Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Heat Shock Transcription Factors in Camellia sinensis Under Abiotic Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of the CsHsf Genes in Camellia sinensis
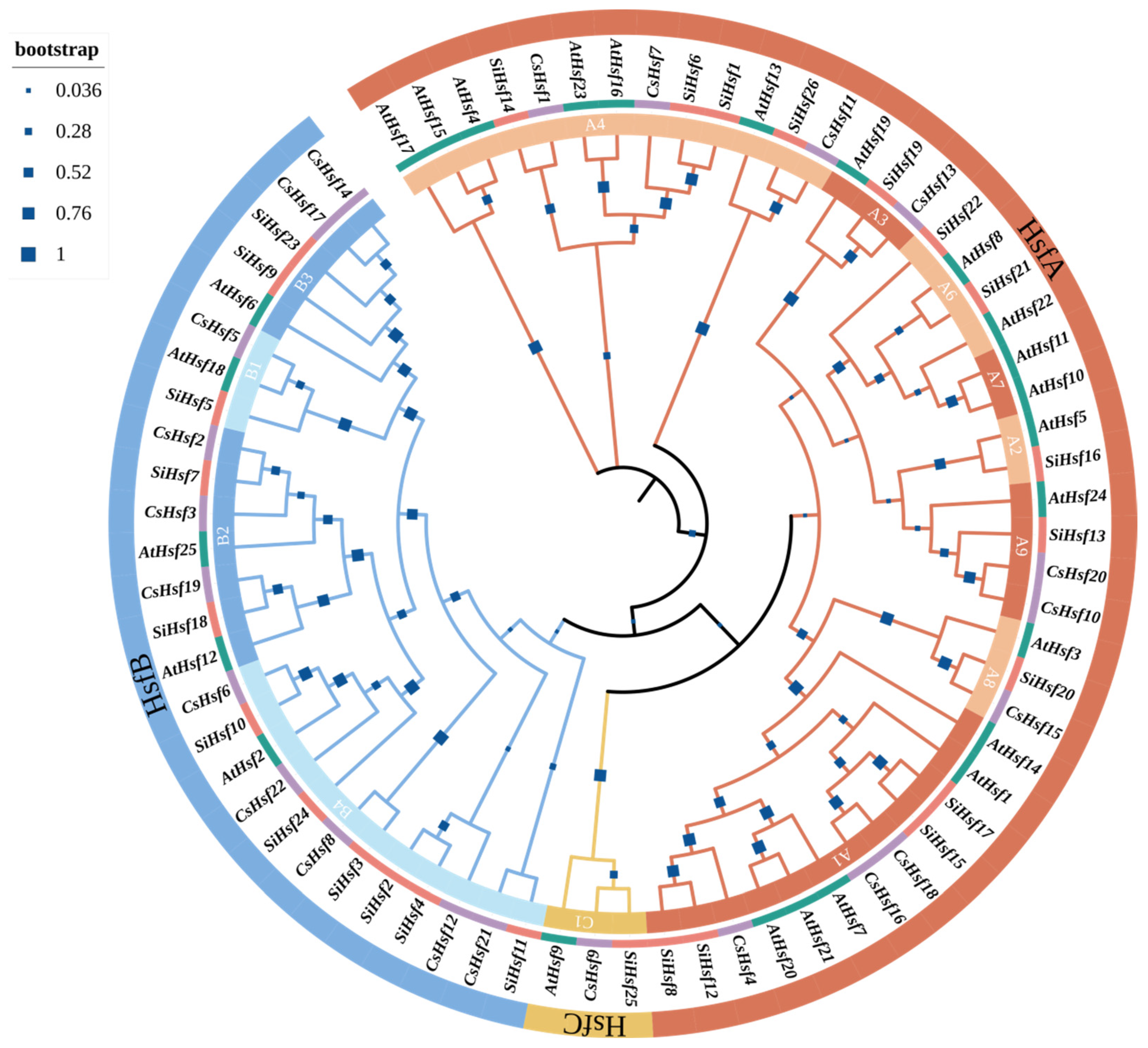
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis and Classification of CsHsfs
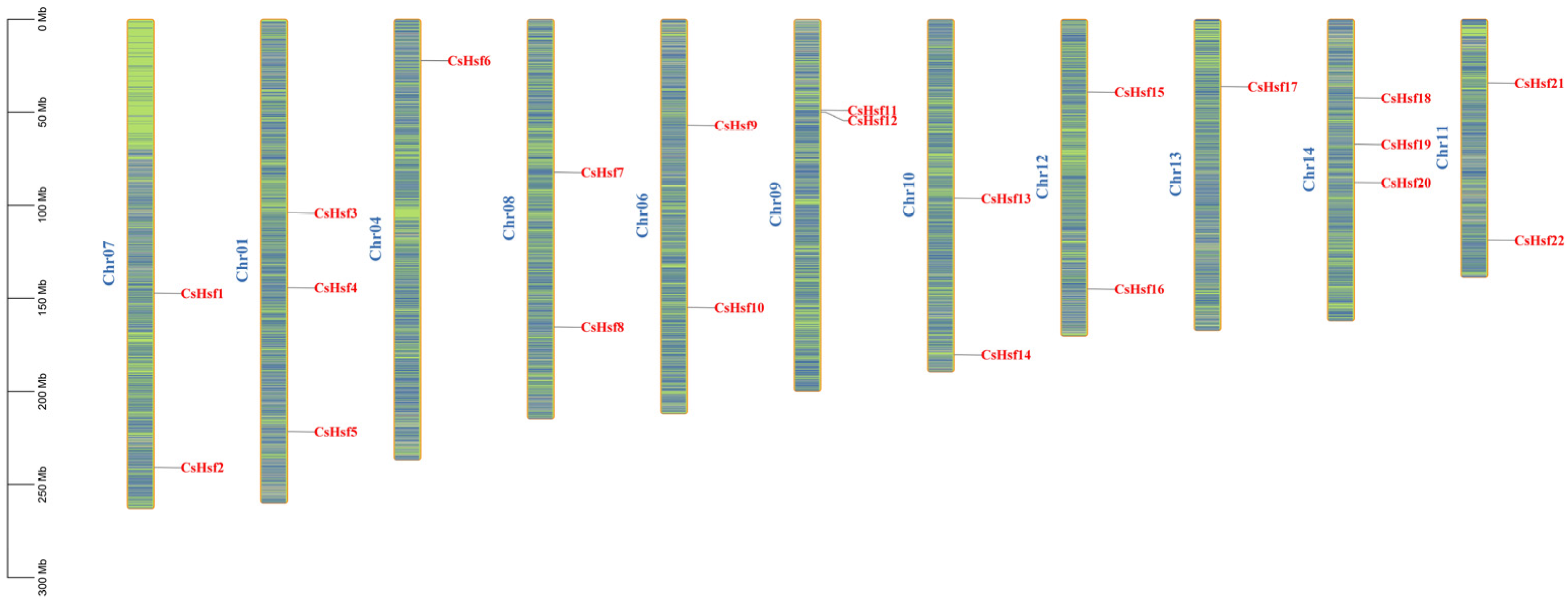
2.3. Distribution of CsHsf Genes Across Chromosomes
2.4. Gene Structure and Conserved Motif Composition
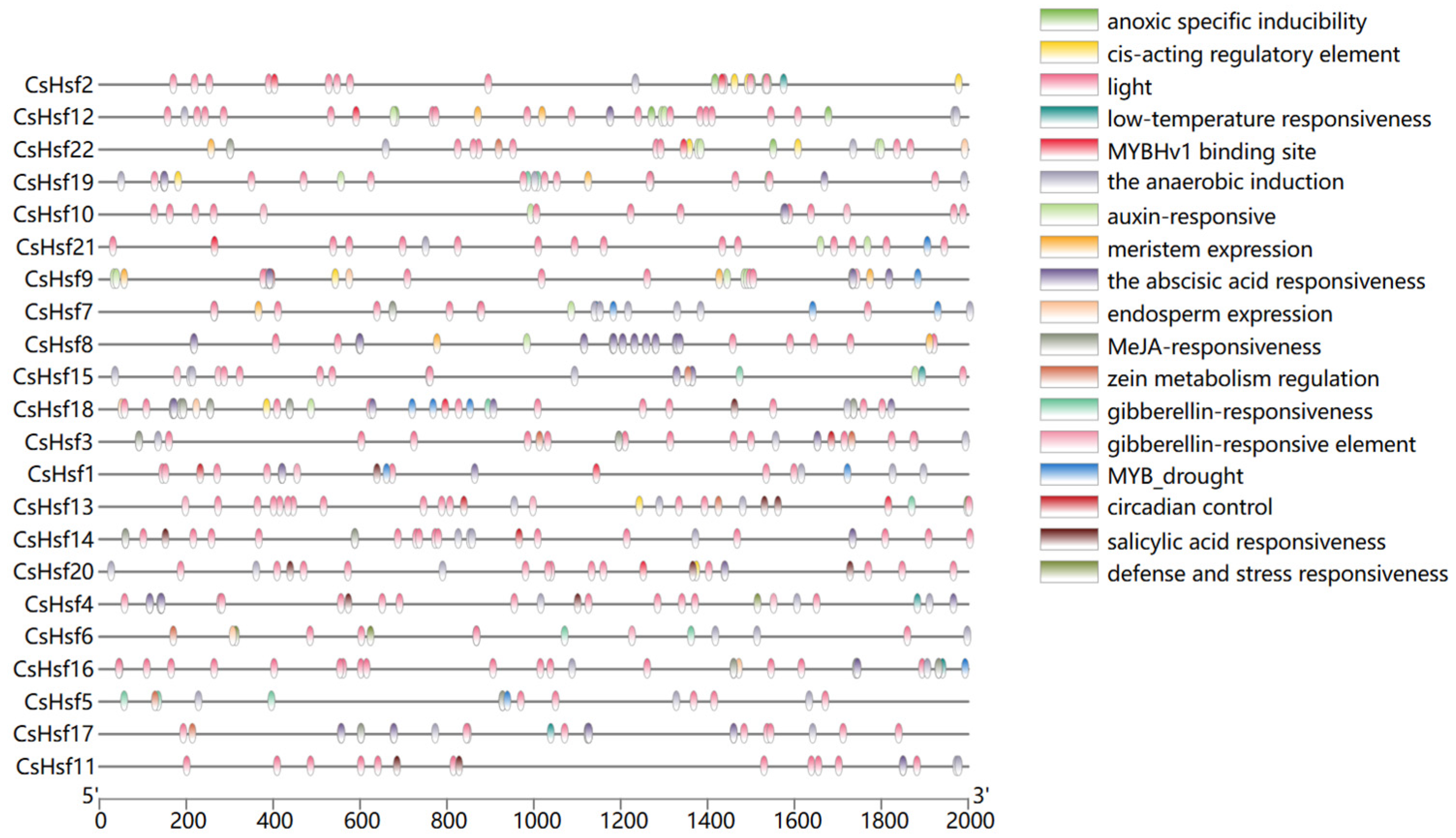
2.5. Analysis of cis-Acting Elements
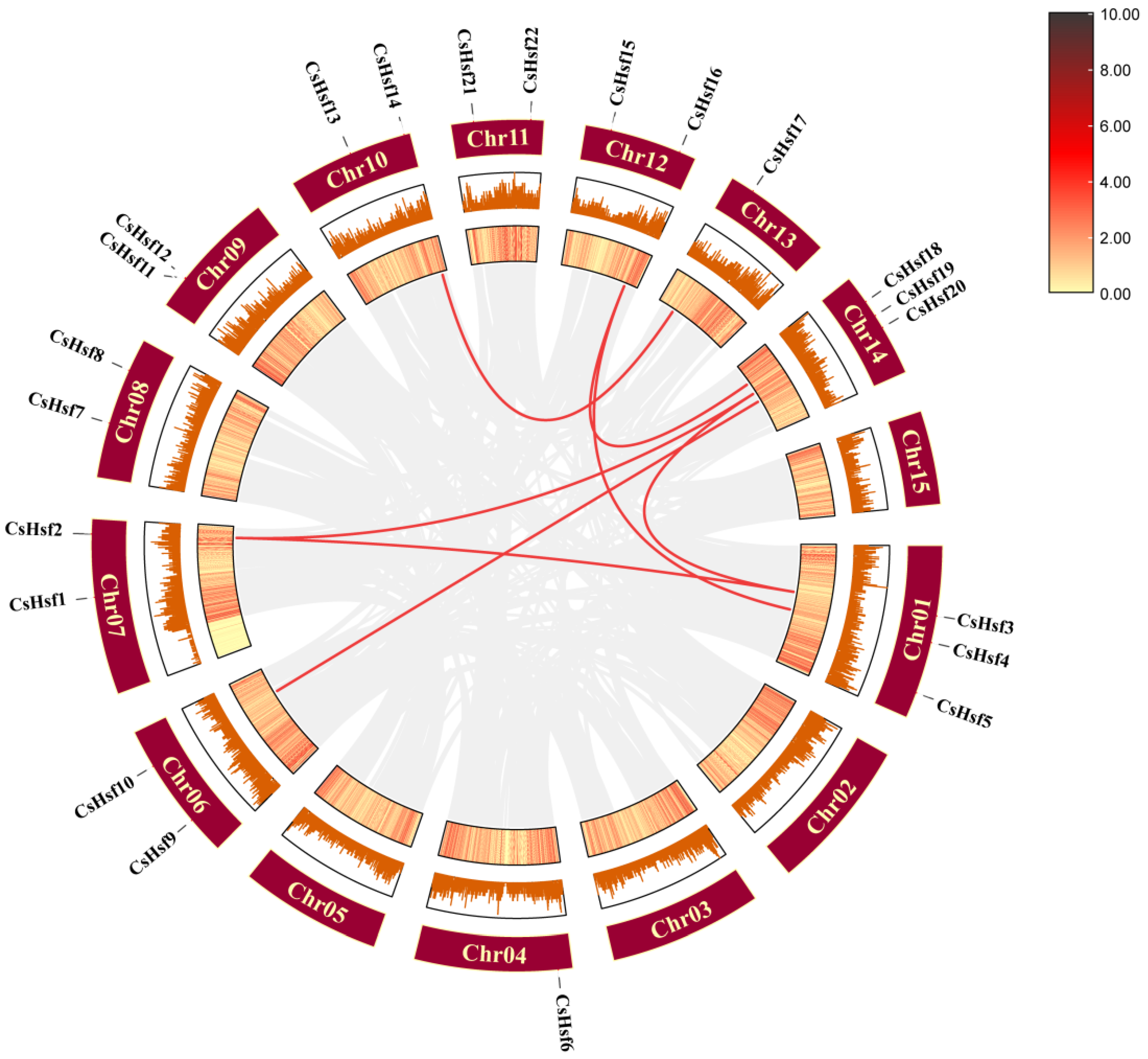
2.6. Intraspecific Collinearity Analysis of CsHsf Genes
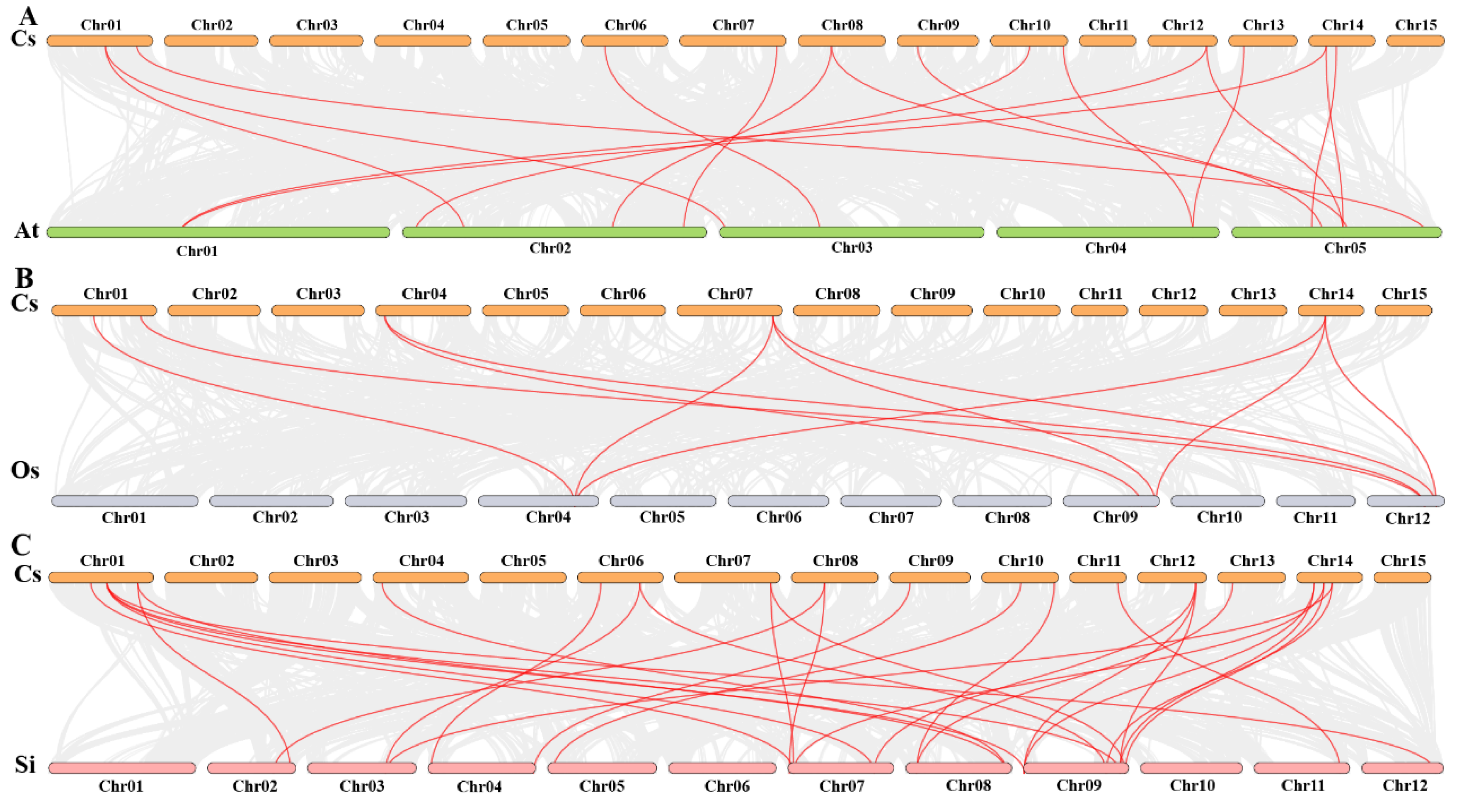
2.7. Synteny Analysis Among CsHsf Genes
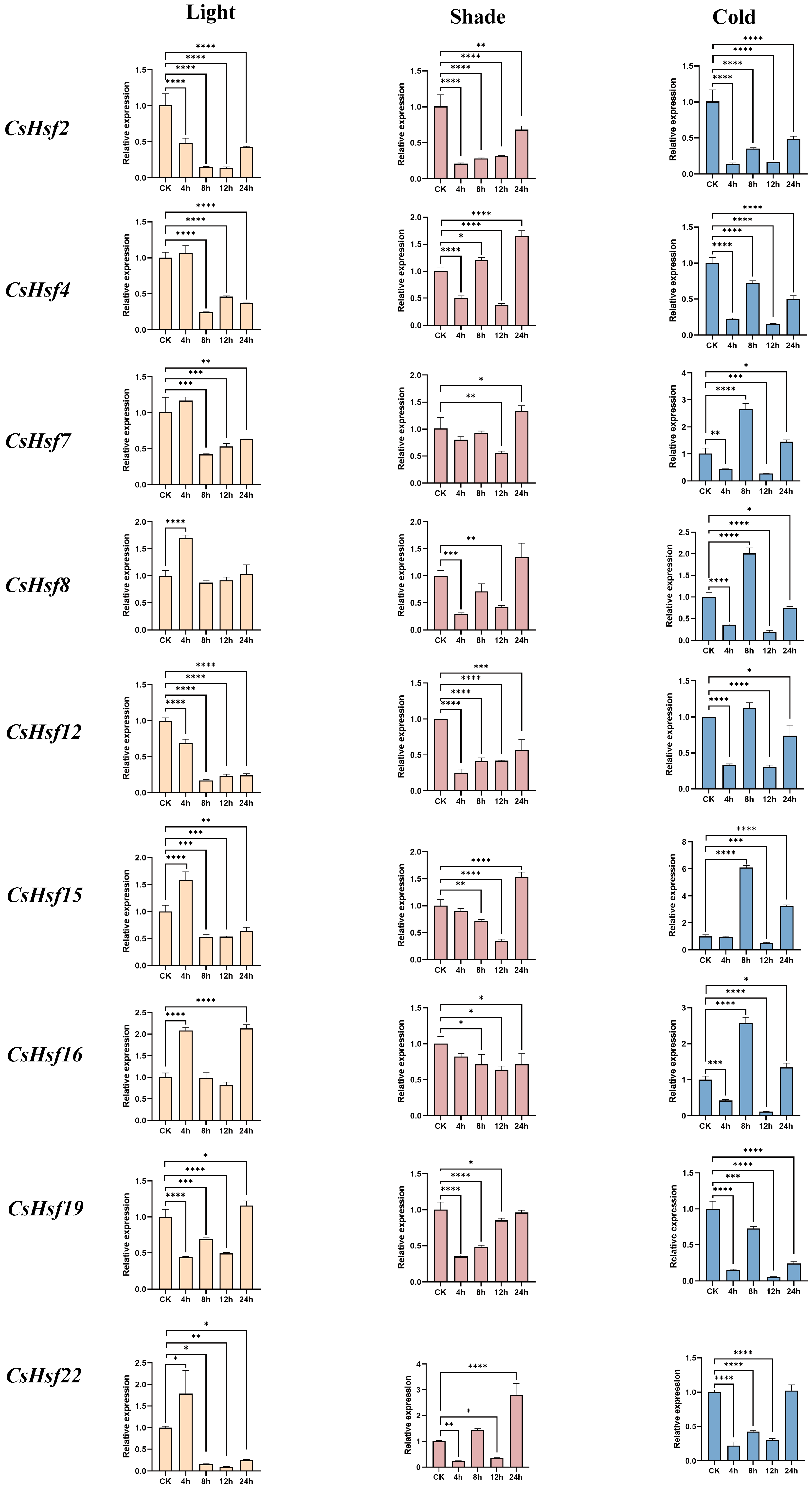
2.8. Expression Patterns of CsHsfs Under Light, Shade, and Cold Stress
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification and Characterization of the Hsf Gene Family in Camellia sinensis
4.2. Evolutionary Analysis and Gene Structure of the CsHsfs
4.3. Physicochemical Characteristics and Subcellular Localization
4.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.5. Collinearity and Repetition Analysis
4.6. Abiotic Stress Treatments
4.7. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paul, A.; Chatterjee, A.; Subrahmanya, S.; Shen, G.; Mishra, N. NHX Gene Family in Camellia sinensis: In-silico Genome-Wide Identification, Expression Profiles, and Regulatory Network Analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 777884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Li, X. Genome-wide analysis of the P450 gene family in tea plant (Camellia sinensis) reveals functional diversity in abiotic stress. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zeng, L.; Hou, X.; Liao, Y.; Yang, Z. Low temperature synergistically promotes wounding-induced indole accumulation by INDUCER OF CBF EXPRESSION-mediated alterations of jasmonic acid signaling in Camellia sinensis. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 2172–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lin, S.; Li, J.; Chen, T.; Gu, Q.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Z. Theanine Improves Salt Stress Tolerance via Modulating Redox Homeostasis in Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 770398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ye, X.; Xing, A.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Shu, Z.; Wang, Y. Camellia sinensis small GTPase gene (CsRAC1) involves in response to salt stress, drought stress and ABA signaling pathway. Gene 2022, 821, 146318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waadt, R.; Seller, C.A.; Hsu, P.K.; Takahashi, Y.; Munemasa, S.; Schroeder, J.I. Plant hormone regulation of abiotic stress responses. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Mostafa, S.; Zeng, W.; Jin, B. Function and Mechanism of Jasmonic Acid in Plant Responses to Abiotic and Biotic Stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murre, C.; McCaw, P.S.; Baltimore, D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell 1989, 56, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riechmann, J.L.; Heard, J.; Martin, G.; Reuber, L.; Jiang, C.; Keddie, J.; Adam, L.; Pineda, O.; Ratcliffe, O.J.; Samaha, R.R.; et al. Arabidopsis transcription factors: Genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science 2000, 290, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baillo, E.H.; Kimotho, R.N.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, P. Transcription Factors Associated with Abiotic and Biotic Stress Tolerance and Their Potential for Crops Improvement. Genes 2019, 10, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, H.; Ishibashi, Y.; Shinmyo, A.; Kanaya, S.; Kato, K. Genome-wide analyses of early translational responses to elevated temperature and high salinity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 448–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeta, T.; Zaizen, Y.; Asami, T.; Yoshida, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Okamoto, S.; Matsuo, T.; Sugimoto, Y. Molecular evidence of the involvement of heat shock protein 90 in brassinosteroid signaling in Arabidopsis T87 cultured cells. Plant Cell Rep. 2014, 33, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, T.; Wan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, W. Genome-Wide Identification, Classification and Expression Analysis of the HSP Gene Superfamily in Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, A.P. Human small heat shock proteins: Protein interactomes of homo- and hetero-oligomeric complexes: An update. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 1959–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpeci, T.E.; Zanor, M.I.; Valle, E.M. Investigating the role of plant heat shock proteins during oxidative stress. Plant Signal. Behav. 2008, 3, 856–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Liu, J.H.; Ma, X.; Luo, D.X.; Gong, Z.H.; Lu, M.H. The Plant Heat Stress Transcription Factors (HSFs): Structure, Regulation, and Function in Response to Abiotic Stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.S.; Yu, T.F.; He, G.H.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Y.B.; Chai, S.C.; Xu, Z.S.; Ma, Y.Z. Genome-wide analysis of the Hsf family in soybean and functional identification of GmHsf-34 involvement in drought and heat stresses. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, D.; Chakrabarti, S.; Sarkar, A.; Singh, A.; Grover, A. Heat shock factor gene family in rice: Genomic organization and transcript expression profiling in response to high temperature, low temperature and oxidative stresses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. PPB 2009, 47, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, N.; Feng, H.; Wang, S.; Punekar, A.S.; Ladenstein, R.; Wang, D.C.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, J.; Liu, W. Structures of heat shock factor trimers bound to DNA. iScience 2021, 24, 102951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerklotz, D.; Döring, P.; Bonzelius, F.; Winkelhaus, S.; Nover, L. The balance of nuclear import and export determines the intracellular distribution and function of tomato heat stress transcription factor HsfA2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyck, R.; Harmening, U.; Höhfeld, I.; Treuter, E.; Scharf, K.D.; Nover, L. Intracellular distribution and identification of the nuclear localization signals of two plant heat-stress transcription factors. Planta 1997, 202, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Meng, P.; Yang, G.; Zhang, M.; Peng, S.; Zhai, M.Z. Genome-wide identification and transcript profiles of walnut heat stress transcription factor involved in abiotic stress. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Xia, M.; Xing, H.; Gong, M.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, H.L. Exploring the Heat Shock Transcription Factor (HSF) Gene Family in Ginger: A Genome-Wide Investigation on Evolution, Expression Profiling, and Response to Developmental and Abiotic Stresses. Plants 2023, 12, 2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xu, J.; Ouyang, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, S. Genome-Wide Identification of HSF Gene Family in Kiwifruit and the Function of AeHSFA2b in Salt Tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, C.; Zhao, X.; Li, Z.; Mou, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wang, J.; Yuan, C.; Li, C.; et al. Hsf transcription factor gene family in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.): Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis under drought and salt stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1214732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Wang, C.; Zheng, L.; Ji, L.; Yang, J.; Song, L.; Shi, Y.; et al. Phylogenetic and expression analyses of HSF gene families in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and characterization of TaHSFB4-2B under abiotic stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1047400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Ma, R.; Xie, M.; Fan, Y.; Feng, L.; Chen, L.; Yang, H.; Wei, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, K.; et al. Genome-wide identification, phylogenetic and expression pattern analysis of HSF family genes in the Rye (Secale cereale L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshad, A.; Rashid, M.; Zaman, Q.U. In-silico analysis of heat shock transcription factor (OsHSF) gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Geng, J.; Du, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, W.; Fang, Q.; Yin, Z.; Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Fan, Y.; et al. Heat shock transcription factor (Hsf) gene family in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris): Genome-wide identification, phylogeny, evolutionary expansion and expression analyses at the sprout stage under abiotic stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, G.; Ye, Y.; Shang, L.; Hong, S.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, C. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of HSF Transcription Factors in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) under Abiotic Stress. Plants 2022, 11, 2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumalaikumar, V.P.; Gorka, M.; Schulz, K.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C.; Sampathkumar, A.; Skirycz, A.; Vierstra, R.D.; Balazadeh, S. Selective autophagy regulates heat stress memory in Arabidopsis by NBR1-mediated targeting of HSP90.1 and ROF1. Autophagy 2021, 17, 2184–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Fan, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.Z.; Song, W.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, W.; Ma, G.; Alolga, R.N.; Li, W.; et al. Integrative omic and transgenic analyses reveal the positive effect of ultraviolet-B irradiation on salvianolic acid biosynthesis through upregulation of SmNAC1. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 104, 781–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Ni, D.; Wang, M.; Guo, G. Genome-wide characterization of tea plant (Camellia sinensis) Hsf transcription factor family and role of CsHsfA2 in heat tolerance. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Dearing, J.A.; Dawson, T.P.; Dong, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W. Poverty alleviation strategies in eastern China lead to critical ecological dynamics. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 506–507, 164–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.; He, S. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of the heat shock transcription factor family in Garlic (Allium sativum L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, E.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, J.H. Genome-wide analysis and molecular characterization of heat shock transcription factor family in Glycine max. J. Genet. Genom. 2013, 40, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, S.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Guo, X. Genome-wide identification and abiotic stress-responsive pattern of heat shock transcription factor family in Triticum aestivum L. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Cai, J.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, D.; Li, Y. Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of Hsf gene family in Verbena bonariensis under low-temperature stress. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.W.; Wu, Z.J.; Li, X.H.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhuang, J. Identification, classification, and expression profiles of heat shock transcription factors in tea plant (Camellia sinensis) under temperature stress. Gene 2016, 576 Pt 1, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, G.; Garg, V.; Kudapa, H.; Doddamani, D.; Pazhamala, L.T.; Khan, A.W.; Thudi, M.; Lee, S.H.; Varshney, R.K. Genome-wide dissection of AP2/ERF and HSP90 gene families in five legumes and expression profiles in chickpea and pigeonpea. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 1563–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwar, M.; Chaudhary, C.; Anand, K.A.; Singh, S.; Garg, M.; Mishra, S.K.; Sirohi, P.; Chauhan, H. An insight into Pisum sativum HSF gene family-Genome-wide identification, phylogenetic, expression, and analysis of transactivation potential of pea heat shock transcription factor. Plant Physiol. Biochem. PPB 2023, 202, 107971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swindell, W.R.; Huebner, M.; Weber, A.P. Transcriptional profiling of Arabidopsis heat shock proteins and transcription factors reveals extensive overlap between heat and non-heat stress response pathways. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Ma, Z.; Chen, H.; Liu, M. MYB Gene Family in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.): Genome-Wide Identification of Hormone-Responsive Reveals Their Potential Functions in Growth and Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Li, X.; Zi, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zhu, L.; Hong, L.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Long, R.; Kang, J.; et al. Characterization of the Heat Shock Transcription Factor Family in Medicago sativa L. and Its Potential Roles in Response to Abiotic Stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Hu, W.; Qian, Y.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, J. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of the Hsf and Hsp70 gene families in maize. Gene 2021, 770, 145348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, B.; Gu, G.; Yuan, J.; Shen, S.; Jin, L.; Lin, Z.; Lin, J.; Xie, X. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the R2R3-MYB gene family in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wan, X.L.; Yu, J.Y.; Wang, K.L.; Zhang, J. Genome-Wide Identification, Classification, and Expression Analysis of the Hsf Gene Family in Carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, B.; Xu, F.; Wang, Y.; Song, C.; Yi, M.; Ma, N.; Zhou, X.; et al. The Heat Stress Transcription Factor LlHsfA4 Enhanced Basic Thermotolerance through Regulating ROS Metabolism in Lilies (Lilium longiflorum). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Guo, S.; Xu, Y.; Meng, Q.; Li, G.; Yang, X. Glycine betaine-mediated potentiation of HSP gene expression involves calcium signaling pathways in tobacco exposed to NaCl stress. Physiol. Plant. 2014, 150, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Lu, S.; Li, Z.; Cheng, J.; Hu, P.; Zhu, T.; Wang, X.; Jin, M.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; et al. CYCLIC NUCLEOTIDE-GATED ION CHANNELs 14 and 16 Promote Tolerance to Heat and Chilling in Rice. Plant Physiol. 2020, 183, 1794–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Yan, H.W.; Wang, Y.Y.; Feng, L.; Chen, Z.; Xiang, Y. Genome Duplication and Evolution of Heat Shock Transcription Factor (HSF) Gene Family in Four Model Angiosperms. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2016, 35, 903–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, P.; Hirt, H.; Bendahmane, A. The heat-shock protein/chaperone network and multiple stress resistance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Pan, L.; Shi, Y.; Zeng, R.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Gong, X.; Huang, W.; et al. Genetic variation in a heat shock transcription factor modulates cold tolerance in maize. Mol. Plant 2024, 17, 1423–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, F.; Khan, M.S.S.; Ahmed, S.; Abdullah, M.; Hannan, F.; Chen, J. OsLPXC negatively regulates tolerance to cold stress via modulating oxidative stress, antioxidant defense and JA accumulation in rice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 199, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Q.; Wang, Y.; He, L.; Huang, F.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Han, M.; Deng, H.; Luo, L.; et al. Molecular basis of methyl-salicylate-mediated plant airborne defence. Nature 2023, 622, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Duan, Y.; Zou, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, X.; Fang, W.; Ma, Y. CsMYB Transcription Factors Participate in Jasmonic Acid Signal Transduction in Response to Cold Stress in Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis). Plants 2022, 11, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene Name | Number of Amino Acids/aa | Molecular Weight/Da | Theoretical PI | Grand Average of Hydropathicity | Instability Index | Aliphatic Index | Subcellular Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CsHsf1 | 423 | 48.81 | 5.28 | −0.852 | 56.04 | 64.23 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf2 | 375 | 41.89 | 5.88 | −0.562 | 62.11 | 74.16 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf3 | 299 | 34.05 | 6.47 | −0.873 | 60.21 | 64.25 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf4 | 508 | 56.45 | 5.13 | −0.553 | 57.85 | 71.14 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf5 | 290 | 32.14 | 5.38 | −0.821 | 38.90 | 59.21 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf6 | 326 | 36.48 | 7.71 | −0.500 | 54.80 | 70.58 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf7 | 407 | 46.42 | 4.98 | −0.774 | 55.45 | 71.35 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf8 | 211 | 24.52 | 8.97 | −0.877 | 68.00 | 63.36 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf9 | 321 | 36.304 | 5.75 | −0.533 | 66.85 | 68.35 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf10 | 416 | 46.937 | 4.95 | −0.647 | 54.37 | 75.22 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf11 | 479 | 53.663 | 5.76 | −0.772 | 56.17 | 64.36 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf12 | 79 | 9.030 | 5.07 | −0.397 | 36.81 | 71.52 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf13 | 546 | 60.823 | 4.95 | −0.563 | 58.24 | 75.31 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf14 | 240 | 27.854 | 8.20 | −0.715 | 53.05 | 64.17 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf15 | 388 | 44.338 | 4.75 | −0.633 | 54.97 | 79.33 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf16 | 495 | 54.879 | 4.89 | −0.600 | 62.72 | 70.69 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf17 | 240 | 27.825 | 5.60 | −0.851 | 80.56 | 62.12 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf18 | 513 | 56.783 | 4.78 | −0.620 | 55.54 | 68.07 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf19 | 314 | 35.057 | 5.37 | −0.680 | 55.13 | 71.46 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf20 | 499 | 55.592 | 5.15 | −0.567 | 54.76 | 81.66 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf21 | 310 | 35.134 | 6.46 | −0.332 | 37.59 | 88.03 | Nucleus. |
| CsHsf22 | 282 | 32.796 | 6.39 | −0.720 | 62.81 | 65.32 | Nucleus. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Shi, X.; Lin, Q.; Lv, M.; Chen, J.; Wen, Y.; Feng, Z.; Azam, S.M.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Heat Shock Transcription Factors in Camellia sinensis Under Abiotic Stress. Plants 2025, 14, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050697
Li G, Shi X, Lin Q, Lv M, Chen J, Wen Y, Feng Z, Azam SM, Cheng Y, Wang S, et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Heat Shock Transcription Factors in Camellia sinensis Under Abiotic Stress. Plants. 2025; 14(5):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050697
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guimin, Xinying Shi, Qinmin Lin, Mengmeng Lv, Jing Chen, Yingxin Wen, Zhiyi Feng, Syed Muhammad Azam, Yan Cheng, Shucai Wang, and et al. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Heat Shock Transcription Factors in Camellia sinensis Under Abiotic Stress" Plants 14, no. 5: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050697
APA StyleLi, G., Shi, X., Lin, Q., Lv, M., Chen, J., Wen, Y., Feng, Z., Azam, S. M., Cheng, Y., Wang, S., & Cao, S. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Heat Shock Transcription Factors in Camellia sinensis Under Abiotic Stress. Plants, 14(5), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050697









