Molecular Pathways Associated with Cold Tolerance in Grafted Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Grafting
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and RNA Extraction
2.4. cDNA Library Preparation and RNA Sequencing
2.5. Transcriptome Analysis
2.6. Functional Annotation
2.7. Transcription Factors
2.8. Validation of RNA Sequencing Data
3. Results
3.1. Summary of RNA Sequencing
3.2. Overview of DEGs
3.3. Functional Annotation and GO Enrichment Analysis
3.4. KEGG Enrichment Analysis
3.5. Genes Associated with Plant Hormone Signal Transduction Pathway
3.6. Common and Unique DEGs
3.7. DEGs Uniquely Associated with C. ficifolia and Tetsukabuto Rootstocks
3.8. Transcriptional Factors Associated with Cold Tolerance Uniquely in C. ficifolia and Tetsukabuto Rootstocks
3.9. Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pal, A. Cultivation of Cucumber in Greenhouse. In Protected Cultivation and Smart Agriculture; New Delhi Publishers: Delhi, India, 2020; pp. 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman, E.; Maguire, K.; Davis, W.V.; Husby, M.; Bovay, J.; Weber, C.; Lee, Y. Trends, Insights, and Future Prospects for Production in Controlled Environment Agriculture and Agrivoltaics Systems. 2024. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10919/117401 (accessed on 14 December 2025).
- Westerfield, R.R. University of Georgia, Extension Service. 2024. Available online: https://fieldreport.caes.uga.edu/publications/C1034/growing-cucumbers-in-the-home-garden/ (accessed on 14 December 2025).
- Brandenberger, L.; Shrefler, J.; Damicone, J. Oklahoma Cooperative Extension Service; Oklahoma State University: Stillwater, OK, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattarai, K.; Ogden, A.B.; Pandey, S.; Sandoya, G.V.; Shi, A.; Nankar, A.N.; Jayakodi, M.; Huo, H.; Jiang, T.; Tripodi, P.; et al. Improvement of Crop Production in Controlled Environment Agriculture through Breeding. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 15, 1524601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriacou, M.C.; Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G.; Zrenner, R.; Schwarz, D. Vegetable Grafting: The Implications of a Growing Agronomic Imperative for Vegetable Fruit Quality and Nutritive Value. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 264809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.R.; Perkins-Veazie, P.; Sakata, Y.; López-Galarza, S.; Maroto, J.V.; Lee, S.G.; Huh, Y.C.; Sun, Z.; Miguel, A.; King, S.R.; et al. Cucurbit Grafting. CRC Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2008, 27, 50–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Sun, S.; Nawaz, M.A.; Sun, J.; Cao, H.; Lu, J.; Huang, Y.; Bie, Z. Grafting Cucumber Onto Pumpkin Induced Early Stomatal Closure by Increasing ABA Sensitivity Under Salinity Conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 487296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Koirala, U.; Acharya, P.; Shrestha, S. Management of Bacterial Wilt Using Grafting Technique in Tomato (Ralstonia Solanacearum). World J. Agric. Res. 2020, 8, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, Ö.F. The Effect of Grafting on Morphological, Physiological and Molecular Changes Induced by Drought Stress in Cucumber. Sustainability 2023, 15, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyad, N.E.-H.; El-Sayed, S.F.; Azoz, S.N. Evaluation of Grafting Using Cucurbit Interspecific Hybrids to Control Fusarium Wilt in Cucumber. Plant Cell Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. 2021, 22, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezeanu, P.M.; Brezeanu, C.; Ambarus, S.; Voda, A.; Robu, T.; Cristea, T.O.; Calin, M. The Influence of Grafting on Yield and Quality of Peppers, Eggplants, Tomatoes and Melons—A Review. Acta Hortic. 2021, 1270, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayoumi, Y.; Abd-Alkarim, E.; El-Ramady, H.; El-Aidy, F.; Hamed, E.S.; Taha, N.; Prohens, J.; Rakha, M. Grafting Improves Fruit Yield of Cucumber Plants Grown under Combined Heat and Soil Salinity Stresses. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhogale, S.; Mahajan, A.S.; Natarajan, B.; Rajabhoj, M.; Thulasiram, H.V.; Banerjee, A.K. MicroRNA156: A Potential Graft-Transmissible MicroRNA That Modulates Plant Architecture and Tuberization in Solanum tuberosum ssp. andigena. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 1011–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhtz, A.; Springer, F.; Chappell, L.; Baulcombe, D.C.; Kehr, J. Identification and Characterization of Small RNAs from the Phloem of Brassica napus. Plant J. 2008, 53, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Mao, L.; Jittayasothorn, Y.; Kang, Y.; Jiao, C.; Fei, Z.; Zhong, G.Y. Messenger RNA Exchange between Scions and Rootstocks in Grafted Grapevines. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeevaart, J.A. Leaf-Produced Floral Signals. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2008, 11, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbesier, L.; Vincent, C.; Jang, S.; Fornara, F.; Fan, Q.; Searle, I.; Giakountis, A.; Farrona, S.; Gissot, L.; Turnbull, C.; et al. FT Protein Movement Contributes to Long-Distance Signaling in Floral Induction of Arabidopsis. Science 2007, 316, 1030–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldschmidt, E.E. Plant Grafting: New Mechanisms, Evolutionary Implications. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 109919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, X.; Xin, Y.; Guo, J.; Wu, F.; Yu, H.; Sun, Z.; Xu, C. Scion-to-Rootstock Mobile Transcription Factor CmHY5 Positively Modulates the Nitrate Uptake Capacity of Melon Scion Grafted on Squash Rootstock. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, A.; Mansoor, S.; Bhat, K.M.; Hassan, G.I.; Baba, T.R.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Alsahli, A.A.; El-Serehy, H.A.; Paray, B.A.; Ahmad, P. Mechanisms Underlying Graft Union Formation and Rootstock Scion Interaction in Horticultural Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 590847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Sang, T.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Pang, G.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, H.; et al. Combined Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analysis Reveals the Regulatory Mechanism of Pumpkin Rootstocks on Fruit Quality of Grafted Cucumbers. Sci. Hortic. 2025, 347, 114189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Di, Q.; Sun, T.; Li, Y.; Duan, Y.; Wang, J.; Yan, Y.; He, C.; Wang, C.; Yu, X. Integrated Metabolome and Transcriptome Analysis Provide Insights into the Effects of Grafting on Fruit Flavor of Cucumber with Different Rootstocks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, A.; Song, T.; Jin, Y.; Xu, X.; Gao, Y.; Ye, X.; Qi, H. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Effects of Grafting on Sugar and α-Linolenic Acid Metabolisms in Fruits of Cucumber with Two Different Rootstocks. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 130, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.J.; Im, Y.J.; Chung, G.C.; Cho, B.H.; Suh, S.R. Physiological Responses of Grafted-Cucumber Leaves and Rootstock Roots Affected by Low Root Temperature. Sci. Hortic. 1999, 81, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, H.; Ai, X. Salicylic Acid Improves Chilling Tolerance via CsNPR1–CsICE1 Interaction in Grafted Cucumbers. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, uhae231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Niu, C.; Nie, X.; Li, Y.; Wei, M. Transcriptome and Physiological Analysis of Rootstock Types and Silicon Affecting Cold Tolerance of Cucumber Seedlings. Plants 2022, 11, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwechheimer, C.; Bevan, M. The Regulation of Transcription Factor Activity in Plants. Trends Plant Sci. 1998, 3, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.K.; Jha, B. Transcription Factors in Plants and ABA Dependent and Independent Abiotic Stress Signalling. Biologia Plant. 2010, 54, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Hu, K.; Xian, S.; Liu, C.; Fan, J.; Tu, J.; Fu, T. Dynamic Transcriptome Analysis Reveals AP2/ERF Transcription Factors Responsible for Cold Stress in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Mol. Genet. Genom. 2016, 291, 1053–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, L.; Lei, W.; Yang, W.; Wang, J.; Gao, J.; Cheng, J.; Sun, Y.; Fan, Z.; Yu, D. Genome-Wide Identification of Cold Responsive Transcription Factors in Brassica napus L. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yin, J.; Liang, Y.; Liu, J.; Jia, J.; Huo, H.; Wu, Z.; Yang, R.; Gong, H. Transcriptomic Dynamics Provide an Insight into the Mechanism for Silicon-Mediated Alleviation of Salt Stress in Cucumber Plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S.N.A.; Azzeme, A.M.; Yousefi, K. Fine-Tuning Cold Stress Response Through Regulated Cellular Abundance and Mechanistic Actions of Transcription Factors. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 850216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, S. Cytokinin Concentrations in Roots and Root Xylem Exudate of Cucumber and Figleaf Gourd as Affected by Root Temperature. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1988, 56, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañizares, K.A.L.; Goto, R. Growth and Production of Cucumber Hybrids as a Function of Grafting. Braz. Hort 1998, 16, 110–113. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, F.H.; El-Hamed, K.E.A.; Elwan, M.W.M.; Hussien, M.N.E. Evaluation of Different Grafting Methods and Rootstocks in Watermelon Grown in Egypt. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 168, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast Gapped-Read Alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, H.; Huang, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, S.; Ruan, J.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Z. A Chromosome-Scale Genome Assembly of Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Gigascience 2019, 8, giz072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, H.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, H.; Huang, X.; Li, S.; Zhou, A.; et al. WEGO 2.0: A Web Tool for Analyzing and Plotting GO Annotations, 2018 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W71–W75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Xing, Q.; Lihong, G.; Qing, L.; Shuzhen, L.; Chaoxing, H.; Yansu, L.; Xianchang, Y. Selection of Reference Genes for Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.), Pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata Duch.) and Cucumber-Pumpkin Grafted Plants. PeerJ 2019, 2019, e6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbussche, F.; Vaseva, I.; Vissenberg, K.; Van Der Straeten, D. Ethylene in Vegetative Development: A Tale with a Riddle. New Phytol. 2012, 194, 895–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanstraelen, M.; Benkov, E. Hormonal Interactions in the Regulation of Plant Development. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 28, 463–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemian, M.; Nambara, E.; Cutler, S.; Kawaide, H.; Kamiya, Y.; McCourt, P. Regulation of Abscisic Acid Signaling by the Ethylene Response Pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatma, M.; Asgher, M.; Iqbal, N.; Rasheed, F.; Sehar, Z.; Sofo, A.; Khan, N.A. Ethylene Signaling under Stressful Environments: Analyzing Collaborative Knowledge. Plants 2022, 11, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, H.; Wilkinson, E.G.; Sageman-Furnas, K.; Strader, L.C. Auxin and Abiotic Stress Responses. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 74, 7000–7014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiiber, J.J.; Rothenberg, M.; Roman, G.; Feldmann, K.A.; Ecker’, J.R. CTRI, a Negative Regulator of the Ethylene Pathway in A II E-a Member of the Raf Family of Prutein Kin. Cell 1993, 72, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaseva, I.I.; Qudeimat, E.; Potuschak, T.; Du, Y.; Genschik, P.; Vandenbussche, F.; Van Der Straeten, D. The Plant Hormone Ethylene Restricts Arabidopsis Growth via the Epidermis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E4130–E4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; He, L.; Li, F. Understanding Cold Stress Response Mechanisms in Plants: An Overview. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1443317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasekaran, D.N.; Kashef, K.; Lee, C.M.; Xu, H.; Reddy, E.P. Scaffold Proteins of MAP-Kinase Modules. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3185–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Liu, H.; Yang, W.; Chong, K.; Xu, Y. OsMAPK3 Phosphorylates OsbHLH002/OsICE1 and Inhibits Its Ubiquitination to Activate OsTPP1 and Enhances Rice Chilling Tolerance. Dev. Cell 2017, 43, 731–743.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Dou, T.; He, W.; Sheng, O.; Bi, F.; Deng, G.; Gao, H.; Dong, T.; Li, C.; Zhang, S.; et al. MaMAPK3-MaICE1-MaPOD P7 Pathway, a Positive Regulator of Cold Tolerance in Banana. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, N.; Zan, T.; Xu, K.; Gao, S.; Yin, Y.; Yao, M.; Wang, F. Genome-Wide Analysis of the TIFY Family and Function of CaTIFY7 and CaTIFY10b under Cold Stress in Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1308721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Kang, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, W.; Xie, P.; Liao, L.; Huang, L.; Yao, M.; Qian, L.; Liu, Z.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Analysis of the TIFY Gene Family in the Response to Multiple Stresses in Brassica napus L. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 2173–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; You, J.; Chan, Z. Identification and Characterization of TIFY Family Genes in Brachypodium distachyon. J. Plant Res. 2015, 128, 995–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Du, H.; Tang, N.; Li, X.; Xiong, L. Identification and Expression Profiling Analysis of TIFY Family Genes Involved in Stress and Phytohormone Responses in Rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 71, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atif, R.M.; Shahid, L.; Waqas, M.; Ali, B.; Rashid, M.A.R.; Azeem, F.; Nawaz, M.A.; Wani, S.H.; Chung, G. Insights on Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinases (CPKs) Signaling for Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrighton, K.H. Decoding Cold-Induced Ca2+ Spikes. Nat. Plants 2022, 8, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yang, H.; Wu, S.; Fu, D.; Li, M.; Gong, Z.; Yang, S. CPK28-NLP7 Module Integrates Cold-Induced Ca2+ signal and Transcriptional Reprogramming in Arabidopsis. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, 7901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foyer, C.H.; Noctor, G. Ascorbate and Glutathione: The Heart of the Redox Hub. Plant Physiol. 2011, 155, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, P.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Q.; Lv, W.; Ma, N. The Role of NAC Transcription Factor in Plant Cold Response. Plant Signal Behav. 2020, 15, 1785668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, N.A. CAMTA Proteins: A Direct Link between Calcium Signals and Cold Acclimation? Plant Cell 2009, 21, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
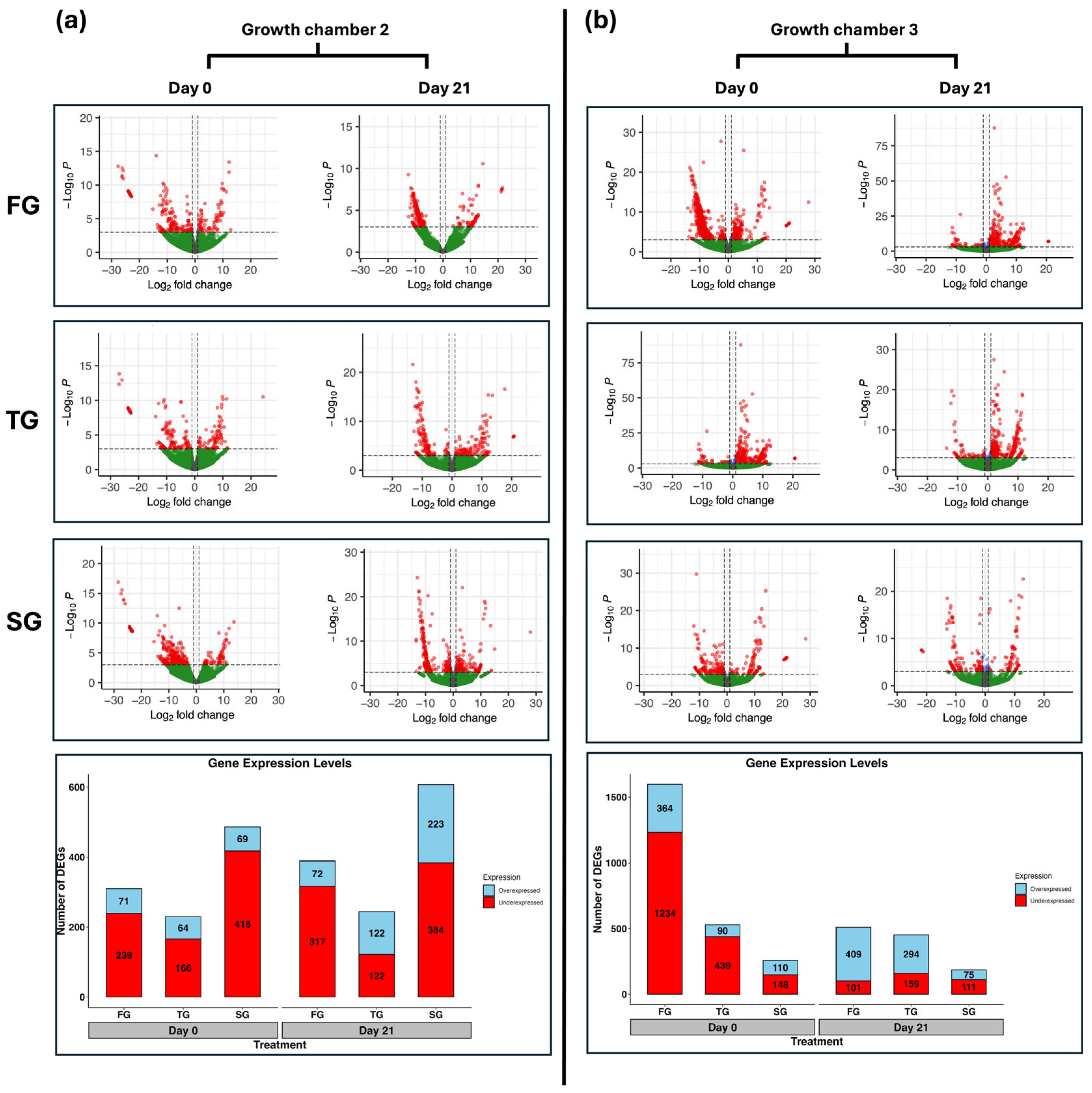
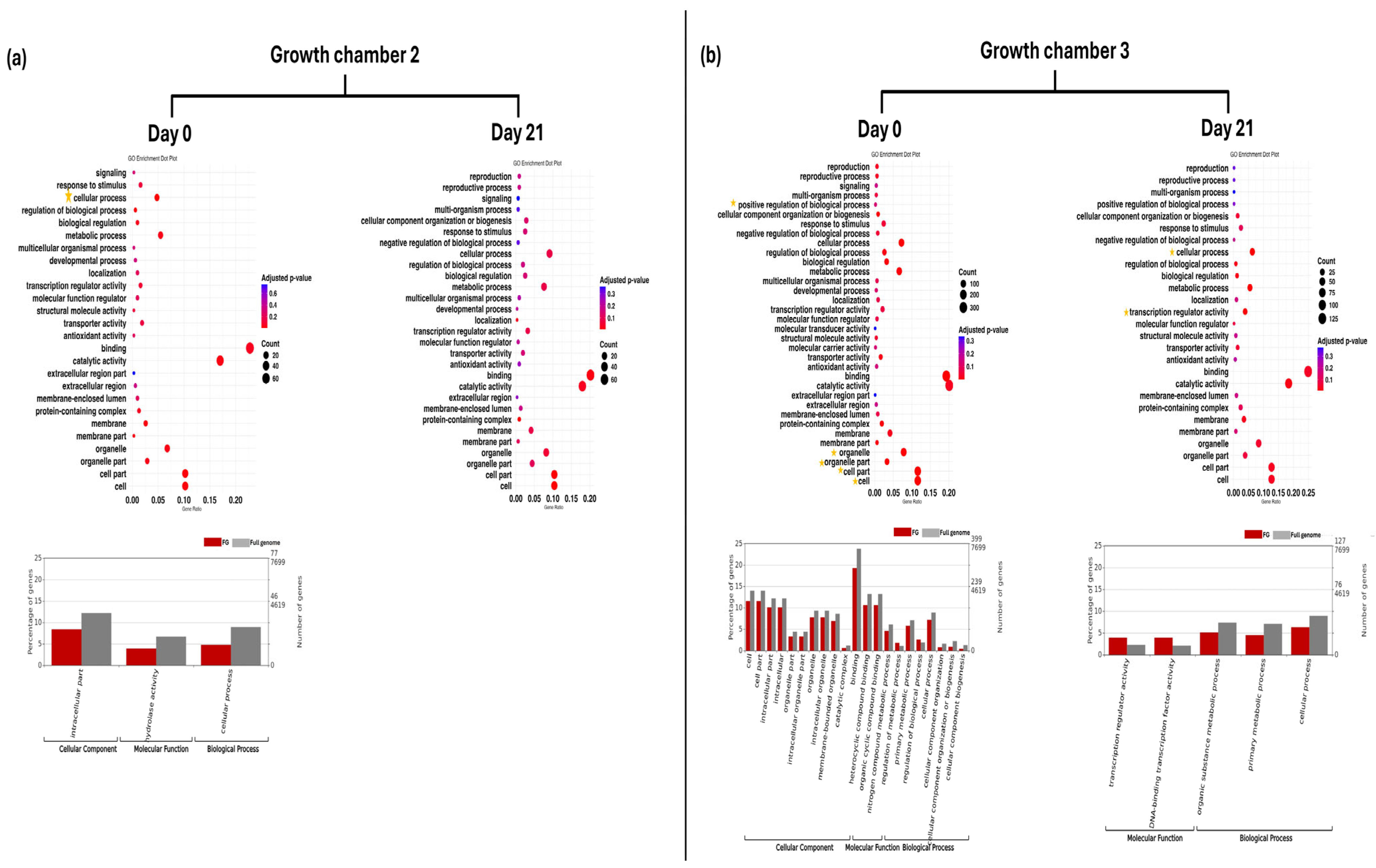


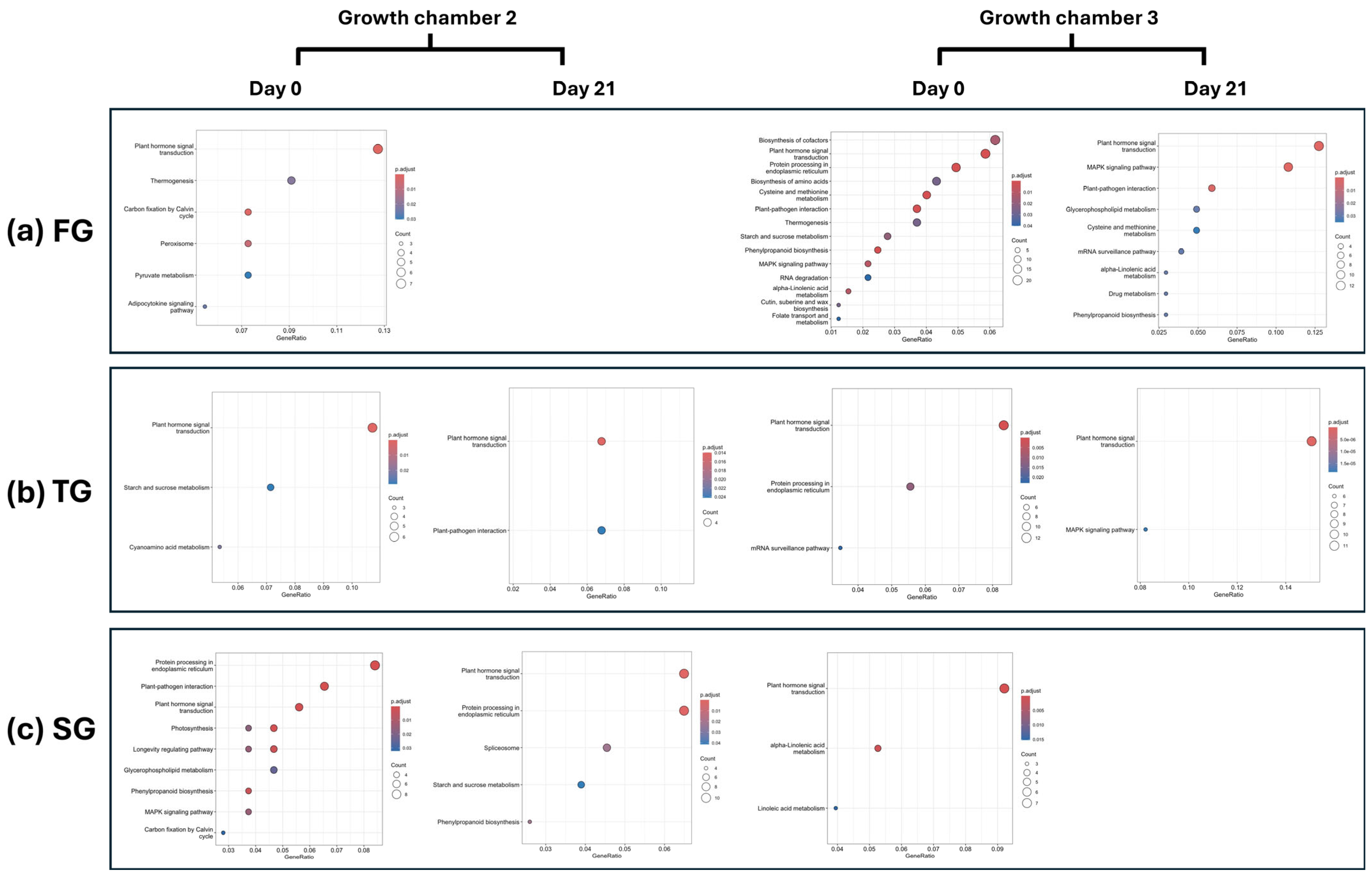
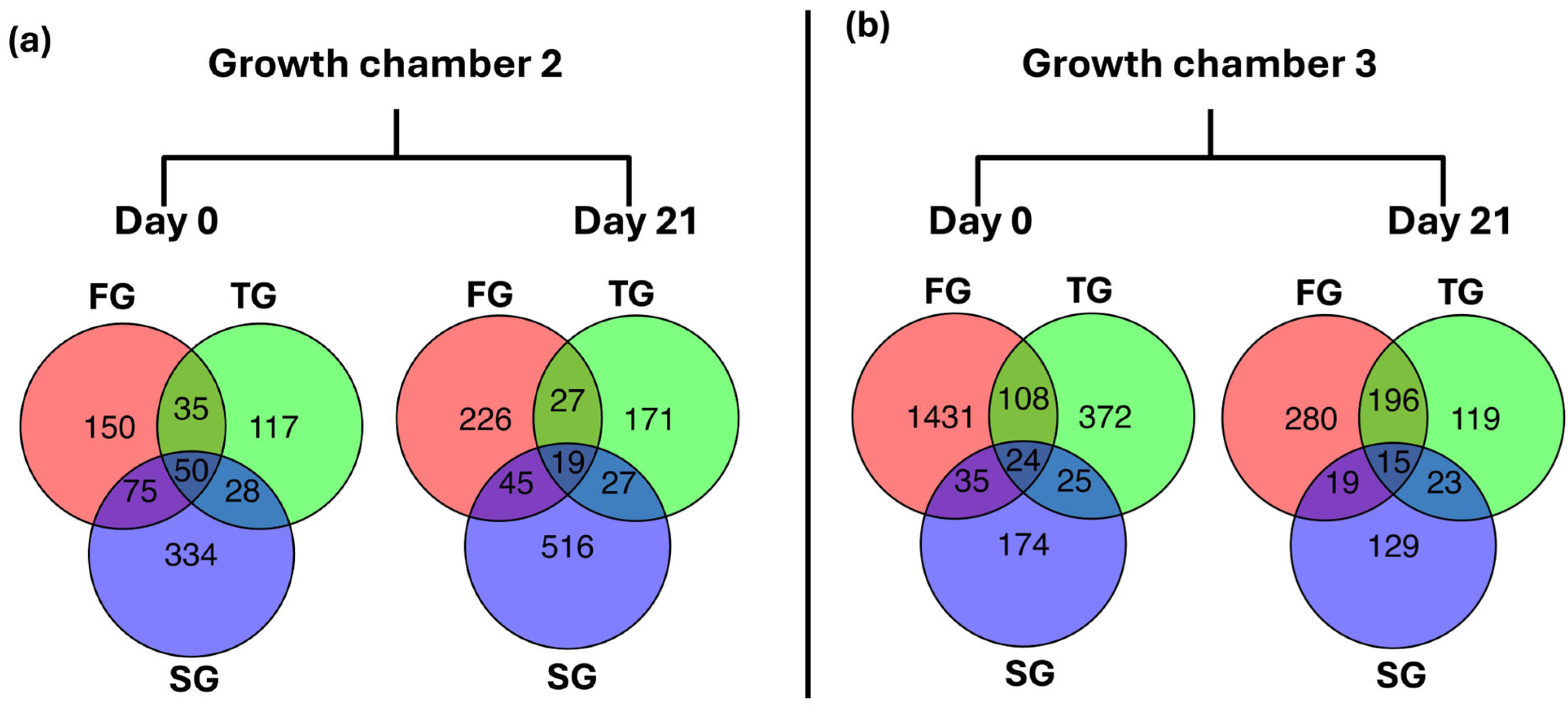



| ID | Gene | Log2FC | Function | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G2_D0 | K14506 | XP_004133822.1 | −13.39 | jasmonoyl--L-amino acid synthetase JAR6, transcript variant X1 |
| K14487 | XP_004141893.1 | −6.31 | probable indole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase GH3.1 | |
| K14496 | XP_004148737.1 | 2.19 | abscisic acid receptor PYR1 | |
| K14516 | XP_004150983.1 | −3.07 | ethylene-response factor C3 | |
| K01915 | XP_011659421.1 | −23.66 | glutamine synthetase nodule isozyme, transcript variant X2 | |
| K16903 | XP_031736085.1 | −23.31 | tryptophan aminotransferase-related protein 2-like, transcript variant X3 | |
| K12126 | XP_031736743.1 | −23.62 | transcription factor PIF3, transcript variant X7 | |
| G3_D0 | K14504 | NP_001267579.1 | 3.22 | probable xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase protein 23-like |
| K13422 | XP_004133809.2 | 2.34 | transcription factor MTB1 | |
| K01915 | XP_004134161.1 | −10.38 | glutamine synthetase leaf isozyme, chloroplastic, transcript variant X1 | |
| K13464 | XP_004137510.1 | −11.53 | protein TIFY 6B, transcript variant X1 | |
| K13412 | XP_004140192.1 | 3.31 | calcium-dependent protein kinase 34 | |
| K14505 | XP_004140711.1 | −10.64 | cyclin-D3-3 | |
| K14487 | XP_004141994.1 | 4.42 | probable indole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase GH3.1 | |
| K14491 | XP_004142954.1 | −8.09 | two-component response regulator ARR11 | |
| K14498 | XP_004143455.1 | −9.92 | serine/threonine-protein kinase SAPK2, transcript variant X1 | |
| K14484 | XP_004145418.1 | −9.10 | auxin-induced protein AUX28 | |
| K14488 | XP_004147006.1 | −8.81 | auxin-responsive protein SAUR23 | |
| K14500 | XP_004147901.1 | −9.30 | serine/threonine-protein kinase BSK6 | |
| K14497 | XP_004148120.2 | −1.58 | probable protein phosphatase 2C 75, transcript variant X1 | |
| K14492 | XP_004149797.1 | −6.65 | two-component response regulator ORR9 | |
| K12126 | XP_011648885.1 | −7.41 | transcription factor PIF3, transcript variant X3 | |
| K14431 | XP_011655928.2 | −2.36 | transcription factor TGA2.2, transcript variant X7 | |
| K13946 | XP_011658595.1 | −9.61 | auxin transporter-like protein 5 | |
| K27625 | XP_031740874.1 | 10.72 | phytosulfokine receptor 1-like | |
| K14489 | XP_031742807.1 | −10.73 | histidine kinase 3, transcript variant X2 | |
| G3_D21 | K14504 | NP_001267579.1 | 3.92 | probable xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase protein 23-like |
| K20536 | NP_001267653.1 | 4.60 | mitogen-activated protein kinase 3-like | |
| K13422 | XP_004133809.2 | 1.56 | transcription factor MTB1 | |
| K13412 | XP_004134863.1 | 1.70 | calcium-dependent protein kinase 28 | |
| K14497 | XP_004135669.1 | 2.10 | probable protein phosphatase 2C 6 | |
| K14515 | XP_004138725.1 | 1.53 | EIN3-binding F-box protein 1 | |
| K27628 | XP_004140059.2 | 2.32 | U-box domain-containing protein 15 | |
| K00924 | XP_004142822.1 | 1.04 | receptor protein kinase TMK1 | |
| K14503 | XP_004143497.1 | 1.36 | BES1/BZR1 homolog protein 2, transcript variant X1 | |
| K14514 | XP_004144109.2 | 0.68 | protein ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE 3, transcript variant X1 | |
| K13464 | XP_004144433.1 | 3.93 | protein TIFY 10a | |
| K13413 | XP_004148562.2 | 1.07 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 5 | |
| K14488 | XP_031744790.1 | −3.76 | auxin-induced protein 15A-like |
| ID | Gene | Log2FC | Function | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G2_D0 | K14500 | XP_004133947.1 | 7.55 | serine/threonine-protein kinase BSK2, transcript variant X2 |
| K14486 | XP_004143252.1 | −11.06 | auxin response factor 18, transcript variant X1 | |
| K14498 | XP_004148038.1 | −10.09 | serine/threonine-protein kinase SRK2I, transcript variant X3 | |
| K01915 | XP_011659421.1 | −23.31 | glutamine synthetase nodule isozyme, transcript variant X2 | |
| K12126 | XP_031736743.1 | −23.28 | transcription factor PIF3, transcript variant X7 | |
| K13464 | XP_031741308.1 | −13.91 | protein TIFY 6B, transcript variant X4 | |
| G2_D21 | K16903 | XP_004138271.1 | 10.45 | tryptophan aminotransferase-related protein 2-like, transcript variant X1 |
| K01535 | XP_004148685.1 | 5.03 | ATPase 11, plasma membrane-type | |
| K14486 | XP_011648570.1 | 11.36 | auxin response factor 19, transcript variant X1 | |
| K13946 | XP_011653685.1 | −10.05 | auxin transporter-like protein 4, transcript variant X1 | |
| G3_D0 | K14486 | NP_001295772.1 | 22.70 | auxin response factor 18 |
| K14505 | XP_004140711.1 | −7.13 | cyclin-D3-3 | |
| K14484 | XP_004145418.1 | −8.42 | auxin-induced protein AUX28 | |
| K14431 | XP_004149279.2 | −7.59 | transcription factor TGA2.3, transcript variant X1 | |
| K14497 | XP_004150316.2 | −12.11 | protein phosphatase 2C 51 | |
| K14498 | XP_011653912.1 | 22.97 | serine/threonine-protein kinase SRK2H, transcript variant X1 | |
| K13464 | XP_011655950.1 | −12.05 | protein TIFY 6B, transcript variant X1 | |
| K01915 | XP_011657677.1 | −9.36 | type-1 glutamine synthetase 1, transcript variant X1 | |
| K14489 | XP_031742807.1 | −10.13 | histidine kinase 3, transcript variant X2 | |
| K14500 | XP_031743575.1 | −10.22 | serine/threonine-protein kinase BSK1, transcript variant X2 | |
| K13412 | XP_031745188.1 | −8.80 | calcium-dependent protein kinase 26, transcript variant X1 | |
| K14490 | XP_031745195.1 | −8.53 | histidine-containing phosphotransfer protein 4, transcript variant X2 | |
| G3_D21 | K14504 | NP_001267579.1 | 3.35 | probable xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase protein 23-like |
| K14515 | XP_004138725.1 | 1.26 | EIN3-binding F-box protein 1 | |
| K27628 | XP_004140059.2 | 1.72 | U-box domain-containing protein 15 | |
| K14503 | XP_004143497.1 | 1.00 | BES1/BZR1 homolog protein 2, transcript variant X1 | |
| K14514 | XP_004144109.2 | 0.58 | protein ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE 3, transcript variant X1 | |
| K13464 | XP_004144433.1 | 2.99 | protein TIFY 10a | |
| K13422 | XP_004148739.1 | 2.40 | transcription factor MYC2 | |
| K14484 | XP_011649125.1 | 10.13 | auxin-responsive protein IAA13, transcript variant X1 | |
| K11816 | XP_011649797.1 | 8.97 | probable indole-3-pyruvate monooxygenase YUCCA4, transcript variant X1 | |
| K14509 | XP_031737453.1 | −10.22 | ethylene receptor 2, transcript variant X3 | |
| K14488 | XP_031744790.1 | −5.04 | auxin-induced protein 15A-like |
| ID | Gene | Log2FC | Function | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G2_D0 | K14487 | XP_004141893.1 | −5.23 | probable indole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase GH3.1 |
| K14516 | XP_004150983.1 | −4.99 | ethylene-response factor C3 | |
| K14432 | XP_011649580.1 | −13.80 | ABSCISIC ACID-INSENSITIVE 5-like protein 5, transcript variant X1 | |
| K01915 | XP_011659421.1 | −23.96 | glutamine synthetase nodule isozyme, transcript variant X2 | |
| K12126 | XP_031736743.1 | −23.92 | transcription factor PIF3, transcript variant X7 | |
| K02183 | XP_031739757.1 | −13.47 | calmodulin, transcript variant X3 | |
| G2_D21 | K13449 | XP_004136924.2 | 5.97 | pathogenesis-related protein 1 |
| K14486 | XP_004139643.1 | 2.33 | auxin response factor 18, transcript variant X1 | |
| K14514 | XP_004140927.1 | −10.31 | ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE 3-like 1 protein, transcript variant X1 | |
| K14488 | XP_004147644.1 | 1.92 | hypothetical protein | |
| K13464 | XP_011649171.1 | −9.53 | protein TIFY 4B, transcript variant X3 | |
| K14432 | XP_011649580.1 | −9.30 | ABSCISIC ACID-INSENSITIVE 5-like protein 5, transcript variant X1 | |
| K01915 | XP_011651002.1 | −1.57 | glutamine synthetase leaf isozyme, chloroplastic, transcript variant X2 | |
| K13946 | XP_011653685.1 | −10.20 | auxin transporter-like protein 4, transcript variant X1 | |
| K14431 | XP_011655928.2 | −2.43 | transcription factor TGA2.2, transcript variant X7 | |
| K14510 | XP_011657691.1 | −8.30 | serine/threonine-protein kinase CTR1, transcript variant X3 | |
| G3_D0 | K13449 | XP_004136924.2 | −4.04 | pathogenesis-related protein 1 |
| K14432 | XP_004144092.1 | −8.88 | ABSCISIC ACID-INSENSITIVE 5-like protein 2, transcript variant X4 | |
| K13422 | XP_004146202.3 | −7.89 | transcription factor MYC3, transcript variant X2 | |
| K14431 | XP_004149279.2 | −8.05 | transcription factor TGA2.3, transcript variant X1 | |
| K14484 | XP_004150206.2 | −3.10 | auxin-responsive protein IAA29 | |
| K13464 | XP_011650896.1 | 10.61 | protein TIFY 6B, transcript variant X2 | |
| K27627 | XP_011651990.1 | −2.20 | phytosulfokines 5 |
| FG | ID | Gene | Log2FC | Function |
| Plant hormone signal transduction | K20536 | NP_001267653.1 | 4.60 | mitogen-activated protein kinase 3-like |
| K14504 | NP_001267702.1 | 6.33 | probable xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase protein 23-like | |
| K13422 | XP_004133809.2 | 1.56 | transcription factor MTB1 | |
| K13412 | XP_004134863.1 | 1.70 | calcium-dependent protein kinase 28 | |
| K14497 | XP_004135669.1 | 2.10 | probable protein phosphatase 2C 6 | |
| K00924 | XP_004142822.1 | 1.04 | receptor protein kinase TMK1 | |
| K13413 | XP_004148562.2 | 1.07 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 5 | |
| K13464 | XP_004149668.1 | 3.94 | protein TIFY 5A | |
| MAPK signaling pathway | K20536 | NP_001267653.1 | 4.60 | mitogen-activated protein kinase 3-like |
| K13424 | NP_001292676.1 | 7.92 | probable WRKY transcription factor 26 | |
| K13422 | XP_004133809.2 | 1.56 | transcription factor MTB1 | |
| K14497 | XP_004135669.1 | 2.10 | probable protein phosphatase 2C 6 | |
| K20604 | XP_004137516.1 | 2.32 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 9 | |
| K13413 | XP_004148562.2 | 1.07 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 5 | |
| K20557 | XP_011658569.1 | 1.61 | uncharacterized LOC101216189 | |
| Cysteine and methionine metabolism | K08967 | XP_004134118.1 | 0.79 | 1,2-dihydroxy-3-keto-5-methylthiopentene dioxygenase 2 |
| K27857 | XP_004136690.1 | 1.13 | cystathionine gamma-synthase 1, chloroplastic | |
| K00640 | XP_011649387.1 | 10.45 | serine acetyltransferase 5, transcript variant X2 | |
| K01919 | XP_031740812.1 | 11.26 | glutamate--cysteine ligase, chloroplastic, transcript variant X2 | |
| K01760 | XP_031743082.1 | 10.74 | cystathionine beta-lyase, chloroplastic, transcript variant X5 | |
| TG | ID | Gene | Log2FC | Function |
| Plant hormone signal transduction | K14484 | XP_011649125.1 | 10.13 | auxin-responsive protein IAA13, transcript variant X1 |
| K11816 | XP_011649797.1 | 8.97 | probable indole-3-pyruvate monooxygenase YUCCA4, transcript variant X1 | |
| K14509 | XP_031737453.1 | −10.22 | ethylene receptor 2, transcript variant X3 |
| FG | |||
| Protein ID | TF | Log2FC | Function |
| XP_004133809.2 | bHLH | 1.56 | transcription factor MTB1 |
| XP_011648566.1 | bHLH | 10.54 | transcription factor BIM1, transcript variant X1 |
| XP_011657919.2 | bHLH | 9.29 | transcription factor bHLH19 |
| XP_011654291.1 | bZIP | 1.58 | bZIP transcription factor 60 |
| XP_011658569.1 | bZIP | 1.61 | uncharacterized LOC101216189 |
| NP_001267641.1 | C2H2 | 1.35 | zinc finger AN1 and C2H2 domain-containing stress-associated protein 11-like |
| XP_004141285.1 | C2H2 | 3.76 | zinc finger protein ZAT10 |
| XP_004147699.1 | C2H2 | 2.51 | zinc finger protein ZAT12 |
| XP_011658172.1 | C2H2 | 6.97 | uncharacterized LOC105435955 |
| XP_011657270.2 | CAMTA | 10.93 | calmodulin-binding transcription activator 5, transcript variant X1 |
| XP_004134413.1 | ERF | −4.69 | ethylene-responsive transcription factor 14 |
| XP_004136839.1 | ERF | 2.25 | ethylene-responsive transcription factor 4 |
| XP_004139438.1 | ERF | 1.47 | ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF039 |
| XP_004140859.1 | ERF | −1.10 | ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF118 |
| XP_004144279.1 | ERF | 7.32 | ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF017 |
| XP_011650877.1 | G2-like | −11.43 | protein PHR1-LIKE 2, transcript variant X2 |
| XP_004149904.1 | GATA | 1.61 | GATA transcription factor 8 |
| XP_004145288.1 | GRAS | 2.19 | scarecrow-like protein 34 |
| XP_004140200.1 | HB-other | 9.64 | uncharacterized LOC101207235, transcript variant X1 |
| XP_004146371.1 | HB-PHD | 9.35 | pathogenesis-related homeodomain protein, transcript variant X1 |
| XP_004135200.1 | HD-ZIP | −2.48 | homeobox-leucine zipper protein HAT5 |
| XP_031744925.1 | MIKC_MADS | −2.86 | MADS-box protein SVP, transcript variant X4 |
| XP_004141899.1 | MYB | 2.26 | transcription factor MYB44 |
| XP_004147145.1 | MYB | 6.48 | transcription factor MYB14 |
| XP_031738637.1 | MYB_related | 8.11 | hypothetical protein, transcript variant X2 |
| XP_031739750.1 | MYB_related | −7.80 | telomere repeat-binding factor 1, transcript variant X4 |
| XP_004139589.2 | NAC | 20.67 | NAC domain-containing protein 40, transcript variant X1 |
| XP_004149802.1 | NAC | 2.99 | NAC domain-containing protein 2 |
| NP_001292676.1 | WRKY | 7.92 | probable WRKY transcription factor 26 |
| XP_004134775.1 | WRKY | 2.42 | probable WRKY transcription factor 31 |
| XP_004149751.1 | WRKY | 6.03 | probable WRKY transcription factor 41 |
| XP_011652902.1 | WRKY | 1.92 | probable WRKY transcription factor 7-like, transcript variant X1 |
| TG | |||
| Protein ID | TF | Log2FC | Function |
| XP_011651831.1 | B3 | 10.11 | B3 domain-containing transcription repressor VAL2, transcript variant X3 |
| XP_004143425.1 | bHLH | 8.25 | transcription factor bHLH18, transcript variant X1 |
| XP_011660048.1 | bHLH | 7.82 | transcription factor bHLH47, transcript variant X1 |
| XP_031741810.1 | C2H2 | 8.76 | protein indeterminate-domain 5, chloroplastic-like, transcript variant X2 |
| XP_011652639.1 | HD-ZIP | 8.41 | homeobox-leucine zipper protein HDG5, transcript variant X1 |
| XP_011657330.1 | NAC | 8.22 | protein CUP-SHAPED COTYLEDON 3, transcript variant X1 |
| XP_031741540.1 | NAC | 10.30 | NAC domain containing protein 50, transcript variant X1 |
| XP_011649248.1 | TALE | −10.98 | BEL1-like homeodomain protein 7, transcript variant X2 |
| XP_031736434.1 | YABBY | −3.35 | axial regulator YABBY 5, transcript variant X2 |
| SG | |||
| Protein ID | TF | Log2FC | Function |
| XP_031743220.1 | B3 | −7.42 | uncharacterized LOC101221625, transcript variant X32 |
| XP_031736097.1 | E2F/DP | 8.47 | E2F transcription factor-like E2FE, transcript variant X4 |
| XP_011656418.1 | ERF | −9.43 | dehydration-responsive element-binding protein 2C, transcript variant X1 |
| XP_031743007.1 | NF-YA | −11.82 | nuclear transcription factor Y subunit A-1, transcript variant X8 |
| XP_011649247.1 | TALE | −12.06 | BEL1-like homeodomain protein 7, transcript variant X1 |
| XP_031736725.1 | TALE | −2.27 | homeobox protein ATH1, transcript variant X7 |
| XP_004136441.1 | Trihelix | 10.67 | trihelix transcription factor ASR3, transcript variant X1 |
| XP_004141520.1 | Whirly | 0.44 | single-stranded DNA-binding protein WHY2, mitochondrial |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pandey, S.; Subedi, B.S.; Ogden, A.B. Molecular Pathways Associated with Cold Tolerance in Grafted Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Plants 2025, 14, 3860. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14243860
Pandey S, Subedi BS, Ogden AB. Molecular Pathways Associated with Cold Tolerance in Grafted Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Plants. 2025; 14(24):3860. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14243860
Chicago/Turabian StylePandey, Sudeep, Bijaya Sharma Subedi, and Andrew B. Ogden. 2025. "Molecular Pathways Associated with Cold Tolerance in Grafted Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.)" Plants 14, no. 24: 3860. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14243860
APA StylePandey, S., Subedi, B. S., & Ogden, A. B. (2025). Molecular Pathways Associated with Cold Tolerance in Grafted Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Plants, 14(24), 3860. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14243860







