Effect of Elaeagnus angustifolia Linn. on the Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community Structure of Inter-Rhizosphere Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Area and Cultivation of Test Materials
2.2. Test Methods
2.3. Soil DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.4. Data Processing
3. Results
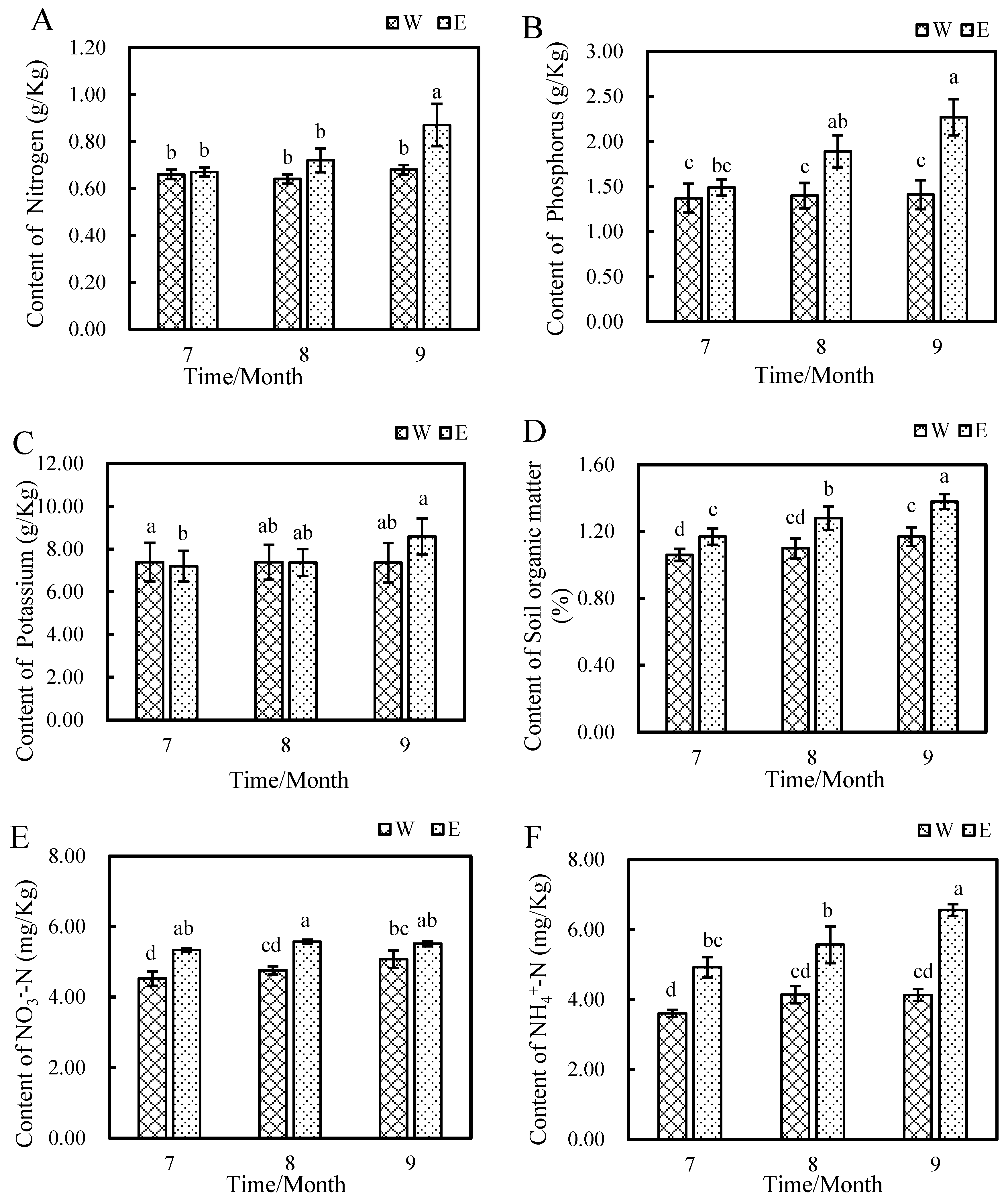
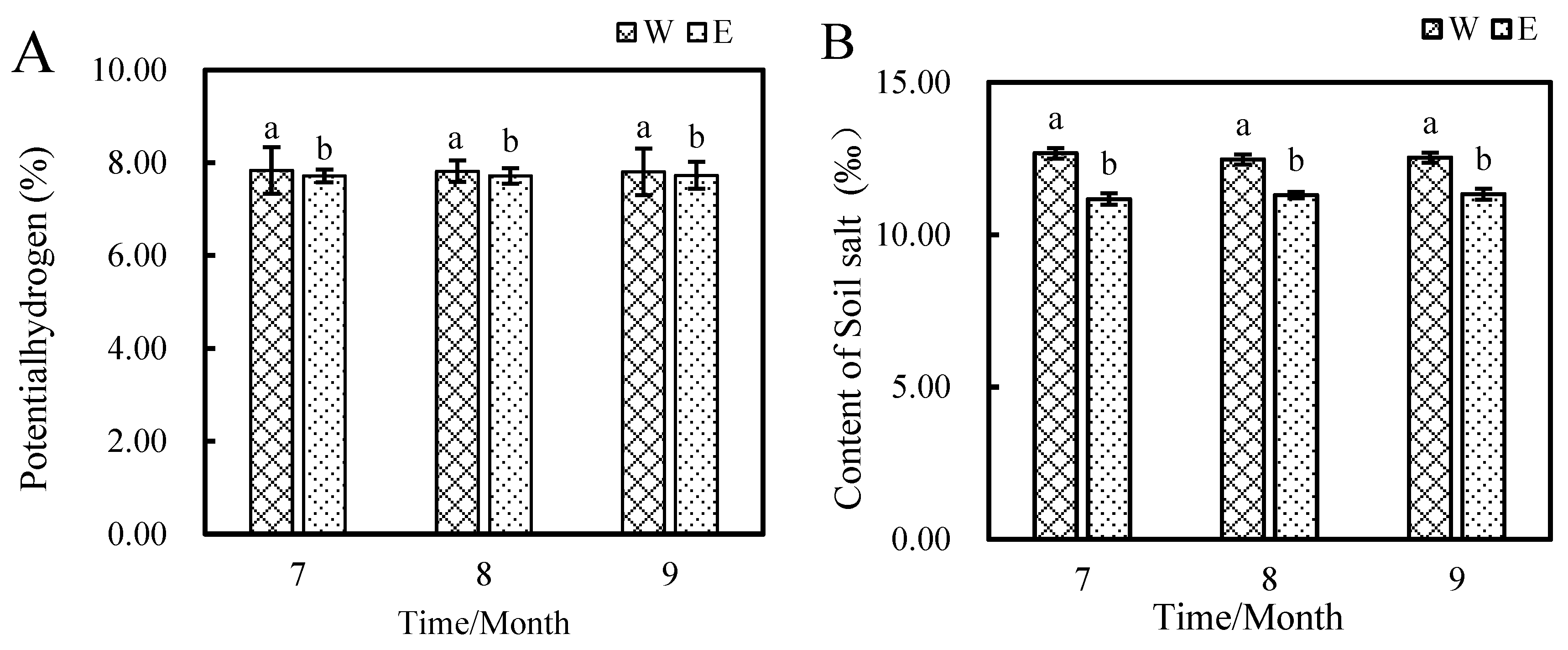
3.1. Effect of E. angustifolia L. on Soil Physicochemical Properties
3.1.1. Effect of E. angustifolia L. on Soil Nutrients
3.1.2. Effect of E. angustifolia L. on Soil Salinity and pH
3.1.3. Effect of E. angustifolia L. on Soil Enzyme Activities
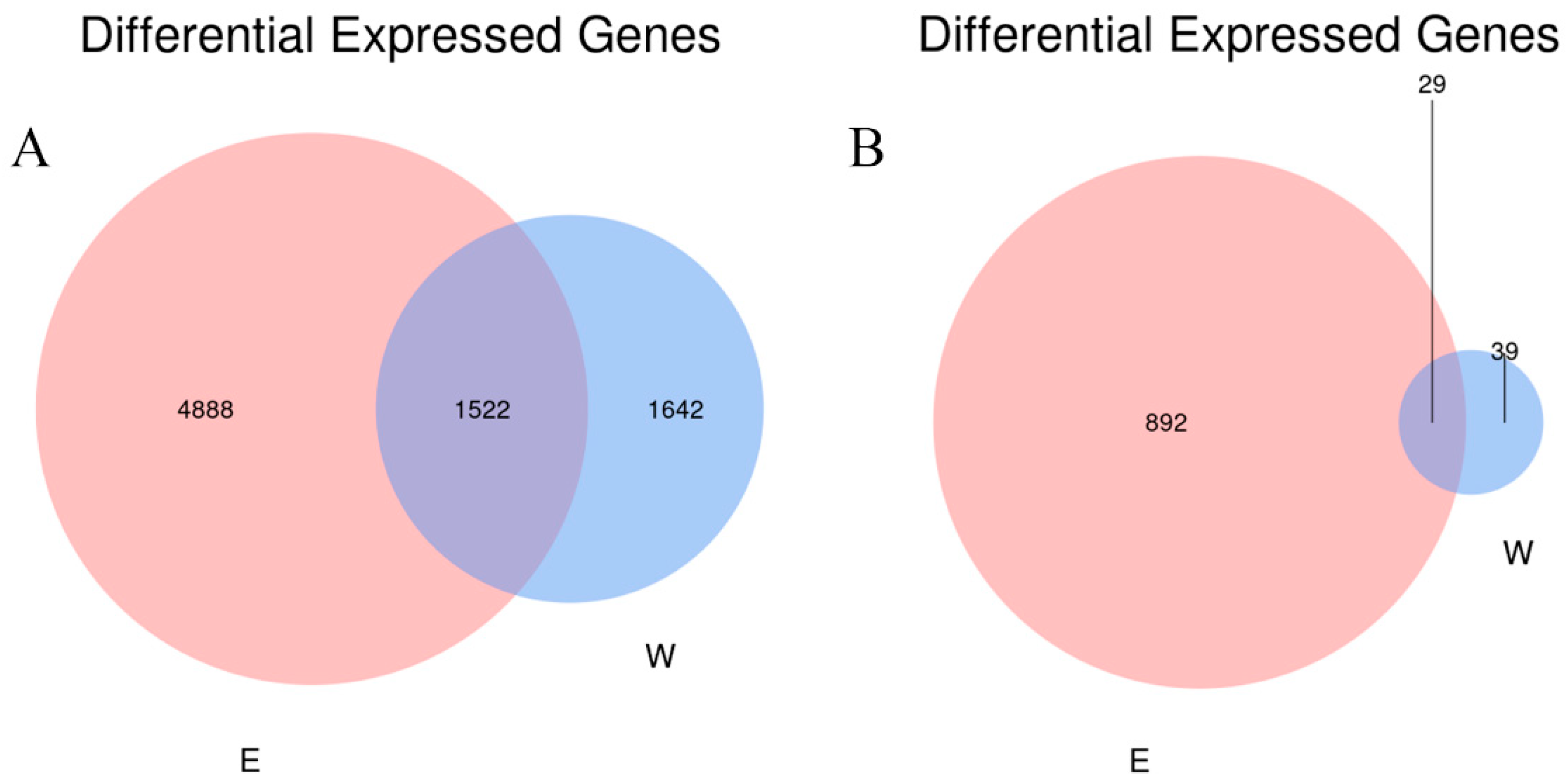
3.2. High-Throughput Sequencing Analysis of Inter-Rhizosphere Soil of E. angustifolia L.
3.3. Effect of E. angustifolia L. on the Composition of Soil Microbial Communities
3.3.1. Soil Bacterial Communities Composition
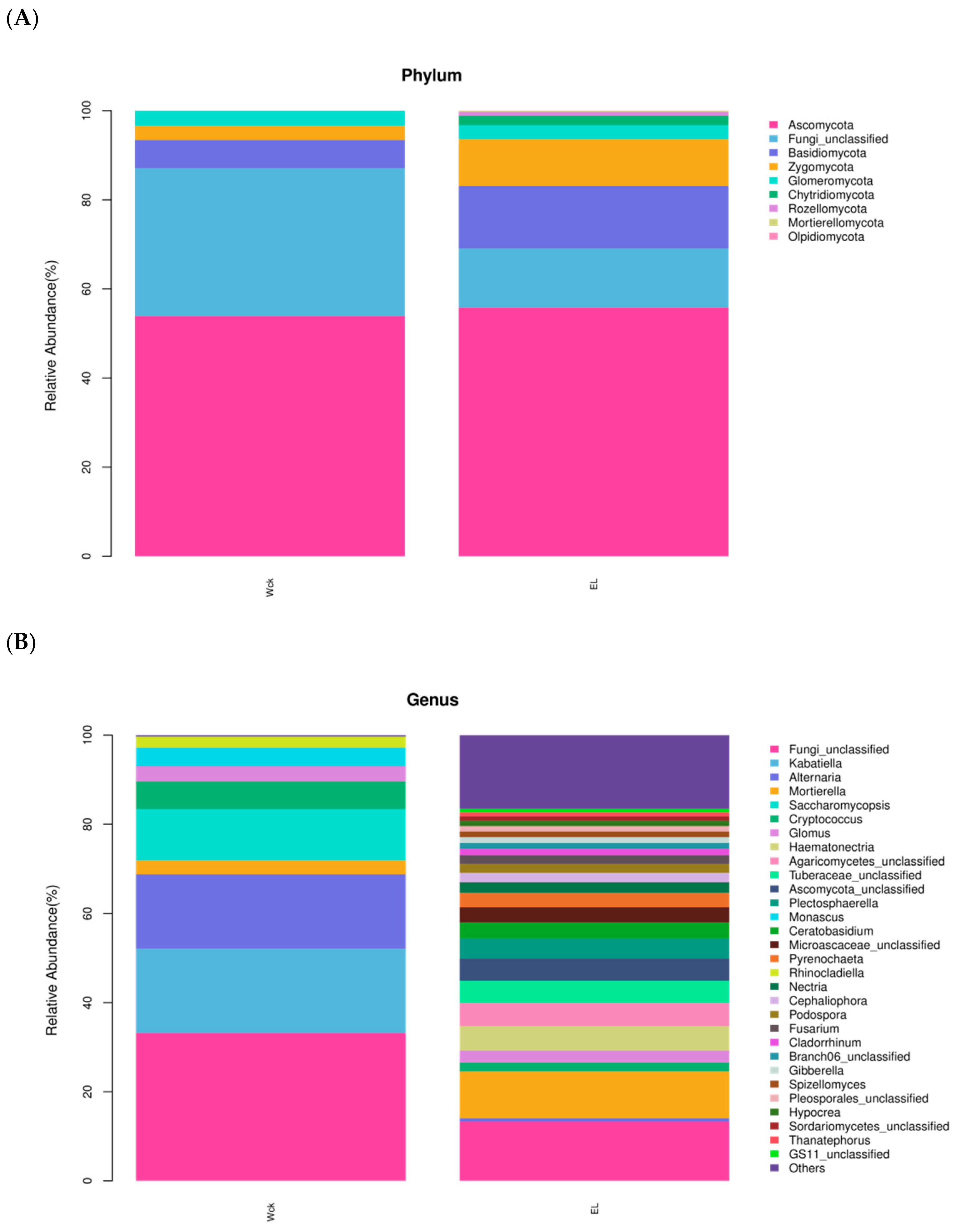
3.3.2. Soil Fungal Community Composition
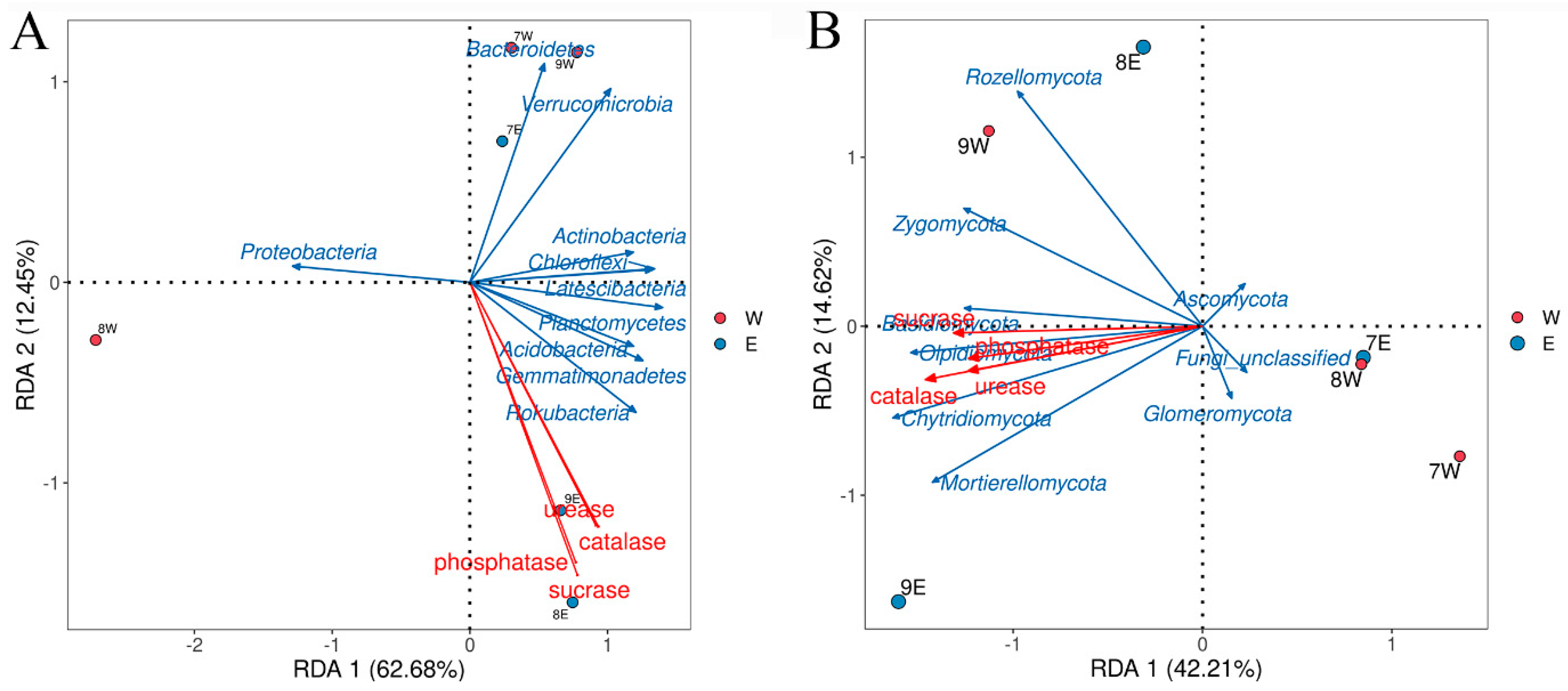
3.4. Correlation Between Soil Microorganisms and Soil Physicochemical Properties
3.4.1. Relationships Between Microbial Phylum Levels and Soil Nutrients
3.4.2. Relationship Between Microbial Phylum Levels and Soil Enzyme Activities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| E. angustifolia L. | Elaeagnus angustifolia Linn. |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| NO3−-N | Nitrate nitrogen |
| NH4+-N | Ammonium nitrogen |
| TP | Total phosphorus |
| TK | Total potassium |
| SOM | Soil organic matter |
| N2 | Atmospheric nitrogen |
| NH4+ | Ammonium |
References
- Zhang, M.; O’Connor, P.J.; Zhang, J.; Ye, X. Linking soil nutrient cycling and microbial community with vegetation cover in riparian zone. Geoderma 2021, 384, 114801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, A.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, P. Comparison of bacterial communities in soil samples with and without tomato bacterial wilt caused by Ralstonia solanacearum species complex. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulgarelli, D.; Schlaeppi, K.; Spaepen, S.; Van Themaat, E.V.L.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Structure and functions of the bacterial microbiota of plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2013, 64, 807–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Yu, F. Effects of invasive plant diversity on soil microbial communities. Diversity 2022, 14, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Q.; Luo, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Hou, G.; Chen, G.; Zhao, K.; Fan, C.; Li, X. Forest gaps alter the soil bacterial community of weeping cypress plantations by modulating the understory plant diversity. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 920905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinauer, K.; Tilman, D.; Wragg, P.D.; Cesarz, S.; Cowles, J.M.; Pritsch, K.; Reich, P.B.; Weisser, W.W.; Eisenhauer, N. Plant diversity effects on soil microbial functions and enzymes are stronger than warming in a grassland experiment. Ecology 2015, 96, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Gu, X.; Zhu, T.; Pan, X.; Zhu, Y.; Long, X.; Shao, H.; Liu, M.; Rengel, Z. Industrial crop Jerusalem artichoke restored coastal saline soil quality by reducing salt and increasing diversity of bacterial community. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 138, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Ge, J.; Cai, B. Elaeagnus angustifolia can improve salt-alkali soil and the health level of soil: Emphasizing the driving role of core microbial communities. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 305, 114401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngom, M.; Oshone, R.; Diagne, N.; Cissoko, M.; Svistoonoff, S.; Tisa, L.S.; Laplaze, L.; Sy, M.O.; Champion, A. Tolerance to environmental stress by the nitrogen-fixing actinobacterium Frankia and its role in actinorhizal plants adaptation. Symbiosis 2016, 70, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, C.; Li, L.; Zheng, X.; Liu, J.; Zhu, T.; Pang, C.; Wang, B.; Chen, M. Adaptive growth response of exotic Elaeagnus angustifolia L. to indigenous saline soil and its beneficial effects on the soil system in the Yellow River Delta, China. Trees 2018, 32, 1723–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Lin, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, L.; Zhao, C.; Chen, M. Phytohormone involved in salt tolerance regulation of Elaeagnus angustifolia L. seedlings. J. For. Res. 2019, 24, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Qu, H.; Ma, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, D.; Zheng, Q.; Xing, D. Protective effects of Elaeagnus angustifolia leaf extract against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in isolated rat heart. J. Chem. 2014, 2014, 693573. [Google Scholar]
- Si, L.J.; Han, Q.; Liu, M. Analysis of the seasonal climate characteristics and their impacts in Tai’an City in 2019. Mod. Agric. Technol. 2020, 18, 171–172. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Wei, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, B.; Han, L. Effect of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens QST713 on Inter-Root Substrate Environment of Cucumber under Low-Calcium Stress. Agronomy 2024, 14, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.M.; Ingram, J.S. Tropical soil biology and fertility: A handbook of methods. Soil Sci. 1994, 157, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, G.; Zhou, J.; Fang, H. Applicability of AB-DTPA method for determining the available content of multi-element in typical soils in China. Acta Agric. Shanghai 2016, 32, 100–107. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.K. Analysis of soil physical properties. In Analytical Method of Soil and Agricultural Chemistry; Chen, S.H., Liu, X.S., Eds.; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 260–338. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, S. Basic properties of soil enzymes. In Soil Enzyme and Its Research Methods; Chen, J.H., Ed.; Agricultural Publisher: Beijing, China, 1986; pp. 22–36. [Google Scholar]
- Okalebo, J.R.; Gathua, K.W.; Woomer, P.L. Laboratory methods of plant and soil analysis: A working manual. Tech. Bull. 2002, 21, 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihrmark, K.; Bödeker, I.T.; Cruz-Martinez, K.; Friberg, H.; Kubartova, A.; Schenck, J.; Strid, Y.; Stenlid, J.; Brandström-Durling, M.; Clemmensen, K.E.; et al. New primers to amplify the fungal ITS2 region–evaluation by 454-sequencing of artificial and natural communities. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 82, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagodatskaya, E.; Kuzyakov, Y. Active microorganisms in soil: Critical review of estimation criteria and approaches. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 67, 192–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Fan, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gao, X.; Song, F.; Geng, G. The effect of Rhizophagus irregularis on salt stress tolerance of Elaeagnus angustifolia roots. J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 2063–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Sun, J. Soil salinity drives the distribution patterns and ecological functions of fungi in saline-alkali land in the Yellow River Delta, China. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 594284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Liu, C.; Ding, N.; Lin, Y.; Guo, B.; Luo, J.; Wang, H. Soil microbial communities and enzyme activities in a reclaimed coastal soil chronosequence under rice–barley cropping. J. Soils Sediments 2012, 12, 1134–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obalum, S.; Chibuike, G.; Peth, S.; Ouyang, Y. Soil organic matter as sole indicator of soil degradation. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Kuzyakov, Y. Soil organic matter priming: The pH effects. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazari, M.; Pausch, J.; Bickel, S.; Bilyera, N.; Rashtbari, M.; Razavi, B.S.; Zamanian, K.; Sharififar, A.; Shi, L.; Dippold, M.A.; et al. Keeping thinning-derived deadwood logs on forest floor improves soil organic carbon, microbial biomass, and enzyme activity in a temperate spruce forest. Eur. J. For. Res. 2023, 142, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parashar, V.; Konkol, M.A.; Kearns, D.B.; Neiditch, M.B. A plasmid-encoded phosphatase regulates Bacillus subtilis biofilm architecture, sporulation, and genetic competence. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 2437–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazisong, I.A.; Senwo, Z.N.; He, Z. Phosphatase hydrolysis of organic phosphorus compounds. Adv. Enzym. Res. 2015, 3, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Tang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Cao, Y. Soil enzyme activity and microbial metabolic function diversity in soda saline–alkali rice paddy fields of northeast China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozlu, E.; Sandhu, S.S.; Kumar, S.; Arriaga, F.J. Soil health indicators impacted by long-term cattle manure and inorganic fertilizer application in a corn-soybean rotation of South Dakota. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diard, M.; Hardt, W.D. Evolution of bacterial virulence. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 679–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, S. Protein phosphatases in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2003, 54, 63–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, D.; Liang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Ai, C.; Zhou, W. Maize biochar addition rate influences soil enzyme activity and microbial community composition in a fluvo-aquic soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 96, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseby, D.C.; Pascual, J.A.; Lynch, J.M. Effect of biocontrol strains of Trichoderma on plant growth, Pythium ultimum populations, soil microbial communities and soil enzyme activities. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 88, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, M.M.; César, S.; Azcón, R.; Barea, J.M. Interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and other microbial inoculants (Azospirillum, Pseudomonas, Trichoderma) and their effects on microbial population and enzyme activities in the rhizosphere of maize plants. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2000, 15, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Pei, H.; Xie, H. Influence of allyl isothiocyanate on the soil microbial community structure and composition during pepper cultivation. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, D.B.; Vogel, C.; Bai, Y.; Vorholt, J.A. The plant microbiota: Systems-level insights and perspectives. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2016, 50, 211–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salo, K.; Domisch, T.; Kouki, J. Forest wildfire and 12 years of post-disturbance succession of saprotrophic macrofungi (Basidiomycota, Ascomycota). For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 451, 117454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasia, A.; Meena, B.R.; Tripathi, A.N.; Pandey, K.K.; Rai, A.B.; Singh, B. Actinomycetes: An unexplored microorganisms for plant growth promotion and biocontrol in vegetable crops. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alishahi, F.; Alikhani, H.A.; Khoshkholgh-Sima, N.A.; Etesami, H. Mining the roots of various species of the halophyte Suaeda for halotolerant nitrogen-fixing endophytic bacteria with the potential for promoting plant growth. Int. Microbiol. 2020, 23, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Liu, Z.; Hao, L.; Song, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Gao, Q.; Liu, X. Effects of Enterobacter cloacae HG-1 on the nitrogen-fixing community structure of wheat rhizosphere soil and on salt tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Sun, L.; Ling, N.; Zhu, C.; Chi, F.Q.; Li, W.Q.; Hao, X.; Zhang, W.; Bian, J.; Chen, L.; et al. Exploring soil factors determining composition and structure of the bacterial communities in saline-alkali soils of Songnen Plain. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 10, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Yang, X.; Yin, S.; Shen, Q.; Ran, W.; Xu, Y. Efficacy of Bacillus-fortified organic fertiliser in controlling bacterial wilt of tomato in the field. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2011, 48, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhong, B.; Zhao, C.; Wang, E.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Shi, F. Change of soil physicochemical properties, bacterial community and aggregation during desertification of grasslands in the Tibetan Plateau. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 72, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Bai, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, G.; Cui, B. Shifts in the soil bacterial community along a salinity gradient in the Yellow River Delta. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 2255–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Z.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Wu, H.; Yan, B. Soil organic matter and salinity as critical factors affecting the bacterial community and function of Phragmites australis dominated riparian and coastal wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, L.A.; Segundo, W.O.P.F.; de Souza, É.S.; Peres, E.G.; Koolen, H.H.F.; de Souza, J.V.B. Ascomycota as a source of natural colorants. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2022, 53, 1199–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Shen, J.; Luo, Y.; Scheu, S.; Ke, X. Tillage, residue burning and crop rotation alter soil fungal community and water-stable aggregation in arable fields. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 107, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sui, M.; Qin, X.; Sun, N.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Guan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Mao, Y.; et al. Effect of Elaeagnus angustifolia Linn. on the Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community Structure of Inter-Rhizosphere Soils. Plants 2025, 14, 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14081242
Sui M, Qin X, Sun N, Liu Y, Yang C, Guan L, Zhang Y, Wang H, Zhang M, Mao Y, et al. Effect of Elaeagnus angustifolia Linn. on the Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community Structure of Inter-Rhizosphere Soils. Plants. 2025; 14(8):1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14081242
Chicago/Turabian StyleSui, Mengyi, Xin Qin, Nan Sun, Yangbo Liu, Chen Yang, Luofei Guan, Yawen Zhang, Haiyan Wang, Manman Zhang, Yunfei Mao, and et al. 2025. "Effect of Elaeagnus angustifolia Linn. on the Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community Structure of Inter-Rhizosphere Soils" Plants 14, no. 8: 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14081242
APA StyleSui, M., Qin, X., Sun, N., Liu, Y., Yang, C., Guan, L., Zhang, Y., Wang, H., Zhang, M., Mao, Y., & Shen, X. (2025). Effect of Elaeagnus angustifolia Linn. on the Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community Structure of Inter-Rhizosphere Soils. Plants, 14(8), 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14081242






