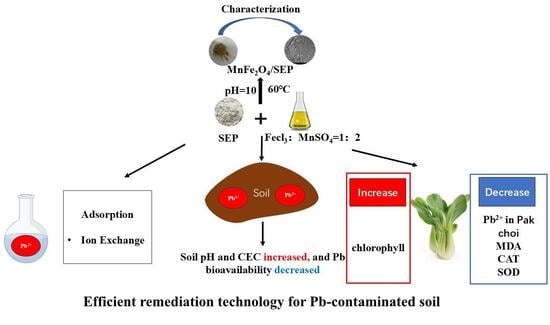
Lead Immobilization in Soil and Uptake Reduction in Brassica chinensis Using Sepiolite-Supported Manganese Ferrite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Adsorbent Characterization
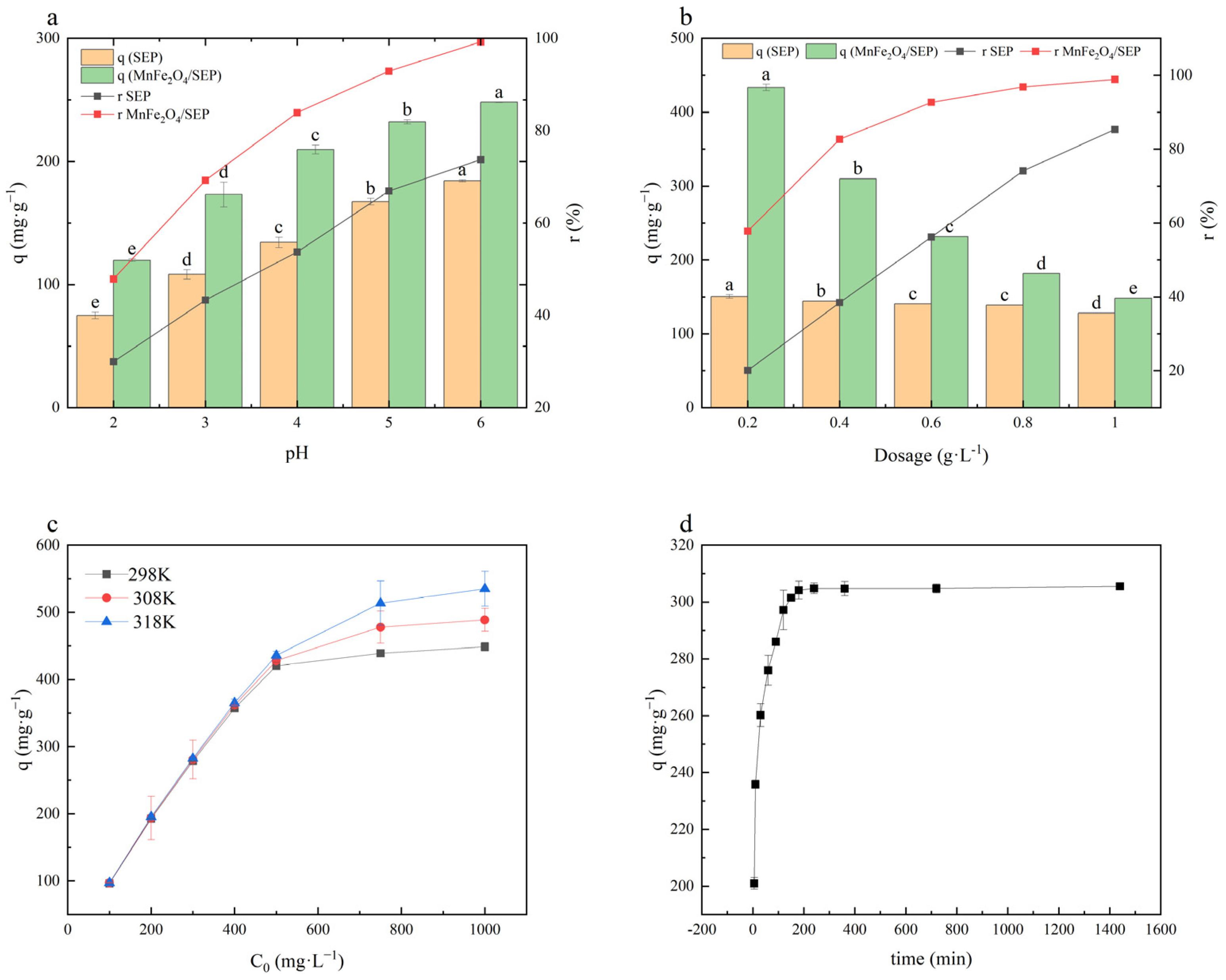
2.2. Adsorption Properties of MnFe2O4/SEP
2.3. Adsorption Kinetics
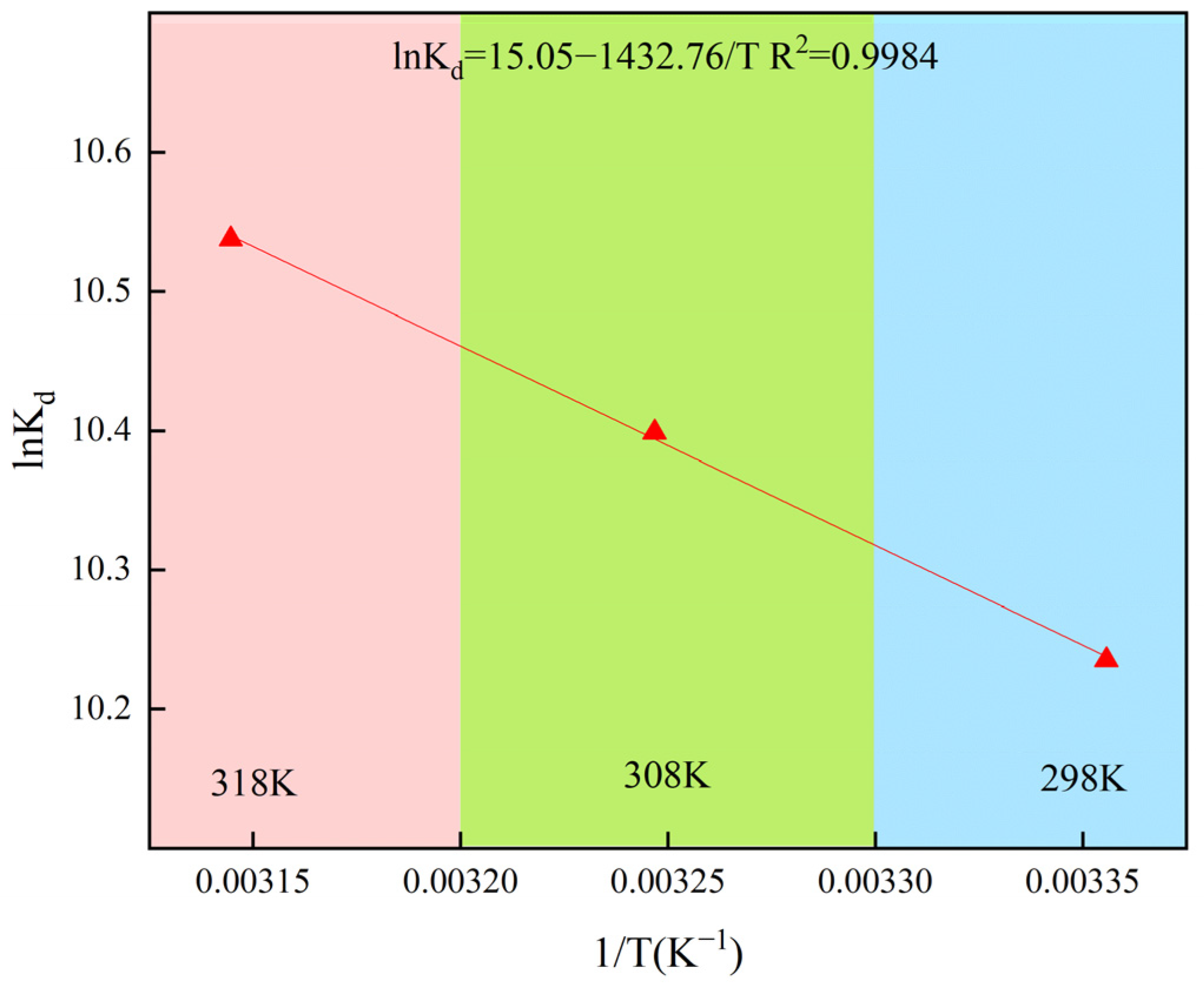
2.4. Thermodynamic Study
2.5. Reusability Assessment
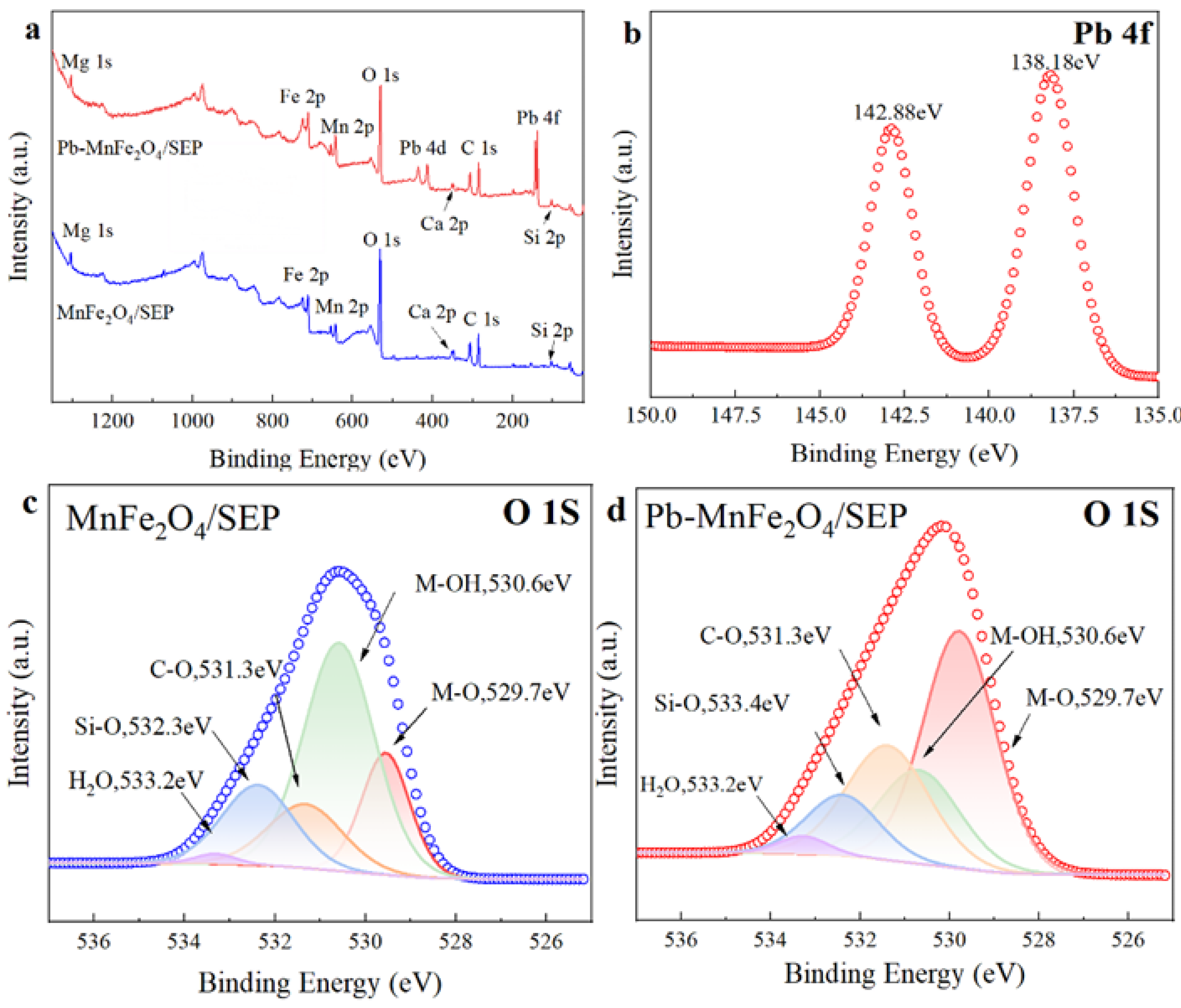
2.6. Adsorption Mechanism
2.7. Application of MnFe2O4/SEP in Pb-Contaminated Soil
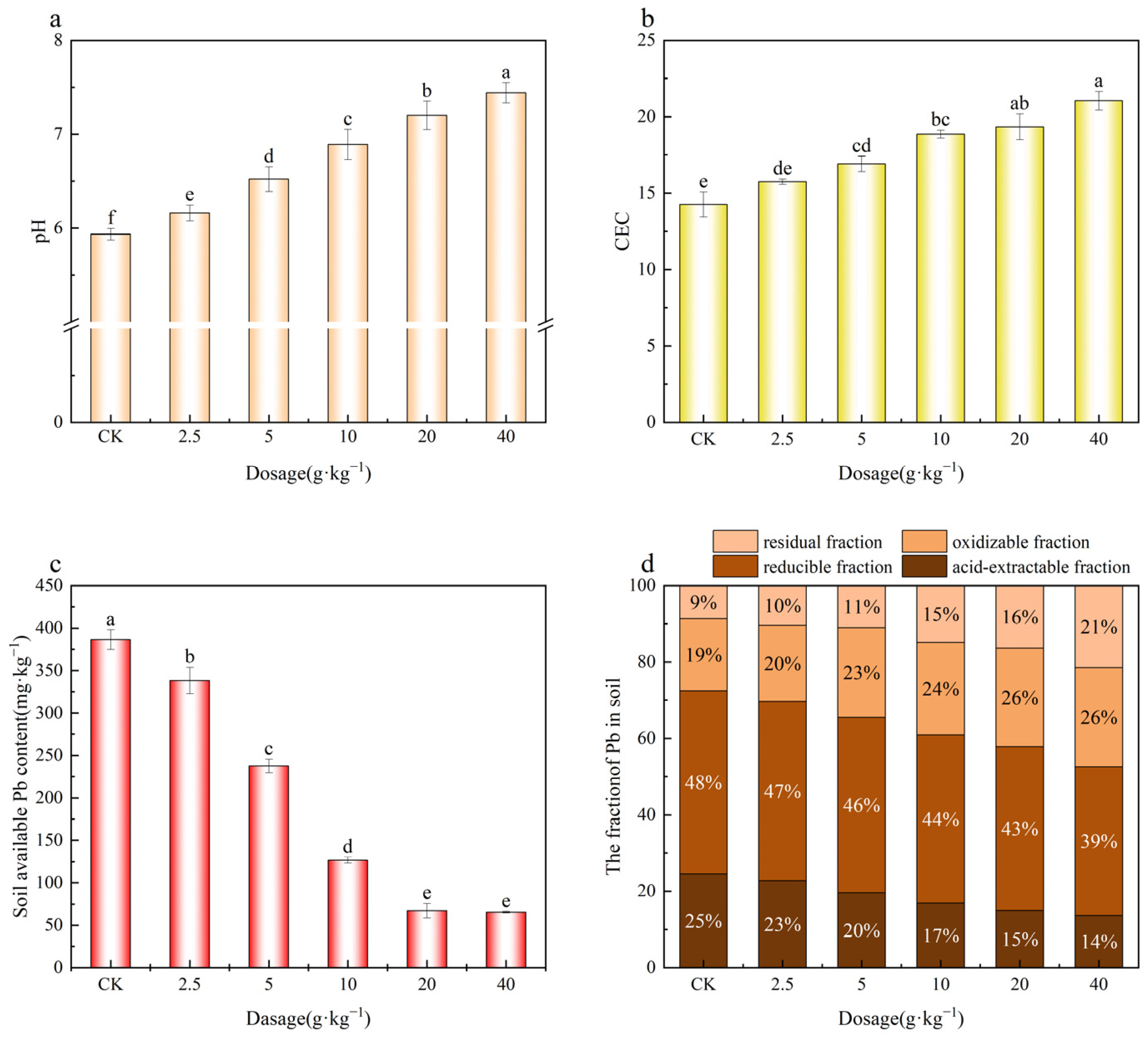
2.7.1. Effects of MnFe2O4/SEP on Soil pH, CEC, and Available Pb Content
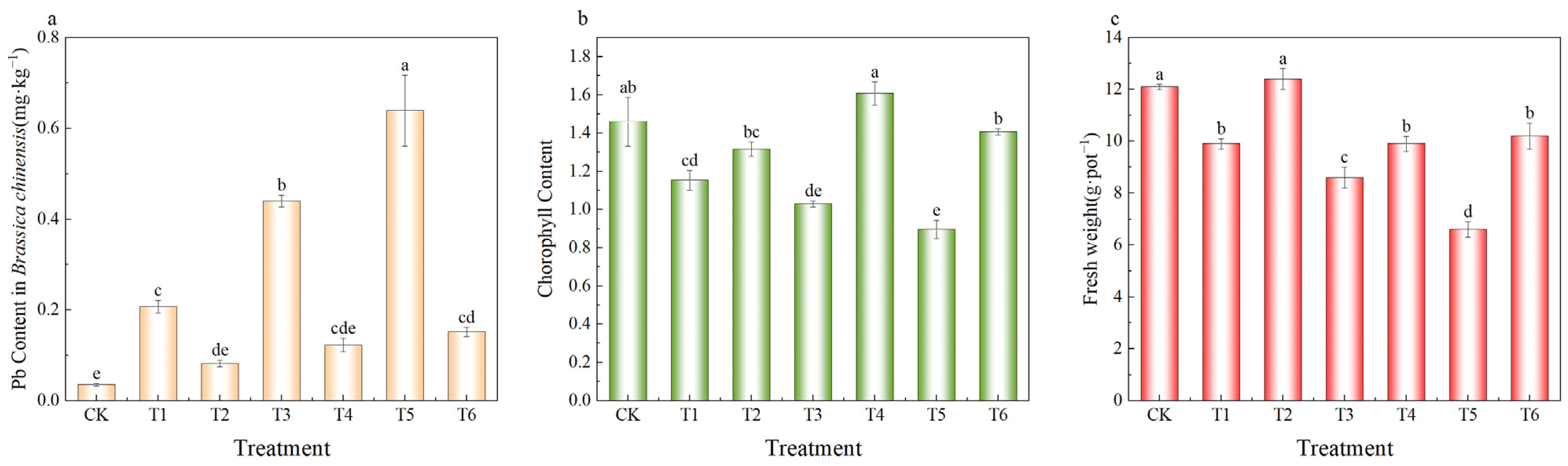
2.7.2. Effect of MnFe2O4/SEP on Pb2+ Uptake, Chlorophyll Content and Yield in Brassica chinensis
2.7.3. Effect of MnFe2O4/SEP on MDA and Antioxidant Enzymes System in Brassica chinensis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Preparation and Characterization
3.2. Synthesis of MnFe2O4/SEP and Characterization
3.3. Adsorption Experiments: SEP and MnFe2O4/SEP Efficiency in Removal of Pb2+
3.4. Regeneration and Reuse Efficiency of MnFe2O4/SEP
3.5. Soil Incubation Experiment
3.6. Pot Experiments for Remediation Assessment
3.7. Statistics and Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, O.V.; Labana, S.; Pandey, G.; Budhiraja, R.; Jain, R.K. Phytoremediation: An overview of metallic ion decontamination from soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 61, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; Ma, W.; Wang, W. The heavy mental lead pollution progress and control measures of the vegetables in China. Process. Agric. Prod. 2012, 9, 105–107+124. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, R.; Hu, H.; Fu, Q.; Li, Z.; Xing, Z.; Ali, U.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y. Remediation of Pb, Cd, and Cu contaminated soil by co-pyrolysis biochar derived from rape straw and orthophosphate: Speciation transformation, risk evaluation and mechanism inquiry. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, F.; Niu, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, R.; Sun, W.; He, D. Efficient removal of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solution by modified red mud. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Peng, L.; Liao, Z.; Zhuo, Z.; Shahzad, A.; Ifthikar, J.; Zhao, M.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z. Selective removal of heavy metals by hydrotalcites as adsorbents in diverse wastewater: Different intercalated anions with different mechanisms. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 1112–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Meng, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, F.; Brookes, P. Zeolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: New findings on simultaneous adsorption of Cd(II), Pb(II), and As(III) in aqueous solution and soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, H.; Wen, T.; Kang, S.; Song, G.; Song, S.; Komarneni, S. Removal of heavy metals and dyes by clay-based adsorbents: From natural clays to 1D and 2D nano-composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, F.; Selvaraj, M.; Zain, J.; Banat, F.; Abu haija, M. Polyethylenimine modified graphene oxide hydrogel composite as an efficient adsorbent for heavy metal ions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Zhang, P.; Hu, Y.; Jin, F.; Liu, Y.; Cai, S.; Song, Z.; Zhang, X.; Nadezhda, T.; Guo, Z.; et al. Combined application of biochar and nano-zeolite enhanced cadmium immobilization and promote the growth of Pak Choi in cadmium contaminated soil. NanoImpact 2022, 28, 100421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, W.; Sun, P.; Li, Y.; Han, J. Functionalized biochar-supported magnetic MnFe2O4 nanocomposite for the removal of Pb(ii) and Cd(ii). RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Meng, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, Z.; Yan, N.; Li, Y.; Teng, M. Magnetic recoverable MnFe2O4/cellulose nanocrystal composites as an efficient catalyst for decomposition of methylene blue. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 122, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, I.; Abu Haija, M.; Kannan, P.; Banat, F. Adsorptive Removal of Methylene Blue from Water Using High-Performance Alginate-Based Beads. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, F.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Chen, L. Simple hydrothermal synthesis of magnetic MnFe2O4-sludge biochar composites for removal of aqueous Pb2+. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 156, 105173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otunola, B.O.; Ololade, O.O. A review on the application of clay minerals as heavy metal adsorbents for remediation purposes. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 18, 100692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; Bi, D. The removal of chromium (VI) and lead (II) from groundwater using sepiolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron (S-NZVI). Chemosphere 2015, 138, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; He, J.; Zhu, L.; Guo, S.; Chen, H. A novel utilization of raw sepiolite: Preparation of magnetic adsorbent directly based on sol-gel for adsorption of Pb(II). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 77448–77461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wu, H.; Xu, L.; Meng, J.; Lu, J.; Zhou, H.; Huo, X.; Huang, L. An insitu ATR-FTIR study of mixed collectors BHA/DDA adsorption in ilmenite-titanaugite flotation system. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2021, 31, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, P.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Feng, S.; Dang, X. Immobilization of cadmium in soil and improved iron concentration and grain yields of maize (Zea mays L.) by chelated iron amendments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 53161–53170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, N.; Yang, L.Y.; Wang, Y.G.; Yu, D.; Ouyang, X.K. Facile Fabrication of ZIF-8/Calcium Alginate Microparticles for Highly Efficient Adsorption of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 6394–6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonietta, M.; Olimpia, T.; Federico, R.; Giancarlo, C.; Olga, S.; Michele, P.; Vincenzo, V.; Serena, E. Enhanced adsorptive removal of chloramphenicol from water by highly defective MOF-808 nanocrystals fine-tuned with reliable synthesis strategy: Mechanism insight by equilibrium, kinetics and molecular dynamics simulations. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 15, 504. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, E.B.; Evgeny, V.G.; Irina, V.B.; Anastassia, E.K.; Shilpi, A.; Alexey, G.K.; Vinod, K.G. Adsorption of heavy metals on conventional and nanostructured materials for wastewater treatment purposes: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Peng, Z.; Xu, R.; et al. Adsorption of Pb(II) by tourmaline-montmorillonite composite in aqueous phase. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 575, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Luo, X.; Liu, C.; You, S.; Rad, S.; Qin, L. Effective adsorption of Pb(ii) from wastewater using MnO2 loaded MgFe-LD(H)O composites: Adsorption behavior and mechanism. RSC Adv. 2023, 28, 19288–19300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani, Y.A.; Ghoreishi, S.M.; Ghani, M. Derived N-doped carbon through core-shell structured metal-organic frameworks as a novel sorbent for dispersive solid phase extraction of Cr(III) and Pb(II) from water samples followed by quantitation through flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuković, G.D.; Marinković, A.D.; Škapin, S.D.; Ristić, M.D.; Aleksić, R.; Perić-Grujić, A.A.; Uskoković, P.S. Removal of lead from water by amino modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Dai, X.; Jian, T.; Tian, W. Enhanced adsorption and reduction of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by sulfide-modified nanoscale zerovalent iron: Characterization, kinetics and mechanisms. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 170, 113496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zain, Z.M.; Abdulhameed, A.S.; Jawad, A.H.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Yaseen, Z.M. A pH-Sensitive Surface of Chitosan/Sepiolite Clay/Algae Biocomposite for the Removal of Malachite Green and Remazol Brilliant Blue R Dyes: Optimization and Adsorption Mechanism Study. J. Polym. Environ. 2023, 31, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Liang, X.; Qin, X.; Sun, Y. Immobilization Remediation Effects of Sepiolite and Phosphate on Cadmium and Lead Compound Contaminated Soil. J. Saf. Environ. 2010, 10, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Rathika, R.; Srinivasan, P.; Alkahtani, J.; Al-Humaid, L.A.; Alwahibi, M.S.; Mythili, R.; Selvankumar, T. Influence of biochar and EDTA on enhanced phytoremediation of lead contaminated soil by Brassica juncea. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbinger, K.; Tausz, M.; Wonisch, A.; Soja, G.; Sorger, A.; Grill, D. Complex interactive effects of drought and ozone stress on the antioxidant defence systems of two wheat cultivars. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2002, 40, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannata, M.G.; Carvalho, R.; Bertoli, A.C.; Augusto, A.S.; Bastos, A.R.R.; Carvalho, J.G.; Freitas, M.P. Effects of Cadmium and Lead on Plant Growth and Content of Heavy Metals in Arugula Cultivated in Nutritive Solution. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2013, 44, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labidi, S.; Firmin, S.; Verdin, A.; Bidar, G.; Laruelle, F.; Douay, F.; Shirali, P.; Fontaine, J.; Lounès-Hadj Sahraoui, A. Nature of fly ash amendments differently influences oxidative stress alleviation in four forest tree species and metal trace element phytostabilization in aged contaminated soil: A long-term field experiment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 138, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 10390; Soil, Treated Biowaste and Sludge—Determination of pH. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Lu, R. Soil Agrochemistry Analysis Protocols; China Agriculture Science Press: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Sun, Q.; Xu, J.; Liu, B.; Li, J. Explore on Best Digestion Conditions of the United Digestive Solution in Soil. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2012, 27, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y.; Yang, X.; Xu, Z.; Hu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Wan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Yang, J.; Tsang, D.C.W. Fabrication of sustainable manganese ferrite modified biochar from vinasse for enhanced adsorption of fluoroquinolone antibiotics: Effects and mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality—Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China; State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Ju, W.; Huang, R.; Liu, R.; Du, M. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of soil from an abandoned site for lead smelting of waste lead batteries. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2023, 13, 769–777. [Google Scholar]
- Pardo, R.; Vega, M.; Barrado, E.; Castrillejo, Y.; Sánchez, I. Three-way principal component analysis as a tool to evaluate the chemical stability of metal bearing residues from wastewater treatment by the ferriteprocess. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipiak-Szok, A.; Kurzawa, M.; Szłyk, E. Determination of toxic metals by ICP-MS in Asiatic and European medicinal plants and dietary supplements. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 30, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| T(K) | Langmuir | D-R | Temkin | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax (mg·g−1) | KL (L·mg−1) | R2 | qmax (mg·g−1) | E (kJ·mol−1) | R2 | A (L·mg−1) | b (kJ·mol−1) | R2 | |
| 298 | 458.72 | 0.09 | 0.99 | 368.5 | 0.37 | 0.88 | 2.26 | 28.01 | 0.91 |
| 308 | 500.00 | 0.08 | 0.99 | 380.0 | 0.43 | 0.86 | 1.94 | 30.06 | 0.95 |
| 318 | 549.45 | 0.07 | 0.99 | 413.5 | 0.49 | 0.87 | 1.83 | 31.80 | 0.97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geng, F.; Lyu, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, J.; Bol, R.; Zhang, P.; Lynch, I.; Dang, X. Lead Immobilization in Soil and Uptake Reduction in Brassica chinensis Using Sepiolite-Supported Manganese Ferrite. Plants 2025, 14, 3077. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193077
Geng F, Lyu Y, Ma L, Zhou Y, Shi J, Bol R, Zhang P, Lynch I, Dang X. Lead Immobilization in Soil and Uptake Reduction in Brassica chinensis Using Sepiolite-Supported Manganese Ferrite. Plants. 2025; 14(19):3077. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193077
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeng, Fengzhuo, Yaping Lyu, Liansheng Ma, Yin Zhou, Jiayue Shi, Roland Bol, Peng Zhang, Iseult Lynch, and Xiuli Dang. 2025. "Lead Immobilization in Soil and Uptake Reduction in Brassica chinensis Using Sepiolite-Supported Manganese Ferrite" Plants 14, no. 19: 3077. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193077
APA StyleGeng, F., Lyu, Y., Ma, L., Zhou, Y., Shi, J., Bol, R., Zhang, P., Lynch, I., & Dang, X. (2025). Lead Immobilization in Soil and Uptake Reduction in Brassica chinensis Using Sepiolite-Supported Manganese Ferrite. Plants, 14(19), 3077. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193077