Codon Usage Bias of the Polyphenol Oxidase Genes in Camellia sinensis: A Comprehensive Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patterns of Codon Composition
2.2. Codon Usage Indices Analysis
2.3. RSCU and RFSC Analyses and Determination of High-Frequency Codons
2.4. Determination of Optimal Codons
2.5. Codon Usage Frequency Analysis
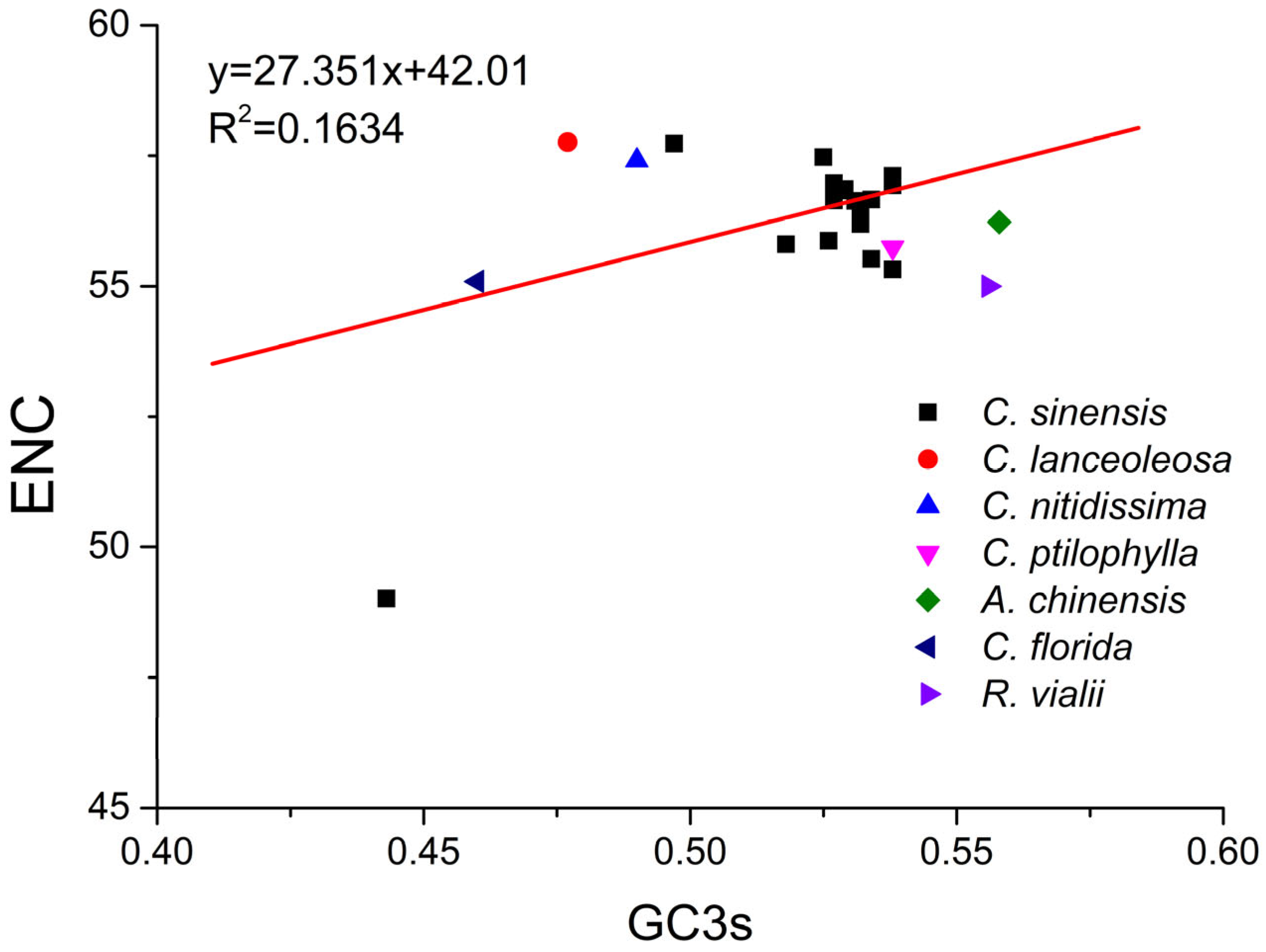
2.6. ENC Plot Analysis of PPO Genes
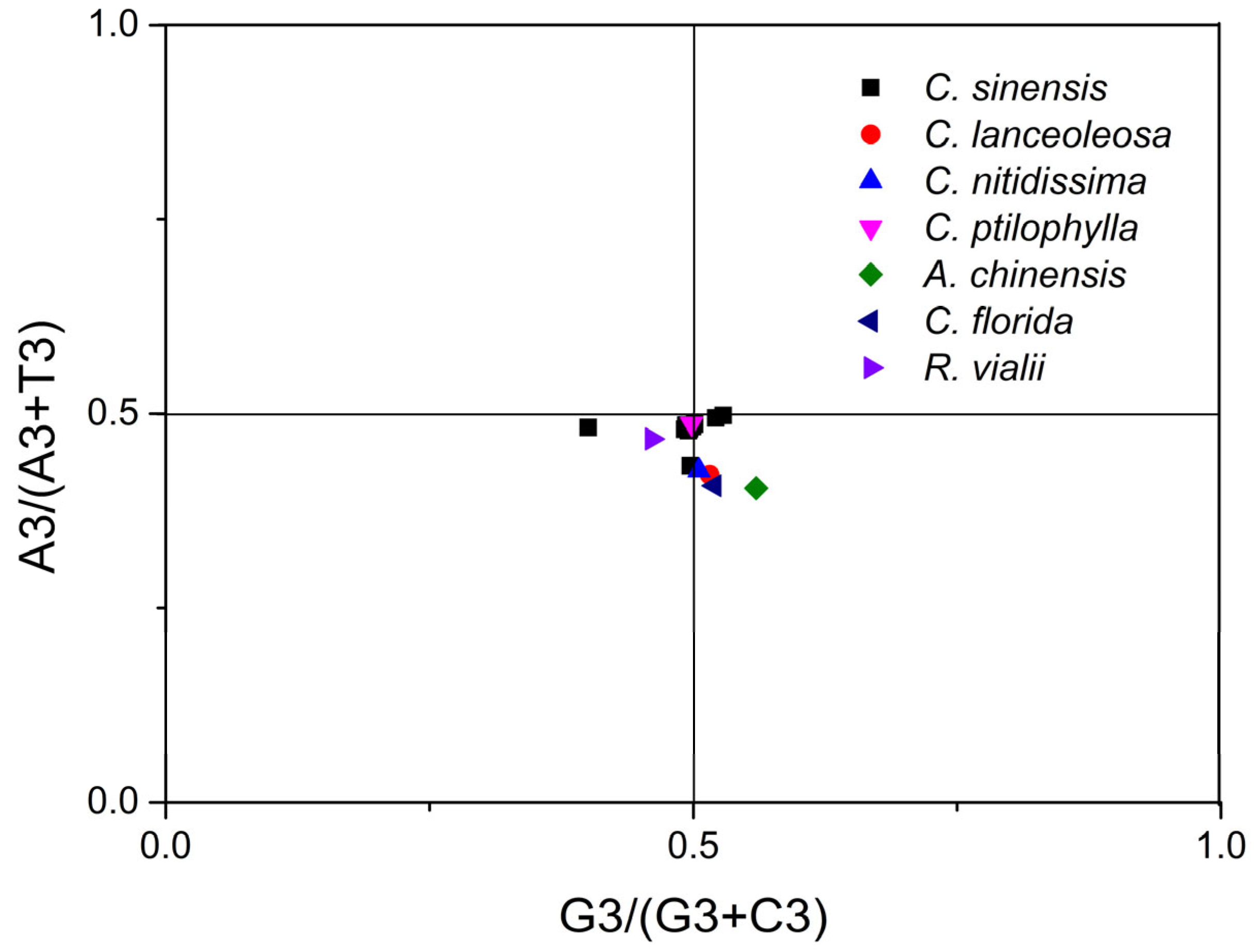
2.7. PR2 Plot Analysis
2.8. Neutrality Plot Analysis
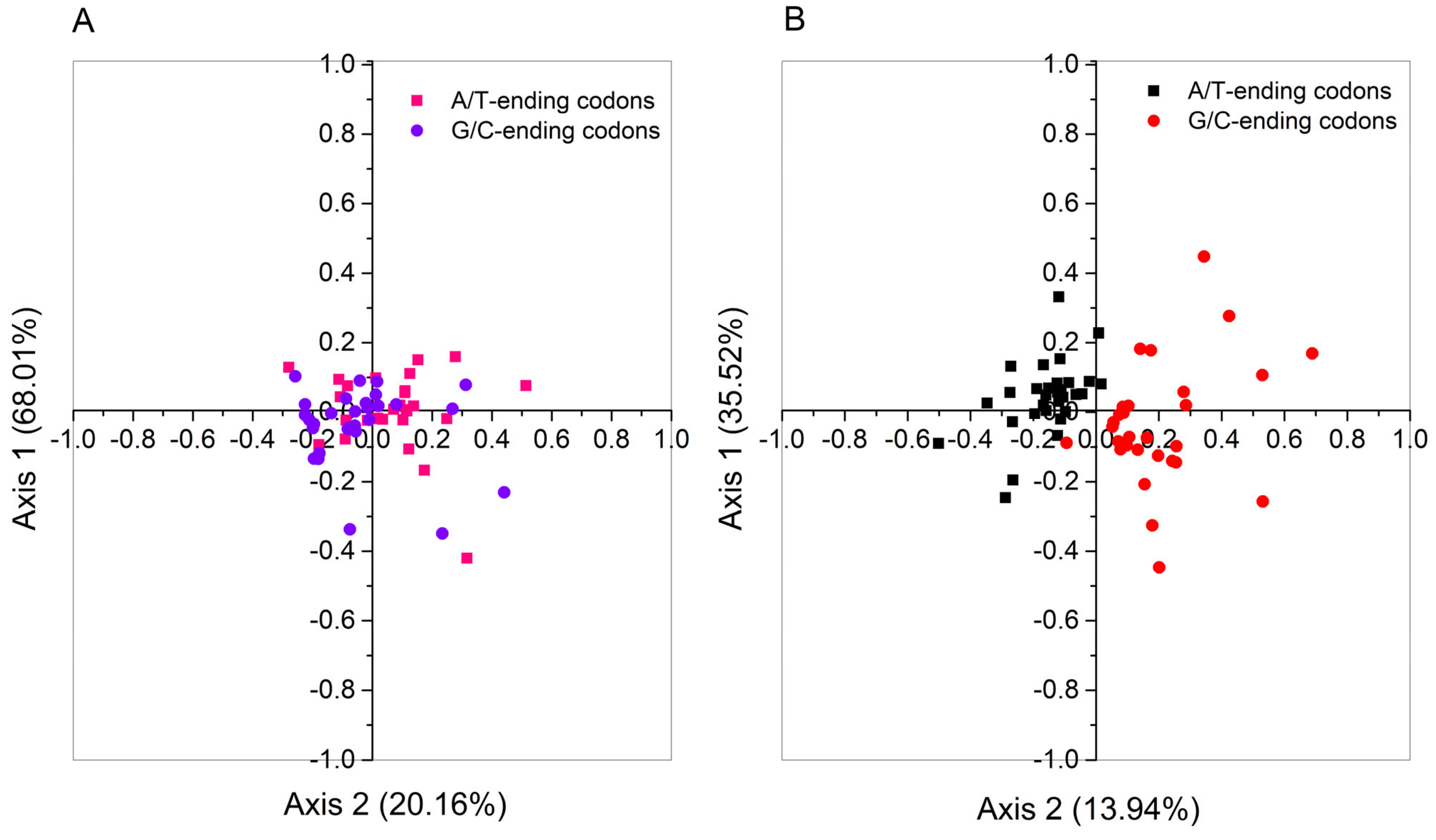
2.9. Correspondence Analysis of PPO Genes
2.10. Amino Acid Usage Frequency
2.11. Impact of Codon Usage Bias on Gene Expression
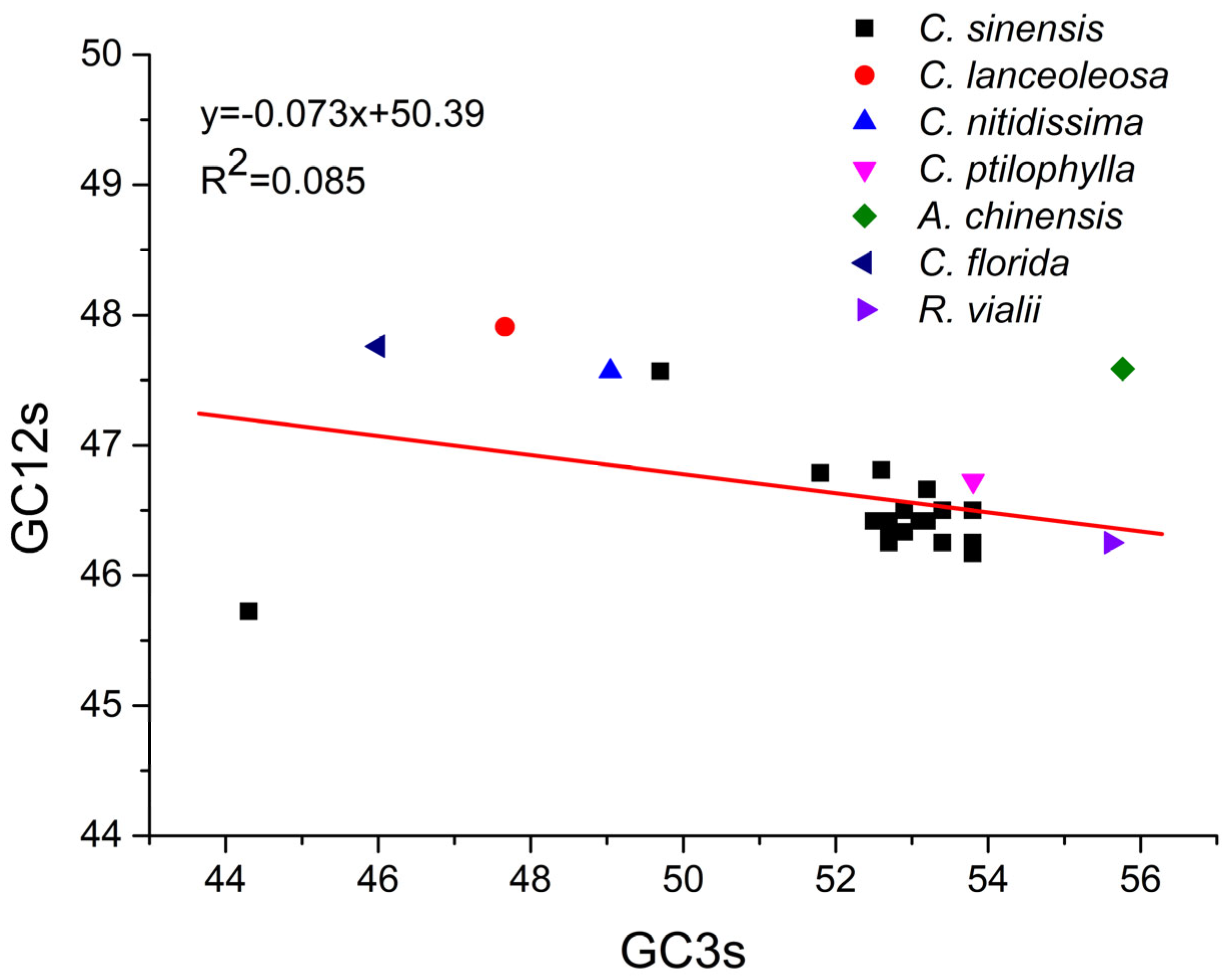
2.12. Correlation Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sequence Retrieval and Nucleotide Composition Analysis
4.2. Codon Adaptation Index (CAI) and Codon Bias Index (CBI)
4.3. Grand Average of Hydropathy (GRAVY) and Aromaticity (AROMA) Analysis
4.4. Analyses of Relative Synonymous Codon Usage (RSCU) and Relative Synonymous Codon Usage Frequency (RFSC)
4.5. Optimal Codons Analysis
4.6. Comparative Analysis of Codon Utilization Frequency
4.7. ENC Plot Analysis
4.8. Paritiy Rule 2 (PR2) Plot Analysis
4.9. Neutrality Analysis
4.10. Correspondence Analysis (COA)
4.11. Gene Expression Level Analysis
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, C.; Lin, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z. Metabolomics Analysis of Camellia sinensis with Respect to Harvesting Time. Food Res. Int. 2020, 128, 108814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, S.M.; Thambi, P.T.; Kuttan, R.; Nishigaki, I. Beneficial Effects of Green Tea: A Literature Review. Chin. Med. 2010, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.F.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Wang, X.C.; Yao, M.Z.; Luo, D.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; et al. Global Transcriptome and Gene Regulation Network for Secondary Metabolite Biosynthesis of Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis). BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, V.L.; Jeong, W.S. Cellular Defensive Mechanisms of Tea Polyphenols: Structure-Activity Relationship. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Rani, A.; Paul, A.; Dutt, S.; Joshi, R.; Gulati, A.; Ahuja, P.S.; Kumar, S. Differential Display Mediated Cloning of Anthocyanidin Reductase Gene from Tea (Camellia sinensis) and Its Relationship with the Concentration of Epicatechins. Tree Physiol. 2009, 29, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Yin, J. Recent Advances Regarding Polyphenol Oxidase in Camellia sinensis: Extraction, Purification, Characterization, and Application. Foods 2024, 13, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.G.; Zhang, S.; Xiong, L.G.; Zhou, J.H.; Huang, J.A.; Zhao, A.Q.; Liu, Z.H.; Liu, A.L. A Comprehensive Review of Polyphenol Oxidase in Tea (Camellia sinensis): Physiological Characteristics, Oxidation Manufacturing, and Biosynthesis of Functional Constituents. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 2267–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Ye, M.; Li, X.W.; Lin, S.B.; Sun, X.L. The Jasmonic Acid Pathway Positively Regulates the Polyphenol Oxidase-Based Defense against Tea Geometrid Caterpillars in the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis). J. Chem. Ecol. 2020, 46, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Bian, W.; Zeng, Z.; Sun, X.; Li, X. Two New Polyphenol Oxidase Genes of Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis) Respond Differentially to the Regurgitant of Tea Geometrid, Ectropis obliqua. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. A Code within the Genetic Code: Codon Usage Regulates Co-Translational Protein Folding. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Wu, J.; Fan, C.; Luo, Y.; Liu, J.; Deng, Z.; Li, Q. Comparative Analysis of Codon Usage Bias in the Chloroplast Genomes of Eighteen Ampelopsideae Species (Vitaceae). BMC Genom. Data 2024, 25, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Xin, C.; Xiao, Q.S.; Lin, Y.T.; Li, L.; Zhao, J.L. Codon Usage Bias in Chloroplast Genes Implicate Adaptive Evolution of Four Ginger Species. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1304264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Song, Y.; Jing, L. Analysis of Codon Usage Bias of WRKY Transcription Factors in Helianthus annuus. BMC Genom. Data 2022, 23, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhou, L.; Nie, J.; Wu, S.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Codon Usage Bias and Genetic Diversity in Chloroplast Genomes of Elaeagnus Species (Myrtiflorae: Elaeagnaceae). Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2023, 29, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, Y.; Wu, X.; Sun, N.; Man, Y.; Jing, Y. Codon Usage Bias Predicts the Functional MYB10 Gene in Populus. J. Plant Physiol. 2021, 265, 153491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Liu, S.; Zheng, H.; Li, B.; Qi, Q.; Wei, L.; Zhao, T.; He, J.; Sun, J. Non-Uniqueness of Factors Constraint on the Codon Usage in Bombyx mori. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Xu, W.; Lu, X.; Wang, L. Analysis of Codon Usage Bias of Chloroplast Genomes in Gynostemma Species. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2021, 27, 2727–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Xiao, M.; Huang, J.; Lou, Y.; Hu, F.; Fu, X.; Li, Y.; He, H.; Cheng, J. An Analysis of Codon Utilization Patterns in the Chloroplast Genomes of Three Species of Coffea. BMC Genom. Data 2023, 24, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, T.H.; Alqahtani, A.M.; Alqahtani, T.; Emran, T.B.; Aldahish, A.A.; Uddin, A. Analysis of Codon Usage of Speech Gene Foxp2 among Animals. Biology 2021, 10, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Alam, P.; Zheng, W.; Faizan, M. Genome Identification of the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis) ASMT Gene Family and Its Expression Analysis under Abiotic Stress. Genes 2023, 14, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liao, Z.; He, Y.; Li, L.; Liang, Z.; Sheng, Q.; Hong, G. Structural and Functional Organization of the MYC Transcriptional Factors in Camellia sinensis. Planta 2021, 253, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, B.; Uddin, A.; Chakraborty, S. Composition, Codon Usage Pattern, Protein Properties, and Influencing Factors in the Genomes of Members of the Family Anelloviridae. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Tong, C.; Shi, J. Analysis of Codon Usage Between Different Poplar Species. J. Genet. Genom. 2007, 34, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, G.; Xiao, G.; Wu, T.; Zhou, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Xia, G.; Wang, M. Alteration of Synonymous Codon Usage Bias Accompanies Polyploidization in Wheat. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 979902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Saif, M.; Khabar, K.S.A. UU/UA Dinucleotide Frequency Reduction in Coding Regions Results in Increased mRNA Stability and Protein Expression. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, L.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, T.; Hu, N.; Sun, J.; Zhou, W. Analysis of Synonymous Codon Usage Bias in the Chloroplast Genome of Five Caragana. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamolle, G.; Simón, D.; Iriarte, A.; Musto, H. Main Factors Shaping Amino Acid Usage Across Evolution. J. Mol. Evol. 2023, 91, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.Z.; Liu, S.; Zeng, Z.; Alemayehu, L.A.; Wei, W.; Guo, F.B. Amino Acid Compositions Contribute to the Proteins’ Evolution under the Influence of Their Abundances and Genomic GC Content. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, S.; He, D.; Liu, J.; He, X.; Lin, C.; Li, J.; Huang, Z.; Huang, L.; Nie, G.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Codon Usage Patterns in the Chloroplast Genomes of Fagopyrum Species. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriarte, A.; Lamolle, G.; Musto, H. Codon Usage Bias: An Endless Tale. J. Mol. Evol. 2021, 89, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Paul, K.; Roy, A. Codon Usage Signatures in the Genus Cryptococcus: A Complex Interplay of Gene Expression, Translational Selection and Compositional Bias. Genomics 2021, 113, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Shi, Z. Comparative Study on Codon Usage Patterns across Chloroplast Genomes of Eighteen Taraxacum Species. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, D.; Uddin, A.; Das, S.; Chakraborty, S. Mutation Pressure and Natural Selection on Codon Usage in Chloroplast Genes of Two Species in Pisum L. (Fabaceae: Faboideae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2019, 30, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Pan, L.L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Ding, Z.T. Codon Bias of the Gene for Chloroplast Glycerol-3-Phosphate Acyltransferase in Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 55, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, E.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Z.T.; Zhang, X.F.; Pan, L.L.; Zheng, C. Codon Usage Bias Analysis for the Spermidine Synthase Gene from Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 7368–7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.L.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.H.; Ding, Z.T.; Li, C. Analysis of Codon Use Features of Stearoyl-Acyl Carrier Protein Desaturase Gene in Camellia sinensis. J. Theor. Biol. 2013, 334, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, G.M.; Holmes, E.C. The Extent of Codon Usage Bias in Human RNA Viruses and Its Evolutionary Origin. Virus Res. 2003, 92, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.J.; Zhou, J.; Li, Z.F.; Wang, L.; Gu, X.; Zhong, Y. Comparative Analysis of Codon Usage Patterns among Mitochondrion, Chloroplast and Nuclear Genes in Triticum aestivum L. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2007, 49, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.P.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Z.T. Analysis of Synonymous Codon Usage in FAD7 Genes from Different Plant Species. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 1414–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clément, Y.; Sarah, G.; Holtz, Y.; Homa, F.; Pointet, S.; Contreras, S.; Nabholz, B.; Sabot, F.; Sauné, L.; Ardisson, M.; et al. Evolutionary Forces Affecting Synonymous Variations in Plant Genomes. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, F.; Tian, F.; Lu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yang, H.; Cui, G. Analysis of Codon Usage Patterns of the Chloroplast Genome in Delphinium grandiflorum L. Reveals a Preference for AT-Ending Codons as a Result of Major Selection Constraints. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Pan, Z.; Gao, S.; He, Y.; Xia, Q.; Jin, Y.; Yao, H. Analysis of Synonymous Codon Usage of Chloroplast Genome in Porphyra umbilicalis. Genes Genom. 2019, 41, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Huang, N.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, L.; Hui, L. Codon Usage Bias Analysis of the Chloroplast Genome of Cassava. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 151, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.L.; Ma, L.B.; Khan, M.S.; Zhang, X.X.; Xu, S.Q.; Xie, J.Y. Analysis of Codon Usage Patterns in Hirudinaria manillensis Reveals a Preference for GC-Ending Codons Caused by Dominant Selection Constraints. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S. Comparative Analysis of Codon Usage Bias in Six Eimeria Genomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvathy, S.T.; Udayasuriyan, V.; Bhadana, V. Codon Usage Bias. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 539–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotkin, J.B.; Kudla, G. Synonymous but Not the Same: The Causes and Consequences of Codon Bias. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 7152–7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoa, E.M.; Ribas de Pouplana, L. Speeding with Control: Codon Usage, TRNAs, and Ribosomes. Trends Genet. 2012, 28, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, P.M.; Li, W.H. The Codon Adaptation Index-a Measure of Directional Synonymous Codon Usage Bias, and Its Potential Applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15, 1281–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xu, M.; Yang, J.R.; Lu, J. Genome-Wide Impact of Codon Usage Bias on Translation Optimization in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Shao, Z.Q.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Hang, Y.Y.; Chen, J.Q. Optimal Codon Identities in Bacteria: Implications from the Conflicting Results of Two Different Methods. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demissie, E.A.; Park, S.Y.; Moon, J.H.; Lee, D.Y. Comparative Analysis of Codon Optimization Tools: Advancing toward a Multi-Criteria Framework for Synthetic Gene Design. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2025, 35, e2411066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Guo, L.; Fang, B. DNA Sequence Changes Resulting from Codon Optimization Affect Gene Expression in Pichia pastoris by Altering Chromatin Accessibility. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; You, H.; Chen, B.; Jia, L.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Ma, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, K.; et al. Specific Selection on XEG1 and XLP1 Genes Correlates with Host Range and Adaptability in Phytophthora. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.K.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, H.Y.; Tang, M.Q.; Xie, S.Q. Comparative Analysis of Codon Usage Patterns in Nuclear and Chloroplast Genome of Dalbergia (Fabaceae). Genes 2023, 14, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xing, H.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, X.; Saeed, M.; Tao, J.; Feng, W.; Zhang, G.; Song, X.; Sun, X. Genome-Wide Analysis of Codon Usage Bias in Four Sequenced Cotton Species. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Shen, M.; Cao, F.; Yang, X. Compare Analysis of Codon Usage Bias of Nuclear Genome in Eight Sapindaceae Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 26, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, K.; Jana, S.; Pramanik, P.; Bera, B. Selection on Synonymous Codon Usage in Soybean (Glycine max) WRKY Genes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, X. Codon Usage Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis of the Mitochondrial Genome in Hemerocallis citrina. BMC Genom. Data 2024, 25, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Meng, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, J. Codon Usage Patterns across Seven Rosales Species. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Gan, Z.; Zhang, F.; Yi, X.; Zhang, J.; Wan, X. Analysis of Codon Usage Patterns in Citrus Based on Coding Sequence Data. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Zhang, S.; Yang, T. Analysis of Codon Usage Bias in Chloroplast Genomes of Dryas octopetala var. asiatica (Rosaceae). Genes 2024, 15, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Gong, W.; Li, Y. Comparative Analysis of the Codon Usage Pattern in the Chloroplast Genomes of Gnetales Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qu, B.; Xu, Y. Analysis of Codon Usage Bias in the Plastid Genome of Diplandrorchis sinica (Orchidaceae). Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 9807–9820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, T.; Nan, Z.B. Synonymous Codon Usage Pattern in Model Legume Medicago truncatula. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 2074–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Chen, Z.; Wu, D.; Wang, Y.; Hou, N. Codon Usage Bias in the Chloroplast Genomes of Cymbidium Species in Guizhou, China. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 164, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktürk Dizman, Y. Exploring Codon Usage Patterns and Influencing Factors in Ranavirus DNA Polymerase Genes. J. Basic Microbiol. 2024, 64, e2400289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershberg, R.; Petrov, D.A. General Rules for Optimal Codon Choice. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktürk Dizman, Y. Comprehensive Analysis of the Codon Usage Patterns in the Polyprotein Coding Sequences of the Honeybee Viruses. Front. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 1567209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buric, F.; Viknander, S.; Fu, X.; Lemke, O.; Carmona, O.G.; Zrimec, J.; Szyrwiel, L.; Mülleder, M.; Ralser, M.; Zelezniak, A. Amino Acid Sequence Encodes Protein Abundance Shaped by Protein Stability at Reduced Synthesis Cost. Protein Sci. 2025, 34, e5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boro, N.; Alexandrino Fernandes, P.; Mukherjee, A.K. Computational Analysis to Comprehend the Structure-Function Properties of Fibrinolytic Enzymes from Bacillus spp. for Their Efficient Integration into Industrial Applications. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, S.; Hayat, Q.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wani, A.S.; Pichtel, J.; Ahmad, A. Role of Proline under Changing Environments: A Review. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Lu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S. Response Mechanism of Plants to Drought Stress. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Q. Connections Between Amino Acid Metabolisms in Plants: Lysine as an Example. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, Y.; Tanford, C. The Solubility of Amino Acids and Related Compounds in Aqueous Thylene Glycol Solutions. J. Biol. Chem. 1965, 240, 3568–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S. Recent Advances of Polyphenol Oxidases in Plants. Molecules 2023, 28, 2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Meng, Z.; Dong, T.; Fan, X.; Wang, Q. Enzymatic Browning and Polyphenol Oxidase Control Strategies. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2023, 81, 102921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Yengkhom, S.; Uddin, A. Analysis of Codon Usage Bias of Chloroplast Genes in Oryza Species: Codon Usage of Chloroplast Genes in Oryza Species. Planta 2020, 252, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cai, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Jiao, C.; Xu, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z. Comparative Analysis of Codon Bias in the Chloroplast Genomes of Theaceae Species. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 824610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, B.C.; Virmani, N.; Kumar, N.; Anand, T.; Pavulraj, S.; Rash, A.; Elton, D.; Rash, N.; Bhatia, S.; Sood, R.; et al. Genetic and Codon Usage Bias Analyses of Polymerase Genes of Equine Influenza Virus and Its Relation to Evolution. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Lv, Y.; Wei, W. Codon Usage Bias of Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus and Its Host Adaption. Virus Res. 2023, 328, 199081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Song, H.; Kuang, Y.; Chen, S.; Tian, P.; Li, C.; Nan, Z. Genome-Wide Analysis of Codon Usage Bias in Epichloë festucae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Luo, X.; Cai, X. Analysis of Codon Usage Pattern in Taenia saginata Based on a Transcriptome Dataset. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andargie, M.; Congyi, Z. Genome-Wide Analysis of Codon Usage in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Heliyon 2022, 8, e08687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puigbò, P.; Bravo, I.G.; Garcia-Vallve, S. CAIcal: A Combined Set of Tools to Assess Codon Usage Adaptation. Biol. Direct 2008, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paola, N.D.; De Melo Freire, C.C.; De Andrade Zanotto, P.M. Does Adaptation to Vertebrate Codon Usage Relate to Flavivirus Emergence Potential? PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, A.; Zinovyev, A.; Képès, F. Codon Adaptation Index as a Measure of Dominating Codon Bias. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 2005–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Luo, Y.; Sha, A.; Xiao, W.; Xiong, Z.; Chen, X.; He, J.; Peng, L.; Zou, L. Analysis of Synonymous Codon Usage Patterns in Mitochondrial Genomes of Nine Amanita Species. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1134228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mandal, S.; Mazumder, T.H.; Panda, A.K.; Kumar, N.S.; Jin, F. Analysis of Synonymous Codon Usage Patterns of HPRT1 Gene across Twelve Mammalian Species. Genomics 2020, 112, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, M.; He, W.; Du, F.; Wu, G.; Wu, B.; Zhou, Z. Analysis of the Codon Usage of the ORF2 Gene of Feline Calicivirus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 54, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Chen, X.; He, J.; Sha, A.; Luo, Y.; Xiao, W.; Xiong, Z.; Li, Q. Intraspecific and Interspecific Variations in the Synonymous Codon Usage in Mitochondrial Genomes of 8 Pleurotus Strains. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.K.; Roy, S. Comparative Analysis of Human Coronaviruses Focusing on Nucleotide Variability and Synonymous Codon Usage Patterns. Genomics 2021, 113, 2177–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, P.M.; Li, W.H. Codon Usage in Regulatory Genes in Escherichia coli Does Not Reflect Selection for “rare” Codons. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986, 14, 7737–7749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, F. The “effective Number of Codons” Used in a Gene. Gene 1990, 87, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, C.; Liao, W. Deciphering Codon Usage Patterns in Genome of Cucumis sativus in Comparison with Nine Species of Cucurbitaceae. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; She, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, Z. Comparative Analysis of Codon Usage Patterns in Chloroplast Genomes of Five Miscanthus Species and Related Species. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueoka, N. Two Aspects of DNA Base Composition: G+C Content and Translation- Coupled Deviation from Intra-Strand Rule of A = T and G = C. J. Mol. Evol. 1999, 49, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.U.; Hu, Y.; Rehman, H.U.; Alrashed, M.M.; Attia, K.A.; Ullah, U.; Liang, H. Analysis of Synonymous Codon Usage Bias of Lassa Virus. Virus Res. 2025, 353, 199528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueoka, N. Directional Mutation Pressure and Neutral Molecular Evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 2653–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; He, W.; Fan, B.; Ni, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, B. Comprehensive Analysis of Codon Usage Patterns of Porcine Deltacoronavirus and Its Host Adaptability. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e2443–e2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Fan, L. GenRCA: A User-Friendly Rare Codon Analysis Tool for Comprehensive Evaluation of Codon Usage Preferences Based on Coding Sequences in Genomes. BMC Bioinform. 2024, 25, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angellotti, M.C.; Bhuiyan, S.B.; Chen, G.; Wan, X.F. CodonO: Codon Usage Bias Analysis within and across Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nambou, K.; Anakpa, M.; Tong, Y.S. Human Genes with Codon Usage Bias Similar to That of the Nonstructural Protein 1 Gene of Influenza A Viruses Are Conjointly Involved in the Infectious Pathogenesis of Influenza A Viruses. Genetica 2022, 150, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supek, F.; Vlahoviček, K. Comparison of Codon Usage Measures and Their Applicability in Prediction of Microbial Gene Expressivity. BMC Bioinform. 2005, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Species | Accession No. | T3s% | C3s% | A3s% | G3s% | GC% | AT% | GC3s% | AT3% | GC1% | GC2% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. sinensis | DQ513313.1 | 29.86 | 34.76 | 28.15 | 35.22 | 49.17 | 50.83 | 53.78 | 45.00 | 52.50 | 40.00 |
| C. sinensis | MK977642.1 | 29.94 | 36.09 | 29.67 | 32.21 | 49.25 | 50.75 | 52.59 | 45.86 | 51.90 | 41.72 |
| C. sinensis | MK977643.1 | 30.67 | 34.15 | 28.60 | 34.57 | 48.89 | 51.11 | 52.75 | 46.00 | 52.33 | 40.33 |
| C. sinensis | MK977644.1 | 35.37 | 31.91 | 27.00 | 32.25 | 48.83 | 51.17 | 49.74 | 48.66 | 53.19 | 41.95 |
| C. sinensis | MK977645.1 | 45.22 | 12.17 | 26.05 | 48.15 | 45.39 | 54.61 | 44.30 | 55.26 | 59.21 | 32.24 |
| C. sinensis | MZ442717.1 | 30.67 | 34.15 | 28.38 | 34.73 | 49.06 | 50.94 | 52.92 | 45.83 | 52.50 | 40.50 |
| C. sinensis | MZ442718.1 | 30.67 | 34.15 | 28.67 | 34.57 | 48.89 | 51.11 | 52.75 | 46.00 | 52.33 | 40.33 |
| C. sinensis | FJ656220.1 | 30.41 | 34.49 | 28.44 | 34.57 | 49.06 | 50.94 | 53.09 | 45.67 | 52.33 | 40.50 |
| C. sinensis | EU787433.1 | 30.67 | 34.15 | 28.67 | 34.57 | 48.89 | 51.11 | 52.75 | 46.00 | 52.33 | 40.33 |
| C. sinensis | JX465712.1 | 30.67 | 34.15 | 28.67 | 34.57 | 48.89 | 51.11 | 52.75 | 46.00 | 52.33 | 40.33 |
| C. sinensis | GQ214317.1 | 30.67 | 34.15 | 28.44 | 34.81 | 48.94 | 51.06 | 52.92 | 45.83 | 52.33 | 40.33 |
| C. sinensis | AY659975.1 | 30.4 | 34.8 | 29.74 | 31.95 | 48.90 | 51.10 | 51.79 | 46.88 | 52.08 | 41.49 |
| C. sinensis | FJ210643.1 | 30.12 | 34.84 | 28.51 | 34.65 | 49.06 | 50.94 | 53.36 | 45.33 | 52.00 | 40.50 |
| C. sinensis | EF650017.1 | 30.88 | 34.15 | 28.51 | 34.65 | 48.89 | 51.11 | 52.75 | 46.00 | 52.33 | 40.33 |
| C. sinensis | EF650016.1 | 30.53 | 34.02 | 28.15 | 35.14 | 49.25 | 50.75 | 53.18 | 45.58 | 52.75 | 40.57 |
| C. sinensis | EF635860.1 | 30.67 | 34.15 | 28.67 | 34.57 | 48.94 | 51.06 | 52.75 | 46.00 | 52.50 | 40.33 |
| C. sinensis | EF623826.1 | 30.67 | 34.15 | 28.6 | 34.57 | 48.89 | 51.11 | 52.75 | 46.00 | 52.33 | 40.33 |
| C. sinensis | MH250121.1 | 30.67 | 34.15 | 28.67 | 34.57 | 48.83 | 51.17 | 52.75 | 46.00 | 52.33 | 40.17 |
| C. sinensis | MH250120.1 | 30.66 | 34.36 | 28.08 | 34.98 | 49.11 | 50.89 | 53.18 | 45.50 | 52.83 | 40.00 |
| C. sinensis | MH250119.1 | 29.8 | 34.49 | 28.08 | 35.47 | 49.33 | 50.67 | 53.78 | 45.00 | 52.50 | 40.50 |
| C. sinensis | MH250118.1 | 30.25 | 34.57 | 28.31 | 35.14 | 49.22 | 50.78 | 53.44 | 45.33 | 52.67 | 40.33 |
| C. sinensis | GQ129142.1 | 29.86 | 34.76 | 28.15 | 35.22 | 49.11 | 50.89 | 53.78 | 45.00 | 52.33 | 40.00 |
| C. sinensis | MZ442720.1 | 30.82 | 33.88 | 28.83 | 34.48 | 48.83 | 51.17 | 52.49 | 46.33 | 52.33 | 40.50 |
| C. sinensis | MZ442719.1 | 29.86 | 34.56 | 28.15 | 35.38 | 49.17 | 50.83 | 53.78 | 45.00 | 52.50 | 40.00 |
| C. lanceoleosa | KAI7999995.1 | 37.45 | 29.76 | 27.27 | 31.68 | 48.38 | 51.62 | 47.66 | 50.67 | 53.68 | 42.14 |
| C. nitidissima | ACM43505.1 | 31.30 | 26.93 | 32.00 | 48.60 | 48.60 | 51.40 | 49.04 | 49.33 | 53.69 | 41.44 |
| C. ptilophylla | ABF19601.1 | 35.05 | 28.21 | 34.81 | 49.50 | 49.50 | 50.50 | 53.81 | 44.97 | 52.85 | 40.60 |
| A. chinensis | PSR98570.1 | 32.26 | 22.14 | 41.00 | 50.75 | 50.75 | 49.25 | 55.77 | 42.93 | 53.41 | 41.76 |
| C. florida | XM_059815174.1 | 28.63 | 27.19 | 31.03 | 47.60 | 47.60 | 52.40 | 46.00 | 52.74 | 52.57 | 42.95 |
| R. vialii | XM_058340762.1 | 38.34 | 25.81 | 32.76 | 49.83 | 49.83 | 50.17 | 55.61 | 43.00 | 50.33 | 42.17 |
| Species | Accession No. | ENC | CBI | CAI | GRAVY | AROMA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. sinensis | DQ513313.1 | 57.07 | −0.048 | 0.196 | −0.479466 | 0.09182 |
| C. sinensis | MK977642.1 | 55.87 | −0.064 | 0.196 | −0.467012 | 0.091537 |
| C. sinensis | MK977643.1 | 56.81 | −0.056 | 0.197 | −0.476628 | 0.09182 |
| C. sinensis | MK977644.1 | 57.73 | −0.092 | 0.193 | −0.411092 | 0.092437 |
| C. sinensis | MK977645.1 | 49.01 | −0.239 | 0.161 | −0.318543 | 0.046358 |
| C. sinensis | MZ442717.1 | 56.83 | −0.054 | 0.197 | −0.489149 | 0.09015 |
| C. sinensis | MZ442718.1 | 56.89 | −0.056 | 0.196 | −0.489983 | 0.09182 |
| C. sinensis | FJ656220.1 | 56.63 | −0.05 | 0.197 | −0.492321 | 0.09182 |
| C. sinensis | EU787433.1 | 56.89 | −0.056 | 0.196 | −0.489983 | 0.09182 |
| C. sinensis | JX465712.1 | 56.89 | −0.056 | 0.196 | −0.489983 | 0.09182 |
| C. sinensis | GQ214317.1 | 56.86 | −0.054 | 0.197 | −0.489983 | 0.09182 |
| C. sinensis | AY659975.1 | 55.80 | −0.015 | 0.2 | −0.451826 | 0.093913 |
| C. sinensis | FJ210643.1 | 56.66 | −0.047 | 0.198 | −0.492321 | 0.093489 |
| C. sinensis | EF650017.1 | 56.64 | −0.059 | 0.195 | −0.479633 | 0.09182 |
| C. sinensis | EF650016.1 | 56.37 | −0.044 | 0.199 | −0.511539 | 0.091973 |
| C. sinensis | EF635860.1 | 56.97 | −0.056 | 0.196 | −0.493155 | 0.09015 |
| C. sinensis | EF623826.1 | 56.81 | −0.056 | 0.197 | −0.476628 | 0.09182 |
| C. sinensis | MH250121.1 | 56.79 | −0.055 | 0.196 | −0.486644 | 0.09182 |
| C. sinensis | MH250120.1 | 56.19 | −0.041 | 0.201 | −0.482304 | 0.09182 |
| C. sinensis | MH250119.1 | 55.32 | −0.039 | 0.198 | −0.478798 | 0.093489 |
| C. sinensis | MH250118.1 | 55.52 | −0.033 | 0.204 | −0.53005 | 0.09182 |
| C. sinensis | GQ129142.1 | 56.93 | −0.046 | 0.198 | −0.47813 | 0.09182 |
| C. sinensis | MZ442720.1 | 57.47 | −0.05 | 0.198 | −0.489316 | 0.09182 |
| C. sinensis | MZ442719.1 | 57.11 | −0.045 | 0.197 | −0.485309 | 0.09182 |
| C. lanceoleosa | KAI7999995.1 | 57.76 | −0.105 | 0.192 | −0.404523 | 0.092127 |
| C. nitidissima | ACM43505.1 | 57.41 | −0.099 | 0.189 | −0.395798 | 0.090756 |
| C. ptilophylla | ABF19601.1 | 55.74 | −0.035 | 0.197 | −0.493109 | 0.092437 |
| A. chinensis | PSR98570.1 | 56.23 | −0.101 | 0.185 | −0.491167 | 0.093333 |
| C. florida | XM_059815174.1 | 55.09 | −0.025 | 0.214 | −0.528904 | 0.094684 |
| R. vialii | XM_058340762.1 | 55.00 | −0.026 | 0.196 | −0.46995 | 0.085142 |
| Species | Number of HF Codons | HF Codons Identified |
|---|---|---|
| C. sinensis | 18 | TTC, CTC, ATT, GTG, TCC, CCG, ACC, GCC, TAC, CAT, CAA, AAC, AAG, GAT, GAG, TGC, CGA, GGG |
| C. lanceoleosa | 20 | TTC, CTT, ATT, GTG, TCC, CCT, ACC, GCC, TAT, TAC, CAT, CAA, AAG, GAT, GAG, TGT, CGA, AGA, GGG |
| C. nitidissima | 21 | TTC, TTG, ATT, GTG, TCC, CCT, CCC, ACC, GCT, TAT, TAC, CAT, CAA, AAT, AAG, GAT, GAG, TGT, TGC, CGG, GGG |
| C. ptilophylla | 19 | TTC, CTC, ATT, GTG, TCC, CCG, ACC, GCC, TAC, CAT, CAA, AAC, AAG, GAT, GAG, TGC, CGA, GGG |
| A. chinensis | 17 | TTT, TTG, ATT, GTG, TCC, CCG, ACC, GCC, TAT, CAC, CAA, AAT, AAG, GAT, GAG, AGG, GGG |
| C. florida | 20 | TTT, TTG, ATA, GTG, TCC, CCA, ACC, GCT, TAC, CAT, CAA, AAT, AAG, GAT, GAG, TGT, TGC, AGG, GGT |
| R. vialii | 20 | TTC, CTT, ATC, GTG, TCC, CCC, ACC, GCC, TAC, CAT, CAA, AAC, AAA, AAG, GAT, GAG, TGC, AGA, AGG, GGG |
| Species | SCUO | MILC |
|---|---|---|
| C. sinensis | 0.06 | 0.50 |
| C. lanceoleosa | 0.06 | 0.50 |
| C. nitidissima | 0.06 | 0.50 |
| C. ptilophylla | 0.06 | 0.49 |
| A. chinensis | 0.07 | 0.49 |
| C. florida | 0.07 | 0.48 |
| R. vialii | 0.06 | 0.49 |
| Indices | GC | GC1 | GC2 | GC3s | A3s | T3s | C3s | G3s | AT3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENC | |||||||||
| r | 0.87924 * | −0.90933 * | 0.8891 * | 0.79626 * | 0.55742 * | −0.82919 * | 0.90027 * | −0.88771 * | −0.82775 * |
| p | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| CAI | |||||||||
| r | −0.4184 * | 0.47938 * | −0.16986 | −0.68726 * | −0.5215 * | 0.64212 * | −0.47633 * | 0.18885 | 0.64205 * |
| p | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.37683 | <0.05 |
| Indices | ENC | A3s | T3s | C3s | G3s | GC3s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRAVY | ||||||
| r | −0.74322 * | −0.64531 * | 0.91663 * | −0.86921 * | 0.68189 * | −0.93131 * |
| p | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| AROMA | ||||||
| r | 0.92501 * | 0.68872 * | −0.93759 * | 0.98578 * | 0.68189 * | 0.89588 * |
| p | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aktürk Dizman, Y. Codon Usage Bias of the Polyphenol Oxidase Genes in Camellia sinensis: A Comprehensive Analysis. Plants 2025, 14, 3074. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193074
Aktürk Dizman Y. Codon Usage Bias of the Polyphenol Oxidase Genes in Camellia sinensis: A Comprehensive Analysis. Plants. 2025; 14(19):3074. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193074
Chicago/Turabian StyleAktürk Dizman, Yeşim. 2025. "Codon Usage Bias of the Polyphenol Oxidase Genes in Camellia sinensis: A Comprehensive Analysis" Plants 14, no. 19: 3074. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193074
APA StyleAktürk Dizman, Y. (2025). Codon Usage Bias of the Polyphenol Oxidase Genes in Camellia sinensis: A Comprehensive Analysis. Plants, 14(19), 3074. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193074







