Abstract
Understanding trait relationships is fundamental in soybean breeding because the goal is to maximize simultaneous gains. Standard multi-trait genome-wide association studies (MT-GWAS) identify variants linked to multiple traits but fail to capture phenotypic structures or interrelations. Structural Equation Models (SEM) account for covariances and recursion, enabling the decomposition of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) effects into direct or indirect components and identifying pleiotropic regions. We applied SEM to analyze morphology (pod thickness, PT) and yield traits (number of pods, NP; number of grains, NG; hundred-grain weight, HGW). The dataset comprised 96 soybean individuals genotyped with 4070 SNP markers. The phenotypic network was constructed using the hill-climbing algorithm, a class of score-based methods commonly applied to learn the structure of Bayesian networks, and structural coefficients were estimated with SEM. According to coefficient signs, we identified negative interrelationships between NG and HGW, and positive ones between NP and NG, and HGW and PT. NG, HGW, and PT showed indirect SNP effects. We also found loci jointly controlling traits. In total, 46 candidate genes were identified: 7 associated exclusively with NP and 4 associated with NG. An additional 15 genes were common to NP and NG, 3 were common to NP and HGW, 6 were common to NG and HGW, and 11 were common to NP, NG, and HGW. In summary, SEM-GWAS revealed novel relationships among soybean traits, including PT, supporting breeding programs.
1. Introduction
Soybean is one of the five crops that dominate global agriculture, along with maize, wheat, cotton, and rice [1]. It is one of the most important commodities in global trade [2]. Brazil is the largest producer of soybeans in the world, producing 129.5 million metric tons, or approximately 36% of global production [1]. Soybean meal is closely linked to the food supply through direct and indirect consumption as an excellent feed supplement, especially for monogastric animals [3]. Soybean oil is highly versatile, with applications in the food and beverage, wax, construction, cosmetics, plastics, and fuel industries [4].
Several studies using the univariate genome-wide association study (GWAS) approach have been used to identify genomic regions associated with important soybean traits, such as disease resistance [5,6,7,8], seed protein and oil content [9,10,11,12,13], salt tolerance [14,15], physiological-related traits [16,17,18], and agronomic traits [10,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. Although the univariate GWAS methodology is the most commonly used in a breeding program, multiple traits are often studied simultaneously. Another approach that allows the detection of genomic regions involved in linkage or pleiotropy is multivariate GWAS (MTM-GWAS). However, both univariate and multivariate GWAS approaches do not allow us to study the interrelationships among the traits.
Given these limitations, some multivariate GWAS approaches have been developed to assess the associations among the traits. Shim et al. [26] proposed a methodology based on the Bayes factor (mvBIMBAM). Gianola and Sorensen [27], Momen et al. [28], and Wang et al. [18] used structural equation modeling in the context of GWAS (SEM-GWAS). SEM makes it possible to interpret results differently from a multiple trait model (MT), which only captures covariances between variables without considering the existence of recursion. In contrast to this phenomenon, SEM explores the interrelationships between variables, in which one trait can be considered a predictor of another trait [27]. Thus, by uniting SEM to GWAS (SEM-GWAS), it becomes possible to model the associations between traits and quantitative trait loci (QTL) by decomposing single nucleotide effects of polymorphisms (SNPs) in a trait into direct or indirect components and also to identify genomic regions with pleiotropic effects [29,30,31].
For this type of methodology, it is common to use Bayesian networks (BNs) to generate connections between variables based on the theory of Direct Acyclic Graph (DAG) and conditional independence; that is, it is used as a hypothesis-generating tool in determining the causal nature of the connections found, as the interrelations between the traits are not always known a priori [32]. Several works have already been proposed based on this type of logic [29,30,31,33,34,35]. From the best network hypothesis created, the SEM methodology was used to identify the structural coefficient.
The SEM-GWAS approach can account for trait interactions and partition single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) effects from the trait itself (direct) and from other related traits (indirect). Thus, the objectives of this study were to (1) estimate genetic components for important traits in soybeans, (2) use Bayesian network approaches to estimate a phenotypic network reflecting the interrelationships among traits, and (3) use SEM-GWAS approaches to estimate direct and indirect SNP effects.
2. Results
2.1. Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics for the number of pods per plant (NP), number of grains per plant (NG), hundred-grain weight (HGW), and pod thickness (PT) were calculated across all genotypes (Table 1). On average, the plants produced 53.47 (±11.72) , 111.40 (±22.54) , and 14.57 (±3.04) , and the thickness of the pod was 6.41 (±0.87) . These values summarize the phenotypic variability present in the population and provide the basis for subsequent genetic analyses.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics for soybeans’ morphological and productivity traits.
2.2. Genetic Parameters
To estimate genetic parameters, we fitted a Bayesian multivariate mixed model including additive genomic relationships among genotypes and independent residuals for the four traits: number of pods per plant (NP), number of grains per pod (NG), hundred-grain weight (HGW), and total pod weight (PT). Narrow-sense heritability was calculated from the ratio of additive genetic to total variance, and genomic and residual correlations were derived from the posterior distributions of the additive and residual covariance matrices. Significance was assessed from the 95% highest posterior density (HPD) intervals, where estimates excluding zero were considered significant.
According to Table 2, narrow-sense heritability was moderate to high for all traits, with posterior means (and 95% HPD) of 0.89 (0.73–1.00) for NP, 0.79 (0.44–1.00) for NG, 0.39 (0.14–0.67) for HGW, and 0.45 (0.24–0.66) for PT. Genomic correlations were consistently significant, ranging from strong positive values, such as 0.96 (0.82–1.00) between NP and NG, to strong negative values, such as –0.88 (–0.99 to –0.68) between NG and PT. In contrast, only the residual correlation between HGW and PT, 0.59 (0.35–0.80), was significant, indicating that most trait associations arise from shared genetic rather than environmental effects.

Table 2.
Posterior means of the genomic heritabilities (diagonal), residual (lower triangular), and genomic (upper triangular) correlations of four traits in the soybeans, with posterior standard deviations in parentheses.
2.3. Bayesian Network Structure
To identify conditional dependencies among traits, we inferred a Bayesian network using a score-based hill-climbing algorithm. The algorithm searched the space of possible directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) and retained the structure with the highest posterior score. Edge strength and direction were estimated from 50,000 bootstrap samples of the posterior distribution.
The resulting network (Figure 1) showed a directed edge from number of pods per plant (NP) to number of grains per pod (NG), with 100% edge strength and 58.57% directional support. A second edge linked NG to hundred-grain weight (HGW) with the same strength and directional support, and a third edge connected HGW to total pod weight (PT), with 99.98% strength and full (100%) directional support. This topology indicates that NP acts as the primary upstream trait, NG is directly influenced by NP, HGW is directly influenced by NG and indirectly by NP through NG, and PT is directly influenced by HGW while also receiving indirect effects from NP and NG.
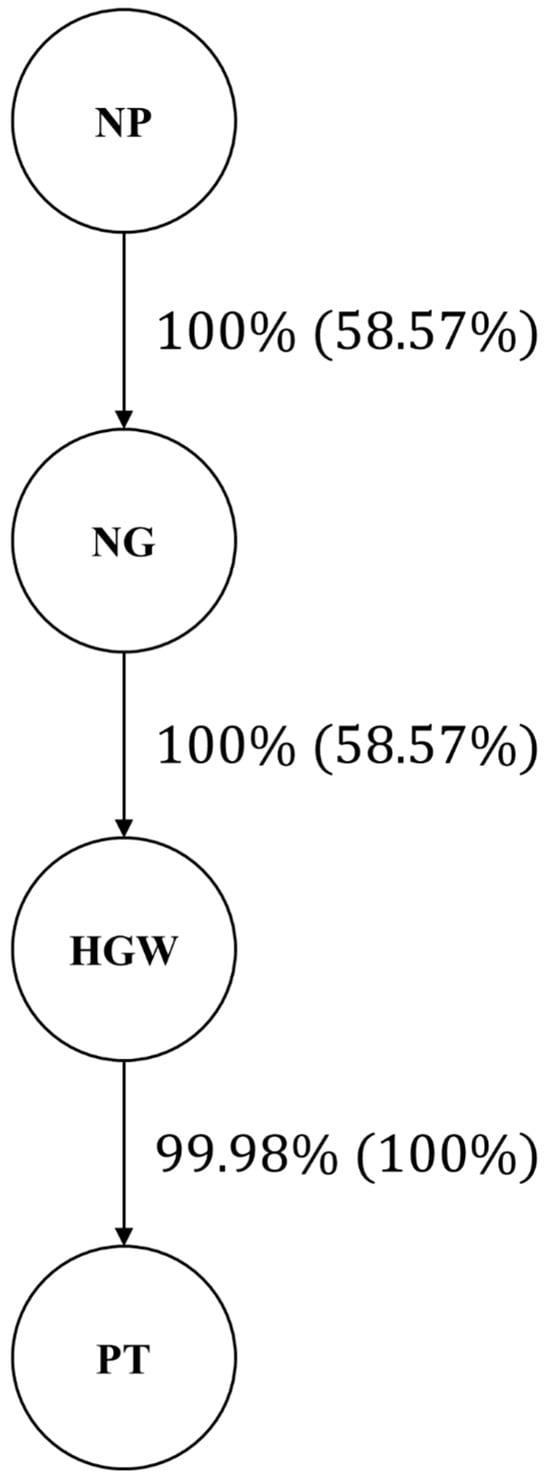
Figure 1.
Path network via the HC algorithm from 50,000 bootstrap samples. Values outside the parentheses represent strength (the percentage of bootstrap samples that had an arc), and values inside the parentheses represent direction (the percentage of bootstrap samples in which a given direction of arcs occurred). NP: number of pods; NG: number of grains; HGW: hundred-grain weight; PT: pod thickness.
Model fit was evaluated by the change in the Bayesian information criterion (BIC) when individual edges were removed from the best-scoring network (Table 3). A larger increase in the BIC after removing an edge indicates a greater contribution of that path to the overall model.

Table 3.
Bayesian network score from the Bayesian information criterion (BIC).
The largest effect was observed for the edge from number of pods per plant (NP) to number of grains per pod (NG): deleting this connection increased the BIC by 35.8808, highlighting it as the most influential link in the phenotypic network.
Removing the edge from NG to hundred-grain weight (HGW) and the edge from HGW to total pod weight (PT) produced smaller, though still meaningful, BIC increases of 13.1780 and 25.9670, respectively, indicating moderate contributions of these paths to the network structure.
2.4. Structural Equation Model
Unlike the univariate GWAS and MTM-GWAS models, the graphical structure inferred from Bayesian networks and SEM explains how phenotypes can be related to each other, directly or indirectly. It allows researchers to understand how changes in one trait might directly influence another, or how they might be connected through a chain of intermediate effects. In addition, this approach can reveal potential causal pathways or correlated factors that connect the phenotypes. This can provide clues about the underlying biological mechanisms that explain how the traits are related.
The estimated values of the structural coefficients represent the average increase in the downstream phenotype for a one-unit increase in the upstream phenotype (Table 4). We observed that the paths between NP and NG and between HGW and PT were positive (0.00006 and 0.00697, respectively), whereas the path between NG and HGW was negative (−0.05450). The magnitude of the estimated structural coefficient values was small, suggesting that the role of upstream traits in mediating SNP effects of downstream traits was marginal. Increasing NP, NG, and HGW by 1 unit each resulted in an average increase of 0.00006, 0.00697, and −0.05450 units in NG, HGW, and PT, respectively. Figure 2 shows the relationship between the inferred phenotypic network and the SNPs, where , , and represent the direct effects of the SNPs on NP, NG, HGW, and PT, respectively, and , and represent the structural coefficients associated with the phenotypic network.

Table 4.
Structural coefficient estimates derived from the structural equation models.
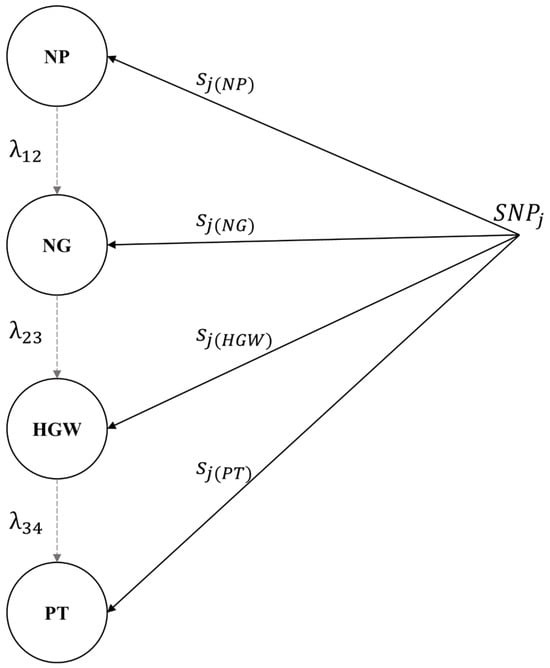
Figure 2.
Path network of the SNP markers’ effects. NP: number of pods; NG: number of grains; HGW: hundred-grain weight; PT: pod thickness. The gray dashed arcs indicate the direction of the interrelations.
: NP → NG; : NG → HGW; : HGW → PT. The black arcs indicate the direct effect of the jth SNP.
2.5. Partitioning of SNP Effects
As shown in Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6, the effects of SNPs could be decomposed into direct, indirect, and total effects for each characteristic using the SEM-GWAS approach.
2.5.1. Number of Pods (NP)
The phenotypic network did not identify any mediator trait for NP (Figure 2). In this case, the total effect of the th SNP on NP consists of its direct effect:
The Manhattan plots of the direct (A) and total (B) SNP effects on NP are presented in Figure 3.
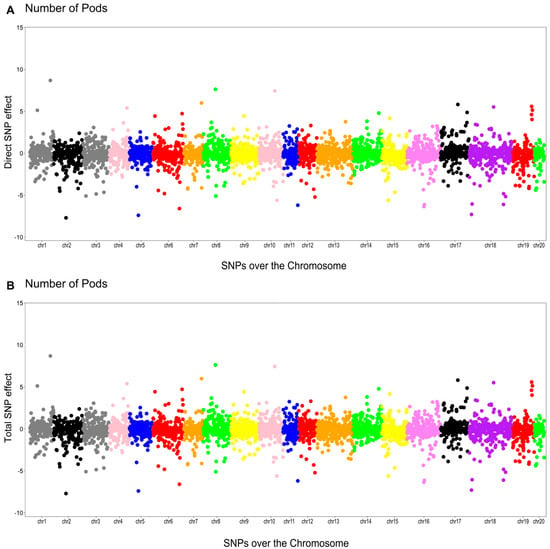
Figure 3.
Manhattan plots for the direct (A) and total (B) SNP effects associated with the number of pods (NP) via the SEM-GWAS approach.
2.5.2. Number of Grains (NG)
In addition to the direct effect of the th SNP associated with NG, there was an indirect effect mediated by NP (). Thus, the total effect was calculated by summing the direct and indirect effects.
The Manhattan plots of the direct (A), indirect (B), and total (C) SNP effects on NG are presented in Figure 4.
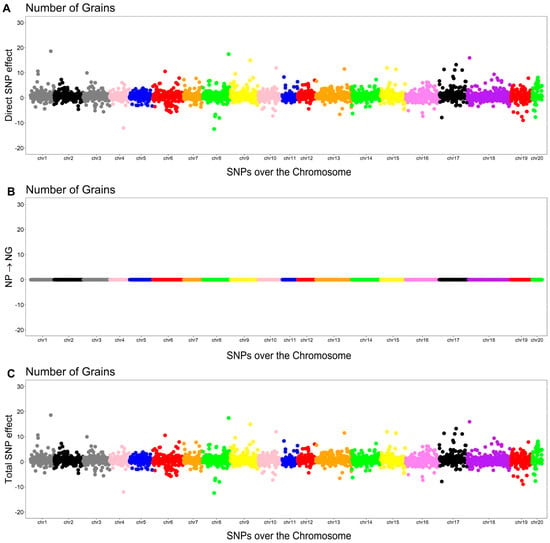
Figure 4.
Manhattan plots for direct (A), indirect (B), and total (C) SNP effects associated with the number of grains (NG) via the SEM-GWAS approach. NP refers to the number of pods.
2.5.3. Hundred-Grain Weight (HGW)
The overall effect of the SNP on HGW was decomposed into a direct effect and two indirect effects mediated by NG and NP. The structural coefficients for the indirect effects were (0.0018) for NG and () for NP. The total effect of the th SNP on HGW was equal to the sum of the direct and indirect effects.
The Manhattan plots of the direct (A), indirect (B), and total (C) SNP effects on HGW are presented in Figure 5.
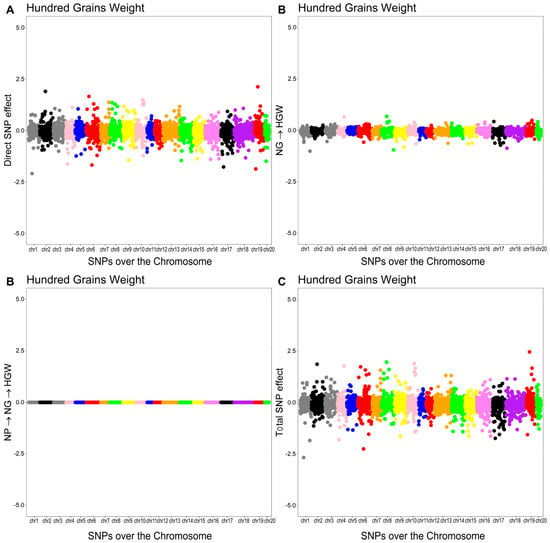
Figure 5.
Manhattan plots for direct (A), indirect (B), and total (C) SNP effects associated with hundred-grain weight (HGW) via the SEM-GWAS approach. NP and NG refer to number of pods and number of grains, respectively.
2.5.4. Pod Thickness (PT)
The overall effect of the SNP on PT was decomposed into a direct effect and three indirect effects mediated by HGW, NG, and NP. The structural coefficients for the indirect effects were (0.0018) for HGW, () for NG, and () for NP. The total effect of the th SNP on PT was equal to the sum of the direct and indirect effects.
The Manhattan plots of the direct (A), indirect (B), and total (C) SNP effects on PT are presented in Figure 6.
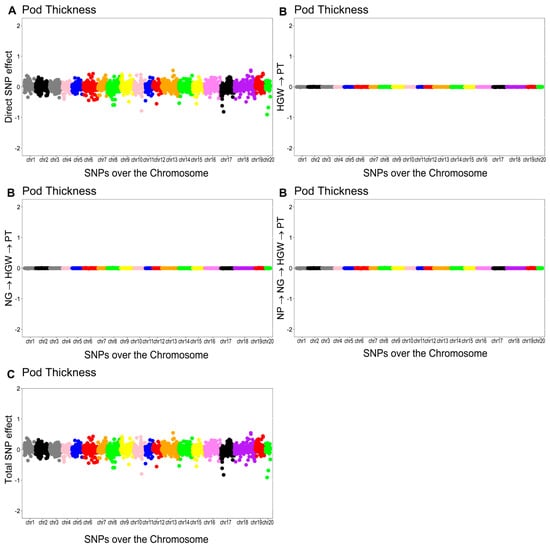
Figure 6.
Manhattan plots for direct (A), indirect (B), and total (C) SNP effects associated with pod thickness (PT) via the SEM-GWAS approach. NP, NG, and HGW refer to number of pods, number of grains, and hundred-grain weight, respectively.
2.6. Integration of Structural Equation Modeling and Genome-Wide Association Study (SEM-GWAS)
In total, 46 SNPs were statistically significant (q-value < 0.01) for the traits studied (Table S5). Of those, 36, 36, and 20 SNPs were associated with NP, NG, and HGW, respectively. No significant SNP was found for PT. All information on significant SNPs, such as the chromosome to which it belongs, position, q-value, gene, auto defline, gene atlas description, GO, traits, and some previously reported references, is illustrated in Table S5.
For NP, relevant GO terms identified include inactive shikimate kinase, serine-threonine protein kinase, GDT1-like protein, polyglutamine-binding, protein DA1-related 2, β-1, 3-glucanase-like protein, DNAJ homolog, fructose-bisphosphate aldolase, amino acid transporter, protein tyrosine kinase, squamosa promoter-binding, xenobiotic monooxygenase, reverse transcriptase, RNA-binding proprotein convertase subtilisin, NADPH oxidase, DNA mismatch repair, Acyl-CoA n-acyltransferase, dynamin, small heat-shock, ribosomal biogenesis, acylglycerol lipase, snare, phosphatase, U3 small nucleolar, AP-4 complex, ABC transporter, WW domain, proprotein convertase, and HNH endonuclease. For NG, relevant GO terms identified include inactive shikimate kinase, MYB-like DNA-binding, glycine-rich protein, ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase, ABC transporter, dentin sialophosphoprotein, threonine-protein kinase SRK-related, monothiol glutaredoxin, and mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase. In Figures S1 and S2, it is possible to observe the number of QTLs found for each GO term.
3. Discussion
3.1. Genetic Parameters
The heritability estimates for NP and NG were similar to those found in the literature. Our heritability estimate for HGW differed from those found in the literature, possibly because we used a different estimation method. No heritability results were found in the literature for PT. According to Aditya et al. [36], using a database of 31 genotypes of G. max (L.) Merrill, a heritability estimate of 0.81 was found for NP. Ghiday et al. [37], using 22 promising genotypes from IITA/Nigeria, found a heritability estimate of 0.93 for NP. Del Conte et al. [38], using 34 soybean populations in a path analysis, found a heritability for NP of 0.83. For NG, Ghiday et al. [37] reported a heritability of 0.98. Similarly, Del Conte et al. [38] and de Albuquerque et al. [39] reported heritability estimates of 0.70 and 0.59, respectively. For HGW, Bisinotto et al. [40] reported a heritability estimate of 0.77 using 31 lines from a breeding program.
The genomic correlation estimates were consistent with those found in the literature. According to Del Conte et al. [38] and Li et al. [41], the genetic correlation estimates between NP and NG were 0.87 and 0.88, respectively. Li et al. [41] reported genetic correlations of −0.25 and −0.29 between NP and HGW and between NG and HGW, respectively. Silva et al. [42] found a correlation of −0.95 between NG and HGW. The signs of the correlations were identical to those found in this work. However, their estimates differed in magnitude, which could be due to the population and environmental differences from the data in this work. No study was found that showed a correlation with PT.
The occurrence of significant genetic correlations, a fact observed among all characteristics, may indicate a hypothesis that the characteristics may be indicators of one of the others. However, genetic manifestation can be recommended for both linkage disequilibrium and pleiotropy. According to our results, we noticed that the most important effects were direct ones; thus, it can be inferred that the correlations may have been the result of existing pleiotropy and, therefore, it may be very difficult to partition the total effect of the QTL into direct and indirect effects [43].
3.2. Integration of Structural Equation Modeling and Genome-Wide Association Study (SEM-GWAS)
The structural equation modeling framework applied here extends multivariate mixed models that are inherently suited for multi-trait genomic data. The estimation proceeds trait by trait within the specified network, keeping overall computational requirements manageable. Previous SEM-GWAS applications illustrate this scalability, with Suela et al. [29] analyzing 21,211 SNPs, Pegolo et al. [30] working with 37,519 SNPs, and Momen et al. [31] including roughly 700,000 SNPs, all reporting successful model fitting without the need for specialized high-performance computing. Within this framework, the component that typically demands the longest runtime is the Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) sampling used to estimate posterior distributions. Although the experimental panel in the present study is compact, statistical corrections were applied to control population structure and relatedness, ensuring that the genetic diversity within the genotypes was effectively captured for association analysis, and the specific strategies adopted to address this smaller population are detailed in the Materials and Methods section.
MTM-GWAS is widely applied, but it remains essentially associative and does not allow the separation of direct genetic effects from those mediated by other phenotypes. Consequently, a single signal may reflect true pleiotropy or merely the indirect influence of an intermediate trait, complicating biological interpretation [44]. Furthermore, studies have shown that different multivariate implementations can inflate type I error rates under deviations from normality or case–control imbalance, thereby reducing statistical robustness [45,46].
By explicitly incorporating causal networks and decomposing the total effect of each SNP into direct and indirect components, SEM-GWAS addresses these limitations and delivers mechanistic insights that MTM-GWAS, by design, cannot achieve. The indirect SNP effects uncovered within the trait network are particularly relevant for breeding programs, as they raise the question of how such effects can be translated into practical selection decisions. As emphasized by Suela et al. [35], statistical equivalence between models does not necessarily imply biological equivalence. Breeding values estimated with traditional multivariate models (MTMs) capture all additive genetic effects—both direct and indirect—arising from pleiotropy, linkage disequilibrium, and shared environmental influences. In contrast, structural equation modeling (SEM) distinguishes direct genetic effects from those mediated through other traits, generating breeding values that are effectively corrected for causal relationships.
This distinction is critical when the objective is to identify precise targets of selection within complex trait networks. While MTM breeding values convey the overall genetic merit required for selection, the structural coefficients and indirect effects estimated by SEM reveal intermediate traits that can be strategically manipulated to maximize genetic gain [35]. In recurrent selection schemes or index-based breeding strategies, such information supports the construction of weighted selection indices that prioritize key mediating traits, enabling more efficient phenotypic and genotypic interventions without the need to redesign the analytical pipeline. Distinguishing direct from indirect genetic effects, therefore, not only refines biological interpretation but also provides actionable guidance for accelerating genetic improvement in complex trait networks [35].
Premature pod opening (PT) of immature soybean pods under water deficits causes significant yield losses across Brazil and globally. Palharini [47] reported that this phenomenon is influenced by genotype and water stress, impacting traits such as the number of pods (NP), number of grains (NG), and hundred-grain weight (HGW). To explore these relationships, we constructed a Bayesian network to model the phenotypic interactions among NP, NG, HGW, and PT, revealing both favorable and unfavorable links associated with pod-opening susceptibility. This phenotypic network was incorporated into a structural equation modeling-based, genome-wide association study (SEM-GWAS) to dissect the SNP effects into direct and indirect contributions within the network.
The SEM-GWAS analysis identified positive direct effects from NP to NG and from HGW to PT, as well as indirect effects from NP to HGW and PT, and from NG to HGW and PT. Positive interrelationships indicate that a higher NP increases NG, and a higher HGW enhances PT, while negative interrelationships suggest that a higher NG reduces HGW (Table 4). Notably, HGW exhibited a substantial indirect effect from NG, suggesting that genetic regulation of seed weight is mediated by grain number, likely through nutrient allocation or stress response pathways. Direct SNP effects were generally stronger than indirect effects for NG and PT, but HGW showed significant indirect effects from NG, underscoring the interconnectedness of these traits (Table 4). Several quantitative trait loci (QTLs) regulated multiple traits, indicating multifunctionality (Table S5), consistent with findings in soybeans [12,22] and rice [31] but contrasting with studies reporting no such pleiotropy [29].
To address the genetic basis of these traits, we analyzed the functions of 46 candidate genes associated with NP, NG, and HGW, several of which control multiple traits simultaneously (Table S5), as previously reported [41,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61]. To provide a deeper functional interpretation, we linked these genes to specific pathways in soybean physiology and abiotic stress tolerance, particularly water deficits, which exacerbate premature pod opening [47]. Below, we discuss key candidate genes and their roles in these pathways.
Glyma.01G052600, a serine-threonine protein kinase, participates in the abscisic acid (ABA) signaling pathway and is crucial for drought stress responses and seed size regulation. Liu et al. [62] showed that this kinase, termed Novel Seed Size (NSS), regulates cell expansion under stress, influencing seed size. Its association with NP, NG, and HGW suggests it coordinates pod and seed development under water deficits by upregulating stress-responsive genes, such as RD29A and DREB, through MAPK cascades [63]. This supports the positive NP-NG relationship, where enhanced stress tolerance promotes higher grain production, potentially reducing pod-opening susceptibility.
Glyma.02G251800, a protein DA1-related 2 gene, is involved in the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway, regulating cell proliferation and organ size. Zhao et al. [64] linked DA1 to adaptive radiation in soybeans, while Li et al. [65] described it as a ubiquitin receptor influencing a wide range of cellular processes [66], including cell cycle control [67], abnormal protein degradation [68,69], hormonal signaling via auxin and gibberellin [70,71], and resistance to abiotic stresses [70,72,73]. Its association with NP indicates a role in pod formation by modulating cell division under water-limited conditions, contributing to reduced PT.
Glyma.02G253800, a β-1,3-glucanase-like protein, is involved in callose metabolism, a critical pathway for cell wall remodeling that influences pod dehiscence. Callose deposition, regulated by β-1,3-glucanases, strengthens pod cell walls under drought stress, reducing opening susceptibility [74,75,76]. Its association with NP suggests it maintains pod integrity, consistent with Palharini’s findings on water deficit-induced pod opening [47].
Glyma.03G183900, a MYB-like DNA-binding protein, regulates stress-responsive pathways, including flavonoid biosynthesis and secondary cell wall formation. Du et al. [77] reported that MYB transcription factors modulate legume-specific nodulation and stress responses. Its association with NG and HGW indicates that it influences seed development and weight by regulating cell-wall reinforcement, potentially mitigating pod dehiscence under water stress.
Glyma.04G086600, an amino acid transporter, supports nutrient allocation pathways by transporting amino acids for seed filling [78]. The significant indirect effect of NG on HGW (Table 4) likely reflects this gene’s role in resource allocation, where disruptions under water deficits reduce seed weight and increase PT susceptibility.
Glyma.04G239000, a leucine-rich repeat (LRR) protein, is part of the receptor-like kinase (RLK) signaling pathway, regulating growth and stress responses [79]. Its association with NP, NG, and HGW suggests a broad role in coordinating pod and seed development under drought through stress signaling cascades that enhance tolerance.
Glyma.05G019000, a squamosa promoter-binding-like protein, regulates developmental transitions and stress responses via jasmonic acid and ethylene pathways [80,81,82,83,84,85,86]. Its association with NP indicates that it controls pod formation by modulating reproductive development timing, which is crucial for minimizing PT under water stress.
Glyma.09G252200, a monothiol glutaredoxin, maintains redox homeostasis through glutathione metabolism, protecting developing pods and seeds from oxidative stress under water deficits [87]. Its association with NG and HGW highlights its role in supporting seed development, contributing to the indirect effects observed in the phenotypic network.
Glyma.12G242300, a dynamin gene, is involved in vesicle trafficking and cell membrane dynamics, and it is essential for cell growth and stress adaptation [88,89]. Its association with NP and NG suggests that it supports pod and grain development under drought stress.
The multifunctionality of QTLs controlling multiple traits (Table S5) likely reflects pleiotropy or tight linkage within pathways such as ABA signaling, ubiquitin-mediated cell cycle control, callose metabolism, and redox homeostasis. These pathways converge to regulate the phenotypic network underlying pod opening and seed traits under water deficits. For instance, the indirect effect of NG on HGW may involve nutrient allocation [78] or redox homeostasis [87], which are disrupted under stress, affecting seed weight and PT.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Phenotypic Data and SNP Genotyping
The phenotypic data of the genotypes from GDM seeds were kindly provided by the soybean breeding program of the Federal University of Viçosa (in Portuguese, the Universidade Federal de Viçosa—UFV). The experiment was conducted in a greenhouse located in the city of Viçosa—MG (Brazil) (lat: 20°45′17″ S; length: 42°52′57″ W) and planted from January to May 2018. The design used was randomized blocks, with 96 soybean genotypes evaluated in 3 blocks. The experimental plot consisted of a plant grown in a pot with a volume of seven liters, containing a substrate prepared with a mixture of soil, sand, and animal manure, in a ratio of 3:1:2. The substrate was corrected based on chemical analysis, using crop extraction values for production of 3000 [90]. The remaining cultural treatments were carried out as recommended for soybean cultivation [90]. The average temperature and humidity of the greenhouse, which were monitored with the aid of a digital thermohygrometer (model K29-5070H-Kasvi), varied from 22.5 to 34 °C and from 35.5 to 40.5%, respectively. The genotypes evaluated came from different soybean genetic improvement companies (widely planted in Brazil) with great genetic variation in their traits, including different transgenic events (conventional, Roundup Ready and Intacta RR2BT), growth types (determinate, semi-determinate, and indeterminate), and maturity groups (five to nine). Although the experimental panel is compact, statistical corrections were applied to control population structure and relatedness, ensuring that the diversity present was effectively captured for the association analysis. The percentage of immature pods opened per plant was evaluated at the R6 development stage (green pods with full grains) based on the total number of pods. Four traits were evaluated in this work: NP—number of pods (), NG—number of grains (), HGW—hundred-grain weight (), and PT—pod thickness (). For the association analysis, a panel of SNP markers was used, with 4070 informative markers for the set of genotypes. The SNP quality control parameters used were call rate () and minor allele frequency (). The genotyping data of the genotypes were provided by GDM Seeds. The DNA of 81 and 18 young trifoliate soybean genotypes was extracted using the hexadecyltrimethyl ammonium bromide method [91]. The genotyping was made via genotyping by sequencing (GBS) at the Institute for Genome Diversity at Cornell University (Ithaca, NY) and the Biotechnology Center at the University of Wisconsin–Madison (Wisconsin, USA) [92]. The DNA library was prepared using the restriction enzyme ApeKI [93], and the DNA sequencing was performed using 90-bp according to the GBS protocol by an Illumina HiSeq [93,94].
4.2. Phenotypic Data Analysis
Prior to GWAS, the phenotypic values were adjusted for systematic effects according to the following statistical model:
where is the vector of observed phenotypes, and are the vectors of overall mean (fixed effect) and between block effect (fixed effect), respectively, and and are the vectors of genotypic effects (random effect) and model residuals (random effect), respectively. , , and are the incidence matrices relating , , and , respectively. The vectors and assume a normal distribution and , where and are the variance components, and is an identity matrix. The adjusted phenotypic values were obtained as the sum of the estimates of random effects and ; that is, [95]. These analyses were conducted using the R software environment [96].
4.3. Bayesian Multi-Trait Genomic Best Linear Unbiased Prediction Model
The corrected phenotypes were used in the following Bayesian multi-trait genomic best linear unbiased prediction model.
where is the vector of adjusted phenotypes for t traits (), , , , and are the incidence matrices (only including the intercepts) for traits; is the vector of the mean effects for traits; , , , and are the incidence matrices associating , , , and with , , , and ; is the vector of additive genetic effect for traits, and is the vector of model residuals for traits. The and vectors assumed a multivariate Gaussian distribution of and , respectively, where and are the covariance matrices of additive genetic effect and model residuals, respectively, indicates the Kronecker product, and and are the genomic relationship matrix and the identity matrix, respectively. The matrix was estimated as G = , where is the centered SNP marker matrix [97], is the allele frequency of the th marker, and is the total number of markers. A non-informative prior was assigned to the vector of . The and matrices followed an inverse Wishart prior distribution, , where and ν are hyperparameters associated with scale and degree of freedom, respectively.
The Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) approach was used with the Gibbs sampling algorithm to obtain marginal posterior densities. Convergence analysis was performed using the boa R package [98] within the R software environment version 4.5.1 [96]. The MCMC included 3,000,000 iterations, with a burn-in of 300,000 and a thinning rate of 50, yielding 54,000 MCMC samples for inference. Convergence analysis included autocorrelations (Tables S1 and S3) and Geweke tests (Tables S2 and S4).
4.4. Bayesian Networks
The Bayesian network (BN) was used to assess the relationships among the traits. A Bayesian network can be viewed as a graphical model based on a directed acyclic graph, where nodes (or vertices) represent random variables and arcs (or edges) represent probabilistic dependencies between them [99,100]. In general, a directed acyclic graph is formed by nodes connected by directed edges, where the probability that an edge exists between nodes (strength) and the probability that the edge has a particular direction (direction) can be estimated.
The hill-climbing (HC) algorithm, implemented in the bnlearn R package [101], was used to estimate a phenotypic network. The HC algorithm finds the best structure of the network by removing arcs and changing their directions. For each edge removal, the Bayesian information criterion (BIC) was computed to infer its relative contribution to the overall BIC of the network. A total of 50,000 bootstrap samples were used to define the strength and direction of each arc. We used the criteria of direction 50% and strength 80% to select high-confidence relationships.
4.5. Multi-Trait Association Analysis (MTM-GWAS)
MTM-GWAS modeling was performed using the SNP Snappy strategy [102] implemented in the WOMBAT program [103].
where is the vector of scaled phenotypes of adjusted traits, , , , and are the SNP vector matrices for the th marker associating , , , and to , , , and , and is the vector of the th SNP marker effect for traits. , , , and are the incidence matrices associating , , , and with , , , and . The covariance structure was the same as shown earlier. The SNP effects, , were obtained by fitting a single SNP, one at a time, for each trait. A statistic was used to obtain values: , where is the point estimate of the th SNP effect and is its standard error. The p-values were then corrected for multiple testing using the false discovery rate (FDR) procedure, and q-values were considered significant at an FDR threshold of 0.01 [104]. The SNP dosage matrix has also been corrected for the population structure, where 23 principal components were used, resulting in approximately 80% of the genetic variability.
4.6. Structural Equations Modeling GWAS (SEM-GWAS)
MTM-GWAS modeling was performed using the SNP Snappy strategy [102] implemented in the WOMBAT program [103].
where is the vector of scaled phenotypes of adjusted traits, , , , and are the SNP vector matrices for the th marker associating , , , and to , , , and , and is the vector of the th SNP marker effect for traits. , , , and are the incidence matrices associating , , , and with , , , and . The covariance structure was the same as shown earlier. The SNP effects, , were obtained by fitting a single SNP, one at a time, for each trait. A statistic was used to obtain values: , where is the point estimate of the th SNP effect and is its standard error. The p-values were then corrected for multiple testing using the false discovery rate (FDR) procedure, and q-values were considered significant at an FDR threshold of 0.01 [104]. The SNP dosage matrix has also been corrected for the population structure, where 23 principal components were used, resulting in approximately 80% of the genetic variability.
4.7. Pathway Enrichment Analyses
We selected the relevant SNPs using the p-value (<0.01) obtained from MTM-GWAS (no window size was used). We used the Glycine max genomic database available at Phytozome [105] (https://phytozome-next.jgi.doe.gov/jbrowse/index.html?data=genomes%2FGmax_Wm82_a2_v1&loc=Chr01%3A5673531..51138829&tracks=Transcripts%2CAlt_Transcripts%2CPASA_assembly%2CBlastx_protein%2CBlatx_Fabidae%2CBlatx_BasalEmbryophyte%2CBlatx_BasalMalvidae&highlight=) (accessed on 13 June 2024) to assess the functionality of each identified gene and the enriched gene ontology (GO) terms.
5. Conclusions
This study presents the first application of SEM-GWAS in soybeans to dissect the genetic architecture of complex, interrelated traits. By partitioning SNP effects for NP, NG, HGW, and PT, we identified QTLs with defined biological functions and quantified both direct and indirect genetic influences. Most genetic effects were direct, but HGW showed a moderate indirect contribution through SNPs influencing NG. These results provide new insight into how trait networks shape yield components and highlight the value of SEM-GWAS for uncovering pathways that conventional univariate or multivariate GWAS cannot capture. The approach offers a practical framework for soybean breeding, enabling more precise selection strategies and potentially greater genetic gain.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://zenodo.org/records/16986530 (accessed on 14 June 2025). Figure S1: Gene ontology (GO) terms for the number of pods. SNP obtained from multi-trait association analysis (MTM-GWAS) considering a p-value < 0.01.; Figure S2: Gene ontology (GO) terms for the number of grains. SNP obtained from multi-trait association analysis (MTM-GWAS) considering a p-value < 0.01.; Table S1: Lags and autocorrelations for genetic chain.; Table S2: Geweke Convergence Diagnostic for genetic chain considering fraction in first window = 0.1 and fraction in last window = 0.5.; Table S3: Lags and autocorrelations for residual chain.; Table S4: Geweke Convergence Diagnostic for residual chain considering fraction in first window = 0.1 and fraction in last window = 0.5.; Table S5: Functional annotation of SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) with significant associations (q < 0.01), chromosome, and position associated for number of reproductive nodes (NRN) and yield (YL).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.S. and M.N.; methodology, M.M.S., G.M. (Gota Morota) and M.N.; software, M.M.S., M.N. and G.M. (Gota Morota); validation, M.M.S., C.F.A., A.C.C.N., M.N. and G.M. (Gota Morota); formal analysis, M.M.S., G.M. (Gota Morota) and M.N.; investigation, M.M.S., M.N. and G.M. (Gota Morota); data curation, N.F.G., G.M. (Gaspar Malone) and F.L.d.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M.S., M.N. and G.M. (Gota Morota); writing—review and editing, M.M.S. and M.N.; visualization, M.M.S., M.N., G.M. (Gota Morota), A.C.C.N. and C.F.A.; supervision, M.N. and G.M. (Gota Morota); project administration, M.N.; funding acquisition, M.N. and C.F.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We would like to thank the Foundation for Research Support of the state of Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG, APQ-01638-18) and the National Council of Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq, 408833/2023-8). M.N. and C.F.A. are supported by scientific productivity (310755/2023-9 and 309856/2023-0), respectively, from the Brazilian Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq).
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study are available from three of the authors, Nizio Fernando Giasson, Gaspar Malone, and Felipe Lopes da Silva, upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- United States Department of Agriculture. World Agricultural Production. In Proceedings of the Circular Series WAP, 6–23 June 2023; pp. 1–47. Available online: https://downloads.usda.library.cornell.edu/usda-esmis/files/5q47rn72z/2z10z531z/ft84b485b/production.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2025).
- Sun, J.; Mooney, H.; Wu, W.; Tang, H.; Tong, Y.; Xu, Z.; Huang, B.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, X.; Wei, D.; et al. Importing Food Damages Domestic Environment: Evidence from Global Soybean Trade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5415–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, F.; García, C.; Pintos, F.; Otero, A. Effects of Irrigation Regime on the Growth and Yield of Irrigated Soybean in Temperate Humid Climatic Conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 193, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, Z.; Singer, W.M.; Zhang, B. Soybean Production, Versatility, and Improvement. Legum. Crop. 2020, 10, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludke, W.H.; Schuster, I.; Da Silva, F.L.; Montecelli, T.D.N.; Soares, B.d.A.; De Oliveira, A.B.; Volpato, L. SNP Markers Associated with Soybean Partial Resistance to Phytophthora Sojae. Crop Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 2019, 19, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Wani, S.H.; Collins, P.J.; Wen, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, N.; McCoy, A.G.; Bi, Y.; Tan, R.; Zhang, S.; et al. QTL Mapping and GWAS for Identification of Loci Conferring Partial Resistance to Pythium Sylvaticum in Soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr). Mol. Breed. 2020, 40, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Silva, F.; Venancio, T.M. Integration of Genome-Wide Association Studies and Gene Coexpression Networks Unveils Promising Soybean Resistance Genes against Five Common Fungal Pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, E.G.C.; Marcelino-Guimarães, F.C. Mapping Major Disease Resistance Genes in Soybean. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Torkamaneh, D., François, B., Eds.; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; ISBN 9781071622377. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, E.Y.; Song, Q.; Jia, G.; Specht, J.E.; Hyten, D.L.; Costa, J.; Cregan, P.B. A Genome-Wide Association Study of Seed Protein and Oil Content in Soybean. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonah, H.; O’Donoughue, L.; Cober, E.; Rajcan, I.; Belzile, F. Identification of Loci Governing Eight Agronomic Traits Using a GBS-GWAS Approach and Validation by QTL Mapping in Soya Bean. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhao, X.; Han, Y.; Li, W.; Xie, F. Genome-Wide Association Mapping for Seed Protein and Oil Contents Using a Large Panel of Soybean Accessions. Genomics 2019, 111, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Van, K.; Sung, M.; Nelson, R.; LaMantia, J.; McHale, L.K.; Mian, M.A.R. Genome-Wide Association Study of Seed Protein, Oil and Amino Acid Contents in Soybean from Maturity Groups I to IV. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 1639–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wu, T.; Wang, L.; Jiang, B.; Zhen, C.; Yuan, S.; Hou, W.; Wu, C.; Han, T.; Sun, S. A Combined Linkage and GWAS Analysis Identifies QTLs Linked to Soybean Seed Protein and Oil Content. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, A.; Chen, P.; Korth, K.; Hancock, F.; Pereira, A.; Brye, K.; Wu, C.; Shi, A. Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) of Salt Tolerance in Worldwide Soybean Germplasm Lines. Mol. Breed. 2017, 37, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.D.; Vuong, T.D.; Dunn, D.; Clubb, M.; Valliyodan, B.; Patil, G.; Chen, P.; Xu, D.; Nguyen, H.T.; Shannon, J. Identification of New Loci for Salt Tolerance in Soybean by High-Resolution Genome-Wide Association Mapping. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Chao, M.; Yin, Z.; Yu, D. Genome-Wide Association Analysis Detecting Significant Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms for Chlorophyll and Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters in Soybean (Glycine max) Landraces. Euphytica 2012, 186, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yin, J.; Chu, S.; Zhang, X.; Yu, K.; Lv, L.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Studies of Photosynthetic Traits Related to Phosphorus Efficiency in Soybean. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Che, Z.; Yuan, W.; Yu, D. GWAS Reveals Two Novel Loci for Photosynthesis-Related Traits in Soybean. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2020, 295, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Soto, R.I.; Mora, F.; De Oliveira, M.A.R.; Higashi, W.; Scapim, C.A.; Schuster, I. A Genome-Wide Association Study for Agronomic Traits in Soybean Using SNP Markers and SNP-Based Haplotype Analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zatybekov, A.; Abugalieva, S.; Didorenko, S.; Gerasimova, Y.; Sidorik, I.; Anuarbek, S.; Turuspekov, Y. GWAS of Agronomic Traits in Soybean Collection Included in Breeding Pool in Kazakhstan. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Ma, Y.; Wu, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yang, R.; Hu, G.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhang, M.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Studies Dissect the Genetic Networks Underlying Agronomical Traits in Soybean. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shook, J.M.; Zhang, J.; Jones, S.E.; Singh, A.; Diers, B.W.; Singh, A.K. Meta-GWAS for Quantitative Trait Loci Identification in Soybean. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2021, 11, jkab117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoosefzadeh-Najafabadi, M.; Torabi, S.; Tulpan, D.; Rajcan, I.; Eskandari, M. Genome-Wide Association Studies of Soybean Yield-Related Hyperspectral Reflectance Bands Using Machine Learning-Mediated Data Integration Methods. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 777028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravelombola, W.; Qin, J.; Shi, A.; Song, Q.; Yuan, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, P.; Yan, L.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, T.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study and Genomic Selection for Yield and Related Traits in Soybean. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Tayade, R.; Kang, B.H.; Hahn, B.S.; Ha, B.K.; Kim, Y.H. Genome-Wide Association Studies of Seven Root Traits in Soybean (Glycine max L.) Landraces. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, H.; Chasman, D.I.; Smith, J.D.; Mora, S.; Ridker, P.M.; Nickerson, D.A.; Krauss, R.M.; Stephens, M. A Multivariate Genome-Wide Association Analysis of 10 LDL Subfractions, and Their Response to Statin Treatment, in 1868 Caucasians. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianola, D.; Sorensen, D. Quantitative Genetic Models for Describing Simultaneous and Recursive Relationships between Phenotypes. Genetics 2004, 167, 1407–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momen, M.; Mehrgardi, A.A.; Roudbar, M.A.; Kranis, A.; Pinto, R.M.; Valente, B.D.; Morota, G.; Rosa, G.J.M.; Gianola, D. Including Phenotypic Causal Networks in Genome-Wide Association Studies Using Mixed Effects Structural Equation Models. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suela, M.M.; Azevedo, C.F.; Nascimento, A.C.C.; Momen, M.; de Oliveira, A.C.B.; Caixeta, E.T.; Morota, G.; Nascimento, M. Genome-Wide Association Study for Morphological, Physiological, and Productive Traits in Coffea Arabica Using Structural Equation Models. Tree Genet. Genomes 2023, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegolo, S.; Momen, M.; Morota, G.; Rosa, G.J.M.; Gianola, D.; Bittante, G.; Cecchinato, A. Structural Equation Modeling for Investigating Multi-Trait Genetic Architecture of Udder Health in Dairy Cattle. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momen, M.; Campbell, M.T.; Walia, H.; Morota, G. Utilizing Trait Networks and Structural Equation Models as Tools to Interpret Multi-Trait Genome-Wide Association Studies. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Töpner, K.; Rosa, G.J.M.; Gianola, D.; Schön, C.C. Bayesian Networks Illustrate Genomic and Residual Trait Connections in Maize (Zea mays L.). G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2017, 7, 2779–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, B.D.; Rosa, G.J.M.; De Los Campos, G.; Gianola, D.; Silva, M.A. Searching for Recursive Causal Structures in Multivariate Quantitative Genetics Mixed Models. Genetics 2010, 185, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suela, M.M.; Nascimento, M.; Nascimento, A.C.C.; Azevedo, C.F.; Teodoro, P.E.; Farias, F.J.C.; de Carvalho, L.P.; Jarquin, D. Integrating Environmental Covariates into Adaptability and Stability Analyses: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach for Cotton Breeding. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suela, M.M.; Azevedo, C.F.; Nascimento, A.C.C.; Moura, E.T.C.; Oliveira, A.C.B.d.; Morota, G.; Nascimento, M. Structural Equation Modeling and Genome-Wide Selection for Multiple Traits to Enhance Arabica Coffee Breeding Programs. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, J.P.; Bhartya, P.; Anuradha, B. Genetic Variability, Heritability and Character Association for Yield and Component Character in Soybean. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2013, 12, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiday, T.; Amogne, A.; Tefera, G.; Malede, M. Heritability, Genetic Advance and Path Coefficient Analysis for Grain Yield and Its Component Characters in Soybean (Glycine max L. Merrill). Int. J. Res. Stud. Agric. Sci. 2017, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Conte, M.V.; Carneiro, P.C.S.; De Resende, M.D.V.; Da Silva, F.L.; Peternelli, L.A. Overcoming Collinearity in Path Analysis of Soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] Grain Oil Content. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Albuquerque, J.R.; Lins, H.A.; Dos Santos, M.G.; de Freitas, M.A.; de Oliveira, F.S.; de Souza, A.R.; da Silveira, L.M.; Nunes, G.H.; Júnior, A.P.B.; Vieira, P.F.M.J. Influence of Genotype-Environment Interaction on Soybean (Glycine max L.) Genetic Divergence under Semiarid Conditions. Rev. Fac. Cienc. Agrar. 2022, 54, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisinotto, F.F.; Hamawaki, O.T.; Oliveira, A.P.; Hamawaki, R.L.; Glansenapp, J.S.; Hamawaki, C.L. Path Analysis and Traits Correlation in Soybean. Commun. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, X.; Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhao, L. Identification of Traits Contributing to High and Stable Yields in Different Soybean Varieties Across Three Chinese Latitudes. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.F.; Sediyama, T.; Silva, F.C.S.; Bezerra, A.R.G.; Ferreira, L. V Correlation and Path Analysis of Yield Components in Soybean Varieties. Turkish J. F. Crop. 2015, 10, 177–179. [Google Scholar]
- Jianng, C.; Zeng, Z.-B. Multiple Trait Analysis of Genetic Mapping for Quantitative Trait Loci. Genetics 1995, 140, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, G.J.M.; Valente, B.D.; De Los Campos, G.; Wu, X.L.; Gianola, D.; Silva, M.A. Inferring Causal Phenotype Networks Using Structural Equation Models. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2011, 43, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, P.F.; Hoggart, C.J.; Pomyen, Y.; Calboli, F.C.F.; Elliott, P.; Jarvelin, M.R.; Coin, L.J.M. MultiPhen: Joint Model of Multiple Phenotypes Can Increase Discovery in GWAS. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Stephens, M. Efficient Multivariate Linear Mixed Model Algorithms for Genome-Wide Association Studies. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 407–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palharini, W.G. Influência Do Estresse Hídrico Sobre Caracteres Agronômicos, Fisiológicos e Abertura de Vagens Imaturas em Soja, Universidade Federal de Viçosa, 2016. Available online: https://locus.ufv.br/server/api/core/bitstreams/2eaebc74-9e67-4130-aeee-226465b81448/content (accessed on 13 January 2024).
- Zhao, J.; Chen, L.; Zhao, T.; Gai, J. Chicken Toes-Like Leaf and Petalody Flower (CTP) Is a Novel Regulator That Controls Leaf and Flower Development in Soybean. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 5565–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Cheng, Q.; Fang, C.; Kong, L.; Yang, H.; Hou, Z.; Li, Y.; Nan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; et al. Parallel Selection of Distinct Tof5 Alleles Drove the Adaptation of Cultivated and Wild Soybean to High Latitudes. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joaquim, P.; Molinari, M.; Marin, S.; Barbosa, D.; Viana, A.; Rech, E.; Henning, F.; Nepomuceno, A.; Mertz-Henning, L. Nitrogen compounds transporters: Candidates to increase the protein content in soybean seeds. J. Plant Interact. 2022, 17, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biová, J.; Dietz, N.; Chan, Y.O.; Joshi, T.; Bilyeu, K.; Škrabišová, M. AccuCalc: A Python Package for Accuracy Calculation in GWAS. Genes 2023, 14, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Panwar, R.; Rustagi, A.; Chakraborty, A.; Roy, A.; Singh, I.K.; Singh, A. Comprehensive and Evolutionary Analysis of Spodoptera Litura-Inducible Cytochrome P450 Monooxygenase Gene Family in Glycine max Elucidate Their Role in Defense. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1221526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Niu, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Hu, Z. Genome-Wide Association Studies Prioritize Genes Controlling Seed Size and Reproductive Period Length in Soybean. Plants 2024, 13, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Hwang, S.; Lee, I. SoyNet: A Database of Co-Functional Networks for Soybean Glycine max. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D1082–D1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadivel, A.K.A. GmMYB176 Interactome and Regulation of Isoflavonoid GmMYB176 Interactome and Regulation of Isoflavonoid Biosynthesis in Soybean. Ph.D. Thesis, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Jiang, C.; Han, R.; Xie, Y.; Liu, L.; Yu, Y. Plasma Membrane Proteomic Analysis by TMT-PRM Provides Insight into Mechanisms of Aluminum Resistance in Tamba Black Soybean Roots Tips. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, S.; Zhang, X.; Yu, K.; Lv, L.; Sun, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, D. Genome-Wide Analysis Reveals Dynamic Epigenomic Differences in Soybean Response to Low-Phosphorus Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Lim, W.J.; Jeong, S.; Lee, H.Y.; Cho, Y.; Moon, J.K.; Kim, N. Genome-Wide Association and Epistatic Interactions of Flowering Time in Soybean Cultivar. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Pan, X.; Wang, F.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q. Novel QTL and Meta-QTL Mapping for Major Quality Traits in Soybean. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 774270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoei, M.A.; Karimi, M.; Karamian, R.; Amini, S.; Soorni, A. Identification of the Complex Interplay Between Nematode-Related LncRNAs and Their Target Genes in Glycine max L. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 779597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.A.G.; Basso, M.F.; Melo, B.P.; Ribeiro, T.P.; Lima, R.N.; Araújo, J.F.; Grossi-de-Sa, M.; Mattos, V.S.; Togawa, R.C.; Albuquerque, E.V.S.; et al. The Mi-EFF1/Minc17998 Effector Interacts with the Soybean GmHub6 Protein to Promote Host Plant Parasitism by Meloidogyne Incognita. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 114, 101630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Jiao, S.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Zhai, H.; Bai, X. GmSTK12 Participates in Salt Stress Resistance in Soybean. Agronomy 2023, 13, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavalan, L.P.; Guttikonda, S.K.; Tran, L.P.; Nguyen, H.T. Physiological and Molecular Approaches to Improve Drought Resistance in Soybean. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009, 50, 1260–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Gu, Y.; He, L.; Chen, Q.; He, C. Sequence and Expression Variations Suggest an Adaptive Role for the DA1-like Gene Family in the Evolution of Soybeans. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, L.; Corke, F.; Smith, C.; Bevan, M.W. Control of Final Seed and Organ Size by the DA1 Gene Family in Arabidopsis Thaliana. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierstra, R.D. The Ubiquitin-26S Proteasome System at the Nexus of Plant Biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, R.W.; Deshaies, R.J.; Peters, J.; Kirschner, M.W. How Proteolysis Drives the Cell Cycle. Science 1996, 274, 1652–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, N.; Doelling, J.H.; Falbel, T.G.; Durski, A.M.; Vierstra, R.D. The Ubiquitin-Specific Protease Family from Arabidopsis. AtUBP1 and 2 Are Required for the Resistance to the Amino Acid Analog Canavanine. Plant Physiol. 2000, 124, 1828–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raasi, S.; Wolf, D.H. Ubiquitin Receptors and ERAD: A Network of Pathways to the Proteasome. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007, 18, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreher, K.; Callis, J. Ubiquitin, Hormones and Biotic Stress in Plants. Ann. Bot. 2007, 99, 787–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santner, A.; Estelle, M. The Ubiquitin-Proteasome System Regulates Plant Hormone Signaling. Plant J. 2010, 61, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, M.; Shirasu, K. Ubiquitination in Plant Immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2010, 13, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Wu, Y.R.; Huang, X.H.; Sun, J.; Xie, Q. AtPUB19, a U-Box E3 Ubiquitin Ligase, Negatively Regulates Abscisic Acid and Drought Responses in Arabidopsis Thaliana. Mol. Plant 2011, 4, 938–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, V.; Vashisht, D.; Cletus, J.; Sakthivel, N. Plant β-1,3-Glucanases: Their Biological Functions and Transgenic Expression against Phytopathogenic Fungi. Biotechnol. Lett. 2012, 34, 1983–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, B.A.; Clarke, A.E. Chemistry and Boilogy of (1→3)-β-Glucans; La Trobe University Press: Bundoora, Australia, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kauss, H. Callose Synthesis. In Membranes: Specialized Functions in Plants; Smallwood, M., Knox, P., Bowles, D.J., Eds.; Bios Scientific: Oxford, UK, 1996; pp. 77–92. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.; Yang, S.S.; Liang, Z.; Feng, B.R.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y.B.; Tang, Y.X. Genome-Wide Analysis of the MYB Transcription Factor Superfamily in Soybean. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Yuan, H.Y.; Ren, R.; Zhao, S.Q.; Han, Y.P.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Ke, D.X.; Wang, Y.X.; Wang, L. Genome-Wide Identification, Classification, and Expression Analysis of Amino Acid Transporter Gene Family in Glycine max. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, L.J. Genome-Wide Identification and Evolutionary Analysis of Leucine-Rich Repeat Receptor-like Protein Kinase Genes in Soybean. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.Y.; Felippes, F.F.; Liu, C.J.; Weigel, D.; Wang, J.W. Negative Regulation of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis by a MiR156-Targeted SPL Transcription Factor. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 1512–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.H.; Ju, Y.; Seo, P.J.; Lee, J.H.; Park, C.M. The SOC1-SPL Module Integrates Photoperiod and Gibberellic Acid Signals to Control Flowering Time in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2012, 69, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.G.; Shan, J.X.; Shi, M.; Gao, J.P.; Lin, H.X. The MiR156-SPL9-DFR Pathway Coordinates the Relationship between Development and Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants. Plant J. 2014, 80, 1108–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Luo, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, W.; WeiTang; Dong, H. Effects of Deficit Irrigation and Plant Density on the Growth, Yield and Fiber Quality of Irrigated Cotton. Field Crops Res. 2016, 197, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidi, E.; Rigas, S.; Tsitsekian, D.; Daras, G.; Alatzas, A.; Makris, A.; Tanou, G.; Argiriou, A.; Alexandrou, D.; Poethig, S.; et al. Trichome Patterning Control Involves TTG1 Interaction with SPL Transcription Factors. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 92, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, J.C.; Jorgensen, S.A.; Orozco, R.; Hileman, L.C. Paralogous SQUAMOSA PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE (SPL) Genes Differentially Regulate Leaf Initiation and Reproductive Phase Change in Petunia. Planta 2016, 243, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Wen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, Y.; Wang, X. Characterization of Squamosa-Promoter Binding Protein-Box Family Genes Reveals the Critical Role of MsSPL20 in Alfalfa Flowering Time Regulation. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 775690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, G.; Srivastava, D.; Tiwari, P.; Chakrabarty, D. ROS Modulation in Crop Plants Under Drought Stress. In Reactive Oxygen, Nitrogen and Sulfur Species in Plants; Hasanuzzaman, M., Fotopoulos, V., Fujita, M., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 311–336. [Google Scholar]
- Diers, B.W.; Specht, J.; Rainey, K.M.; Cregan, P.; Song, Q.; Ramasubramanian, V.; Graef, G.; Nelson, R.; Schapaugh, W.; Wang, D.; et al. Genetic Architecture of Soybean Yield and Agronomic Traits. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2018, 8, 3367–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, N.G. A Role for Arabidopsis Dynamin Related Proteins DRP2A/B in Endocytosis; DRP2 Function Is Essential for Plant Growth. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 76, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.; Borém, A.; Sediyama, T.; Câmara, G. Soja: Do Plantio à Colheita, 2nd ed.; Oficina de Textos: São Paulo, Brazil, 2022; ISBN 9786586235531. [Google Scholar]
- Kisha, T.J.; Sneller, C.H.; Diers, B.W. Relationship between Genetic Distance among Parents and Genetic Variance in Populations of Soybean. Crop Sci. 1997, 37, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, L.D.O.; da Silva, M.F.; da Cunha, F.F.; Picoli, E.A.T.; Silva, F.C.S.; da Silva, F.L. Water Deficit as a Trigger to Immature Soybean Pod Opening. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2023, 209, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshire, R.J.; Glaubitz, J.C.; Sun, Q.; Poland, J.A.; Kawamoto, K.; Buckler, E.S.; Mitchell, S.E. A Robust, Simple Genotyping-by-Sequencing (GBS) Approach for High Diversity Species. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonah, H.; Bastien, M.; Iquira, E.; Tardivel, A.; Légaré, G.; Boyle, B.; Normandeau, É.; Laroche, J.; Larose, S.; Jean, M.; et al. An Improved Genotyping by Sequencing (GBS) Approach Offering Increased Versatility and Efficiency of SNP Discovery and Genotyping. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de los Campos, G.; Hickey, J.M.; Pong-Wong, R.; Daetwyler, H.D.; Calus, M.P.L. Whole-Genome Regression and Prediction Methods Applied to Plant and Animal Breeding. Genetics 2013, 193, 327–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2025. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 25 September 2025).
- VanRaden, P.M. Efficient Methods to Compute Genomic Predictions. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 4414–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.J. Boa: An R Package for MCMC Output Convergence Assessment and Posterior Inference. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 21, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korb, K.B.; Nicholson, A.E. Bayesian Artificial Intelligence; Chapman & Hall/CRC: London, UK, 2004; Volume 7, pp. 221–223. [Google Scholar]
- Korb, K.B.; Nicholson, A.E. Bayesian Artificial Intelligence, 2nd ed.; Chapman & Hall/CRC: London, UK, 2010; ISBN 2013206534. [Google Scholar]
- Scutari, M. Learning Bayesian Networks with the Bnlearn R Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 35, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.; Tier, B. “SNP Snappy”: A Strategy for Fast Genome-Wide Association Studies Fitting a Full Mixed Model. Genetics 2012, 190, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K. WOMBAT: A Tool for Mixed Model Analyses in Quantitative Genetics by Restricted Maximum Likelihood (REML). J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B. 2007, 8, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, J.D.; Tibshirani, R. Statistical Significance for Genomewide Studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9440–9445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodstein, D.M.; Shu, S.; Howson, R.; Neupane, R.; Hayes, R.D.; Fazo, J.; Mitros, T.; Dirks, W.; Hellsten, U.; Putnam, N.; et al. Phytozome: A Comparative Platform for Green Plant Genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).