Effects of Different Nitrogen Fertilizer Rates on Spring Maize Yield and Soil Nitrogen Balance Under Straw Returning Conditions of Cold Regions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Maize Yield and Economic Benefits
2.2. Nitrogen Fertilizer Utilization Rate and Agronomic Efficiency
2.3. Changes in Inorganic Nitrogen in Soil Profiles
2.4. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rates on Nitrogen Balance
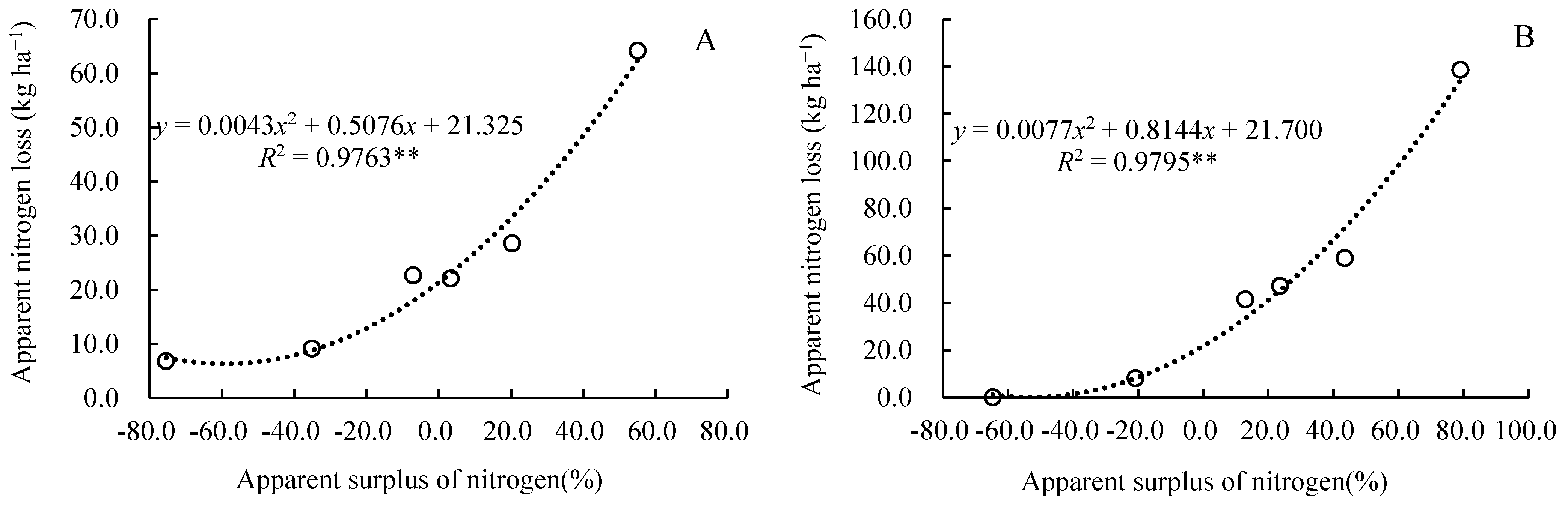
2.5. The Relationship Between Nitrogen Surplus Rate, Nitrogen Application Rate, and Nitrogen Loss Amount
3. Discussion
3.1. Environmental Effects of Residual Nitrate Nitrogen in Soil Profiles
3.2. Appropriate Nitrogen Fertilizer Application Rate for Maize Under Straw Returning Conditions in Cold Black Soil Areas
4. Materials and Methods
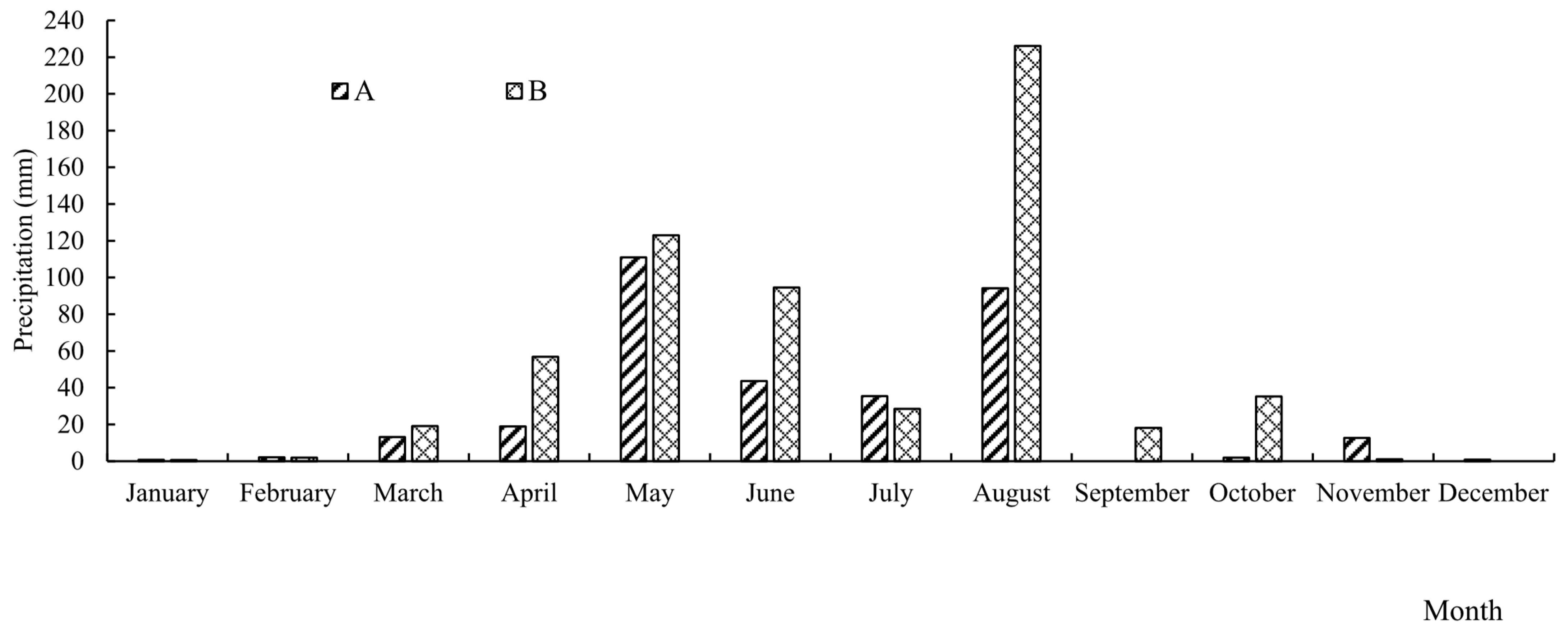
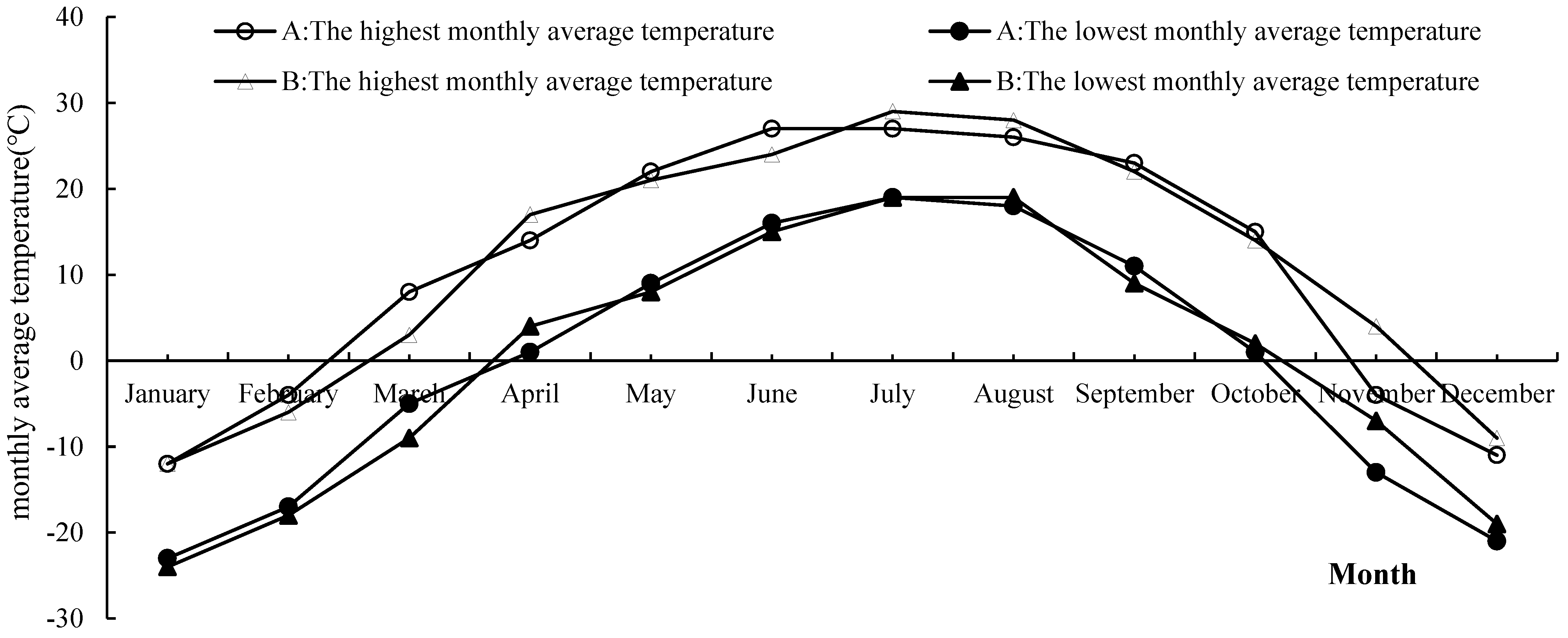
4.1. Study Site
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Soil and Plant Sampling Analysis, Crop Yield Measurement
4.4. Statistical Analysis and Calculated Formulation
4.4.1. Statistical Analysis
4.4.2. Calculate Formulation
- (1)
- Apparent nitrogen surplus rate (kg·ha−1) = (the amount of applied nitrogen − nitrogen amount uptake by aboveground plant parts)/nitrogen amount uptake by aboveground plant parts × 100%. (Note: The amount of applied nitrogen here includes both fertilizer nitrogen and nitrogen from straw.)
- (2)
- Soil residual mineral nitrogen content (calculated in 20 cm layers) (kg·ha−1) = soil bulk density × 20 × mineral nitrogen concentration/10.
- (3)
- Apparent mineralization of nitrogen (kg ha−1) = nitrogen amount uptake by aboveground plant parts in no-nitrogen treatment + residual soil mineral nitrogen in no-nitrogen treatment − initial soil mineral nitrogen in no-nitrogen treatment.
- (4)
- Apparent nitrogen loss (kg·ha−1) = the amount of applied nitrogen + initial soil mineral nitrogen + apparent mineralization of nitrogen − nitrogen amount uptake by aboveground plant parts − accumulated soil mineral nitrogen at harvest.
- (5)
- Nitrogen fertilizer utilization rate (%) = (nitrogen uptake by crops in nitrogen application treatment − nitrogen uptake by crops in no-nitrogen treatment)/nitrogen fertilizer input × 100.
- (6)
- Nitrogen agronomy efficiency(kg·kg−1) = (yield in nitrogen application treatment − yield in no-nitrogen treatment)/nitrogen fertilizer input.
- (7)
- Economic benefits = maize yield × maize prices − fertilizer prices × the amount.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lao, X.R.; Sun, W.H.; Wang, Z.; Hao, Y.R.; Zhang, C.A. Effect of matching use of straw and chemical fertilizer on soil fertility. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2003, 40, 618–623. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, D.J.; Nie, F.; Zhang, B. Effect of long-term straw application on soil fertility. Soils 2007, 39, 782–786. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z. The comprehensive utilization rate of straw in Heilongjiang has remained above 95% for four consecutive years. Beijing News 2024, 10, 23. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics. China Statistical Year Book 2024; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, C.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Zhang, L.Y.; Zhang, M.L.; Huang, S.; Wang, S.Y.; Zhou, W. Research progress on associative nitrogen fixation of gramineous crops. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2024, 30, 1307–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Ding, X.Q.; Zhu, Z.K.; Wang, J.; Peng, P.Q.; Ge, T.D.; Wu, J.S. Effect of Straw Application on the Dynamics of Exogenous Nitrogen and Microbial Activity in Paddy Soil. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.T.; Song, Q.L.; Yan, C.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.H.; Tian, J.F.; Deng, Y.X.; Ma, C.M. Nitrogen accumulation and nitrogen substitution effect of maize under straw returning with continuous cropping. Acta Agron. Sin. 2022, 48, 962–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.X.; Ma, Z.M.; Wang, J.C. Determination of the input threshold of nitrogen fertilizer based on environment-friendly agriculture and maize yield. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2022, 39, 726–733. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, W.Y.; Xu, K.W.; Liu, M.P.; Xiao, H.; Pei, L.Z.; Peng, D.D.; Chen, Y.X. Effects of Different Nitrogen Application Levels on Photosynthetic Characteristics, Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Yield of Spring Maize in Sichuan Province. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2022, 55, 1735–1748. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Chen, D. Nitrogen fertilizer use in China–Contributions to food production, impacts on the environment and best management strategies. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2002, 63, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.Y.; Sha, S.Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, S.J.; Feng, G.Z.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Y. Optimizing Nitrogen Fertilizer Rate for High Yield Maize in Black Soil Region Based on Ecological and Social Benefits. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2023, 56, 2129–2140. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, W.; Song, Z.F.; Qian, X.Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.Y. Appropriate Rate of Efficiency Enhancing Nitrogen Fertilizers to Achieve High Yield and Environmental Friendliness of Maize in the Black Soil of Jilin Province. J. Maize Sci. 2024, 32, 106–113. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.M.; Gao, Y.S.; Sun, Y.Y.; Dou, J.G.; Hou, Z.H.; Liu, H.T.; Wand, L.C. Research Progress of the Factors Influencing Straw Decomposition Regularity and Nutrient Release Characteristics. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2018, 57, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.M.; Wang, X.Y.; Sun, B. Characteristics of Nutrient Release and Its Affecting Factors during Plant Residue Decomposition under Different Climate and Soil Conditions. Acta Pedoloqica Sin. 2017, 54, 1206–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Mian, Y.M.; Hou, X.Q.; Li, P.F.; Wang, X.N. Effects of nitrogen application on decomposition and nutrient release of returning straw, soil fertility, and maize yield Acta. Agron. Sin. 2023, 49, 2012–2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.G.; Zhang, E.P.; Wang, H.Y.; Yin, D.P.; Dong, C.S.; Pang, X.Y.; Li, Q.Z.; Wang, Y.Q. Effects of Reduced Nitrogen Application on Maize Yield and Nitrogen Utilization under Long-Term Straw Return. J. Northeast Agric. Sci. 2021, 46, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, C.; Shi, Z.; Wang, S.J.; Yan, L.; Gao, Q. Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer Regulation on Nitrogen Utilization and Ammonia Volatilization from Maize Farmland in Black Soil Region of Northeast China. J. Maize Sci. 2021, 29, 118–126. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, X.T.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, F.S. Study on Effect of Nitrogen Fertilizer and Nitrogen Balance in Winter Wheat and Summer Maize Rotation System. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2002, 35, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, D.J.; Gao, Q.; He, W.T.; He, P. Effect of N application on N utilization and N balance in spring maize. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2010, 16, 552–558. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.B.; Xu, X.P.; Hou, Y.P.; Hu, C.; He, P.; Wu, Y.P. Optimum nitrogen application rate for maize under continuous straw returning in black soil of central Northeast China. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2022, 41, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Dai, X.L.; Zheng, X.F.; Li, S.X.; Zhou, J.B. Net Nitrogen Balance in Soil under Different Cultivation Pattern and Nitrogen Application Rate in Semiarid Region. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2011, 17, 934–941. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, M.; Raven, J.A.; Lea, P.J. Do plants need nitrate? The mechanisms by which nitrogen form affects plants. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2013, 163, 174–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.D.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.H.; Yang, J.M. Research progress on the response and mechanism of maize (Zea mays L.) to nitrogen forms. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2024, 30, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.Z.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, L.; Bai, Y.; Lu, Y. Optimizing nitrogen input and nitrogen use efficiency through soil nitrogen balance in a long-term winter wheat-summer maize rotation system in North China. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 149, 126908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Xu, X.P.; Hou, Y.P.; Zhang, J.J.; Huang, S.H.; Ding, W.C.; Liu, Y.X.; He, P. Increasing yield and nitrogen use efficiency of spring maize in Northeast China through ecological intensification management. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2020, 26, 461–471. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Zhou, H.Z.; Chen, L.; Shen, Z.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, H.B. Pollution grade assessment of nitrogen leaching from farmland fertilizer in three northeastern provinces. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2018, 35, 405–411. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.Q.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, B.R.; Zhu, P.; Huang, S.M.; Bao, D.J.; Li, Y.T.; Song, H.B. Results from long-term fertilizer experiments in China: The risk of groundwater pollution by nitrate. NJAS—Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2011, 58, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.J.; Li, G.D. Nitrogen leaching and phosphorus accumulation in a perennial pasture after composted goat manure was topdressed and incorporated in the Three Gorges region. J. Soils Sediments 2012, 12, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.M.; Ru, S.H.; Sun, S.Y.; Zhao, O.Y.; Hou, L.M.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, G.Y. Impact of nitrogen application on nitrate nitrogen leaching in winter wheat and summer maize rotation system based on a literature analysis. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2022, 30, 116–125. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.L.; Yin, C.X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.Q.; Hou, Y.P.; Gao, H.J.; Xu, X.P. Input threshold of one-time application of nitrogen fertilizer to coordinate maize yield and environmental effects in thin layer black soil region of Northeast China. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2025, 33, 656–666. [Google Scholar]
- Velthof, G.L.; Lesschen, J.P.; Webb, J.; Pietrzak, S.; Miatkowski, Z.; Pinto, M.; Kros, J.; Oenema, O. The impact of the Nitrates Directive on nitrogen emissions from agriculture in the EU-27 during 2000−2008. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468/469, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Chen, X.P.; Cui, Z.L. Estimated reactive nitrogen losses for intensive maize production in China. Agriculture. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 197, 293−300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.S.; Kou, C.L.; Wang, X.F.; Li, T.K.; Wang, H.Y. Effects of nitrogen application on nitrogen and phosphorus leaching in fluvo-aquic soil on a winter wheat-summer maize rotation farmland. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2021, 29, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Jemison, J.M.; Fox, R.H. Nitrate leaching from nitrogen-fertilized and manured corn measured with zero-tension pan lysimeters. J. Environ. Qual. 1994, 23, 337–343. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.J.; Ju, X.T.; Pan, J.R. Nitrogen balance and apparent loss in winter wheat and summer maize rotation system. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2002, 39, 228–237. [Google Scholar]
- Hofma, G. Nutrient Management Legislation in Eruopean Countries. NUMALEC Report, 1999, Concerted Action Fair 6-C98-4215.
- Zhong, Q.; Ju, X.T.; Zhang, F.S. Analysis of environmental endurance of winter wheat/summer maize rotation system to nitrogen in North China Plain. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2006, 12, 285–293. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.M. The Variety of Soil Nitrogen Under Different Cultivation Conditions in Maize continuous System of Jilin. Master’s Thesis, Jilin Agricultural University, Changchun, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, X.T. Improvement and validation of theoretical N rate (TNR)—discussing the methods for N fertilizer recommendation. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2015, 52, 249–261. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; He, C.E.; Ge, X.Y.; Ou-Yang, Z. Effects of straw returning to field on soil inorganic nitrogen, enzyme activity and crop yield. Chin. J. Ecol. Agric. 2016, 24, 1633–1642. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.G.; Yang, L.Z.; Pi, J.H. Soil fertility evolution nutrient balance and reasonable fertilization in paddy field in southern area of Jiangsu Province. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 14, 1889–1892. [Google Scholar]
- Di, H.J.; Zhang, R.L.; Wu, S.X.; Zhang, H.Z.; Zhang, W.L. Analysis of fertilizer input and nutrient balance of farmland in Taihu watershed. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2008, 5, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X.J.; Fu, W.B.; Zhu, L.Q.; Chen, C.Q.; Bian, X.M. Fertilizer Application and Nutrient Balance Under Different Cropping Systems in Taihu Lake Region. Jiangsu Province. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2011, 27, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. Spring Maize and Different Soil Fertilities Nitrogen Optimization Technology. Master’s Thesis, Shanxi University, Taiyuan, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.J.; Wang, L.; Cheng, S.; Liu, J.Z.; Wang, Y.L.; Pang, N.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, S.M.; Ren, J.; Cai, H.G. Suitable nitrogen application rate for spring maize under full straw mulching in black soil area of central Jilin Province. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2022, 28, 835–844. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Z.P.; Deng, N.Z.; Song, Q.L.; Li, Z.T. Decomposing characteristics of maize straw returning in Songnen Plain in long-time located experiment. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agricultural-Chemical Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.N.; Li, S.Q.; Li, S.X. Utilization Rate of Fertilizer N and Dynamic Changes of Soil NO3-N in Summer Maize Field in Semi-humidarea of North West China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 19, 799–806. [Google Scholar]
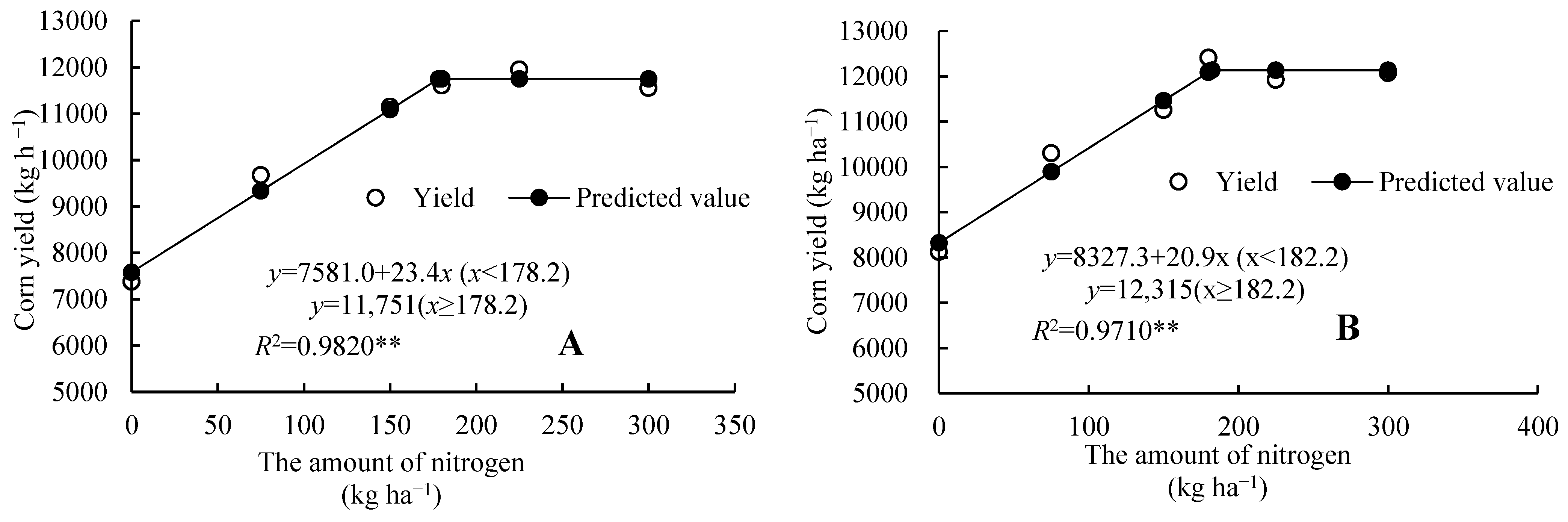
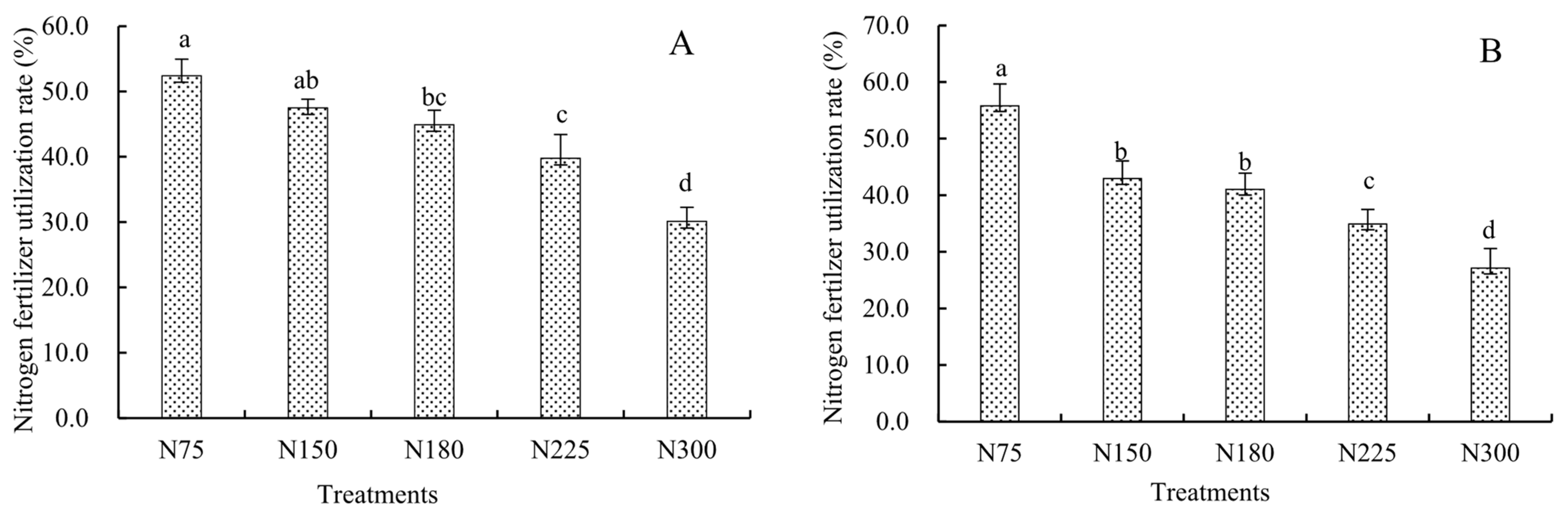


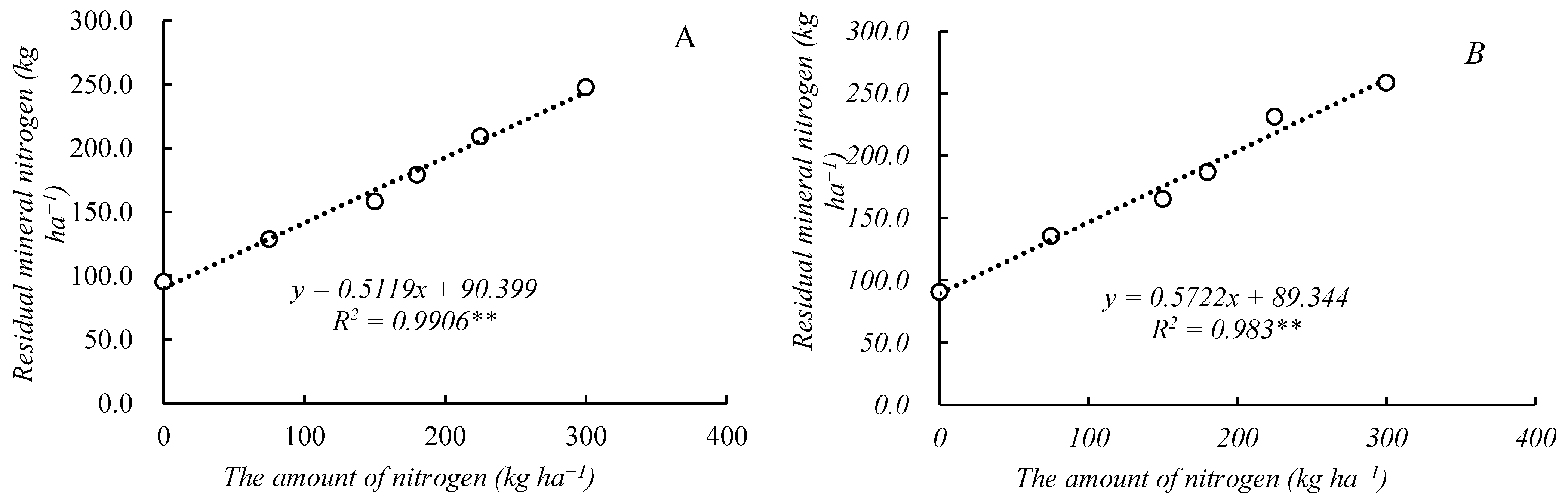
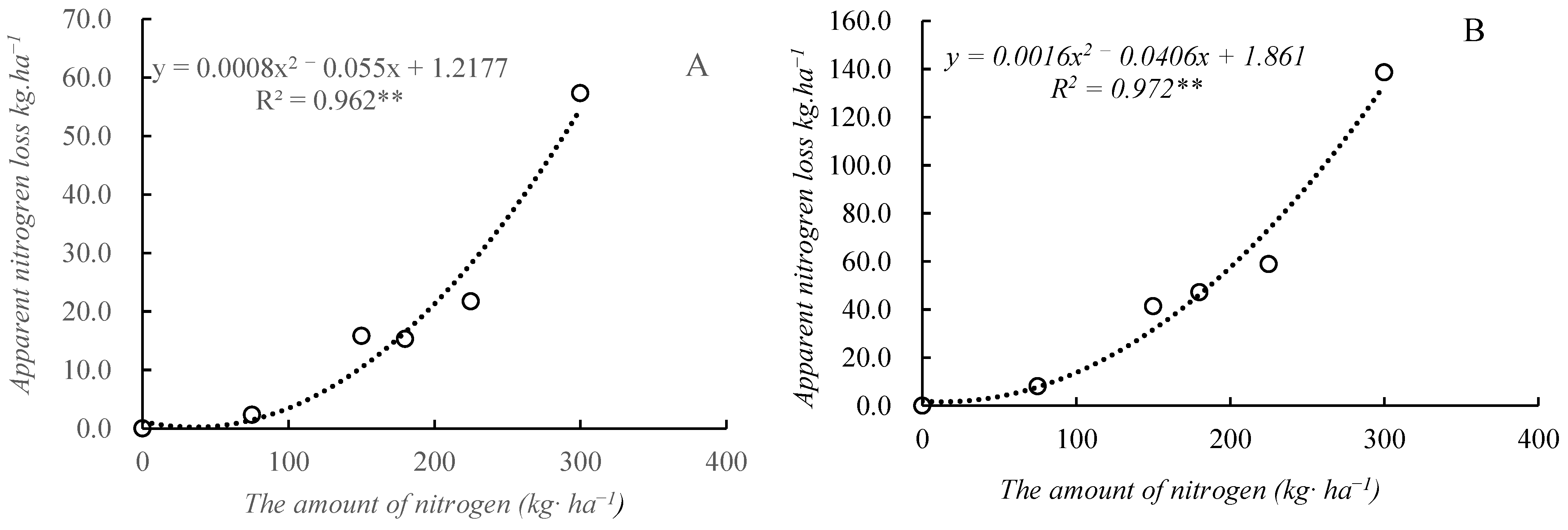


| Year | Treatment | Yield/ (kg·ha−1) | Increase Production/ (kg·ha−1) | Increase Rate/ % | Increase Economic Benefits/ (CNY·ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | N0 | 7376 d | — | — | — |
| N75 | 9671 c | 2295 c | 31.11 c | 4101 c | |
| N150 | 11150 b | 3774 b | 51.17 b | 6570 b | |
| N180 | 11605 ab | 4229 ab | 57.33 ab | 7284 a | |
| N225 | 11949 a | 4573 a | 62.00 a | 7679 a | |
| N300 | 11552 ab | 4176 ab | 56.62 ab | 6395 b | |
| 2024 | N0 | 8124 d | — | — | — |
| N75 | 10301 c | 2177.2 c | 26.80 c | 2065 d | |
| N150 | 11259 b | 3134.7 b | 38.58 b | 3074 c | |
| N180 | 12436 a | 4287.9 a | 53.08 a | 4618 a | |
| N225 | 11922 a | 3798.1 a | 46.75 a | 3648 b | |
| N300 | 12071 a | 3946.9 a | 48.58 a | 3461 b |
| Year | Items | N0 | N75 | N150 | N180 | N225 | N300 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | Input | (I) Nitrogen rate | 0 | 75 | 150 | 180 | 225 | 300 |
| (II) Initial mineral nitrogen | 162.2 | 162.2 | 162.2 | 162.2 | 162.2 | 162.2 | ||
| (III) Net nitrogen mineralization | 55.6 | 55.6 | 55.6 | 55.6 | 55.6 | 55.6 | ||
| (IV) Nitrogen release from straw | 30.1 | 30.1 | 30.1 | 30.1 | 30.1 | 30.1 | ||
| Total input (I + II + III + IV) | 247.9 | 322.9 | 397.9 | 427.9 | 472.9 | 547.9 | ||
| Output | (V) Nitrogen uptake by maize | 122.5 c | 161.8 b | 193.7 a | 203.3 a | 211.9 a | 212.8 a | |
| (VI) Residual mineral nitrogen | 95.3 e | 128.7 d | 158.3 c | 179.3 c | 209.2 b | 247.7 a | ||
| (VII) Apparent nitrogen loss | 0 | 2.3 d | 15.8 c | 15.3 c | 21.7 b | 57.3 a | ||
| Nitrogen surplus (VI + VII) | 95.3 e | 131.0 d | 174.1 c | 194.5 c | 230.9 b | 305.0 a | ||
| 2024 | Input | (I) Nitrogen rate | 0 | 75 | 150 | 180 | 225 | 300 |
| (II) Initial mineral nitrogen | 132.5 | 152.3 | 162.8 | 169.6 | 185.5 | 220.2 | ||
| (III) Net nitrogen mineralization | 68.9 | 68.9 | 68.9 | 68.9 | 68.9 | 68.9 | ||
| (IV) Nitrogen release from straw | 39.1 | 45.8 | 47.8 | 48.2 | 46.6 | 43.9 | ||
| Total input (I + II + III + IV) | 240.5 | 342.0 | 429.4 | 466.6 | 526.0 | 633.0 | ||
| Output | (V) Nitrogen uptake by maize | 110.6 c | 152.5 b | 175.0 ab | 184.5 a | 189.2 a | 191.9 a | |
| (VI) Residual mineral nitrogen | 90.8 d | 135.6 c | 165.2 bc | 186.8 b | 231.3 a | 258.6 a | ||
| (VII) Apparent nitrogen loss | 0 | 8.1 d | 41.4 c | 47.2 bc | 58.9 b | 138.6 a | ||
| Nitrogen surplus (VI + VII) | 90.8 e | 143.7 d | 206.6 c | 234.0 c | 290.2 b | 397.2 a | ||
| Treatments | 2023 | 2024 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount of Straw Input (kg·ha−1) | Nitrogen Content of Straw (%) | Nitrogen from Straw (kg·ha−1) | Amount of Straw Input (kg·ha−1) | Nitrogen Content of Straw (%) | Nitrogen from Straw in 2023 (kg·ha−1) | Nitrogen from Straw in 2022 (kg·ha−1) (II) | Nitrogen from Straw (kg·ha−1) (I + II) | |
| 0 | 10,000 | 0.571 | 30.1 | 9300 | 0.589 | 28.8 | 10.3 | 39.1 |
| N75 | 10,000 | 0.571 | 30.1 | 10,762 | 0.627 | 35.5 | 10.3 | 45.8 |
| N150 | 10,000 | 0.571 | 30.1 | 11,200 | 0.636 | 37.5 | 10.3 | 47.8 |
| N180 | 10,000 | 0.571 | 30.1 | 11,750 | 0.612 | 37.9 | 10.3 | 48.2 |
| N225 | 10,000 | 0.571 | 30.1 | 11,800 | 0.585 | 36.3 | 10.3 | 46.6 |
| N300 | 10,000 | 0.571 | 30.1 | 11,700 | 0.545 | 33.6 | 10.3 | 43.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, J.; Liu, S.; Hao, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, Y.; Xing, Z.; Guo, W. Effects of Different Nitrogen Fertilizer Rates on Spring Maize Yield and Soil Nitrogen Balance Under Straw Returning Conditions of Cold Regions. Plants 2025, 14, 3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193087
Ji J, Liu S, Hao X, Zheng Y, Zhao Y, Xia Y, Xing Z, Guo W. Effects of Different Nitrogen Fertilizer Rates on Spring Maize Yield and Soil Nitrogen Balance Under Straw Returning Conditions of Cold Regions. Plants. 2025; 14(19):3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193087
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Jinghong, Shuangquan Liu, Xiaoyu Hao, Yu Zheng, Yue Zhao, Yuqi Xia, Zhanqiang Xing, and Wei Guo. 2025. "Effects of Different Nitrogen Fertilizer Rates on Spring Maize Yield and Soil Nitrogen Balance Under Straw Returning Conditions of Cold Regions" Plants 14, no. 19: 3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193087
APA StyleJi, J., Liu, S., Hao, X., Zheng, Y., Zhao, Y., Xia, Y., Xing, Z., & Guo, W. (2025). Effects of Different Nitrogen Fertilizer Rates on Spring Maize Yield and Soil Nitrogen Balance Under Straw Returning Conditions of Cold Regions. Plants, 14(19), 3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193087





