Unraveling Paracetamol Metabolism and Its Circadian Regulation: Insights from Tobacco Hairy Roots as a Model System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
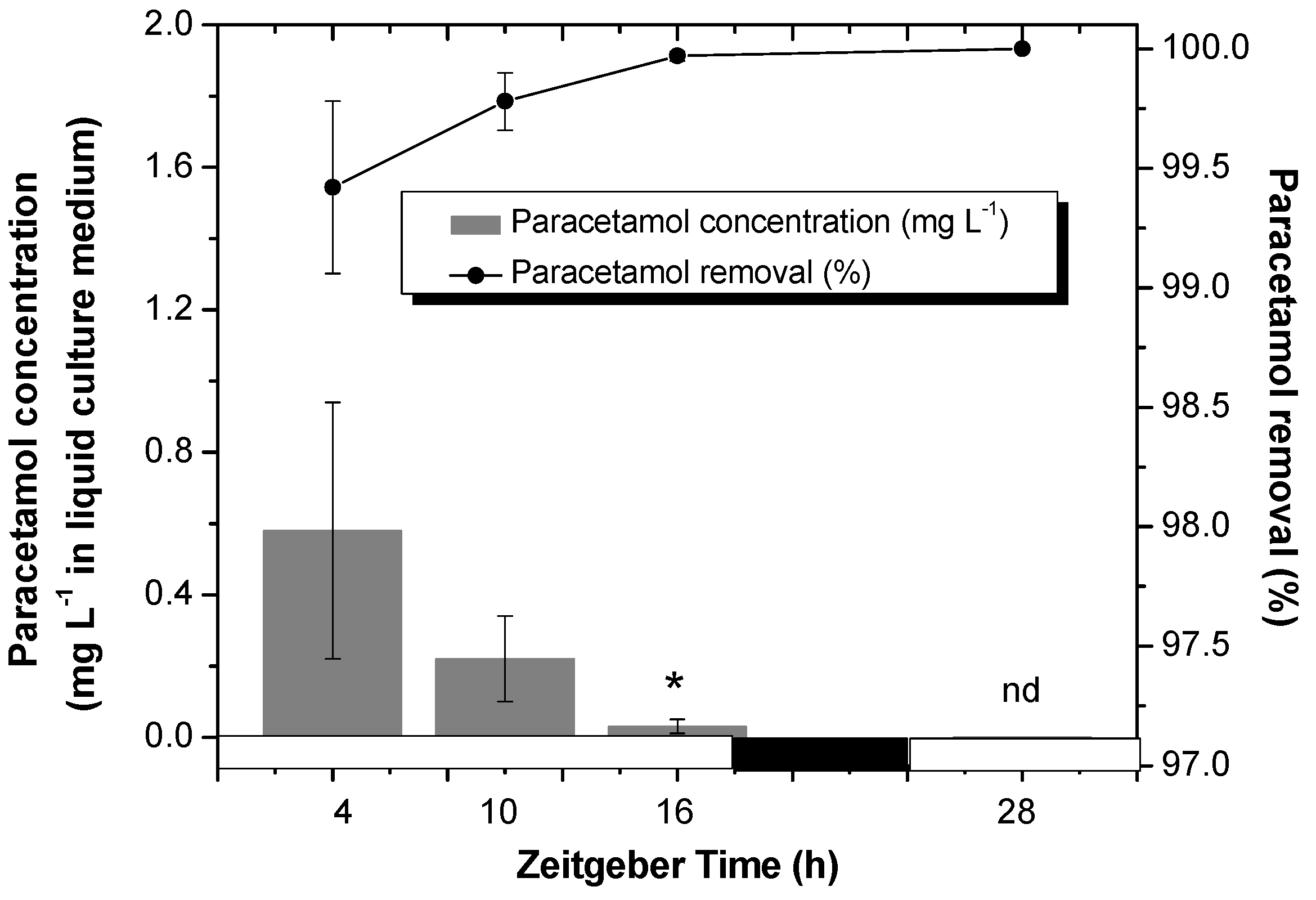
2.1. Analysis of Paracetamol Removal
2.2. Biochemical Response to Paracetamol Treatment
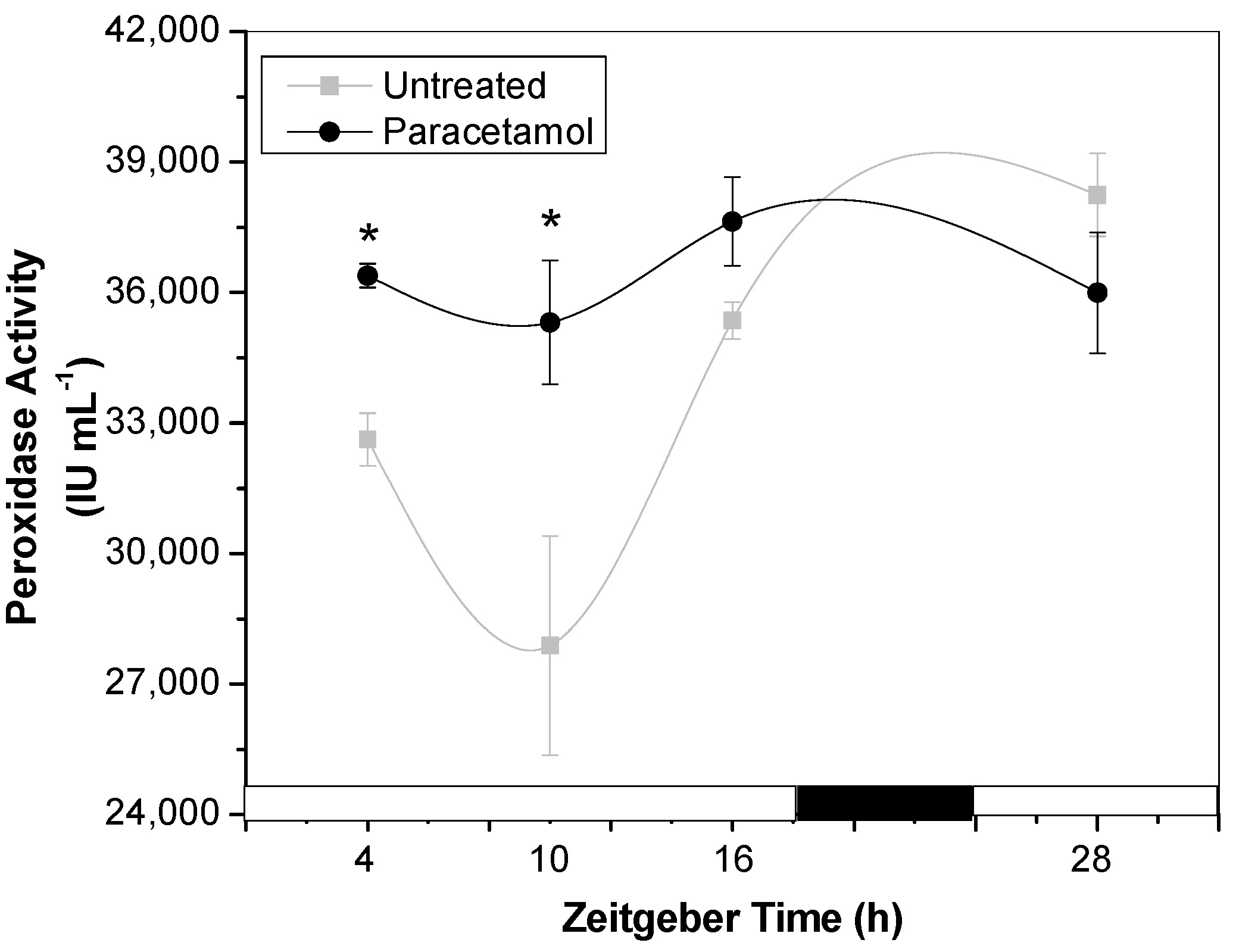
2.2.1. POD Activity
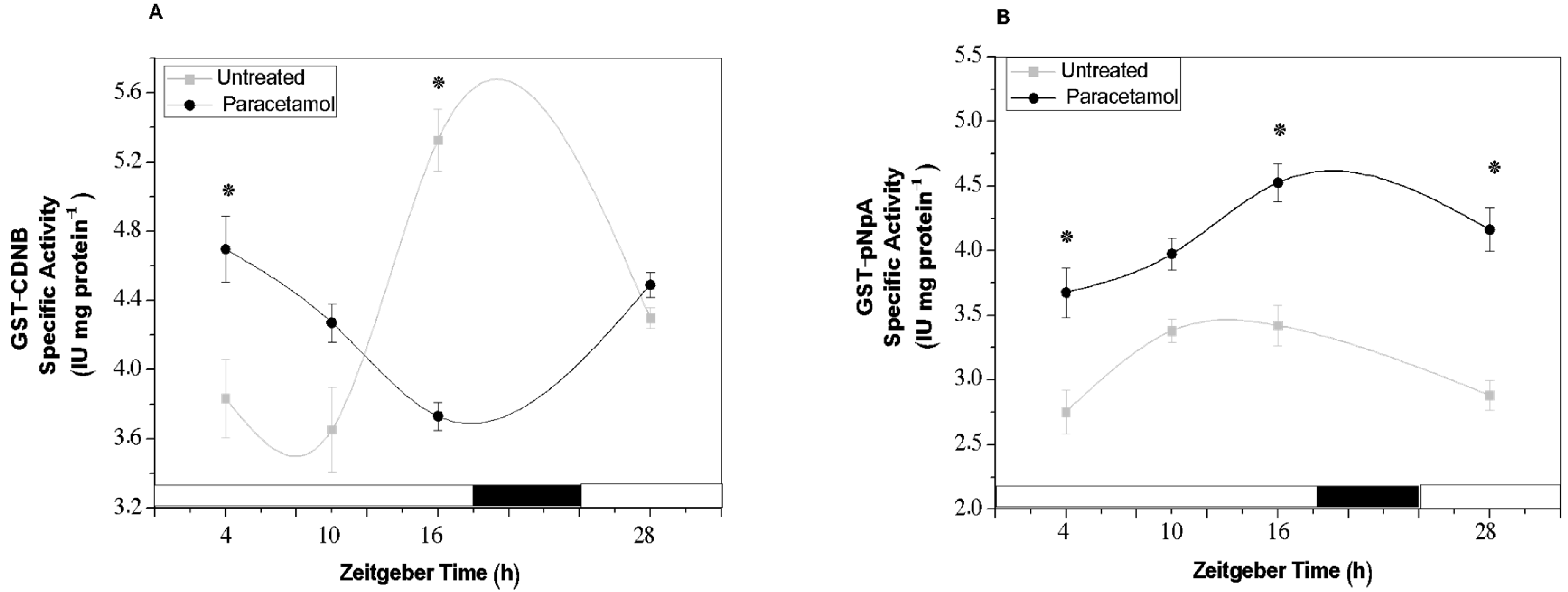
2.2.2. GST Activity
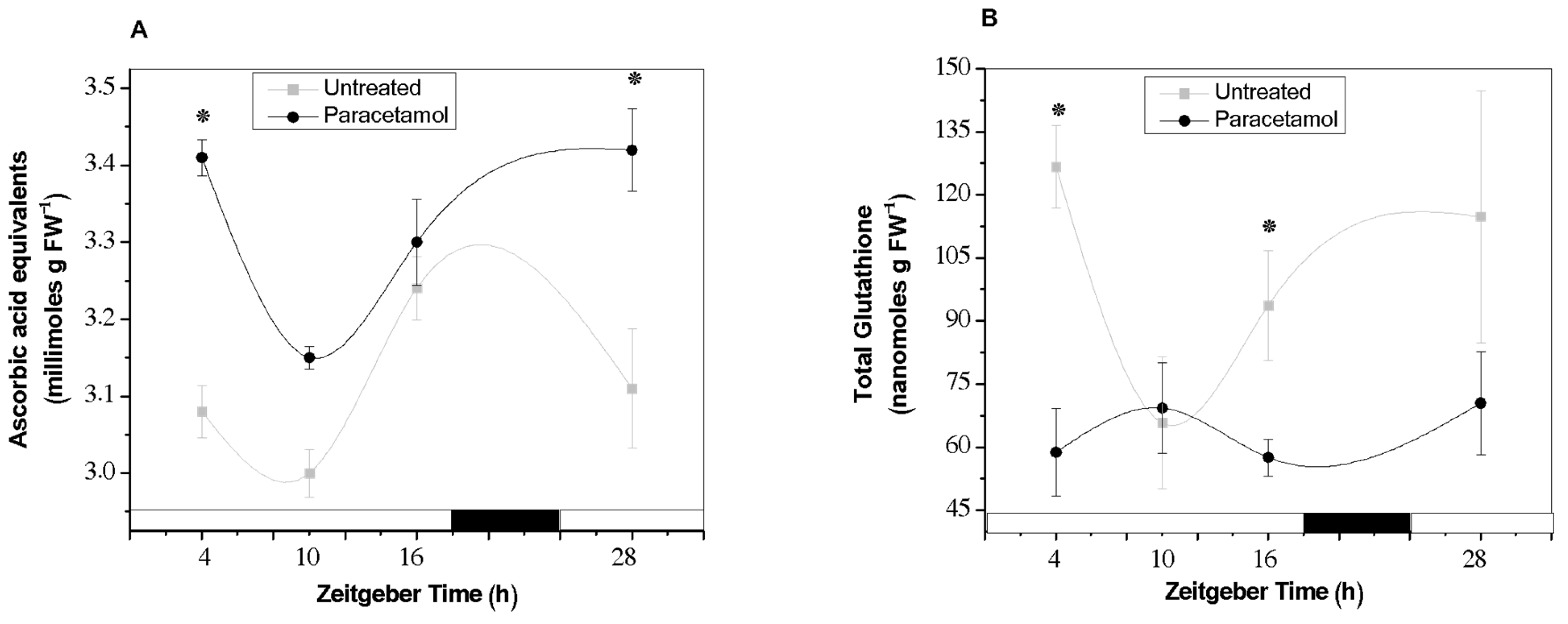
2.2.3. TAA and GSH Content
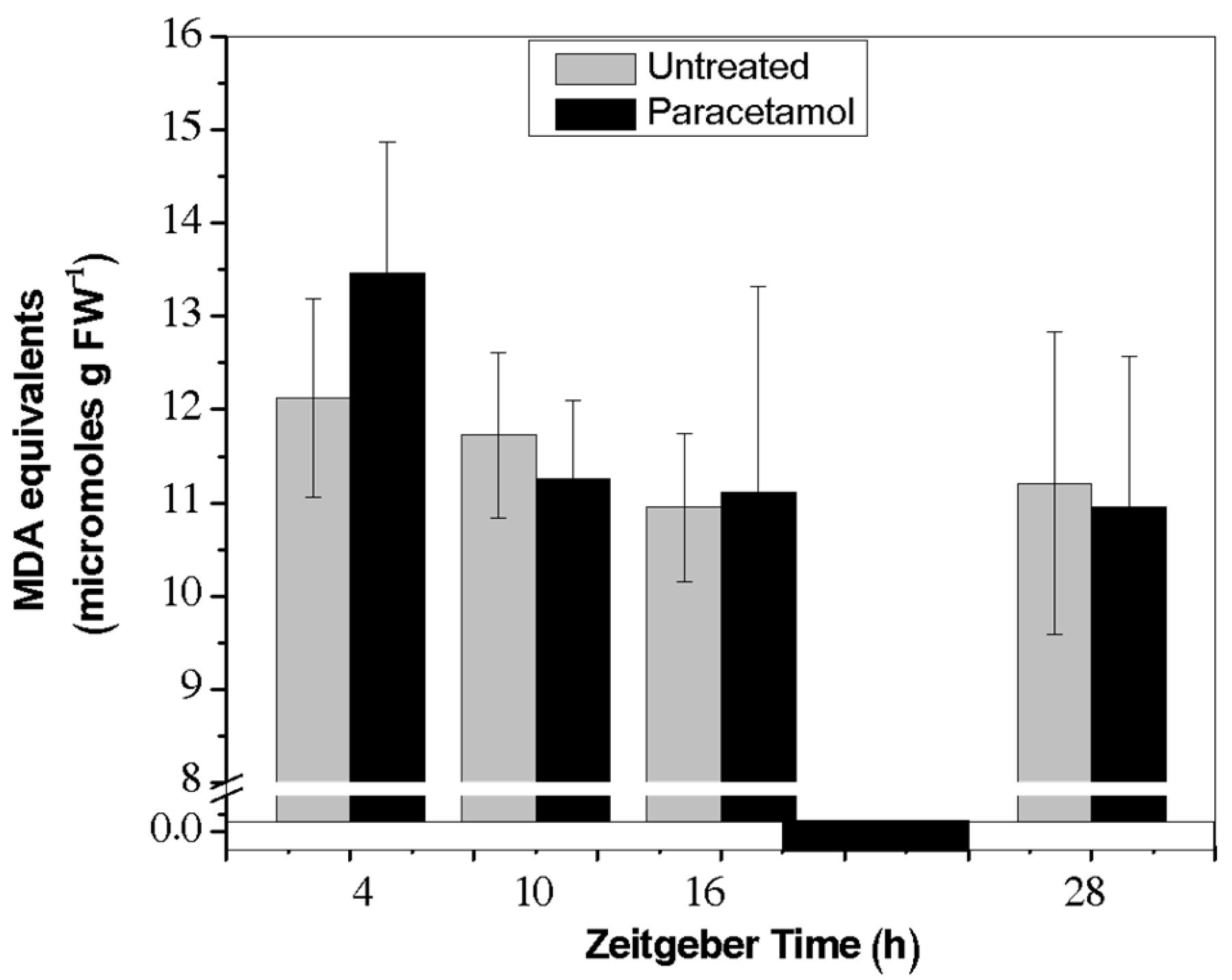
2.2.4. TBARs Content
2.3. Impact of Paracetamol Treatment on Gene Expression
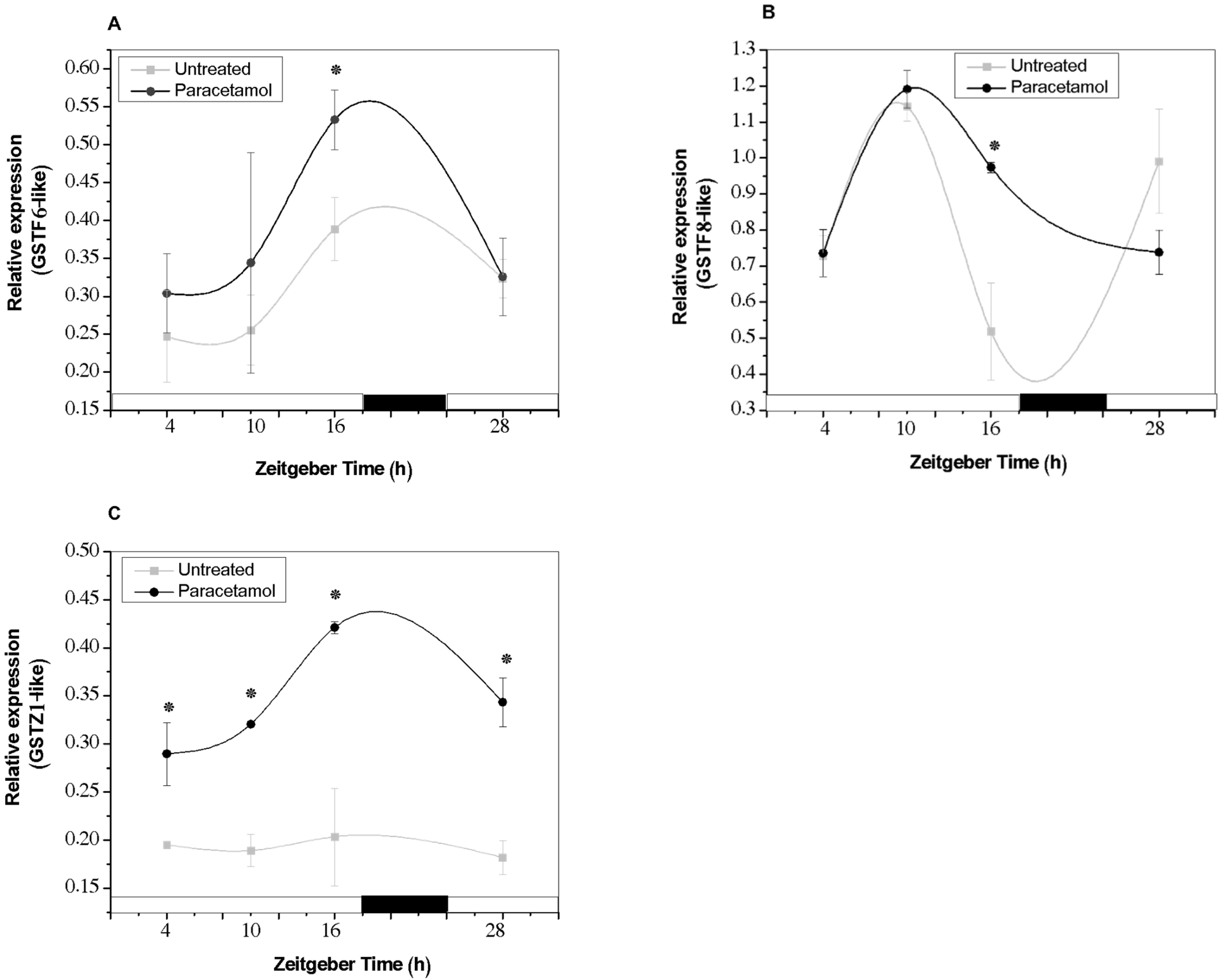
2.3.1. GST Gene Expression
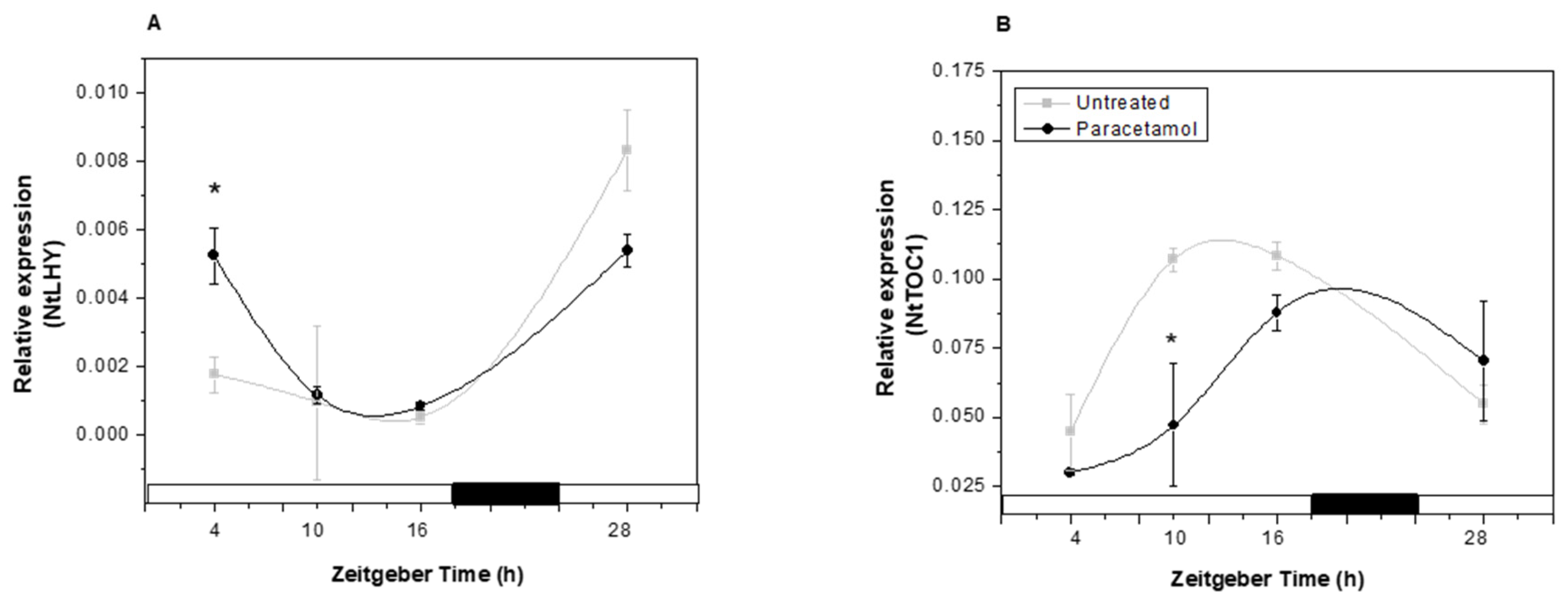
2.3.2. Clock Gene Expression
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Biological Material and Growth Conditions
3.3. Paracetamol Treatments
3.4. Paracetamol Removal Analysis
3.5. Biochemical Analysis
3.5.1. Determination of POD Activity
3.5.2. Determination of GST Activity
3.5.3. Total Antioxidant Activity (TAA)
3.5.4. Evaluation of Glutathione (GSH) Concentration
3.5.5. Evaluation of Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances (TBARs) Content
3.6. Analysis of GST and Clock Genes
3.6.1. Identification of Putative GST Genes in N. tabacum
3.6.2. Identification of Circadian Clock Cis-Elements in the Promoter Regions of GST Genes
3.6.3. qPCR Analysis of GST and Clock Genes Expression
3.7. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barrios-Estrada, C.; de Jesús Rostro-Alanis, M.; Muñoz-Gutiérrez, B.D.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Kannan, S.; Parra-Saldívar, R. Emergent contaminants: Endocrine disruptors and their laccase-assisted degradation—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 1516–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Qiu, J.; Weng, C.H.; Tao, J.; Tang, Z.; Zeng, J.; Liu, N.; Wang, X. Target and non-target screening for the existence, ecological risk and source analysis of contaminants of emerging concern (CECs) in groundwater. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2025, 7, 1315–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Carabalí, L.A.; Sachdeva, R.; Rojas-Trigos, J.B.; Marín, E.; Garcia, C.D. Monitoring the advanced oxidation of paracetamol using ZnO films via capillary electrophoresis. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 41, 102051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elessawy, N.A.; Alhamzani, A.G.; Almahmoud, S.A.J.; Hsiao, B.S. Evaluation, optimization study, and life cycle assessment of novel eco-friendly PVA-based nanocomposite hydrogel adsorbents for methylene blue and paracetamol removal. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 285, 117123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romdhani, M.; Attia, A.; Charcosset, C.; Mahouche-Chergui, S.; Ates, A.; Duplay, J.; Ben Amar, R. Optimization of Paracetamol and Chloramphenicol Removal by Novel Activated Carbon Derived from Sawdust Using Response Surface Methodology. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta-Hernández, J.M.; Brillas, E. A critical review over the removal of paracetamol (acetaminophen) from synthetic waters and real wastewaters by direct, hybrid catalytic, and sequential ozonation processes. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, T.I.; El-Shahat, M.; Abdelhameed, R.M. Size-tunable effect of CaCO3/nanocellulose hybrid composites on the removal of paracetamol from aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 43287–43299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaltro, A.; Pila, M.N.; Colasurdo, D.D.; Noseda Grau, E.; Román, G.; Simonetti, S.; Ruiz, D.L. Removal of paracetamol from aqueous solution by activated carbon and silica. Experimental and computational study. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 236, 103739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuel, M.; Laurent, J.; Bois, P.; Heintz, D.; Wanko, A. Seasonal and ageing effect on the behaviour of 86 drugs in a full-scale surface treatment wetland: Removal efficiencies and distribution in plants and sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandermann, H., Jr. Higher plant metabolism of xenobiotics: The “green liver” concept. Pharmacogenetics 1994, 4, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsik, P.; Sisa, M.; Lacina, O.; Motkova, K.; Langhansova, L.; Rezek, J.; Vanek, T. Metabolism of ibuprofen in higher plants: A model Arabidopsis thaliana cell suspension culture system. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterhuizen, M.; Pflugmacher, S. Phytoremediation of diclofenac using the Green Liver System: Macrophyte screening to system optimization. New Biotechnol. 2023, 76, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, E.; Talano, M.A.; González, P.S.; Oller, A.L.W.; Medina, M.I. Application of hairy roots for phytoremediation: What makes them an interesting tool for this purpose? Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, J.; Misra, A.; Banerjee, N. Genetic transfection, hairy root induction and solasodine accumulation in elicited hairy root clone of Solanum erianthum D. Don. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 323, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, C.; Bartha, B.; Harpaintner, R.; Schröder, P. Metabolism of acetaminophen (paracetamol) in plants-two independent pathways result in the formation of a glutathione and a glucose conjugate. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2009, 16, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa Alderete, L.; Sauvêtre, A.; Chiron, S.; Tadić, Đ. Investigating the Transformation Products of Selected Antibiotics and 17 α-Ethinylestradiol under Three In Vitro Biotransformation Models for Anticipating Their Relevance in Bioaugmented Constructed Wetlands. Toxics 2023, 11, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badar, Z.; Shanableh, A.; El-Keblawy, A.; Mosa, K.A.; Semerjian, L.; Mutery, A.; Al Hussain, M.I.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Tsombou, F.M.; Ayyaril, S.S.; et al. Assessment of Uptake, Accumulation and Degradation of Paracetamol in Spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) under Controlled Laboratory Conditions. Plants 2022, 11, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qiu, J.X.; Zeng, Q.H.; Yi Zhuang Zhang, N.; Xu, S.X.; Jin, J.; Dong, Z.C.; Chen, L.; Huang, W. OsTOC1 plays dual roles in the regulation of plant circadian clock by functioning as a direct transcription activator or repressor. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Delgado, A.; Jiménez-Gómez, J.M.; Wabnik, K. Regulatory principles of photoperiod-driven clock function in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2025, 30, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigott, Y.; Chowdhury, S.P.; Pérez, S.; Montemurro, N.; Manasfi, R.; Schröder, P. Effect of the pharmaceuticals diclofenac and lamotrigine on stress responses and stress gene expression in lettuce (Lactuca sativa) at environmentally relevant concentrations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, S.; Ibañez, S.G.; Agostini, E.; Sosa Alderete, L.G. Influence of arsenic exposure on the daily changes of glycerophospholipid turnover and assessment of defence mechanisms in tobacco hairy roots. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 223, 109880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibañez, S.G.; Travaglia, C.N.; Medina, M.I.; Agostini, E. Vicia villosa Roth: A cover crop to phytoremediate arsenic polluted environments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 38604–38612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omotola, E.O.; Genthe, B.; Ndlela, L.; Olatunji, S.O. Phytotoxicity and apoptotic impact assessment of an over-the-counter drug (paracetamol) residue using Allium cepa as a bioindicator. TASUED J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2023, 2, 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Kotyza, J.; Soudek, P.; Kafka, Z.; Vaněk, T. Phytoremediation of pharmaceuticals-preliminary study. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2010, 12, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, C.D.T.; Costa, J.H.; Germano, T.A.; de O Rocha, R.; Ramos, M.V.; Bezerra, L.P. Class III plant peroxidases: From classification to physiological functions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandermann, H.; Diesperger, J.H.; Scheel, D. Metabolism of Xenobiotics by Plant Cell Cultures. In Plant Tissue Culture and Its Bio-Technological Application, Proceedings of the First International Congress on Medicinal Plant Research, Section B, Held at the University of Munich, Germany, 6–10 September 1976; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1977; pp. 178–196. [Google Scholar]
- Sosa Alderete, L.G.; Ronchi, H.; Monjes, N.M.; Agostini, E. Tobacco hairy root’s peroxidases are rhythmically controlled by phenol exposure. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2021, 149, 109856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartha, B.; Huber, C.; Harpaintner, R.; Schröder, P. Effects of acetaminophen in Brassica juncea L. Czern.: Investigation of uptake, translocation, detoxification, and the induced defense pathways. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2010, 17, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, P.; Lyubenova, L.; Huber, C. Do heavy metals and metalloids influence the detoxification of organic xenobiotics in plants? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2009, 16, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, I.; Dixon, D.P.; Freitag-Pohl, S.; Skipsey, M.; Edwards, R. Multiple roles for plant glutathione transferases in xenobiotic detoxification. Drug Metab. Rev. 2011, 43, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Dudley, S.; Mcginnis, M.; Trumble, J.; Gan, J. Science of the Total Environment Acetaminophen detoxi fi cation in cucumber plants via induction of glutathione S -transferases. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, B.; Lopes, J.; Leal, A.; Martins, M.; Soares, C.; Azenha, M.; Fidalgo, F.; Teixeira, J. Specific glutathione-S-transferases ensure an efficient detoxification of diclofenac in Solanum lycopersicum L. plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 168, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallé, Á.; Czékus, Z.; Bela, K.; Horváth, E.; Csiszár, J.; Poór, P. Diurnal changes in tomato glutathione transferase activity and expression: Short communication. Acta Biol. Hung. 2018, 69, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadarajah, K.K. ROS homeostasis in abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, B.; Lopes, J.; Leal, A.; Martins, M.; Soares, C.; Valente, I.M.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Fidalgo, F.; Teixeira, J. Response of Solanum lycopersicum L. to diclofenac—Impacts on the plant’s antioxidant mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezza, M.E.; Sosa Alderete, L.G.; Agostini, E.; Talano, M.A. Expression of circadian clock genes and diurnal oscillations of key physiological events in response to AsV and AsIII in soybean plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 174, 104054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallé, Á.; Czékus, Z.; Bela, K.; Horváth, E.; Ördög, A.; Csiszár, J.; Poór, P. Plant glutathione transferases and light. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Liu, W.C.; Han, C.; Wang, S.; Bai, M.Y.; Song, C.P. Reactive oxygen species: Multidimensional regulators of plant adaptation to abiotic stress and development. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2024, 66, 330–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, A.; Antoniou, C.; Christodoulou, C.; Hapeshi, E.; Stavrou, I.; Michael, C.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Fotopoulos, V. Stress-related phenomena and detoxification mechanisms induced by common pharmaceuticals in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557–558, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Han, R.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, X. Effects of bisphenol A on antioxidant system in soybean seedling roots. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Rey, M.; Bebianno, M.J. Does non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) ibuprofen induce antioxidant stress and endocrine disruption in mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis? Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 33, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombini, C.; Kazakova, J.; Villar-Navarro, M.; Hampel, M.; Fernández-Torres, R.; Bello-López, M.Á.; Blasco, J. Bioaccumulation and biochemical responses in the peppery furrow shell Scrobicularia plana exposed to a pharmaceutical cocktail at sub-lethal concentrations. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 242, 113845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, D.F.; de Carvalho, N.R.; Leite, M.B.; Courtes, A.A.; Hartmann, D.D.; Stefanello, S.T.; da Silva, I.K.; Franco, J.L.; Soares, F.A.A.; Dalla Corte, C.L. Caffeine and acetaminophen association: Effects on mitochondrial bioenergetics. Life Sci. 2018, 193, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Nagata, T. parB: An auxin-regulated gene encoding glutathione S-transferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widdup, E.E.; Chatfield-Reed, K.; Henry, D.; Chua, G.; Samuel, M.A.; Muench, D.G. Identification of detoxification pathways in plants that are regulated in response to treatment with organic compounds isolated from oil sands process-affected water. Chemosphere 2015, 139, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa Alderete, L.G.; Guido, M.E.; Agostini, E.; Mas, P. Identification and characterization of key circadian clock genes of tobacco hairy roots: Putative regulatory role in xenobiotic metabolism. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.; Köster, T. On the move through time—A historical review of plant clock research. Plant Biol. 2019, 21, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendix, C.; Marshall, C.M.; Harmon, F.G. Circadian Clock Genes Universally Control Key Agricultural Traits. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1135–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenham, K.; McClung, C.R. Integrating circadian dynamics with physiological processes in plants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamichi, N.; Kusano, M.; Fukushima, A.; Kita, M.; Ito, S.; Yamashino, T.; Saito, K.; Sakakibara, H.; Mizuno, T. Transcript profiling of an arabidopsis PSEUDO RESPONSE REGULATOR arrhythmic triple mutant reveals a role for the circadian clock in cold stress response. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009, 50, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa Alderete, L.G.; Talano, M.A.; Ibáñez, S.G.; Purro, S.; Agostini, E.; Milrad, S.R.; Medina, M.I. Establishment of transgenic tobacco hairy roots expressing basic peroxidases and its application for phenol removal. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 139, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roenneberg, T.; Kumar, C.J.; Merrow, M. The human circadian clock entrains to sun time. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, R44–R45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, P.; Maier, H.; Debus, R. Detoxification of herbicides in Phragmites australis. Z. Naturforschung-Sect. C J. Biosci. 2005, 60, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a Free Radical Method to Evaluate Antioxidant Activity. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezza, M.E.; Pramparo, R.D.P.; Wevar Oller, A.L.; Agostini, E.; Talano, M.A. Promising co-inoculation strategies to reduce arsenic toxicity in soybean. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 88066–88077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.E. Determination of Glutathione and Glutathione Disulfide in Biological Samples. Methods Enzymol. 1985, 113, 548–555. [Google Scholar]
- Heath, R.L.; Packer, L. Photoperoxidation in isolated Chloroplasts I. Kinetics and Stoichiometry of Fatty Acid Peroxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1968, 126, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nianiou-Obeidat, I.; Madesis, P.; Kissoudis, C.; Voulgari, G.; Chronopoulou, E.; Tsaftaris, A.; Labrou, N.E. Plant glutathione transferase-mediated stress tolerance: Functions and biotechnological applications. Plant Cell Rep. 2017, 36, 791–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa, P.; Prerostova, S.; Langhansova, L.; Marsik, P.; Vanek, T. Transcriptomic response of Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. roots to ibuprofen. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2017, 19, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Dehais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouze, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, G.W.; Delaney, S.K. Stable internal reference genes for normalization of real-time RT-PCR in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) during development and abiotic stress. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2010, 283, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sosa Alderete, L.G.; Vezza, M.; Ibañez, S.G.; Schroeder, P.; Agostini, E.; Talano, M.A. Unraveling Paracetamol Metabolism and Its Circadian Regulation: Insights from Tobacco Hairy Roots as a Model System. Plants 2025, 14, 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172812
Sosa Alderete LG, Vezza M, Ibañez SG, Schroeder P, Agostini E, Talano MA. Unraveling Paracetamol Metabolism and Its Circadian Regulation: Insights from Tobacco Hairy Roots as a Model System. Plants. 2025; 14(17):2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172812
Chicago/Turabian StyleSosa Alderete, Lucas G., Mariana Vezza, Sabrina G. Ibañez, Peter Schroeder, Elizabeth Agostini, and Melina A. Talano. 2025. "Unraveling Paracetamol Metabolism and Its Circadian Regulation: Insights from Tobacco Hairy Roots as a Model System" Plants 14, no. 17: 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172812
APA StyleSosa Alderete, L. G., Vezza, M., Ibañez, S. G., Schroeder, P., Agostini, E., & Talano, M. A. (2025). Unraveling Paracetamol Metabolism and Its Circadian Regulation: Insights from Tobacco Hairy Roots as a Model System. Plants, 14(17), 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172812






