Manganese Phytoremediation Potential of Koelreuteria paniculata: Detoxification Mechanisms, Chemical Speciation, and Ultrastructural Adaptations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Growth Status and Heavy Metal Enrichment Characteristics of K. paniculata Under Mn Stress
2.2. Physiological and Biochemical Responses and Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) of K. paniculata Under Mn Stress
2.3. Subcellular Distribution, Chemical Speciation, and Ultrastructural Alterations in K. Paniculata Under Manganese Stress
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Materials
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Measurement Indices and Methods
4.3.1. Plant Growth Indices
4.3.2. Chlorophyll Content, Soluble Protein, and Enzyme Activity
4.3.3. Mn Content in Plants
4.4. Data Analysis Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noh, S.; Triwigati, P.T.; Sim, G.; Lee, J.; Kim, E.; Moon, S.; Park, Y. Dual benefits of manganese recovery and carbon mineralization via pH swing-assisted carbonation process in iron and steelmaking by-products. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115987. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, N.; Dan, Z.; Wang, F.; Pan, C.; Zhou, C.; Jiang, L. Electrolytic manganese metal industry experience based China’s new model for cleaner production promotion. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 2082–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Lin, F.; Chen, M.; Li, B.; Wei, L.; Wang, J.; Luo, Z.; Wang, R. An innovative method to enhance manganese and ammonia nitrogen leaching from electrolytic manganese residue by surfactant and anode iron plate. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 193, 105311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, M.; Baltrėnaitė-Gedienė, E.; Ditta, A.; Ullah, H.; Kanwal, A.; Ullah, S.; Faraj, T.K. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in a soil–plant system from an open dumpsite and the associated health risks through multiple routes. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.-B.; He, J.; Polle, A.; Rennenberg, H. Heavy metal accumulation and signal transduction in herbaceous and woody plants: Paving the way for enhancing phytoremediation efficiency. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1131–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, A.; Caldelas, C.; Weiss, D.; Aranjuelo, I.; Navarro, E. Assessment of metal immission in urban environments using elemental concentrations and zinc isotope signatures in leaves of Nerium oleander. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2071–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhakypbek, Y.; Kossalbayev, B.D.; Belkozhayev, A.M.; Murat, T.; Tursbekov, S.; Abdalimov, E.; Pashkovskiy, P.; Kreslavski, V.; Kuznetsov, V.; Allakhverdiev, S.I. Reducing heavy metal contamination in soil and water using phytoremediation. Plants 2024, 13, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mleczek, M.; Magdziak, Z.; Rissmann, I.; Golinski, P. Effect of different soil conditions on selected heavy metal accumulation by Salix viminalis tissues. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2009, 44, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar]
- Guidi Nissim, W.; Palm, E.; Mancuso, S.; Azzarello, E. Trace element partitioning in a poplar phytoextraction stand in relation to stem size. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 247, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockwood, D.; Carter, D.; Langholtz, M.; Stricker, J. Eucalyptus and Populus short rotation woody crops for phosphate mined lands in Florida USA. Biomass Bioenergy 2006, 30, 728–734. [Google Scholar]
- Su, R.; Xie, T.; Yao, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Dai, X.; Wang, Y.; Shi, L.; Luo, Y. Lead responses and tolerance mechanisms of Koelreuteria paniculata: A newly potential plant for sustainable phytoremediation of Pb-contaminated soil. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leotta, L.; Toscano, S.; Ferrante, A.; Romano, D.; Francini, A. New strategies to increase the abiotic stress tolerance in woody ornamental plants in mediterranean climate. Plants 2023, 12, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monterroso, C.; Rodríguez, F.; Chaves, R.; Diez, J.; Becerra-Castro, C.; Kidd, P.S.; Macías, F. Heavy metal distribution in mine-soils and plants growing in a Pb/Zn-mining area in NW Spain. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 44, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, B.; Qiu, B. Phytochelatin synthesis plays a similar role in shoots of the cadmium hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii as in non-resistant plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.J.; Zheng, B. the role of polyphenols in abiotic stress tolerance and their antioxidant properties to scavenge reactive oxygen species and free radicals. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutteridge, J.M.C.; Halliwell, B. Antioxidants: Molecules, medicines, and myths. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 393, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomova, K.; Raptova, R.; Alomar, S.Y.; Alwasel, S.H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: Chronic diseases and aging. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 2499–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Li, F.; Wu, D.; Ma, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Z.; He, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; et al. Poly(ethylene glycol)-modified catalase blocking reactive oxygen species for the treatment of hepatic ischemia. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2025, 46, 2500367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Fan, Z.; Hu, Z.; Li, Z.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Lin, X.; Feng, Y. Synthetic communities derived from the core endophytic microbiome of hyperaccumulators and their role in cadmium phytoremediation. Microbiome 2024, 12, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Habib, M.; Kakavand, S.N.; Zahid, Z.; Zahra, N.; Sharif, R.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Phytoremediation of cadmium: Physiological, biochemical, and molecular mechanisms. Biology 2020, 9, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Xing, Q.; Sun, J.; Wang, P.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Z. The mechanism of KpMIPS gene significantly improves resistance of Koelreuteria paniculata to heavy metal cadmium in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Su, R.; Chen, Y. Phytostabilization of heavy metals and fungal community response in manganese slag under the mediation of soil amendments and plants. Toxics 2024, 12, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, C.-M.; Fu, X.-P.; Chen, X.-C.; Shi, J.-Y.; Chen, Y.-X. Accumulation and detoxification of manganese in hyperaccumulator. Plant Biol. 2009, 11, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejandro, S.; Höller, S.; Meier, B.; Peiter, E. Manganese in plants: From acquisition to subcellular allocation. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Du, L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Han, L. The potential of Paulownia fortunei seedlings for the phytoremediation of manganese slag amended with spent mushroom compost. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 196, 110538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Feng, S.; Huang, Q.; Liang, S.; Liu, B.; Lin, Y. Effects of manganese stress on photosynthesis and physiological characteristics of Dalbergia odorifera seedlings. Rural Econ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 34, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Hu, J.; Liu, W.; Zeng, W. Characteristics of Manganese accumulation and physiological response of Rhus chinensis under manganese stress. Acta Bot. Boreal.-Occid. Sin. 2022, 42, 628–636. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Luo, X.; Tian, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Tian, L.; Wang, X. Biphasic effects of lanthanum on Vicia faba L. Seedlings under cadmium stress, implicating finite antioxidation and potential ecological risk. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Chen, Y.; Du, L.; Liu, Z.; He, L. Spent mushroom compost and calcium carbonate modification enhances phytoremediation potential of Macleaya cordata to lead-zinc mine tailings. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 294, 113029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Chen, G.; Xiong, L.; Liu, Q.; Yang, W. Accurate digitization of the chlorophyll distribution of individual rice leaves using hyperspectral imaging and an integrated image analysis pipeline. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Shukla, P. Lead bioaccumulation mediated by bacillus cereus BPS-9 from an industrial waste contaminated site encoding heavy metal resistant genes and their transporters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidri, I.; Ishfaq, A.; Shahid, M.; Hussain, S.; Shahzad, T.; Shafqat, U.; Mustafa, S.; Mahmood, F. Enhancement of antioxidants’ enzymatic activity in the wheat crop by Shewanela sp. mediated zinc oxide nanoparticles against heavy metals contaminated wastewater. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 7068–7089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijalkowski, K.L.; Kwarciak-Kozlowska, A. Phytotoxicity assay to assess sewage sludge phytoremediation rate using guaiacol peroxidase activity (GPX): A comparison of four growth substrates. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 263, 110413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ham, Y.-K.; Song, D.-H.; Kim, H.-W. Effects of toxic heavy metal salts on oxidative quality deterioration in ground pork model during aerobic display storage. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Pan, G.; Li, X.; Kuang, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, W. Effects of exogenous manganese on its plant growth, subcellular distribution, chemical forms, physiological and biochemical traits in Cleome viscosa L. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 198, 110696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, L.; Kristensen, R.K.; Guo, J.; Chen, F.; Pedas, P.R.; Zhang, G.; Schjoerring, J.K.; Yuan, L. Assessing the variation in traits for manganese deficiency tolerance among maize genotypes. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 183, 104344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.P.; Zhu, J.; Wang, P.; Zeng, J.; Tan, R.; Yang, Y.Z.; Liu, Z.M. Effect of Cd on growth, physiological response, Cd subcellular distribution and chemical forms of Koelreuteria paniculata. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 160, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Du, L.; Zhang, M.; Han, L. Accumulation and subcellular distribution of heavy metal in Paulownia fortunei cultivated in lead-zinc slag amended with peat. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2019, 21, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
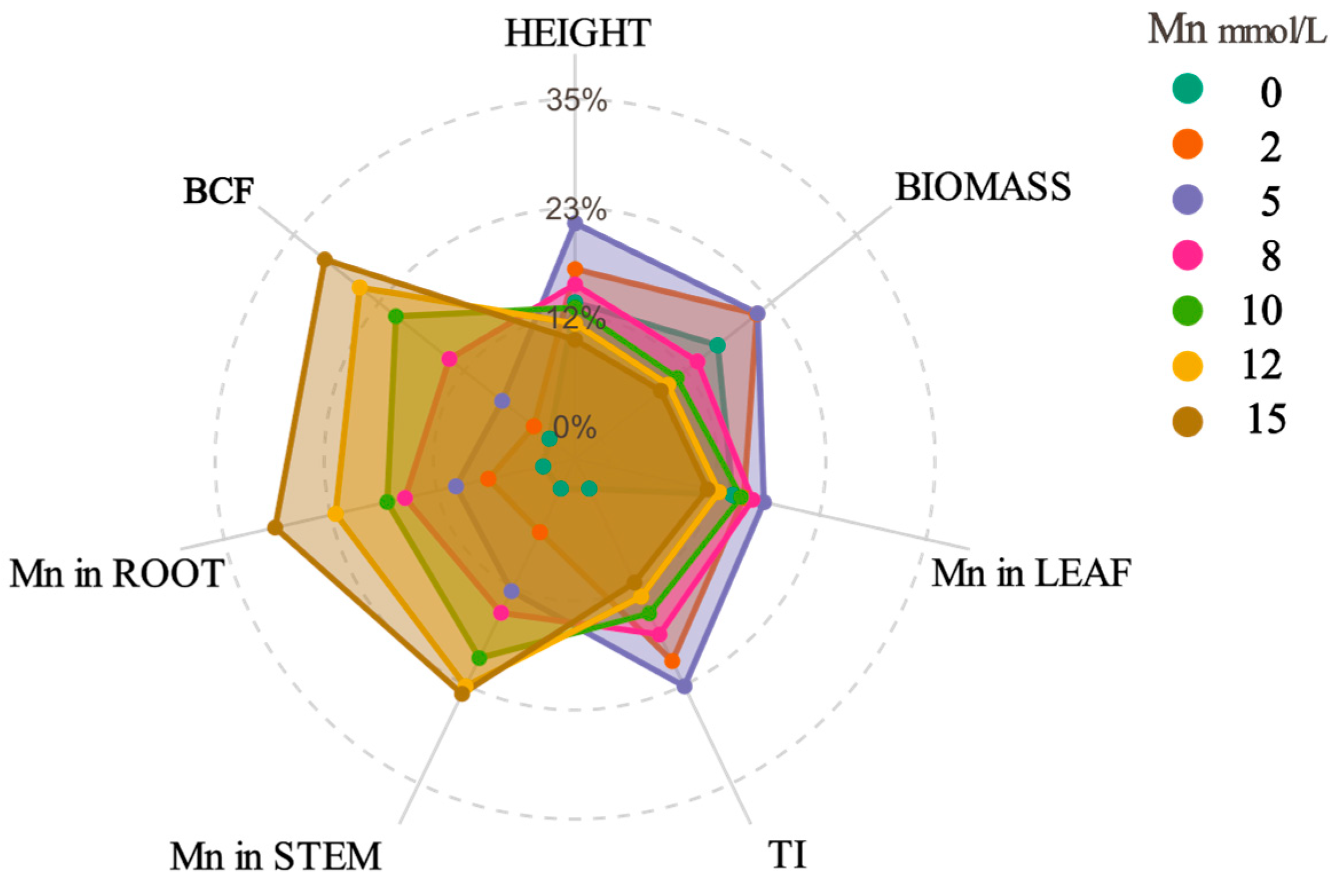


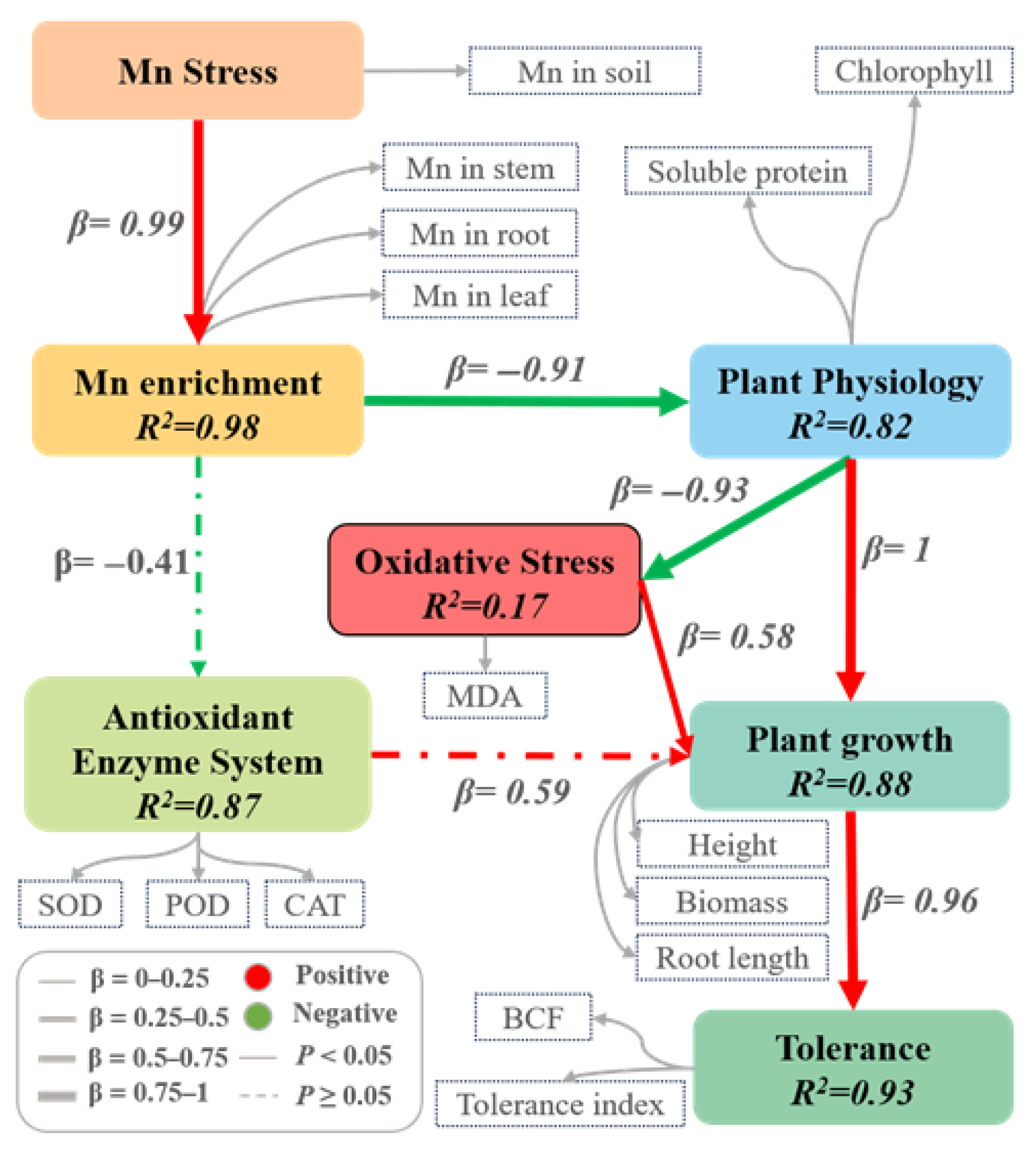
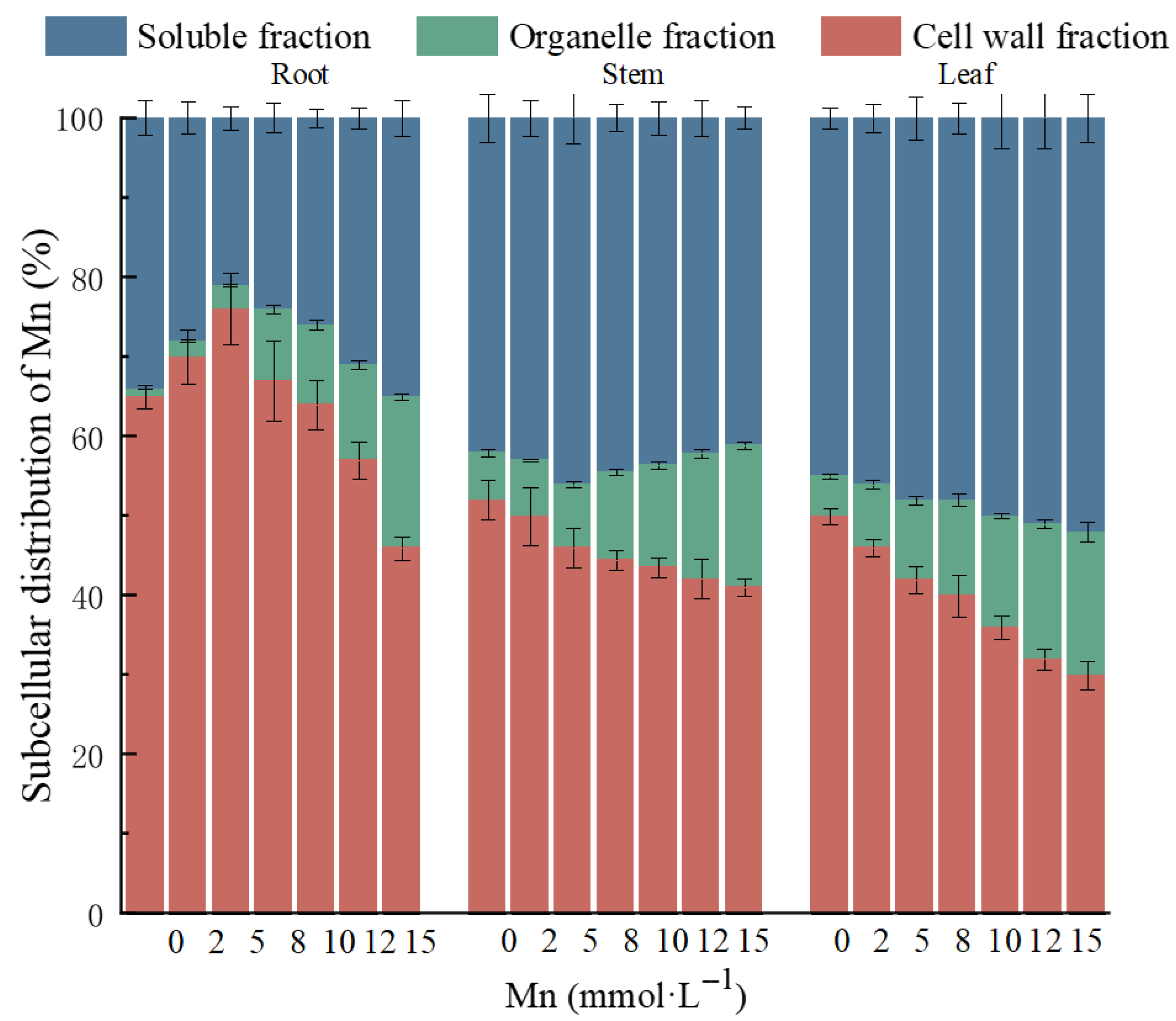
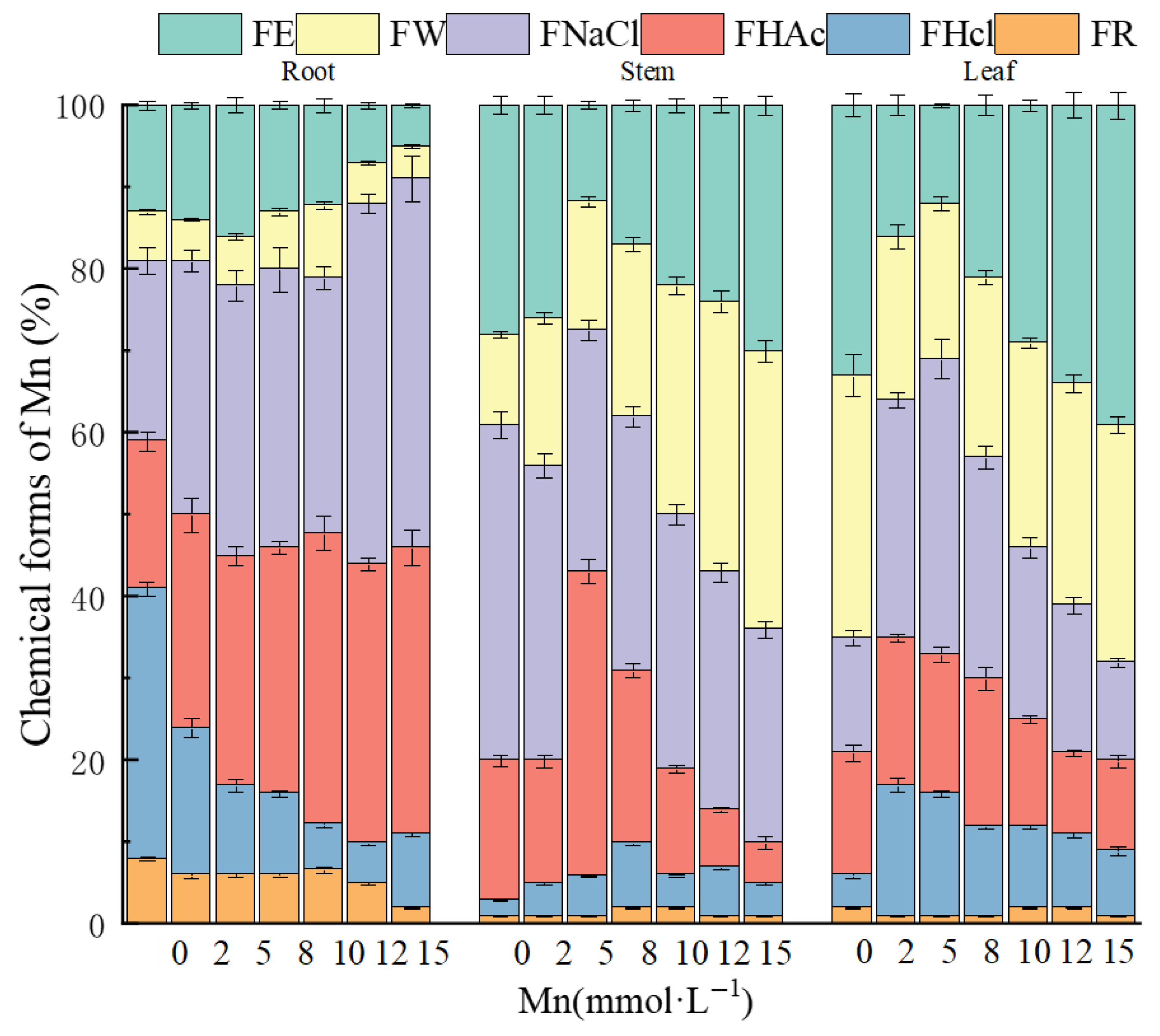

| Mn Concentration (mmol·L−1) | Plant Height (cm) | Biomass (g) | Root Length (cm) | TI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 22.32 ± 1.89 d | 11.12 ± 0.03 b | 116.35 ± 1.24 d | / |
| 2 | 28.27 ± 1.14 b | 14.84 ± 1.14 a | 126.60 ± 9.13 c | 123 |
| 5 | 36.53 ± 1.99 a | 14.92 ± 0.13 a | 145.19 ± 10.76 a | 141 |
| 8 | 25.52 ± 0.98 c | 9.20 ± 0.15 c | 134.61 ± 5.76 b | 104 |
| 10 | 21.34 ± 1.14 d | 7.25 ± 0.12 d | 124.03 ± 1.95 c | 89 |
| 12 | 18.49 ± 1.03 e | 6.42 ± 0.06 e | 103.67 ± 1.44 e | 77 |
| 15 | 15.55 ± 0.49 f | 5.71 ± 0.14 f | 92.92 ± 4.64 f | 67 |
| Mn Concentration (mmol·L−1) | Distribution of Manganese in Different Organs (mg·kg−1) | BCF | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root | Stem | Leaf | ||
| 2 | 616.71 ± 70.15 f | 98.27 ± 3.87 f | 76.31 ± 1.35 f | 0.873 ± 0.03 a |
| 5 | 1453.55 ± 29.61 e | 156.23 ± 2.70 e | 167.10 ± 3.88 e | 0.647 ± 0.01 b |
| 8 | 1760.28 ± 25.77 d | 247.58 ± 24.01 d | 229.81 ± 1.42 d | 0.597 ± 0.03 d |
| 10 | 2401.27 ± 27.70 c | 279.45 ± 32.58 c | 309.39 ± 5.39 c | 0.589 ± 0.04 ef |
| 12 | 2803.18 ± 58.62 b | 372.02 ± 27.43 b | 361.28 ± 1.25 b | 0.611 ± 0.02 c |
| 15 | 2910.24 ± 62.79 a | 480.36 ± 29.81 a | 371.96 ± 22.35 a | 0.568 ± 0.03 g |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, W.; Wang, H.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, M.; Qin, P.; Chen, Y. Manganese Phytoremediation Potential of Koelreuteria paniculata: Detoxification Mechanisms, Chemical Speciation, and Ultrastructural Adaptations. Plants 2025, 14, 2867. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182867
Zhou W, Wang H, Jiang H, Zhang M, Qin P, Chen Y. Manganese Phytoremediation Potential of Koelreuteria paniculata: Detoxification Mechanisms, Chemical Speciation, and Ultrastructural Adaptations. Plants. 2025; 14(18):2867. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182867
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Wanyi, Hao Wang, Huaizhong Jiang, Muhan Zhang, Pufeng Qin, and Yonghua Chen. 2025. "Manganese Phytoremediation Potential of Koelreuteria paniculata: Detoxification Mechanisms, Chemical Speciation, and Ultrastructural Adaptations" Plants 14, no. 18: 2867. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182867
APA StyleZhou, W., Wang, H., Jiang, H., Zhang, M., Qin, P., & Chen, Y. (2025). Manganese Phytoremediation Potential of Koelreuteria paniculata: Detoxification Mechanisms, Chemical Speciation, and Ultrastructural Adaptations. Plants, 14(18), 2867. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182867





