Host Range Expansion and Dual Ecological Roles of an Invasive African Seed Predator on Native and Introduced Plants in Hawai‘i
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
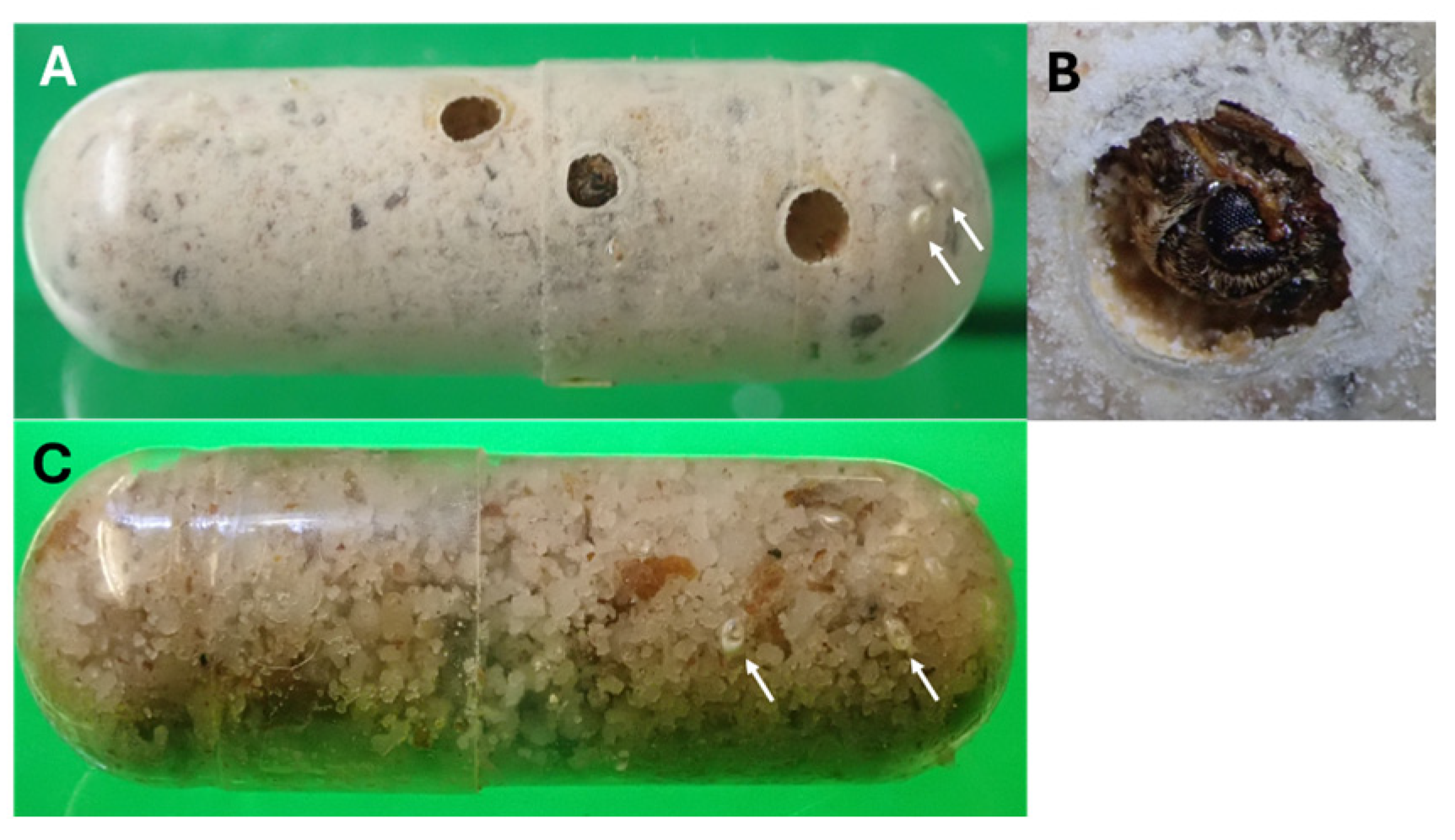
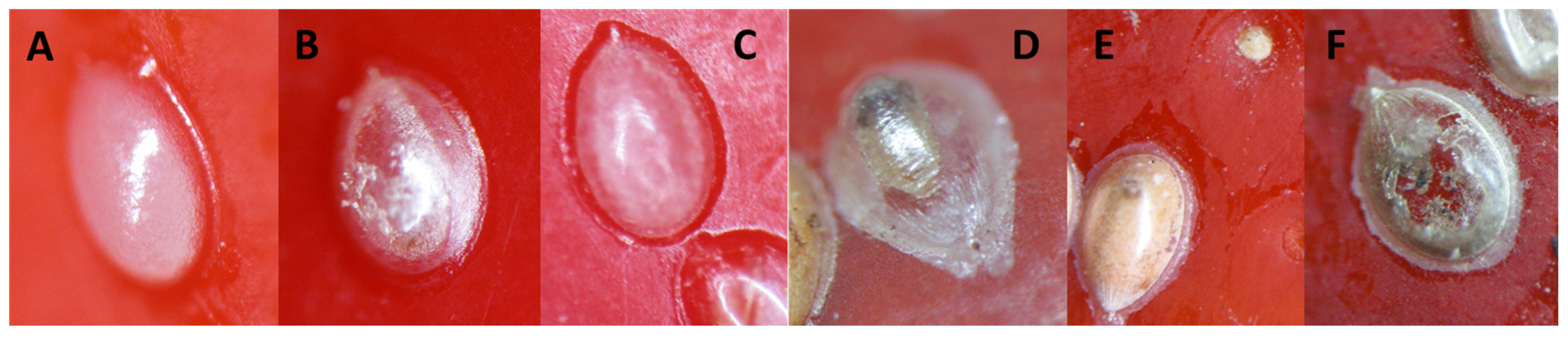
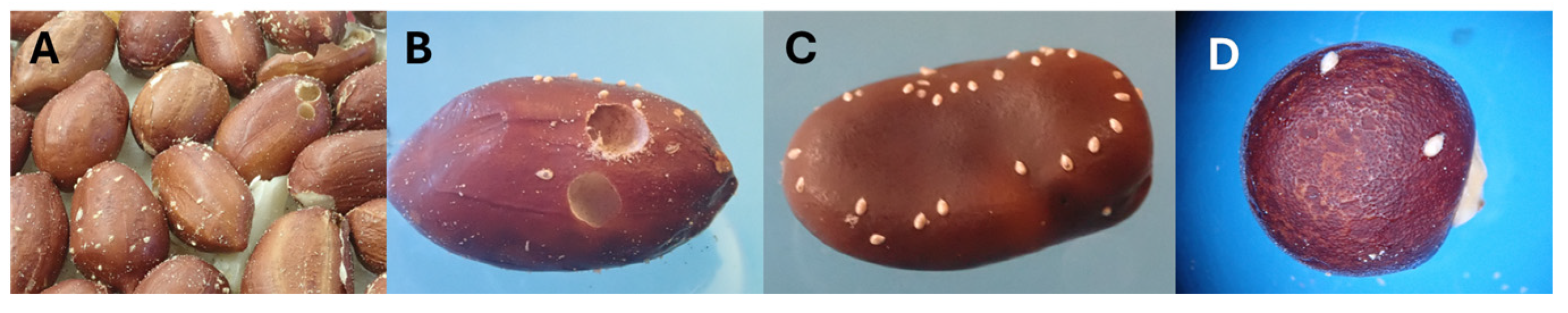
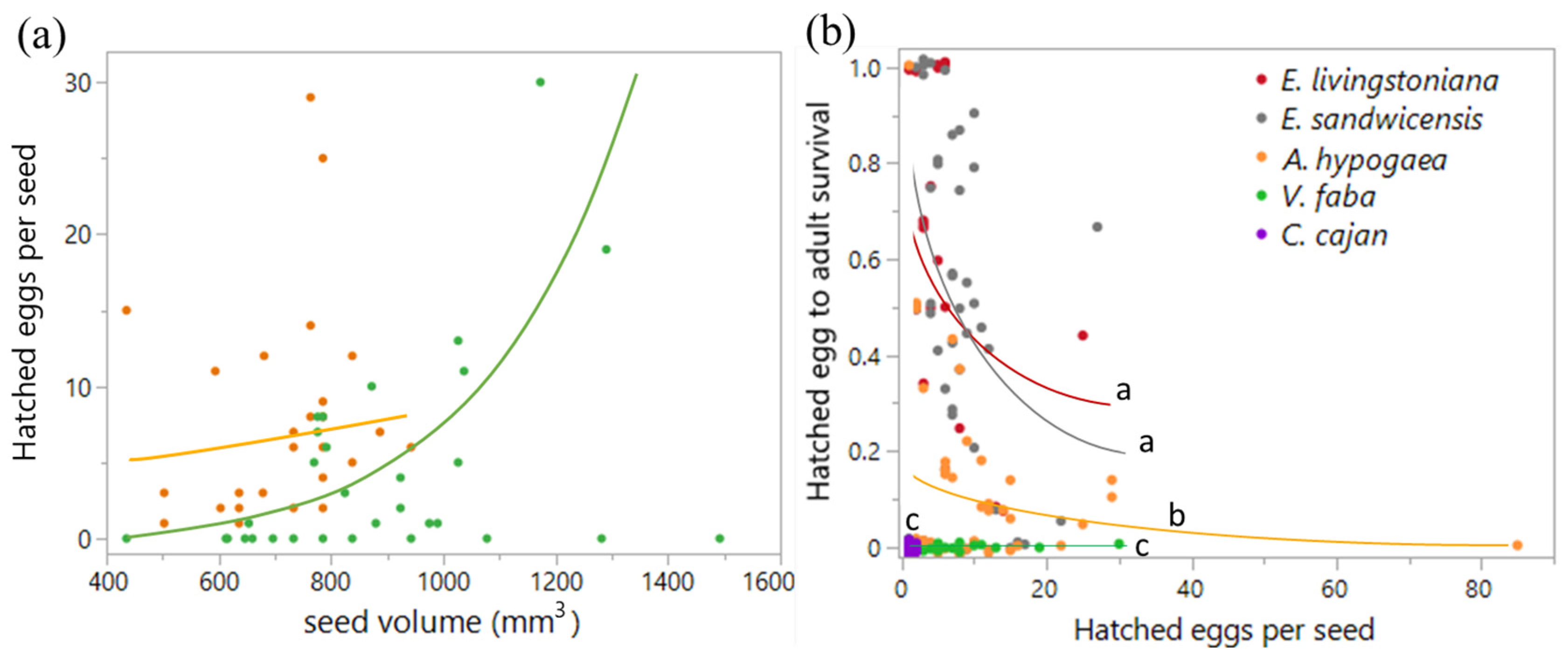
2.1. Plant Suitability and Seed Size Effects on Specularius impressithorax Egg Deposition
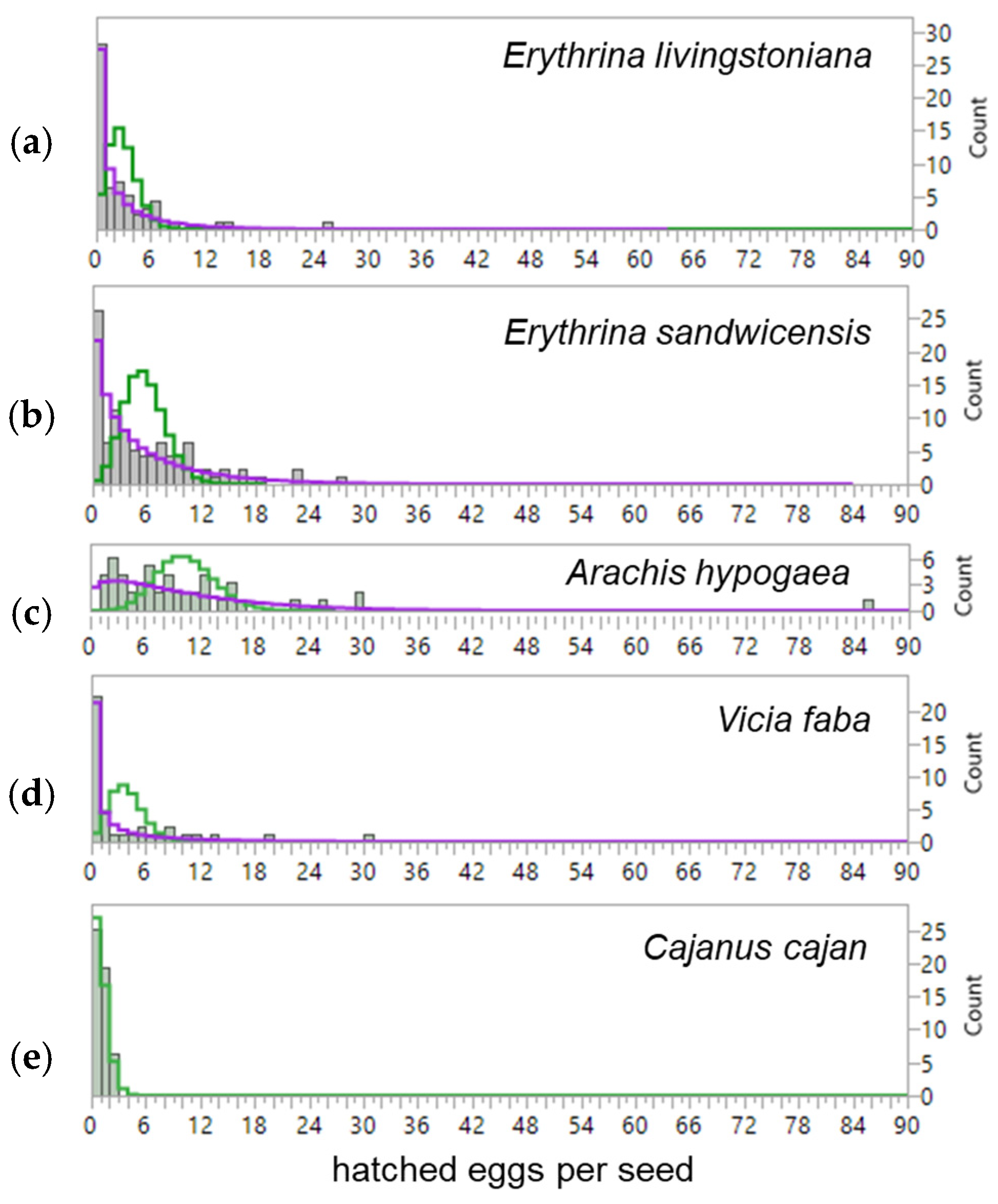
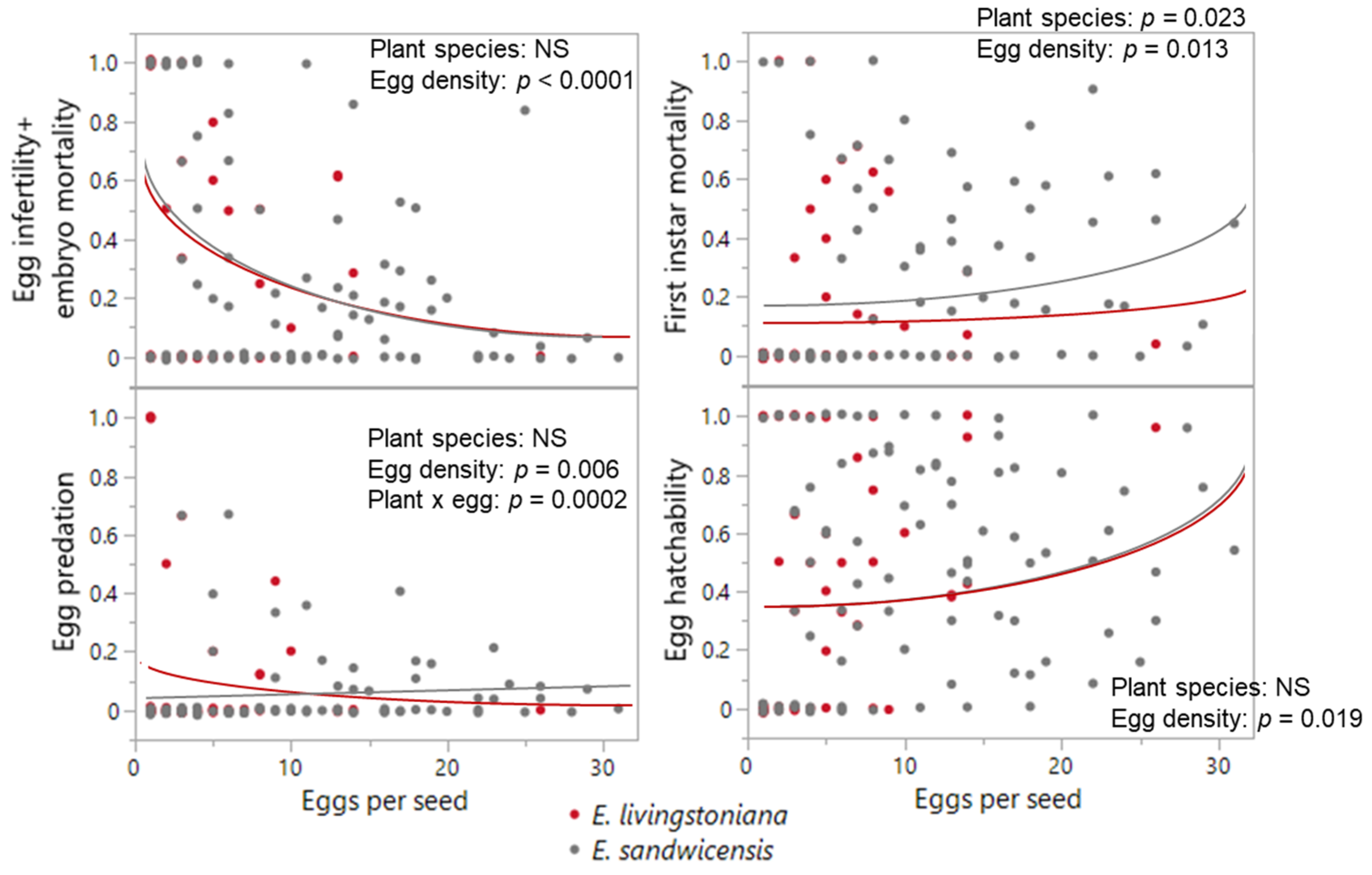
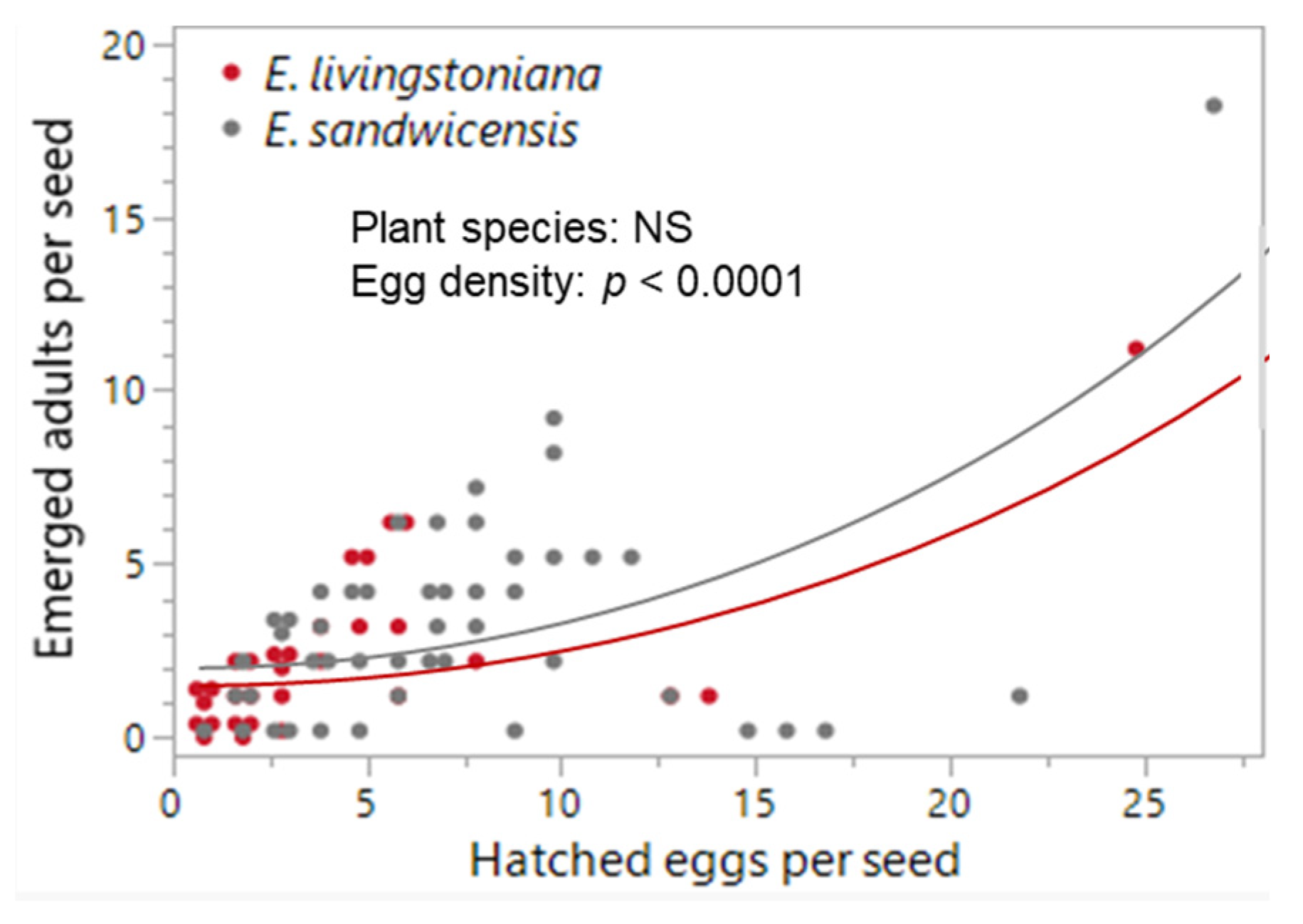
2.2. Egg Distribution, Egg and Larval Density Effects, and Infestation Capacity
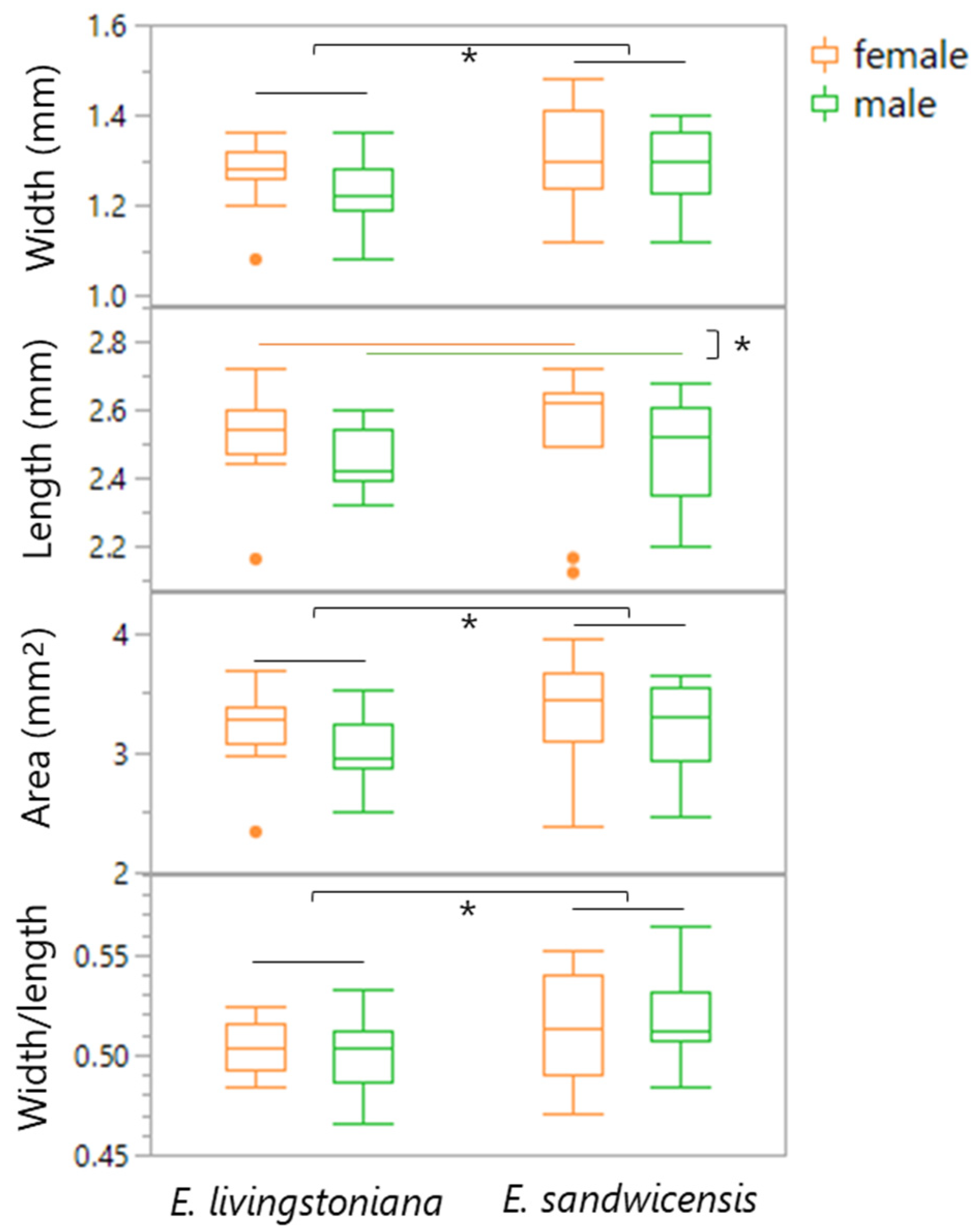
2.3. Body Size
2.4. Choice Experiment
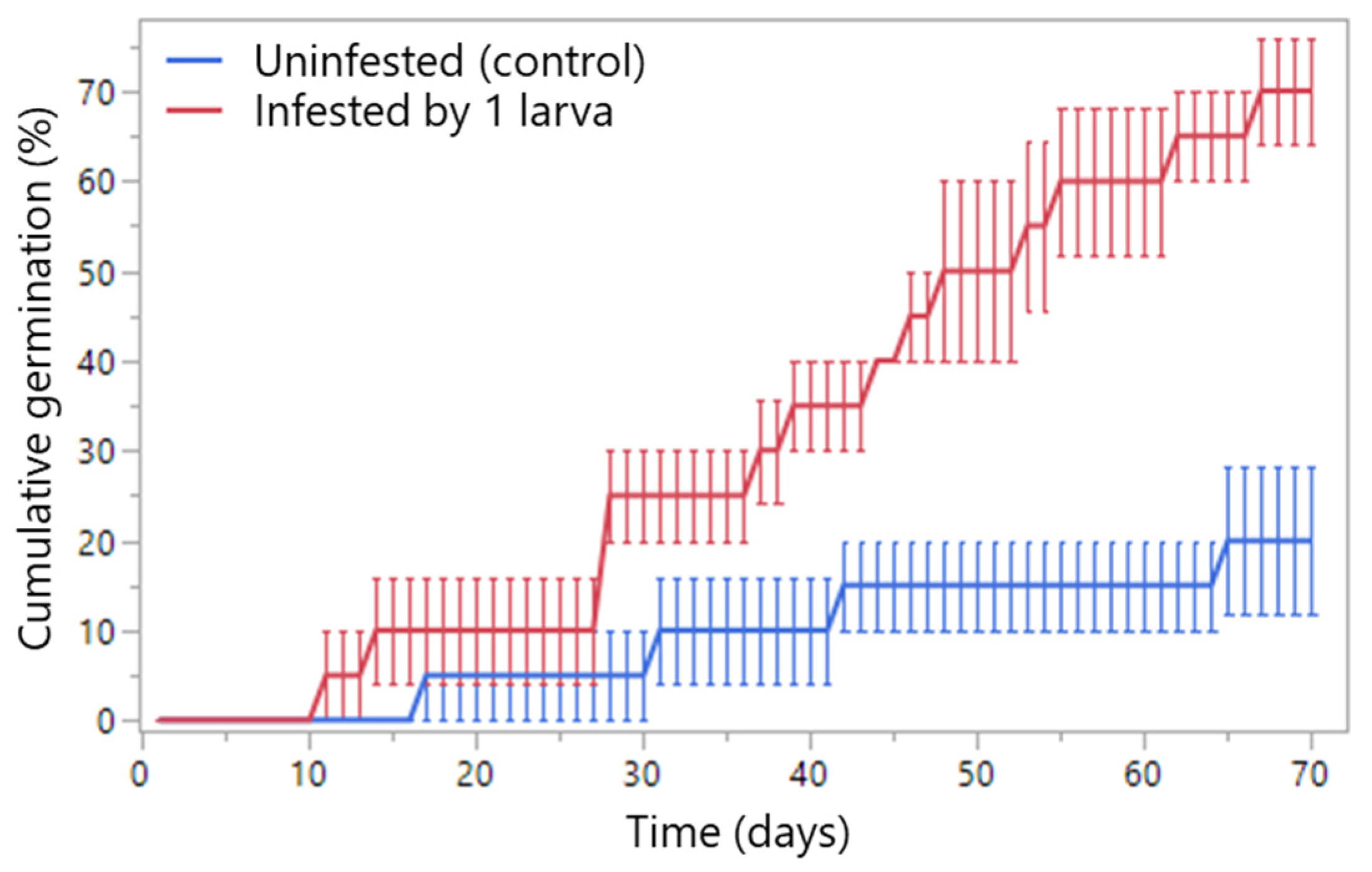
2.5. Seed Germination
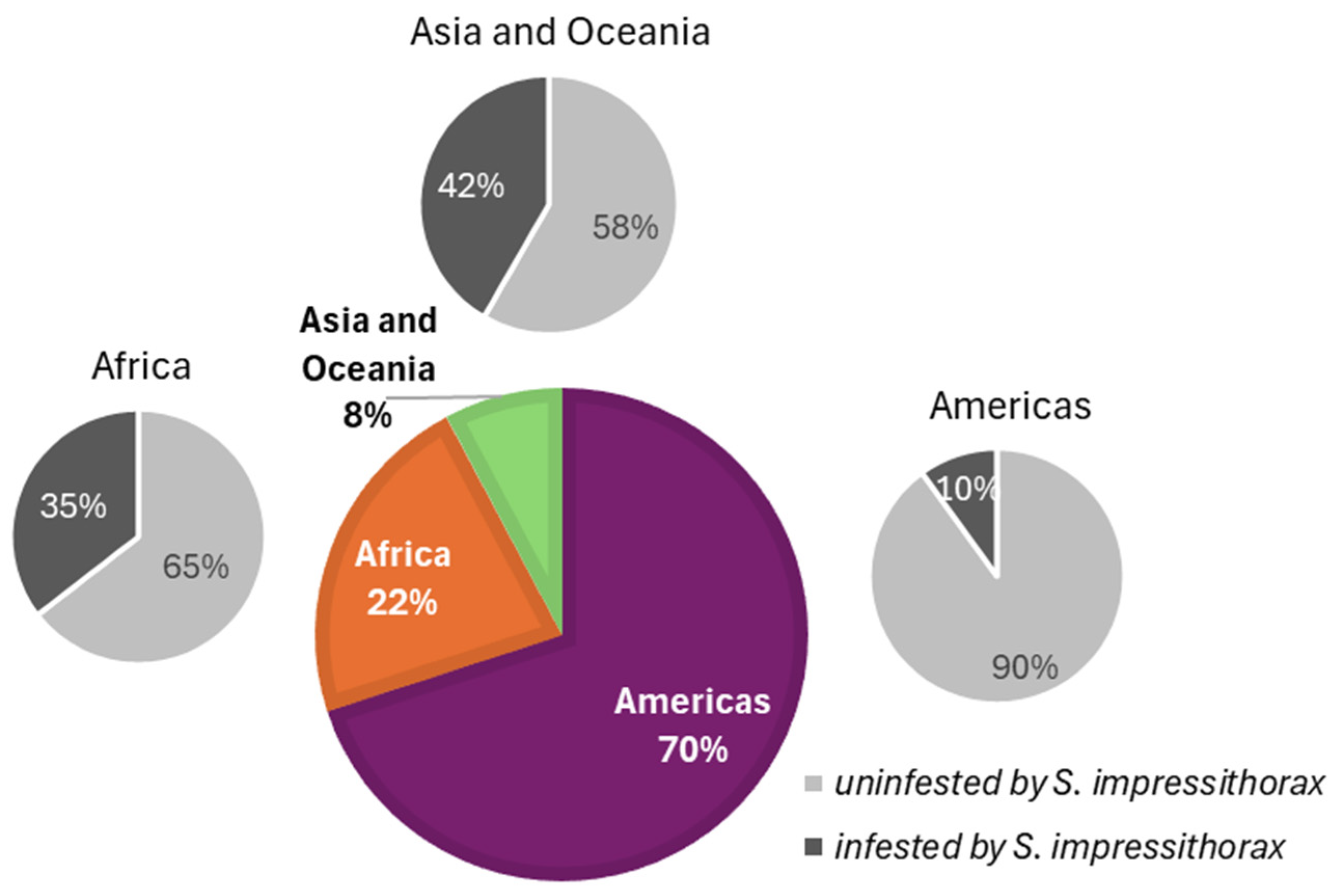
2.6. Literature Review of Native Host Plant Range
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
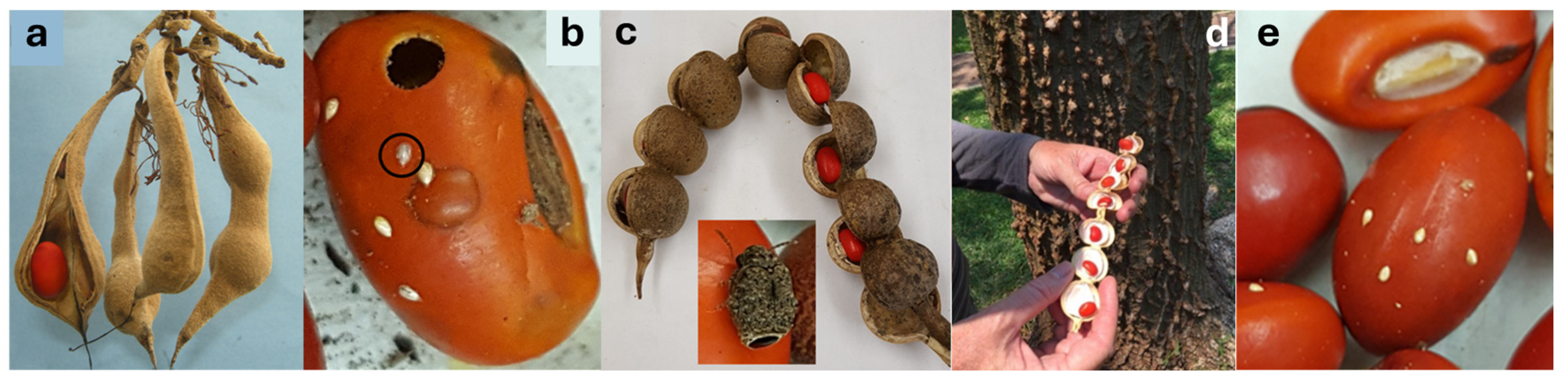
4.1. Field Collection of Erythrina and Laboratory Rearing
4.2. Host Plant Range, Egg and Larval Density Effects, and Seed Size
4.3. Development Using Seed Powder
4.4. Choice Experiment
4.5. Seed Germination
4.6. Literature Search for Host Plant Associations
4.7. Statistical Analysis and Vouchers
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SI | Specularius impressithorax |
Appendix A

| Species | Native Regions | Field Infestation | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Erythrina abyssinica Lam. ex DC. | Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Republic of the Congo, Rhodesia, South Africa, Sudan, Tanzania, Mozambique, Nyasaland, Uganda, Zaire, Zimbabwe | Field | [25,55,56] |
| Erythrina americana Mill. | Mexico, C. America, Belize, Guatemala, southern N. America | Field, Hawaii 2006 | [22,23,57] |
| Erythrina berteroana Urb. | Central America, Colombia, Guatemala, Mexico, Venezuela | Field, Hawaii 2017, Honduras 2024 | [58] |
| Erythrina caffra Thunb. | Mozambique, South Africa | Field | [51] |
| Erythrina coralloides DC. | Mexico, and Central America | Field | [59] |
| Erythrina crista-galli L. | Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Paraguay, United States of America, Uruguay | Field, Hawaii 2006 | [22] |
| Erythrina eudiphylla Hassk. ex Backh | Indonesia | Field, Hawaii 2006 | [22,23] |
| Erythrina folkersii Krukoff & Moldenke | Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico Gulf, Mexico Southeast, Mexico Southwest | Field, Kaluakauila, Coll. Mexico | [52] |
| Erythrina humeana Spreng. | South Africa, Mozambique | Field, Mozambique 2007 | [12,22,52] |
| Erythrina latissima E.Mey. | South Africa | Field | [52] |
| Erythrina livingstoniana Baker | East Africa, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Malawi, Tanzania, Zambia | Field, Hawaii 2020 | This study |
| Erythrina lysistemon Hutch. | South Africa, Mozambique | Field, Mozambique 2007 | [22,52] |
| Erythrina microcarpa Koord. & Valeton | Jawa, Philippines | Field, Hawaii 2006 | [22,23] |
| Erythrina orophila Ghesq. | Burundi, Democratic Republic of Congo, Zaïre | [12,59] | |
| Erythrina pallida Britton & Rose | Tobago, Trinidad, Venezuela, Venezuelan Antilles | Field | [59] |
| Erythrina sacleuxii Hua | Kenya, Tanzania | Field | [52] |
| Erythrina sandwicensis O.Deg. | Hawaii | Field, Hawaii 2001 | [22,52] |
| Erythrina senegalensis DC. | Angola, Cameroon, Chad, Ghana, Nigeria, West Africa, Mauritania | Field | [12] |
| Erythrina sykesii Barneby & Krukoff | (as hybrid: sykesii × variegata) native to Australia | Field, Hawaii 2006 | [27] |
| Erythrina variegata L. | Africa, Australia, coast of India, east Asia, India, Malaysia, Oceania | Field, Hawaii 2006 | [12,22,25,52] |
| Strophostyles sarmentosa Elliott | United States of America | Field | [26] |
| Physostigmana mesoponticum Taub. | Angola | Field | [27] |
References
- Janzen, D.H. Herbivores and the number of tree species in tropical forests. Am. Nat. 1970, 104, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, O.T.; Gripenberg, S. Insect seed predators and environmental change. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 45, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowiec, L. The genera of seed-beetles (Coleoptera, Bruchidae). Pol. Pismo Entomol. 1987, 57, 3–207. [Google Scholar]
- Kingsolver, J.M. Handbook of the Bruchidae of the United States and Canada (Insecta, Coleoptera); Technical Bulletin Number 1912; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; p. 324. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, C.D. Seed beetles host specificity and the systematics of the Leguminosae. In Advances in Leguminosae Systematics; Polhill, R.M., Raven, P.H., Eds.; Royal Botanic Gardens: London, UK, 1981; Volume 2, pp. 995–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Southgate, B.J. Biology of the Bruchidae. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1979, 24, 449–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuda, M.; Chou, L.-Y.; Niyomdham, C.; Buranapanichpan, S.; Tateishi, Y. Ecological factors associated with pest status in Callosobruchus (Coleoptera: Bruchidae): High host specificity of non-pests to Cajaninae (Fabaceae). J. Stored Prod. Res. 2005, 41, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kergoat, G.J.; Silvain, J.-F.; Delobel, A.; Tuda, M.; Anton, K.-W. Defining the limits of taxonomic conservatism in host-plant use for phytophagous insects: Molecular systematics and evolution of host-plant associations in the seed-beetle genus Bruchus Linnaeus (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Bruchinae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 43, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kergoat, G.J.; Silvain, J.-F.; Buranapanichpan, S.; Tuda, M. When insects help to resolve plant phylogeny: Evidence for a paraphyletic genus Acacia from the systematics and host-plant range of their seed-predators. Zool. Scr. 2007, 36, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beenen, R. Translocation in Leaf beetles (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Bonn. Zool. Beitr. 2005, 54, 179–199. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, W.L.; Herbst, D.R.; Sohmer, S.H. Manual of the Flowering Plants of Hawai’i, 2nd ed.; Bishop Museum: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1999; p. 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Neill, D.A. The Genus Erythrina: Taxonomy, Distribution and Ecological Differentiation. In Erythrina in the New and Old Worlds Nitrogen Fixing Tree Research Reports—Special Issue; Westley, S.B., Powell, M.H., Eds.; Nitrogen Fixing Tree Association: Morrilton, AR, USA, 1993; pp. 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- IUCN 2024. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2024-2. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/search/list?query=erythrina&searchType=species (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Ikabanga, D.U.; Bidault, E.; Paradis, A.-H.; Texier, N.; Stévart, T. Erythrina wieringae. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020, e.T172511949A172511959. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/172511949/172511959 (accessed on 24 November 2025). [CrossRef]
- Russo, R.; Budowski, G. Effect of pollarding frequency on biomass of Erythrina poeppigiana as a coffee shade tree. Agrofor. Syst. 1986, 4, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedane, K.G.; Kusari, S.; Masesane, I.B.; Spiteller, M.; Majinda, R.R.T. Flavanones of Erythrina livingstoniana with antioxidant properties. Fitoterapia 2016, 108, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlquist, S. The biota of long distance dispersal. III. Loss of dispersibility in the Hawaiian flora. Brittonia 1966, 18, 310–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loope, L.; VanGelder, E. Appendix E: Invasive species report. In Pacific Island Network Vital Signs Monitoring Plan,(Natural Resource Report NPS/PACN/NRR—2006/003); HaySmith, L., Klasner, F.L., Stephens, S.H., Dicus, G.H., Eds.; National Park Service: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Grave, E.; Kroessig, T. Erythrina sandwicensis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020, e.T120702630A120702761. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/120702630/120702761 (accessed on 24 November 2025). [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.K.; Delvare, G.; LaSalle, J. A new species of Quadrastichus (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae): A gall-inducing pest on Erythrina spp. (Fabaceae). J. Hymenopt. Res. 2004, 13, 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Heu, R.A.; Tsuda, D.M.; Nagamine, W.T.; Yalemar, J.A.; Suh, T.H. Erythrina Gall Wasp Quadrastichus erythrinae Kim (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae); New Pest Advisory no. 05–03; State of Hawaii Department of Agriculture: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros, A.C.; Vonallmen, E.; Fukada, M.; Samuelson, A.; Lau, T. Impact of the newly arrived seed-predating beetle Specularius impressithorax (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Bruchinae) in Hawaii. Pac. Conserv. Biol. 2008, 14, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelson, G.A.; Medeiros, A.C. Specularius impressithorax, an adventive bean weevil on Erythrina new to the Hawaiian Islands (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Bruchinae). In Bishop Museum Occasional Papers No. 88; Bishop Museum Press: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2006; pp. 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Bridwell, J.C. Specularius erythrinae, a new bruchid affecting seeds of Erythrina (Coleoptera). J. Wash. Acad. Sci. 1938, 28, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- GBIF Secretariat 2023. Erythrina livingstoniana Baker, GBIF Backbone Taxonomy. Checklist Dataset. Available online: https://www.gbif.org/dataset/d7dddbf4-2cf0-4f39-9b2a-bb099caae36c (accessed on 9 November 2024). [CrossRef]
- Kingsolver, J.M.; Decelle, J.E. Host associations of Specularius impressithorax (Pic) (Insecta: Coleoptera: Bruchidae) with species of Erythrina (Fabales: Fabaceae). Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1979, 66, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decelle, J. Les Coleopteres Bruchides d’Angola; Publicacoes culturais da Companhia de Diamantes de Angola: Lisboa, Portugal, 1975; Volume 98, pp. 13–32. [Google Scholar]
- Tuda, M.; Ronn, J.; Buranapanichpan, S.; Wasano, N.; Arnqvist, G. Evolutionary diversification of the bean beetle genus Callosobruchus (Coleoptera: Bruchidae): Traits associated with stored-product pest status. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 3541–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwanze, K.F.; Horber, E. Seed Coats of Cowpeas Affect Oviposition and Larval Development of Callosobruchus maculatus. Environ. Entomol. 1976, 5, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, H.; Ohsawa, K. Chemical ecology for stored product insects. J. Pestic. Sci. 1990, 15, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, W.H.O. Food consumption, life history and determinants of host range in the bruchid beetle Specularius impressithorax (Coleoptera: Bruchidae). J. Stored Prod. Res. 1993, 29, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janzen, D.H. The ecology and evolutionary biology of seed chemistry as relates to seed predation. In Biochemical Aspects of Plant and Animal Coevolution; Harborne, J.B., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1978; pp. 163–206. [Google Scholar]
- Raven, P.H. Erythrina (Fabaceae): Achievements and opportunities. Lloydia 1974, 37, 321–331. [Google Scholar]
- Cope, J.M.; Fox, C.W. Oviposition decisions in the seed beetle, Callosobruchus maculatus (Coleoptera: Bruchidae): Effects of seed size on superparasitism. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2003, 39, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeny, P. Plant apparency and chemical defense. Recent Adv. Phytochem. 1976, 10, 140. [Google Scholar]
- Weissich, P.R. Hawaiian native plants in the landscape. Comb. Proc. Int. Plant Propagators’ Soc. 1995, 44, 332–335. [Google Scholar]
- Sari, L.T.; Ribeiro-Costa, C.S.; da Silva Pereira, P.R.V. Biological aspects of Zabrotes subfasciatus (Bohemann, 1833) (Coleoptera, Bruchidae) on Phaseolus vulgaris L., cv. Carioca (Fabaceae), under laboratory conditions. Rev. Bras. Entomol. 2003, 47, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouzat, J. Egg distribution by Acanthoscelides obtectus on identical seeds of Phaseolus vulgaris. Biol. Behav. 1983, 8, 215–230. [Google Scholar]
- Nakai, Z.; Kondo, T.; Akimoto, S. Parasitoid attack of the seed-feeding beetle Bruchus loti enhances the germination success of Lathyrus japonicus seeds. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2011, 5, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grave, E.F.; Kroessig, T.I.; Ticktin, T. Pollination Biology of an Endemic Hawaiian Tree, Erythrina sandwicensis (Fabaceae: Papilionoideae), in a Novel Ecosystem. Pac. Sci. 2021, 75, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakura, K. The specialist seed predator Bruchidius dorsalis (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) plays a crucial role in the seed germination of its host plant, Gleditsia japonica (Leguminosae). Funct. Ecol. 2002, 16, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A.; Rossi, M.N. When a seed-feeding beetle is a predator and also increases the speed of seed germination: An intriguing interaction with an invasive plant. Evol. Ecol. 2019, 33, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, E.; Sajna, N. Exploring the impact of a non-native seed predator on the seed germination of its non-native host. Biol. Invas. 2021, 23, 3703–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.W.; Wallin, W.G.; Bush, M.L.; Czesak, M.E.; Messina, F.J. Effects of seed beetles on the performance of desert legumes depend on host species, plant stage, and beetle density. J. Arid Environ. 2012, 80, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Gil, P.d.J.; Espinosa-Vásquez, G.; Lucio-Cruz, C.Y.; Romero-Nápoles, J.; Arce-Cervantes, O. Damage to the seeds of Erythrina americana Mill. (Leguminosae: Faboideae: Erythrininae) by the bruchid Specularius impressithorax (Pic, 1932) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) and its effect on germination. Acta Zool. Mex. 2023, 39, e2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center, T.; Johnson, C.D. Coevolution of some Seed beetles (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) and their hosts. Ecology 1974, 55, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Salcedo, C.; Montaño-Arias, S.A.; Jansson, R. Restoration implications of the germination ecology of six dry-forest woody Fabaceae species in Mexico. Trees 2025, 39, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auld, T.D.; O’Connell, M.A. Predicting patterns of post-fire germination in 35 eastern Australian Fabaceae. Aust. J. Ecol. 1991, 16, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.; Delibes, M.; Fedriani, J.M. Hierarchical levels of seed predation variation by introduced beetles on an endemic Mediterranean palm. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuda, M.; Wu, L.-H.; Tateishi, Y.; Niyomdham, C.; Buranapanichpan, S.; Morimoto, K.; Wu, W.-J.; Wang, C.-P.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, H.; et al. A novel host shift and invaded range of a seed predator, Acanthoscelides macrophthalmus (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Bruchinae), of an invasive weed, Leucaena leucocephala. Entomol. Sci. 2009, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyorgy, Z.; Tuda, M. Host plant range expansion to Gymnocladus dioica by an introduced seed predatory beetle Megabruchidius dorsalis. Entomol. Sci. 2020, 23, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumovsky, A.V.; Ramadan, M.M. Biology, immature and adult morphology, and molecular characterization of a new species of the genus Entedon (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) associated with the invasive pest Specularius impressithorax (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Bruchinae) on Erythrina plants. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2011, 101, 715–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Costa, C.S.; Almeida, L.M. Seed-Chewing Beetles (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae, Bruchinae). In Insect Bioecology and Nutrition for Integrated Pest Management; Panizzi, A.R., Parra, J.R.P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 325–352. [Google Scholar]
- Tuda, M.; Wu, L.-H.; Yamada, N.; Wang, C.-P.; Wu, W.-J.; Buranapanichpan, S.; Kagoshima, K.; Chen, Z.-Q.; Teramoto, K.K.; Kumashiro, B.R.; et al. Host shift capability of a specialist seed predator of an invasive plant: Roles of competition, population genetics and plant chemistry. Biol. Inv. 2014, 16, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridwell, J.C. Notes on the Bruchidae (Coleoptera) and their Parasites in the Hawaiian Islands, 3rd Paper. Proc. Hawaii. Entomol. Soc. 1920, 4, 403–409. [Google Scholar]
- Gillett, J.B. The Fruit and seeds of Erythrina brucei and the identity of E. abyssinica. Kew Bull. 1962, 15, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Montiel, C.; Martínez Hernández Mde, J.; Romero Nápoles, J.; Rios Reyes, A.V. Primer reporte de Specularius impressithorax (Pic.) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) alimentándose de semillas de Erythrina americana miller en los estados de Veracruz y Morelos, México. Acta Zool. Mex. 2012, 28, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos-Ordoñez, M.E.; Romero-Nápoles, J.; González-Hernández, H.; Pérez-Panduro, A.; Zetina, D.A.H. New Distribution Records of Specularius impressithorax (Pic) in Honduras on Erythrina berteroana. Southwest. Entomol. 2024, 49, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, N.J.; Johnson, C.D. BRUCOL, a database for Bruchidae (Insecta, Coleoptera). Entomol. Mex. 2002, 1, 519–526. [Google Scholar]

| Parameter/Seed | E. livingstoniana | E. sandwicensis | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean ± SE | n | Mean ± SE | Host Plant | Egg Density per Seed | |||||
| χ2 | df | p | χ2 | df | p | |||||
| In the field: | ||||||||||
| eggs per collected seed | 164 | 1.67 ± 0.28 | 103 | 9.92 ± 0.77 | 101.2 | 1 | <0.0001 | - | - | - |
| In the lab: | ||||||||||
| eggs (excluding seeds with 0 egg) | 58 | 4.59 ± 0.62 | 98 | 10.46 ± 0.77 | 36.12 | 1 | <0.0001 | - | - | - |
| egg infertility or embryo mortality | 58 | 0.401 ± 0.058 | 98 | 0.271 ± 0.037 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.773 | 39.82 | 1 | <0.0001 |
| egg predation | 58 | 0.091 ± 0.033 | 98 | 0.049 ± 0.013 | 0.02 | 1 | 0.884 | 7.62 | 1 | 0.006 & |
| first-instar larval mortality | 58 | 0.127 ± 0.034 | 98 | 0.227 ± 0.031 | 5.14 | 1 | 0.023 | 6.11 | 1 | 0.013 |
| egg hatchability | 58 | 0.381 ± 0.054 | 98 | 0.453 ± 0.038 | 0.00 | 1 | 0.961 | 5.47 | 1 | 0.019 |
| Host plant | Hatched egg density per seed | |||||||||
| survival from hatched eggs to adults | 31 | 0.506 ± 0.071 | 47 | 0.464 ± 0.051 | 0.003 | 1 | 0.956 | 1.64 | 1 | 0.200 |
| Seed size (cm), volume (mm3) and weight (g): | ||||||||||
| Width | 19 | 0.81 ± 0.013 | 20 | 0.86 ± 0.019 | 4.65 | 1, 37 | 0.038 | |||
| Length | 19 | 1.37 ± 0.013 | 20 | 1.47 ± 0.037 | 5.44 | 1, 37 | 0.025 | |||
| Height | 19 | 0.85 ± 0.011 | 20 | 0.85 ± 0.018 | 0.06 | 1, 37 | 0.809 | |||
| Volume (estimated) | 19 | 498 ± 13 | 20 | 571 ± 34 | 3.80 | 1, 37 | 0.059 | |||
| Weight | 19 | 0.649 ± 0.013 | 20 | 0.652 ± 0.035 | 0.004 | 1, 37 | 0.947 | |||
| Egg distribution | n | Deviation | n | Deviation | ||||||
| Poisson | 164 | χ2 = 1242.7, p < 0.0001 | 103 | χ2 = 622.6, p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| Negative binomial | χ2 = 139.1, p = 0.913 | χ2 = 86.4, p = 0.866 | ||||||||
| Elytron Dimension | Sex | E. livingstoniana | E. sandwicensis | Wilcoxon Test (One-Sided) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean ± SE (mm) | n | Mean ± SE (mm) | Z | p | |||
| Width | female | 10 | 1.27 ± 0.025 | 10 | 1.30 ± 0.038 | plant | 1.82 | 0.034 |
| male | 10 | 1.23 ± 0.025 | 10 | 1.29 ± 0.027 | sex | −0.95 | 0.170 | |
| Length | female | 10 | 2.51 ± 0.046 | 10 | 2.54 ± 0.068 | plant | 1.47 | 0.071 |
| male | 10 | 2.45 ± 0.030 | 10 | 2.49 ± 0.049 | sex | −1.77 | 0.038 | |
| Area (estimated) | female | 10 | 3.19 ± 0.11 | 10 | 3.33 ± 0.17 | plant | 1.84 | 0.033 |
| male | 10 | 3.02 ± 0.09 | 10 | 3.22 ± 0.12 | sex | −1.35 | 0.088 | |
| Width/length | female | 10 | 0.505 ± 0.0042 | 10 | 0.514 ± 0.0086 | plant | 1.72 | 0.085 |
| male | 10 | 0.501 ± 0.0068 | 10 | 0.520 ± 0.0074 | sex | 0.18 | 0.430 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramadan, M.M.; Tuda, M. Host Range Expansion and Dual Ecological Roles of an Invasive African Seed Predator on Native and Introduced Plants in Hawai‘i. Plants 2025, 14, 3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233620
Ramadan MM, Tuda M. Host Range Expansion and Dual Ecological Roles of an Invasive African Seed Predator on Native and Introduced Plants in Hawai‘i. Plants. 2025; 14(23):3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233620
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamadan, Mohsen M., and Midori Tuda. 2025. "Host Range Expansion and Dual Ecological Roles of an Invasive African Seed Predator on Native and Introduced Plants in Hawai‘i" Plants 14, no. 23: 3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233620
APA StyleRamadan, M. M., & Tuda, M. (2025). Host Range Expansion and Dual Ecological Roles of an Invasive African Seed Predator on Native and Introduced Plants in Hawai‘i. Plants, 14(23), 3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233620







