The Effect of Light Cycles on the Predation Characteristics of Phytoseiulus persimilis (Acari: Phytoseiidae) Feeding on Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
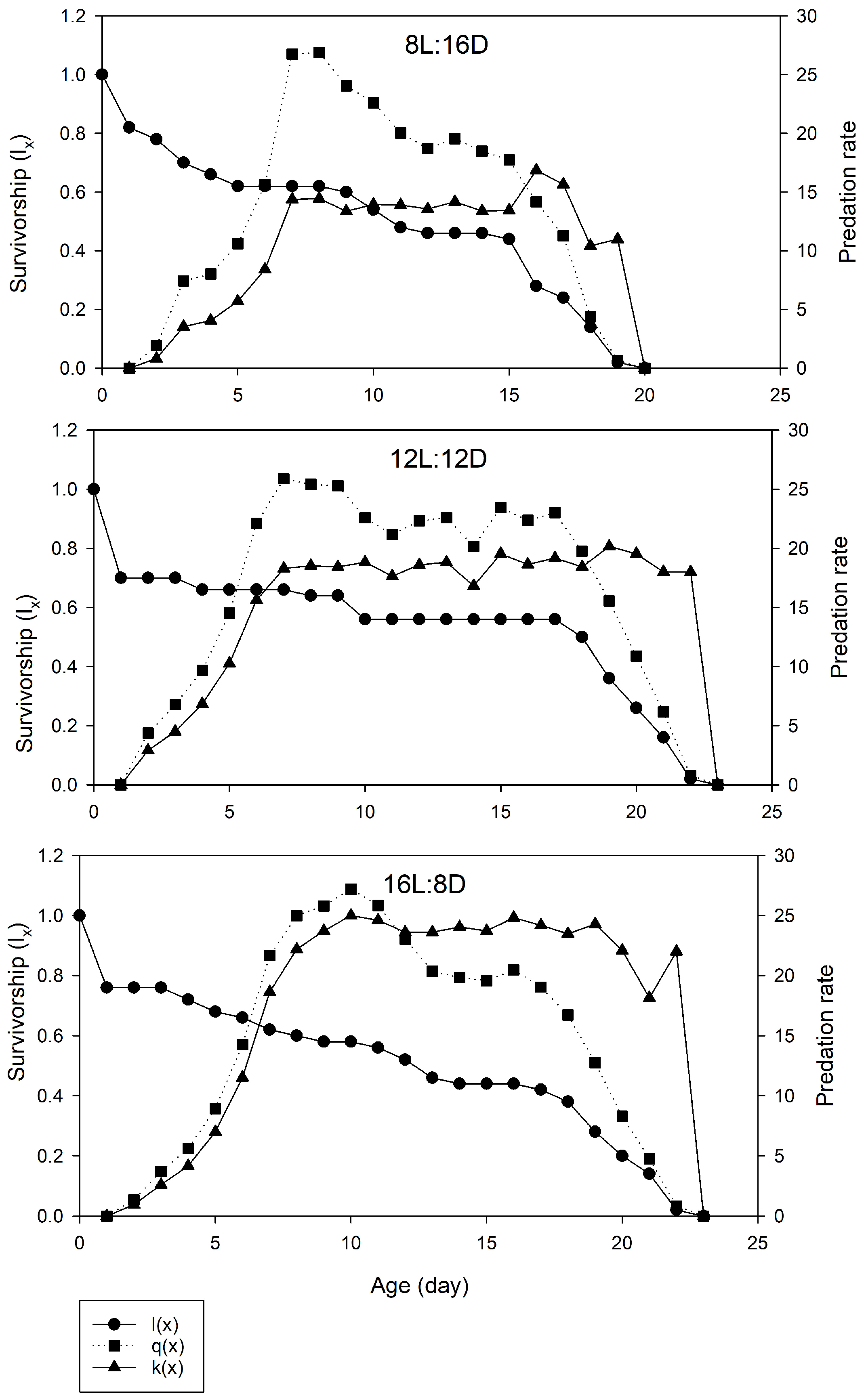
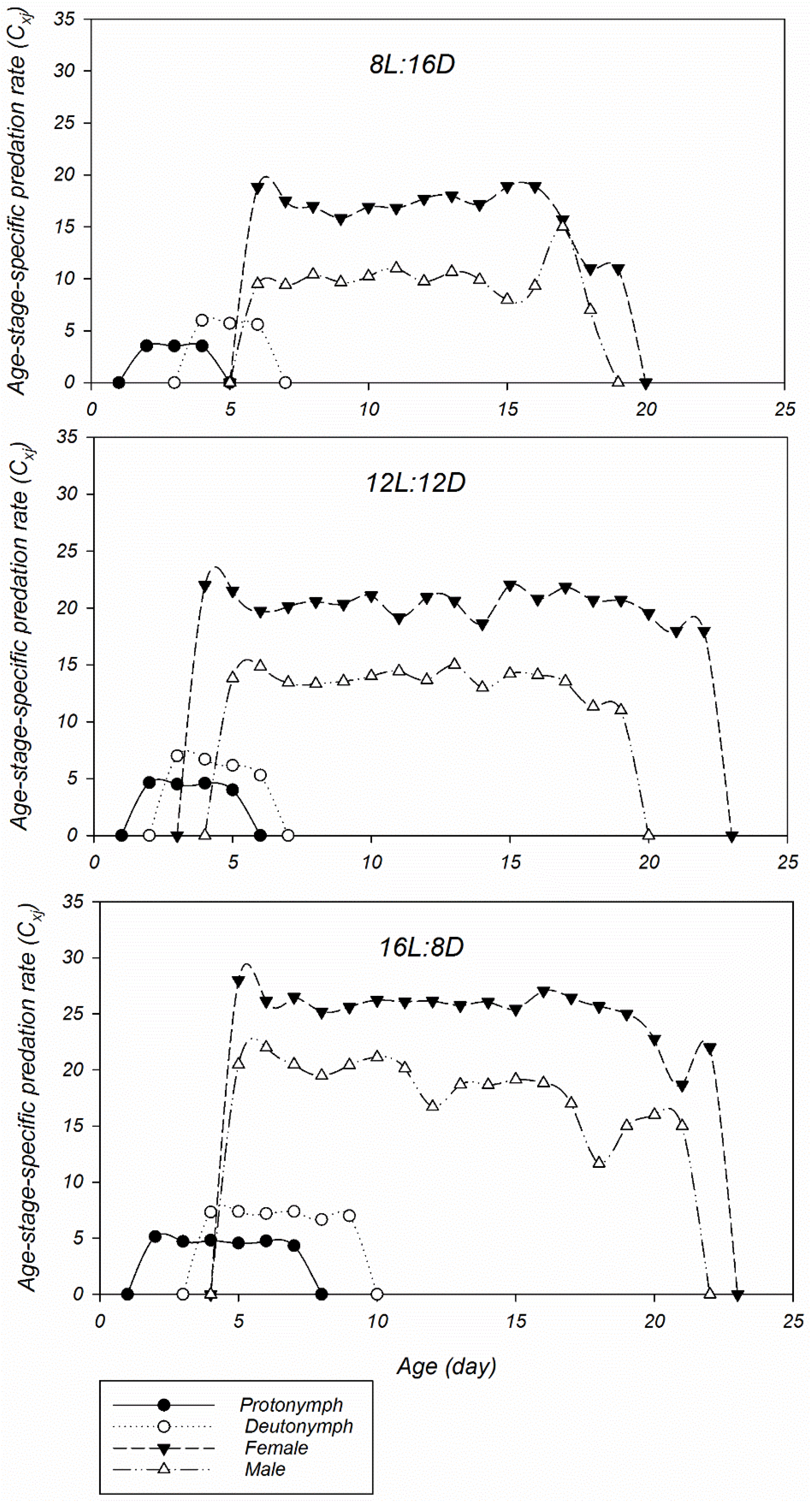
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Rearing of Prey and Predators
4.2. Experimental Arena
4.3. Experimental Design
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IPM | Integrated Pest Management |
| L:D | Light–Dark |
| RH | Relative Humidity |
References
- Mcmurtry, J.A.; Moraes, G.J.D.; Sourassou, N.F. Revision of the Lifestyles of Phytoseiid Mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and Implications for Biological Control Strategies. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2013, 18, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadasi, M.; Allahyari, H.; Saboori, A.; Zahedi Golpayegani, A. Life Table and Predation Capacity of Phytoseiulus persimilis Athias-Henriot (Acari: Phytoseiidae) Feeding on Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae) on Rose. JAST 2016, 18, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar]
- Broufas, G.D.; Pappas, M.L.; Koveos, D.S. Effect of Cold Exposure and Photoperiod on Diapause Termination of the Predatory Mite Euseius finlandicus (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Environ. Entomol. 2006, 35, 1216–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurtry, J.A.; Sourassou, N.F.; Demite, P.R. The Phytoseiidae (Acari: Mesostigmata) as Biological Control Agents. In Prospects for Biological Control of Plant Feeding Mites and Other Harmful Organisms; Carrillo, D., De Moraes, G.J., Peña, J.E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 133–149. ISBN 978-3-319-15041-3. [Google Scholar]
- Barbar, Z.; Skinner, M.; Parker, B.L.; Kreiter, S. Species of Phytoseiidae (Acari: Mesostigmata) Predators of Thrips and Whiteflies: A Review. Acarologia 2024, 64, 745–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, M.; Van Houten, Y.; Van Baal, E.; Groot, T. Use of Predatory Mites in Commercial Biocontrol: Current Status and Future Prospects. Acarologia 2018, 58, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Q. Mites of Greenhouses: Identification, Biology and Control; CABI Books; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2003; ISBN 978-0-85199-590-8. [Google Scholar]
- Abou-Haidar, A.; Tawidian, P.; Sobh, H.; Skinner, M.; Parker, B.; Abou-Jawdah, Y. Efficacy of Phytoseiulus persimilis and Amblyseius swirskii for Integrated Pest Management for Greenhouse Cucumbers under Mediterranean Environmental Conditions. Can. Entomol. 2021, 153, 598–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerson, U.; Weintraub, P.G. Mites for the Control of Pests in Protected Cultivation. Pest Manag. Sci. 2007, 63, 658–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, T. Biological Control and IPM in Strawberry Fields—Current Status and Future of IPM in Miyagi Prefecture, Japan. Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2019, 63, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiftikçi, P.; Kök, Ş.; Kasap, İ. Biological Control of Twospotted Spider Mites [Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae)] Using Phytoseiulus persimilis Athias-Henriot (Acari: Phytoseidae) at Different Ratios of Release on Field-Grown Tomatos. Biol. Control 2020, 151, 104404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiftikçi, P.; Kök, Ş.; Kasap, İ. The Effect of Host Plant on the Biological Control Efficacy of the Predatory Mite, Phytoseiulus persimilis Athias-Henriot against Two-Spotted Spidermites, Tetranychus urticae Koch on Field-Grown Vegetables. Crop Prot. 2022, 158, 106012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad-Moyano, R.; Pina, T.; Pérez-Panadés, J.; Carbonell, E.A.; Urbaneja, A. Efficacy of Neoseiulus californicus and Phytoseiulus persimilis in Suppression of Tetranychus urticae in Young Clementine Plants. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2010, 50, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, S.; Mostafa, E.; Mahrous, M.; Salem, A. Prey Consumption and Fecundity of Phytoseiulus persimilis Athias-Henriot Fed on Different Stages and Densities of Tetranychus urticae Koch. (Acari: Phytoseiidae: Tetranychidae) under Laboratory Conditions. Zagazig J. Agric. Res. 2019, 46, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadalupe Rojas, M.; Morales-Ramos, J.A.; Riddick, E.W. Determining an Optimal Temperature Range for Reproduction of Phytoseiulus persimilis, a Predator of the Two-Spotted Spider Mite Tetranychus urticae. Biopest. Int. 2013, 9, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Pakyari, H.; Arbab, A.; Sedaratian-Jahromi, A. The Influence of Photoperiod on Development and Population Growth Performance of the Phytoseiulus persimilis Fed on Tetranychus urticae. Int. J. Acarol. 2024, 50, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, H.; Chant, D.A. Life History and Reproduction of Two Species of Predacious Mites, Phytoseiulus persimilis Athias-Henriot and Amblyseius andersoni (Chant) (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Can. J. Zool. 1977, 55, 1978–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad-Moyano, R.; Pina, T.; Ferragut, F.; Urbaneja, A. Comparative Life-History Traits of Three Phytoseiid Mites Associated with Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae) Colonies in Clementine Orchards in Eastern Spain: Implications for Biological Control. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2009, 47, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Tan, X.-L.; Guo, X.-J.; Zhang, F. Effect of Temperature and Photoperiod on the Development, Reproduction, and Predation of the Predatory Ladybird Cheilomenes sexmaculata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 2621–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikulecky, M.; Zemek, R. Does the Moon Influence the Predatory Activity of Mites? Experientia 1992, 48, 530–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bissattini, A.M.; Buono, V.; Vignoli, L. Moonlight Rather than Moon Phase Influences Activity and Habitat Use in an Invasive Amphibian Predator and Its Native Amphibian Prey. Acta Oecol. 2020, 103, 103529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratas-Santiago, L.P.; Gonçalves, A.L.S.; Da Maia Soares, A.M.V.; Spironello, W.R. The Moon Cycle Effect on the Activity Patterns of Ocelots and Their Prey. J. Zool. 2016, 299, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi-Qoort, A.; Sedaratian-Jahromi, A. Assessing Predation Parameters of Predatory Mite Typhlodromus bagdasarjani (Acari: Phytoseiidae) on Different Host Plants. Persian J. Acarol. 2024, 13, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano, Y.; Delgado, N.; Morales, J.; Vasquez, C. Biological Studies and Life Table of Cycloneda sanguinea (L.) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) on Aphis craccivora Koch (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Entomotropica 2016, 31, 267–275. [Google Scholar]
- Khanamani, M.; Fathipour, Y.; Hajiqanbar, H.; Sedaratian, A. Two-Spotted Spider Mite Reared on Resistant Eggplant Affects Consumption Rate and Life Table Parameters of Its Predator, Typhlodromus bagdasarjani (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2014, 63, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathipour, Y.; Karimi, M.; Farazmand, A.; Talebi, A.A. Age-Specific Functional Response and Predation Capacity of Phytoseiulus persimilis (Phytoseiidae) on the Two-Spotted Spider Mite. Acarologia 2018, 58, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangansbeke, D.; Gobin, B.; Tirry, L.; De Clercq, P. Are Larger Phytoseiids Better Biocontrol Agents? In Proceedings of the Fifth Meeting of the IOBC Working Group “Integrated Control of Mite Pests”, Castello de la Plana, Spain, 12–15 September 2015; Broufas, G., Knapp, M., De Clercq, P., Walzer, A., Zemek, R., Palevsky, E., Eds.; International Organization for Biological and Integrated Control of Noxious Animals and Plants (OIBC/OILB), West Palaearctic Regional Section (WPRS/SROP): Dijon, France, 2016; Volume 120, pp. 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S. Light Dependency of Life Trails, Reproduction, Locomotion, and Predation in the Polyphagous Ladybird Hippodamia variegata. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2014, 152, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Omkar, O. Temperature and Photoperiod Influence Prey Consumption and Utilization by Two Sympatric Coccinella Species (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in Conspecific and Heterospecific Combinations. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2015, 58, 297–307. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Yuan, X.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, C.; Sun, L. A Long Photoperiod Promoted the Development, Reproduction, and Predation of Harmonia axyridis Pallas (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) at an Average Greenhouse Temperature during the Winter. Insects 2024, 15, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazak, C.; Cone, W.W.; Wright, L.C. Influence of Variable Photoperiods on the Feeding Activity and Fecundity of Galendromus occidentalis (Nesbitt) (Acari: Phytoseiidae) under Laboratory Conditions. J. Pest Sci. 2004, 77, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.C.; Newsom, L.D. Laboratory Evaluation of Amblyseius fallacis as a Predator of Tetranychid Mites. J. Econ. Entomol. 1970, 63, 1876–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, A.E.-T.A.; El-keifl, A.H.; Metwally, A.M. Zur Wirkung von Temperatur und Photoperiode auf die Entwicklung, Ernährung und Eiablage der Raubmilbe Amblyseius swirskii Ath.-Henr. (Acari, Gamasida, Phytoseiidae). Anz. Schadlingskde Pflanzenschutz Umweltschutz 1982, 55, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathipour, Y.; Maleknia, B. Mite Predators. In Ecofriendly Pest Management for Food Security; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 329–366. ISBN 978-0-12-803265-7. [Google Scholar]
- Pakyari, H.; McNeill, M.R. Effects of Photoperiod on Development and Demographic Parameters of the Predatory Thrips Scolothrips longicornis Fed on Tetranychus urticae. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2020, 110, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omkar; Pathak, S. Effects of Different Photoperiods and Wavelengths of Light on the Life-history Traits of an Aphidophagous Ladybird, Coelophora saucia (Mulsant). J. Appl. Entomol. 2006, 130, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, M.S.; Kirk, W.D.J. The Effect of Photoperiod on Walking, Feeding, and Oviposition in the Western Flower Thrips. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2004, 111, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; Takabayashi, J.; Yano, S.; Takafuji, A. Effects of Light on the Tritrophic Interaction between Kidney Bean Plants, Two-Spotted Spider Mites and Predatory Mites, Amblyseius womersleyi (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2000, 24, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, R.; Gholizadeh, M.; Chi, H.; Mou, D.-F.; Allahyari, H.; Yu, J.-Z.; Huang, Y.-B.; Yang, T.-C. Finite Predation Rate: A Novel Parameter for the Quantitative Measurement of Predation Potential of Predator at Population Level. Nat. Preced. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, S.-J.; Yeh, C.-C.; Atlihan, R.; Chi, H. Linking Life Table and Predation Rate for Biological Control: A Comparative Study of Eocanthecona furcellata (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) Fed on Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sayas, C.; Aguilar-Fenollosa, E.; Hurtado, M.A.; Jaques, J.A.; Pina, T. When Do Predatory Mites (Phytoseiidae) Attack? Understanding Their Diel and Seasonal Predation Patterns. Insect Sci. 2018, 25, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabelis, M.W. Predation on Spider Mites. In Spider Mites: Their Biology, Natural Enemies, and Control; Helle, W., Sabelis, M.W., Eds.; World crop pests; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1985; pp. 103–129. ISBN 978-0-444-42372-6. [Google Scholar]
- Riahi, E.; Fathipour, Y.; Talebi, A.A.; Mehrabadi, M. Linking Life Table and Consumption Rate of Amblyseius swirskii (Acari: Phytoseiidae) in Presence and Absence of Different Pollens. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2016, 110, saw091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Yang, T.-C. Two-Sex Life Table and Predation Rate of Propylaea japonica Thunberg (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) Fed on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae). Environ. Entomol. 2003, 32, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-Z.; Chi, H.; Chen, B.-H. Comparison of the Life Tables and Predation Rates of Harmonia dimidiata (F.) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) Fed on Aphis gossypii Glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae) at Different Temperatures. Biol. Control 2013, 64, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shen, X.; Ni, J.; Xie, D.; Da, A.; Luo, Y. Effect of Photoperiods on Development and Acaricide Susceptibility in the Two-Spotted Spider Mite, Tetranychus urticae. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2020, 80, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Fukunaga, Y.; Amano, H.; Takeda, M.; Goto, E. Effects of Light Quality and Intensity on Diapause Induction in the Two-Spotted Spider Mite, Tetranychus urticae. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2008, 43, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Suzuki, T.; Ghazy, N.A.; Amano, H.; Ohyama, K. Effect of Photoperiod on Immature Development and Diapause Induction in the Kanzawa Spider Mite, Tetranychus kanzawai (Acari: Tetranychidae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2011, 55, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Takeda, M. Utilizing LED Technology for Arthropod Pest Control. In Handbook of Light Emitting and Schottky Diode Research; Chen, N., Ed.; Nova Science Pub Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2009; p. 359. ISBN 978-1-60692-462-4. [Google Scholar]
- Goto, S.G. Physiological and Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Photoperiodism in the Spider Mite: Comparisons with Insects. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2016, 186, 969–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakyari, H.; Zemek, R. Effects of Visible Light Wavelength on Development and Demographic Parameters of Phytoseiulus persimilis (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2023, 28, 1843–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savi, P.; Hall, S.; Hernandez, M.; Mantri, A.; Kliebenstein, D.; Nansen, C. Effects of Timed LED Regimes on Tomato Plant Traits, Performance of Two-spotted Spider Mites, and Predatory Mites (Phytoseiulus persimilis). Pest Manag. Sci. 2025. Early View. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H. CONSUME-MSChart: A Computer Program for Consumption Rate Based on the Age Stage, Two-Sex Life Table Analysis. Available online: https://lifetablechi.com/software/ (accessed on 18 February 2025).
- Chi, H.; Liu, H. Two New Methods for the Study of Insect Population Ecology. Bull. Inst. Zool. Acad. Sin. 1985, 24, 225–240. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Chi, H. Age-stage, Two-sex Life Tables of Bactrocera cucurbitae (Coquillett) (Diptera: Tephritidae) with a Discussion on the Problem of Applying Female Age-specific Life Tables to Insect Populations. Insect Sci. 2012, 19, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Developmental Stage | 8L:16D | 12L:12D | 16L:8D | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dj ± S.E. * | n | Dj ± S.E. * | n | Dj ± S.E. * | n | |
| Protonymph | 3.54 ± 0.21 b | 35 | 4.55 ± 0.23 a | 35 | 4.74 ± 0.18 a | 38 |
| Deutonymph | 5.70 ± 0.34 c | 31 | 6.27 ± 0.31 b | 33 | 7.26 ± 0.28 a | 30 |
| Female (adult) | 17.02 ± 1.00 c | 19 | 20.43 ± 1.00 b | 24 | 25.66 ± 1.00 a | 23 |
| Male (adult) | 9.91 ± 0.58 c | 12 | 13.76 ± 0.67 b | 9 | 18.85 ± 0.74 a | 7 |
| Developmental Stage | 8L:16D | 12L:12D | 16L:8D | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pj ± S.E. * | n | Pj ± S.E. * | n | Pj ± S.E. * | n | |
| Protonymph | 7.06 ± 0.17 c | 31 | 8.7 ± 0.42 b | 33 | 9.7 ± 0.36 a | 30 |
| Deutonymph | 11.23 ± 0.32 a | 31 | 9.12 ± 0.53 b | 33 | 11.37 ± 0.63 a | 30 |
| Preadult | 15.65 ± 0.60 c | 31 | 18.83 ± 0.78 b | 33 | 22 ± 0.70 a | 30 |
| Female (adult) | 145.16 ± 4.36 b | 19 | 261.29 ± 4.90 a | 24 | 282.22 ± 4.80 a | 23 |
| Male (adult) | 94.17 ± 3.46 c | 21 | 181.89 ± 3.00 a | 9 | 210 ± 2.65 a | 7 |
| Parameter | 8L:16D * | 12L:12D * | 16L:8D * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Net predation rate, C0 (prey/predator) | 89.77 ± 12.38 b | 170.28 ± 20.47 a | 173.22 ± 22.61 a |
| Finite predation rate, ω (d−1) | 5.02 ± 0.42 c | 6.55 ± 0.45 b | 7.08 ± 0.59 a |
| Transformation rate, Qp | 11.04 ± 1.48 b | 7.99 ± 0.79 c | 14.37 ± 1.50 a |
| Stable predation rate (ψ) (prey/predator) | 4.21 ± 0.29 c | 5.09 ± 0.28 b | 5.84 ± 0.42 a |
| Parameter | Equation | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Age-specific predation rate | The number of prey consumed by the surviving predators at age x. | |
| Age–stage-specific predation rate | The number of prey consumed by predators at age x and stage j. | |
| Age-specific net predation rate | The mean number of prey consumed by an individual at age x. | |
| Net predation rate | The total number of prey consumed by an individual during its life span. | |
| Transformation rate | The number of prey consumed to produce one offspring. | |
| Predation rate for the stage | The predation rate of each predator in stage j. | |
| Daily predation rate | The daily predation rate per predator in stage j. | |
| Finite predation rate | axj indicates the proportion of individuals at age x and stage j. | |
| Stable predation rate | The total predation capacity of a stable population. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pakyari, H.; Zemek, R. The Effect of Light Cycles on the Predation Characteristics of Phytoseiulus persimilis (Acari: Phytoseiidae) Feeding on Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). Plants 2025, 14, 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050687
Pakyari H, Zemek R. The Effect of Light Cycles on the Predation Characteristics of Phytoseiulus persimilis (Acari: Phytoseiidae) Feeding on Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). Plants. 2025; 14(5):687. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050687
Chicago/Turabian StylePakyari, Hajar, and Rostislav Zemek. 2025. "The Effect of Light Cycles on the Predation Characteristics of Phytoseiulus persimilis (Acari: Phytoseiidae) Feeding on Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae)" Plants 14, no. 5: 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050687
APA StylePakyari, H., & Zemek, R. (2025). The Effect of Light Cycles on the Predation Characteristics of Phytoseiulus persimilis (Acari: Phytoseiidae) Feeding on Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). Plants, 14(5), 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050687








