Chromatin-Associated Pea Apyrase psNTP9 Function as a DNA-Binding Regulatory Protein in Yeast and Arabidopsis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Targeting of PS to Plant Nuclei
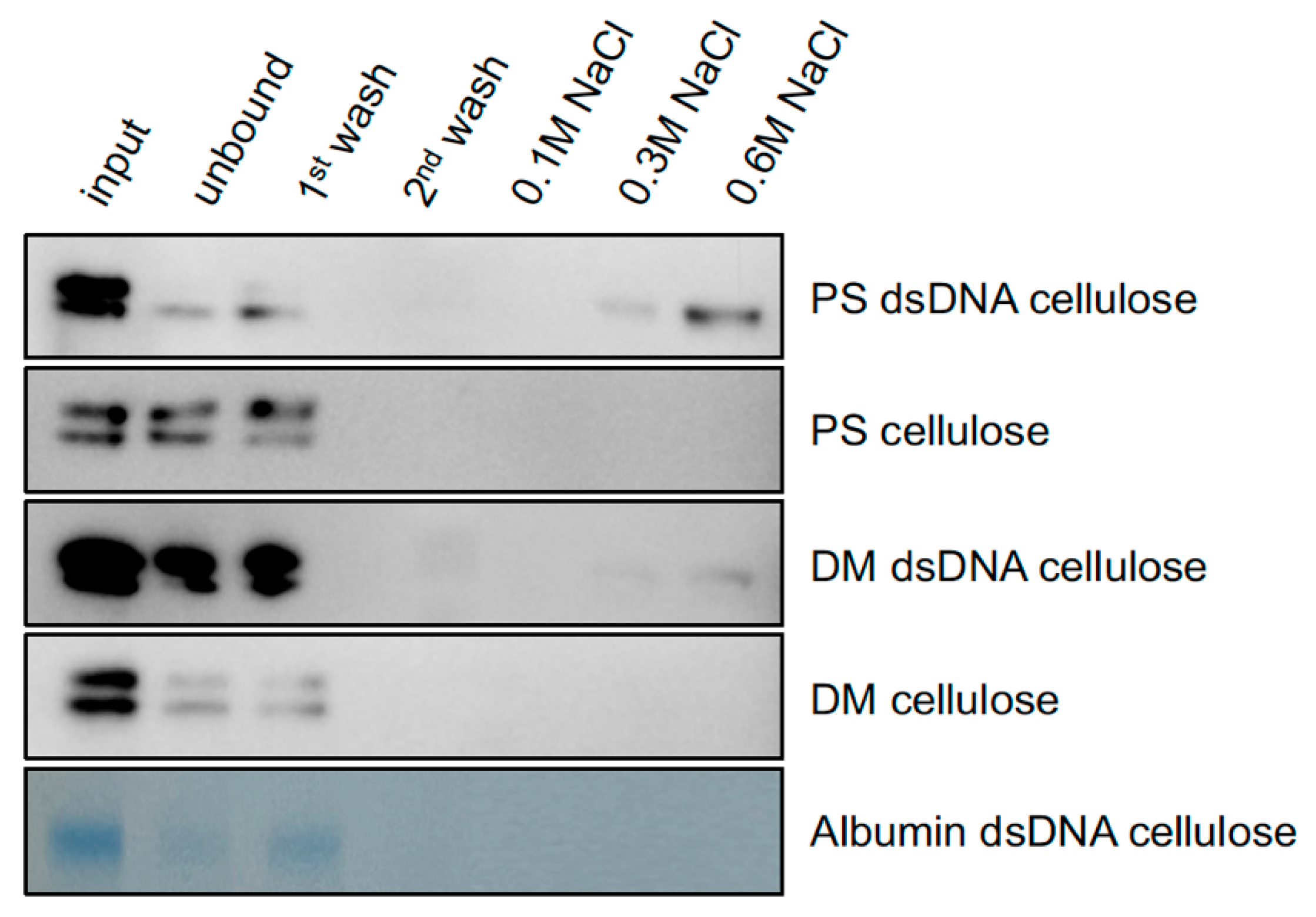
2.2. PS and DM Have Different Binding Affinities for Heterologous dsDNA
2.3. Identification of PS and DM Binding Sites in the Promoters of Arabidopsis Genes and Integration with Gene Expression Data
2.4. Identification of Enriched Transcription Factor Binding Site Motifs in PS and DM Binding Sites of Arabidopsis Genes
2.5. Functional Characterization of PS and DM Binding Site Motifs in Yeast and Arabidopsis Genes Using EMSA
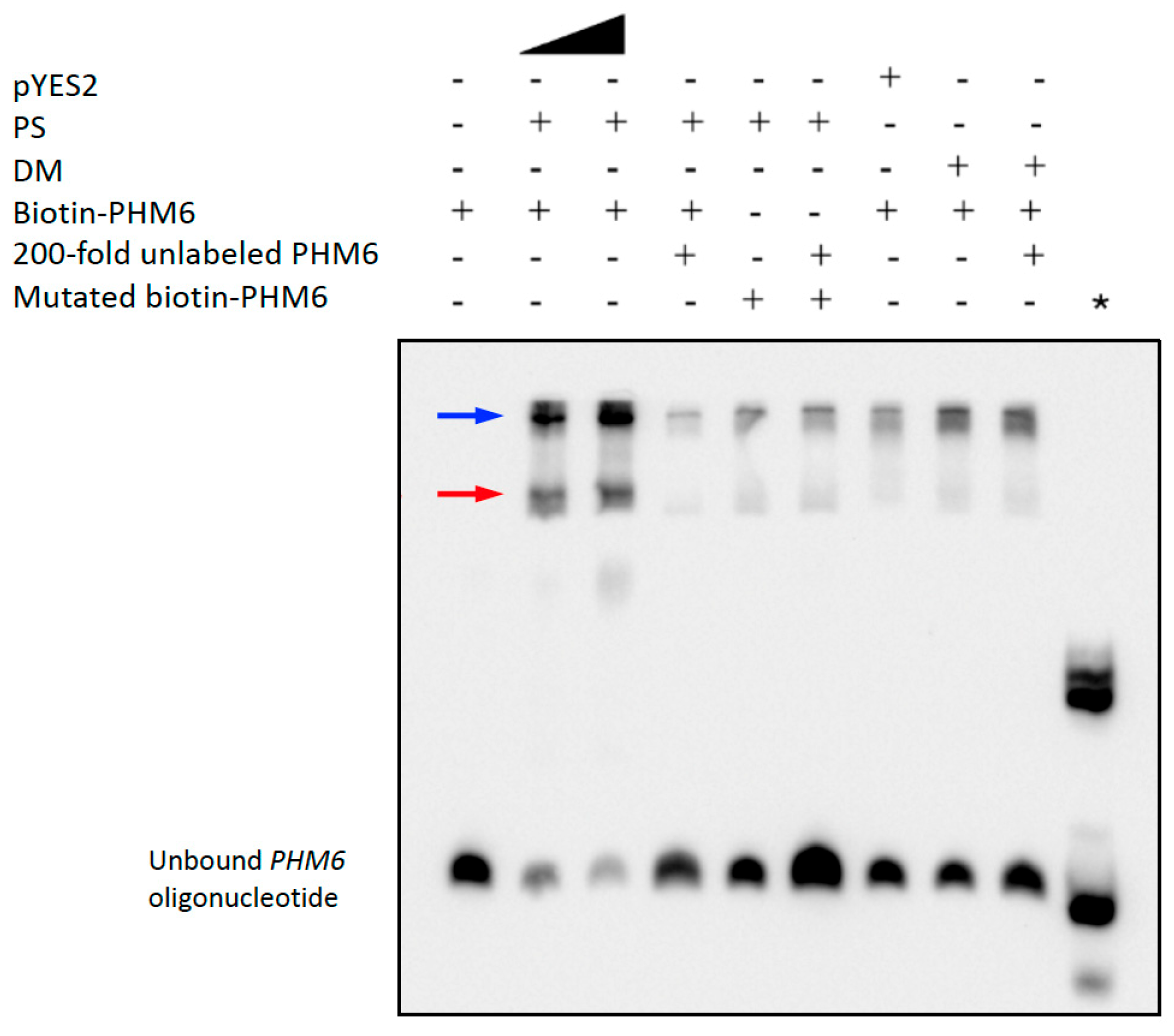
2.5.1. A PS Binding Site in the PHM6 Promoter Contains an E-Box Motif
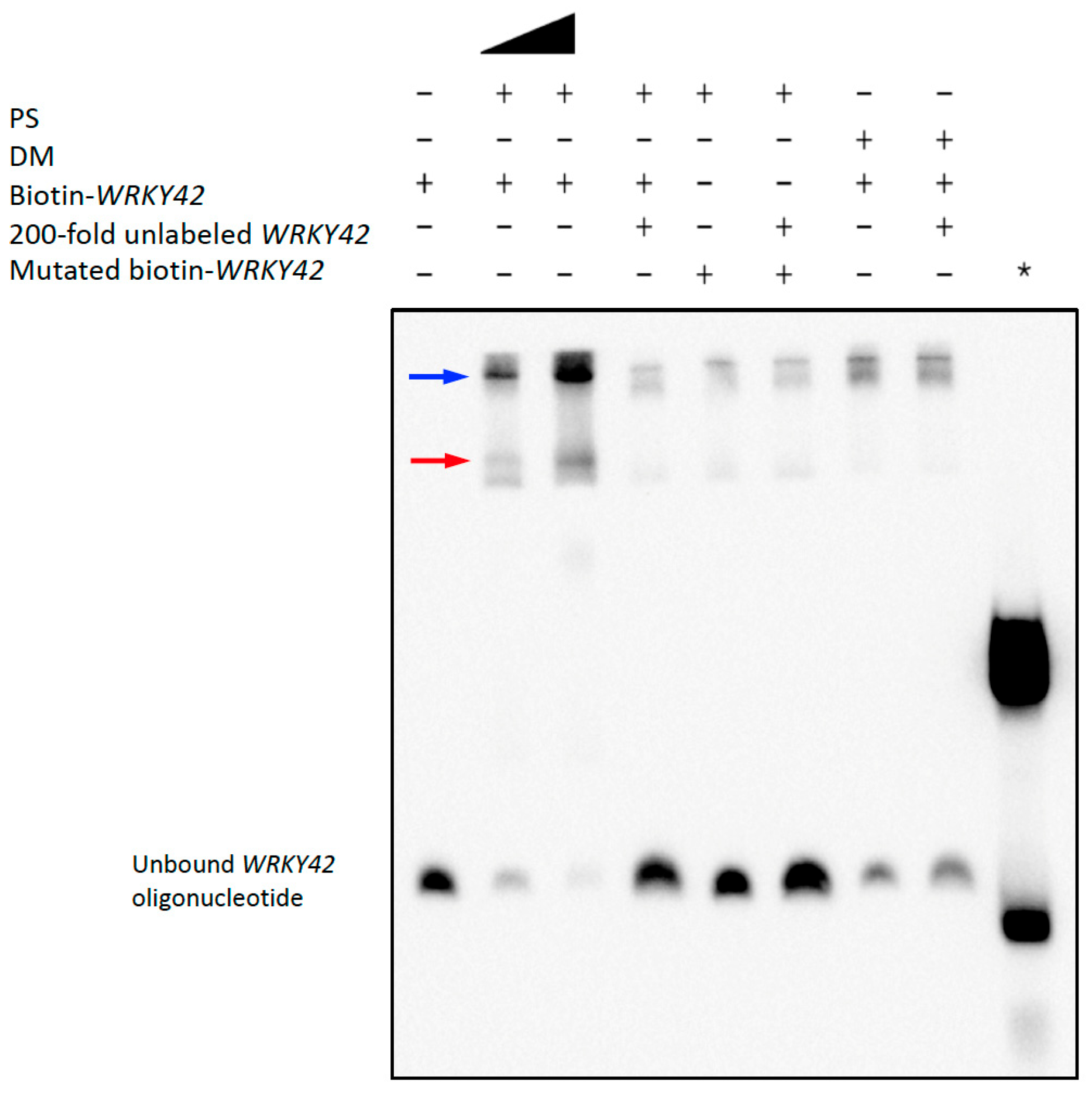
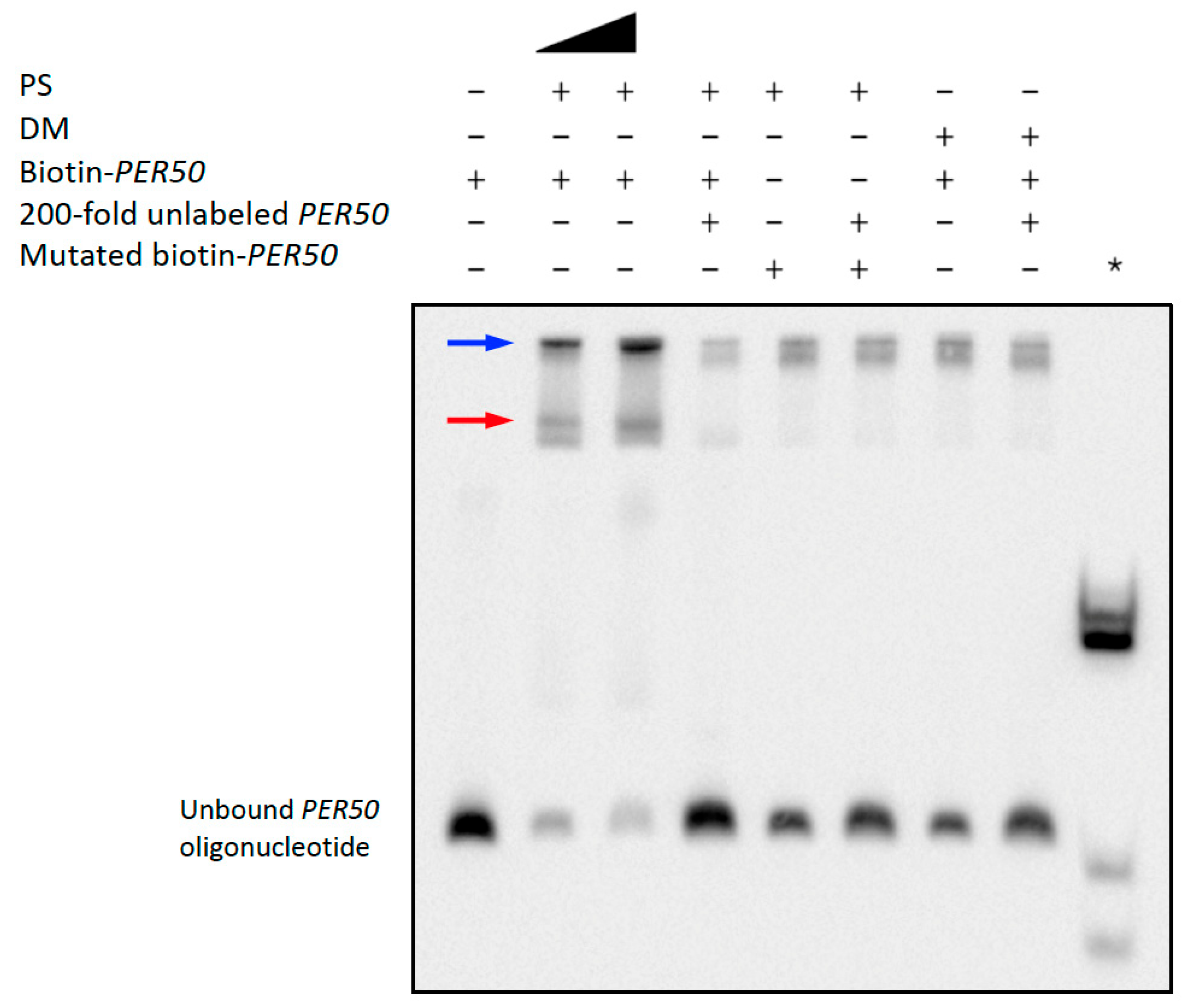
2.5.2. PS Binds to Arabidopsis WRKY42 and PER50 Promoter Sequences with Enriched TF Motifs
2.6. Co-Immunoprecipitation Analyses of PS- and DM-Interacting Proteins in Yeast and Arabidopsis
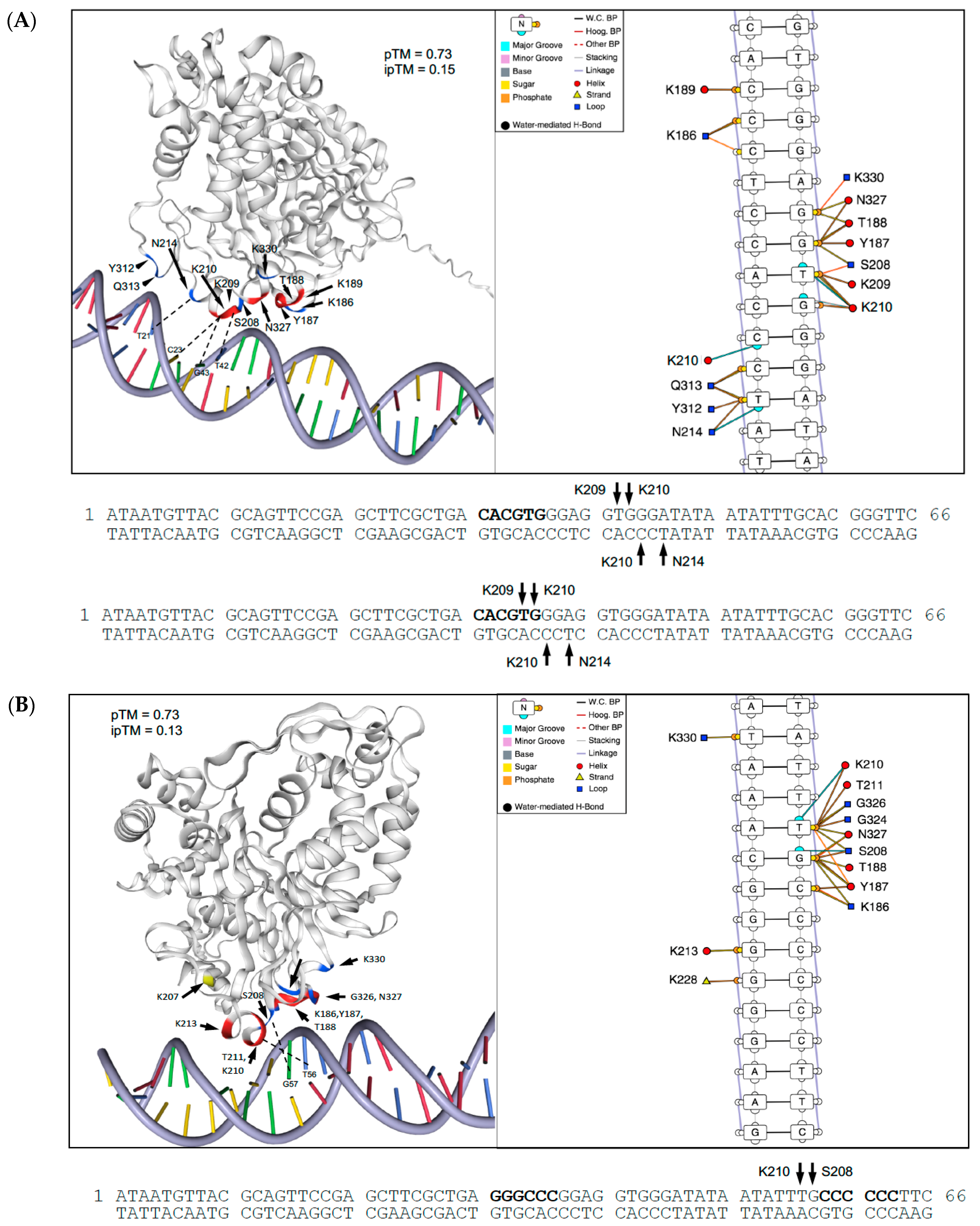
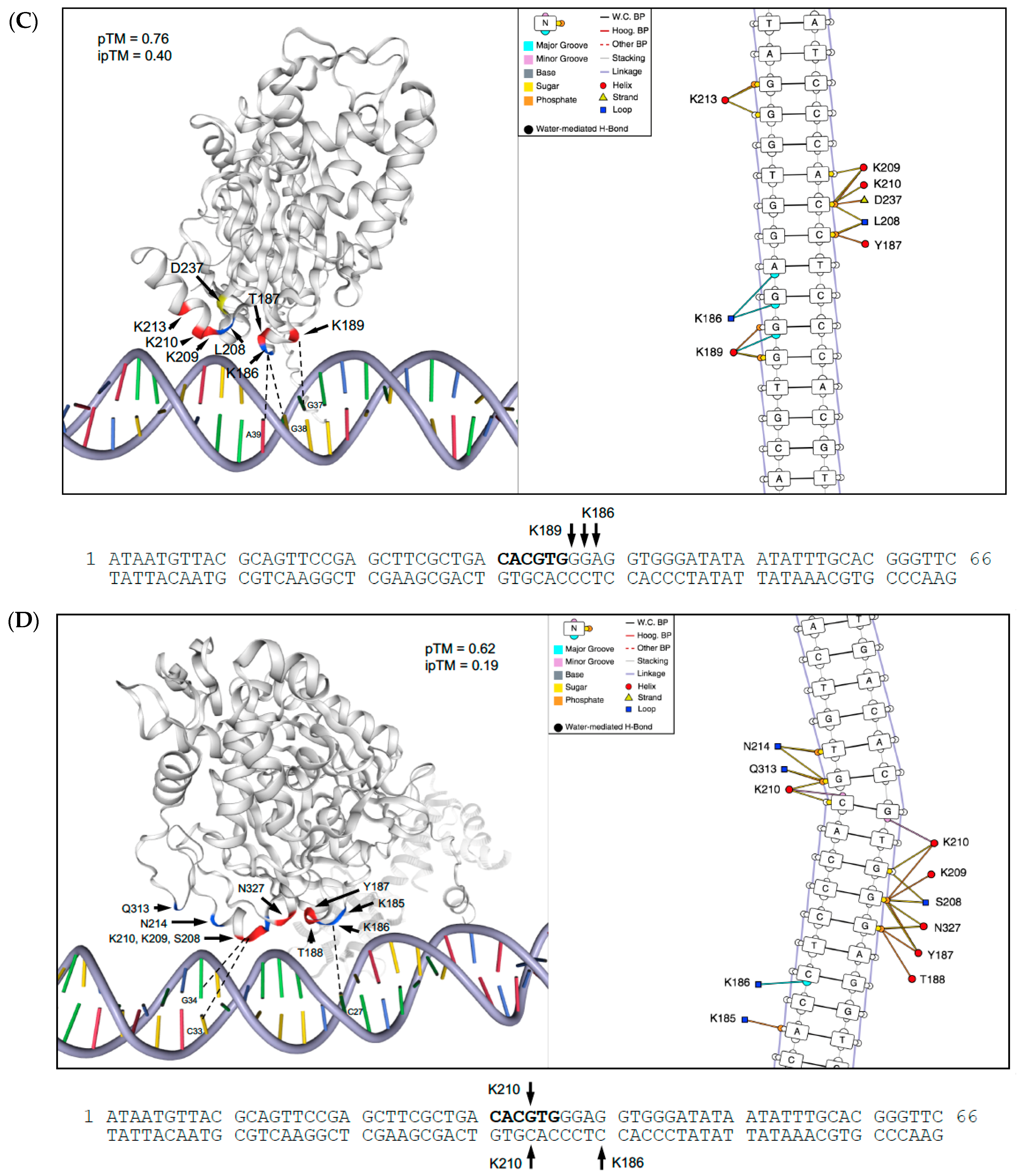
2.7. Structural Basis for Differences in DNA-Binding by PS and DM Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
5.2. Assay for Differential Binding of PS and DM to dsDNA-Cellulose
5.3. ChIP-Seq Analyses
5.3.1. Construction and Verification of 4Myc-Tagged PS and DM Overexpression Lines
5.3.2. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and Sequencing Library Preparation
5.3.3. ChIP-Seq Data Processing, Peak Calling, and Functional Annotation
5.3.4. PS and DM Binding Site Motif Enrichment Analyses
5.4. Functional Characterization of PS and DM Binding Sites Using Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assays
5.4.1. Oligonucleotide Probe Preparation
5.4.2. EMSA Procedure
5.5. Purification of PS and DM Proteins
5.6. Co-IP for Yeast and Arabidopsis
5.6.1. Yeast Protein Preparation
5.6.2. Arabidopsis Protein Preparation
5.6.3. Co-Immunoprecipitation
5.6.4. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
5.6.5. Identification of Potential PS and DM Co-IPs
5.7. Gene Expression Analyses
5.8. Structural Studies of PS and DM
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NTPDase | nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase |
| eATP | extracellular ATP |
| CaM | calmodulin |
| PS | pea apyrase psNTP9 |
| DM | “double mutation” version of PS |
| DEG | differentially expressed genes |
| TF | transcription factor |
| EMSA | electrophoretic mobility shift assay |
| NLS_BP | bipartite nuclear localization signal |
| PCBD1 | potential calmodulin-binding domain 1 |
References
- Knowles, A.F. The GDA1_CD39 Superfamily: NTPDases with Diverse Functions. Purinergic Signal. 2011, 7, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, G.B.; Morgan, R.O.; Fernandez, M.P.; Salmi, M.L.; Roux, S.J. Breakthroughs Spotlighting Roles for Extracellular Nucleotides and Apyrases in Stress Responses ands Growth and Development. Plant Sci. 2014, 225, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, G.; Brown, K.A.; Tripathy, M.K.; Roux, S.J. Recent Advances Clarifying the Structure and Function of Plant Apyrases (Nucleoside Triphosphate Diphosphohydrolases). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, G.; Tripathy, M.K.; Roux, S.J. Growth Regulation by Apyrases: Insights from Altering Their Expression Level in Different Organisms. Plant Physiol. 2024, 194, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Clark, G.; Lundy, S.; Lim, M.; Arnold, D.; Chan, J.; Tang, W.; Muday, G.K.; Gardner, G.; et al. Role for Apyrases in Polar Auxin Transport in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 1985–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Steinebrunner, I.; Sun, Y.; Butterfield, T.; Torres, J.; Arnold, D.; Gonzalez, A.; Jacob, F.; Reichler, S.; Roux, S.J. Apyrases (Nucleoside Triphosphate-Diphosphohydrolases) Play a Key Role in Growth Control in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2007, 144, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, G.; Darwin, C.; Mehta, V.; Jackobs, F.; Perry, T.; Hougaard, K.; Roux, S. Effects of Chemical Inhibitors and Apyrase Enzyme Further Document a Role for Apyrases and Extracellular ATP in the Opening and Closing of Stomates in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal. Behav. 2013, 8, e26093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, T.-Y.; Lao, J.; Manalansan, B.; Loqué, D.; Roux, S.J.; Heazlewood, J.L. Biochemical Characterization of Arabidopsis APYRASE Family Reveals Their Roles in Regulating Endomembrane NDP/NMP Homoeostasis. Biochem. J. 2015, 472, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-R.; Datta, N.; Roux, S.J. Purification and Partial Characterization of a Calmodulin-Stimulated Nucleoside Triphosphatase from Pea Nuclei. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 10689–10694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, K.; Abe, S.; Yoneda, M.; Davies, E. Sub-Cellular Distribution and Isotypes of a 49-KDa Apyrase from Pisum sativum. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2002, 40, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerappa, R.; Slocum, R.D.; Siegenthaler, A.; Wang, J.; Clark, G.; Roux, S.J. Ectopic Expression of a Pea Apyrase Enhances Root System Architecture and Drought Survival in Arabidopsis and Soybean. Plant. Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabharwal, T.; Lu, Z.; Slocum, R.D.; Kang, S.; Wang, H.; Jiang, H.-W.; Veerappa, R.; Romanovicz, D.; Nam, J.C.; Birk, S.; et al. Constitutive Expression of a Pea Apyrase, PsNTP9, Increases Seed Yield in Field-Grown Soybean. Sci. Reports 2022, 12, 10870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.; Sun, Y.; Naus, K.; Lloyd, A.; Roux, S. Apyrase Functions in Plant Phosphate Nutrition and Mobilizes Phosphate from Extracellular ATP. Plant Physiol. 1999, 119, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathy, M.K.; Wang, H.; Slocum, R.D.; Jiang, H.-W.; Nam, J.-C.; Sabharwal, T.; Veerappa, R.; Brown, K.A.; Cai, X.; Allen Faull, P.; et al. Modified Pea Apyrase Has Altered Nuclear Functions and Enhances the Growth of Yeast and Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1584871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.L.; Song, C.J.; Roux, S.J. Regulation of a Recombinant Pea Nuclear Apyrase by Calmodulin and Casein Kinase II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gene Struct. Expr. 2000, 1494, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massalski, C.; Bloch, J.; Zebisch, M.; Steinebrunner, I. The Biochemical Properties of the Arabidopsis Ecto-Nucleoside Triphosphate Diphosphohydrolase AtAPY1 Contradict a Direct Role in Purinergic Signaling. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.-L.; Tong, C.-G.; Thomas, C.; Roux, S.J. Light-Modulated Abundance of an mRNA Encoding a Calmodulin-Regulated, Chromatin-Associated NTPase in Pea. Plant Mol. Biol. 1996, 30, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate Structure Prediction of Biomolecular Interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosugi, S.; Hasebe, M.; Matsumura, N.; Takashima, H.; Miyamoto-Sato, E.; Tomita, M.; Yanagawa, H. Six Classes of Nuclear Localization Signals Specific to Different Binding Grooves of Importinα. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Molina, L.; Mongrand, S.; McLachlin, D.T.; Chait, B.T.; Chua, N.H. ABI5 Acts Downstream of ABI3 to Execute an ABA-Dependent Growth Arrest during Germination. Plant J. 2002, 32, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Tohge, T.; Ivakov, A.; Mueller-Roeber, B.; Fernie, A.R.; Mutwil, M.; Schippers, J.H.M.; Persson, S. Salt-Related MYB1 Coordinates Abscisic Acid Biosynthesis and Signaling during Salt Stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 1027–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, B.; Reynaga-Peña, C.G.; Springer, P.S. The Lateral Organ Boundaries Gene Defines a Novel, Plant-Specific Gene Family. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Scheres, B.; Blilou, I. JACKDAW Controls Epidermal Patterning in the Arabidopsis Root Meristem through a Non-Cell-Autonomous Mechanism. Development 2010, 137, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhong, S.; Mo, X.; Liu, N.; Nezames, C.D.; Deng, X.W. HFR1 Sequesters PIF1 to Govern the Transcriptional Network Underlying Light-Initiated Seed Germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 3770–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Barron, C.; Schiefelbein, J.; Chen, J.G. Distinct Relationships between GLABRA2 and Single-Repeat R3 MYB Transcription Factors in the Regulation of Trichome and Root Hair Patterning in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2010, 185, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, O.; Cho, H.Y.; Kim, M.R.; Lee, H.; Lee, M.S.; Song, E.; Park, J.H.; Nam, K.H.; Chun, J.Y.; Kim, H.J.; et al. Induction of a Homeodomain–Leucine Zipper Gene by Auxin Is Inhibited by Cytokinin in Arabidopsis Roots. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 326, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aharoni, A.; Dixit, S.; Jetter, R.; Thoenes, E.; Van Arkel, G.; Pereira, A. The SHINE Clade of AP2 Domain Transcription Factors Activates Wax Biosynthesis, Alters Cuticle Properties, and Confers Drought Tolerance When Overexpressed in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 2463–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passardi, F.; Penel, C.; Dunand, C. Performing the Paradoxical: How Plant Peroxidases Modify the Cell Wall. Trends Plant Sci. 2004, 9, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.H.; Wu, J.; Yao, J.; Gallardo, I.F.; Dugger, J.W.; Webb, L.J.; Huang, J.; Salmi, M.L.; Song, J.; Clark, G.; et al. Apyrase Suppression Raises Extracellular ATP Levels and Induces Gene Expression and Cell Wall Changes Characteristic of Stress Responses. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 2054–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; MacHanick, P. Inferring Direct DNA Binding from ChIP-Seq. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellman, L.M.; Fried, M.G. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) for Detecting Protein–Nucleic Acid Interactions. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1849–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, S.; Mayer, A. Phosphate Homeostasis—A Vital Metabolic Equilibrium Maintained Through the INPHORS Signaling Pathway. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 539723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, H.M.; Cheng, S.; Olson, E.J.; Crone, M.; Maerkl, S.J. Perfect Adaptation Achieved by Transport Limitations Governs the Inorganic Phosphate Response in S. cerevisiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2212151120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulakovskaya, E.; Zvonarev, A.; Kulakovskaya, T. PHM6 and PHM7 Genes Are Essential for Phosphate Surplus in the Cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, V.; Kakkar, M.; Kumari, P.; Zinta, G.; Gahlaut, V.; Kumar, S. Multifaceted Roles of GRAS Transcription Factors in Growth and Stress Responses in Plants. iScience 2022, 25, 105026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.C.; Xue, Z.; Mélèse, T. The NSR1 Gene Encodes a Protein That Specifically Binds Nuclear Localization Sequences and Has Two RNA Recognition Motifs. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 113, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Liao, W. Calmodulin-Binding Transcription Factors: Roles in Plant Response to Abiotic Stresses. Plants 2025, 14, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, F.C.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.Q.; Wu, W.H.; Chen, Y.F. WRKY42 Modulates Phosphate Homeostasis through Regulating Phosphate Translocation and Acquisition in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2015, 167, 1579–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Shin, H.S.; Dewbre, G.R.; Harrison, M.J. Phosphate Transport in Arabidopsis: Pht1;1 and Pht1;4 Play a Major Role in Phosphate Acquisition from Both Low- and High-Phosphate Environments. Plant J. 2004, 39, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Kuo, R.; Coulter, M.; Calixto, C.P.G.; Entizne, J.C.; Guo, W.; Marquez, Y.; Milne, L.; Riegler, S.; Matsui, A.; et al. A High-Resolution Single-Molecule Sequencing-Based Arabidopsis Transcriptome Using Novel Methods of Iso-Seq Analysis. Genome Biol. 2022, 23, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Malley, R.C.; Huang, S.S.C.; Song, L.; Lewsey, M.G.; Bartlett, A.; Nery, J.R.; Galli, M.; Gallavotti, A.; Ecker, J.R. Cistrome and Epicistrome Features Shape the Regulatory DNA Landscape. Cell 2016, 165, 1280–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. MaxQuant Enables High Peptide Identification Rates, Individualized p.p.b.-Range Mass Accuracies and Proteome-Wide Protein Quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.; Hein, M.Y.; Luber, C.A.; Paron, I.; Nagaraj, N.; Mann, M. Accurate Proteome-Wide Label-Free Quantification by Delayed Normalization and Maximal Peptide Ratio Extraction, Termed MaxLFQ. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 2513–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
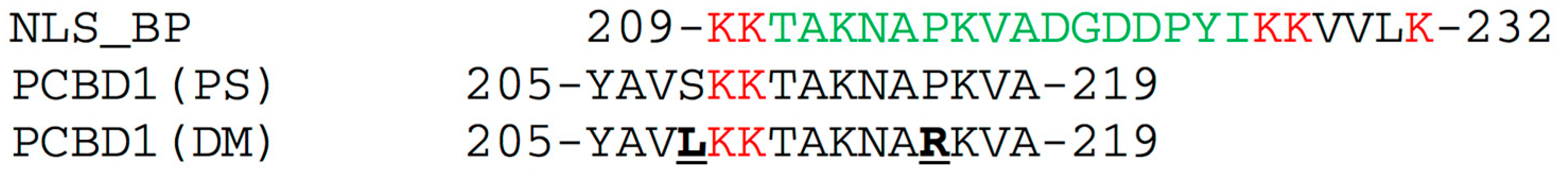
| Binding Site Specificity | TF Family (DAP Database) | TF Motif | TF Motif Consensus Sequence | Binding Sites with Motif | Percent Total Sites with a TF Motif | p-Value (FDR-Corrected) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS | ABI3VP1 | VRN1 | VWKTTTTTTTTTTTTTTKB | 35 | 15.56 | 2.67 × 10−4 |
| PS | AP2EREBP | SHN3 | WCCDCCGCCRCCDCCGCCGCC | 11 | 4.89 | 1.12 × 10−2 |
| PS | LOBAS2 | LOB | WCCGCCGCCDYCKCCGCCGCH | 22 | 9.78 | 4.06 × 10−3 |
| PS | C2H2 | JKD, IDD10 | WWWWTTTTTGTCKTTTTSTD | 15 | 6.67 | 9.60 × 10−3 |
| PS | Homeobox | ATHB53 | HCAATAATTGD | 37 | 16.44 | 1.11 × 10−2 |
| PS | ATHB20, GL2 | HYAATAATTRA | 37 | 16.44 | 1.11 × 10−2 | |
| PS | ATHB1, HAT5 | HYAATAATTRW | 30 | 13.33 | 1.13 × 10−2 | |
| PS | BBRBPC | BPC1 | CTCTYTCTCTCTCTC | 66 | 29.33 | 7.38 × 10−3 |
| PS | C2H2 | TF3A | CYTCCTCCTCCTCCTCCTC | 26 | 11.56 | 5.66 × 10−3 |
| PS | ND | FRS9 | CTCTCTCTCTCTCTCTCTCTC | 24 | 10.67 | 3.50 × 10−3 |
| PS | WRKY | WRKY27 | ANCGTTGACTTTT | 26 | 11.56 | 1.47 × 10−3 |
| PS | WRKY7 | DNCGTTGACTTTTT | 32 | 14.22 | 3.30 × 10−3 | |
| DM | bZIP | ABI5 | DDTGRWSACGTGGCA | 10 | 9.35 | 5.99 × 10−3 |
| DM | MYB related | MYBS1 | HWWAWYCTTATCYWH | 13 | 12.15 | 1.09 × 10−2 |
| DM | MYBS1 | DWWDWRGATAAGRTT | 10 | 9.35 | 5.99 × 10−3 | |
| DM | SRM1 | DWWDWRGATAAGR | 10 | 9.35 | 5.99 × 10−3 | |
| DM | SRM1 | YCTTATCYWHW | 11 | 10.28 | 5.01 × 10−4 | |
| PS | C2C2dof | DOF1.1 | TTTTYACTTTTTYTTTTTTTTTTTTTW | 59 | 26.22 | 7.71 × 10−5 |
| PS | DOF1.5, COG1 | RWAAAAADDAAAAAGTRAAAA | 60 | 26.67 | 9.20 × 10−3 | |
| PS | DOF1.7, Adof1 | AAAAAVAAAAAGTARAAAAWR | 22 | 9.78 | 1.86 × 10−3 | |
| PS | DOF5.1 | HWTTWACTTTTTBDHTTWW | 30 | 13.33 | 1.13 × 10−2 | |
| PS | DOF5.6, HCA2 | RAAAAAADVAAAAAGKWAAWA | 40 | 17.78 | 1.60 × 10−3 | |
| DM | DOF3.2 | KTWACTTTTTNNYTTTTTT | 17 | 15.89 | 3.72 × 10−3 | |
| DM | DOF5.8 | TTTWTTTACTTTTTBYTTTTT | 17 | 15.89 | 3.72 × 10−3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Slocum, R.D.; Cai, X.; Clark, G.; Roux, S.J. Chromatin-Associated Pea Apyrase psNTP9 Function as a DNA-Binding Regulatory Protein in Yeast and Arabidopsis. Plants 2025, 14, 3514. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14223514
Wang H, Slocum RD, Cai X, Clark G, Roux SJ. Chromatin-Associated Pea Apyrase psNTP9 Function as a DNA-Binding Regulatory Protein in Yeast and Arabidopsis. Plants. 2025; 14(22):3514. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14223514
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Huan, Robert D. Slocum, Xingbo Cai, Greg Clark, and Stanley J. Roux. 2025. "Chromatin-Associated Pea Apyrase psNTP9 Function as a DNA-Binding Regulatory Protein in Yeast and Arabidopsis" Plants 14, no. 22: 3514. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14223514
APA StyleWang, H., Slocum, R. D., Cai, X., Clark, G., & Roux, S. J. (2025). Chromatin-Associated Pea Apyrase psNTP9 Function as a DNA-Binding Regulatory Protein in Yeast and Arabidopsis. Plants, 14(22), 3514. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14223514










