Features of Translocation of Copper Nanoparticles in Mentha spicata L. and Extraction into Infusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
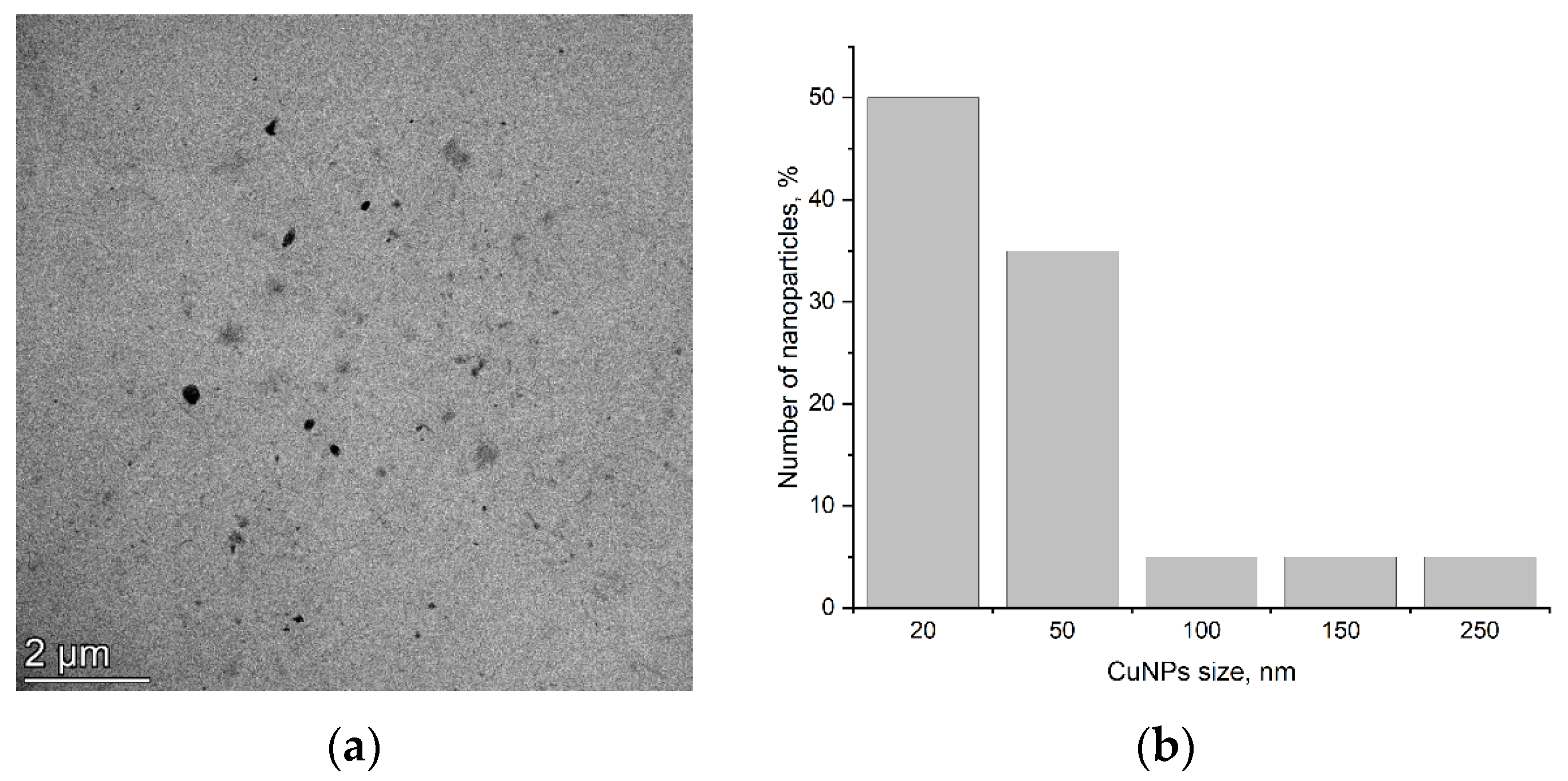
2.1. Nanoparticle’s Description
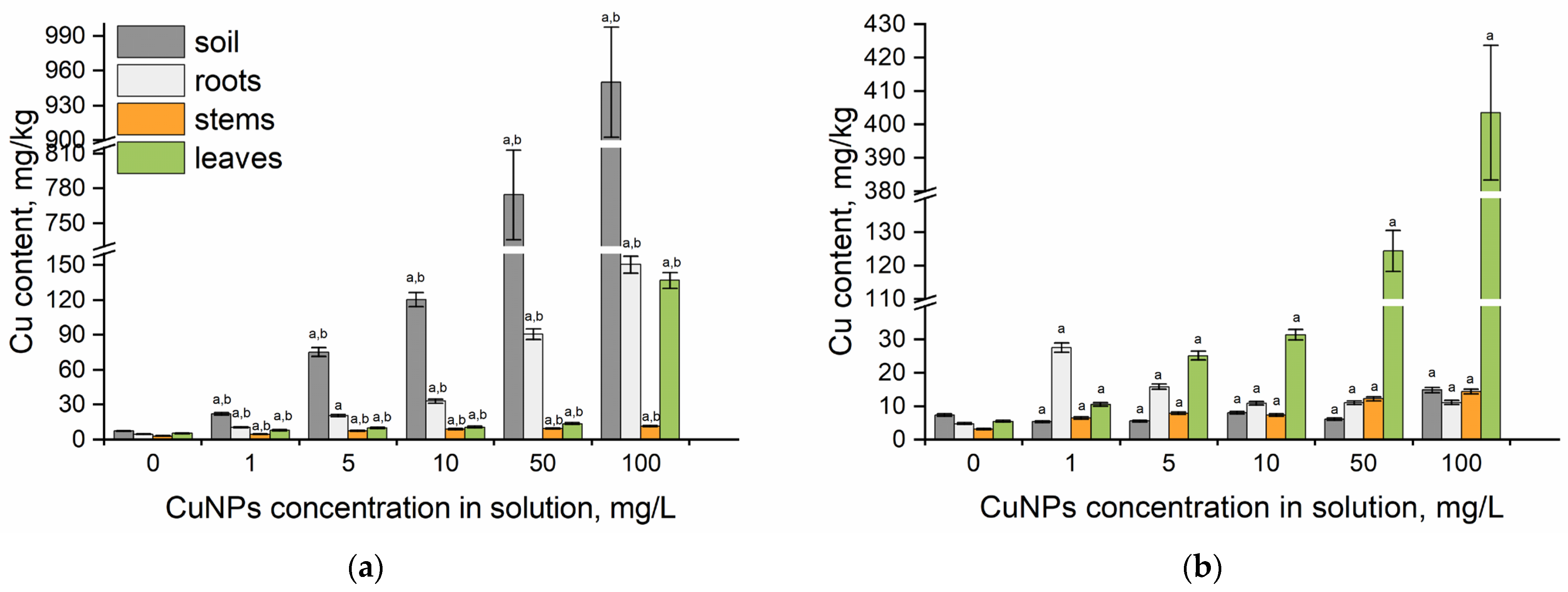
2.2. Copper Uptake and Translocation in Spearmint’s Segments
2.3. Effect of Foliar Application and Irrigation of CuNPs on Spearmint Biochemical Parameters
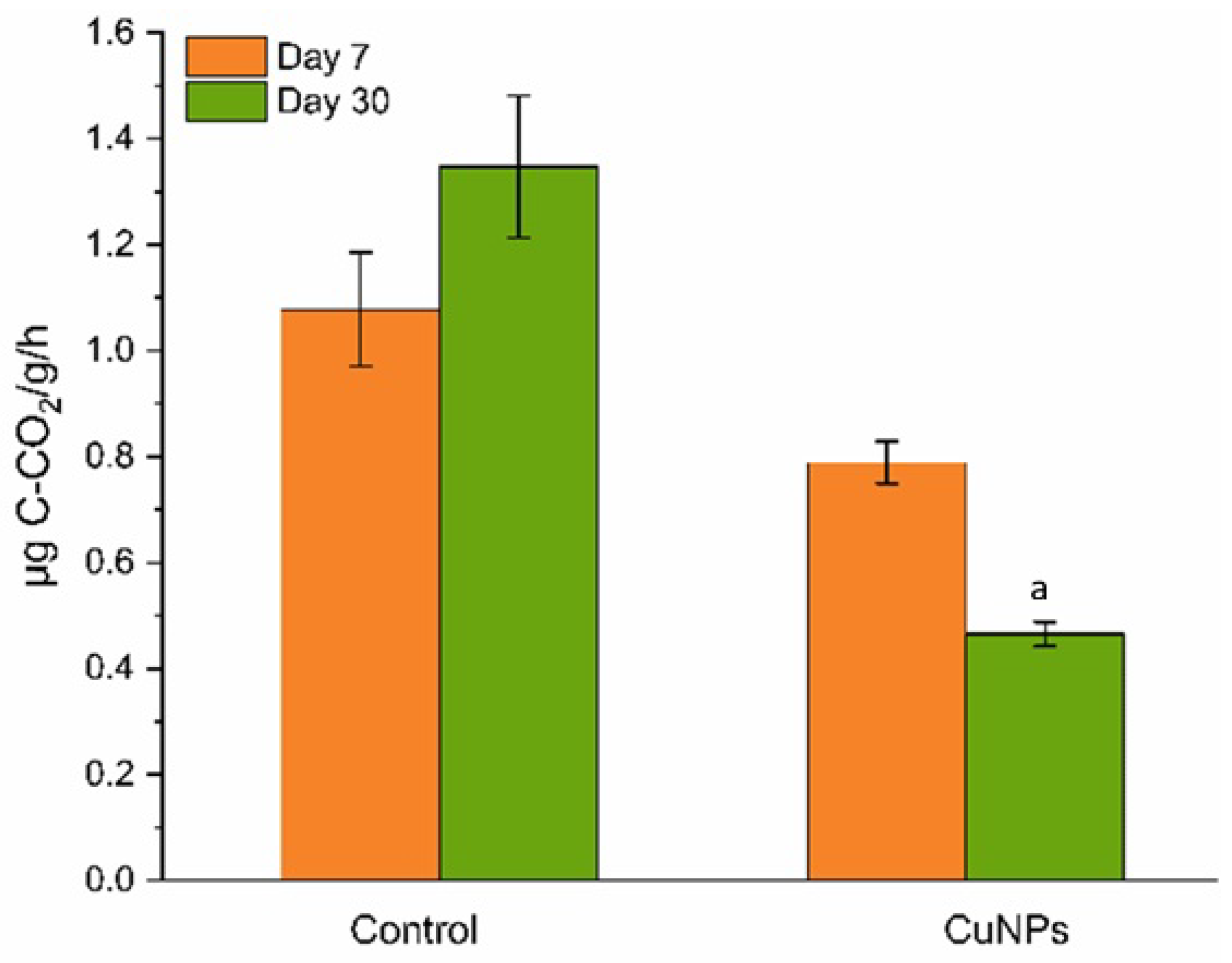
2.4. Soil Microbial Activity
2.5. Assessment of Copper Transfer from Plants in the Infusion and Health Risk Assessment
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Mentha Treatment with CuNPs
3.3. Herbal Tea Preparation
3.4. Analytical Techniques
3.5. Biochemical Analysis and Antioxidant Activity
3.5.1. Pigments Extraction and Quantification (Mint Leaves)
3.5.2. Antioxidant Activity
3.6. Soil Microbial Activity Measurment
3.7. Data Evaluation
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michaela Corina, C.; Teodora, M.; Lucian, M. Copper Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Characterization, Physiology, Toxicity and Antimicrobial Applications. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copper Nanoparticle Market Report 2025 (Global Edition). Available online: https://www.cognitivemarketresearch.com/copper-nanoparticle-market-report (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- Naz, S.; Gul, A.; Zia, M. Toxicity of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles: A Review Study. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, X.; Qin, B.; Xing, D.; Guo, Y.; Fan, R. Investigation of the Mending Effect and Mechanism of Copper Nano-Particles on a Tribologically Stressed Surface. Tribol. Lett. 2004, 17, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongbet, A.; Mishra, A.K.; Mohanta, Y.K.; Mahanta, S.; Ray, M.K.; Khan, M.; Baek, K.H.; Chakrabartty, I. Nanofertilizers: A Smart and Sustainable Attribute to Modern Agriculture. Plants 2022, 11, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Hu, D.; Cheng, E.W.C.; Vargas-Reus, M.A.; Reip, P.; Allaker, R.P. Characterisation of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Applications. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 33, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawande, M.B.; Goswami, A.; Felpin, F.X.; Asefa, T.; Huang, X.; Silva, R.; Zou, X.; Zboril, R.; Varma, R.S. Cu and Cu-Based Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications in Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3722–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T.; Suskova, S.; Mandzhieva, S.; Tsitsuashvili, V.; Chapligin, V.; Fedorenko, A. Effects of Copper Nanoparticles (CuO NPs) on Crop Plants: A Mini Review. Bionanoscience 2018, 8, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, D.; Afreen, S.; Talreja, N.; Ashfaq, M. Multifunctional Copper Polymer-Based Nanocomposite for Environmental and Agricultural Applications; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; ISBN 9780128213544. [Google Scholar]
- Bramhanwade, K.; Shende, S.; Bonde, S.; Gade, A.; Rai, M. Fungicidal Activity of Cu Nanoparticles against Fusarium Causing Crop Diseases. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2016, 14, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, K.L.; Keller, A.A. Emerging Patterns for Engineered Nanomaterials in the Environment: A Review of Fate and Toxicity Studies. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2014, 16, 2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaine, S.J.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Batley, G.E.; Fernandes, T.F.; Handy, R.D.; Lyon, D.Y.; Mahendra, S.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Lead, J.R. Nanomaterials in the Environment: Behavior, Fate, Bioavailability, and Effects. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1825–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottschalk, F.; Ort, C.; Scholz, R.W.; Nowack, B. Engineered Nanomaterials in Rivers—Exposure Scenarios for Switzerland at High Spatial and Temporal Resolution. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3439–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.A.; Lazareva, A. Predicted Releases of Engineered Nanomaterials: From Global to Regional to Local. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2013, 1, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.A.; Adeleye, A.S.; Conway, J.R.; Garner, K.L.; Zhao, L.; Cherr, G.N.; Hong, J.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L.; Godwin, H.A.; Hanna, S.; et al. Comparative Environmental Fate and Toxicity of Copper Nanomaterials. NanoImpact 2017, 7, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musial, J.; Krakowiak, R.; Mlynarczyk, D.T.; Goslinski, T.; Stanisz, B.J. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Food and Personal Care Products—What Do We Know about Their Safety? Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.A.; McFerran, S.; Lazareva, A.; Suh, S. Global Life Cycle Releases of Engineered Nanomaterials. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2013, 15, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, F.; Sonderer, T.; Scholz, R.W.; Nowack, B. Modeled Environmental Concentrations of Engineered Nanomaterials (TiO2, ZnO, Ag, CNT, Fullerenes) for Different Regions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 9216–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, M.; Kumar, A. Copper-Based Nanoparticles in the Soil-Plant Environment: Assessing Their Applications, Interactions, Fate and Toxicity. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, T.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Chi, Q. Multifaceted Impacts of Nanoparticles on Plant Nutrient Absorption and Soil Microbial Communities. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1497006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafeez, A.; Razzaq, A.; Mahmood, T.; Jhanzab, H.M. Potential of Copper Nanoparticles to Increase Growth and Yield of Wheat. J. Nanosci. Adv. Technol. 2015, 1, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.I.; Shah, G.A.; Sadiq, M.; Amin, N.U.; Ali, A.M.; Ondrasek, G.; Shahzad, K. Nanobiochar and Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Mixture Improves Wheat Production. Plants 2023, 12, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nguyen, D.; Mai, H.; Thanh, N.; Kien, L.; Nguyen, H.; Thi, H.; Huong, N.; Le, M. Copper Nanoparticle Application Enhances Plant Growth and Grain Yield in Maize Under Drought Stress Conditions. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 41, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malandrakis, A.A.; Kavroulakis, N.; Chrysikopoulos, C.V. Use of Copper, Silver and Zinc Nanoparticles against Foliar and Soil-Borne Plant Pathogens. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Abd Samad, M.Y.; Uddin, M.K.; Quddus, M.A.; Motalib Hossain, M.A. Recent Trends in the Foliar Spraying of Zinc Nutrient and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Tomato Production. Agronomy 2021, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Wang, C.; Wagner, D.C.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L.; He, F.; Rico, C.M. Foliar Application of Nanoparticles: Mechanisms of Absorption, Transfer, and Multiple Impacts. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 1196–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vargas, E.R.; Ortega-Ortíz, H.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; de Alba Romenus, K.; de la Fuente, M.C.; Benavides-Mendoza, A.; Juárez-Maldonado, A. Foliar Application of Copper Nanoparticles Increases the Fruit Quality and the Content of Bioactive Compounds in Tomatoes. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekoukhou, M.; Fallah, S.; Pokhrel, L.R.; Abbasi-Surki, A.; Rostamnejadi, A. Foliar Enrichment of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Promotes Biomass, Photosynthetic Pigments, and Commercially Valuable Secondary Metabolites and Essential Oils in Dragonhead (Dracocephalum moldavica L.) under Semi-Arid Conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Rico, C.M.; Zhao, L.; Adeleye, A.S.; Keller, A.A.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Toxic Effects of Copper-Based Nanoparticles or Compounds to Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) and Alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, T.A.; Bayoumi, Y.; Abdalla, N.; Taha, H.; Alshaal, T.; Shehata, S.; Amer, M.; Domokos-Szabolcsy, É.; El-Ramady, H. Nanoparticles, Soils, Plants and Sustainable Agriculture. In Nanoscience in Food and Agriculture 1; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 283–312. ISBN 9783319393032. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; White, J.C.; Dhankher, O.P.; Xing, B. Metal-Based Nanotoxicity and Detoxification Pathways in Higher Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7109–7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, B. RSC Advances Understanding the Phyto-Interaction of Heavy Metal Oxide Bulk and Nanoparticles: Evaluation of Metallothionein Production. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 4210–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fu, Y.; Zheng, S.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y. Phytotoxicity and Accumulation of Copper-Based Nanoparticles in Brassica under Cadmium Stress. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Peng, C.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, X.; Chen, Y.; Hu, T. Phytotoxicity and Accumulation of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles to the Cu-Tolerant Plant Elsholtzia Splendens. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosa, K.A.; El-Naggar, M.; Ramamoorthy, K.; Alawadhi, H.; Elnaggar, A.; Wartanian, S.; Ibrahim, E.; Hani, H. Copper Nanoparticles Induced Genotoxicty, Oxidative Stress, and Changes in Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Gene Expression in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus) Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, B.; Khan, M.S. Phytotoxic Impact of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Fabricated from Rose Petals (Rosa indica) on Germination, Biological Growth, and Phytochemicals of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). S. Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 172, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apodaca, S.A.; Cota-ruiz, K.; Hernandez-viezcas, J.A.; Gardea-torresdey, J.L. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Alleviate Phytotoxic E Ff Ects of Copper-Based Nanoparticles/Compounds in Spearmint (Mentha spicata). ACS Agric. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 661–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peshkova, A.; Zinicovscaia, I.; Cepoi, L.; Rudi, L.; Chiriac, T.; Yushin, N.; Sohatsky, A. Features of Copper and Gold Nanoparticle Translocation in Petroselinum Crispum Segments. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peshkova, A.; Zinicovscaia, I.; Cepoi, L.; Rudi, L.; Chiriac, T.; Yushin, N.; Ganea, L.; Corcimaru, S. Uptake of Gold, Silver, and Copper Nanoparticles by Calendula Officinalis L. and Their Effect on the Plant Biochemical Parameters. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, R.P.; Kumar, A.; Garg, A.N. Analysis of Indian Mint (Mentha spicata) for Essential, Trace and Toxic Elements and Its Antioxidant Behaviour. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 41, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, R.; Gayathri, S.; Rathnavel, C.; Raj, V. Analysis of Mineral and Heavy Metals in Some Medicinal Plants Collected from Local Market. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, S74–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Pandita, S.; Preet, G.; Sidhu, S.; Sharma, A.; Khanna, K.; Kaur, P.; Shreeya, A.; Setia, R. Chemosphere Copper Bioavailability, Uptake, Toxicity and Tolerance in Plants: A Comprehensive Review. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barsova, N.; Yakimenko, O.; Tolpeshta, I.; Motuzova, G. Current State and Dynamics of Heavy Metal Soil Pollution in Russian Federation d A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqeel, U.; Aftab, T.; Khan, M.M.A.; Naeem, M. Plant Stress Excessive Copper Induces Toxicity in Mentha arvensis L. by Disturbing Growth, Photosynthetic Machinery, Oxidative Metabolism and Essential. Plant Stress 2023, 8, 100161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.A.; Huang, Y.; Nelson, J. Detection of Nanoparticles in Edible Plant Tissues Exposed to Nano-Copper Using Single-Particle ICP-MS. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2018, 20, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wairich, A.; De Conti, L.; Lamb, T.I.; Keil, R.; Neves, L.O.; Brunetto, G.; Sperotto, R.A.; Ricachenevsky, F.K. Throwing Copper Around: How Plants Control Uptake, Distribution, and Accumulation of Copper. Agronomy 2022, 12, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohatsu, M.Y.; Pelegrino, M.T.; Monteiro, L.R.; Freire, B.M.; Pereira, R.M.; Fincheira, P.; Rubilar, O.; Tortella, G.; Batista, B.L.; de Jesus, T.A.; et al. Comparison of Foliar Spray and Soil Irrigation of Biogenic CuO Nanoparticles (NPs) on Elemental Uptake and Accumulation in Lettuce. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 16350–16367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Ma, J.; Xian, J.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Du, Y.; Tian, D.; Xiao, H.; He, Y.; Luo, L.; Deng, O.; et al. Copper Accumulation and Physiological Markers of Soybean (Glycine Max) Grown in Agricultural Soil Amended with Copper Nanoparticles. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 229, 113088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Dumat, C.; Dappe, V.; Vezin, H.; Schreck, E.; Shahid, M.; Pierart, A.; Sobanska, S. Copper Oxide Nanoparticle Foliar Uptake, Phytotoxicity, and Consequences for Sustainable Urban Agriculture. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5242–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birbaum, K.; Brogioli, R.; Schellenberg, M.; Martinoia, E.; Stark, W.J.; Günther, D.; Limbach, L.K. No Evidence for Cerium Dioxide Nanoparticle Translocation in Maize Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8718–8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feichtmeier, N.S.; Walther, P.; Leopold, K. Uptake, Effects, and Regeneration of Barley Plants Exposed to Gold Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 8549–8558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Guo, H.; Ma, C.; Li, C.; Chefetz, B.; Polubesova, T.; Xing, B. Science of the Total Environment Maize (Zea mays L.) Root Exudates Modify the Surface Chemistry of CuO Nanoparticles: Altered Aggregation, Dissolution and Toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Lei, C.; Xu, J.; Li, R. Foliar Uptake and Leaf-to-Root Translocation of Nanoplastics with Different Coating Charge in Maize Plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biodiversity, E.; Alshaal, T.; El-ramady, H.R. Foliar Application: From Plant Nutrition to Biofortification. Environ. Biodivers. Soil Secur. 2017, 1, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.; Ahmed, S.; Abbasi, A.; Khan, M.T.; Subhan, M.; Bukhari, N.A.; Hatamleh, A.A.; Abdelsalam, N.R. Plant Mediated Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles, Process Optimization, and Impact on Tomato Plant. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.A.S.; Amin, J.; Valipour, M.; Iqbal, R.; Aslam, M.U.; Zulfiqar, B.; Muhammad, F.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Elshikh, M.S.; et al. Cu-Nanoparticles Enhance the Sustainable Growth and Yield of Drought-Subjected Wheat through Physiological Progress. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawale, K.S.; Nandini, B.; Giridhar, P. Copper and Silver Nanoparticle Seed Priming and Foliar Spray Modulate Plant Growth and Thrips Infestation in Capsicum spp. ACS Omega 2023, 9, 3430–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbanna, H.M.; Ahmed, O.K.; Fayed, S.A.K.; Hammam, K.A.M.; Yousef, R.S. Enhancing French Basil Growth through Synergistic Foliar Treatment with Copper Nanoparticles and Spirulina sp. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peshkova, A.; Zinicovscaia, I.; Cepoi, L.; Rudi, L.; Chiriac, T.; Yushin, N.; Anh, T.T.; Manh Dung, H.; Corcimaru, S. Effects of Gold Nanoparticles on Mentha Spicata L., Soil Microbiota, and Human Health Risks: Impact of Exposure Routes. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, G. Antimicrobial Silver Nanoparticles—Regulatory Situation in the European Union. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, S200–S207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrinenko, Y.; Plieva, A.; Zinicovscaia, I.; Hristozova, G.; Frontasyeva, M.; Tkachenko, K.; Dogadkin, D.; Gromyak, I.; Kolotov, V. Elemental Composition of Infusions of Herbs (Tisanes) of North Ossetia (the Caucasus). Agriculture 2021, 11, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassahun, B.M.; Egata, D.F.; Lulseged, T.; Yosef, W.B.; Tadesse, S. Variability in Agronomic and Chemical Characteristics of Spearmint (Mentha spicata L.)Genotypes in Ethiopia. Int. J. Adv. Biol. Biomed. Res. 2014, 10, 2704–2711. [Google Scholar]
- El Menyiy, N.; Mrabti, H.N.; El Omari, N.; Bakili, A.E.I.; Bakrim, S.; Mekkaoui, M.; Balahbib, A.; Amiri-ardekani, E.; Ullah, R.; Alqahtani, A.S.; et al. Medicinal Uses, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Toxicology of Mentha Spicata. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 7990508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboubi, M. Mentha Spicata L. Essential Oil, Phytochemistry and Its Effectiveness in Flatulence. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2021, 11, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Mishra, S.; Malik, A.; Satya, S. Insecticidal Properties of Mentha Species: A Review. Ind. Crops Prod. 2011, 34, 802–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, F.; Farooq, M. Application of Micronutrients in Rice-Wheat Cropping System of South Asia. Rice Sci. 2019, 26, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczycha-Madeja, A.; Welna, M.; Pohl, P. Elemental Analysis of Teas and Their Infusions by Spectrometric Methods. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 35, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K. Chlorophylls and Carotenoids: Pigments of Photosynthetic Biomembranes. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; Volume 148, pp. 350–382. ISBN 0076-6879. [Google Scholar]
- Re, R.; Nicoletta, P.; Anna, P.; Ananth, P.; Min, Y.; Catherine, R.-E. Antioxidant Activity Applying an Improved ABTS Radical Cation Decolorization Assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, L.M.; Segundo, M.A.; Reis, S.; Lima, J.L.F.C. Methodological Aspects about in Vitro Evaluation of Antioxidant Properties. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 613, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjosé, I.; Navarro-Roldán, F.; Montero, Y.; Ramírez-Acosta, S.; Jiménez-Nieva, F.J.; Infante-Izquierdo, M.D.; Polo-ávila, A.; Muñoz-Rodríguez, A.F. The Bioconcentration and the Translocation of Heavy Metals in Recently Consumed Salicornia Ramosissima, J. Woods in Highly Contaminated Estuary Marshes and Its Food Risk. Diversity 2022, 14, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.A.; Tsuji, J.S.; McArdle, M.E.; Adams, W.J.; Goodfellow, W.L. Recommended Reference Values for Risk Assessment of Oral Exposure to Copper. Risk Anal. 2023, 43, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Concentration of CuNPs in Solution, mg/L | BCF | TF | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roots | Stems | Leaves | Stems/Roots | Leaves/Stems | Leaves/Roots | |
| Root irrigation | ||||||
| 1 | 0.48 ± 0.014 | 0.21 ± 0.006 | 0.36 ± 0.01 | 0.44 ± 0.01 | 1.70 ± 0.05 | 1.1 ± 0.01 |
| 5 | 0.27 ± 0.008 | 0.10 ± 0.003 | 0.13 ± 0.004 | 0.37 ± 0.01 | 1.31 ± 0.03 | 0.8 ± 0.003 |
| 10 | 0.28 ± 0.008 | 0.08 ± 0.002 | 0.09 ± 0.003 | 0.28 ± 0.008 | 1.18 ± 0.03 | 0.5 ± 0.004 |
| 50 | 0.12 ± 0.003 | 0.01 ± 0.0003 | 0.02 ± 0.0006 | 0.11 ± 0.003 | 1.45 ± 0.04 | 0.3 ± 0.008 |
| 100 | 0.16 ± 0.005 | 0.01 ± 0.0003 | 0.14 ± 0.004 | 0.08 ± 0.0001 | 11.95 ± 0.35 | 0.2 ± 0.001 |
| Foliar spraying | ||||||
| Roots/Stems | Stems/Leaves | Roots/Leaves | ||||
| 1 | 4.21 ± 0.13 | 0.62 ± 0.01 | 2.62 ± 0.08 | |||
| 5 | 2.01 ± 0.06 | 0.31 ± 0.009 | 0.63 ± 0.02 | |||
| 10 | 1.49 ± 0.04 | 0.23 ± 0.007 | 0.35 ± 0.01 | |||
| 50 | 0.91 ± 0.027 | 0.10 ± 0.003 | 0.09 ± 0.003 | |||
| 100 | 0.77 ± 0.023 | 0.04 ± 0.001 | 0.03 ± 0.0009 | |||
| Copper Content in Leaves Under Root Exposure, mg/kg | Extraction, % | Copper Content in Leaves Under Foliar Spraying Condition, mg/kg | Extraction, % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 5.48 ± 0.16 | 64 | 5.48 ± 0.16 | 64 |
| 1 | 8.03 ± 0.24 | 31 | 10.5 ± 0.3 | 55 |
| 5 | 9.92 ± 0.3 | 33 | 25.1 ± 0.7 | 24 |
| 10 | 10.81 ± 0.3 | 31 | 31.4 ± 0.9 | 37 |
| 50 | 13.83 ± 0.4 | 23 | 124.3 ± 3.7 | 10 |
| 100 | 137 ± 4.1 | 3 | 403.5 ± 12.1 | 8 |
| Copper Content in Infusion, mg/L | EDI | HQ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root Exposure | Foliar Spraying Condition | Root Exposure | Foliar Spraying Condition | Root Exposure | Foliar Spraying Condition | |
| Control | 0.175 ± 0.05 | 0.175 ± 0.05 | 3.13 × 10−3 | 3.13 × 10−3 | 7.81 × 10−2 | 7.81 × 10−2 |
| 1 | 0.125 ± 0.004 | 0.238 ± 0.007 | 2.23 × 10−3 | 3.13 × 10−3 | 5.56 × 10−2 | 1.1 × 10−1 |
| 5 | 0.165 ± 0.005 | 0.242 ± 0.007 | 2.95 × 10−3 | 4.25 × 10−3 | 7.38 × 10−2 | 1.1 × 10−1 |
| 10 | 0.169 ± 0.05 | 0.583 ± 0.01 | 3.01 × 10−3 | 4.33 × 10−3 | 7.53 × 10−2 | 2.6 × 10−1 |
| 50 | 0.158 ± 0.004 | 0.619 ± 0.02 | 2.83 × 10−3 | 1.04 × 10−2 | 7.07 × 10−2 | 2.8 × 10−1 |
| 100 | 0.215 ± 0.006 | 1.53 ± 0.04 | 3.85 × 10−3 | 1.11 × 10−2 | 9.62 × 10−2 | 6.8 × 10−1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peshkova, A.; Zinicovscaia, I.; Cepoi, L.; Rudi, L.; Chiriac, T.; Corcimaru, S.; Yushin, N.; le Roux, R. Features of Translocation of Copper Nanoparticles in Mentha spicata L. and Extraction into Infusion. Plants 2025, 14, 3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14213318
Peshkova A, Zinicovscaia I, Cepoi L, Rudi L, Chiriac T, Corcimaru S, Yushin N, le Roux R. Features of Translocation of Copper Nanoparticles in Mentha spicata L. and Extraction into Infusion. Plants. 2025; 14(21):3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14213318
Chicago/Turabian StylePeshkova, Alexandra, Inga Zinicovscaia, Liliana Cepoi, Ludmila Rudi, Tatiana Chiriac, Serghei Corcimaru, Nikita Yushin, and Rikus le Roux. 2025. "Features of Translocation of Copper Nanoparticles in Mentha spicata L. and Extraction into Infusion" Plants 14, no. 21: 3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14213318
APA StylePeshkova, A., Zinicovscaia, I., Cepoi, L., Rudi, L., Chiriac, T., Corcimaru, S., Yushin, N., & le Roux, R. (2025). Features of Translocation of Copper Nanoparticles in Mentha spicata L. and Extraction into Infusion. Plants, 14(21), 3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14213318