Impact of Fresh Leaf Elements on Flavor Components and Aroma Quality in Ancient Dancong Tea Gardens Across Varying Altitudes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of the Differences in Flavor Components of Fresh Leaves from Different Altitudes Dancong Ancient Tea Gardens
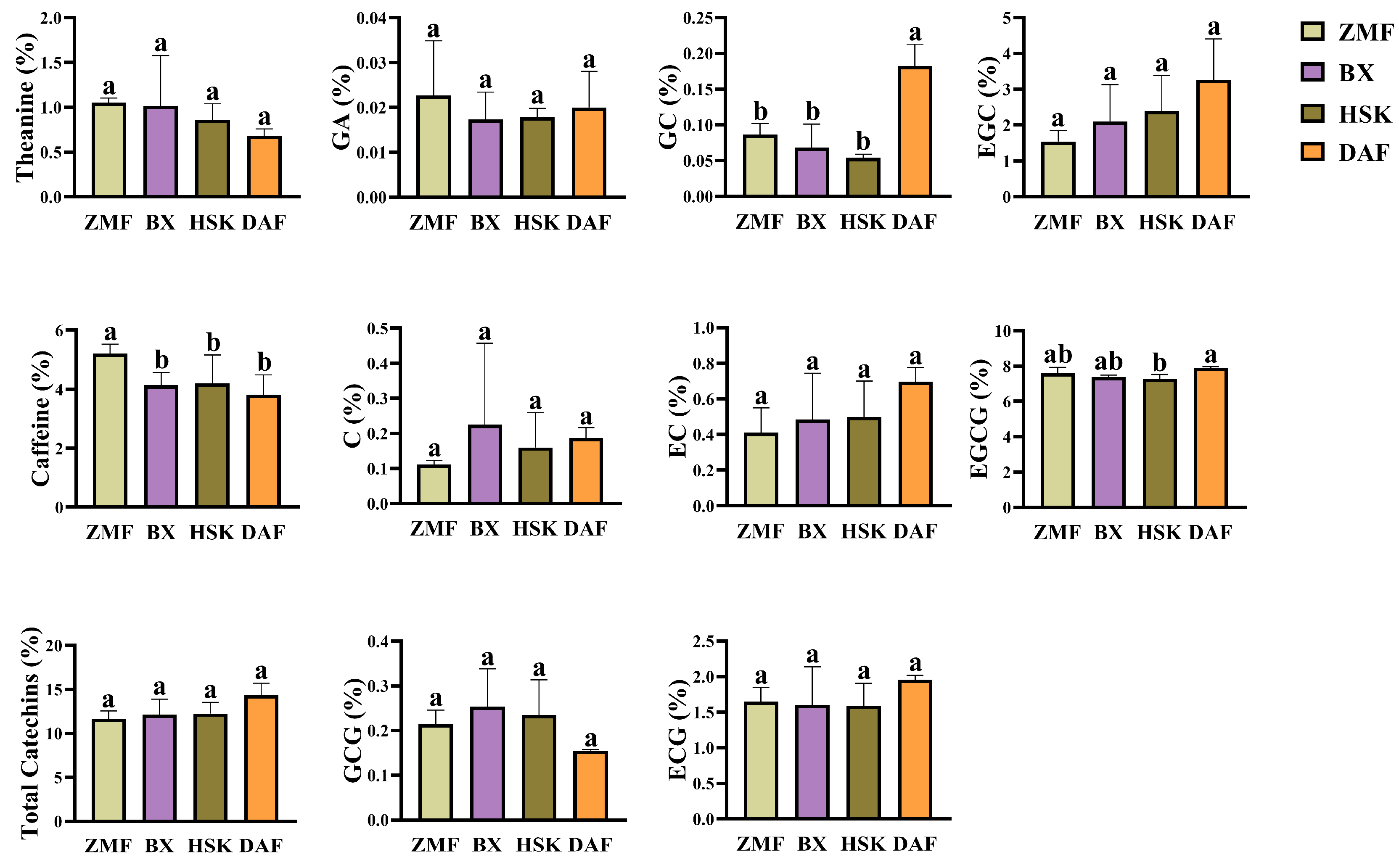
2.1.1. ZMF Fresh Leaves from Low-Altitude Dancong Ancient Tea Gardens Have a More Bitter Flavor
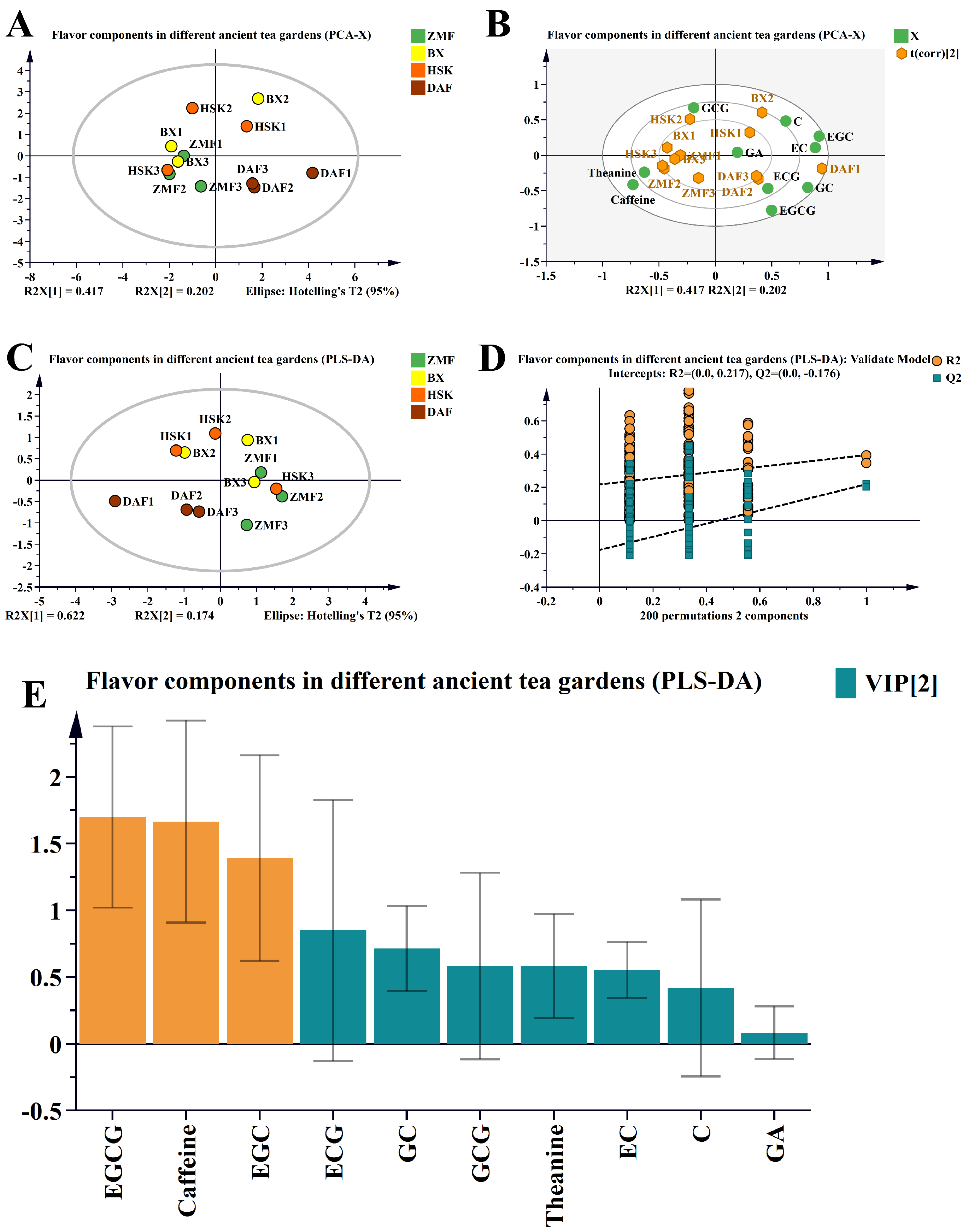
2.1.2. Principal Component Analysis of Non-Volatile Substances in Fresh Leaves of Different Ancient Tea Gardens
2.2. Differential Analysis of Aroma Compounds of Fresh Leaves of Different Altitudes Dancong Ancient Tea Gardens
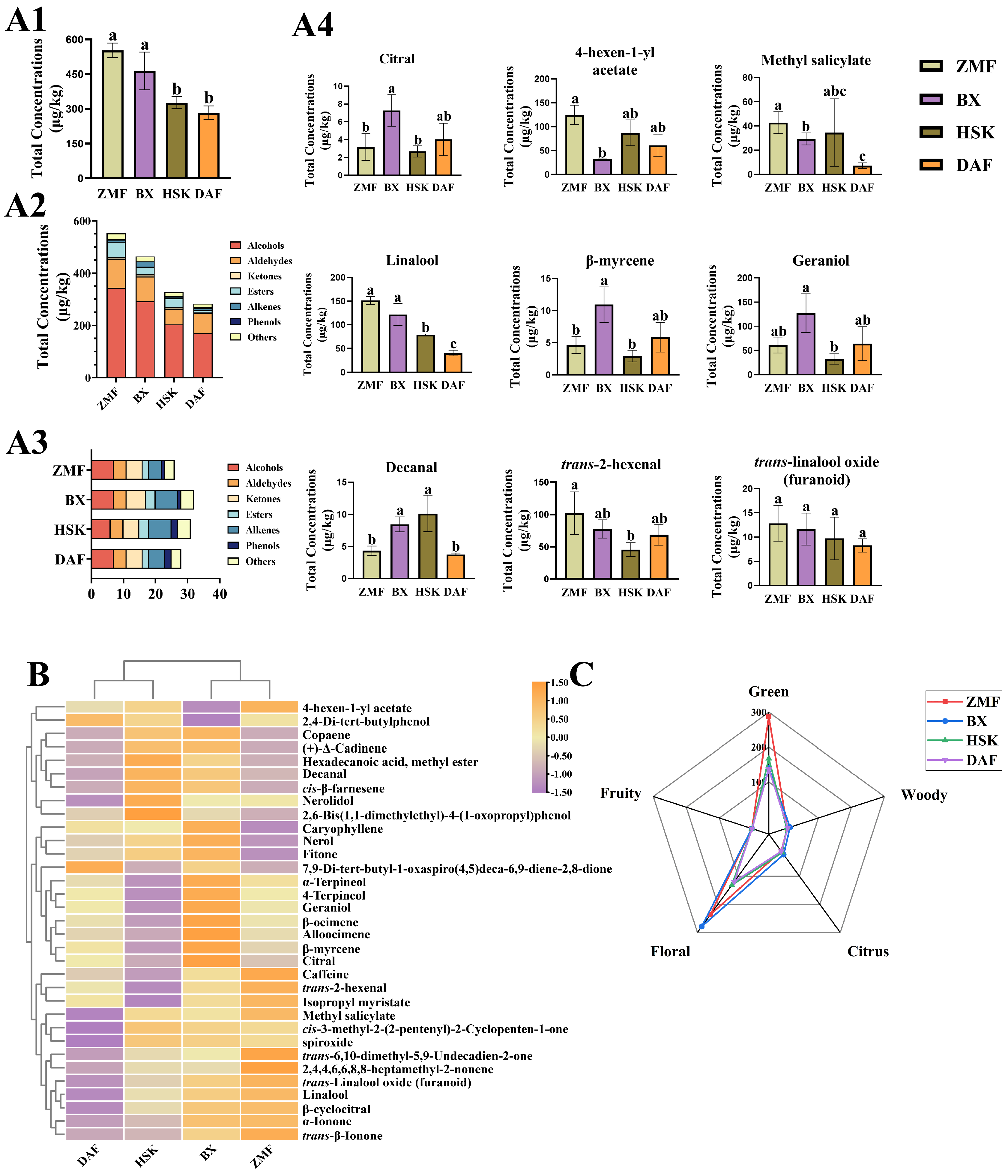
2.2.1. Low-Altitude ZMF Fresh Leave Have Highest Concentration Yet Least Variety of Aroma Compounds
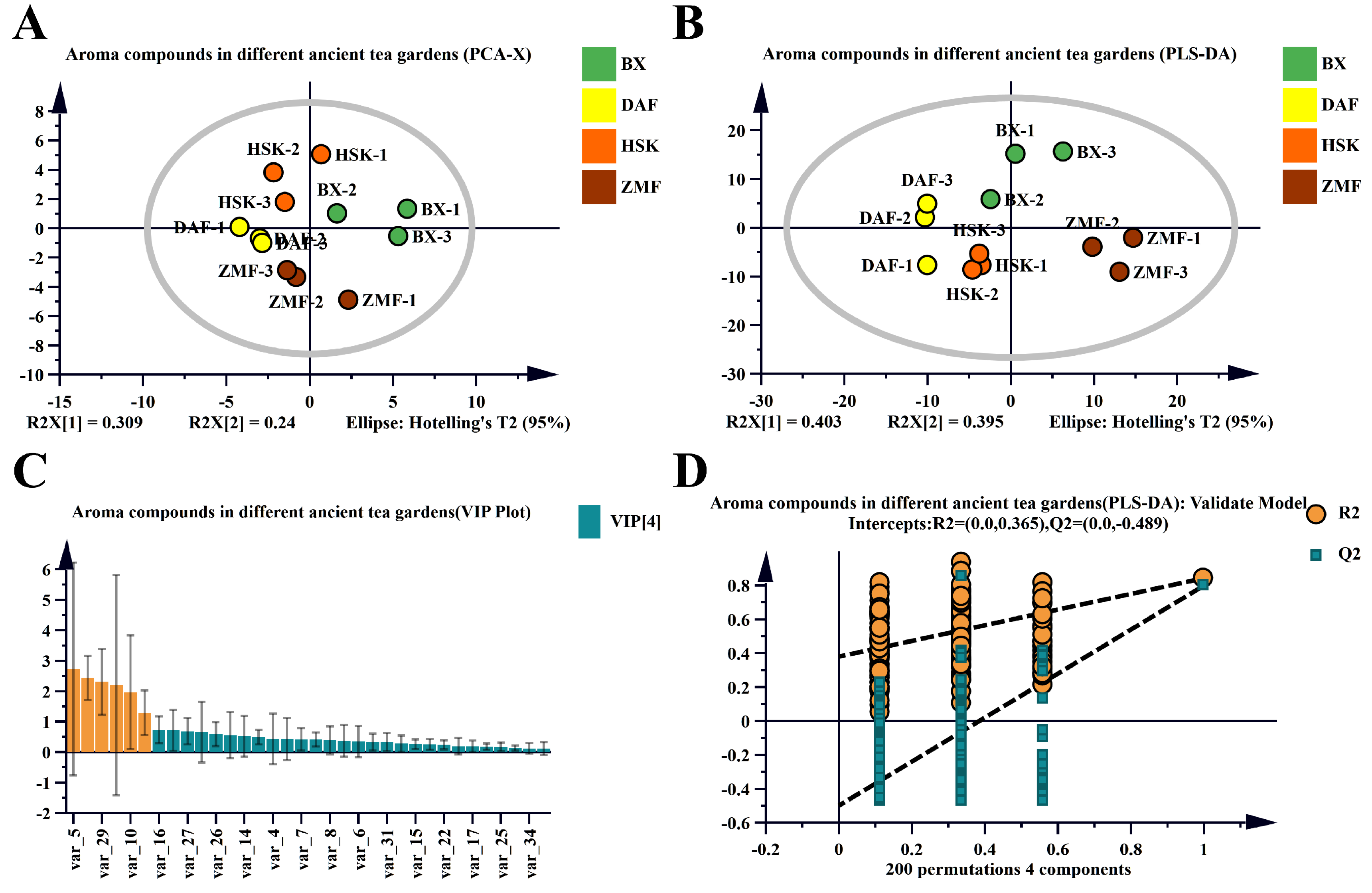
2.2.2. Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Volatile Compounds in Tea Fresh Leaves
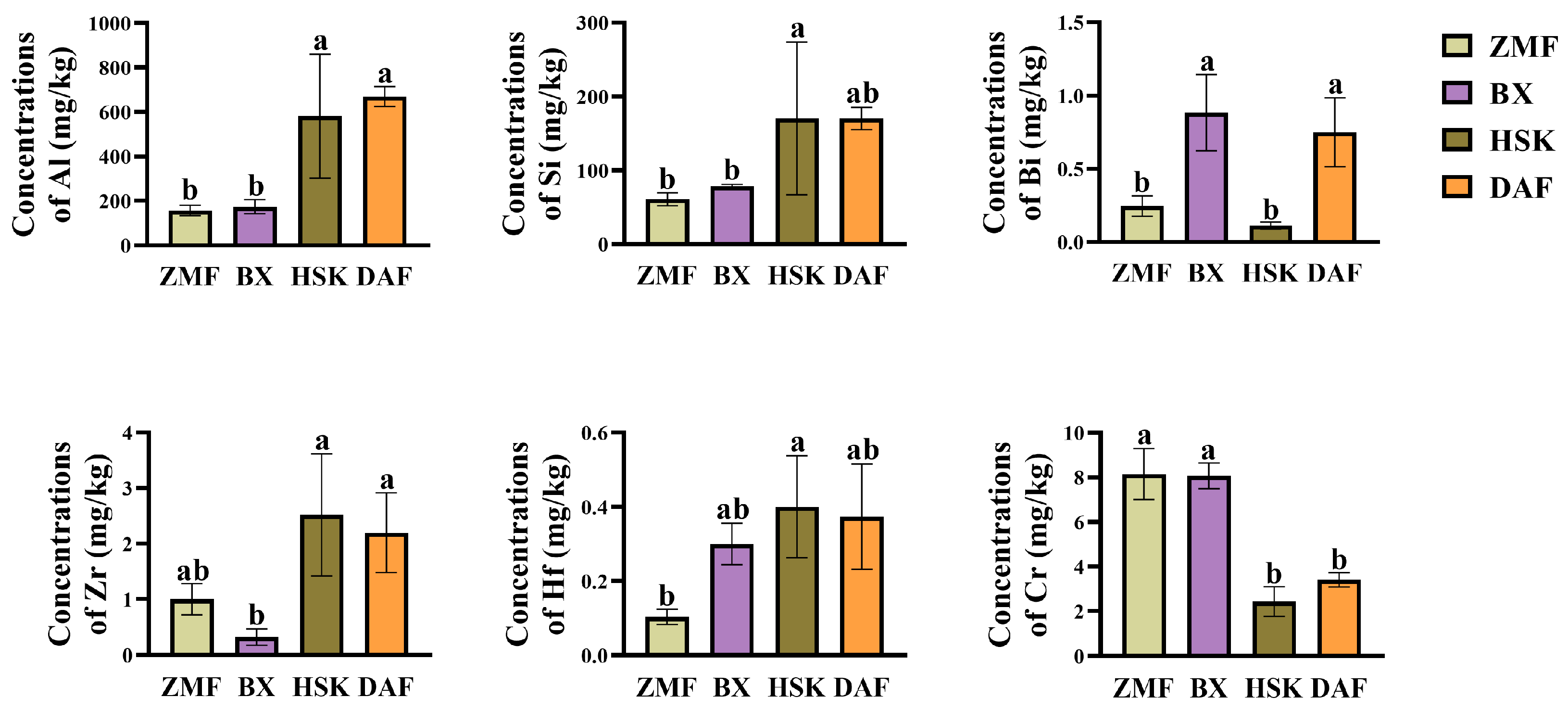
2.3. Analysis of Elemental Content of Fresh Leaves in Different Ancient Tea Gardens
2.3.1. Differences in Elemental Content of Fresh Leaves in Different Ancient Tea Gardens
2.3.2. Principal Component Analysis of Fresh Leaf Elements in Different Ancient Tea Gardens
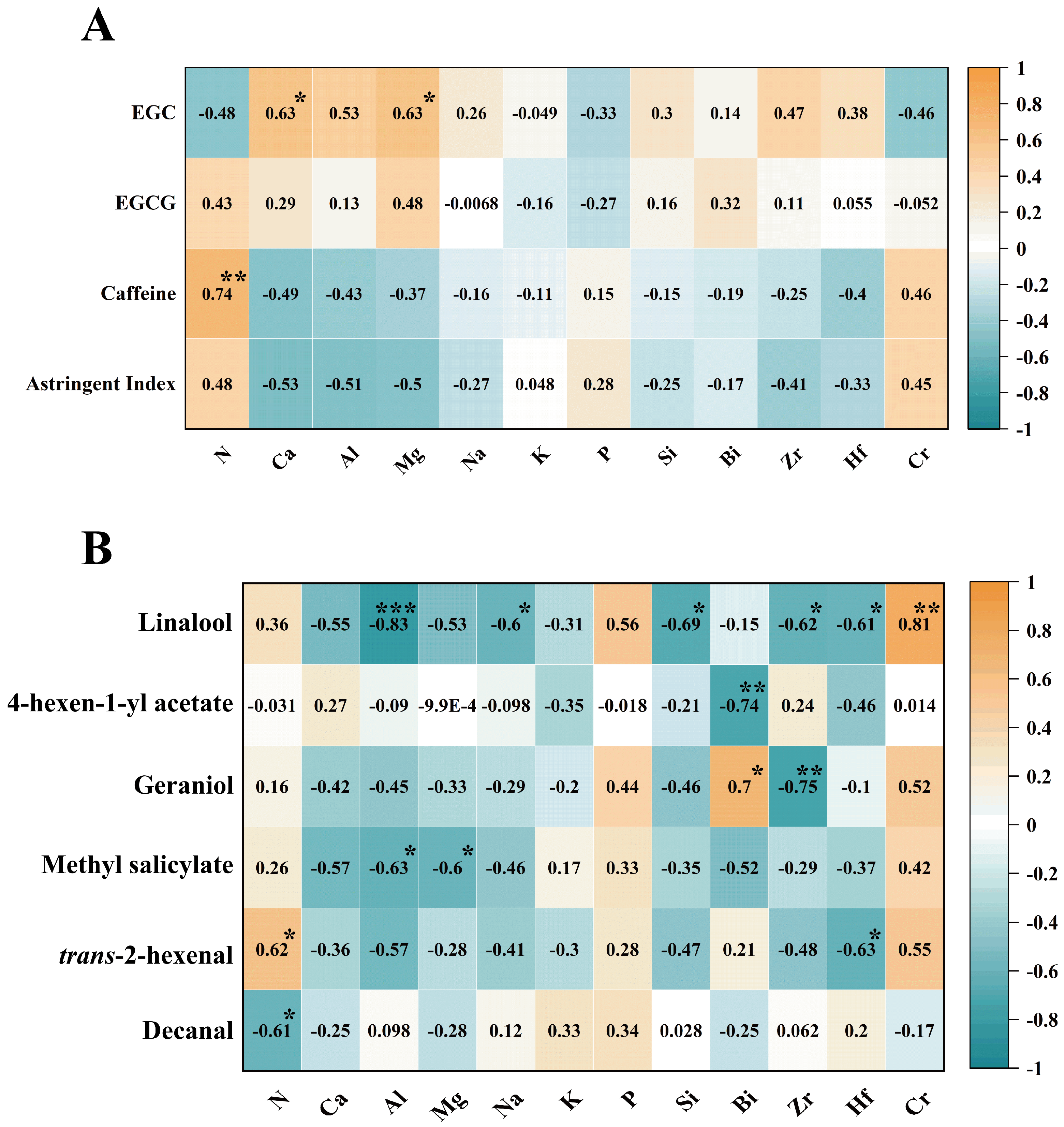
2.4. Correlation Analysis of Fresh Leaf Elements with Key Flavor Compounds and Potential Key Aroma Substances in Different Ancient Tea Gardens
2.4.1. Heat Map of Correlation Between Fresh Leaf Elements and Key Flavor Compounds in Different Ancient Tea Gardens
2.4.2. Heat Map of Correlation Between Fresh Leaf Elements and Key Aroma Compounds in Different Ancient Tea Gardens
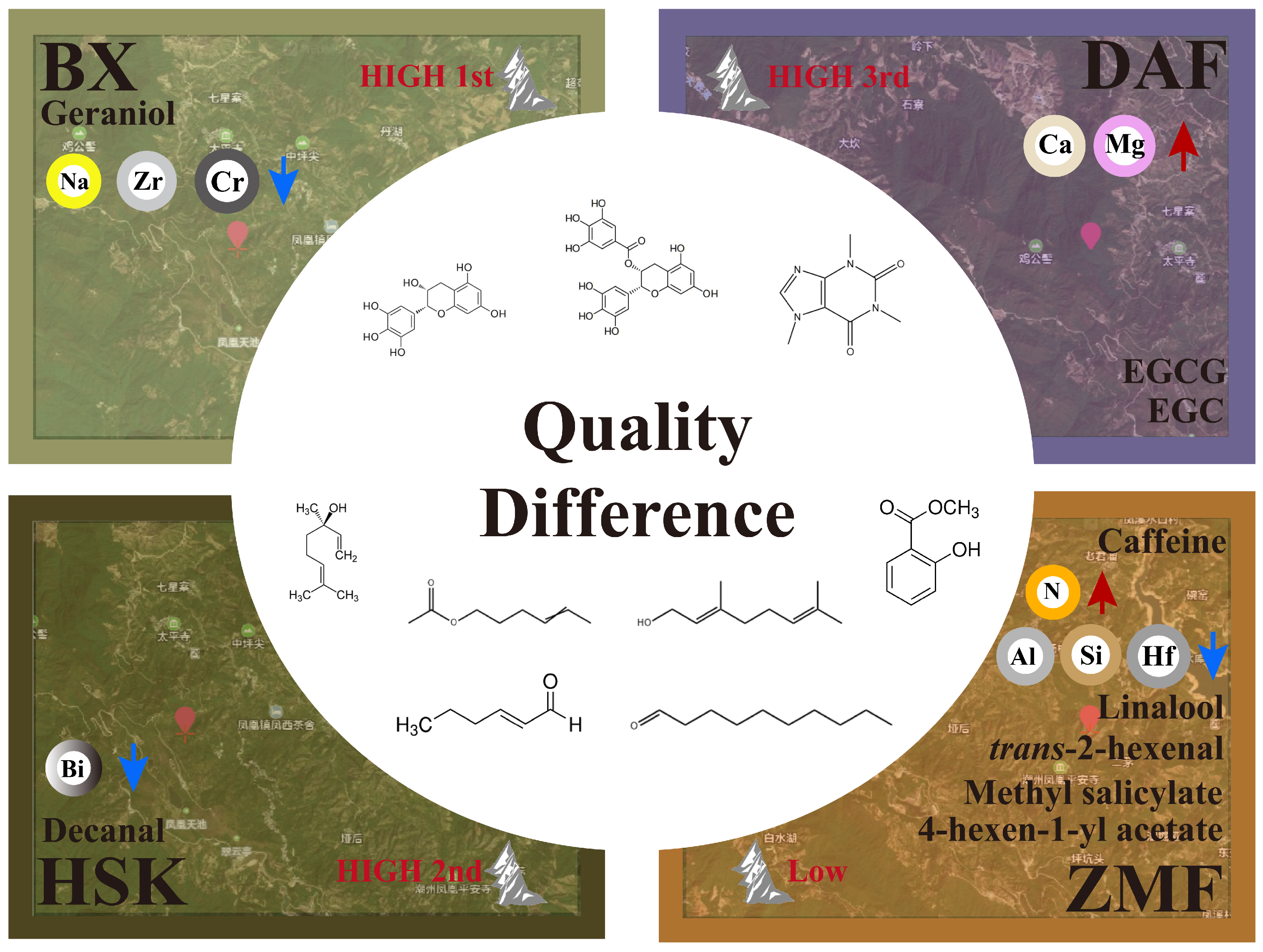
3. Discussion
3.1. Elements and Taste Compounds of Dancong Ancient Tea Gardens
3.2. Elements and Aroma Compounds of Dancong Ancient Tea Gardens
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Determination of the Contents of Tea Flavor Compounds
4.3. Determination of the Contents of Tea Volatiles Compounds
4.4. Calculation of Tea Astringency Index
4.5. Calculation of Odor Activity Thresholds (OAVs)
4.6. Determination of All-Element Content in Fresh Tea Leaves
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, H.; Yu, F.; Qin, L.; Zhang, N.; Cao, Q.; Schwab, W.; Li, D.; Song, C. Dynamic Change in Amino Acids, Catechins, Alkaloids, and Gallic Acid in Six Types of Tea Processed from the Same Batch of Fresh Tea (Camellia sinensis L.) Leaves. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 77, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.-W.; Cai, S.; Zhao, T.-S.; Li, M.; Tian, Y. Green Tea Derivative (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) Confers Protection against Ionizing Radiation-Induced Intestinal Epithelial Cell Death Both in Vitro and in Vivo. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 161, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Z.; Liao, J.; Chen, J.; Li, A.; Lin, M.; Liu, H.; Huang, W.; Sun, B.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Fresh Tea (Camellia sinensis Cv. Lingtou Dancong) Leaf Quality under Different Nitrogen Fertilization Regimes. Food Chem. 2024, 439, 138127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, X.; Xiong, B.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, D. Genome-Level Diversification of Eight Ancient Tea Populations in the Guizhou and Yunnan Regions Identifies Candidate Genes for Core Agronomic Traits. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, J.-J.; Wei, Y.; Deng, W.-W.; Wan, X.; Bao, G.-H.; Xie, Z.; Ling, T.-J.; Ning, J. Metabolomics Based on UHPLC-Orbitrap-MS and Global Natural Product Social Molecular Networking Reveals Effects of Time Scale and Environment of Storage on the Metabolites and Taste Quality of Raw Pu-Erh Tea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 12084–12093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Lan, Z.; Tao, Y.; Shi, M.; Yang, W.; Ren, Y.; Yang, T. Comprehensive evaluation of tea biochemical quality and soil environmental factors in ancient tea gardens. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2023, 51, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, N.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, D. Tea Plant β-1, 4-Glucanase Enhances the Propagation of Camellia tachangensis F. C. Zhang by Promoting Graft Wound Healing. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 331, 113156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhou, D.; Wan, R.; Wang, C.; Xie, J.; Ma, C.; Li, Y. HPLC and High-Throughput Sequencing Revealed Higher Tea-Leaves Quality, Soil Fertility and Microbial Community Diversity in Ancient Tea Plantations: Compared with Modern Tea Plantations. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Li, N.; Fu, Y.; Yu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Wu, J.-L.; Jiang, Z.-H. Deciphering Superior Quality of Pu-Erh Tea from Thousands of Years’ Old Trees Based on the Chemical Profile. Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-T.; Zeng, X.-Y.; Lin, X.-L.; Chen, D.-S.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.-J.; Yu, Z.-C.; Zhu, H. Exploring Aromatic Components Differences and Composition Regularity of 5 Kinds of These 4 Aroma Types Phoenix Dancong Tea Based on GC–MS. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaparakou, E.H.; Daferera, D.; Kanakis, C.D.; Skotti, E.; Kokotou, M.G.; Tarantilis, P.A. Chemical Composition of the Essential Oils of Three Popular Sideritis Species Cultivated in Greece Using GC-MS Analysis. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kfoury, N.; Morimoto, J.; Kern, A.; Scott, E.R.; Orians, C.M.; Ahmed, S.; Griffin, T.; Cash, S.B.; Stepp, J.R.; Xue, D.; et al. Striking Changes in Tea Metabolites Due to Elevational Effects. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Boorboori, M.R.; Xu, Y.; Lin, W. The Appearance of Volatile Aromas in Tieguanyin Tea with Different Elevations. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 4405–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yu, J.; Jin, S.; Chen, S.; Yue, C.; Wang, W.; Gao, S.; Cao, H.; Zheng, Y.; Gu, M.; et al. Genetic Basis of High Aroma and Stress Tolerance in the Oolong Tea Cultivar Genome. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Baldermann, S.; Watanabe, N. Recent Studies of the Volatile Compounds in Tea. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, P.; Chen, X.; Sun, Y.; Yue, C.; Ye, N. Transcriptome and Metabolite Profiling Reveal Novel Insights into Volatile Heterosis in the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis). Molecules 2019, 24, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-Y.; Burgos, A.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, D.; Ruan, J. Lipidomics Analysis Unravels the Effect of Nitrogen Fertilization on Lipid Metabolism in Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Tan, R.; Jiao, L.; Mao, Y. Application of Tea-Specific Fertilizer Combined with Organic Fertilizer Improves Aroma of Green Tea. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lin, S.; Chen, M.; Cheng, P.; Du, M.; Jia, X.; Ye, J.; Wang, H. Study on the Effect of Magnesium on Leaf Metabolites, Growth and Quality of Tea Tree. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1192151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongsheng, W.; Qihui, L.; Qian, T. Effect of Pb on Growth, Accumulation and Quality Component of Tea Plant. Procedia Eng. 2011, 18, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, H.; Han, Z.; Lei, X.; Chen, X.; Xiao, Y.; Njeri Ndombi, S.; Zhu, X.; Fang, W. Tea Quality Estimation Based on Multi-Source Information from Leaf and Soil Using Machine Learning Algorithm. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 100975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.; Yang, Z.; Huang, H.; Yang, F.; Zhu, L.; Han, D. Nitrogen Fertilization in Soil Affects Physiological Characteristics and Quality of Green Tea Leaves. Horts 2018, 53, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, L.; Cui, Y.; Li, J.; Tang, H.; Liu, J.; Tang, J. Soil Nutrient Deficiency Decreases the Postharvest Quality-Related Metabolite Contents of Tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze) Leaves. Food Chem. 2022, 377, 132003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, C.; Qian, J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Jia, Y.; Tang, J.; Zeng, L. Characterization of Key Odorants in Lingtou Dancong Oolong Tea and Their Differences Induced by Environmental Conditions from Different Altitudes. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ho, C.-T.; Wan, X.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Q.; Wen, Z. Changes of Volatile Compounds and Odor Profiles in Wuyi Rock Tea during Processing. Food Chem. 2021, 341, 128230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Chen, Y.; Feng, W.; Shen, S.; Wei, Y.; Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Deng, W.; Ning, J. Effects of Three Different Withering Treatments on the Aroma of White Tea. Foods 2022, 11, 2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.-P.; Feng, L.; Xu, Y.-Q.; Zheng, L.; Yin, P.; Ye, F.; Gui, A.-H.; Wang, S.-P.; Wang, X.-P.; Teng, J.; et al. Characterization of Stale Odor in Green Tea Formed during Storage: Unraveling Improvements Arising from Reprocessing by Baking. LWT 2023, 174, 114458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-W.; Li, H.; Liu, J.-X.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, J. Integrative Transcriptome, Proteome, and microRNA Analysis Reveals the Effects of Nitrogen Sufficiency and Deficiency Conditions on Theanine Metabolism in the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis). Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oades, J.M. Soil Organic Matter and Structural Stability: Mechanisms and Implications for Management. Plant Soil. 1984, 76, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, T.; Zheng, Z. Effects of Tea Plantation Age on Soil Aggregate-Associated C- and N-Cycling Enzyme Activities in the Hilly Areas of Western Sichuan, China. CATENA 2018, 171, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Lin, M.; Liao, J.; Li, A.; Tsewang, W.; Chen, X.; Sun, B.; Liu, S.; Zheng, P. Effects of Potassium Deficiency on the Growth of Tea (Camelia sinensis) and Strategies for Optimizing Potassium Levels in Soil: A Critical Review. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, Y.; Liao, Y.; Tang, J.; Dong, F.; Zeng, L. Effects of Temperature and Light on Quality-Related Metabolites in Tea [Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze] Leaves. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Z.; Liao, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, P.; Sun, B.; Li, A.; Pan, Y.; Liu, H.; Zheng, P.; Liu, S. The Cultivar Effect on the Taste and Aroma Substances of Hakka Stir-Fried Green Tea from Guangdong. Foods 2023, 12, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Gong, S. Research progress on tea aroma. J. Tea 2012, 38, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Zhao, M.; Jing, T.; Wang, J.; Lu, M.; Pan, Y.; Du, W.; Zhao, C.; Bao, Z.; Zhao, W.; et al. (Z)-3-Hexenol Integrates Drought and Cold Stress Signaling by Activating Abscisic Acid Glucosylation in Tea Plants. Plant Physiol. 2023, 193, 1491–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Bao, D.; Wang, N.; Sun, J.; Huang, F.; Yang, M.; et al. Plant-derived Monoterpene S -linalool and Β-ocimene Generated by Cs LIS and Cs OCS-SCZ Are Key Chemical Cues for Attracting Parasitoid Wasps for Suppressing Ectropis Obliqua Infestation in Camellia sinensis L. Plant Cell Environ. 2024, 47, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, L.; Cai, X.; Li, X.; Bian, L.; Luo, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xin, Z. (E)-Nerolidol Is a Volatile Signal That Induces Defenses against Insects and Pathogens in Tea Plants. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, R. Mining of Genetic Locus of Phenylethyl Alcohol Primrose Glycoside Abundance in Tea Plants. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2024, 51, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhou, C. Attracting Effect of Volatile Infochemicals from Tea Shoots and Flowers on Winged Tea Aphids. J. Tea Sci. 2004, 24, 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Pan, C.; Han, B. Changes in Volatiles of Tea Shoots Damaged by Tea Green Leafhoppers and Their Attraction to Schizophragma parvula Ogloblin. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2016, 32, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Ma, L.; Shi, Y. Potassium Management in Tea Plantations: Its Uptake by Field Plants, Status in Soils, and Efficacy on Yields and Quality of Teas in China. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenk. 2013, 176, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhou, J.; Pan, W.; Sun, T.; Liu, M.; Tang, R.; Li, Z.; Ma, Q.; Wu, L. Effects of Combined Application of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Fertilizers on Tea (Camellia sinensis) Growth and Fungal Community. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 181, 104661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Xu, B.; Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, W.; Wan, S.; Tan, H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Synthetic Nitrogen Fertilizers Alter the Soil Chemistry, Production and Quality of Tea. A Meta-Analysis. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 38, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Jin, J.; Zhang, N.; Lei, L.; Gao, T.; Jing, T.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; et al. Induction of Priming by Cold Stress via Inducible Volatile Cues in Neighboring Tea Plants. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Yu, Z.; Chen, J.; Zheng, P.; Sun, B.; Guo, J.; Liu, S. The Physiology of Postharvest Tea (Camellia sinensis) Leaves, According to Metabolic Phenotypes and Gene Expression Analysis. Molecules 2022, 27, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Cai, J.; Zheng, P.; Yuan, Y.; Tsewang, W.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, X.; Liao, J.; Sun, B.; Liu, S. Quantitatively Unravelling the Impact of High Altitude on Oolong Tea Flavor from Camellia sinensis Grown on the Plateaus of Tibet. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Han, Q.; Dong, G.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Lei, S.; Liu, Y. Quality Assessment of Rose Tea with Different Drying Methods Based on Physicochemical Properties, HS–SPME–GC–MS, and GC–IMS. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 1378–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Liu, Z. Mathematical modeling of the chemical substance of summer tea bitterness and astringency. J. Tea Sci. 1987, 7, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shen, S.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Hua, J.; Yuan, H. Novel Insight into the Effect of Fermentation Time on Quality of Yunnan Congou Black Tea. LWT 2022, 155, 112939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Schwab, W.; Ho, C.-T.; Song, C.; Wan, X. Characterization of the Aroma Profiles of Oolong Tea Made from Three Tea Cultivars by Both GC–MS and GC-IMS. Food Chem. 2022, 376, 131933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Zhang, L.; Granvogl, M.; Ho, C.; Wan, X. Flavor of Tea (Camellia Sinensis): A Review on Odorants and Analytical Techniques. Comp. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3867–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, J.; Ma, C.; Huang, Y. GC–MS and LC-MS/MS Metabolomics Revealed Dynamic Changes of Volatile and Non-Volatile Compounds during Withering Process of Black Tea. Food Chem. 2023, 410, 135396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ho, C.-T.; Schwab, W.; Wan, X. Aroma Profiles of Green Tea Made with Fresh Tea Leaves Plucked in Summer. Food Chem. 2021, 363, 130328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-Q.; Ma, W.-J.; Shi, J.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Lv, H.-P. Characterization of the Key Aroma Compounds in Longjing Tea Using Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction (SBSE) Combined with Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS), Gas Chromatography-Olfactometry (GC-O), Odor Activity Value (OAV), and Aroma Recombination. Food Res. Int. 2020, 130, 108908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ho, C.-T.; Schwab, W.; Wan, X. Effect of the Roasting Degree on Flavor Quality of Large-Leaf Yellow Tea. Food Chem. 2021, 347, 129016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cao, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Lai, X.; Sun, L.; Chen, R.; Wen, S.; Sun, S.; Lai, Z. HS-SPME and GC/MS Volatile Component Analysis of Yinghong No. 9 Dark Tea during the Pile Fermentation Process. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Feng, J.; Chen, Q.; Lin, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, J.; Tan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. Comparative Volatiles Profiling in Milk-Flavored White Tea and Traditional White Tea Shoumei via HS-SPME-GC-TOFMS and OAV Analyses. Food Chem. X 2023, 18, 100710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, M.; Xiao, Y. Effects of Solid-State Fermentation with Bacillus Subtilis LK-1 on the Volatile Profile, Catechins Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Dark Teas. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| EGCG | GCG | ECG | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZMF | 0.65 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.82 |
| BX | 0.61 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.76 |
| HSK | 0.60 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.75 |
| DAF | 0.55 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.70 |
| Var. No. | Volatile Compounds | Odor | VIP 1 | OT 2 (μg/kg) | OAVs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BX | DAF | HSK | ZMF | |||||
| var_5 | Linalool | Floral | 2.73 | 0.22 a | 554.45 | 184.14 | 359.21 | 687.78 |
| var_1 | trans-2-hexenal | Green | 2.44 | 17 b | 4.56 | 4.01 | 2.67 | 6.00 |
| var_29 | 4-hexen-1-yl acetate | Green | 2.31 | 100 b | 0.32 | 0.61 | 0.87 | 1.25 |
| var_13 | Geraniol | Floral | 2.20 | 1.1 c | 115.72 | 58.47 | 29.43 | 55.54 |
| var_10 | Methyl salicylate | Green | 1.96 | 40 a | 0.73 | 0.18 | 0.86 | 1.48 |
| var_11 | Decanal | Citrus | 1.29 | 0.3 d | 28.11 | 12.44 | 33.74 | 14.38 |
| Location | ID | Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) | Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zimao | ZMF | 116.68° E | 23.95° N | 578.13 |
| Baixiang | BX | 116.65° E | 23.96° N | 1131.63 |
| Xialiao | HSK | 116.65° E | 23.96° N | 1066.77 |
| Da′an | DAF | 116.64° E | 23.97° N | 965.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, X.; Huang, W.; Qiu, Z.; Yao, J.; Zhao, H.; Khan, W.; Sun, B.; Liu, S.; Zheng, P. Impact of Fresh Leaf Elements on Flavor Components and Aroma Quality in Ancient Dancong Tea Gardens Across Varying Altitudes. Plants 2025, 14, 1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091339
Lin X, Huang W, Qiu Z, Yao J, Zhao H, Khan W, Sun B, Liu S, Zheng P. Impact of Fresh Leaf Elements on Flavor Components and Aroma Quality in Ancient Dancong Tea Gardens Across Varying Altitudes. Plants. 2025; 14(9):1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091339
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Xinyuan, Wei Huang, Zihao Qiu, Jiyuan Yao, Hongbo Zhao, Waqar Khan, Binmei Sun, Shaoqun Liu, and Peng Zheng. 2025. "Impact of Fresh Leaf Elements on Flavor Components and Aroma Quality in Ancient Dancong Tea Gardens Across Varying Altitudes" Plants 14, no. 9: 1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091339
APA StyleLin, X., Huang, W., Qiu, Z., Yao, J., Zhao, H., Khan, W., Sun, B., Liu, S., & Zheng, P. (2025). Impact of Fresh Leaf Elements on Flavor Components and Aroma Quality in Ancient Dancong Tea Gardens Across Varying Altitudes. Plants, 14(9), 1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091339







