Genetic Architecture and Meta-QTL Identification of Yield Traits in Maize (Zea mays L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Information Collection and Distribution of QTLs Related to Maize Yield Components
2.2. Construction and QTL Projection of Consensus Map
2.3. Meta-QTL Analysis and the Relationship Among 11 Components of Maize Yield
2.4. Identification of Candidate Genes in MQTLs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Literature Retrieval and QTL Data Collection of Maize Yield-Related Traits
4.2. Consensus Map Construction and QTL Projection
4.3. Meta-QTL Analysis of Maize Yield Components
4.4. Identification of Candidate Genes in the MQTLs Interval
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, J.K.; Sa, K.J.; Park, D.H.; Lim, S.E.; Ryu, S.H.; Park, J.Y.; Park, K.J.; Rhee, H.I.; Lee, M.; Lee, J.K. Construction of genetic linkage map and identification of QTLs related to agronomic traits in DH population of maize (Zea mays L.) using SSR Markers. Genes Genom. 2019, 41, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.L.; Gan, Y.J.; Le, L.; Pu, L. Epigenetic variation in maize agronomical traits for breeding and trait improvement. J. Genet. Genom. 2025, 52, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, F.; Jing, J.G.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Chen, S.B.; Sang, Z.Q.; Li, W.H. GWAS and Meta-QTL analysis of yield-related ear traits in maize. Plants 2023, 12, 3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.F.; Wang, W.; Gong, S.L.; Zuo, J.H.; Li, S.J.; Xu, S.Z. High density linkage map construction and mapping of yield trait QTLs in Maize (Zea mays) using the genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) technology. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.R.; Meng, Z.D.; Yue, R.Q.; Lu, S.P.; Li, W.L.; Li, W.C.; Meng, H.; Sun, Q. Genome wide association analysis for yield related traits in maize. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.S.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Yong, H.J.; Zhang, X.C.; Hao, Z.F.; Zhang, F.J.; Li, M.S.; Zhang, D.G.; Li, X.H.; Wang, Z.H.; et al. Analysis of the genetic architecture of maize ear and grain morphological traits by combined linkage and association mapping. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 130, 1011–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Cao, Y.Y. Genetic dissection of maize grain yield and yield-related traits through association mapping and genomic prediction. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 690059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Li, C.H.; Li, Y.X.; Song, Y.C.; Zhang, D.F.; Wang, T.Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, Y.S. Quantitative trait loci mapping of yield and related traits using a high-density genetic map of maize. Mol. Breed. 2016, 36, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.T.; Yu, D.S.; Gu, W.; Khalid, M.H.B.; Kuang, H.Y.; Dang, D.D.; Wang, H.; Prasanna, B.; Zhang, X.C.; Zhang, A.; et al. Genetic architecture of kernel-related traits in sweet and waxy maize revealed by genome-wide association analysis. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1431043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.P.; Dong, E.F.; Liang, Q.Y.; Bai, Y.; Nan, J.; Yang, Y.; Cai, Y.L. Identification of QTL for fasciated ear related traits in maize. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, K.P.; Karthikeyan, A.; Mohanapriya, B.; Ganesan, K.N.; Paranidharan, V.; Ramalingam, J.; Senthil, N. Quantitative trait locus mapping reveals the genomic regions associated with yield-related traits in maize (Zea mays L.). Cereal Res. Commun. 2024, 52, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.L.; Zhuang, Z.L.; Bian, J.W.; Tang, R.; Ren, Z.P.; Peng, Y.L. Candidate gene for kernel-related traits in maize revealed by a combination of GWAS and Meta-QTL analyses. Plants 2025, 14, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, M.; Saini, D.K.; Devi, V.; Kaur, C.; Singh, M.P.; Singh, J.; Pruthi, G.; Kaur, A.; Singh, J.; Chaudhary, D.P. Unravelling the genetic framework associated with grain quality and yield-related traits in maize (Zea mays L.). Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1248697. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Miao, Y.P.; Ma, J.F.; Zhang, P.P.; Chen, T.; Liu, Y.; Che, Z.; Shahinnia, F.; Yang, D.L. Consensus genomic regions for grain quality traits in wheat revealed by Meta-QTL analysis and in silico transcriptome integration. Plant Genome. 2023, 16, e20336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffinet, B.; Gerber, S. Quantitative Trait Loci: A Meta-analysis. Genetics 2000, 155, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, D.K.; Srivast, P.; Pal, N.; Gupta, P.K. Meta-QTLs, ortho-meta-QTLs and candidate genes for grain yield and associated traits in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 1049–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, D.; Joshi, S.; Das, A.; Vikal, Y.; Sahi, G.K.; Neelam, K.; Kaur, K.; Singh, K. Introgression of yield component traits in rice (Oryza sativa ssp. indica) through interspecific hybridization. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 1557–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.X.; Shi, Y.S.; Song, Y.C.; Zhang, D.F.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.Y.; Yang, D.G.; Li, C.H. Meta-QTL analysis and identification of candidate genes related to root traits in maize. Euphytica 2018, 214, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.L.; Wang, Y.L.; Li, D.D.; Guo, Y.H.; Zhou, Z.P.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.F.; Wuerschum, T.; Liu, W.X. Meta-quantitative trait loci analysis and candidate gene mining for drought tolerance-associated traits in maize (Zea mays L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, X.; Deng, D.X. Integrated Meta-QTL and genome-wide association study analyses reveal candidate genes for maize yield. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 39, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.P.; Li, G.L.; Tan, S.Y.; Li, D.D.; Weiss, T.M.; Wang, X.F.; Chen, S.J.; Wuerschum, T.; Liu, W.X. A QTL atlas for grain yield and its component traits in maize (Zea mays). Plant Breed. 2020, 139, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; An, Y.X.; Li, Y.X.; Li, C.H.; Shi, Y.S.; Song, Y.C.; Zhang, D.F.; Wang, T.Y.; Li, Y. Candidate loci for yield-related traits in maize revealed by a combination of Meta-QTL analysis and regional association mapping. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.K.; Soriano, J.M.; Tuberosa, R.; Koumproglou, R.; Jahrmann, T.; Salvi, S. Yield QTLome distribution correlates with gene density in maize. Plant Sci. 2016, 242, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Q.; Peng, Y.L.; Zhang, J.W.; Fang, P.; Wu, B.Y. Identification of QTLs and Meta-QTLs for seven agronomic traits in multiple maize populations under well-watered and water-stressed conditions. Crop Sci. 2018, 58, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, E.; Rocheford, T.R. Genetic and QTL analysis of pericarp thickness and ear architecture traits of Korean waxy maize germplasm. Euphytica 2011, 183, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.J.; Chen, Z.L.; Liu, Z.P.; Wang, B.B.; Song, W.B.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Dai, J.R.; Lai, J.S. Identification of genetic factors affecting plant density response through QTL mapping of yield component traits in maize (Zea mays L.). Euphytica 2011, 182, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Li, X.H.; Li, J.Z.; Fu, J.F.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wei, M.G. Dent maize genetic background influences QTL detection for grain yield and yield components in high-oil maize. Euphytica 2009, 169, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Guo, X.H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.P.; Zhang, G.D.; Tian, Y.C.; Wang, Z.L. Mapping QTLs for grain yield and yield components under high and low phosphorus treatments in maize (Zea mays L.). Plant Sci. 2010, 178, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.W.; Sun, C.L.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zheng, Y.L.; Qiu, F.Z. Genetic analysis and major QTL detection for maize kernel size and weight in multi-environments. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 1019–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Xie, C.X.; Li, X.H.; Hao, Z.F.; Li, M.S.; Weng, J.F.; Zhang, D.G.; Bai, L.; Zhang, S.H. Mapping of quantitative trait loci for kernel row number in maize across seven environments. Mol. Breed. 2011, 28, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.J.; Sa, K.J.; Kim, B.W.; Koh, H.J.; Lee, J.K. Genetic mapping and QTL analysis for yield and agronomic traits with an F2:3 population derived from a waxy maize x sweet maize cross. Genes Genom. 2014, 36, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.H.; Li, Y.L.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Y.G.; Zhou, Q.; Shen, B.T.; Zhang, F.F.; Liang, X.J. Detection and integration of quantitative trait loci for grain yield components and oil content in two connected recombinant inbred line populations of high-oil maize. Mol. Breed. 2012, 29, 313–333. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.W.; Liu, Z.H.; Chen, Q.; Qu, Y.Z.; Tang, J.H.; Lübberstedt, T.; Li, H.C. Mapping of QTL for grain yield components based on a DH population in maize. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Liu, Z.H.; Hu, Y.M.; Li, W.H.; Fu, Z.Y.; Ding, D.; Li, H.C.; Qiao, M.M.; Tang, J.H. QTL analysis of kernel-related traits in maize using an immortalized F2 population. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.H.; Chang, L.G.; Li, Y.N.; Qu, J.Z.; Cui, T.T.; Xu, S.T.; Xue, J.Q.; Liu, J.C. QTL mapping of ear traits of maize with and without N input. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2017, 23, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, L.; Jia, A.M.; Rong, T.Z. Identification of QTL for maize grain yield and kernel-related traits. J. Genet. 2016, 95, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.B.; Tang, H.; Huang, Y.Q.; Zheng, Y.L.; Li, J.S. Quantitative trait loci mapping and epistatic analysis for grain yield and yield components using molecular markers with an elite maize hybrid. Euphytica 2006, 149, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommert, P.; Il Je, B.; Goldshmidt, A.; Jackson, D. The maize Gα gene COMPACT PLANT2 functions in CLAVATA signalling to control shoot meristem size. Nature 2013, 52, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuck, G.S.; Brown, P.J.; Meeley, R.; Hake, S. Maize SBP-box transcription factors unbranched2 and unbranched3 affect yield traits by regulating the rate of lateral primordia initiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18775–18780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Il Je, B.; Gruel, J.; Lee, Y.K.; Bommert, P.; Arevalo, E.D.; Eveland, A.L.; Wu, Q.Y.; Goldshmidt, A.; Meeley, R.; Bartlett, M.; et al. Signaling from maize organ primordia via FASCIATED EAR3 regulates stem cell proliferation and yield traits. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zheng, H.Y.; Jin, L.; Xing, L.J.; Zou, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.M.; Chu, J.F.; Xu, M.Y.; Wang, L. miR169o and ZmNF-YA13 act in concert to coordinate the expression of ZmYUC1 that determines seed size and weight in maize kernels. New Phytol. 2022, 235, 2270–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, Z.L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.Q.; Zhou, L.N.; Zhong, S.Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, C.; Lin, Z.W. Krn1, a major quantitative trait locus for kernel row number in maize. New Phytol. 2019, 223, 1634–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.A.; Ding, L.; Feng, W.Q.; Cao, Y.; Lu, F.Z.; Yang, Q.Q.; Li, W.C.; Lu, Y.L.; Shabek, N.; Fu, F.L. Maize transcription factor ZmBES1/BZR1-5 positively regulates kernel size. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 1714–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.M.; Su, C.F. Mapping quantitative trait loci for yield-related traits and predicting candidate genes for grain weight in maize. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, R.C.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, G.M.; Zhao, Y.J.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.S.; Zhao, X.Y. ZmADT2 regulates maize kernel development via the auxin signaling pathway. Crop J. 2025, 13, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, M.; Ohta, D.; Merchant, S.; Briggs, W.R.; Ort, D. Diversification of P450 genes during land plant evolution. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 291–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, P.L.; Wei, X.; Xiao, Z.L.; Wang, X.L.; Ma, S.P.; Lin, S.J.; Li, F.P.; Bu, S.H.; Liu, Z.P.; Zhu, H.T.; et al. GW10, a member of P450 subfamily regulates grain size and grain number in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 3941–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Wang, N.N.; Lu, R.; Wu, Y.W.; Li, X.B. Pollen-specific protein PSP231 activates callose synthesis to govern male gametogenesis and pollen germination. Plant Physiol. 2020, 184, 1024–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, Y.B.C.J.; Aizza, L.C.B.; Armanhi, J.S.L.; Dornelas, M.C. A Passiflora homolog of a D-type cyclin gene is differentially expressed in response to sucrose, auxin, and cytokinin. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2013, 115, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.G.; Jiang, H.; Zeng, F.K. The sugar transporter proteins in plants: An elaborate and widespread regulation network-A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 294, 139252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.F.; Hou, M.M.; Sun, F.; Shen, Y.; Xiu, Z.H.; Wang, X.M.; Chen, Z.L.; Sun, S.S.M.; Small, I.; et al. Small kernel 1 encodes a pentatricopeptide repeat protein required for mitochondrial nad7 transcript editing and seed development in maize (Zea mays) and rice (Oryza sativa). Plant J. 2014, 79, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvasi, A.; Soller, M. A simple method to calculate resolving power and confidence interval of QTL map location. Behav. Genet. 1997, 27, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Zhang, J.G.; Cao, J.S.; Cao, S.L.; Li, W.Y.; Yang, G.B. A meta-analysis of low temperature tolerance QTL in maize. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 58, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, B.P.M.; Vikram, P.; Dixit, S.; Ahmed, H.U.; Kumar, A. Meta-analysis of grain yield QTL identified during agricultural drought in grasses showed consensus. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chardon, F.; Jasinski, S.; Durandet, M.; Le’cureuil, A.; Soulay, F.; Bedu, M.; Guerche, P.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C. QTL meta-analysis in Arabidopsis reveals an interaction between leaf senescence and resource allocation to seeds. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 3949–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheoran, S.; Gupta, M.; Kumari, S.; Kumar, S.; Rakshit, S. Meta-QTL analysis and candidate genes identification for various abiotic stresses in maize (Zea mays L.) and their implications in breeding programs. Mol. Breed. 2022, 42, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Yankanchi, S.; Singh, R.; Pushpendra; Sarkar, D.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, K.; Choudhary, M.; Jat, B.S.; Jat, H.S. Dissecting the genetic architecture of polygenic nutritional traits in maize through meta-QTL analysis. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2025, 10, 100256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
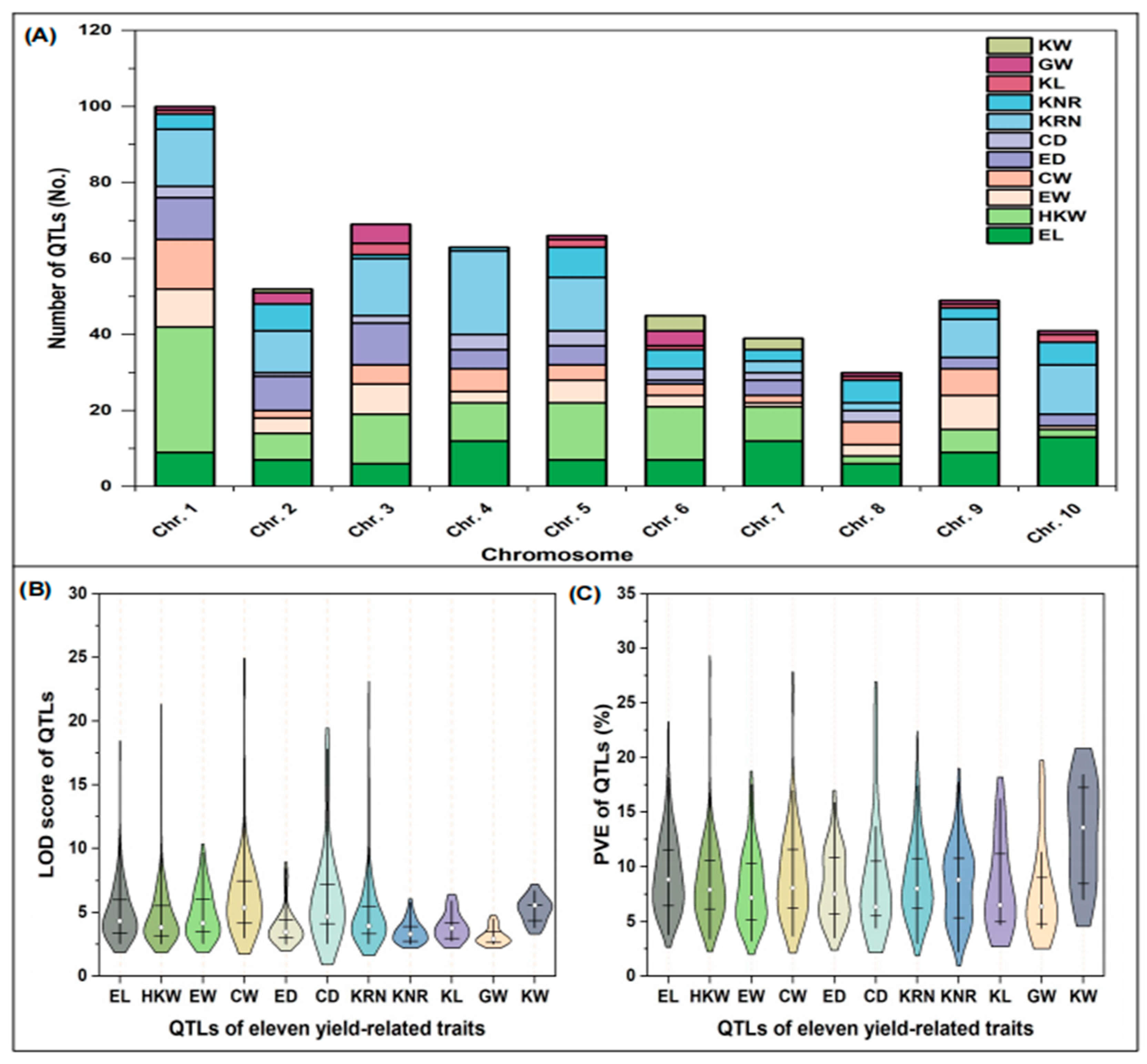
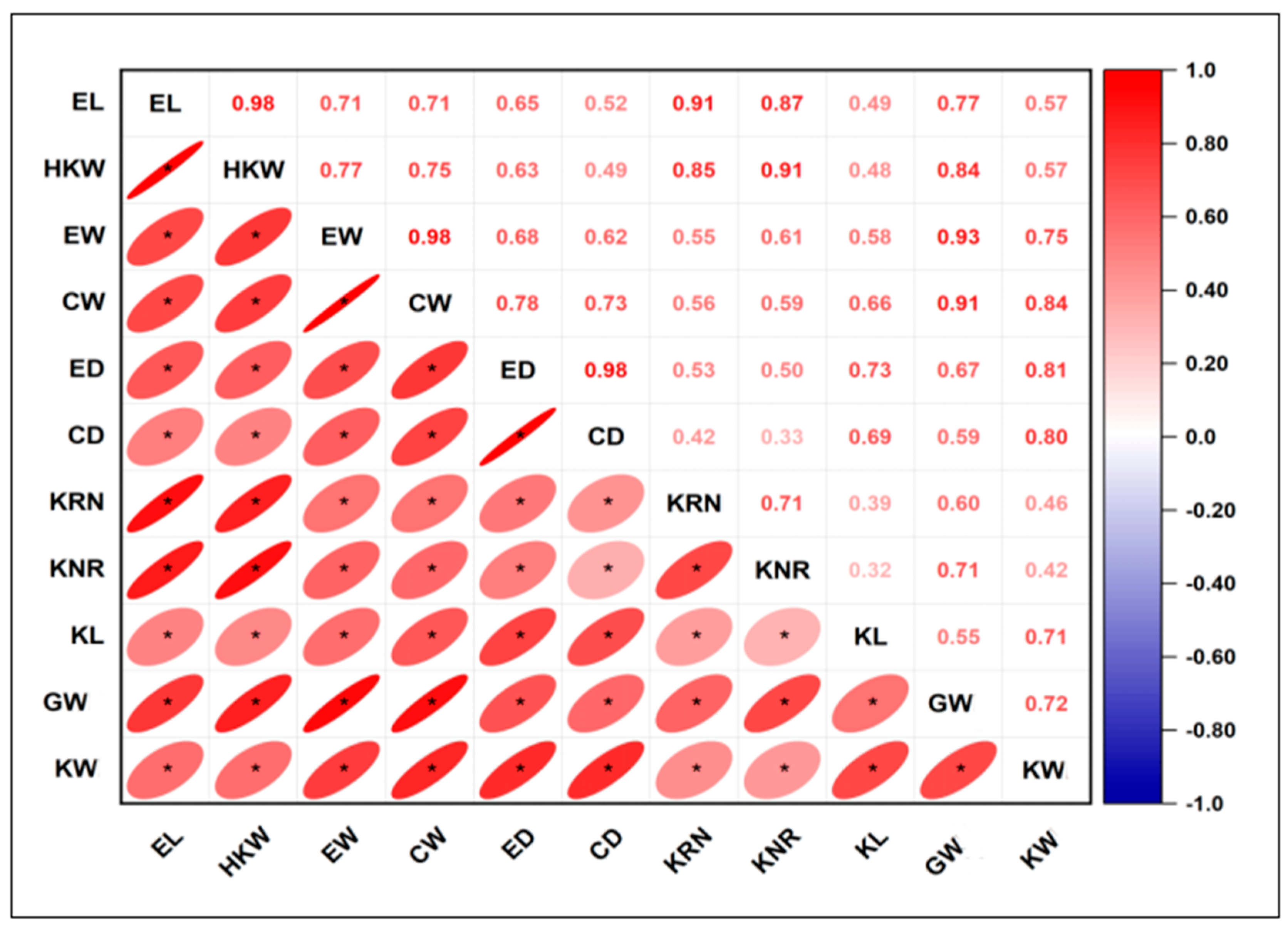
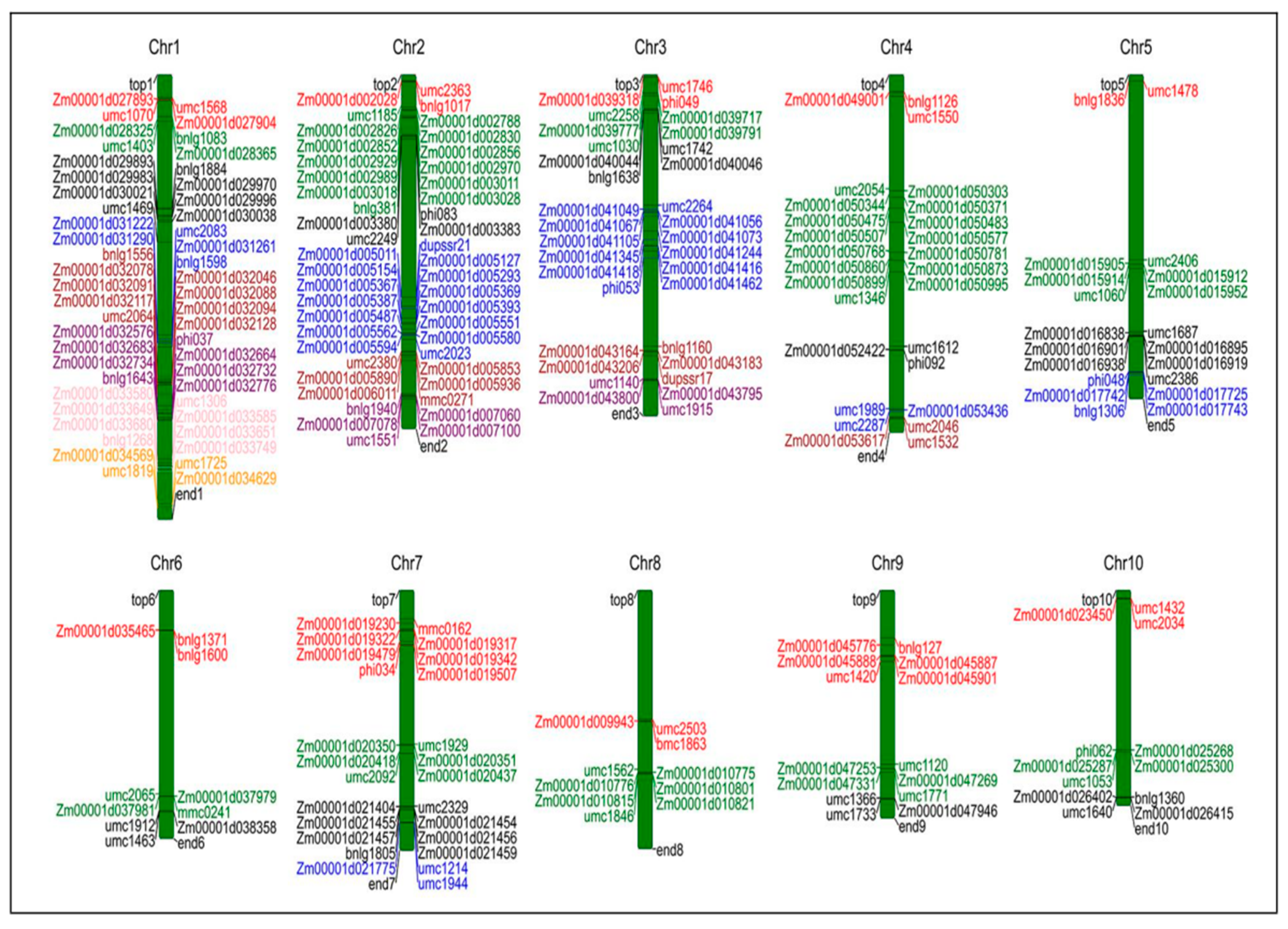
| Population | QTL Number | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross Group | Type | Size | Env. | Marker | Length (cM) | Approach | EL | HKW | EW | CW | ED | CD | KRN | KNR | KL | GW | KW | Reference |
| HF1 × 11S6169 | DH | 121 | 1 | 200/SSR | 1145.4 | – | 2 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | [1] |
| Langhuang × TS141 | F2:3 | 202 | 4 | 213/SSR | 1542.5 | CIM | 11 | 9 | 14 | 13 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | [24] |
| Chang7–2 × TS141 | F2:3 | 218 | 4 | 217/SSR | 1648.8 | CIM | 9 | 8 | 13 | 16 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| BH20 × BH30 | F2:3 | 264 | 1 | 100/SSR | 1281.0 | CIM | 3 | 9 | 2 | 8 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 6 | – | – | [25] |
| Zheng58 × Chang7–2 | F2:3 | 231 | 2 | 140/SSR,24/MITE | 2245.1 | CIM | 13 | 7 | 5 | 11 | 10 | 15 | 15 | 7 | – | – | – | [26] |
| 8984 × GY220 | F2:3 | 285 | 3 | 185/SSR | 2111.7 | CIM | 4 | 5 | – | – | 3 | – | 4 | 1 | – | – | – | [27] |
| 8622 × GY220 | F2:3 | 265 | 3 | 173/SSR | 2298.5 | CIM | 4 | 1 | – | – | 3 | – | 4 | 1 | – | – | – | |
| 5003 (107) × 178 | F2:3 | 210 | 4 | 207/SSR | 1725.1 | CIM | 10 | 12 | – | – | 11 | – | 12 | 11 | – | – | – | [28] |
| Mc × V671 | F2:3 | 270 | 4 | 256/SSR | 1351.7 | CIM | – | 15 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | [29] | |
| Ye478 × D340 | F2:3 | 397 | 7 | 150/SSR | 1478.7 | CIM | – | – | – | – | – | – | 13 | – | – | – | – | [10] |
| B73 × Yi16 | F2 | 236 | 1 | 218/SSR | 2769.3 | ICIM | 2 | 3 | – | – | – | – | 3 | – | – | – | – | [30] |
| B73 × Yi16 | F2:3 | 216 | 2 | 218/SSR | 2769.3 | ICIM | 1 | 4 | – | – | – | – | 9 | – | – | – | – | |
| 02S6140 × KSS22 | F2:3 | 158 | 1 | 303/SSR | 2626.5 | – | 2 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | [31] | |
| 8984 × GY220 | RIL | 282 | 4 | 216/SSR | 2285.3 | CIM | 9 | 10 | 8 | – | 10 | – | 14 | 9 | – | 5 | – | [32] |
| 8622 × GY220 | RIL | 263 | 4 | 208/SSR | 2217.2 | CIM | 7 | 19 | 6 | – | 2 | – | 10 | 1 | – | 5 | – | [33] |
| Zheng58 × Chang7–2 | DH | 162 | 4 | 119/SSR | 2315.0 | CIM | 8 | 8 | – | – | 6 | – | 12 | 8 | – | 7 | – | |
| Huang C × Xu 178 | RIL | 166 | 4 | 217/SSR | 2438.2 | CIM | – | – | – | – | – | – | 5 | 8 | [34] | |||
| Xu178 × K12 | RIL | 150 | 4 | 191/SSR | 2069.1 | ICIM | 3 | – | – | – | 2 | – | 4 | 2 | – | – | [35] | |
| Trait | MQTL | Chr. | Position (cM) | QTLs Number | Bin | Marker Interval | CI (cM) | Physical Interval (Mb) | Contig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CW, EL, HKW, ED, KRN | MQTL1 | 1 | 145.30 | 11 | 1.02 | umc1568–umc1070 | 141.80–148.80 | 15.80–17.67 | ctg6–ctg9 |
| EW, HKW, KRN, KNR, GW | MQTL2 | 1 | 205.90 | 8 | 1.02–1.03 | bnlg1083–umc1403 | 198.30–210.60 | 29.26–33.13 | ctg9–ctg10 |
| CW, ED, EL, EW, KL, HKW, KRN, KNR | MQTL3 | 1 | 431.20 | 9 | 1.05 | bnlg1884–umc1469 | 419.80–438.00 | 91.88–115.66 | ctg23–ctg28 |
| HKW | MQTL4 | 1 | 519.70 | 2 | 1.05–1.06 | umc2083–bnlg1598 | 506.40–532.80 | 179.61–187.92 | ctg37–ctg38 |
| CD, ED, EL, HKW | MQTL5 | 1 | 662.40 | 10 | 1.07 | bnlg1556–umc2064 | 658.60–668.30 | 208.48–220.66 | ctg44 |
| CD, CW, ED, EL, EW, HKW, KRN | MQTL6 | 1 | 748.10 | 16 | 1.08 | phi037–bnlg1643 | 722.40–768.50 | 228.38–238.45 | ctg46–ctg50 |
| CD, KRN | MQTL7 | 1 | 874.80 | 2 | 1.09 | umc1306–bnlg1268 | 866.00–898.70 | 265.24–273.4 | ctg57 |
| CW, KRN | MQTL8 | 1 | 1113.00 | 4 | 1.12 | umc1725–umc1819 | 1096.50–1119.20 | 296.28–298.64 | ctg65–ctg66 |
| ED, EL, EW, HKW, GWP, KRN, KNR | MQTL9 | 2 | 56.40 | 17 | 2.01–2.02 | umc2363–bnlg1017 | 51.10–62.60 | 4.16–4.9 | ctg69–ctg71 |
| CW, EW, KRN | MQTL10 | 2 | 229.20 | 4 | 2.03–2.04 | umc1185–bnlg381 | 213.40–241.60 | 21.39–29.89 | ctg74 |
| EL | MQTL11 | 2 | 287.50 | 3 | 2.04 | phi083–umc2249 | 281.60–293.20 | 41.22–44.26 | ctg77–ctg78 |
| ED, HKW, KRN, GW | MQTL12 | 2 | 372.10 | 11 | 2.05–2.06 | dupssr21–umc2023 | 366.90–380.40 | 153.48–182.63 | ctg90–ctg96 |
| EW, KRN, KW, HKW, GW | MQTL13 | 2 | 421.90 | 16 | 2.07 | umc2380–mmc0271 | 414.80–435.20 | 190.73–197.18 | ctg98–ctg100 |
| ED, EL, KRN | MQTL14 | 2 | 584.30 | 3 | 2.08–2.09 | bnlg1940–umc1551 | 574.50–596.00 | 219.78–223.63 | ctg105–ctg108 |
| ED, EL, HKW | MQTL15 | 3 | 7.60 | 3 | 3.00–3.01 | umc1746–phi049 | 6.70–8.80 | 1.63–1.73 | ctg111 |
| CW, ED, EL, KL, EW, KNR, KRN, HKW, GW | MQTL16 | 3 | 141.50 | 21 | 3.02–3.04 | umc2258–umc1030 | 127.00–158.20 | 10.08–14.94 | ctg112–ctg114 |
| CW, ED, HKW | MQTL17 | 3 | 189.00 | 5 | 3.04 | umc1742–bnlg1638 | 188.20–189.90 | 23.37–26.31 | ctg116 |
| C, ED, EL, EW, HKW, GW | MQTL18 | 3 | 280.70 | 19 | 3.04–3.05 | umc2264–phi053 | 260.30–297.60 | 90.04–126.49 | ctg121–ctg124 |
| KRN | MQTL19 | 3 | 508.40 | 3 | 3.06 | bnlg1160–dupssr17 | 490.60–517.20 | 187.49–194.08 | ctg138–ctg139 |
| ED, EL, KRN | MQTL20 | 3 | 612.60 | 10 | 3.08 | umc1140–umc1915 | 608.40–616.70 | 209.72–210.93 | ctg145–ctg146 |
| CD, CW, EL, HKW | MQTL21 | 4 | 141.50 | 6 | 4.03 | bnlg1126–umc1550 | 135.30–152.00 | 11.93–14.88 | ctg158–ctg159 |
| CD, ED, EL, KRN | MQTL22 | 4 | 303.20 | 5 | 4.05 | umc2054–umc1346 | 302.50–304.30 | 78.64–136.1 | ctg174 |
| CW, EL, EW, HKW, KRN | MQTL23 | 4 | 511.70 | 17 | 4.08 | umc1612–phi092 | 493.00–522.10 | 187.53–190.23 | ctg185–ctg187 |
| CW, EW, HKW, KRN | MQTL24 | 4 | 608.10 | 13 | 4.09 | umc1989–umc2287 | 599.60–618.10 | 230.28–232.44 | ctg198 |
| ED, EL, KRN | MQTL25 | 4 | 663.60 | 5 | 4.09–4.10 | umc2046–umc1532 | 657.00–671.90 | 236.3–237.5 | ctg201 |
| HKW | MQTL26 | 5 | 82.40 | 2 | 5.01 | umc1478–bnlg1836 | 79.20–87.60 | 4.49–4.58 | ctg204–ctg205 |
| CD, EL, KNR | MQTL27 | 5 | 313.40 | 6 | 5.04 | umc2406–umc1060 | 311.30–317.60 | 127.64–136.49 | ctg233–ctg234 |
| ED, KL, HKW, KRN | MQTL28 | 5 | 420.50 | 9 | 5.05 | umc1687–umc2386 | 411.10–428.00 | 176.94–180.49 | ctg240–ctg242 |
| ED, EL, EW | MQTL29 | 5 | 543.80 | 7 | 5.07 | phi048–bnlg1306 | 536.60–564.60 | 204.66–207.03 | ctg252 |
| CW, HKW | MQTL30 | 6 | 70.10 | 2 | 6.01 | bnlg1371–bnlg1600 | 68.70–71.80 | 27.97–28.31 | ctg262 |
| EL, HKW | MQTL31 | 6 | 308.00 | 5 | 6.05 | umc2065–mmc0241 | 307.10–308.80 | 142.75–144.32 | ctg285 |
| CD, KL, EL, KW | MQTL32 | 6 | 386.30 | 8 | 6.06 | umc1912–umc1463 | 384.70–389.90 | 154.35–155.33 | ctg287 |
| ED, HKW, KRN | MQTL33 | 7 | 164.90 | 3 | 7.02 | mmc0162–phi034 | 154.00–170.50 | 20.34–38.91 | ctg304 |
| EL, ED, HKW, KRN | MQTL34 | 7 | 248.20 | 5 | 7.02 | umc1929–umc2092 | 246.80–250.60 | 107.95–114.7 | ctg310–ctg312 |
| CW, ED, HKW, KRN | MQTL35 | 7 | 385.70 | 5 | 7.03 | umc2329–bnlg1805 | 382.10–389.80 | 151.28–153.7 | ctg322 |
| EL | MQTL36 | 7 | 463.30 | 2 | 7.03–7.04 | umc1214–umc1944 | 462.20–464.50 | 162.29–162.85 | ctg322–ctg323 |
| CW, EL | MQTL37 | 8 | 239.00 | 2 | 8.03 | umc2503–bmc1863 | 238.90–239.20 | 90.3–91.64 | ctg340 |
| EL, EW, KNR, GW | MQTL38 | 8 | 343.50 | 9 | 8.05 | umc1562–umc1846 | 336.40–351.40 | 125.43–130.27 | ctg354 |
| EL, KRN | MQTL39 | 9 | 218.20 | 3 | 9.03 | bnlg127–umc1420 | 214.50–225.40 | 33.59–50.02 | ctg375–ctg377 |
| ED, EL, KNR, GW | MQTL40 | 9 | 302.00 | 11 | 9.04 | umc1120–umc1771 | 298.10–305.30 | 121.84–127.58 | ctg384–ctg385 |
| EL, HKW, KRN | MQTL41 | 9 | 479.70 | 8 | 9.06 | umc1366–umc1733 | 478.10–480.50 | 145.6–146.47 | ctg389 |
| EL, HKW, KRN, KNR | MQTL42 | 10 | 96.30 | 5 | 10.02 | umc1432–umc2034 | 91.40–103.50 | 5.77–6.38 | ctg392 |
| EL, KL, HKW | MQTL43 | 10 | 249.40 | 3 | 10.04 | phi062–umc1053 | 243.90–255.60 | 111.86–114.31 | ctg411–ctg412 |
| ED, EL, EW, KNR, KRN, GW | MQTL44 | 10 | 460.10 | 18 | 10.07 | bnlg1360–umc1640 | 452.70–467.00 | 144.91–145.62 | ctg419 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Sun, S.; He, M.; Wang, J.; Xiang, X.; Niu, Y. Genetic Architecture and Meta-QTL Identification of Yield Traits in Maize (Zea mays L.). Plants 2025, 14, 3067. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193067
Li X, Zhao X, Sun S, He M, Wang J, Xiang X, Niu Y. Genetic Architecture and Meta-QTL Identification of Yield Traits in Maize (Zea mays L.). Plants. 2025; 14(19):3067. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193067
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xin, Xiaoqiang Zhao, Siqi Sun, Meiyue He, Jing Wang, Xinxin Xiang, and Yining Niu. 2025. "Genetic Architecture and Meta-QTL Identification of Yield Traits in Maize (Zea mays L.)" Plants 14, no. 19: 3067. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193067
APA StyleLi, X., Zhao, X., Sun, S., He, M., Wang, J., Xiang, X., & Niu, Y. (2025). Genetic Architecture and Meta-QTL Identification of Yield Traits in Maize (Zea mays L.). Plants, 14(19), 3067. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193067







