A Systematic Preparation of Liposomes with Yerba Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) Extract
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
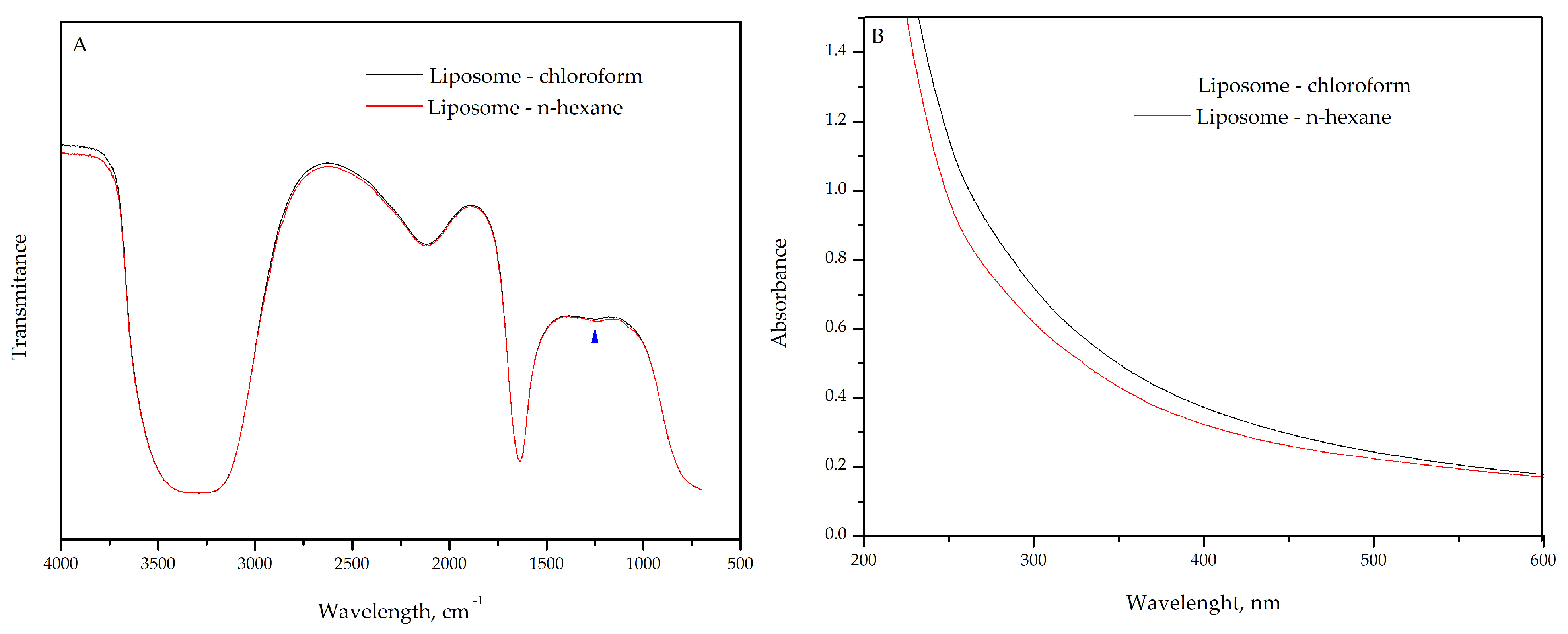
2.1. FTIR and UV–Vis Characterization of Liposome for Solvent Selection
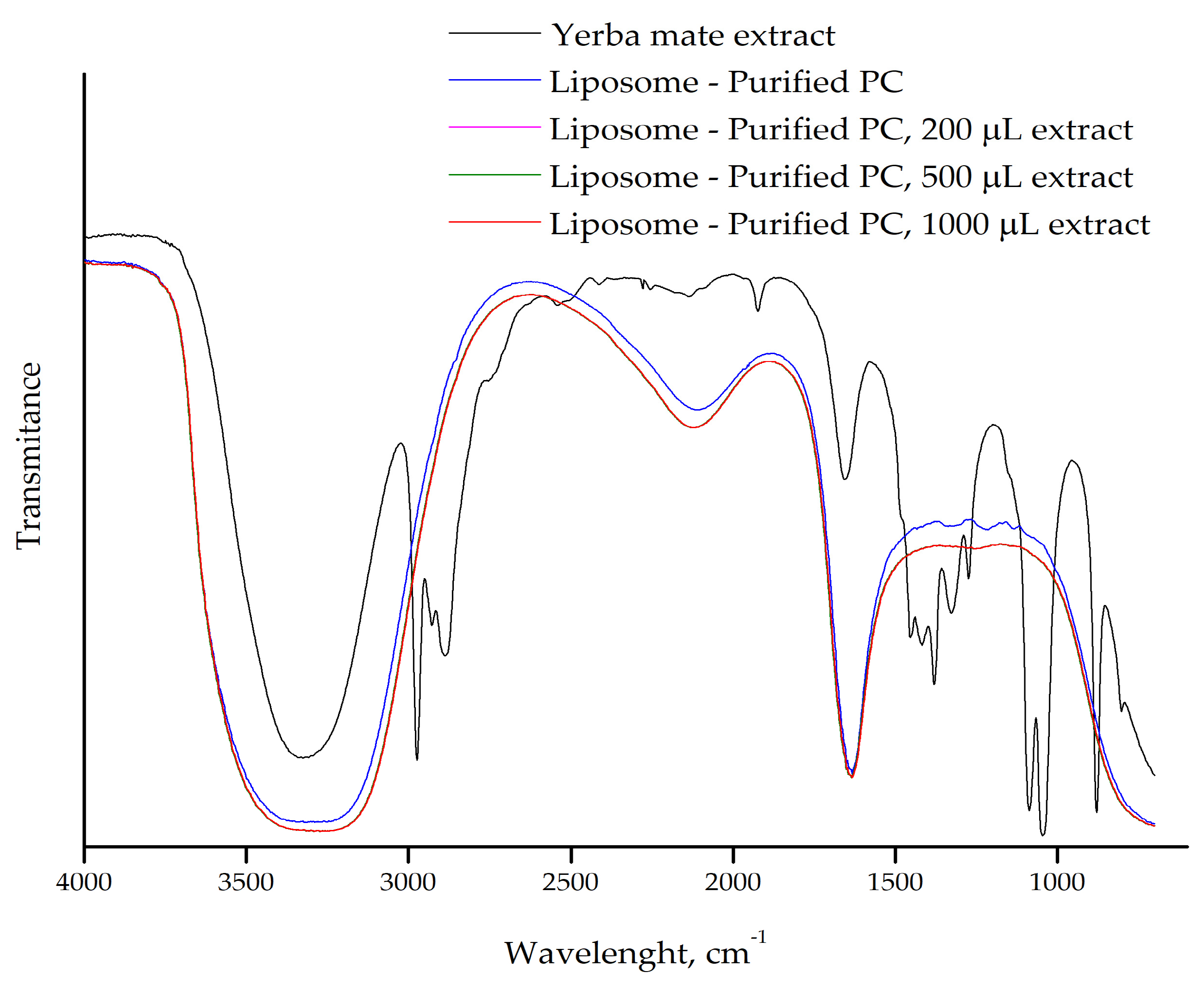
2.2. FTIR of Liposomes With or Without Yerba Mate Extract
2.3. UV–Vis of Liposomes With or Without Yerba Mate Extrac
2.4. Potential Zeta (PZ) and Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials, Yerba Mate Extract, and Phosphatidylcholine (PC) Preparation
3.2. Lipossome Preparation
3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.4. UV–Vis Spectroscopy
3.5. Potential Zeta (PZ) and Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| PC | Phosphatidylcholine |
| PDI | Polydispersity Index |
| PZ | Zeta Potential |
References
- Nsairat, H.; Khater, D.; Sayed, U.; Odeh, F.; Al Bawab, A.; Alshaer, W. Liposomes: Structure, Composition, Types, and Clinical Applications. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bot, F.; Cossuta, D.; O’Mahony, J.A. Inter-Relationships between Composition, Physicochemical Properties and Functionality of Lecithin Ingredients. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Oomah, B.D.; Akoetey, W.; Zhang, Y.; Daneshfozoun, H.; Hosseinian, F. Liposomes as Sustainable Delivery Systems in Food, Cosmetic, and Pharmaceutical Applications. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2025, 102, 547–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, N.; Afzaal, M.; Saeed, F.; Shah, Y.A.; Faisal, Z.; Asghar, A.; Ateeq, H.; Nayik, G.A.; Wani, S.H.; Hussain, M.; et al. Liposomes: A Promising Delivery System for Active Ingredients in Food and Nutrition. Int. J. Food Prop. 2023, 26, 2476–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ye, A.; Han, F.; Han, J. Advances and Challenges in Liposome Digestion: Surface Interaction, Biological Fate, and GIT Modeling. Adv. Coll. Int. Sci. 2019, 263, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Haldorai, Y.; Hwang, S.K.; Bajpai, V.K.; Huh, Y.S.; Han, Y.-K. Current Demands for Food-Approved Liposome Nanoparticles in Food and Safety Sector. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado Martin, J.G.; Porto, E.; De Alencar, S.M.; Da Glória, E.M.; Corrêa, C.B.; Ribeiro Cabral, I.S. Antimicrobial Activity of Yerba Mate (Ilex Paraguariensis St. Hil.) against Food Pathogens. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2013, 45, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, H.R.; Puranik, P.K. Chlorogenic Acid-Optimized Nanophytovesicles: A Novel Approach for Enhanced Permeability and Oral Bioavailability. Futur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, V.Z.; Pilatti-Riccio, D.; Paim, B.T.; Costa, L.D.V.; Amorin, S.G.D.; Meinhart, A.D. Ilex paraguariensis—Green Gold from South America. In Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of Medicinal Plants; Pullaiah, T., Ed.; Apple Academic Press: Palm Bay, FL, USA, 2023; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos, D.F.; Alves, V.; Costa, E.; Martins, A.; Vieira, A.F.F.; Dos Santos, G.H.F.; Francisco, C.T.D.P.; Pinto, V.Z. Yerba Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) Processing and Extraction: Retention of Bioactive Compounds. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2023, 78, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilatti-Riccio, D.; Dos Santos, D.F.; Meinhart, A.D.; Knapp, M.A.; Hackbart, H.C.D.S.; Pinto, V.Z. Impact of the Use of Saccharides in the Encapsulation of Ilex paraguariensis Extract. Food Res. Int. 2019, 125, 108600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambero, A.; Ribeiro, M. The Positive Effects of Yerba Maté (Ilex paraguariensis) in Obesity. Nutrients 2015, 7, 730–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paim, B.T.; Rosas, A.L.G.; Lorini, A.; Pinto, V.Z.; Peres, G.L.; Zavareze, E.D.R.; Galli, V.; Hackbart, H.C.D.S.; Kringel, D.H.; Meinhart, A.D. Exploring the Potential of Ilex paraguariensis Coproduct: High Concentration of Chlorogenic Acids and Enhanced Thermal Stability. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 3, 100524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paim, B.T.; Jansen-Alves, C.; Rosas, A.L.G.; De Albuquerque Sousa, T.C.; Massaut, Y.V.B.; Alves, V.; Dos Santos, G.H.F.; Deon, V.G.; Pinto, V.Z.; Meinhart, A.D. Does the Encapsulation of Chlorogenic Acids from Ilex paraguariensis Co-Product by Spray-Drying Increase Their Stability? Food Biophys. 2024, 19, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, T.; Nunes, A.; Moreira, B.R.; Maraschin, M. Yerba Mate (Ilex paraguariensis A. St.-Hil.) for New Therapeutic and Nutraceutical Interventions: A Review of Patents Issued in the Last 20 Years (2000–2020). Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 527–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, R.T.; Da Rosa, J.L.; Vendruscolo, R.G.; Cichoski, A.J.; Meinhart, A.D.; Lorini, A.; Paim, B.T.; Galli, V.; Robalo, S.S.; Dos Santos, B.A.; et al. Lipid Oxidation and Sensory Characterization of Omega-3 Rich Buffalo Burgers Enriched with Chlorogenic Acids from the Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) Tree Harvesting Residues. Meat Sci. 2021, 179, 108534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Sun, C.; Yuan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wan, J.; Firempong, C.K.; Omari-Siaw, E.; Xu, Y.; Pu, Z.; Yu, J.; et al. Enhanced Oral Bioavailability and in Vivo Antioxidant Activity of Chlorogenic Acid via Liposomal Formulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 501, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Majhi, S.; Saha, B.P.; Mukherjee, P.K. Chlorogenic Acid–Phospholipid Complex Improve Protection against UVA Induced Oxidative Stress. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2014, 130, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human, C.; Aucamp, M.; De Beer, D.; Van Der Rijst, M.; Joubert, E. Food-grade Phytosome Vesicles for Nanoencapsulation of Labile C-glucosylated Xanthones and Dihydrochalcones Present in a Plant Extract Matrix—Effect of Process Conditions and Stability Assessment. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 8093–8111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutt, Y.; Pandey, R.P.; Dutt, M.; Gupta, A.; Vibhuti, A.; Raj, V.S.; Chang, C.-M.; Priyadarshini, A. Liposomes and Phytosomes: Nanocarrier Systems and Their Applications for the Delivery of Phytoconstituents. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 491, 215251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertins, O.; Sebben, M.; Henrique Schneider, P.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Silveira, N.P.D. Caracterização da pureza de fosfatidilcolina da soja através de RMN de 1H e de 31P. Quím. Nova 2008, 31, 1856–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendawy, O.M.; Al-Sanea, M.M.; Elbargisy, R.M.; Rahman, H.U.; Gomaa, H.A.M.; Mohamed, A.A.B.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Kassem, A.M.; Elmowafy, M. Development of Olive Oil Containing Phytosomal Nanocomplex for Improving Skin Delivery of Quercetin: Formulation Design Optimization, In Vitro and Ex Vivo Appraisals. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallan, S.; Sguizzato, M.; Drechsler, M.; Mariani, P.; Montesi, L.; Cortesi, R.; Björklund, S.; Ruzgas, T.; Esposito, E. The Potential of Caffeic Acid Lipid Nanoparticulate Systems for Skin Application: In Vitro Assays to Assess Delivery and Antioxidant Effect. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohle, W.; Gauger, D.R.; Fritzsche, H.; Rattay, B.; Selle, C.; Binder, H.; Böhlig, H. FTIR-Spectroscopic Characterization of Phosphocholine-Headgroup Model Compounds. J. Mol. Struct. 2001, 563–564, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, H.; Zschörnig, O. The Effect of Metal Cations on the Phase Behavior and Hydration Characteristics of Phospholipid Membranes. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2002, 115, 39–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genova, J.; Petrov, M.; Bivas, I.; Rafailov, P.; Naradikian, H.; Katranchev, B. Fourier-Transform Infrared and Raman Characterization of Bilayer Membranes of the Phospholipid SOPC and Its Mixtures with Cholesterol. Coll. Surf. A 2018, 557, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheletto, Y.M.S.; Da Silveira, N.P.; Barboza, D.M.; Dos Santos, M.C.; De Lima, V.R.; Giacomelli, F.C.; Martinez, J.C.V.; Frizon, T.E.A.; Bó, A.G.D. Investigation of Self-Association between New Glycosurfactant N-Acetyl-β-d-Glucosaminyl-PEG-Docosanate and Soybean Phosphatidylcholine into Vesicles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 467, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugster, R.; Luciani, P. Liposomes: Bridging the Gap from Lab to Pharmaceuticals. Curr. Opin. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2025, 75, 101875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Deng, X.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J. Sustained Release of Chlorogenic Acid by Co-Encapsulation of Sodium Alginate Binding to the Northern Pike (Esox lucius) Liver Ferritin. Food Chem. 2023, 429, 136924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, K.; Leneweit, G.; Nirschl, H. How to Achieve High Encapsulation Efficiencies for Macromolecular and Sensitive APIs in Liposomes. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.C.; Crist, R.M.; Clogston, J.D.; McNeil, S.E. Zeta Potential: A Case Study of Cationic, Anionic, and Neutral Liposomes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 5779–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athirojthanakij, W.; Rashidinejad, A. Delivery of Catechins from Green Tea Waste in Single- and Double-Layer Liposomes via Their Incorporation into a Functional Green Kiwifruit Juice. Molecules 2023, 28, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Liu, S.; Dai, Z.; Jiang, C.; Li, W. Polydiacetylene Vesicles as a Novel Drug Sustained-Release System. Colloids Surf. B 2010, 76, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Ortega, R.; Šturm, L.; Skrt, M.; Di Mattia, C.D.; Pittia, P.; Poklar Ulrih, N. Liposomal Encapsulation of Oleuropein and an Olive Leaf Extract: Molecular Interactions, Antioxidant Effects and Applications in Model Food Systems. Food Biophys. 2021, 16, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Samples | PZ (mV) | Diameter (nm) 1 | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liposome pure PC | −46.8 ± 1.8 | 625.1 ± 15.1 | 0.434 |
| Liposome purified PC | −67.5 ± 0.9 | 690.0 ± 35.4 | 0.657 |
| Liposome pure PC, yerba mate extract | −51.9 ± 3.2 | 440.5 ± 22.3 | 0.660 |
| Liposome purified PC, yerba mate extract | −47.5 ± 0.5 | 518.6 ± 16.0 | 0.589 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Micheletto, Y.M.S.; Jesus, B.V.d.; Peres, G.L.; Pinto, V.Z. A Systematic Preparation of Liposomes with Yerba Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) Extract. Plants 2025, 14, 1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091325
Micheletto YMS, Jesus BVd, Peres GL, Pinto VZ. A Systematic Preparation of Liposomes with Yerba Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) Extract. Plants. 2025; 14(9):1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091325
Chicago/Turabian StyleMicheletto, Yasmine Miguel Serafini, Brenda Vieira de Jesus, Gisele Louro Peres, and Vânia Zanella Pinto. 2025. "A Systematic Preparation of Liposomes with Yerba Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) Extract" Plants 14, no. 9: 1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091325
APA StyleMicheletto, Y. M. S., Jesus, B. V. d., Peres, G. L., & Pinto, V. Z. (2025). A Systematic Preparation of Liposomes with Yerba Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) Extract. Plants, 14(9), 1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091325






