Soil Carbon Sequestration: Role of Fe Oxides and Polyphenol Oxidase Across Temperature and Cultivation Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
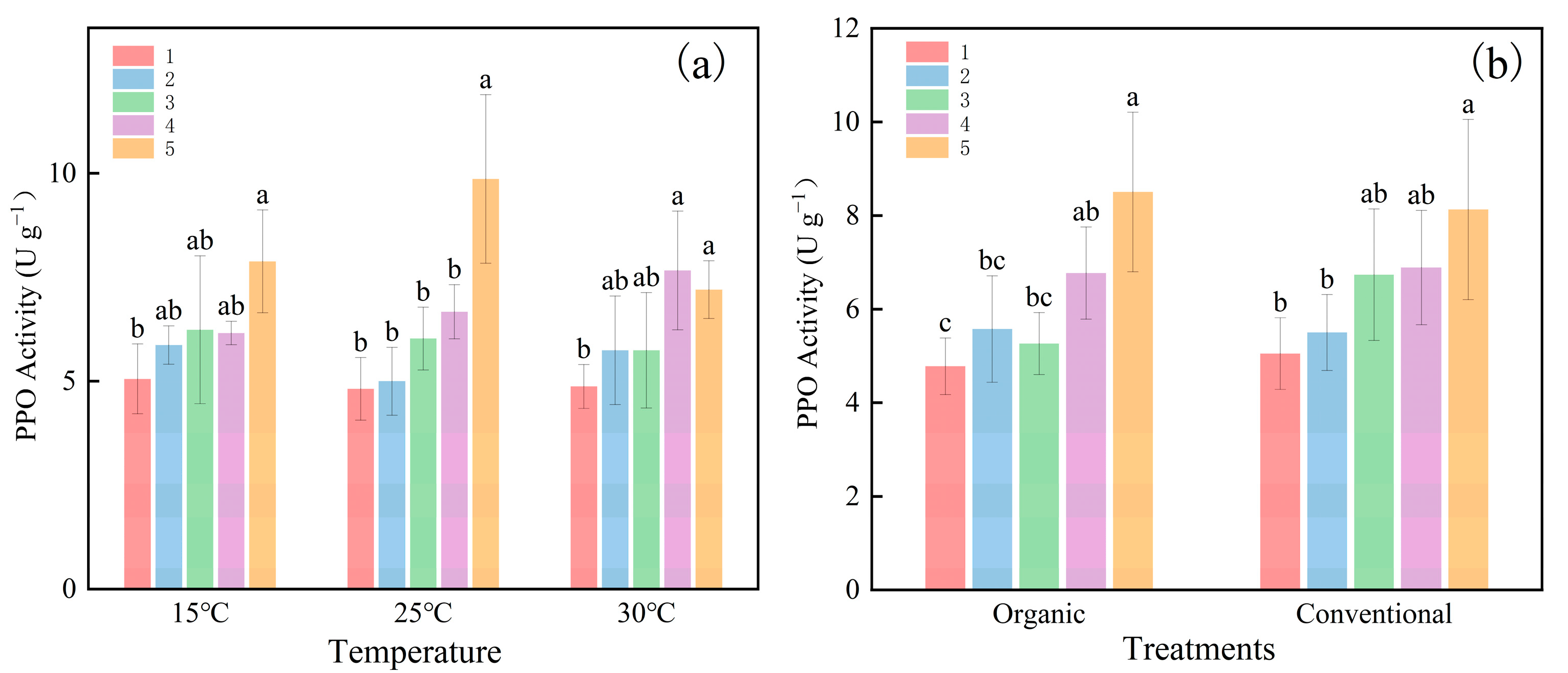
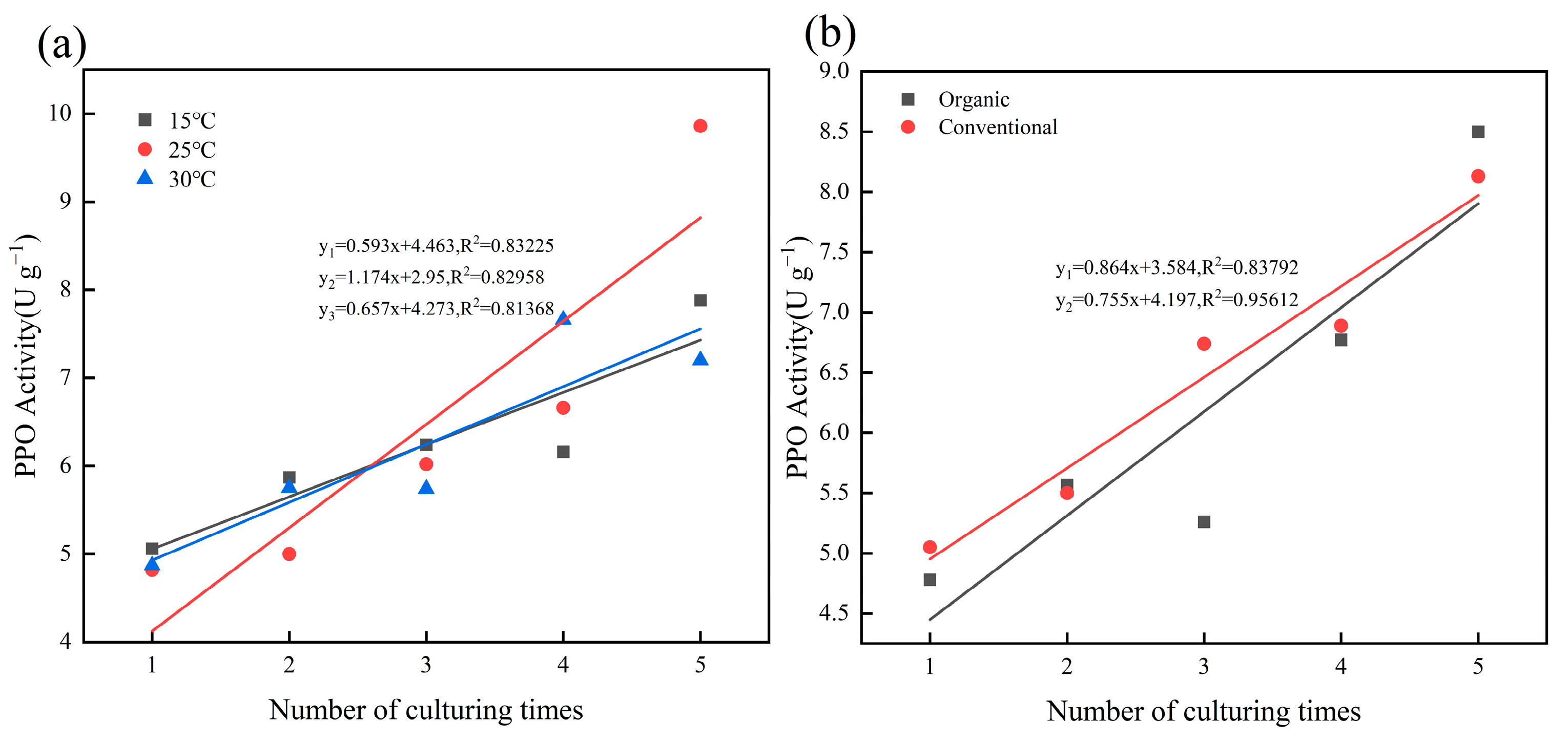
2.1. Effect of Temperature and Cultivation Methods on PPO Activity
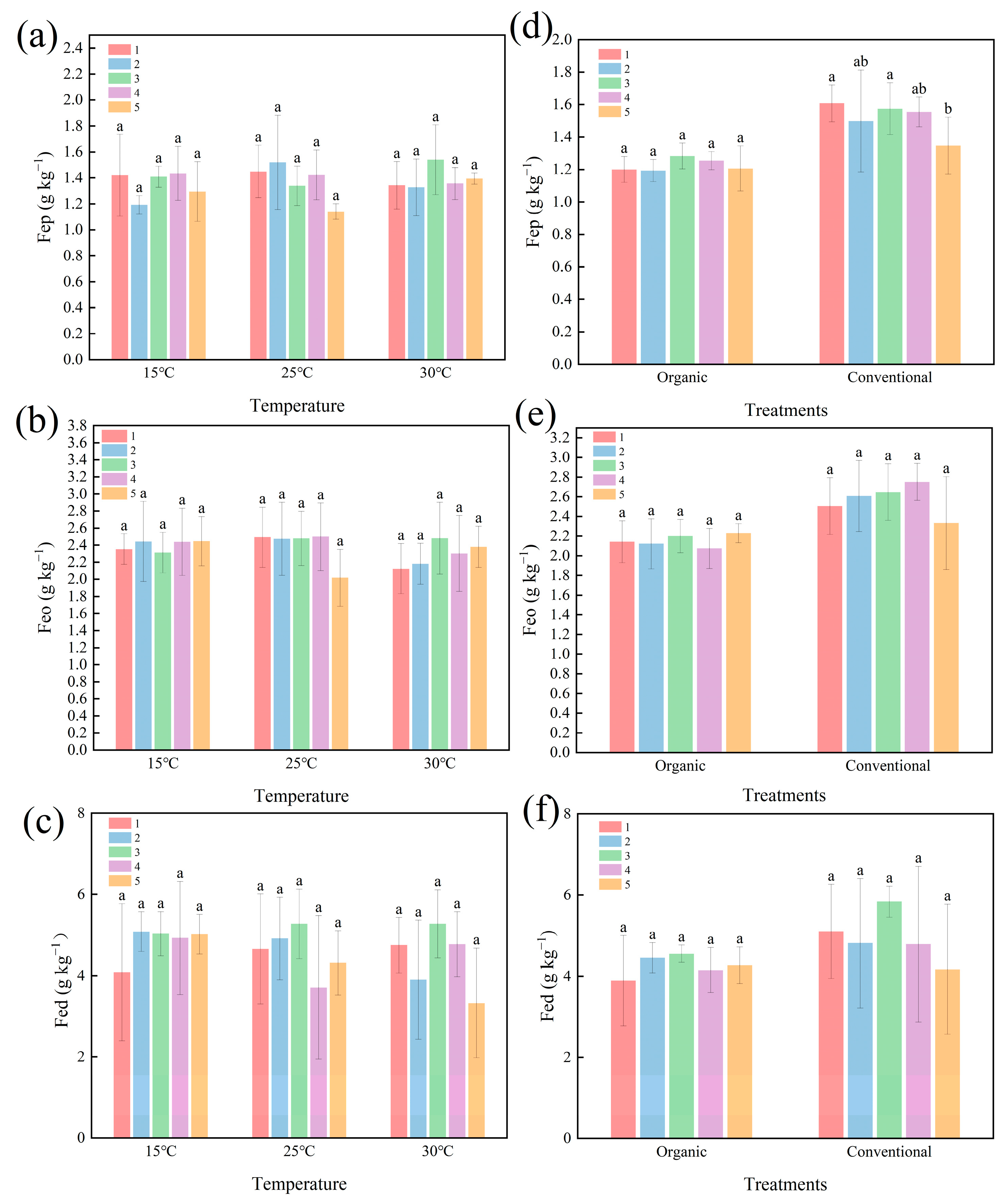
2.2. Effect of Temperature and Cultivation Methods on Fe Oxide Concentration
2.3. Integrated Analysis of Soil Physicochemical Properties
3. Discussion
3.1. The Role of PPO in SOC Stabilization
3.2. The Role of Fe Oxides in SOC Stabilization
3.3. Integrated Consideration of PPO Activity and Fe Oxides in Carbon Sequestration
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Site
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. PPO Activity Analysis
4.4. Analysis of Soil Fe Oxide Content
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SOC | Soil organic carbon |
| PPO | Polyphenol oxidase |
| CK | Control check |
| Fep | Fe bound to organic matter. |
| Feo | Reactive Fe |
| Fed | Total free Fe |
| OM | Organic matter |
References
- Miao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Niu, Y.; He, T.; Liu, D.; Ding, W. Correction for Miao et al., “Long-Term Compost Amendment Spurs Cellulose Decomposition by Driving Shifts in Fungal Community Composition and Promoting Fungal Diversity and Phylogenetic Relatedness”. mBio 2022, 13, e0295622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Xiao, J.; Goodman, B.A.; He, X. Effects of organic amendments on the transformation of Fe (oxyhydr) oxides and soil organic carbon storage. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ge, T.; van Groenigen, K.J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, P.; Cheng, K.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Guggenberger, G. Rice paddy soils are a quantitatively important carbon store according to a global synthesis. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Z. The Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Organic Carbon and Its Effects on Topsoil under Different Karst Landforms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FreemanC, O.; Kang, H. An enzymic ‘latch’ on a global carbon store: A shortage of oxygen locks up carbon in peatlands by restraining a single enzyme. Nature 2001, 409, 149G149. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Xu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Li, Q.; Long, C.; Chen, Q.; Chen, J.; Cheng, X. Inhibited enzyme activities in soil macroaggregates contribute to enhanced soil carbon sequestration under afforestation in central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Huang, X.; Li, L.; Li, T.; Duan, Y.; Ling, N.; Yu, G. Rejuvenation of iron oxides enhances carbon sequestration by the ‘iron gate’ and ‘enzyme latch’ mechanisms in a rice-wheat cropping system. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; He, J.-S.; Feng, X. Iron-mediated soil carbon response to water-table decline in an alpine wetland. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bodegom, P.M.; Broekman, R.; Van Dijk, J.; Bakker, C.; Aerts, R. Ferrous Iron Stimulates Phenol Oxidase Activity and Organic Matter Decomposition in Waterlogged Wetlands. Biogeochemistry 2005, 76, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.; Mikutta, R.; Guggenberger, G. Increased stability of organic matter sorbed to ferrihydrite and goethite on aging. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 71, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zheng, N.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Yao, H. Soil carbon and nitrogen cycles driven by iron redox: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 918, 170660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, K.; Guggenberger, G. Sorptive stabilization of organic matter by microporous goethite: Sorption into small pores vs. surface complexation. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2007, 58, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.C.; Doane, T.A.; Corrêa, R.S.; Valverde, V.; Pereira, E.I.; Horwath, W.R. Iron-mediated stabilization of soil carbon amplifies the benefits of ecological restoration in degraded lands. Ecol. Appl. 2015, 25, 1226–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, C.; Southard, R.J.; Horwath, W.R. Mineral control of organic carbon mineralization in a range of temperate conifer forest soils. Glob. Change Biol. 2006, 12, 834–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Y. The role of iron oxides in the preservation of soil organic matter under long-term fertilization. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H. Iron-bound organic carbon dynamics in peatland profiles: The preservation equivalence of deep and surface soil. Fundam. Res. 2023, 3, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Tao, R.; Ling, N.; Chu, G. Chemical, organic and bio-fertilizer management practices effect on soil physicochemical property and antagonistic bacteria abundance of a cotton field: Implications for soil biological quality. Tillage Res. 2017, 167, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhaolei, L.; Naishun, B.; Jun, C.; Xueping, C.; Manqiu, X.; Feng, W.; Zhiping, S.; Changming, F. Effects of long-term cultivation of transgenic Bt rice (Kefeng-6) on soil microbial functioning and C cycling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, W.; Zhang, J.; Yu, G.; Liu, Y.; Kong, Z.; Wu, L. Long-term cultivation reduces soil carbon storage by altering microbial network complexity and metabolism activity in macroaggregates. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witing, F.; Gebel, M.; Kurzer, H.J.; Friese, H.; Franko, U. Large-scale integrated assessment of soil carbon and organic matter-related nitrogen fluxes in Saxony (Germany). J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 237, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Zhang, R.; Nielsen, S.; Joseph, S.D.; Huang, D.; Thomas, T. A Combination of Biochar-Mineral Complexes and Compost Improves Soil Bacterial Processes, Soil Quality, and Plant Properties. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, R.; Rodríguez-Berbel, N.; Sánchez-Cañete, E.P.; Villafuerte, A.B.; Ortega, R.; Miralles, I. Organic amendments from recycled waste promote short-term carbon sequestration of restored soils in drylands. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 327, 116873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.L.; Wang, X.L.; Duan, J.J.; Liu, A.K.; Luo, A.H.; Li, R.D.; Hou, Z.F. Effects of chemical N fertilizer reduction combined with biochar application on soil organic carbon active components and mineralization in paddy fields of yellow soil. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao = J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 4117–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarek, I.; Grata, K. The influence of the organic matter of sewage sediments on biological activity of microorganisms which carry out the transformations of carbon and nitrogen compounds. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebeke, M.; Strittmatter, N.; Fearn, S.; Morgan, A.J.; Kille, P.; Fuchser, J.; Wallis, D.; Palchykov, V.; Robertson, J.; Lahive, E.; et al. Unique metabolites protect earthworms against plant polyphenols. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhou, J.C.; Lin, W.S.; Zheng, Y.; Li, C.; Li, X.F.; Ji, Y.H.; Yang, Z.J. Effects of soil warming on soil microbial extracellular enzyme activities with different depths in a young Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) plantation of subtropics. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao = J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.L.; Zhao, W.Q.; Liu, M. Responses of polyphenoloxidase and catalase activities of rhizosphere and bulk soils to warming during the growing season in an alpine scrub ecosystem. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao = J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 3681–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzner, M.S.; Mueller, C.W.; Malusova, M.; Baur, M.; Nikeleit, V.; Scholten, T.; Hoeschen, C.; Byrne, J.M.; Borch, T.; Kappler, A.; et al. Iron mineral dissolution releases iron and associated organic carbon during permafrost thaw. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hall, S.J.; Coward, E.; Thompson, A. Iron-mediated organic matter decomposition in humid soils can counteract protection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Meile, C.; Wilmoth, J.; Barcellos, D.; Thompson, A. Influence of pO2 on Iron Redox Cycling and Anaerobic Organic Carbon Mineralization in a Humid Tropical Forest Soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7709–7719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Campbell, A.N.; Tfaily, M.M.; Lin, Y.; Kukkadapu, R.K.; Silver, W.L.; Nico, P.S.; Pett-Ridge, J. Redox Fluctuations Control the Coupled Cycling of Iron and Carbon in Tropical Forest Soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 14129–14139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, D.B. Microbial change in warming soils. Science 2017, 358, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Balser, T.C. Warming and nitrogen deposition lessen microbial residue contribution to soil carbon pool. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Tian, Y.; Heinzle, J.; Salas, E.; Kwatcho-Kengdo, S.; Borken, W.; Schindlbacher, A.; Wanek, W. Long-term soil warming decreases soil microbial necromass carbon by adversely affecting its production and decomposition. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindlbacher, A.; Schnecker, J.; Takriti, M.; Borken, W.; Wanek, W. Microbial physiology and soil CO2 efflux after 9 years of soil warming in a temperate forest—No indications for thermal adaptations. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 4265–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, L.A.; Hobbs, J.K.; Rutledge, S.; Arcus, V.L. Thermodynamic theory explains the temperature optima of soil microbial processes and high Q10 values at low temperatures. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 3578–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matschiavelli, N.; Kluge, S.; Podlech, C.; Standhaft, D.; Grathoff, G.; Ikeda-Ohno, A.; Warr, L.N.; Chukharkina, A.; Arnold, T.; Cherkouk, A. The Year-Long Development of Microorganisms in Uncompacted Bavarian Bentonite Slurries at 30 and 60 °C. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10514–10524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Yuan, J.; Chen, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y. Animal manures promoted soil phosphorus transformation via affecting soil microbial community in paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Battaglia-Brunet, F.; Hellal, J.; Joulian, C.; Gautret, P.; Motelica-Heino, M. Impact of Fe (III)(oxyhydr) oxides mineralogy on iron solubilization and associated microbial communities. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 571244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, Q.-H.; Huang, D.-Y.; Zhu, H.-H.; Xu, C.; Su, S.-M.; Zeng, X.-B. Influence of straw-derived humic acid-like substance on the availability of Cd/As in paddy soil and their accumulation in rice grain. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Wang, C.-C.; Lin, H.-H.; Lee, S.S.; Tsang, D.C.; Jien, S.-H.; Ok, Y.S. In-situ biochar application conserves nutrients while simultaneously mitigating runoff and erosion of an Fe-oxide-enriched tropical soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattinger, A.; Muller, A.; Haeni, M.; Skinner, C.; Fliessbach, A.; Buchmann, N.; Mäder, P.; Stolze, M.; Smith, P.; Scialabba Nel, H.; et al. Enhanced top soil carbon stocks under organic farming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 18226–18231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durrer, A.; Gumiere, T.; Zagatto, M.R.G.; Feiler, H.P.; Silva, A.M.M.; Longaresi, R.H.; Homma, S.K.; Cardoso, E.J. Organic farming practices change the soil bacteria community, improving soil quality and maize crop yields. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Espíndola, I.P.; Ferrara-Guerrero, M.J.; Luna-Guido, M.L.; Ramírez-Villanueva, D.A.; De León-Lorenzana, A.S.; Gómez-Acata, S.; González-Terreros, E.; Ramírez-Barajas, B.; Navarro-Noya, Y.E.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, L. The bacterial community structure and microbial activity in a traditional organic milpa farming system under different soil moisture conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.; Wang, X.; Feng, Z.; et al. Assessing the formation and stability of paddy soil aggregate driven by organic carbon and Fe/Al oxides in rice straw cyclic utilization strategies: Insight from a six-year field trial. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Thompson, A. Ferrous Iron Oxidation under Varying pO2 Levels: The Effect of Fe(III)/Al(III) Oxide Minerals and Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.; Buckeridge, K.; Ziegler, S.E.; Edwards, K.A.; Bagchi, S.; Billings, S.A. Temperature sensitivity of biomass-specific microbial exo-enzyme activities and CO2 efflux is resistant to change across short- and long-term timescales. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 1793–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Lin, X.; Qi, J. Soil Carbon Sequestration: Role of Fe Oxides and Polyphenol Oxidase Across Temperature and Cultivation Systems. Plants 2025, 14, 927. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060927
He Y, Wang Z, Zhu J, Lin X, Qi J. Soil Carbon Sequestration: Role of Fe Oxides and Polyphenol Oxidase Across Temperature and Cultivation Systems. Plants. 2025; 14(6):927. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060927
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Yuhao, Zhiyu Wang, Jiayi Zhu, Xiang Lin, and Jianying Qi. 2025. "Soil Carbon Sequestration: Role of Fe Oxides and Polyphenol Oxidase Across Temperature and Cultivation Systems" Plants 14, no. 6: 927. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060927
APA StyleHe, Y., Wang, Z., Zhu, J., Lin, X., & Qi, J. (2025). Soil Carbon Sequestration: Role of Fe Oxides and Polyphenol Oxidase Across Temperature and Cultivation Systems. Plants, 14(6), 927. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060927






