Evaluation of Rice Quality Storage Stability: From Variety Screening to Trait Identification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Variable Amplitude
2.2. Screening of Rice Varieties
2.2.1. Construction of the Comprehensive Evaluation Index System
2.2.2. The Quality Storage Stability Index
2.2.3. Screening of Rice Varieties with High Storage Stability for Quality
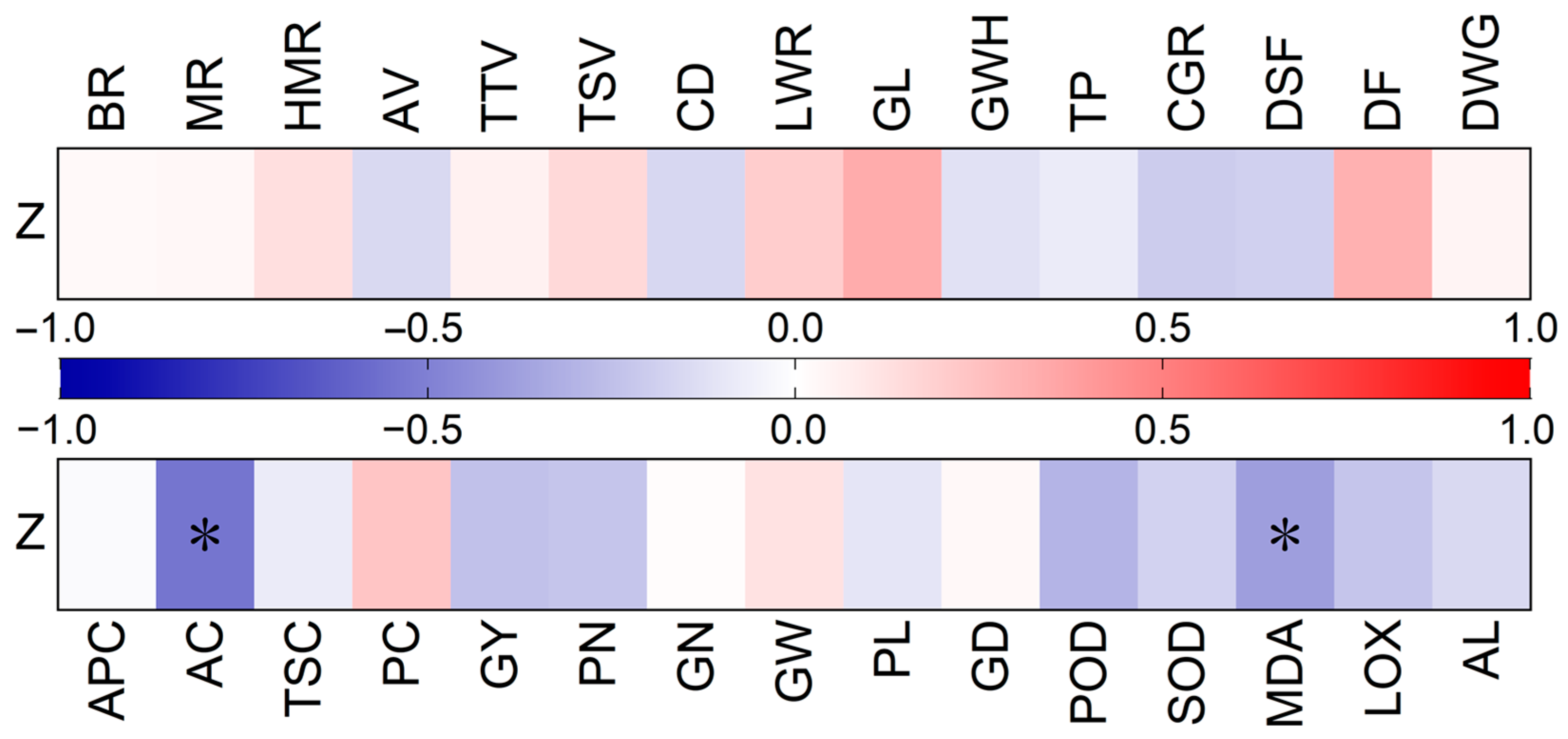
2.3. Characteristics of Rice Varieties with High Storage Stability
3. Discussion
3.1. Comprehensive Evaluation and Variety Screening for Quality Storage Stability in Rice Grains
3.2. Characteristics of Rice Varieties with High Storage Stability
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Trial Material
4.2. Trial Site and Meteorological Information
4.3. Trial Design
4.4. Sampling and Measurement
4.4.1. Rice Grain Quality
4.4.2. Grain Yield and Its Composition
4.4.3. Key Growth Stages of Rice
4.4.4. Grain Size and Visual Characteristics
4.4.5. Major Component Content in Grains
4.4.6. Physiological Indicator
4.5. Formula Calculation and Statistical Analysis
4.5.1. Variable Amplitude of the Rice Grain Quality
4.5.2. Comprehensive Evaluation
- (1)
- Storage stability score calculation (normalization method).
- (2)
- Weighted value of the storage stability score of the rice grain quality determined by the hierarchical analysis method.
- I.
- Establishing a recursive hierarchical structure.
- II.
- Constructing a judgment matrix.
- III.
- Calculating the weighted value.
- IV.
- The consistency test.
- (3)
- Calculating the quality storage stability index.
4.5.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wing, R.A.; Purugganan, M.D.; Zhang, Q.F. The rice genome revolution: From an ancient grain to Green Super Rice. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Zhu, X.Y.; Qi, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.Q.; He, J.W. Rice seed storability: From molecular mechanisms to agricultural practices. Plant Sci. 2024, 348, 112215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.Y.; Zhang, Q.L.; Wei, H.R.; Shi, Y. An efficient multiscale integrated attention method combined with hyperspectral system to identify the quality of rice with different storage periods and humidity. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 213, 108259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.; Chi, C.D. Impact of long-term storage on multi-scale structures and physicochemical properties of starch isolated from rice grains. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.W.; Li, M.; Fang, C.Y.; Yu, J.; Zhu, Z.W.; Yu, Y.H.; Shao, Y.F. Effects of storage on the starch fine structure and physicochemical properties of different rice variety types. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 300, 120273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.Y.; Xing, Z.P.; Li, S.P.; Cheng, S.; Guo, B.W.; Hu, Y.J.; Wei, H.Y.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Fan, P.; et al. Influence of Wheat Straw Return on Yield and Grain Quality in Different Direct-Seeding Rice Production Systems. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.W.; Zhang, Y.N.; Zhang, F.; Wang, W.S.; Xu, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, J.S. Genome-Wide Association Study of Cooked Rice Textural Attributes and Starch Physicochemical Properties in indica Rice. Rice Sci. 2024, 31, 300–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Tong, C.; Hu, Y.Q.; Liu, L.; Bao, J.S. Starch lysophospholipids contents affect storage quality of paddy rice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 348, 122818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Sun, D.W. Hardness of cooked rice as affected by varisties, cooling methods and chill storage. J. Food Process Eng. 2009, 32, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.K.; Robards, K.; Helliwell, S.; Blanchard, C. Effect of storage temperature on rice thermal properties. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.L.; Xia, Y.Z.; Yang, Q.K.; Li, W.H.; Hu, M.; Lu, P. Novel insights into rice deterioration for nitrogen controlled atmosphere and re-aeration storage based on no-targeted metabolomics. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 178, 114631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Zhao, C.J.; Yan, M.; Huang, D.C.; David Julian, M.C.; Huang, Z.G.; Cao, C.J. Influence of gene regulation on rice quality: Impact of storage temperature and humidity on flavor profile. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, T.A.; Brackmann, A.; Da Silva, L.P.; Nicoletti, A.M.; Roberto, B.S. Changes in culinary, viscoamylographic and sensory characteristics during rice storage at different temperatures. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2013, 53, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizzolara, S.; Manganaris, G.A.; Fotopoulos, V.; Watkins, C.B.; Tonutti, P. Primary Metabolism in Fresh Fruits During Storage. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Q.; Zhu, F.Q.; Zhang, Y.R.; Peng, C. Analysis of the Storage Property, Physiological, Biochemical Indicators Parameters and the Pasting Characteristics of Rice in Different Storage Time. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2020, 35, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.S.; Yu, D.; Wu, L.B.; Xu, Y.S.; Duan, M.J.; Yuan, D.Y. Seed Storability in Rice: Physiological Bases, Molecular Mechanisms, and Application to Breeding. Rice Sci. 2024, 31, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.X.; Xu, H.B.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Y.R.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Cai, Q.H.; He, W.; Xie, H.A.; Zhang, J.F. The lipoxygenase OsLOX10 affects seed longevity and resistance to saline-alkaline stress during rice seedlings. Plant Mol. Biol. 2023, 111, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.Y.; Wang, T.T.; Liu, X.Y.; Bi, J.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, X.F.; Wang, P.P.; Shu, Z.X. Quality changes in Chinese high-quality indica rice under different storage temperatures with varying initial moisture contents. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1334809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.C.; Lai, H.M. Characteristics of the starch fine structure and pasting properties of waxy rice during storage. Food Chem. 2014, 152, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.W.; Shao, Y.W.; Fang, C.Y.; Li, M.; Yu, Y.H.; Qin, Y.B. Effect of storage time on chemical compositions, physiological and cooking quality characteristics of different rice types. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 103, 2077–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadele, W.; Kulawik, P.; Szymkowiak, A.; Režek Jambrak, A.; Ozogul, Y.; Ozogul, F. Cold-storage preservation of cooked rice quality: Exploring challenges and strategies, featuring insights on sushi rice. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Zhou, L.; Tian, J.Y.; Cheng, S.; Tao, Y.; Xing, Z.P.; Liu, G.D.; Wei, H.Y.; Zhang, H.C. Comprehensive Evaluation of Nitrogen Efficiency and Screening of Varieties with High Grain Yield and High Nitrogen Efficiency of Inbred Middle-Ripe Japonica Rice in the Middle and Lower Reaches of Yangtze River. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2021, 54, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Yang, T.L.; Zhu, S.L.; Wang, Z.J.; Zhang, M.Y.; Wei, H.Y.; Liu, G.D. Preliminary Study on Appearance Quality Evaluation of Semi-Waxy Rice in Yangtze River Delta Region. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2024, 57, 3105–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.M.; Du, Z.F. Some Problems in Comprehensive Evaluation in the Principal Component Analysis. Stat. Res. 2013, 30, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cretin, G.; Galochkina, T.; Vander Meersche, Y.; De Brevern, A.G.; Postic, G.; Gelly, J.C. SWORD2: Hierarchical analysis of protein 3D structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W732–W738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.B. Effects of Temperature and Light Factors on Yield, Nitrogen Uptake and Utilization and Quality of High-Quality Rice in the Lower Reaches of Huai River Basin. Ph.D. Thesis, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Z. Study on Comprehensive Productivity and Temperatureand Solar Radiation Utilization Characteristics of LateSowing Rice Stubble Wheat in Different Wheat Regions. Ph.D. Thesis, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.Q.; Wang, J.Z.; Cao, X.Y.; Ran, H.F.; Teng, D.X.; Chen, J.; He, X.; Zheng, X. Possibility of using multiscale normalized difference vegetation index data for the assessment of total suspended solids (TSS) concentrations in surface water: A specific case of scale issues in remote sensing. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Cai, Y.; He, Y.T.; Li, Q.Q.; Du, X.Y.; Wang, C.Q.; Luo, D.Q. Dynamic Simulation of Dry Matter Accumulation in Flue-cured Tobacco and Analysis of Its Characteristics Based on Normalized Method. Acta Agron. Sin. 2017, 43, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, M.; Arai-Sanoh, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Mukouyama, T.; Adachi, S.; Yabe, S.; Nakagawa, H.; Tsutsumi, K.; Taniguchi, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; et al. Characterization of high-yielding rice cultivars with different grain-filling properties to clarify limiting factors for improving grain yield. Field Crops Res. 2018, 219, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Song, N.Y.; Chen, Q.L.; Sun, H.Z.; Peng, T.; Huang, S.; Zhao, Q.Z.Y. Response of grain filling rate and grain quality of mid-season indica rice to nitrogen application. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.Y.; Li, Z.K.; Li, E.P.; Wang, W.L.; Yuan, L.M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Gu, J.F.; Yang, J.C. Optimization of nitrogen fertilization improves rice quality by affecting the structure and physicochemical properties of starch at high yield levels. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 1576–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, C.; Zigrida, Z. Changes in peptide subunit composition of albumins, globulins, prolamins, and oryzenin in maturing rice grains. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 2152–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.H.; Yuan, Z.Y.; Yu, Y.Y.; Yu, S.B.; He, H.Z. OsCSD2 and OsCSD3 Enhance Seed Storability by Modulating Antioxidant Enzymes and Abscisic Acid in Rice. Plants 2024, 13, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Yang, S.Y.; Tu, Z.H.; Yu, F.Y.; Qiu, C.Q.; Huang, G.J.; Fang, S. An indole-3-acetic acid inhibitor mitigated mild cadmium stress by suppressing peroxide formation in rice seedling roots. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 213, 108823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Zhuang, J.Y.; Fan, Y.Y.; Shen, B. Mapping of QTLs for Leaf Malondialdehyde Content Associated with Stress Tolerance in Rice. Rice Sci. 2009, 16, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wu, X.J.; Wu, W. Effects of oxidative modification by malondialdehyde on the in vitro digestion properties of rice bran protein. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 97, 103158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Huang, S.S.; Wang, Q.; Shang, B.; Liu, J.L.; Xing, X.T.; Hong, Y.; Liu, H.; Duan, X.L.; Sun, H. Lipidomics and volatilomics reveal the changes in lipids and their volatile oxidative degradation products of brown rice during accelerated aging. Food Chem. 2023, 421, 136157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, W.F.; Li, Z.; Xu, L.; Lan, D.M.; Wang, Y.H. Lipidomics analysis unveils the dynamic alterations of lipid degradation in rice bran during storage. Food Res. Int. 2024, 184, 114243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.Y.; Li, S.P.; Cheng, S.; Liu, Q.Y.; Zhou, L.; Tao, Y.; Xing, Z.P.; Hu, Y.J.; Guo, B.W.; Wei, H.Y.; et al. Increasing appropriate seedling density for higher yield in dry direct-seeded rice sown by multifunctional seeder after wheat-straw returning. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 400–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohaich, K.; Baaziz, M. New investigations on the guaiacol peroxidase of Opuntia ficus indica L. and its modulation by ascorbic acid and copper. Towards an optimization of quantitative and qualitative tests. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2015, 119, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopiv, T.M.; Fedorovych, D.V.; Boretsky, Y.R.; Sibirny, A.A. Oversynthesis of Riboflavin in the Yeast Pichia guilliermondii is Accompanied by Reduced Catalase and Superoxide Dismutases Activities. Curr. Microbiol. 2013, 66, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.Y.; Zhang, H.C.; Qun, M.; Dai, Q.G.; Huo, Z.Y.; Xu, K.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, L.F. Characteristics of Leaf Senescence in Rice Genotypes with Different Nitrogen Use Efficiencies. Acta Agron. Sin. 2010, 36, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, I.; Trostchansky, A.; Rubbo, H. Structural considerations on lipoxygenase function, inhibition and crosstalk with nitric oxide pathways. Biochimie 2020, 178, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thrikawala, V.S.; Deraniyagala, S.A.; Dilanka Fernando, C.; Udukala, D.N. In Vitro α-Amylase and Protein Glycation Inhibitory Activity of the Aqueous Extract of Flueggea leucopyrus Willd. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 2787138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Index | Range | Mean Value | CV (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brown rice rate (%) | 78.1–81.6 | 79.9 | 0.98 | ||
| The processing quality | Milled rice rate (%) | 63.1–74.9 | 70.2 | 3.49 | |
| Head milled rice rate (%) | 51.8–71.0 | 61.9 | 6.75 | ||
| The fresh rice | The appearance quality | Chalkiness degree (%) | 1.25–11.9 | 6.61 | 36.0 |
| Appearance values of cooked rice | 5.70–7.75 | 6.82 | 6.98 | ||
| The eating quality | Texture values of cooked rice | 5.20–7.35 | 6.47 | 7.88 | |
| Taste values of cooked rice | 55.5–74.3 | 65.1 | 6.66 | ||
| Brown rice rate (%) | 76.2–81.0 | 79.1 | 1.63 | ||
| The processing quality | Milled rice rate (%) | 64.2–73.7 | 69.3 | 3.36 | |
| Head milled rice rate (%) | 53.6–70.0 | 60.6 | 6.03 | ||
| The stored rice | The appearance quality | Chalkiness degree (%) | 2.15–20.0 | 8.54 | 37.1 |
| Appearance values of cooked rice | 3.70–6.55 | 5.53 | 12.3 | ||
| The eating quality | Texture values of cooked rice | 3.55–6.20 | 5.24 | 13.5 | |
| Taste values of cooked rice | 43.1–67.2 | 55.9 | 10.9 | ||
| Judgment Matrix and Consistency Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Judgment matrix | Z | C1 | C2 | C3 |
| C1 | 1 | 1/2 | 1/4 | |
| C2 | 2 | 1 | 1/2 | |
| C3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| Consistency test | = 3.00, CI = 0.00, RI = 0.00, CR = 0.000 < 0.10 | |||
| Judgment matrix | C1 | X1 | X2 | X3 |
| X1 | 1 | 1/3 | 1/5 | |
| X2 | 3 | 1 | 1/3 | |
| X3 | 5 | 3 | 1 | |
| Consistency test | = 3.04, CI = 0.019, RI = 0.58, CR = 0.033 < 0.10 | |||
| Judgment matrix | C3 | X5 | X6 | X7 |
| X5 | 1 | 1/3 | 1/5 | |
| X6 | 3 | 1 | 1/3 | |
| X7 | 5 | 3 | 1 | |
| Consistency test | = 3.04, CI = 0.019, RI = 0.58, CR = 0.033 < 0.10 | |||
| Z | (Z) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level C versus top level | (C1) | (C2) | (C3) | ||||
| 0.143 | 0.286 | 0.571 | |||||
| Level X versus top level | (X1) | (X2) | (X3) | (X4) | (X5) | (X6) | (X7) |
| 0.0149 | 0.0369 | 0.0910 | 0.286 | 0.060 | 0.148 | 0.364 | |
| Variety Type | Index | Mean Value | Median Value | Variable Amplitude (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stable variety | Amylose starch content (%) | 17.4 | 17.7 | 15.4–19.8 |
| Malondialdehyde content (%) | 3.24 | 3.33 | 2.49–3.55 | |
| Intermediate variety | Amylose starch content (%) | 18.1 | 17.8 | 15.3–22.6 |
| Malondialdehyde content (%) | 3.35 | 3.35 | 2.90–3.66 | |
| Sensitive variety | Amylose starch content (%) | 19.5 | 18.9 | 16.8–22.9 |
| Malondialdehyde content (%) | 3.44 | 3.39 | 3.27–3.62 |
| Scale | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 1 | Equal importance of both indicators |
| 3 | Slightly more important for one indicator compared to the other |
| 5 | Noticeably more important for one indicator compared to the other |
| 7 | Extremely more important for one indicator compared to the other |
| 9 | Vitally more important for one indicator compared to the other |
| 2, 4, 6, 8 | The median of two adjacent judgments |
| Order n | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RI value | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.58 | 0.90 | 1.12 | 1.24 | 1.32 | 1.41 | 1.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, J.; Ji, G.; Zhang, J.; Luo, D.; Zhang, F.; Li, L.; Jiang, M.; Zhu, D.; Li, M. Evaluation of Rice Quality Storage Stability: From Variety Screening to Trait Identification. Plants 2025, 14, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14030356
Tian J, Ji G, Zhang J, Luo D, Zhang F, Li L, Jiang M, Zhu D, Li M. Evaluation of Rice Quality Storage Stability: From Variety Screening to Trait Identification. Plants. 2025; 14(3):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14030356
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Jinyu, Guangmei Ji, Jiafeng Zhang, Danqiu Luo, Fang Zhang, Lijiang Li, Mingjin Jiang, Dawei Zhu, and Min Li. 2025. "Evaluation of Rice Quality Storage Stability: From Variety Screening to Trait Identification" Plants 14, no. 3: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14030356
APA StyleTian, J., Ji, G., Zhang, J., Luo, D., Zhang, F., Li, L., Jiang, M., Zhu, D., & Li, M. (2025). Evaluation of Rice Quality Storage Stability: From Variety Screening to Trait Identification. Plants, 14(3), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14030356






