A Regulatory Network of Arabinogalactan Proteins, Glycosylation, and Nucleotide Sugars for Optimizing Mara des Bois Strawberries Postharvest Storage Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
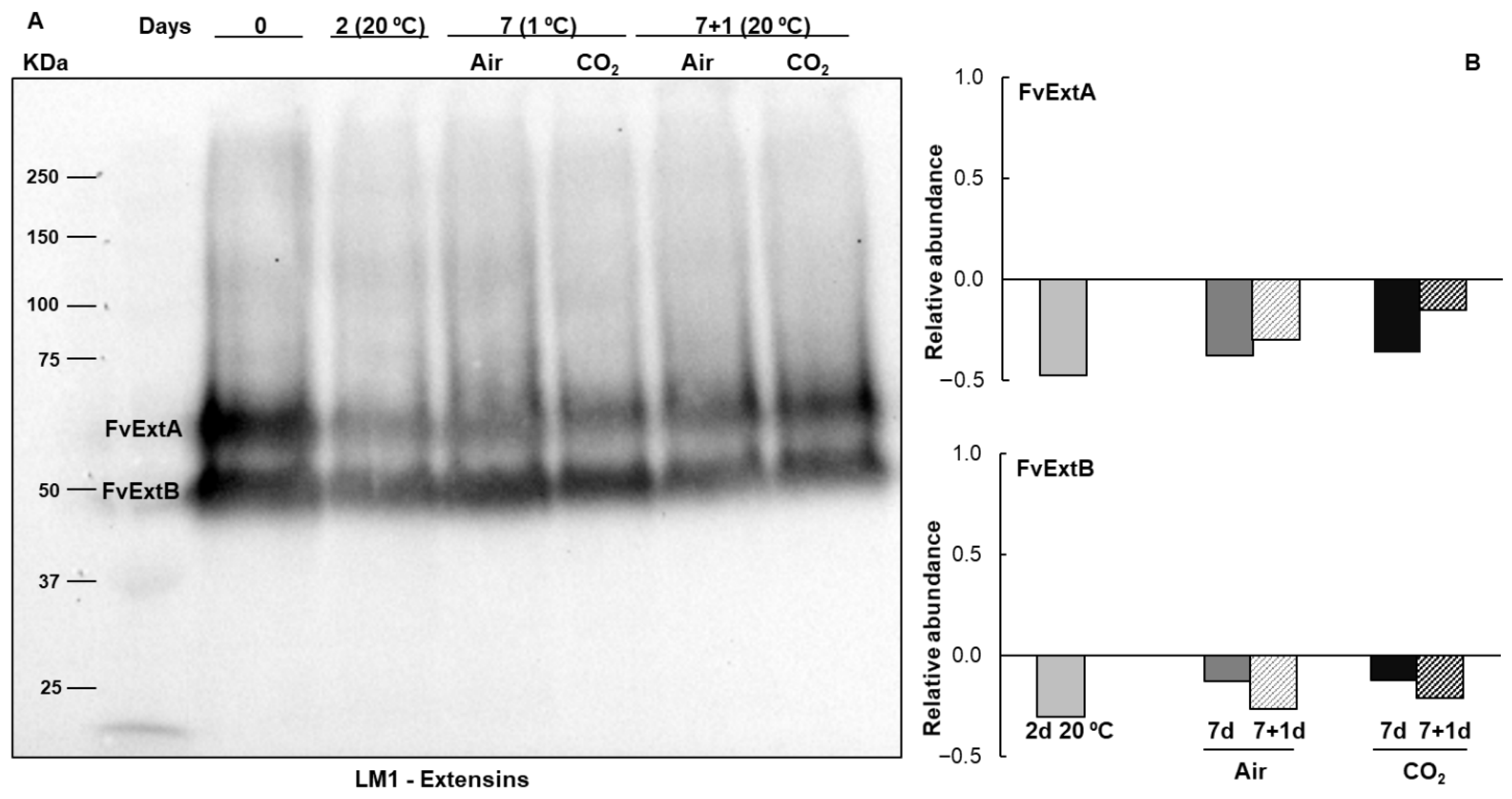
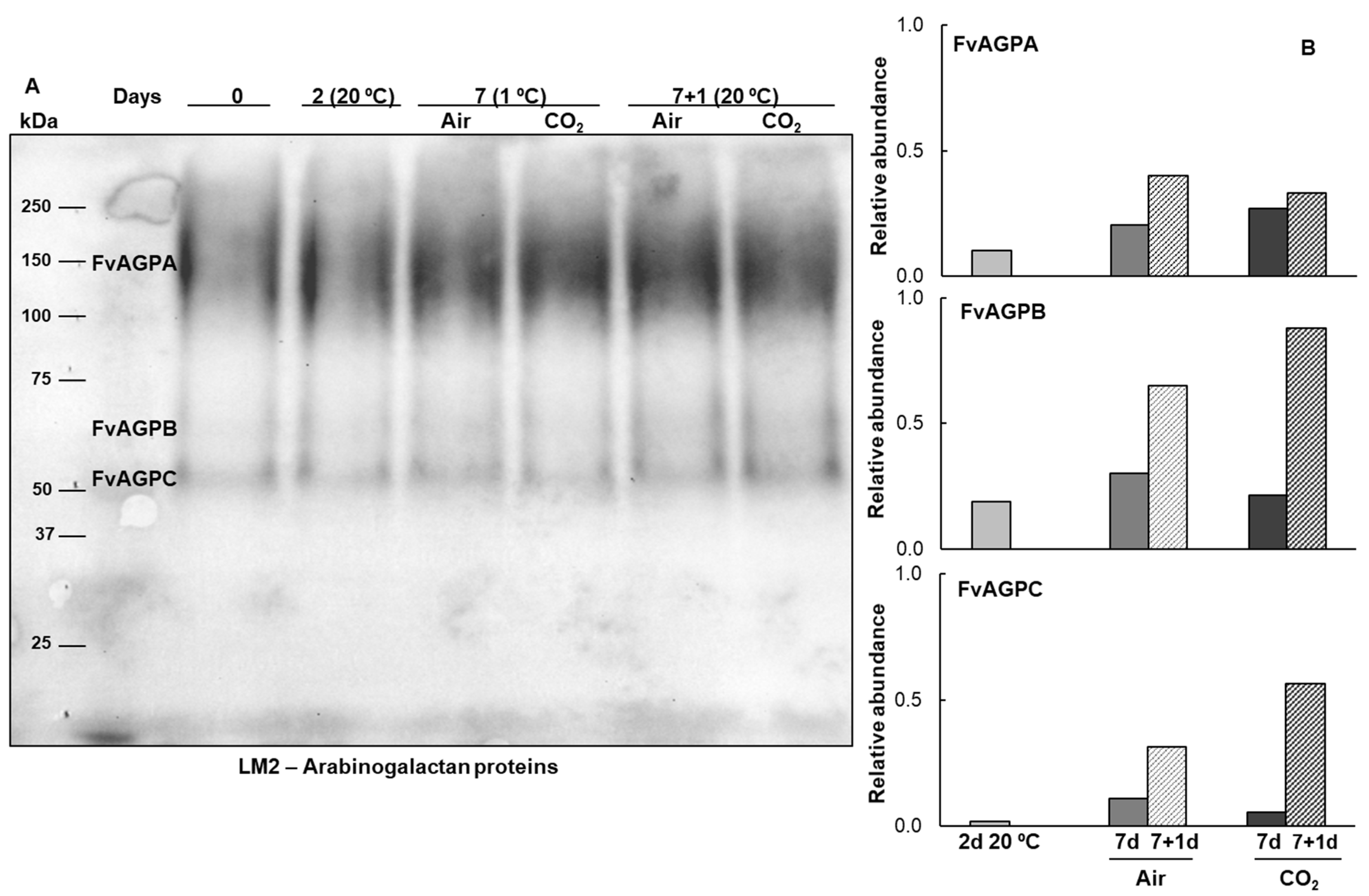
2.1. Extensins and Arabinogalactan Proteins Pattern During Strawberries Postharvest Storage
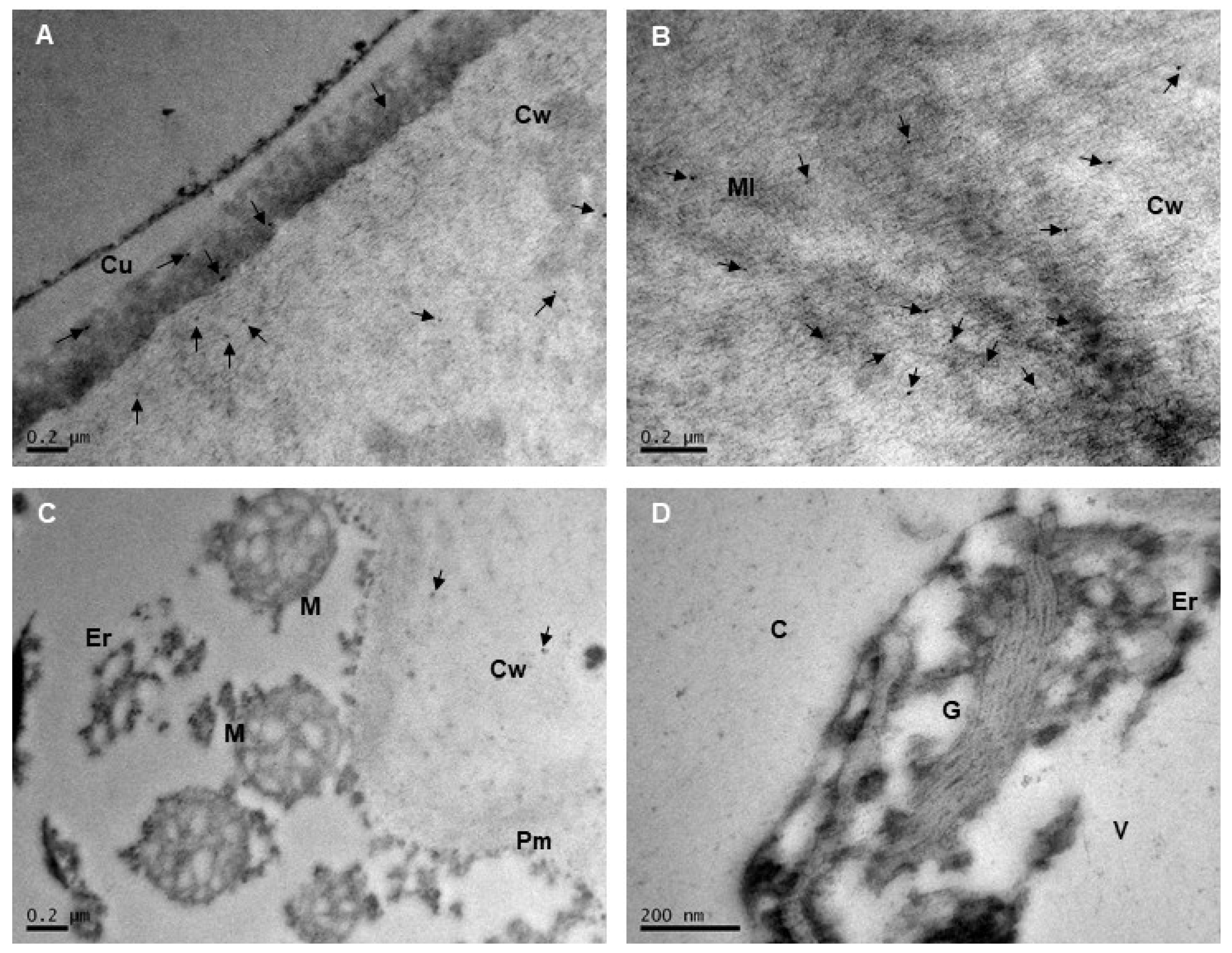
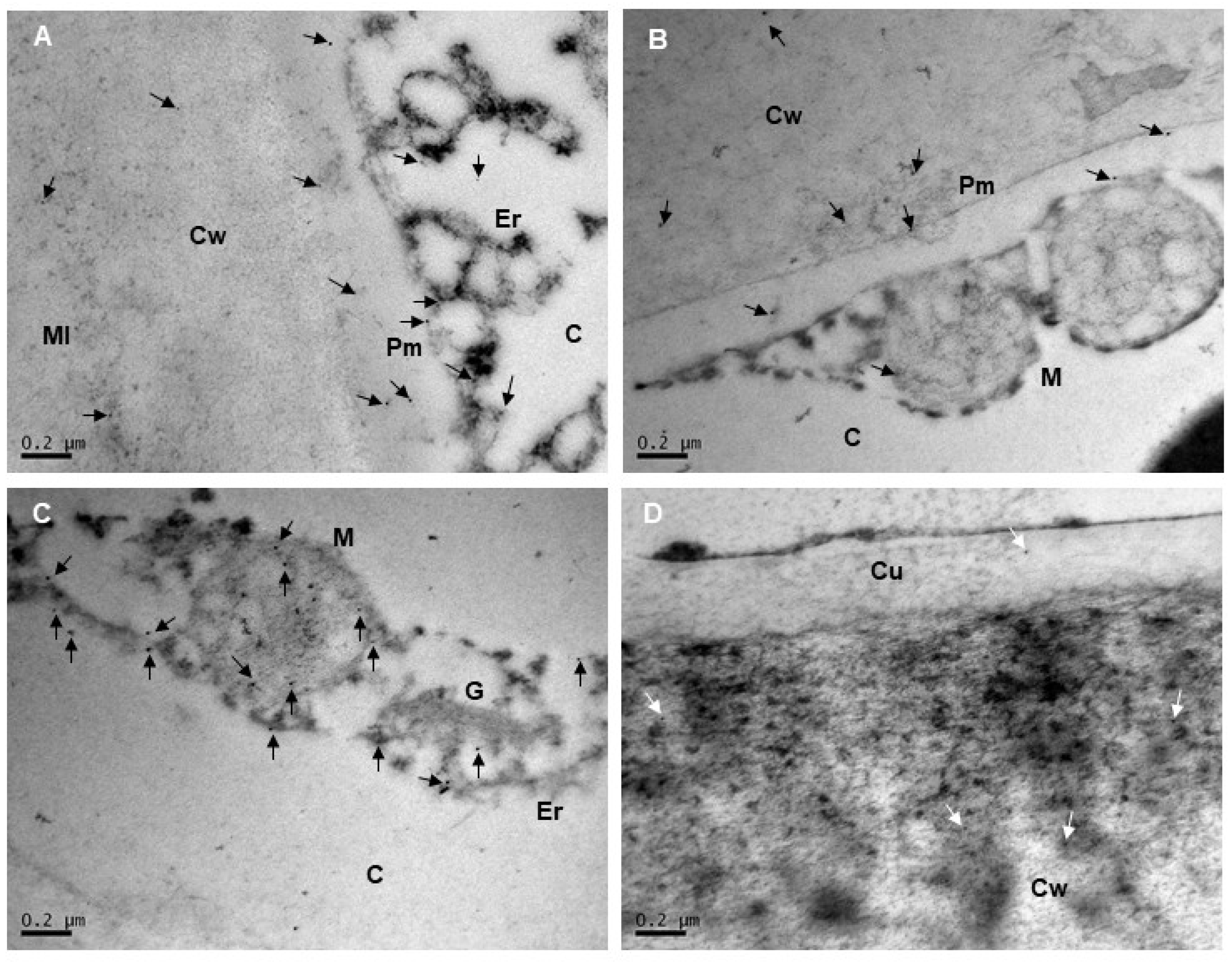
2.2. Subcellular Localization of Extensins and Arabinogalactan Proteins in Mara des Bois Strawberries
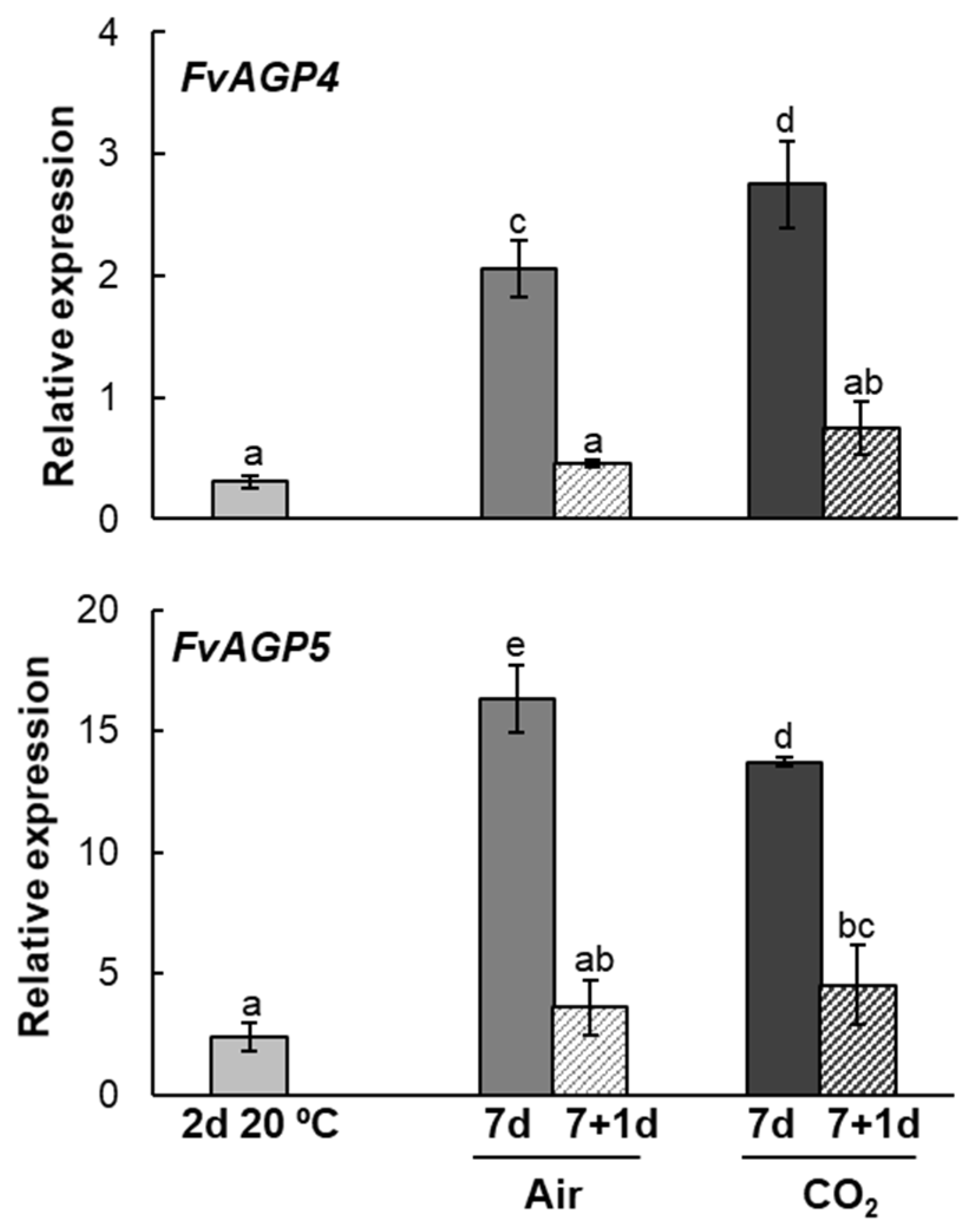
2.3. Arabinogalactan Protein Genes Expression Pattern During Strawberries Postharvest Storage
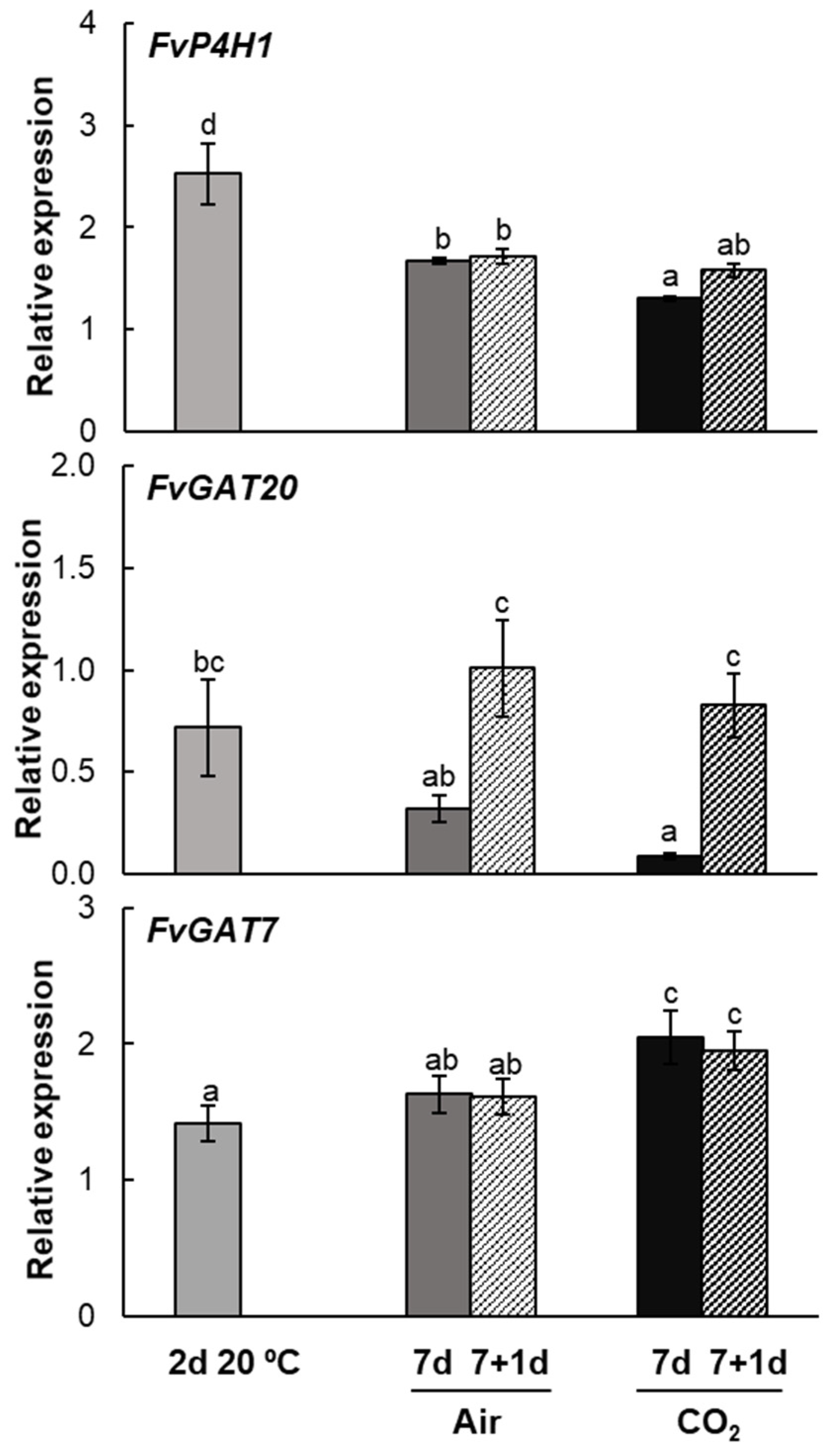
2.4. Post-Transcriptional Arabinogalactan Protein Genes Expression Pattern During Strawberries Postharvest Storage
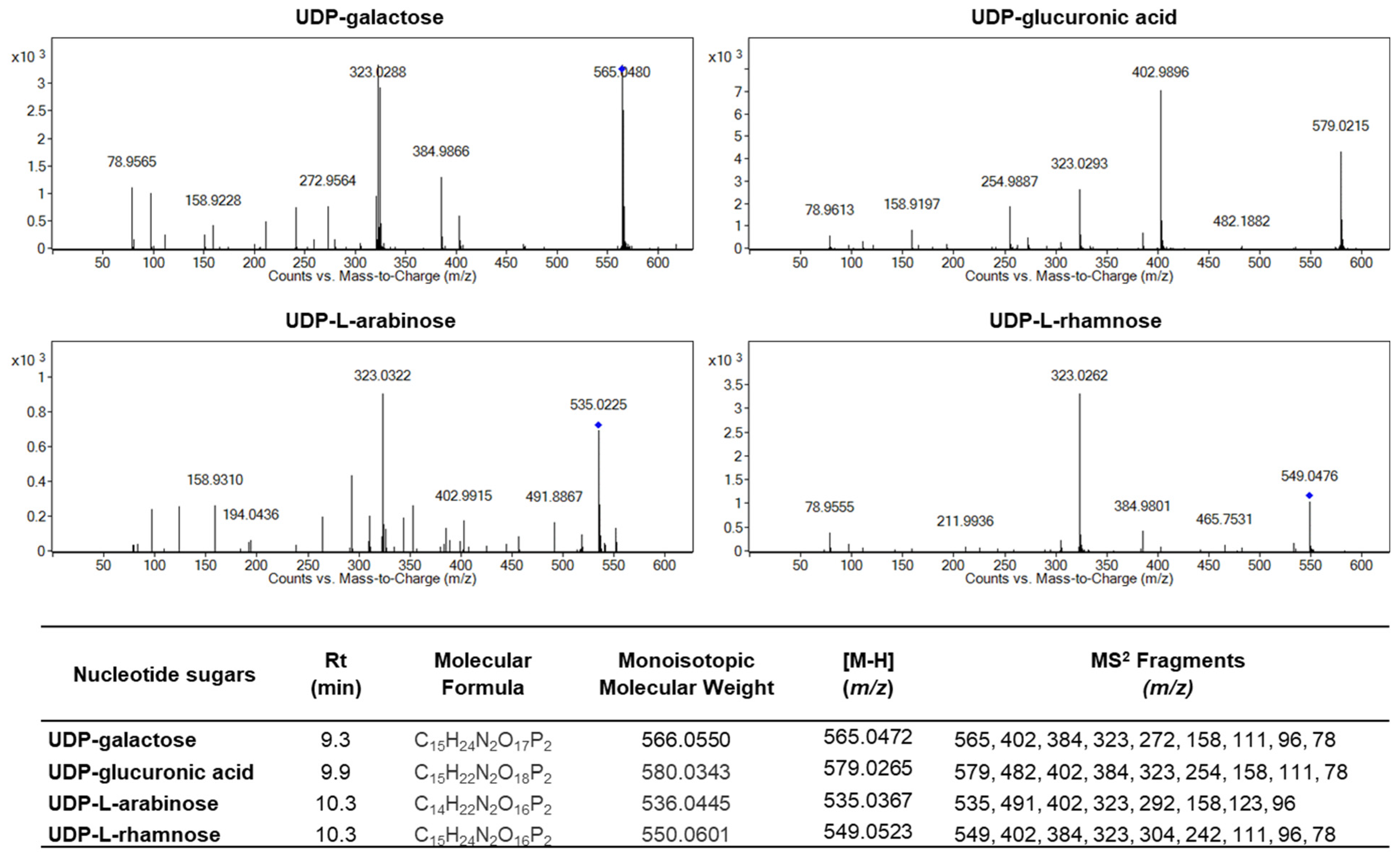
2.5. Identification and Quantification of UDP-Sugars Involved in Arabinogalactan Protein Glycosylation During Strawberries Postharvest Storage
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Postharvest Treatments
4.2. Isolation of Protein Fraction and Immunoblotting
4.3. Immunogold Electron Microscopy
4.4. Relative Gene Expression by Semi-Quantitative and Quantitative RT-PCR
4.5. Extraction and Analysis of UDP-Sugars by MS and MS2
4.6. Bioinformatic Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, K.L.; Cassin, A.M.; Lonsdale, A.; Bacic, A.; Doblin, M.S.; Schultz, C.J. A motif and amino acid bias bioinformatics pipeline to identify hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins. Plant Physiol. 2017, 174, 886–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, M.; Velasquez, S.M.; Jamet, E.; Estevez, J.M.; Albenne, C. An update on post-translational modifications of hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins: Toward a model highlighting their contribution to plant cell wall architecture. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguema-Ona, E.; Vicré-Gibouin, M.; Gotté, M.; Plancot, B.; Lerouge, P.; Bardor, M.; Driouich, A. Cell wall O-glycoproteins and N-glycoproteins: Aspects of biosynthesis and function. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canut, H.; Albenne, C.; Jamet, E. Post-translational modifications of plant cell wall proteins and peptides: A survey from a proteomics point of view. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1864, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, M.; Egelund, J.; Schultz, C.J.; Bacic, A. Arabinogalactan-proteins: Key regulators at the cell surface? Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Showalter, A.M.; Basu, D. Extensin and arabinogalactan-protein biosynthesis: Glycosyltransferases, research challenges, and biosensors. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Johnson, K. Arabinogalactan proteins—Multifunctional glycoproteins of the plant cell wall. Cell Surf. 2023, 9, 100102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, F.; Suyama, A.; Oka, T.; Yoko-O, T.; Matsuoka, K.; Jigami, Y.; Shimma, Y. Identification of novel peptidyl serine O-galactosyltransferase gene family in plants. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 30, 20405–20420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamport, D.T.A.; Kieliszewski, M.J.; Chen, Y.; Cannon, M.C. Role of the extensin superfamily in primary cell wall architecture. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilleux, R.; Plancot, B.; Vicré, M.; Nguema-Ona, E.; Driouich, A. Extensin, an underestimated key component of cell wall defence? Ann. Bot. 2021, 127, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Olmo, I.; Blanch, M.; Romero, I.; Vazquez-Hernandez, M.; Sanchez-Ballesta, M.T.; Escribano, M.I.; Merodio, C. Involvement of oligosaccharides and sucrose-related genes on sucrose retention in strawberries from ripening to shelf-life. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 169, 111301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Olmo, I.; Romero, I.; Alvarez, M.D.; Tarradas, R.; Sanchez-Ballesta, M.T.; Escribano, M.I.; Merodio, C. Transcriptomic analysis of CO2-treated strawberries (Fragaria vesca) with enhanced resistance to softening and oxidative stress at consumption. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 983976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanch, M.; Alvarez, I.; Sanchez-Ballesta, M.T.; Escribano, M.I.; Merodio, C. Trisaccharides isomers, galactinol and osmotic imbalance associated with CO2 stress in strawberries. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2017, 131, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Guerrero, J.D.; Alvarez, M.D.; Herranz, B.; Escribano, M.I.; Merodio, C.; Romero, I.; Sanchez-Ballesta, M.T. Effect of short-term high CO2 treatments on maintaining the firmness of highbush and rabbiteye blueberries during cold storage. Plants 2024, 13, 3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, I.; Toledo-Guerrero, J.D.; Alvarez, M.D.; Herranz, B.; Escribano, M.I.; Merodio, C.; Sanchez-Ballesta, M.T. Short-term gaseous treatments preserve firmness and fruit quality in raspberries stored at low temperature: Impact on the expression of cell wall remodeling genes. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 230, 113777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Ferraz, R.; Dupree, P.; Showalter, A.M.; Coimbra, S. Three decades of advances in arabinogalactan-protein biosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 15, 610377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y. The plant cell wall: Biosynthesis, construction, and functions. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, D.J. Structure and growth of plant cell walls. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024, 25, 340–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, R.; Voesenek, L.; Pierik, R. Cell wall modifying proteins mediate plant acclimatization to biotic and abiotic stresses. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2011, 30, 548–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua, C.; Santiago-Domenech, N.; Kirby, A.; Gunning, A.; Morris, V.; Quesada, M.A.; Matas, A.J.; Mercado, J.A. Structural changes in cell wall pectins during strawberry fruit development. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 118, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moya-León, M.A.; Mattus-Araya, E.; Herrera, R. Molecular events occurring during softening of strawberry fruit. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, M.; Watkins, C.B. Firmness and aroma composition of strawberries following short-term high carbon dioxide treatment. HortScience 1995, 30, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harker, F.R.; Elgar, H.J.; Watkins, C.B.; Jackson, P.J.; Hallett, I.C. Physical and mechanical changes in strawberry fruit after high carbon dioxide treatments. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2000, 19, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Chu, P.K.; Chen, Y.J.; Wu, Y.H.; Huang, M.D. Exploring the extensin gene family: An updated genome-wide survey in plants and algae. J. Exp. Bot. 2024, 75, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.P.; Fangel, J.U.; Willats, W.G.T.; Vivier, M.A. Pectic-b (1,4)-galactan, extensin and arabinogalactan-protein epitopes differentiate ripening stages in wine and table grape cell walls. Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 1279–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Showalter, A.M. Arabinogalactan-proteins: Structure, expression and function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 1399–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, G.J.; Roberts, K. The Biology of Arabinogalactan Proteins. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2007, 58, 137–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leszczuk, A.; Kalaitzis, P.; Blazakis, K.N.; Zdunek, A. The role of arabinogalactan proteins (AGPs) in fruit ripening—A review. Hort. Res. 2020, 7, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkostefanakis, S.; Dandachi, F.; Kalaitzis, P. Expression of arabinogalactan proteins during tomato fruit ripening and in response to mechanical wounding, hypoxia and anoxia. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 52, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leszczuk, A.; Zając, A.; Kurzyna-Szklarek, M.; Cybulska, J.; Zdunek, A. Investigations of changes in the arabinogalactan proteins (AGPs) structure, size and composition during the fruit ripening process. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutyrieva-Nowak, N.; Leszczuk, A.; Zając, A.; Kalaitzis, P.; Zdunek, A. Arabinogalactan protein is a molecular and cytological marker of particular stages of the tomato fruit ripening process. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 310, 1365490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbančič, J.; Lunn, J.E.; Stitt, M.; Persson, S. Carbon Supply and the Regulation of Cell Wall Synthesis. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewska-Sawka, A.; Nothnagel, E.A. The multiple roles of arabinogalactan proteins in plant development. Plant Physiol. 2000, 122, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaj, J.; Samajová, O.; Peters, M.; Baluska, E.; Lichtscheidl, I.; Knox, J.P.; Volkmann, D. Immunolocalization of LM2 arabinogalactan protein epitope associated with endomembranes of plant cells. Protoplasma 2000, 212, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contigiani, E.V.; Jaramillo-Sánchez, G.; Castro, M.A.; Gómez, P.L.; Alzamora, S.M. Postharvest quality of strawberry fruit (Fragaria x Ananassa Duch cv. Albion) as affected by ozone washing: Fungal spoilage, mechanical properties, and structure. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Eberhard, S.; Pattathil, S.; Warder, C.; Glushka, J.; Yuan, C.; Hao, Z.; Zhu, X.; Avci, U.; Miller, J.S.; et al. An Arabidopsis cell wall proteoglycan consists of pectin and arabinoxylan covalently linked to an arabinogalactan protein. Plant Cell. 2013, 25, 270–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Meng, J.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Su, Z.; Chen, C.; Ning, T.; He, Z.; Dai, L.; Xu, C. Different responses of banana classical AGP genes and cell wall AGP components to low-temperature between chilling sensitive and tolerant cultivars. Plant Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 1693–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leszczuk, A.; Pieczywek, P.M.; Gryta, A.; Frąc, M.; Zdunek, A. Immunocytochemical studies on the distribution of arabinogalactan proteins (AGPs) as a response to fungal infection in Malus x domestica fruit. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yan, C.; Li, H.; Wu, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ma, H. Bioinformatics prediction and evolution analysis of arabinogalactan proteins in the plant kingdom. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Persson, S.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, C. At the border: The plasma membrane–cell wall continuum. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 6, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeats, T.; Bacic, A.; Johnson, K. Plant glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchored proteins at the plasma membrane-cell wall nexus. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2018, 60, 649–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamport, D.T.A.; Varnai, P. Periplasmic arabinogalactan glycoproteins act as a calcium capacitor that regulates plant growth and development. New Phytol. 2013, 197, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hengel, A.J.; Roberts, K. AtAGP30, an arabinogalactan-protein in the cell walls of the primary root, plays a role in root regeneration and seed germination. Plant J. 2003, 36, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, D.; Tian, L.; Wang, W.; Bobbs, S.; Herock, H.; Travers, A.; Showalter, A.M. A small multigene hydroxyproline-O-galactosyltransferase family functions in arabinogalactan-protein glycosylation, growth and development in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albornos, L.; Iriondo-Ocampo, P.; Dopico, B.; Martin, L. Reduction of galactose side chains in type II arabinogalactan alters homogalacturonan methyl esterification in Arabidopsis thaliana seed coat mucilage. Planta 2025, 262, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Peled, M.; O’Neill, M.A. Plant Nucleotide Sugar Formation, Interconversion, and Salvage by Sugar Recycling. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol. 2011, 62, 127–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Hernandez, M.; Romero, I.; Sanchez-Ballesta, M.T.; Merodio, C.; Escribano, M.I. Tissue-specific modulation of functional stress responsive proteins and organic osmolytes by a single or dual short-term high CO2 treatment during long-term cold storage Autumn Royal table grapes. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 205, 112501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Z.; Yu, H.; Chen, Q. Comparison and improvement of different methods of RNA isolation from strawberry (Fragria × ananassa). J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrivault, S.; Guenther, M.; Ivakov, A.; Feil, R.; Vosloh, D.; Van Dongen, J.T.; Sulpice, R.; Stitt, M. Use of reverse-phase liquid chromatography, linked to tandem mass spectrometry, to profile the Calvin cycle and other metabolic intermediates in Arabidopsis rosettes at different carbon dioxide concentrations. Plant J. 2009, 59, 826–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behmüller, R.; Forstenlehner, I.C.; Tenhaken, R.; Huber, C.G. Quantitative HPLC-MS analysis of nucleotide sugars in plant cells following off-line SPE sample preparation. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 3229–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| FvAGP4 | FvAGP5 | |
|---|---|---|
| total aa/calculated mol mass (kDa)/pI | 196/18.16/6.13 | 133/12.43/5.82 |
| proline (P) | 47 (24.0) a | 25 (18.8) |
| alanine (A) | 49 (25.0) | 32 (24.1) |
| serine (S) | 19 (9.7) | 15 (11.3) |
| threonine (T) | 19 (9.7) | 19 (14.3) |
| lysine (K) | 6 (3.1) | 1 (0.8) |
| PAST (%) | 68.4 | 68.5 |
| AP dipeptide repeats | 16 | 9 |
| PA dipeptide repeats | 15 | 11 |
| SP dipeptide repeats | 7 | 6 |
| TP dipeptide repeats | 9 | 5 |
| N-terminal Signal peptide | Y | Y |
| C-terminal GPI | Y | Y |
| aliphatic index (thermostability) | 71.58 | 72.26 |
| instability index | 83.57 | 77.58 |
| grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) | 0.253 | 0.431 |
| alpha helix (%) | 2.55 | 3.01 |
| beta sheet | 10.20 | 10.53 |
| random coil (%) | 87.24 | 86.47 |
| Subcellular location | Extracellular—Cell membrane | Extracellular—Cell membrane |
| 0 Days (20 °C) | 2 Days (20 °C) | 7 Days (1 °C) + 1 Day (20 °C) | ||
| Air | CO2 | |||
| UDP-galactose | 0.47 ± 0.03 c | 0.22 ± 0.02 a | 0.37 ± 0.02 b | 0.38 ± 0.04 b |
| UDP-L-arabinose | 0.30 ± 0.01 c | 0.22 ± 0.01 a | 0.24 ± 0.01 ab | 0.25 ± 0.01 b |
| UDP-glucuronic acid | 0.30 ± 0.01 c | 0.21 ± 0.00 a | 0.26 ± 0.01 b | 0.26 ± 0.01 b |
| UDP-L-rhamnose | 0.25 ± 0.01 c | 0.21 ± 0.00 a | 0.23 ± 0.00 b | 0.24 ± 0.01 bc |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Escribano, M.I.; Romero, I.; Sanchez-Ballesta, M.T.; Merodio, C. A Regulatory Network of Arabinogalactan Proteins, Glycosylation, and Nucleotide Sugars for Optimizing Mara des Bois Strawberries Postharvest Storage Quality. Plants 2025, 14, 2796. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172796
Escribano MI, Romero I, Sanchez-Ballesta MT, Merodio C. A Regulatory Network of Arabinogalactan Proteins, Glycosylation, and Nucleotide Sugars for Optimizing Mara des Bois Strawberries Postharvest Storage Quality. Plants. 2025; 14(17):2796. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172796
Chicago/Turabian StyleEscribano, María Isabel, Irene Romero, María Teresa Sanchez-Ballesta, and Carmen Merodio. 2025. "A Regulatory Network of Arabinogalactan Proteins, Glycosylation, and Nucleotide Sugars for Optimizing Mara des Bois Strawberries Postharvest Storage Quality" Plants 14, no. 17: 2796. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172796
APA StyleEscribano, M. I., Romero, I., Sanchez-Ballesta, M. T., & Merodio, C. (2025). A Regulatory Network of Arabinogalactan Proteins, Glycosylation, and Nucleotide Sugars for Optimizing Mara des Bois Strawberries Postharvest Storage Quality. Plants, 14(17), 2796. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172796






