Mapping Genomic Regions for Grain Protein Content and Quality Traits in Milled Rice (Oryza sativa L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Construction of Genetic Map Using F2 Population
2.2. Identification of QTLs for GPC, Quality Traits, and Yield
2.3. Identification of Epistatic QTLs
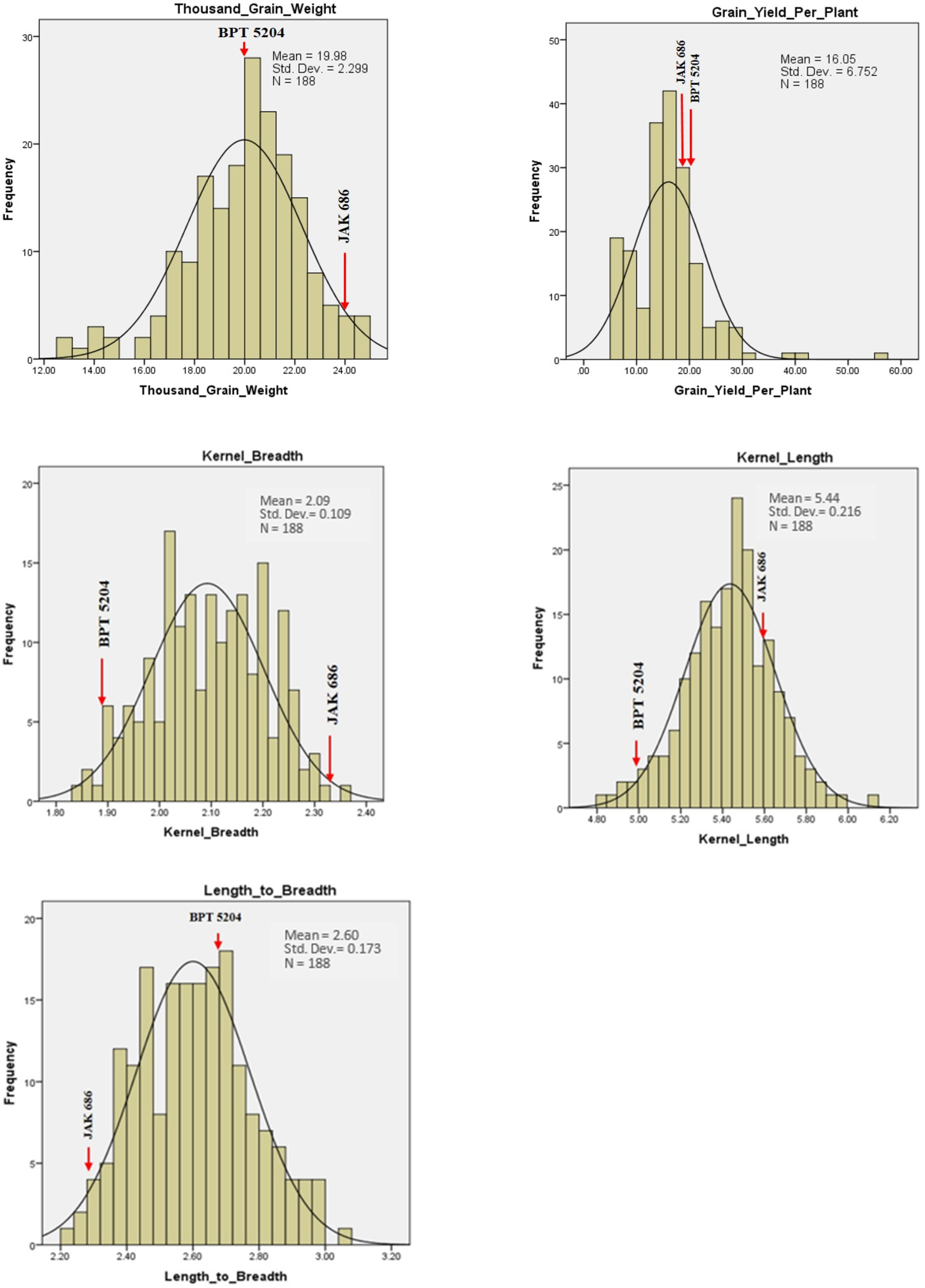
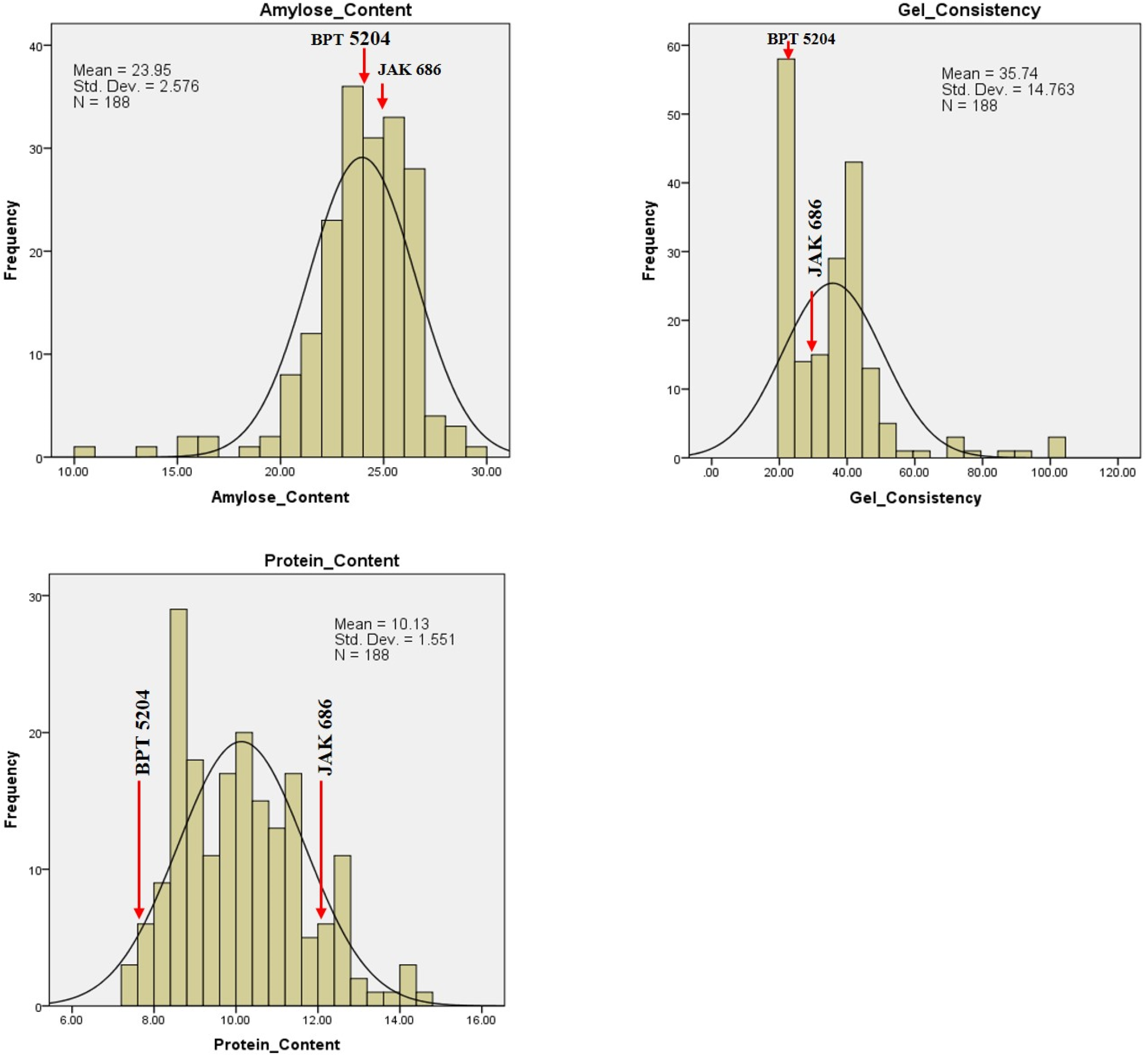
2.4. Variability for GPC, Grain Quality Traits, and Yield
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Grain Protein Content, Grain Quality, Yield, and Yield Attributing Traits
4.3. QTL Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, L.; Cong, W.-F.; Suter, B.; Zhang, F.; van der Werf, W.; Stomph, T.J. How much can Zn or Fe fertilization contribute to Zn and Fe mass concentration in rice grain? A global meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2023, 301, 109033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhao, C.F.; Zhou, L.H.; Yao, S.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Chen, T.; Wang, C.L. Mapping QTLs for rice (Oryza sativa L.) grain protein content via chromosome segment substitution lines. Cereal Res. Commun. 2022, 50, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, M.; Sun, S.; Zou, Y.; Yin, S.; Liu, Y.; Tang, S.; Gu, M.; Yang, Z.; Yan, C. Natural variation of OsGluA2 is involved in grain protein content regulation in rice. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakatsu, T.; Yamamoto, M.P.; Hirose, S.; Yano, M.; Takaiwa, F. Characterization of a new rice glutelin gene GluD-1 expressed in the starchy endosperm. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 4233–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.H.; Messing, J. Amplification of prolamin storage protein genes in different subfamilies of the Poaceae. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 119, 1397–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, G.; Bhat, M.A.; Tan, X.; Wang, Y.; He, Y. Research progress on the relationship between rice protein content and cooking and eating quality and its influencing factors. Seed Biol. 2023, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaker, B.R.; Griffin, V.K. Effect of disulfide bond containing protein on rice starch gelatinization and pasting. Cereal Chem. 1993, 70, 377–380. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.J.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, N.S. Simple Sequence Repeat Polymorphisms (SSRPs) for evaluation of molecular diversity and germplasm classification of minor crops. Molecules 2009, 14, 4546–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R.; Singh, A.K.; Salgotra, R.K.; Sharma, M.; Mushtaq, M.; Bagati, S.; Hangloo, S.; Singh, A. Detection of QTL for panicle architecture in F2 population of rice. J. Genet. 2019, 98, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluko, G.; Martinez, C.; Tohme, J.; Castano, C.; Bergman, C.; Oard, J.H. QTL mapping of grain quality traits from the interspecific cross Oryza sativa× O. glaberrima. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.L.; Li, P.; Zhou, M.Q.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, L.X.; Zhu, L.H.; Zhu, Y.G. Mapping of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for rice protein and fat content using doubled haploid lines. Euphytica 2004, 135, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Yu, B.; Tondi-yacouba, N.; Gao, G.J.; Zhang, Q.L.; He, Y.Q. QTLs mapping of protein content and crude fat content in rice. Hu Bei Agric. Sci. 2012, 51, 4709–4713, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B. Mapping of QTLs for the Major Rice Grain Qualities by Using Chromosome Segment Substitution Lines. Master’s Thesis, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, 2013. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.; Tan, X.; Zhang, H.; Lou, G.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Y.; He, Y. QTL Mining and validation of grain nutritional quality characters in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using two introgression line populations. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Shin, D.; Marmagne, A.; Lim, P.O.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C.; An, G.; Nam, H. OsASN1 Overexpression in Rice Increases Grain Protein Content and Yield under Nitrogen-Limiting Conditions. Plant Cell Physiol. 2020, 61, 1309–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, B.; Sun, X.; Tian, X.; Kong, D.; He, L.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, G.; Sun, Y.; Pang, R.; et al. OsNAC74 affects grain protein content and various biological traits by regulating OsAAP6 expression in rice. Mol. Breed. 2023, 43, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xie, Z.; Luo, Y.; Long, Q.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, B.; He, D.; et al. Natural variations of OsAUX5, a target gene of OsWRKY78, control the neutral essential amino acid content in rice grains. Mol. Plant. 2023, 16, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terao, T.; Hirose, T. Control of grain protein contents through SEMIDWARF1 mutant alleles: sd1 increases the grain protein content in Dee-geo-woo-genbut not in Reimei. Mol Genet. Genom. 2015, 290, 939–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. QTL IciMapping: Integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop J. 2015, 3, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Han, J.H.; Lee, Y.K.; Shin, N.H.; Kang, Y.J.; Kim, C.K.; Chin, J.H. Mapping and validation of QTLs for the amino acid and total protein content in brown rice. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Wang, L.Q.; Yuan, D.J.; Luo, L.J.; Xu, C.G.; He, Y.Q. Identification of QTL affecting protein and amino acid contents in rice. Rice Sci. 2011, 18, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, K.; Behera, L.; Bagchi, T.B.; Sardar, S.S.; Moharana, N.; Patra, N.R.; Sharma, S. Detection of stable QTLs for grain protein content in rice (Oryza sativa L.) employing high throughput phenotyping and genotyping platforms. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Kim, S.; Sohn, J. QTL analysis of protein content in double-haploid lines of rice. Korean J. Crop Sci. 2009, 54, 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Ma, J.; Chen, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wan, J. Dynamic QTL analysis of rice protein content and protein index using recombinant inbred lines. J. Plant Biol. 2011, 54, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Kong, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhong, M.; Sun, L.; He, Y. OsAAP6 functions as an important regulator of grain protein content and nutritional quality in rice. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiaz, S.; Sheng, Z.; Zeb, A.; Barman, H.N.; Shar, T.; Ali, U.; Tang, S. Analysis of genomic regions for crude protein and fractions of protein using a recombinant inbred population in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2021, 15, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.H.; Li, G.; Fan, Y.Y.; Zhang, K.Q.; Min, J.; Zhu, Z.W.; Zhuang, J.Y. Genetic relationship between grain yield and the contents of protein and fat in a recombinant inbred population of rice. J. Cereal Sci. 2009, 50, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.K.; Pandit, E.; Pawar, S.; Bharati, B.; Chatopadhyay, K.; Singh, S.; Reddy, J.N. Association mapping reveals multiple QTLs for grain protein content in rice useful for biofortification. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2019, 294, 963–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, M.; Hurrel, R. Improving iron, zinc and vitamin A nutrition through plant biotechnology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahender, A.; Anandan, A.; Pradhan, S.K.; Pandit, E. Rice grain nutritional traits and their enhancement using relevant genes and QTLs through advanced approaches. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.; Marndi, B.C.; Sharma, S.; Das, A. Biochemical characterization of two high protein rice cultivars from Assam rice collections. Oryza 2011, 48, 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Pu, Y.; Sun, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, D.; He, S. Global, regional, and national burden of protein–energy malnutrition: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatun, M.M.; Ali, M.H.; Dela Cruz, Q.D. Correlation studies on grain physicochemical characteristics of aromatic rice. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2003, 6, 511–513. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, D.; Kohli, B.; Deo, I. Deciphering correlation studies for yield and quality traits in basmati rice (Oryza sativa L.) mated through line × tester mating design. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2021, 10, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, N.K.; Reddy, V.R.; Chandramohan, Y. Correlation and path coefficient studies of yield and quality traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Res. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 7, 606–609. [Google Scholar]
- Soharu, A.; Pandey, D.P. Correlation and path analysis for yield and its component traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Rice Res. 2018, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Thongbam, P.D.; Raychaudhury, M.; Durai, A.; Das, S.P.; Ramesh, T.; Ramya, K.T.; Ngachan, S.V. Studies on grain and food quality traits of some indigenous rice cultivars of North-eastern hill region of India. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 4, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadia, D.K. Genetic variability studies in Lasora (Cordia myxa Roxb.). Indian J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2005, 18, 236–240. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhari, M.; Motirmani, N.K.; Pravin, J. Variability and genetic divergence of aromatic rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ann. Agric. Res. New Ser. 2007, 28, 268–272. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, E.; Choi, Y.S.; Chung, I.K.; Kim, K.M. QTLs and analysis of the candidate gene for amylose, protein and moisture content in rice (Oryza sativa L.). 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathima, M.A.; Geetha, S.; Amudha, K.; Uma, D. Genetic variability, frequency distribution and association analysis in ADT (R) 48 x Kavuni derived F2 population of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Electron. J. Plant Breed. 2021, 12, 659–666. [Google Scholar]
- Nandeshwar, B.C.; Pal, S.; Senapati, B.K.; De, D.K. Genetic variability and character association among biometrical traits in F2 generation of some Rice crosses. Electron. J. Plant Breed. 2010, 1, 758–763. [Google Scholar]
- Seneega, T.A.; Gnanamalar, R.P.; Parameswari, C.; Vellaikumar, S.; Priyanka, A.R. Genetic variability and association studies in F2 generation of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Electron. J. Plant Breed. 2019, 10, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.B.; Li, G.; Zhu, Y.J.; Cheng, Y.C.; Yang, J.Y.; Chen, H.Z.; Ying, J.Z. Genome-wide identification of QTLs for grain protein content based on genotyping-by-resequencing and verification of qGPC1-1 in rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.Z.; Arifuzzaman, M.; Banik, S.; Hossain, M.A.; Ferdous, J.; Khalequzzaman, M.; Ali, M.P. Mapping QTLs underpin nutrition components in aromatic rice germplasm. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.F.; Sun, M.; Xing, Y.Z.; Hua, J.P.; Sun, X.L.; Zhang, Q.F.; Corke, H. Mapping quantitative trait loci for milling quality, protein content and color characteristics of rice using a recombinant inbred line population derived from an elite rice hybrid. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2001, 103, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhong, M.; Li, X.; Yuan, D.; Xu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Q. The QTL controlling amino acid content in grains of rice (Oryza sativa) are co-localized with the regions involved in the amino acid metabolism pathway. Mol. Breed. 2008, 21, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.; Ismail, I.; Osman, M.; Hashim, H. Mapping of quantitative trait loci for aroma, amylose content and cooked grain elongation traits in rice. Plant Omics 2014, 7, 152–157. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.F.; Wan, J.M.; Xia, J.F.; Zhai, H.Q.; Ikehashi, H. Identification of quantitative trait loci underlying milling quality of rice (Oryza sativa) grains. Plant Breed. 2004, 123, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, D.K.; Sahoo, S.; Barik, S.R.; Sanghamitra, P.; Sangeeta, S.; Pandit, E.; Pradhan, S.K. Association mapping for protein, total soluble sugars, starch, amylose and chlorophyll content in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, B.M.; Kaladhar, K.; Shobha, R.N.; Prasad, G.S.V.; Viraktamath, B.C.; Reddy, G.A.; Sarla, N. QTL analysis for grain quality traits in 2 BC2F2 populations derived from crosses between Oryza sativa cv Swarna and 2 accessions of O. nivara. J. Hered. 2012, 103, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wu, J.G.; Lou, X.Y.; Xu, H.M.; Shi, C.H. The QTL analysis on maternal and endosperm genome and their environmental interactions for characters of cooking quality in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 116, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikami, I.; Uwatoko, N.; Ikeda, Y.; Yamaguchi, J.; Hirano, H.Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Sano, Y. Allelic diversification at the wx locus in landraces of Asian rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 116, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanceras, J.C.; Huang, Z.L.; Naivikul, O.; Vanavichit, A.; Ruanjaichon, V.; Tragoonrung, S. Mapping of genes for cooking and eating qualities in Thai jasmine rice (KDML105). DNA Res. 2000, 7, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Han, Y.; Jiang, L.; Xu, C.; Lu, J.; Xu, M. Functional analysis of starch-synthesis genes in determining rice eating and cooking qualities. Mol. Breed. 2006, 18, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.F.; Li, J.X.; Yu, S.B.; Xing, Y.Z.; Xu, C.G.; Zhang, Q. The three important traits for cooking and eating quality of rice grains are controlled by a single locus in an elite rice hybrid, Shanyou 63. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1999, 99, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, A.K.; Sharma, T.R.; Singh, A.; Singh, N.K. Fine mapping of grain length QTLs on chromosomes 1 and 7 in Basmati rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 21, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiei, B.; Valizadeh, M.; Ghareyazie, B.; Moghaddam, M.; Ali, A.J. Identification of QTLs for rice grain size and shape of Iranian cultivars using SSR markers. Euphytica 2004, 137, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, K.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Lin, X.; Fu, X. Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, K.; Zha, W.; Zhou, L.; Li, M.; Xu, H.; You, A. Identification and verification of grain shape QTLs by SNP array in rice. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Wu, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Fu, X. The OsSPL16-GW7 regulatory module determines grain shape and simultaneously improves rice yield and grain quality. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, D.; Surapaneni, M.; Yadavalli, V.R.; Addanki, K.R.; Mesapogu, S.; Beerelli, K.; Neelamraju, S. Detecting CSSLs and yield QTLs with additive, epistatic and QTL× environment interaction effects from Oryza sativa × O. nivara IRGC81832 cross. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piper, C.S. Soil and Plant Analysis; Hans Publishers: Bombay, India, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Sadasivam, S.; Manickam, A. Biochemical Methods for Agricultural Sciences; New Age International (P) Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 1996; pp. 1–97. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, G.W.; Devane, E.W. Estimating heritability in tall fescue (Festuca arundiraceae) from replicated clonal material. Agron. J. 1953, 45, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, R.W. Principles of Plant Breeding; John Wiley and Sons. Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1960; 485p. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, H.W.; Robinson, H.F.; Comstock, R.E. Estimation of genetic and environmental variability in soybean. Agron. J. 1955, 47, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.J.; Huang, W.; Shi, M.; Zhu, M.Z.; Lin, H.X. A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shomura, A.; Izawa, T.; Ebana, K.; Ebitani, T.; Kanegae, H.; Konishi, S.; Yano, M. Deletion in a gene associated with grain size increased yields during rice domestication. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, J.; Gu, S.; Wan, X.; Gao, H.; Guo, T.; Su, N.; Lei, C.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Z.; Guo, X.; et al. Isolation and initial characterization of GW5, a major QTL associated with rice grain width and weight. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Zheng, X.; Wu, F.; Lin, Q.; Heng, Y.; Tian, P.; Cheng, Z.; Yu, X.; Zhou, K.; et al. GW5 acts in the brassinosteroid signalling pathway to regulate grain width and weight in rice. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 17043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.S.; Li, Q.F.; Zhang, C.Q.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Q.Q.; Pan, L.X.; Ren, X.Y.; Lu, J.; Gu, M.H.; Liu, Q.Q. GS9 acts as a transcriptional activator to regulate rice grain shape and appearance quality. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Xu, C.; Guo, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, C.; Sun, S.; Yan, C. Genetic improvement of panicle-erectness japonica rice toward both yield and eating and cooking quality. Mol. Breed. 2020, 40, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Zhang, X.; He, F.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Yao, J.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, W.; Yu, G. Genetic Improvements in Rice Grain Quality: A Review of Elite Genes and Their Applications in Molecular Breeding. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechanova, S.L.; Bhattarai, K.; Simon, E.V.; Clave, G.; Karunarathne, P.; Ahn, E.-K.; Li, C.-P.; Lee, J.-S.; Kohli, A.; Hamilton, N.R.S.; et al. Development of a genome-wide InDel marker set for allele discrimination between rice (Oryza sativa) and the other seven AA-genome Oryza species. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orjuela, J.; Garavito, A.; Bouniol, M.; Arbelaez, J.D.; Moreno, L.; Kimball, J.; Wilson, G.; Rami, J.F.; Tohme, J.; McCouch, S.R.; et al. A universal core genetic map for rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2010, 120, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
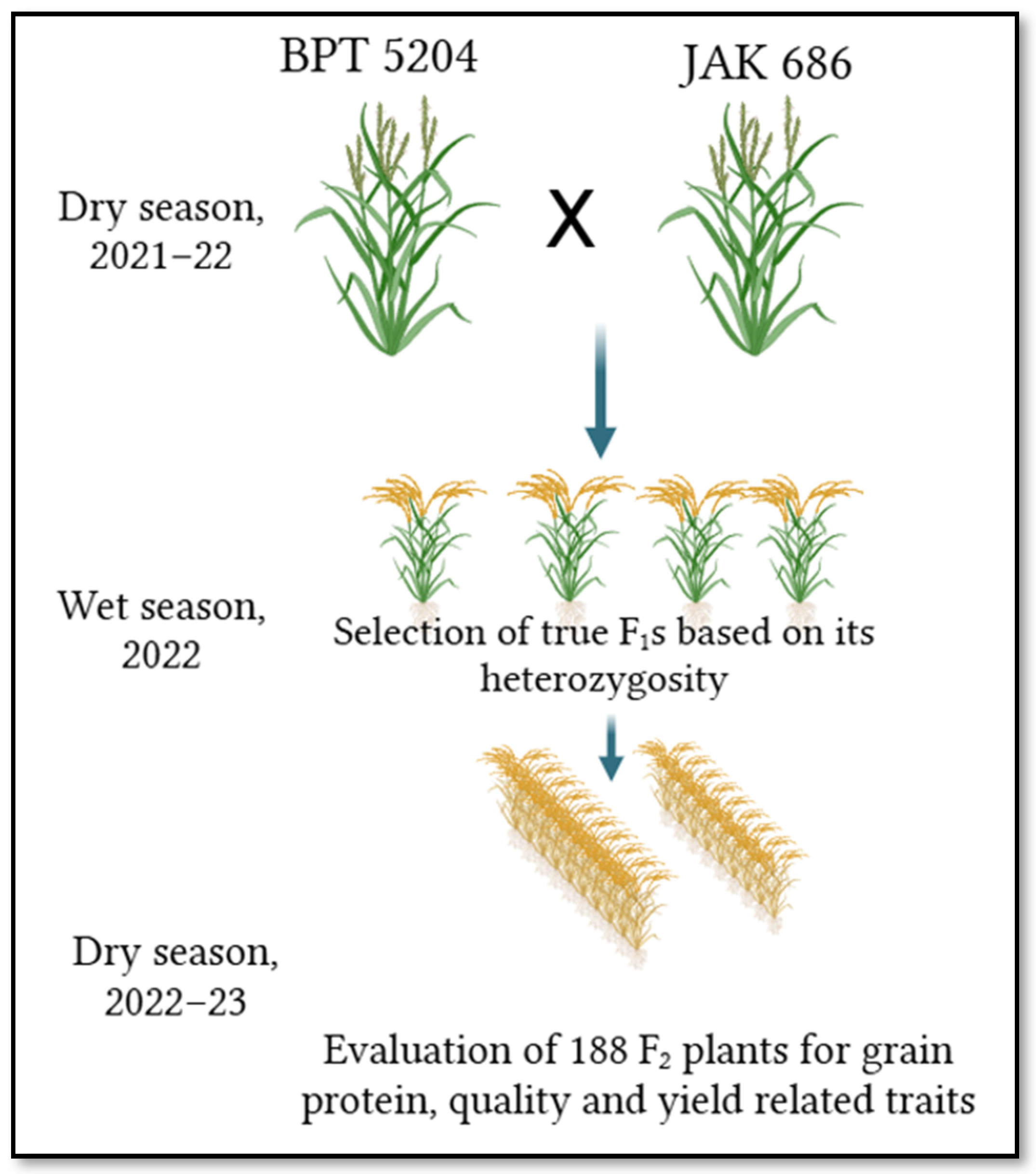

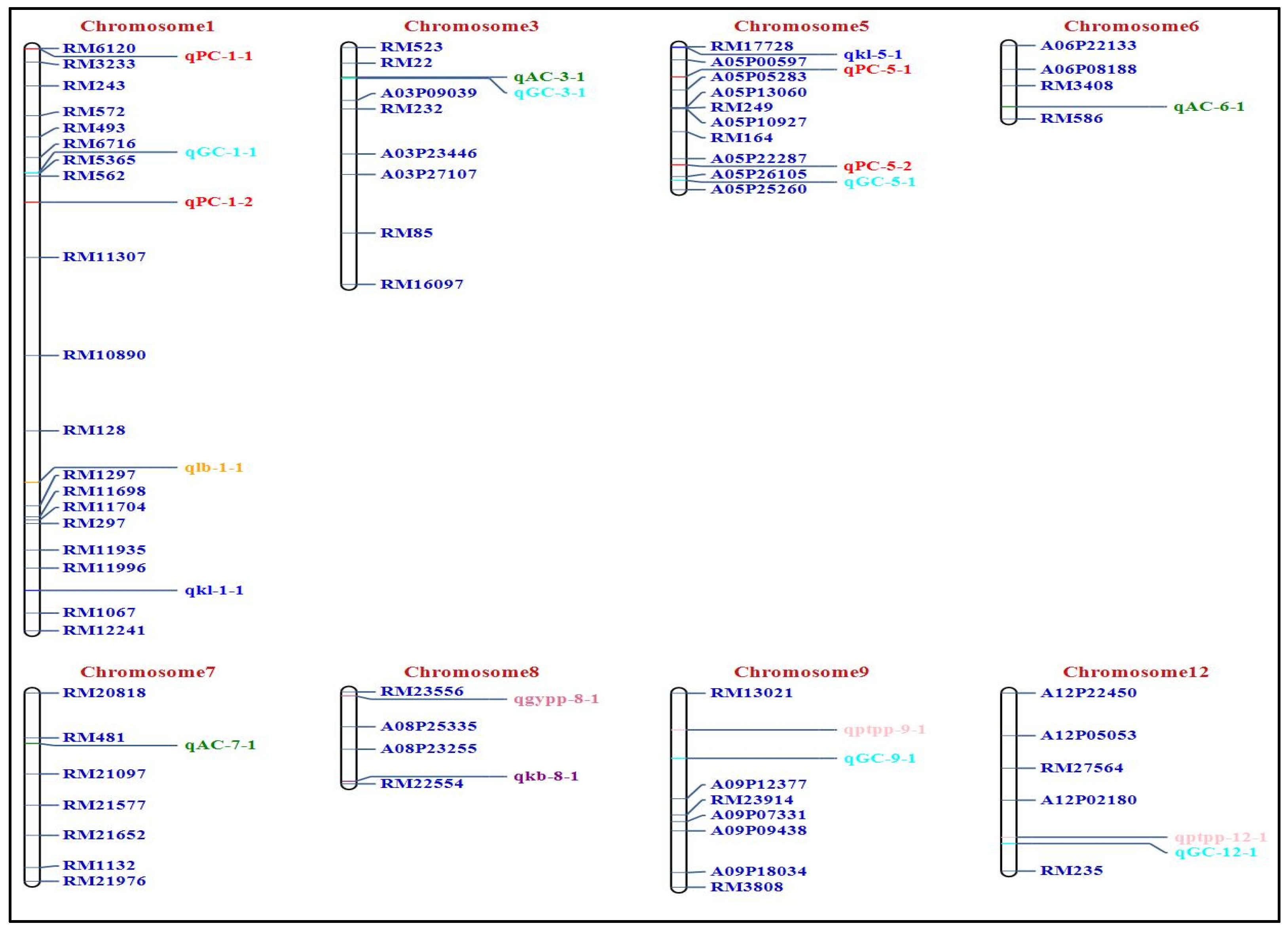
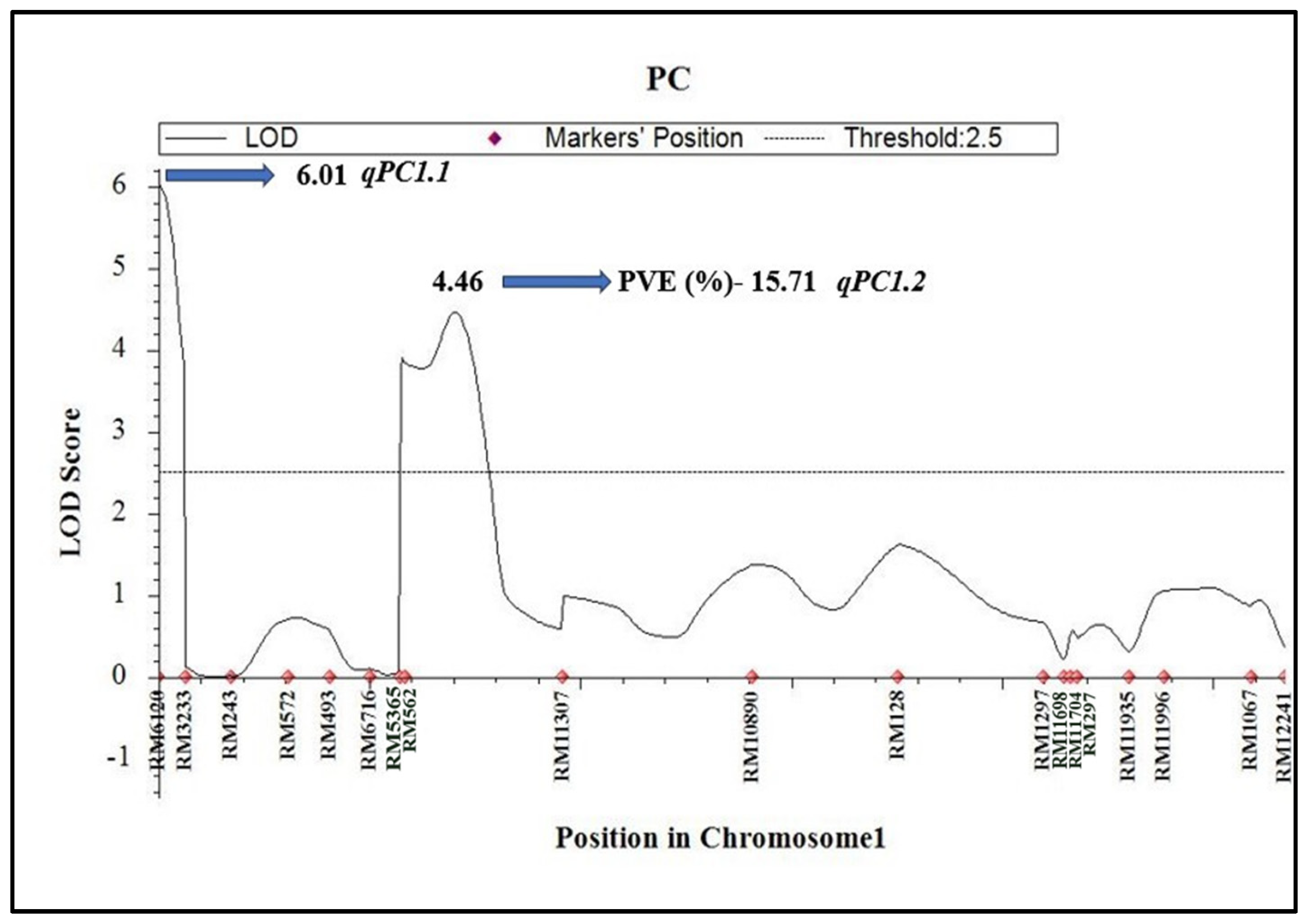
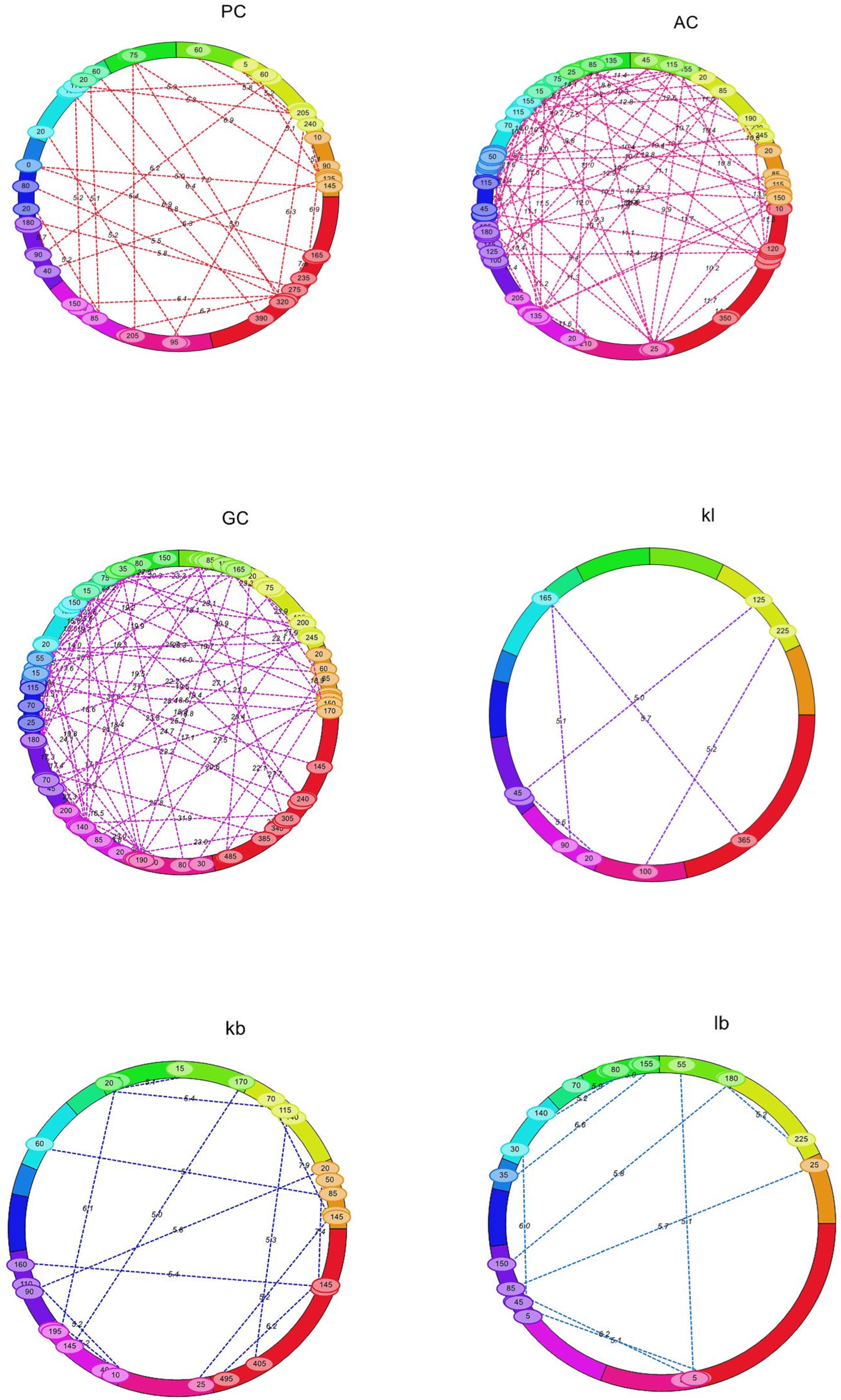
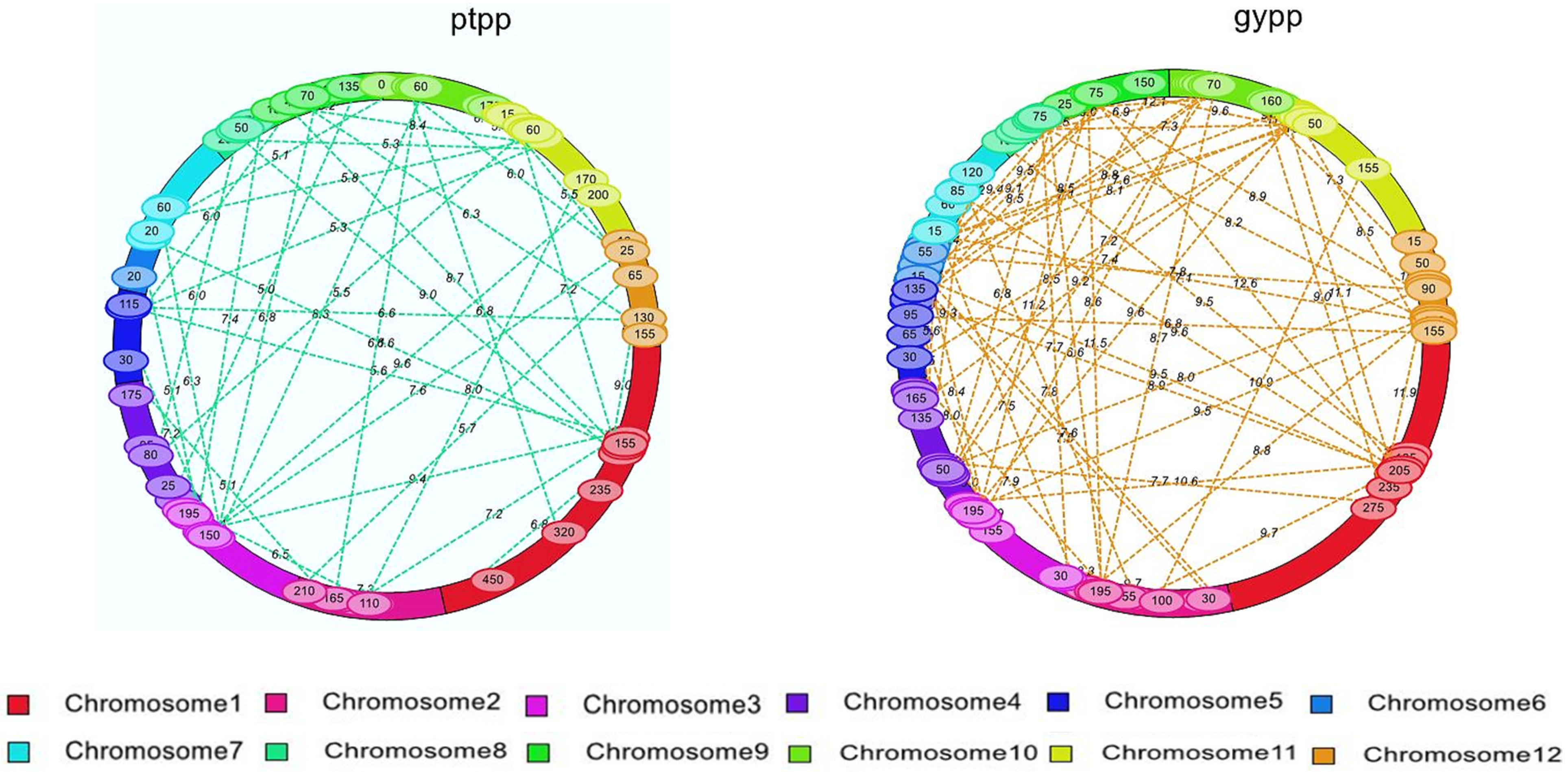
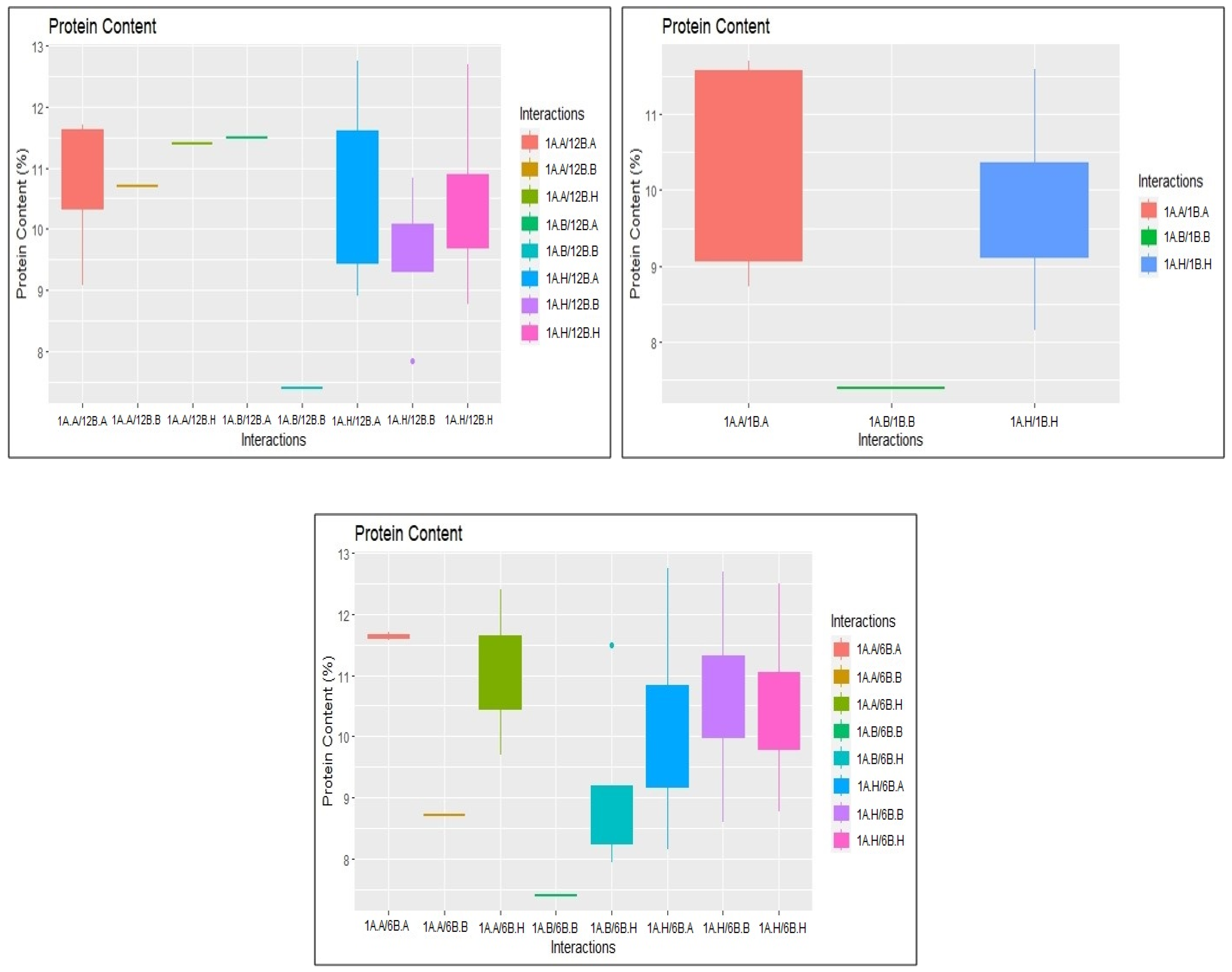
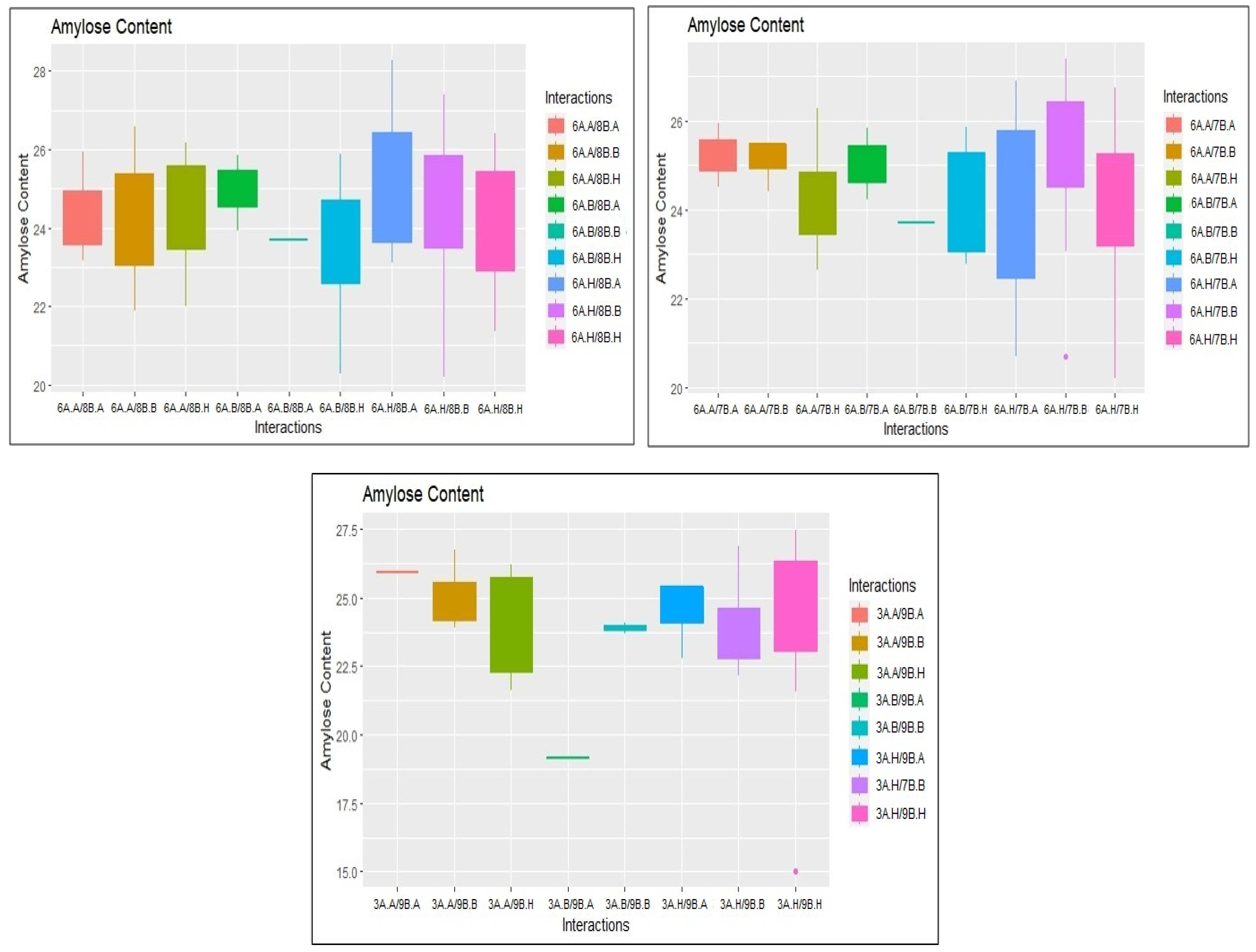
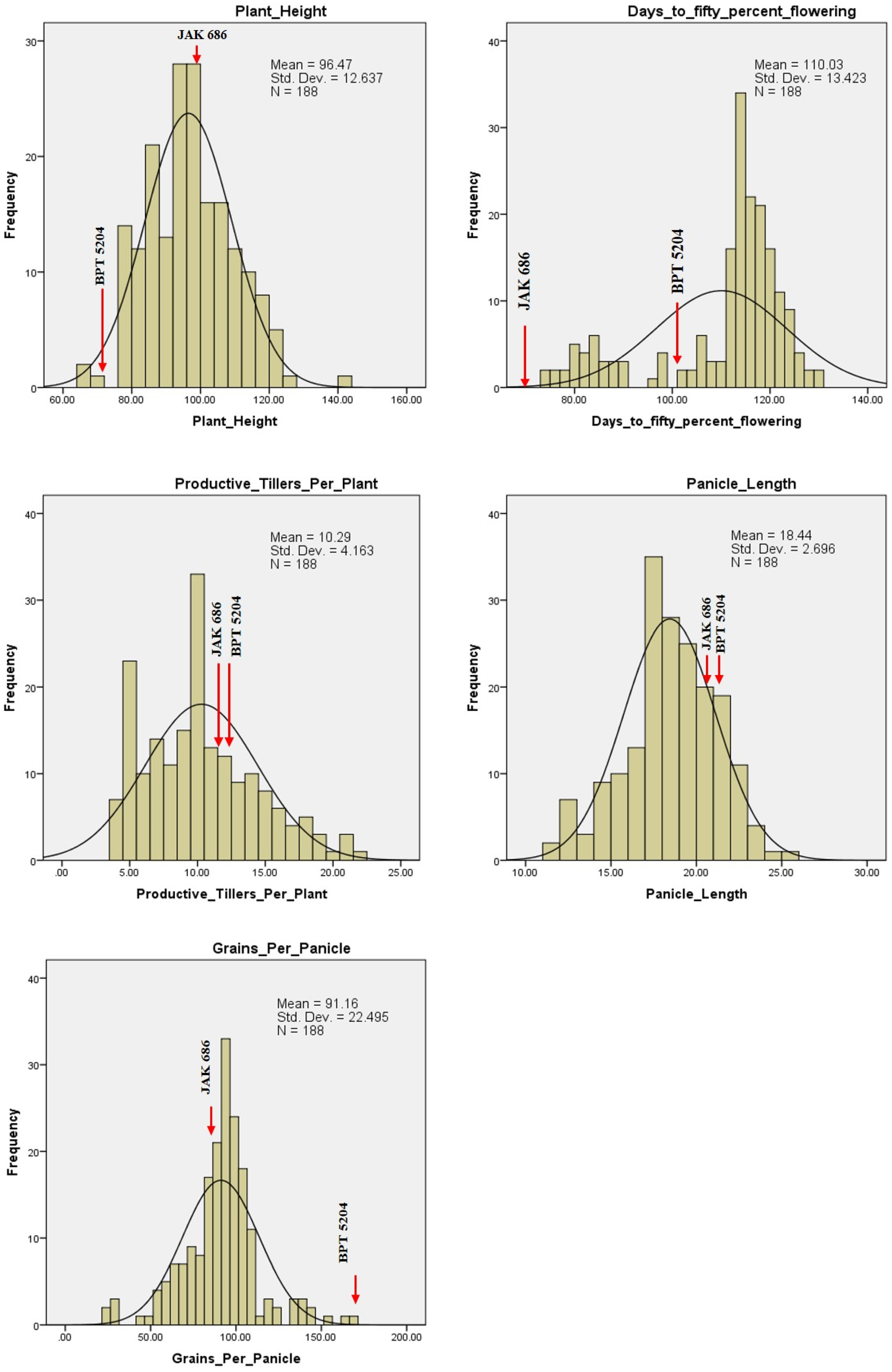
| S. No. | Chromosome | Total Markers | Polymorphic Markers | Polymorphism (%) | Length (cM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 185 | 19 | 10.27 | 534.05 |
| 2 | 2 | 94 | 10 | 10.63 | 228.58 |
| 3 | 3 | 168 | 8 | 4.76 | 223.58 |
| 4 | 4 | 119 | 12 | 10.08 | 198.74 |
| 5 | 5 | 92 | 10 | 10.86 | 138.02 |
| 6 | 6 | 112 | 4 | 3.57 | 74.40 |
| 7 | 7 | 96 | 7 | 7.29 | 179.37 |
| 8 | 8 | 89 | 4 | 4.49 | 91.60 |
| 9 | 9 | 95 | 7 | 7.36 | 184.76 |
| 10 | 10 | 61 | 10 | 16.39 | 184.65 |
| 11 | 11 | 68 | 7 | 10.29 | 270.94 |
| 12 | 12 | 101 | 5 | 4.95 | 170.26 |
| Total | 1280 | 103 | 8.04 | 2478.95 |
| S. No. | Trait | CHR | QTL | Position | Marker Interval | LOD | PVE(%) | Add | Parental Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PC | 1 | qPC1.1 | 0 | RM6120-RM3233 | 6.01 | 5.38 | 0.67 | J |
| 2 | PC | 1 | qPC1.2 | 141 | RM562-RM11307 | 4.46 | 15.71 | 1.28 | J |
| 3 | PC | 5 | qPC5.1 | 29 | A05P00597-A05P05283 | 2.84 | 4.59 | 0.20 | J |
| 4 | PC | 5 | qPC5.2 | 114 | A05P22287-A05P26105 | 2.88 | 3.09 | 0.57 | J |
| 5 | AC | 3 | qAC3.1 | 28 | RM22-A03P09039 | 6.37 | 7.15 | 4.10 | J |
| 6 | AC | 6 | qAC6.1 | 62 | RM3408-RM586 | 3.25 | 2.71 | 1.36 | J |
| 7 | AC | 7 | qAC7.1 | 48 | RM481-RM21097 | 2.91 | 1.52 | 0.66 | J |
| 8 | GC | 1 | qGC1.1 | 114 | RM6716-RM5365 | 3.57 | 1.22 | −6.00 | B |
| 9 | GC | 3 | qGC3.1 | 29 | RM22-A03P09039 | 5.56 | 6.23 | −21.56 | B |
| 10 | GC | 5 | qGC5.1 | 129 | A05P26105-A05P25260 | 3.35 | 1.27 | 1.57 | J |
| 11 | GC | 9 | qGC9.1 | 62 | RM13021-A09P12377 | 3.68 | 5.90 | 12.64 | J |
| 12 | GC | 12 | qGC12.1 | 144 | A12P02180-RM235 | 3.00 | 5.89 | 12.37 | J |
| 13 | KL | 1 | qkl1.1 | 497 | RM11996-RM1067 | 2.86 | 9.63 | −0.0005 | B |
| 14 | KL | 5 | qkl5.1 | 0 | RM17728-A05P00597 | 4.77 | 4.24 | 0.07 | J |
| 15 | KB | 8 | qkb8.1 | 89 | A08P23255-RM22554 | 3.30 | 7.79 | 0.04 | J |
| 16 | L:B | 1 | qlb1.1 | 398 | RM128-RM1297 | 2.51 | 6.19 | 0.002 | J |
| 17 | PTPP | 9 | qptpp9.1 | 35 | RM13021-A09P12377 | 4.34 | 5.65 | 3.55 | J |
| 18 | PTPP | 12 | qptpp12.1 | 138 | A12P02180-RM235 | 3.55 | 5.78 | 3.63 | J |
| 19 | GYPP | 8 | qgypp8.1 | 4 | RM23556-A08P25335 | 2.57 | 6.07 | −2.30 | B |
| Trait | Chromosome | Identified QTLs | Previously Known QTLs | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Physical Position (Mbp) | Name | Physical Position (Mbp) | |||
| Protein content | 1 | qPC1.1 | 4.31–5.05 | qPC1.1 | 4.63–4.70 | [20] |
| 1 | qPC1.2 | 14.61–23.92 | qPr1 | 12.20–14.63 | [21] | |
| 1 | qGPC1.1 | 0.6–1.1 | [22] | |||
| 1 | qPC1.1 | 8.07 | [23] | |||
| 1 | qRPC-1 | 11.07 | [11] | |||
| 1 | qPC-1 | 25.02–26.19 | [24] | |||
| 1 | Pro-1 | 32.09–34.02 | [10] | |||
| 1 | qPC1 | 37.88–40.16 | [25] | |||
| 1 | qPC1.2 | 39.16–39.23 | [20] | |||
| 1 | qPC1 | 40.13–41.16 | [26] | |||
| 5 | qPC5.1 | 0.59–5.28 | qPC5 | 1.94 | [26] | |
| 5 | qPC5.2 | 22.28–26.10 | qPC-5 | 23.48–24.26 | [27] | |
| 5 | qPC5.1 | 0.53 | [28] | |||
| 5 | qGPC5 | 7.8 | [2] | |||
| Genotypes | GPC (%) | PH (cm) | PTPP | PL (cm) | GPP | TGW (g) | GYPP (g) | DFF | AC (%) | GC (mm) | KL (mm) | KB (mm) | L:B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F2-140 | 14.67 | 93 | 18 | 21 | 126 | 24.5 | 29.03 | 114 | 25.87 | 22 | 5.65 | 2.18 | 2.59 |
| F2-12 | 14.36 | 91 | 10 | 16.83 | 90 | 21.3 | 19.12 | 119 | 23.46 | 49 | 5.74 | 1.98 | 2.89 |
| F2-7 | 14.32 | 85 | 21 | 20.27 | 82 | 18.4 | 16.54 | 119 | 23.17 | 24 | 5.5 | 2.02 | 2.72 |
| F2-147 | 13.60 | 104 | 10 | 19.4 | 155 | 23.6 | 25.90 | 115 | 23.61 | 48 | 5.47 | 2.28 | 2.39 |
| F2-41 | 13.36 | 95 | 12 | 19.43 | 103 | 23.6 | 15.87 | 116 | 21.88 | 52 | 6.1 | 2.11 | 2.89 |
| Traits | PC | AC | GC | KL | KB | L:B | PH | PTPP | PL | GPP | TGW | GYPP | DFF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | 1 | −0.060 | −0.054 | 0.104 | −0.019 | 0.082 | −0.049 | 0.019 | 0.087 | 0.078 | 0.052 | 0.025 | 0.064 |
| AC | −0.060 | 1 | −0.245 ** | −0.135 * | 0.143 * | −0.187 ** | 0.021 | −0.102 | 0.029 | −0.023 | 0.075 | −0.044 | −0.043 |
| GC | −0.054 | −0.245 ** | 1 | 0.024 | 0.090 | −0.057 | −0.034 | 0.000 | 0.089 | 0.074 | −0.036 | 0.135 * | 0.088 |
| KL | 0.104 | −0.135 * | 0.024 | 1 | 0.014 | 0.585 ** | −0.068 | 0.305 ** | 0.208 ** | 0.187 ** | 0.258 ** | 0.263 ** | 0.049 |
| KB | −0.019 | 0.143 * | 0.090 | 0.014 | 1 | −0.801 ** | 0.133 * | −0.056 | −0.012 | −0.043 | 0.389 ** | 0.005 | −0.047 |
| L:B | 0.082 | −0.187 ** | −0.057 | 0.585 ** | −0.801 ** | 1 | −0.145 * | 0.238 ** | 0.146 * | 0.154 * | −0.163 * | 0.160 * | 0.062 |
| PH | −0.049 | 0.021 | −0.034 | −0.068 | 0.133 * | −0.145 * | 1 | −0.158 * | −0.047 | −0.149 * | 0.003 | −0.130 * | −0.507 ** |
| PTPP | 0.019 | −0.102 | 0.000 | 0.305 ** | −0.056 | 0.238 ** | −0.158 * | 1 | 0.503 ** | 0.456 ** | 0.166 ** | 0.651 ** | 0.100 |
| PL | 0.087 | 0.029 | 0.089 | 0.208 ** | −0.012 | 0.146 * | −0.047 | 0.503 ** | 1 | 0.390 ** | 0.038 | 0.487 ** | 0.078 |
| GPP | 0.078 | −0.023 | 0.074 | 0.187 ** | −0.043 | 0.154 * | −0.149 * | 0.456 ** | 0.390 ** | 1 | 0.137 * | 0.836 ** | 0.159 * |
| TGW | 0.052 | 0.075 | −0.036 | 0.258 ** | 0.389 ** | −0.163 * | 0.003 | 0.166 ** | 0.038 | 0.137 * | 1 | 0.125 * | 0.044 |
| GYPP | 0.025 | −0.044 | 0.135 * | 0.263 ** | 0.005 | 0.160 * | −0.130 * | 0.651 ** | 0.487 ** | 0.836 ** | 0.125 * | 1 | 0.109 |
| DFF | 0.064 | −0.043 | 0.088 | 0.049 | −0.047 | 0.062 | −0.507 ** | 0.100 | 0.078 | 0.159 * | 0.044 | 0.109 | 1 |
| Characters | Vg | Vp | Ve | PCV | GCV | h2 BS | GA | GAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant height (cm) | 149.2 | 160.4 | 11.2 | 13.2 | 12.7 | 93.0 | 24.2 | 25.3 |
| Productive tillers per plant (No.) | 15.1 | 16.9 | 1.8 | 39.0 | 36.8 | 89.2 | 7.5 | 71.7 |
| Panicle length (cm) | 7.0 | 7.2 | 0.2 | 14.4 | 14.1 | 96.4 | 5.3 | 28.6 |
| Grains per panicle (No.) | 357.4 | 496.2 | 138.7 | 23.1 | 19.6 | 72.0 | 33.0 | 34.3 |
| 1000-grain weight (g) | 3.1 | 5.0 | 1.9 | 11.1 | 8.7 | 61.4 | 2.8 | 14.1 |
| Grain yield per plant (g) | 42.7 | 44.0 | 1.2 | 40.4 | 39.8 | 97.0 | 13.2 | 80.8 |
| Kernel length (mm) | 0.016 | 0.045 | 0.029 | 3.9 | 2.3 | 35.1 | 0.15 | 2.8 |
| Kernel breadth (mm) | 0.005 | 0.012 | 0.017 | 5.2 | 4.8 | 44.9 | 0.10 | 4.8 |
| Length-to-breadth ratio | 0.01 | 0.029 | 0.019 | 6.6 | 3.8 | 33.8 | 0.12 | 4.6 |
| Days to 50% flowering | 125.1 | 182.6 | 57.4 | 12.3 | 10.2 | 68.5 | 19.1 | 17.3 |
| Gel consistency (mm) | 191.2 | 211.6 | 20.4 | 41.3 | 39.2 | 90.3 | 27.0 | 76.9 |
| Protein content (%) | 1.2 | 2.3 | 1.1 | 15.1 | 10.9 | 52.4 | 1.6 | 16.2 |
| Amylose content (%) | 4.9 | 6.6 | 1.6 | 10.6 | 9.2 | 75.4 | 4.0 | 16.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bharali, V.; Yadla, S.; Thati, S.; Bitra, B.; Karapati, D.; Chirravuri, N.N.; Badri, J.; Sundaram, R.M.; Jukanti, A.K. Mapping Genomic Regions for Grain Protein Content and Quality Traits in Milled Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plants 2025, 14, 905. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060905
Bharali V, Yadla S, Thati S, Bitra B, Karapati D, Chirravuri NN, Badri J, Sundaram RM, Jukanti AK. Mapping Genomic Regions for Grain Protein Content and Quality Traits in Milled Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plants. 2025; 14(6):905. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060905
Chicago/Turabian StyleBharali, Violina, Suneetha Yadla, Srinivas Thati, Bhargavi Bitra, Divya Karapati, Neeraja Naga Chirravuri, Jyothi Badri, Raman Meenakshi Sundaram, and Aravind Kumar Jukanti. 2025. "Mapping Genomic Regions for Grain Protein Content and Quality Traits in Milled Rice (Oryza sativa L.)" Plants 14, no. 6: 905. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060905
APA StyleBharali, V., Yadla, S., Thati, S., Bitra, B., Karapati, D., Chirravuri, N. N., Badri, J., Sundaram, R. M., & Jukanti, A. K. (2025). Mapping Genomic Regions for Grain Protein Content and Quality Traits in Milled Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plants, 14(6), 905. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060905







