Sulfur Enhances Rice Cadmium Accumulation in Organic Deficient Soil: The Significance of Incorporation with Straw
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Soil and Straw
2.2. Pot Experiment and Sampling
2.3. Analytical Determinations
2.3.1. Soil and Soil Pore Water
2.3.2. Iron Plaque and Plant Tissues
2.3.3. qPCR Amplification of DsrB Gene and 16S rRNA Sequencing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Pore Water Properties and Cd Fractions
3.2. Soil SRB and DsrB Gene Abundance
3.3. Cd and Fe in Iron Plaque of Root Surface
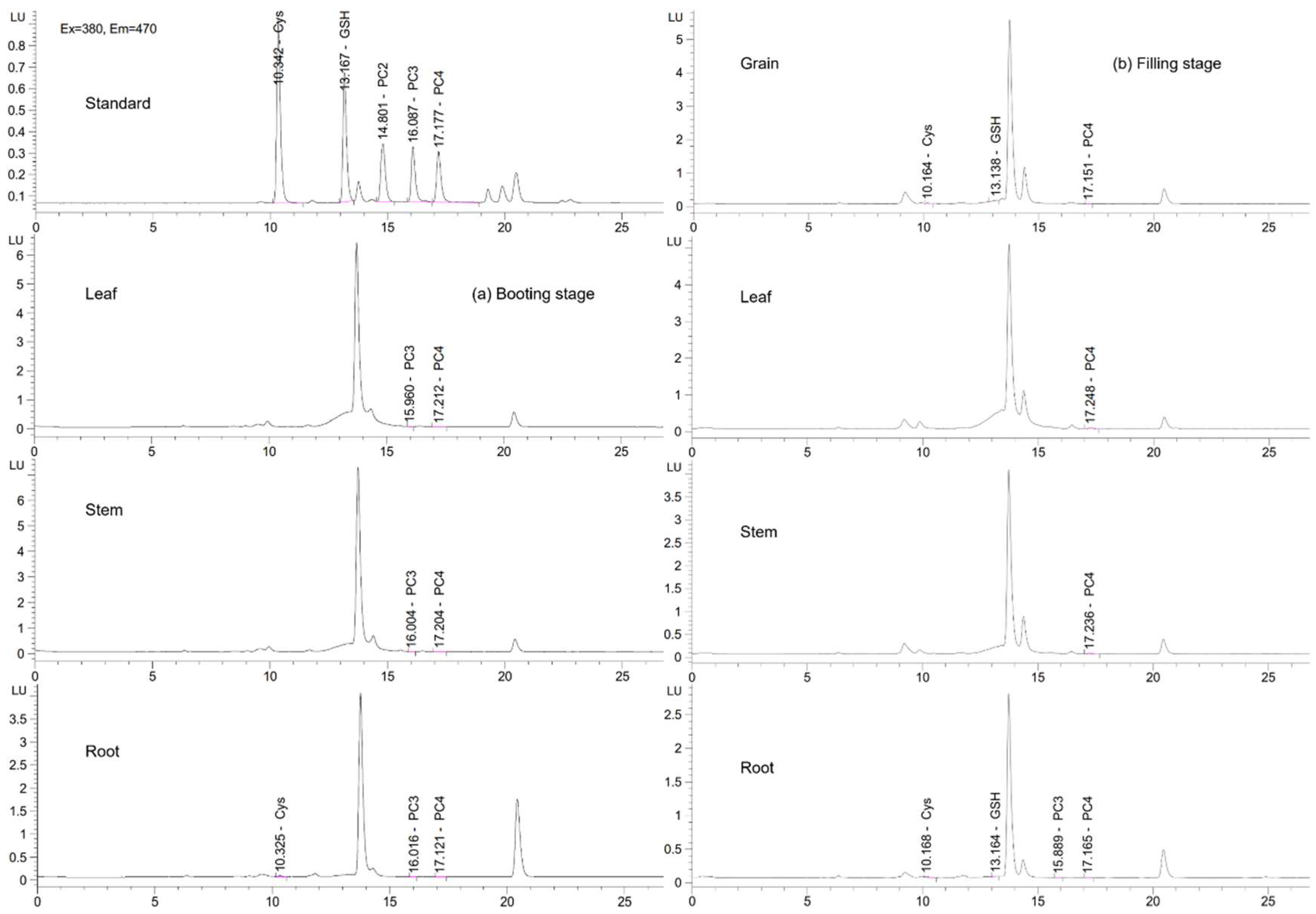
3.4. Total S and Organic S Compounds in Rice Plant Tissues
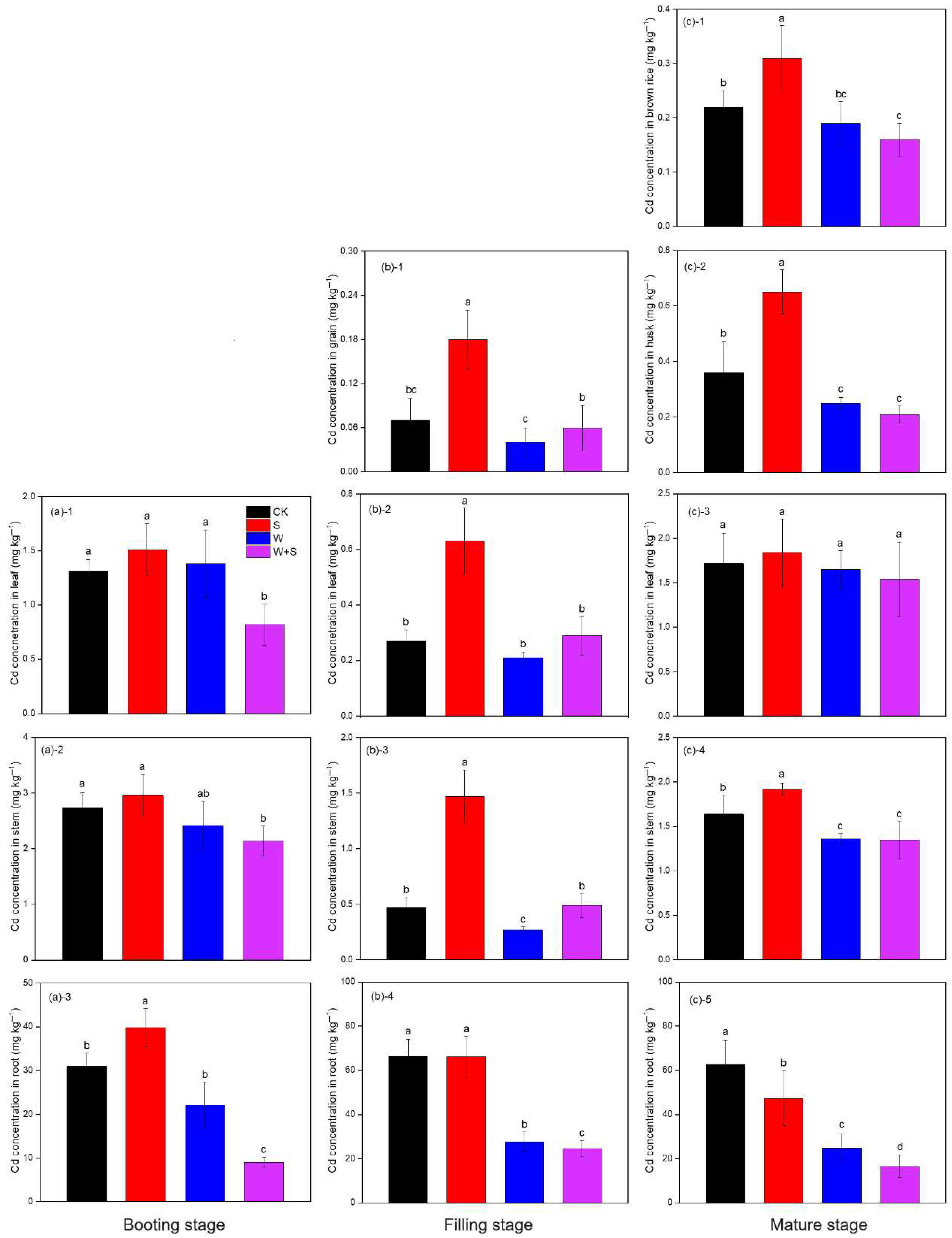
3.5. Cd Concentration in Rice Plant Tissues
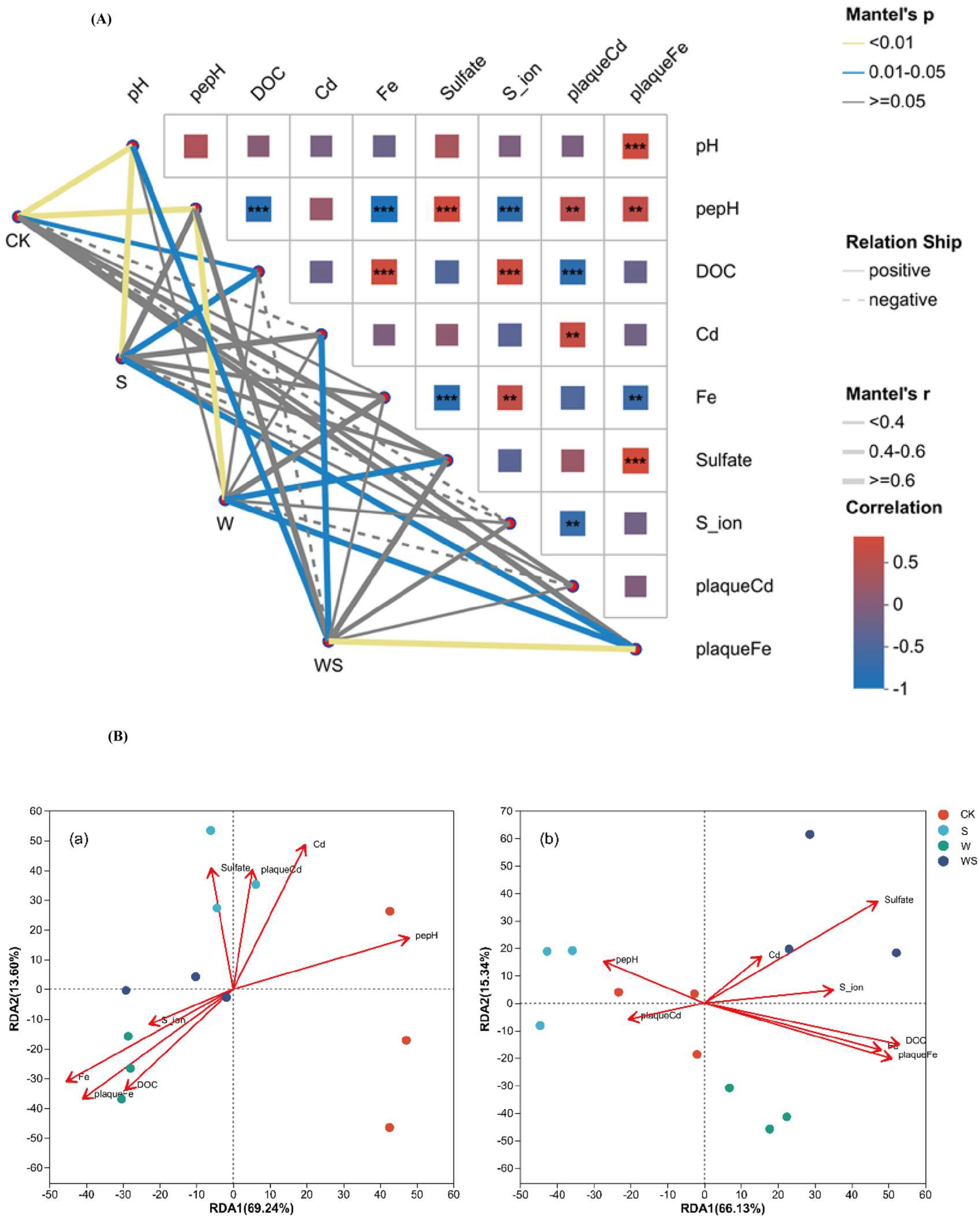
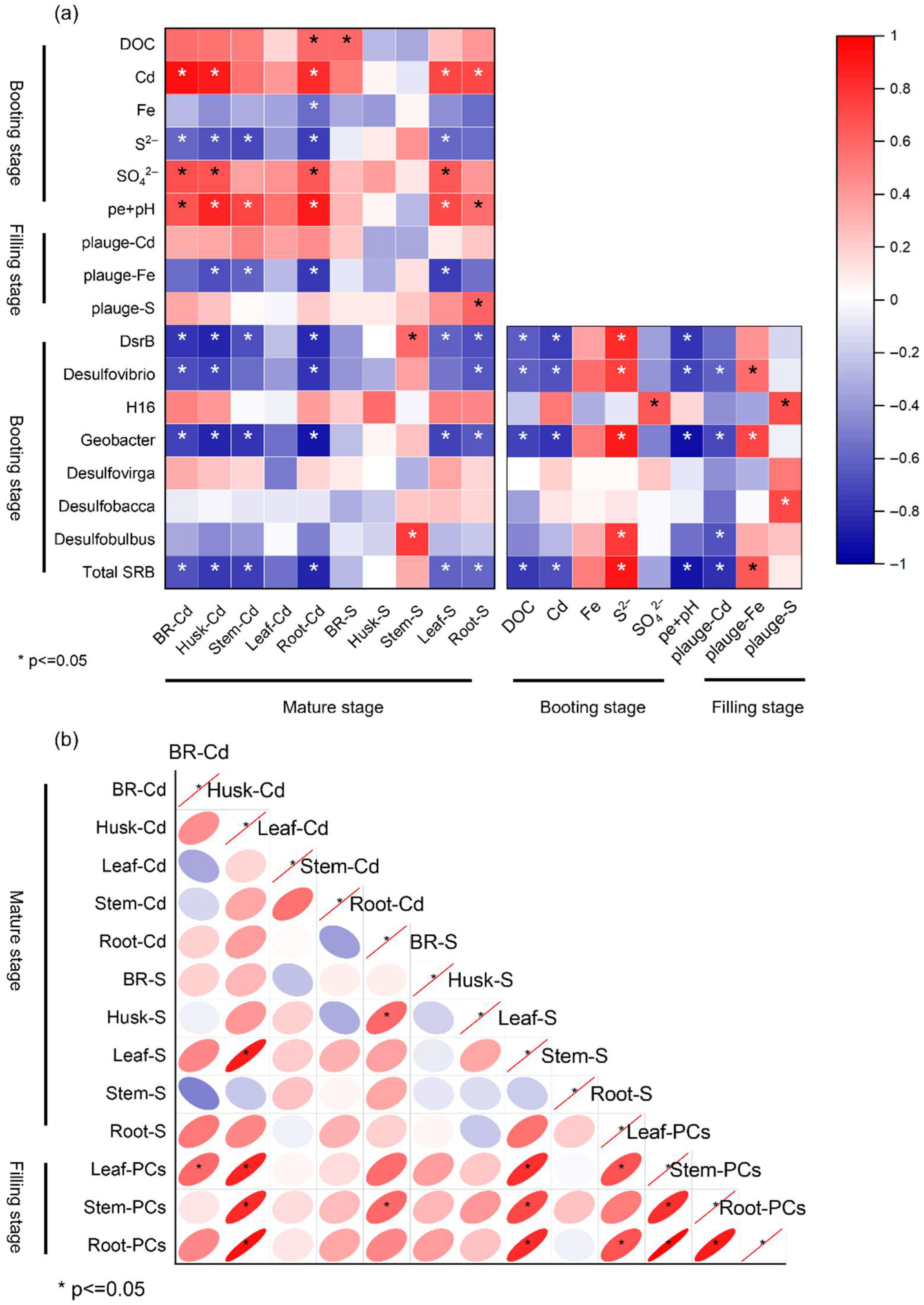
3.6. Correlation Between Environmental Factors and Microbial Communities
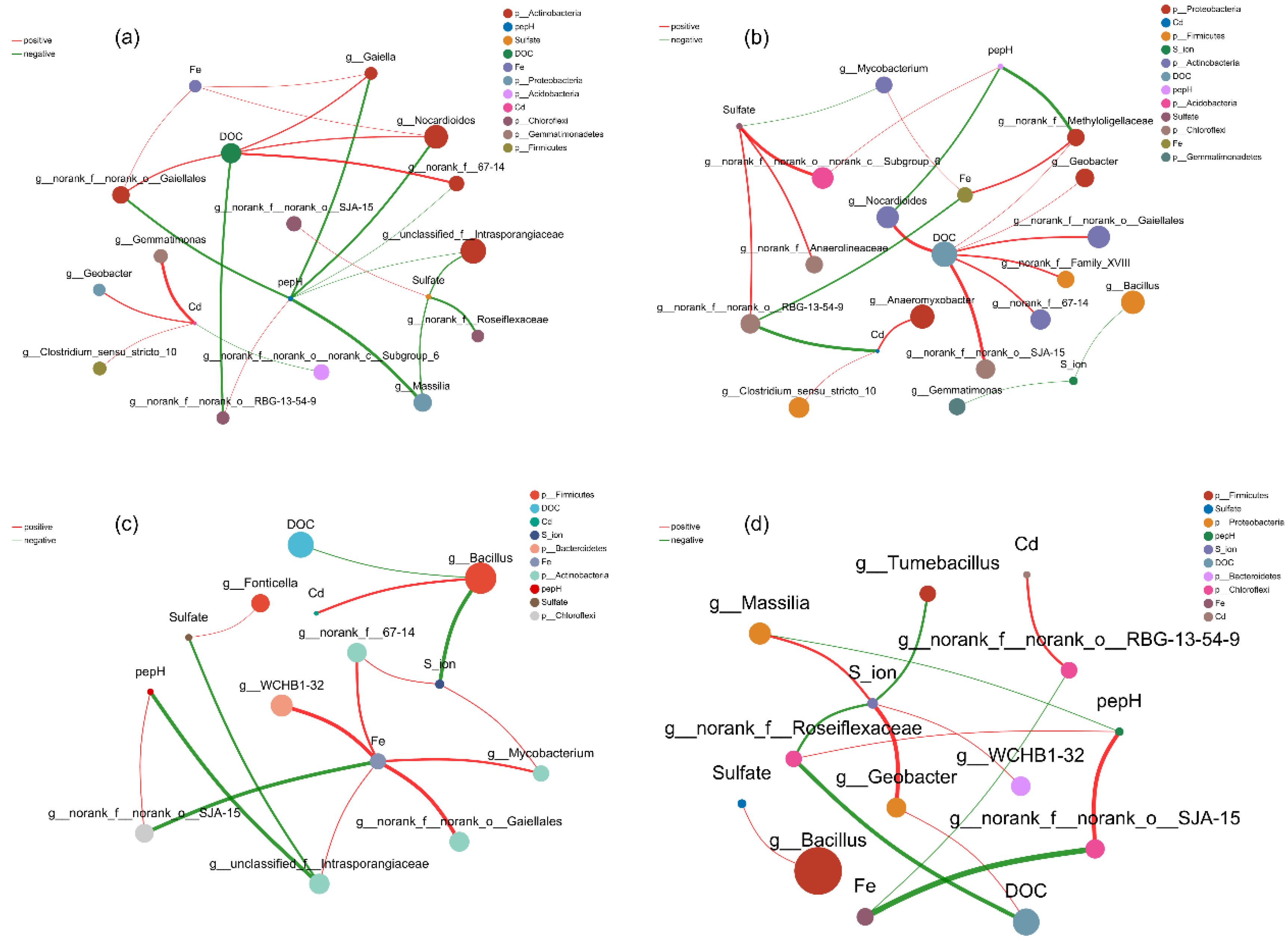
3.7. Co-Occurrence Network Between Microbial Genera and Environmental Factors
3.8. Correlation of Cd and Sulfur Accumulation in Rice Tissues with Soil and Plaque Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Sulfur on the Cd Availability Under Straw Amendment During Rice Growth
4.2. Effect of Sulfur on Iron Plaque of Rice Root Under Straw Amendment
4.3. Availability of Soil Cd Induced by Microbial Community and SRB Under Combined Application of Sulfur and Straw
4.4. Effect of Sulfate on Cd Accumulation in Rice Under Straw Amendment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Livera, J.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Hettiarachchi, G.M. Cadmium solubility in paddy soils: Effects of soil oxidation, metal sulfides and competitive ions. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meharg, A.A.; Norton, G.; Deacon, C.; Williams, P.; Adomako, E.E.; Price, A.; Zhu, Y.; Li, G.; Zhao, F.J.; McGrath, S.; et al. Variation in rice cadmium related to human exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5613–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.J.; Wang, P. Arsenic and cadmium accumulation in rice and mitigation strategies. Plant Soil. 2020, 446, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Liu, X.; Tian, G.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, C.; Kong, L. Cadmium (Cd) distribution and contamination in Chinese paddy soils on national scale. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17941–17952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Zheng, X.W.; Tao, L.X.; Gao, L.; Xiong, J. Aeration Increases Cadmium (Cd) Retention by Enhancing Iron Plaque Formation and Regulating Pectin Synthesis in the Roots of Rice (Oryza sativa) Seedlings. Rice 2019, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Hu, Z.; Ziadi, N.; Xia, X.; Wu, C. Excessive sulfur supply reduces cadmium accumulation in brown rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Qin, M.; Lin, X.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, M. Sulfur supply reduces cadmium uptake and translocation in rice grains (Oryza sativa L.) by enhancing iron plaque formation, cadmium chelation and vacuolar sequestration. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulda, B.; Voegelin, A.; Kretzschmar, R. Redox-controlled changes in cadmium solubility and solid-phase speciation in a paddy soil as affected by reducible sulfate and copper. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 12775–12783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.X.; Hu, Z.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.L.; Zhang, X.R.; Li, M. Sulfur controlled cadmium dissolution in pore water of cadmium contaminated soil as affected by DOC under waterlogging. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.N.; Camara, A.Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Guo, T.L.; Zhu, L.N.; Li, H.F. Cadmium dynamics in soil pore water and uptake by rice: Influences of soil-applied selenite with different water managements. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ok, Y.S.; Usman, A.R.A.; Lee, S.S. Effects of rapeseed residue on lead and cadmium availability and uptake by rice plants in heavy metal contaminated paddy soil. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Gu, C.; Tao, T.; Chen, G.; Shan, Y. Straw incorporation increases solubility and uptake of cadmium by rice plants. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 2013, 63, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ding, X.D.; Khan, S.; Brusseau, M.; Khan, A.; Nawab, J. The influence of various organic amendments on the bioavailability and plant uptake of cadmium presents in mine-degraded soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.X.; Su, L.L.; Li, S.Y.; Wang, P.F.; Li, D.D.; Ye, X.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.P.; Wang, C. The characteriazatioin of dissolved organic matter extracted from different sources and their influence on Cadmium uptake by Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 1856–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wan, Y.A.; Camara, A.Y.; Li, H.F. Effects of the addition and aging of humic acid-based amendments on the solubility of Cd in soil solution and its accumulation in rice. Chemosphere 2018, 196, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Zhu, W.; Yang, W.T.; Gu, J.F.; Gao, Z.X.; Chen, L.W.; Du, W.Q.; Zhang, P.; Liao, B.H. Cadmium uptake, accumulation, and remobilization in iron plaque and rice tissues at different growth stages. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 152, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Kopittke, P.M.; Zhao, F.J. Cadmium contamination in agricultural soils of China and the impact on food safety. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.L.; Li, F.B.; Cao, W.H.; Yang, Z.; Hu, M.; Sun, W.M. Cadmium solubility in paddy soil amended with organic matter, sulfate, and iron oxide in alternative watering conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 378, 120672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.J.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Yang, X.S.; Mu, J.; Xie, Z.J.; Li, S.Y.; Wu, G.M.; Hu, Z.Y. Effects of sulfur application on cadmium accumulation in brown rice under wheat-rice rotation. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashem, M.A.; Singh, B.R. Metal availability in contaminated soils: I. Effects of flooding and organic matter on changes in Eh, pH and solubility of Cd, Ni and Zn. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2001, 61, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Seshadri, B.; Bolan, N.; Saint, C.P.; Kirkham, M.B.; Chowdhury, S.; Yamaguchi, N.; Lee, D.Y.; Li, G.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; et al. Root Iron Plaque on Wetland Plants as a Dynamic Pool of Nutrients and Contaminants. In Advance in Agronomy; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 1–96. [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Pugalenthi, V. A comparative study of the determination of sulphide in tannery waste water by ion selective electrode (ISE) and iodimetry. Water Res. 2000, 34, 4201–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.J.; Yang, J.S.; Wang, X.P.; Jin, W.H.; Yao, R.J.; Yu, S.P. Effects of fertilization on soil organic carbon and distribution of soc in aggregates in tidal flat polders. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2015, 52, 818–827. [Google Scholar]
- Katyal, J.C.; Sharma, B.D. DTPA-extractable and total Zn, Cu, Mn, and Fe in Indian soils and their association with some soil properties. Geoderma 1991, 49, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, J.; Wanman, P. Examination of ester sulfates in Podzolic and Regosolic soils using an immobilized arylsulfatase reactor. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1996, 23, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.X.; Hu, Z.Y.; Wang, G.D.; Xia, X. Effect of elemental sulfur supply on cadmium uptake into rice seedlings when cultivated in low and excess cadmium soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan. 2010, 41, 990–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.H.; Tang, S.R.; Jia, Y.; Guo, J.K.; Ding, Y.; Song, Z.G.; Zhao, Y. Determination and characterization of cysteine, glutathione and phytochelatins (PC2–6) in Lolium perenne L. exposed to Cd stress under ambient and elevated carbon dioxide using HPLC with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 1717–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.Y.; Xu, W.; Li, J.Y.; Yu, Z.Y.; Zeng, Q.C.; Tan, W.F.; Mi, W.T. Short-term effect of manure and straw application on bacterial and fungal community compositions and abundances in an acidic paddy soil. J. Soil Sediment. 2021, 21, 3057–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, E.W.; Lindsay, W.L. The role of pyrite in controlling metal ion activities in highly reduced soils. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 3609–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, S.B.; Wang, M.; Lei, X.Q.; Zheng, H.; Sun, X.Y.; Wang, L.F.; Han, Y. Redistribution of iron oxides in aggregates induced by pe + pH variation alters Cd availability in paddy soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 142–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillan-Medrano, J.; Jurinak, J.J. The chemistry of lead and cadmium in soil: Solid phase formation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1975, 39, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Li, S.; Wang, G.; Yang, X.; Tao, M.; Qiu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, L.; Hu, Z. Application of wheat straw-derived amendments combined with sulfate increases soil microbial diversity, reduces soil cadmium mobility and cadmium accumulation in rice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 303, 118916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.H.; Ke, X.L.; Tao, M.M.; Li, Y.F.; Hu, Z.Y. Effect of organic materials and sulfate addition on cadmium bioavailability and accumulation of rice in cadmium sulfide nanoparticles- and cadmium chloride-treated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 494, 138571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.W.; Xue, Z.L.; Li, B.; Qu, L.Y.; Yan, L.Z.; Yang, L.Z.; Yin, K.; Jabrane, J.; Shao, P.H.; Zeng, Z.B.; et al. High-performance spent coffee grounds-based 3D microporous biochar for the efficient capture of Cd2+ via a multi-pathway mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 485, 149537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Ke, X.; Ma, J.; Liu, L.; Qiu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Liu, F. Dissolved organic matter (DOM)–Driven variations of cadmium mobility and bioavailability in waterlogged paddy soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 492, 138065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.J.; Song, K.; Shi, L.Z.; Duan, D.C.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.F.; Qin, Q.; Xue, Y. Influence of elemental sulfur on cadmium bioavailability, microbial community in paddy soil and Cd accumulation in rice plants. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.R.; Ren, J.Y.; Sun, K.; Zhang, W.; He, W.; Dai, C.C. Sulfate-reducing bacteria block cadmium and lead uptake in rice by regulating sulfur metabolism. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2025, 136, lxaf022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Ke, X.L.; Qiu, Y.H.; Tao, M.M.; Li, S.Y.; Yang, X.S.; Hu, Z.Y. Effects of wheat straw and sulfate application at different levels on the uptake and accumulation of cadmium in brown rice under different cadmium stress. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2025, 12, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Yu, G.; Sun, F.; Usman, M.; Goodman, B.A.; Ran, W.; Shen, Q. Iron minerals inhibit the growth of Pseudomonas brassicacearum J12 via a freeradical mechanism: Implications for soil carbon storage. Biogeoscienes 2019, 16, 1433–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kölbl, A.; Marschner, P.; Mosley, L.; Fitzpatrick, R.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Alteration of organic matter during remediation of acid sulfate soils. Geoderma 2018, 332, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, A.F.; Salgado, L.; Galicia, L.; González, I. Predominance-zone diagrams of Fe (III) and Fe (II) sulfate complexes in acidic media. Voltammetric and spectrophotometric studies. Talanta 1995, 42, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, D.; Beveridge, T.J. Microbial sulfate reduction within sulfidic mine tailings: Formation of diagenetic Fe sulfides. Geomicrobiol. J. 1997, 14, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.A.; Voegelin, A.; Kretzschmar, R. Multi-metal contaminant dynamics in temporarily flooded soil under sulfate limitation. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 5513–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, L.L.; Fauque, G.D. Chapter 2 biochemistry, physiology and biotechnology of sulfate-reducing bacteria. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 68, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- GB2762-2012; Maximum Permitted Levels of Contaminants in Food. Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Xu, C.; Qin, L.; Li, Y.; Zu, Y.Q.; Wang, J.X. Effects of different sulfur compounds on the distribution characteristics of subcellular lead content in Arabis alpina L. var. parviflora Franch under lead stress. Plants 2023, 12, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.X.; Wang, J.N.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.Q.; E, Y.; Meng, J.; He, T.Y. Combined application of biochar and sulfur alleviates cadmium toxicity in rice by affecting root gene expression and iron plaque accumulation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 266, 115596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.N.; Yang, W.T.; Chen, Y.L.; Yang, L.Y.; Zhou, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Z.J.; Wu, P.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M. Exploring the mechanism of Cd uptake and translocation in rice: Future perspectives of rice safety. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 165369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Wang, G.X.; Yang, X.S.; Ke, X.L.; Huang, L.J.; Li, Y.F.; Qiu, Y.H.; Tao, M.M.; Hu, Z.Y. Effects of sulfur supply on cadmium transfer and concentration in rice at different growth stages exposed to sulfur-deficient but highly cadmium-contaminated soil. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2023, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, H.; Wu, D.; Li, C.L.; Hou, M.M. Advances in molecular mechanisms underlying cadmium uptake and translocation in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1003953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.X.; Du, G.H.; Chen, D.; Shi, G.L.; Rao, W.; Lin, X.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, S.L.; Wang, D.C. Effect of elemental sulfur and gypsum application on the bioavailability and redistribution of cadmium during rice growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1460–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Wang, H.; Yu, L.F.; Li, C.F.; Ding, L.; Shao, G.S. Interactions of Fe, Mn, Zn, and Cd in soil–rice systems: Implications for reducing Cd accumulation in rice. Toxics 2025, 13, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| CK | S | W | WS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DsrB gene | 5.64 ± 0.89 c | 3.32 ± 1.17 d | 7.93 ± 1.46 b | 12.65 ± 2.21 a |
| Geobacter | 1.47 ± 0.08 b | 1.07 ± 0.10 c | 2.33 ± 0.31a | 2.69 ± 0.29 a |
| Desulfovibrio | 0.42 ± 0.06 b | 0.25 ± 0.11 c | 0.70 ± 0.24 a | 0.87 ± 0.35 a |
| H16 ‡ | 0.07 ± 0.01 c | 0.31 ± 0.00 a | 0.13 ± 0.04 b | 0.20 ± 0.09 b |
| Desulfovirga | 0.13 ± 0.08 a | 0.10 ± 0.05 a | 0.15 ± 0.07 a | 0.17 ± 0.04 a |
| Desulfobacca | 0.05 ± 0.01 b | 0.09 ± 0.04 a | 0.08 ± 0.04 a | 0.09 ± 0.05 a |
| Desulfobulbus | 0.01 ± 0.01 c | 0.06 ± 0.02 b | 0.08 ± 0.04 b | 0.22 ± 0.15 a |
| Total SRB | 2.25 ± 0.14 c | 2.05 ± 0.29 c | 3.60 ± 0.39 b | 4.38 ± 0.74 a |
| CK | S | W | WS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Booting stage | ||||
| Leaf | 2286.1 ± 137.1 b | 2487.5 ± 124.9 a | 2270.2 ± 164.5 b | 2553.2 ± 78.9 a |
| Stem | 1537.2 ± 88.5 a | 1500.5 ± 151.2 a | 1581.4 ± 83.2 a | 1550.3 ± 102.1 a |
| Root | 648.6 ± 48.8 b | 731.9 ± 46.3 a | 685.2 ± 64.8 a | 670.2 ± 42.2 ab |
| Filling stage | ||||
| Grain | 684.32 ± 40.9 c | 996.6 ± 88.6 a | 584.4 ± 58.8 d | 792.2 ± 46.3 b |
| Leaf | 1058.3 ± 82.9 bc | 2095.1 ± 93.5 a | 935.3 ± 61.9 c | 1183.3 ± 103.1 b |
| Stem | 823.13 ± 51.7 b | 1243.4 ± 133.6 a | 615.6 ± 38.6 c | 759.7 ± 66.1 b |
| Root | 933.69 ± 35.2 a | 1004.2 ± 86.1 a | 927.6 ± 54.8 a | 960.9 ± 81.4 a |
| Mature stage | ||||
| Brown rice | 851.1 ± 72.4 b | 936.1 ± 68.9 a | 824.2 ± 72.4 b | 832.5 ± 46.3 b |
| Husk | 471.1 ± 46.3 b | 526.1 ± 62.7 a | 412.7 ± 45.4 b | 587.3 ± 76.2 a |
| Leaf | 1201.8 ± 200.5 b | 1605.2 ± 197.7 a | 1019.3 ± 173.7 bc | 1062.8 ± 78.6 bc |
| Stem | 781.1 ± 22.9 b | 848.2 ± 37.6 a | 745.9 ± 42.5 b | 726.3 ± 35.7 b |
| Root | 863.5 ± 45.2 ab | 925.6 ± 40.3 a | 959.9 ± 78.6 a | 857.9 ± 27.8 b |
| Booting Stage | Filling Stage | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cys | GSH | PCs | Cys | GSH | PCs | ||
| Grain | CK | N | N | N | 67.6 ± 11.2 a | 75.4 ± 10.0 b | 79.26 ± 5.4 b |
| S | N | N | N | 66.0 ± 9.5 a | 79.2 ± 17.2 b | 92.42 ± 4.3 a | |
| W | N | N | N | 66.3 ± 6.7 a | 95.3 ± 8.3 a | 81.11 ± 8.7 ab | |
| WS | N | N | N | 62.3 ± 8.2 a | 68.3 ± 7.5 b | 75.48 ± 6.5 b | |
| Leaf | CK | Nd | Nd | 61.3 ± 9.7 a | Nd | Nd | 81.74 ± 18.2 b |
| S | Nd | Nd | 76.2 ± 8.4 a | Nd | Nd | 165.1 ± 31.5 a | |
| W | Nd | Nd | 61.3 ± 12.5 a | Nd | Nd | 79.7 ± 8.9 b | |
| WS | Nd | Nd | 63.2 ± 3.9 a | Nd | Nd | 84.5 ± 7.3 b | |
| Stem | CK | Nd | Nd | 52.1 ± 9.2 a | Nd | Nd | 81.7 ± 6.5 a |
| S | Nd | Nd | 58.6 ± 6.3 a | Nd | Nd | 86.4 ± 17.1 a | |
| W | Nd | Nd | 59.5 ± 11.5 a | Nd | Nd | 77.5 ± 5.0 a | |
| WS | Nd | Nd | 61.2 ± 7.7 a | Nd | Nd | 82.8 ± 10.6 a | |
| Root | CK | 70.1 ± 16.2 a | Nd | 51.1 ± 5.4 a | 65.6 ± 5.1 b | 67.1 ± 6.4 b | 138.9 ± 16.2 a |
| S | 67.2 ± 11.1 a | Nd | 54.2 ± 9.3 a | 78.1 ± 7.2 a | 76.5 ± 3.3 a | 147.4 ± 21.5 a | |
| W | 76.4 ± 9.6 a | Nd | 59.2 ± 5.7 a | 62.9 ± 5.9 b | 65.1 ± 5.2 b | 135.0 ± 22.4 a | |
| WS | 75.4 ± 7.4 a | Nd | 57.6 ± 11.3 a | 64.6 ± 13.3 ab | 63.4 ± 4.1 b | 136.9 ± 12.7 a | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, K. Sulfur Enhances Rice Cadmium Accumulation in Organic Deficient Soil: The Significance of Incorporation with Straw. Plants 2025, 14, 3519. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14223519
Wang G, Zhang L, Wang Y, Jiang X, Wang K. Sulfur Enhances Rice Cadmium Accumulation in Organic Deficient Soil: The Significance of Incorporation with Straw. Plants. 2025; 14(22):3519. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14223519
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Guoxi, Lan Zhang, Yan Wang, Xia Jiang, and Kun Wang. 2025. "Sulfur Enhances Rice Cadmium Accumulation in Organic Deficient Soil: The Significance of Incorporation with Straw" Plants 14, no. 22: 3519. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14223519
APA StyleWang, G., Zhang, L., Wang, Y., Jiang, X., & Wang, K. (2025). Sulfur Enhances Rice Cadmium Accumulation in Organic Deficient Soil: The Significance of Incorporation with Straw. Plants, 14(22), 3519. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14223519






