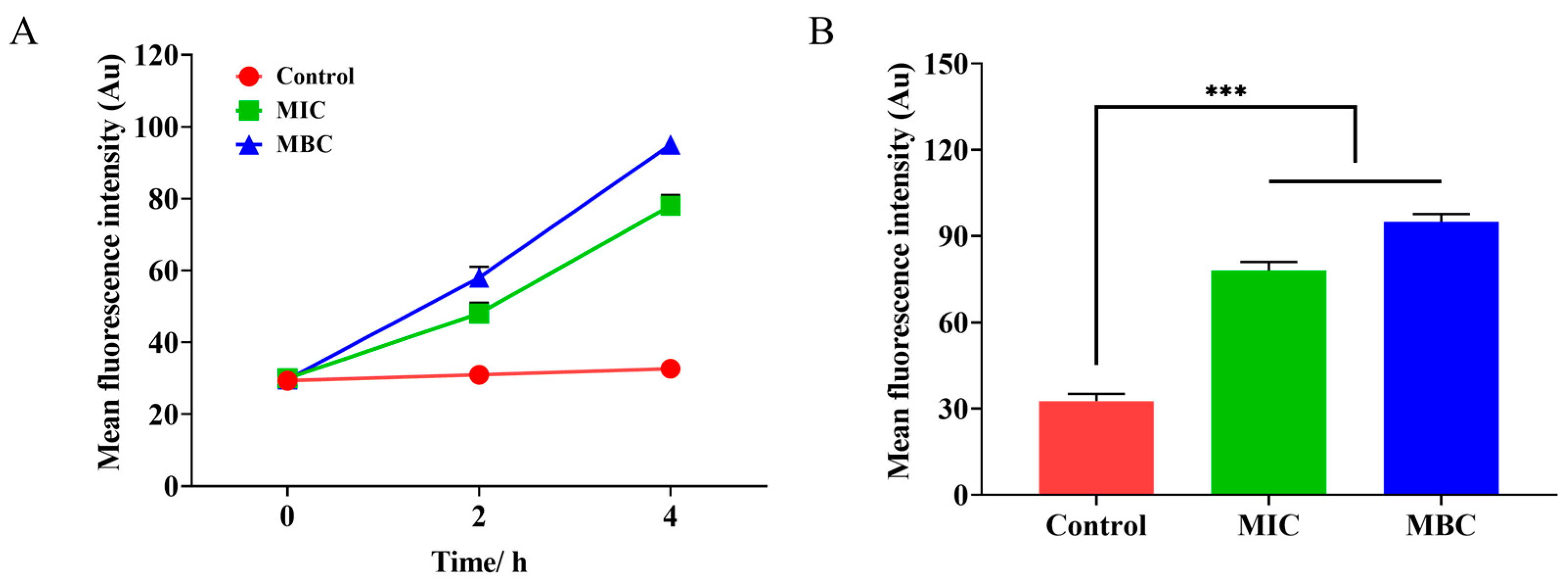
2.5.1. The Influence of LCEO on the Cell Membrane Potential of S.Tm
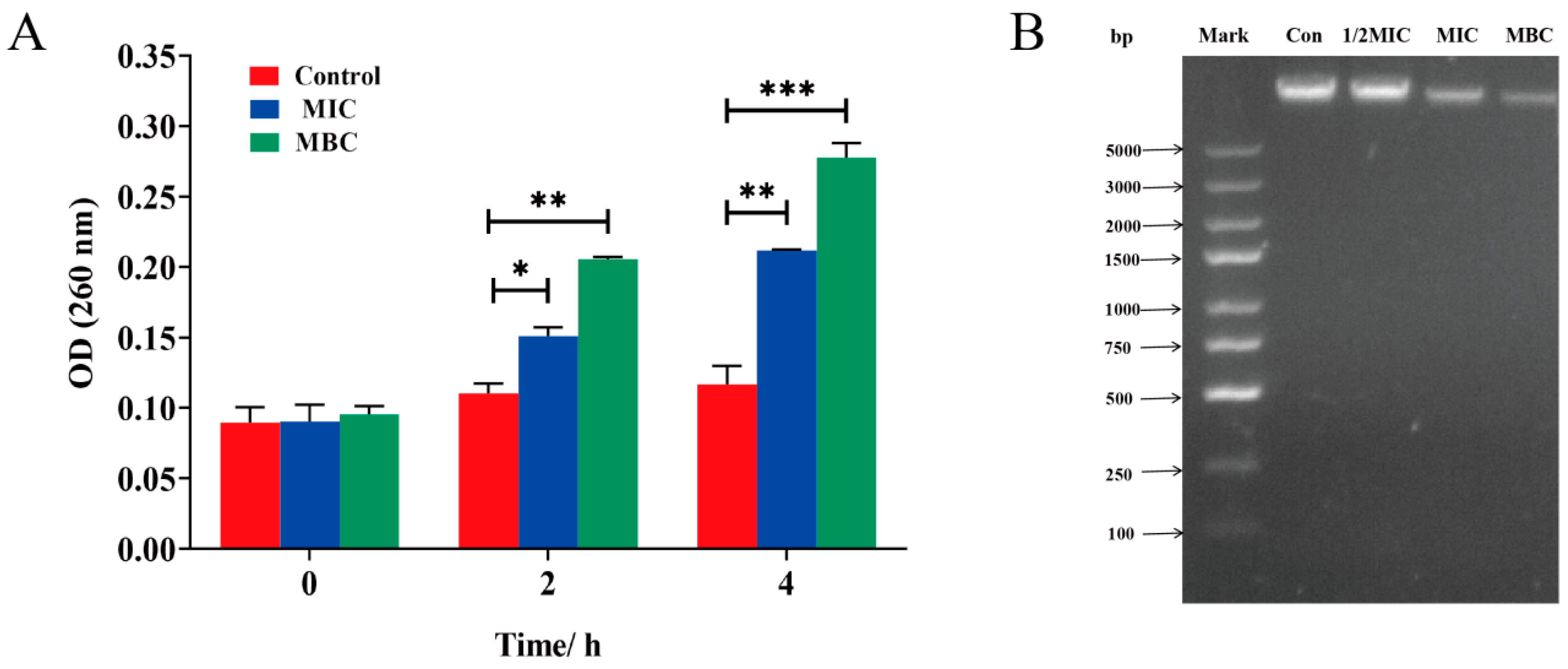
2.5.2. Nucleic Acid Leakage Analysis
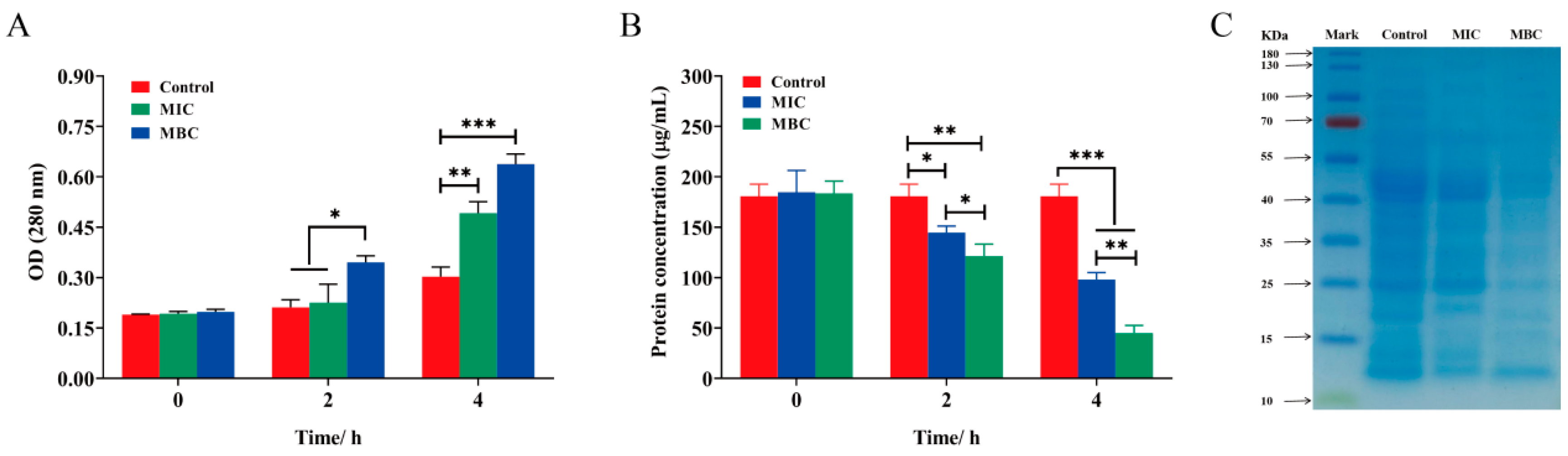
2.5.3. Intracellular Protein Leakage
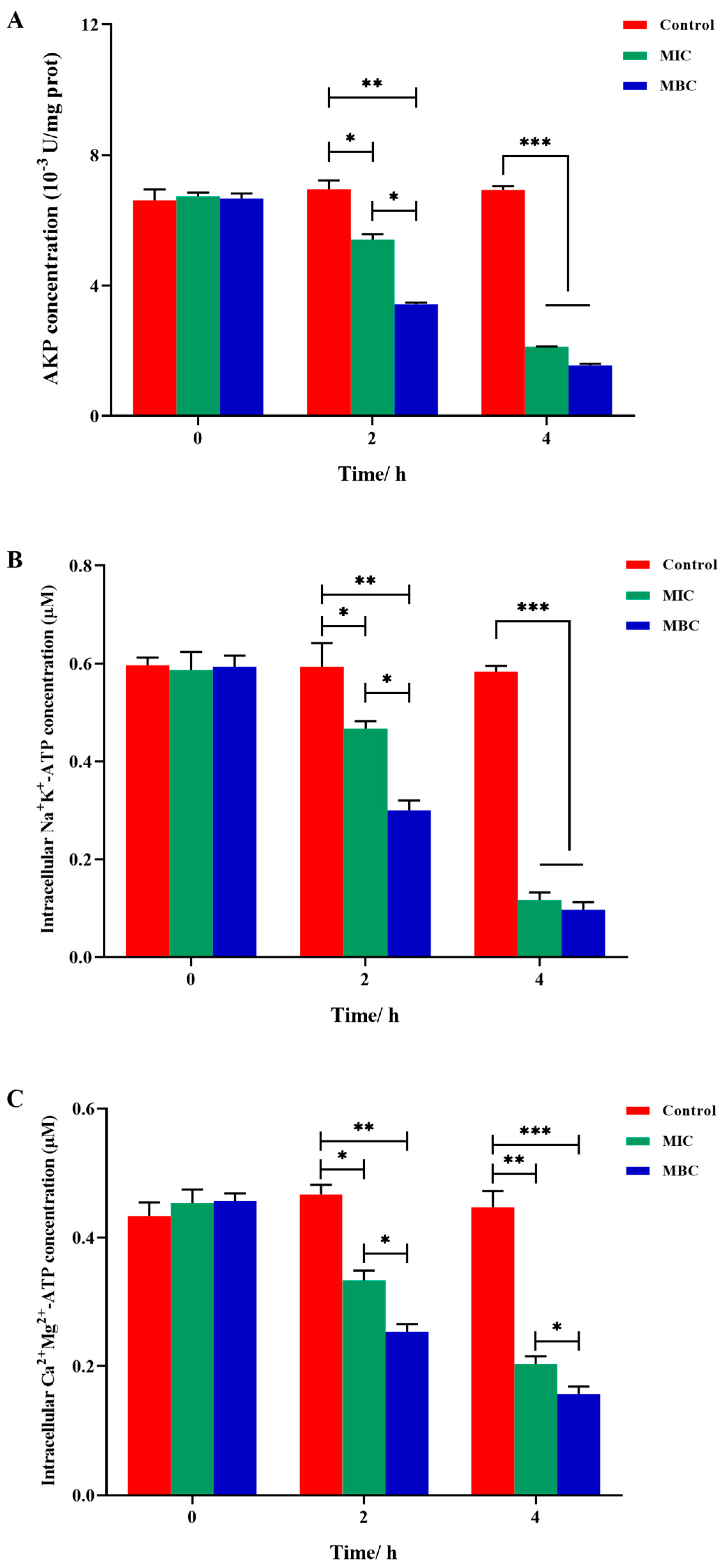
2.6. Intracellular Enzyme Activity
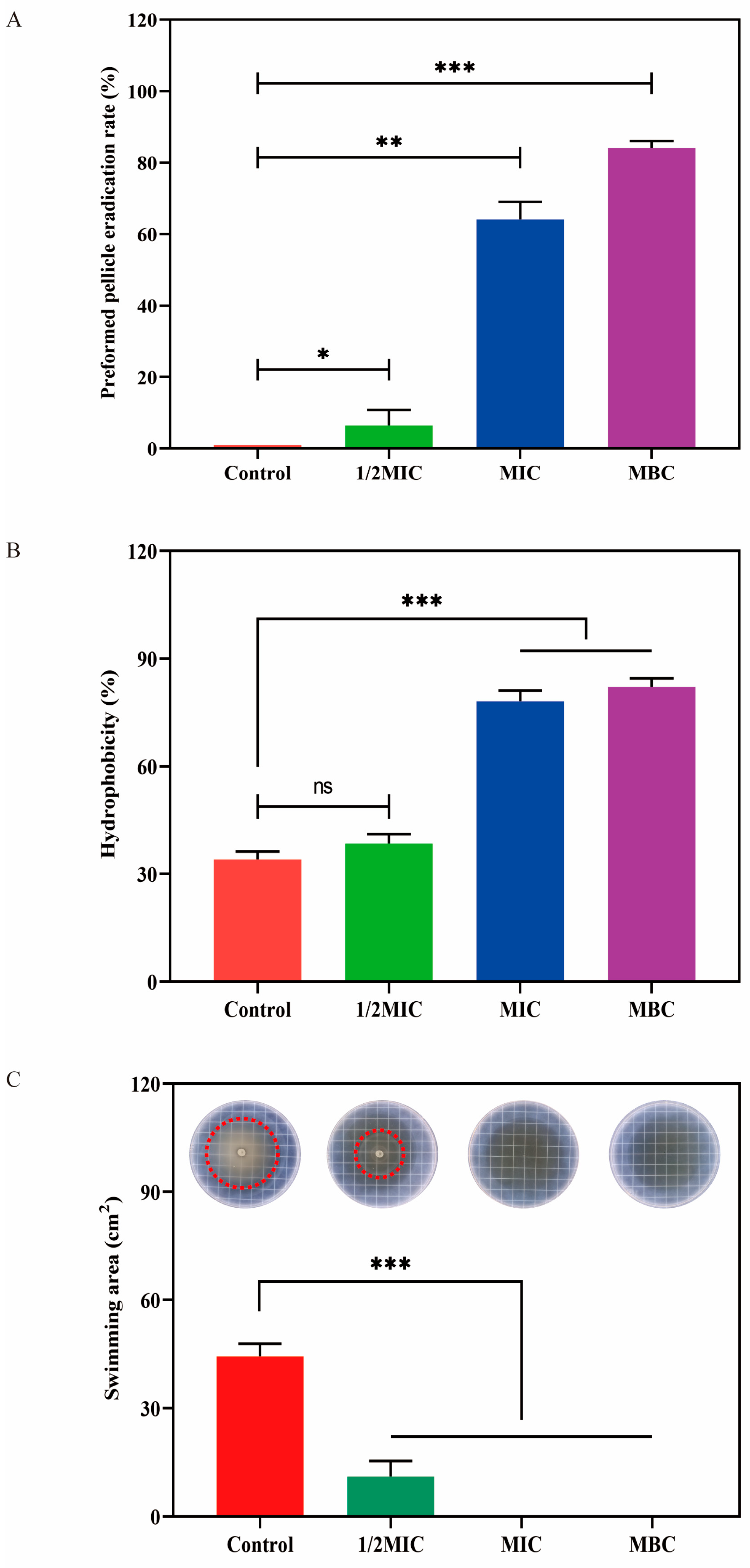
2.7. Effect of LCEO on S.Tm Biofilm
2.8. The Antibacterial Activity of LCEO Chemical Components Against S.Tm
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. LCEO Compound Analysis
4.3. Antibacterial Activity
4.3.1. Agar Paper Diffusion Method
4.3.2. Determination of MIC and MBC
4.3.3. Time–Killing Curve
4.4. Study on Antibacterial Stability of LCEO
4.4.1. Effect of Temperature on the Antibacterial Activity of LCEO
4.4.2. Effect of Light Exposure on the Antibacterial Activity of LCEO
4.4.3. The Effect of pH on the Antibacterial Activity of LCEO
4.5. Cell Morphology and Membrane Damage
4.5.1. Morphological Analysis Using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.5.2. Membrane Damage Assessment
4.6. Research on Antibacterial Mechanisms
4.6.1. Membrane Potential Analysis
4.6.2. Determination of Extracellular Nucleic Acid and Protein
4.6.3. BCA Protein Quantification Test Kit for Determining Protein Content
4.7. Effect of LCEO on Bacterial Enzyme Activity
4.7.1. Determination of Alkaline Phosphatase (AKP) Activity
4.7.2. Content and Activity of Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
4.8. Antibiofilm Activity of LCEO
4.8.1. Biofilm Clearance Rate
4.8.2. Determination of Bacterial Surface Hydrophobicity
4.8.3. Cell Swimming Ability Analysis
4.9. Antibacterial Activity of Chemical Components in LCEO
4.10. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garvey, M. Foodborne Clostridioides Species: Pathogenicity, Virulence and Biocontrol Options. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Martinez, Z.; Julianingsih, D.; Tabashsum, Z.; Aditya, A.; Tung, C.; Phung, A.; Suh, G.; Hshieh, K.; Wall, M.; Kapadia, S.; et al. Assessment of the prevalence, serotype, and antibiotic resistance pattern of Salmonella enterica in integrated farming systems in the Maryland-DC area. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1240458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, H.M.; Prathan, R.; Hein, S.T.; Chuanchuen, R. Microbiological Quality and Antimicrobial Resistance of Commercial Probiotic Products for Food-Producing Animals. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvigioni, M.; Cara, A.; Celandroni, F.; Mazzantini, D.; Panattoni, A.; Tirloni, E.; Bernardi, C.; Pinotti, L.; Stella, S.; Ghelardi, E. Characterization of a Bacillus cereus strain associated with a large feed-related outbreak of severe infection in pigs. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 1078–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, L.; Onyeaka, H.O.; Neill, S. Listeria monocytogenes Biofilms in Food-Associated Environments: A Persistent Enigma. Foods 2023, 12, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamas, A.; Miranda, J.M.; Regal, P.; Vázquez, B.; Franco, C.M.; Cepeda, A. A comprehensive review of non-enterica subspecies of Salmonella enterica. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 206, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, G.; Matuszewska, M.; Jia, M.; Zhou, J.; Ba, X.; Duan, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, J.; Tao, M.; Fan, J.; et al. A Survey of Chinese Pig Farms and Human Healthcare Isolates Reveals Separate Human and Animal Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Populations. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2103388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majowicz, S.E.; Musto, J.; Scallan, E.; Angulo, F.J.; Kirk, M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Jones, T.F.; Fazil, A.; Hoekstra, R.M. The Global Burden of Nontyphoidal Salmonella Gastroenteritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente-Nunez, C.; Cesaro, A.; Hancock, R.E.W. Antibiotic failure: Beyond antimicrobial resistance. Drug Resist. Update 2023, 71, 101012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Teng, Z.; Xie, F.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, S. Loading of cinnamon essential oil into electrospun octenylsuccinylated starch-pullulan nanofiber mats: Electrospinnability evaluation, structural characterization, and antibacterial potential. Food Hydrocolloid 2024, 148, 109426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Li, W.; Fu, B.; Fu, M.; Ren, Q.; Yang, F.; Qin, C. Physical, antibacterial and antioxidant properties of chitosan films containing hardleaf oatchestnut starch and Litsea cubeba oil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas-González, R.; Yilmaz, B.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A.; Hano, C.; Shariati, M.A.; Bangar, S.P.; Goksen, G.; Dhama, K.; Lorenzo, J.M. Cinnamon: An antimicrobial ingredient for active packaging. Food Packag. Shelf 2023, 35, 101026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Wu, X. Antibacterial Effects and Mechanism of Mandarin (Citrus reticulata L.) Essential Oil against Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2020, 25, 4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perricone, M.; Arace, E.; Corbo, M.R.; Sinigaglia, M.; Bevilacqua, A. Bioactivity of essential oils: A review on their interaction with food components. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Li, R.; Tao, T.; Zhong, R.; Du, H.; Liao, Z.; Sun, Z.; Xu, C. Therapeutic potential of Litsea cubeba essential oil in modulating inflammation and the gut microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1233934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Chen, J.; Jin, K.; Peng, K.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Ouyang, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Effects of Litsea cubeba essential oil on growth performance, blood antioxidation, immune function, apparent digestibility of nutrients, and fecal microflora of pigs. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1166022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, W.; Deng, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, X. Antibacterial activity of Litsea cubeba essential oil and its mechanism against Botrytis cinerea. Rsc Adv. 2019, 9, 28987–28995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.V.; Caruso, D.; Lebrun, M.; Nguyen, N.T.; Trinh, T.T.; Meile, J.C.; Chu-Ky, S.; Sarter, S. Antibacterial activity of Litsea cubeba (Lauraceae, May Chang) and its effects on the biological response of common carp Cyprinus carpio challenged with Aeromonas hydrophila. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Dai, J.; Hu, W.; Li, C.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. The inhibition effect and mechanism of Litsea cubeba essential oil on the hemolytic activity of listeriolysin O. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.V.; Hoang, H.N.T.; Nguyen, N.H.; Do, H.B.; Vo, H.Q.; Le, A.T.; Le, T.Q.; Pham, T.V. GC-MS Characterization, in Vitro Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Essential oil from the Leaves of Litsea balansae Lecomte. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2023, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, L.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Zhan, Z.; Tian, S.; Cui, Q.; Wang, Y. Chemical Composition of Essential Oils of Litsea cubeba Harvested from Its Distribution Areas in China. Molecules 2012, 17, 7057–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Li, P.; Wan, J.; He, C. A review on phytochemical and pharmacological properties of Litsea coreana. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogoi, R.; Loying, R.; Sarma, N.; Munda, S.; Kumar Pandey, S.; Lal, M. A comparative study on antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, genotoxicity, anti-microbial activities and chemical composition of fruit and leaf essential oils of Litsea cubeba Pers from North-east India. Ind. Crop Prod. 2018, 125, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, W.; Wan, S.; Zhou, J.; Qin, Z.; Gao, H. Antibacterial activity of Amomum tsaoko essential oil and its interaction with Staphylococcus aureus. LWT 2024, 191, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lin, M.; Feng, S.; Gu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, D.; Gao, M. Chemical composition, antibacterial activity, and mechanism of action of essential oil from Litsea cubeba against foodborne bacteria. J. Food Process Pres. 2020, 44, e14724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhang, X.; Guo, N. The antimicrobial activities and action-mechanism of tea tree oil against food-borne bacteria in fresh cucumber juice. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 125, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lan, W.; Xie, J. Natural preservative Litsea cubeba essential oil: With emphasis on its biological activities, encapsulation methods and application in food preservation. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Wills, R.B.H.; Bowyer, M.C.; Golding, J.B.; Kirkman, T.; Pristijono, P. Efficacy of Orange Essential Oil and Citral after Exposure to UV-C Irradiation to Inhibit Penicillium digitatum in Navel Oranges. Horticulturae 2020, 6, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi, M.; Mostafavi, A.; Shamspur, T. Effect of Storage on Essential Oil Content and Composition of Rosa damascena Mill. Petals under Different Conditions. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Pl. 2011, 14, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misharina, T.A.; Polshkov, A.N.; Ruchkina, E.L.; Medvedeva, I.B. Changes in the composition of the essential oil of marjoram during storage. Appl. Biochem. Micro 2003, 39, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hąc-Wydro, K.; Flasiński, M.; Romańczuk, K. Essential oils as food eco-preservatives: Model system studies on the effect of temperature on limonene antibacterial activity. Food Chem. 2017, 235, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Guo, H.; Zhu, M.; Xie, L.; Jin, J.; Korma, S.A.; Jin, Q.; Wang, X.; Cacciotti, I. Intrinsic properties and extrinsic factors of food matrix system affecting the effectiveness of essential oils in foods: A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2024, 64, 7363–7396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badie, F.; Saffari, M.; Moniri, R.; Alani, B.; Atoof, F.; Khorshidi, A.; Shayestehpour, M. The combined effect of stressful factors (temperature and pH) on the expression of biofilm, stress, and virulence genes in Salmonella enterica ser. Enteritidis and Typhimurium. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 4475–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, A.; Havelaar, A.H.; Schneider, K.R. Antimicrobial Efficacy of Un-Ionized Ammonia (NH3) against Salmonella Typhimurium in Buffered Solutions with Variable pH, NH3 Concentrations, and Urease-Producing Bacteria. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Costa, F.K.C.; Cascaes, J.M.; Severo, D.S.; Santana, M.B.; Carciofi, B.A.M.; de Aragão, G.M.F.; Ienczak, J.L. Influence of pH and oxygen levels on the antimicrobial efficacy of acetic acid against Salmonella Typhimurium. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2025, 136, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabanelli, G.; Montanari, C.; Patrignani, F.; Siroli, L.; Lanciotti, R.; Gardini, F. Modeling with the Logistic Regression of the Growth/No Growth Interface of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in Relation to 2 Antimicrobial Terpenes (Citral and Linalool), pH, and a(w). J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, M391–M398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi, A.; Rafieian, F.; Sami, M.; Rezaei, A. Fabrication, characterization and antimicrobial activity of chitosan/tragacanth gum/polyvinyl alcohol composite films incorporated with cinnamon essential oil nanoemulsion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 245, 125225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajpai, V.K.; Sharma, A.; Baek, K. Antibacterial mode of action of Cudrania tricuspidata fruit essential oil, affecting membrane permeability and surface characteristics of food-borne pathogens. Food Control. 2013, 32, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Song, L.; Sun, P.; Su, R.; Wang, S.; Cheng, S.; Zhan, X.; Lü, X.; Xia, X.; Shi, C. Synergistic bactericidal effect of ultrasound combined with citral nanoemulsion on Salmonella and its application in the preservation of purple kale. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 92, 106269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Woo, E.; Lee, D.G. Phytol has antibacterial property by inducing oxidative stress response in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Free. Radic. Res. 2016, 50, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Veldhuisen, T.W.; Altenburg, W.J.; Verwiel, M.A.M.; Lemmens, L.J.M.; Mason, A.F.; Merkx, M.; Brunsveld, L.; van Hest, J.C.M. Enzymatic Regulation of Protein–Protein Interactions in Artificial Cells. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, N.; Shapiro, L.; Honig, B.; Wu, Y.; Rubinstein, R. On the formation of ordered protein assemblies in cell–cell interfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, N.; Arthur, S.; Haynes, J.; Palaniappan, B.; Sundaram, U. Mechanism of Na-K-ATPase Inhibition by PGE2 in Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishnu, N.; Venkatesan, M.; Madaris, T.R.; Venkateswaran, M.K.; Stanley, K.; Ramachandran, K.; Chidambaram, A.; Madesh, A.K.; Yang, W.; Nair, J.; et al. ERMA (TMEM94) is a P-type ATPase transporter for Mg2+ uptake in the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol. Cell 2024, 84, 1321–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumbaugh, K.P.; Whiteley, M. Towards improved biofilm models. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2025, 23, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues Dos Santos, E.A.; Ereno Tadielo, L.; Arruda Schmiedt, J.; Silva Orisio, P.H.; de Cássia Lima Brugeff, E.; Sossai Possebon, F.; Olivia Pereira, M.; Gonçalves Pereira, J.; Dos Santos Bersot, L. Inhibitory effects of piperine and black pepper essential oil on multispecies biofilm formation by Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella Typhimurium, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. LWT 2023, 182, 114851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, M.; Oh, J.K.; Perez, K.; Zhou, W.; Wang, X.; Castillo, A.; Taylor, M.; Min, Y.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Akbulut, M. Effect of wax chain length on the adhesion dynamics and interfacial rigidity of Salmonella Typhimurium LT2. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 44, 103745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guo, W.; Feng, M.; Bai, Y.; Huang, J.; Cao, Y. Antibacterial, anti-biofilm activity and underlying mechanism of garlic essential oil in water nanoemulsion against Listeria monocytogenes. LWT 2024, 196, 115847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wang, W. Composition and biological activities of the essential oil from Schisandra chinensis obtained by solvent-free microwave extraction. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahar, B.; Chongtham, N. Traditional uses and advances in recent research on wild aromatic plant Mentha longifolia and its pharmacological importance. Phytochem. Rev. 2024, 23, 529–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathalizadeh, M.; Homayouni Tabrizi, M.; Tehranipour, M. A novel alpha-terpineol-loaded niosome formulation coated with hyaluronic acid and evaluation of its anticancer properties in vitro. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 424, 127139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Xie, P.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, J. Characterization, Thermal Stability and Antimicrobial Evaluation of the Inclusion Complex of Litsea cubeba Essential Oil in Large-Ring Cyclodextrins (CD9–CD22). Foods 2023, 12, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhabal, S.; Abdelaal, N.; Saeed Al-Zuhairy, S.; Elrefai, M.; Elsaid Hamdan, A.; Khalifa, M.; Hababeh, S.; Khasawneh, M.; Khamis, G.; Nelson, J.; et al. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Althaea officinalis Flower Extract Coated with Chitosan for Potential Healing Effects on Diabetic Wounds by Inhibiting TNF-α and IL-6/IL-1β Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 3045–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Kang, J.; Liu, L. Thymol as a critical component of Thymus vulgaris L. essential oil combats Pseudomonas aeruginosa by intercalating DNA and inactivating biofilm. LWT 2021, 136, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taggar, R.; Jangra, M.; Dwivedi, A.; Bansal, K.; Patil, P.B.; Bhattacharyya, M.S.; Nandanwar, H.; Sahoo, D.K. Bacteriocin isolated from the natural inhabitant of Allium cepa against Staphylococcus aureus. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaderi, L.; Aliahmadi, A.; Ebrahimi, S.N.; Rafati, H. Effective Inhibition and eradication of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms by Satureja khuzistanica essential oil nanoemulsion. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Tec. 2021, 61, 102260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Nie, D.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ou, N.; Li, Y. Selective antibacterial activity of Citrus Medica limonum essential oil against Escherichia coli K99 and Lactobacillus acidophilus and its antibacterial mechanism. LWT 2023, 186, 115215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Number | RT (min) | RI | Compounds | PA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7.04 | 968 | α-pinene | 3.18 |
| 2 | 7.94 | 989 | α-phellandrene | 2.76 |
| 3 | 8.36 | 999 | 6-methyl-5-hepten-2-one | 1.56 |
| 4 | 12.24 | 1088 | α-terpinene | 1.01 |
| 5 | 15.03 | 1153 | citronellal | 2.11 |
| 6 | 16.32 | 1183 | isocitral | 0.55 |
| 7 | 16.59 | 1189 | α-terpineol | 6.25 |
| 8 | 17.79 | 1219 | cis-isopiperitenol | 0.53 |
| 9 | 18.23 | 1231 | nerol | 1.79 |
| 10 | 18.67 | 1243 | neral | 29.76 |
| 11 | 19.25 | 1258 | geraniol | 3.43 |
| 12 | 19.79 | 1273 | geranial | 35.62 |
| 13 | 21.68 | 1328 | 2,6,11-Trimethyldodecane | 0.60 |
| 14 | 22.01 | 1338 | γ-elemene | 0.71 |
| 15 | 22.41 | 1351 | α-terpinyl acetate | 0.42 |
| 16 | 23.21 | 1377 | ylangene | 4.38 |
| 17 | 23.51 | 1386 | lavandulyl acetate | 0.47 |
| 18 | 23.71 | 1393 | β-elemene | 0.21 |
| 19 | 25.56 | 1459 | β-famesene | 0.93 |
| 20 | 26.93 | 1510 | α-bisabolene | 2.85 |
| 21 | 27.30 | 1525 | δ-cadinene | 0.36 |
| Germs | DIZ (mm) | MIC (mg/ mL) | MBC (mg/ mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bh | LCEO | Bh | LCEO | Bh | LCEO | |
| E. coli | 19.0 ± 0.1 | 22.1 ± 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| S. Tm | 19.9 ± 0.3 | 25.5 ± 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 1.2 | 0.8 |
| L. m | 16.6 ± 0.3 | 20.2 ± 1.2 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 2.4 | 1.6 |
| B. c | 17.2 ± 0.2 | 18.9 ± 0.5 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 2.4 | 2.0 |
| Components | DIZ (mm) | MIC (mg/mL) | MBC (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| citral | 30.7 ± 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| α-terpineol | 0 | - | - |
| ylangene | 1.1 ± 0.2 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, M.; Tang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Hao, Z. Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Litsea cubeba Essential Oil Against Salmonella typhimurium. Plants 2025, 14, 1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091343
Wang C, Chen X, Liu M, Tang X, Li Y, Zhan Y, Hao Z. Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Litsea cubeba Essential Oil Against Salmonella typhimurium. Plants. 2025; 14(9):1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091343
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Cuncai, Xiying Chen, Mingjie Liu, Xiaoquan Tang, Youzhi Li, Yuming Zhan, and Zhihui Hao. 2025. "Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Litsea cubeba Essential Oil Against Salmonella typhimurium" Plants 14, no. 9: 1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091343
APA StyleWang, C., Chen, X., Liu, M., Tang, X., Li, Y., Zhan, Y., & Hao, Z. (2025). Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Litsea cubeba Essential Oil Against Salmonella typhimurium. Plants, 14(9), 1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091343







