Adaptability and Stability of Proso Millet Grain Yield: A Multi-Environment Evaluation Using AMMI, GGE, and GYT Biplots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of Variance for Yield Traits and the Impact of Environmental Differences on Phenotypes
2.2. Integrated Multi-Model Analysis of Genotypic Yield Performance, Stability, and Adaptability
2.2.1. Basic Characteristics of Yield Mean and Stability
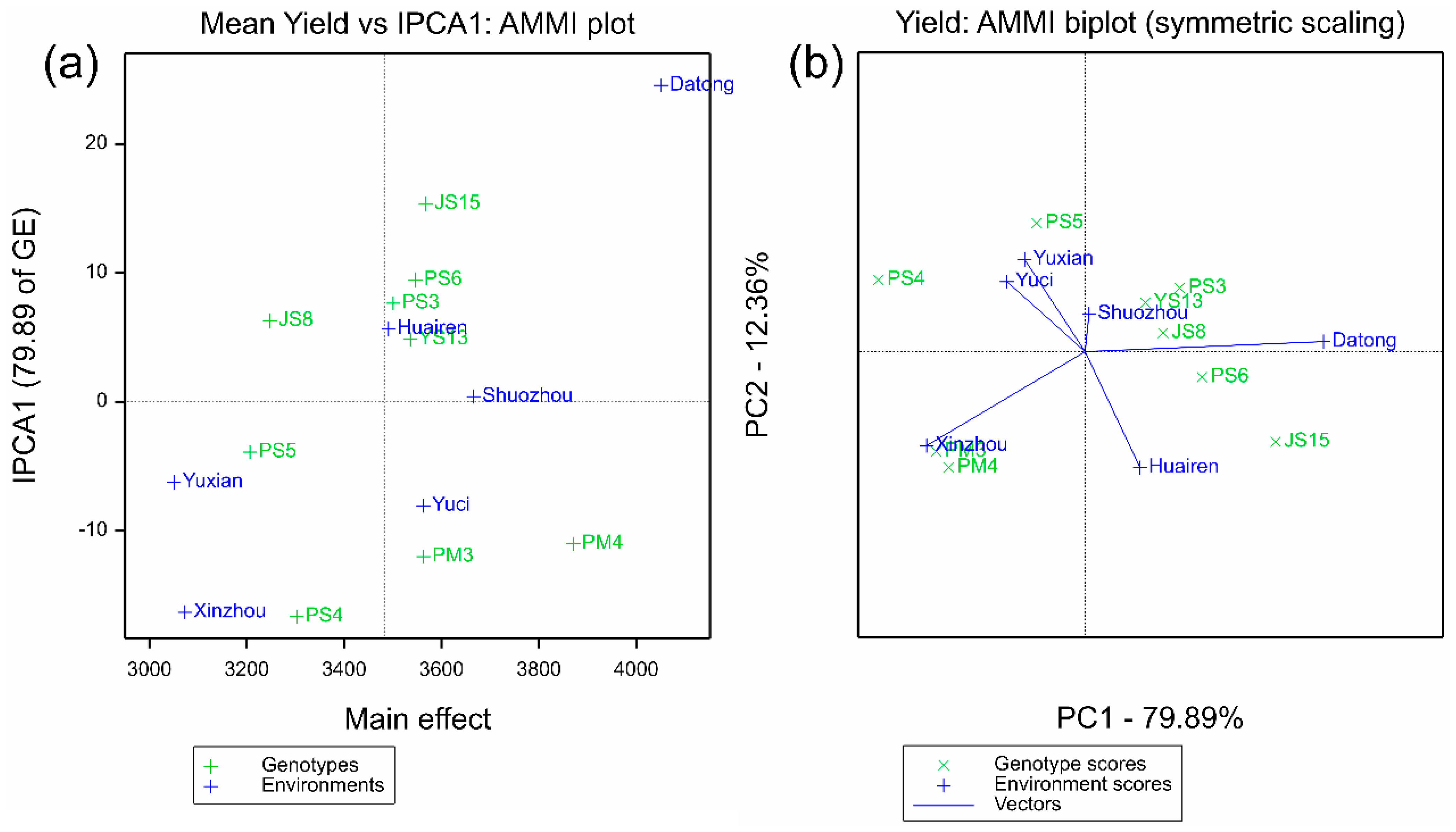
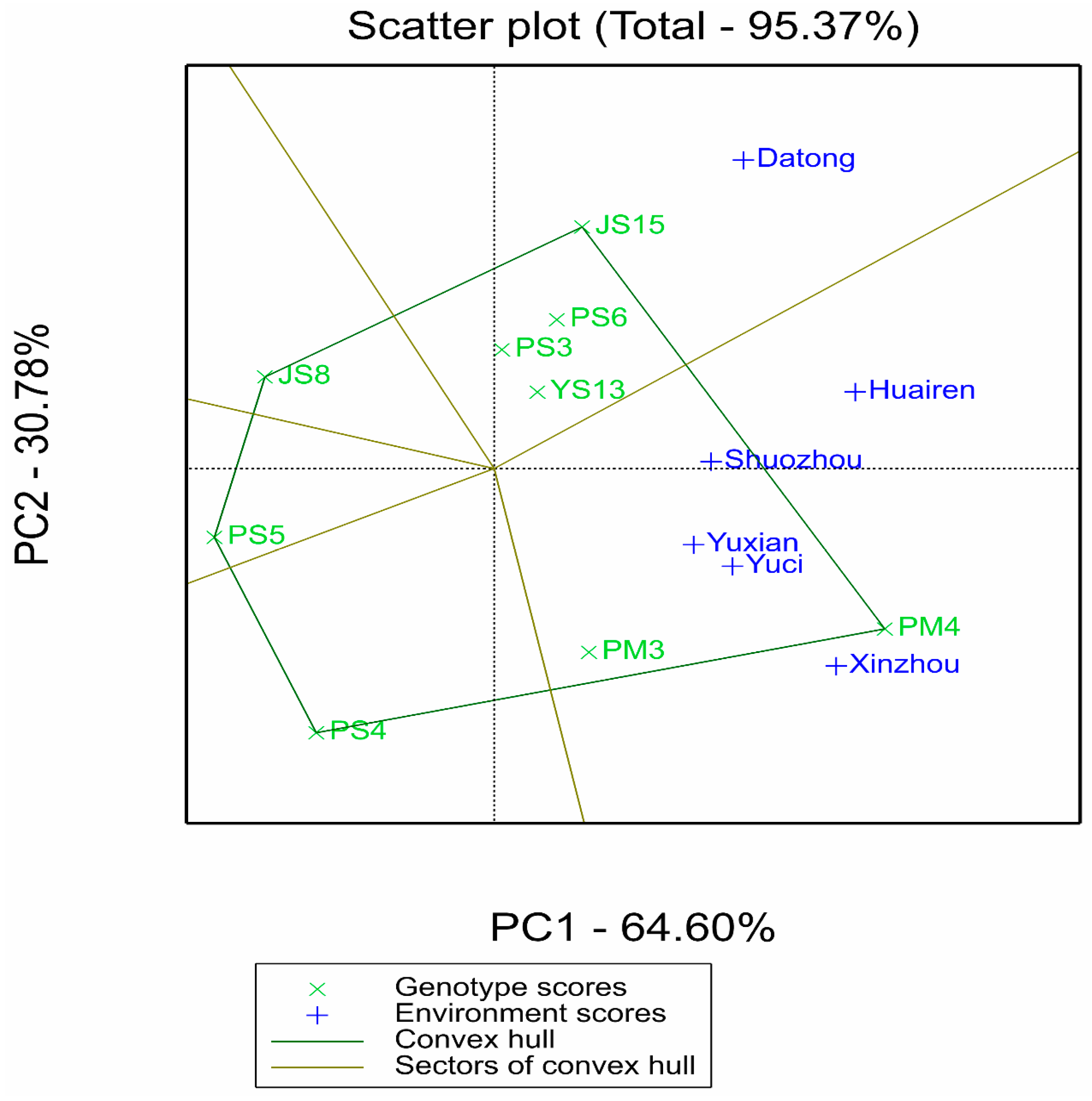
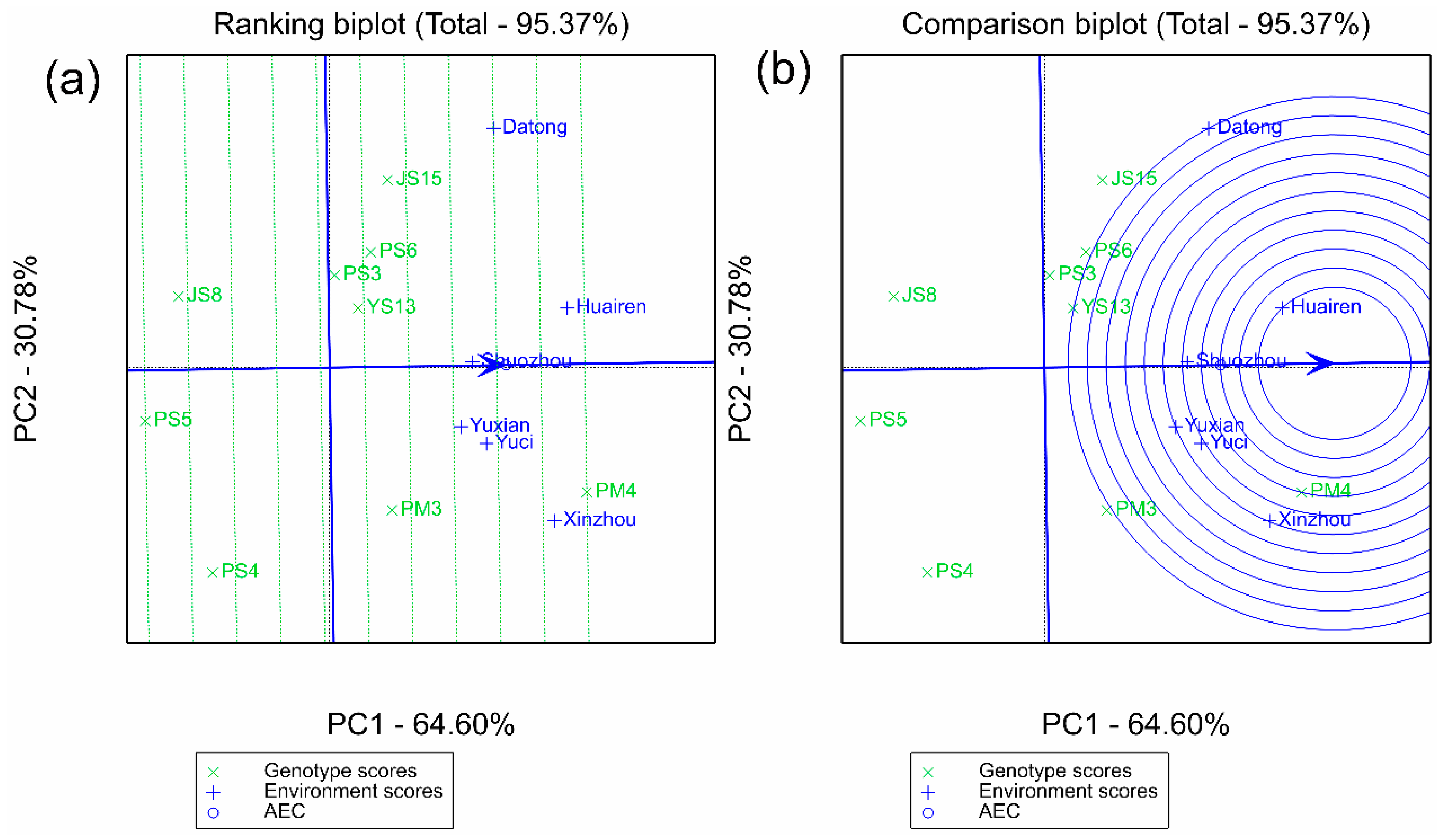
2.2.2. Synergistic Verification of Stability and Adaptability by AMMI and GGE Models
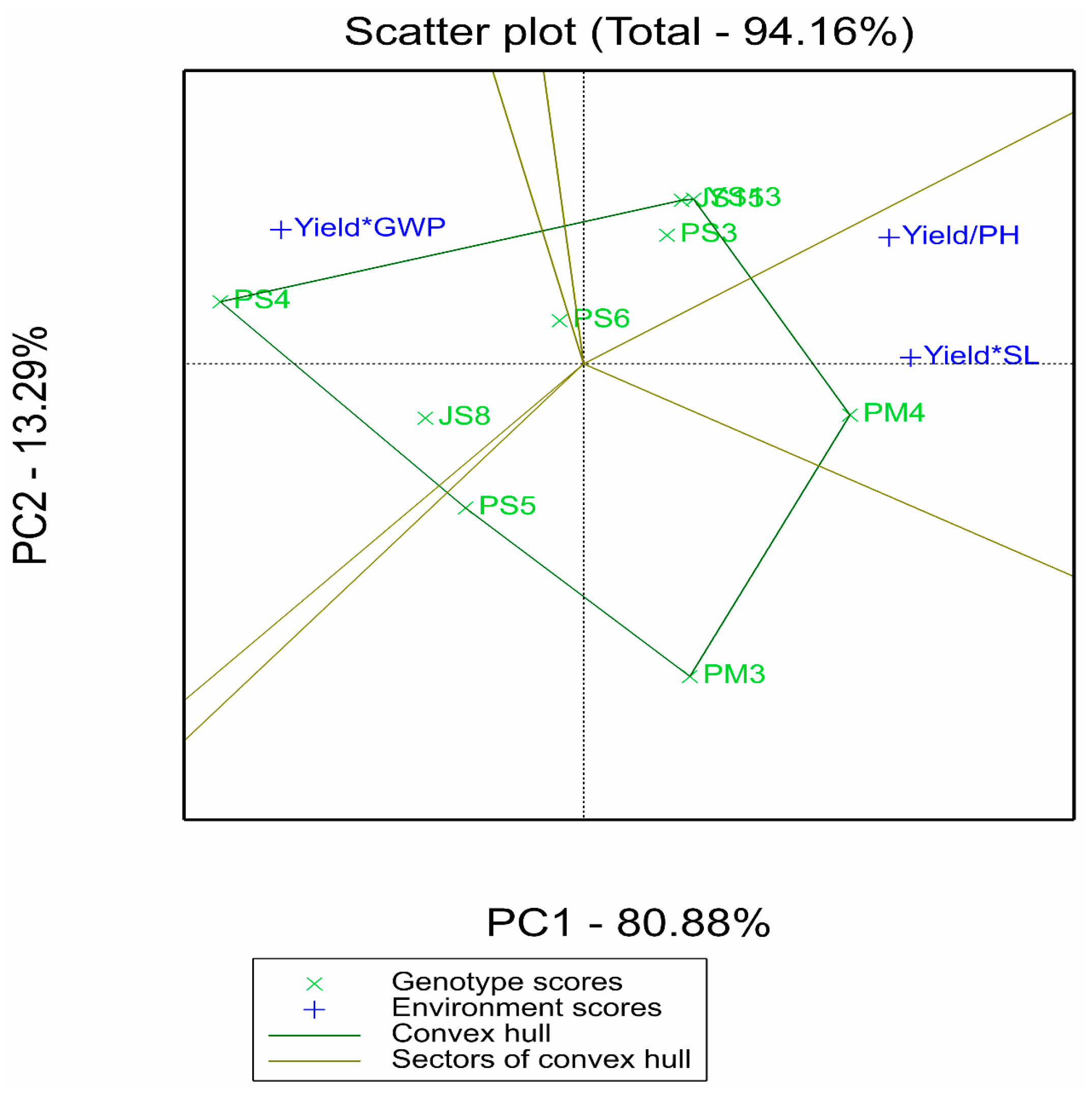
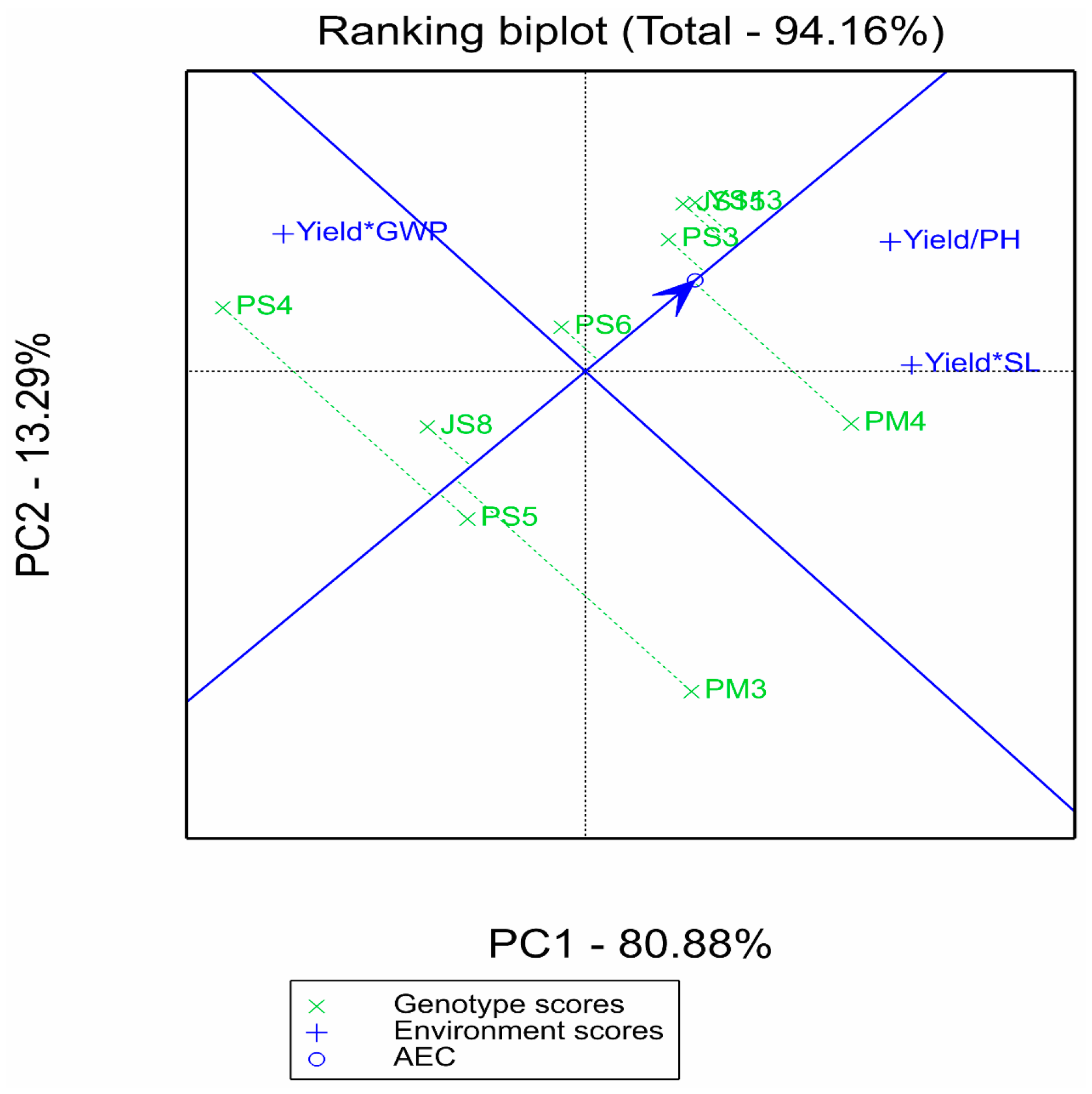
2.2.3. Supplementary Analysis of Comprehensive Multi-Trait Advantages by GYT Model
2.3. Discrimination, Representativeness of Test Environments, and Determination of Ideal Environments
2.4. Comprehensive Screening of Superior Genotypes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Test Germplasm Materials and Trial Sites
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Ma, Q.; Wu, E.; Gao, J.; Yang, Q.; Feng, B. Transcriptome analysis reveals the mechanism of nitrogen fertilizers in starch synthesis and quality in waxy and non-waxy proso millet. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 323, 121372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samineni, S.; Gummadi, S.; Thushar, S.; Khan, D.N.; Gkanogiannis, A.; Becerra Lopez-Lavalle, L.A.; Singh, R.K. Exploring Proso Millet Resilience to Abiotic Stresses: High-Yield Potential in Desert Environments of the Middle East. Agronomy 2025, 15, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, B.; Guo, Y.; Wang, T.; Wei, Q.; Luo, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Identification of Drought-Resistant Response in Proso Millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) Root through Physiological and Transcriptomic Analysis. Plants 2024, 13, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Z.; Panhwar, R.B.; Liu, J.J.; Gong, X.W.; Liang, J.B.; Liu, M.X.; Lu, P.; Gao, X.L.; Feng, B.L. Morphological diversity and correlation analysis of phenotypes and quality traits of proso millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) core collections. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Xiao, C.; Lu, H.; Deng, X. Effects of extrusion temperature on structure and physicochemical properties of proso millet starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 299, 140011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Hong, S.; Zhang, J.R.; Liu, P.H.; Li, S.; Wen, Z.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, G.; Habimana, O.; Shah, N.P.; et al. The effect of lactic acid bacteria fermentation on physicochemical properties of starch from fermented proso millet flour. Food Chem. 2024, 437, 137764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinman, T.; Braden, J.; Miller, N.D.; Murphy, K.M. Mineral, seed morphology, and agronomic characteristics of proso millet grown in the inland Pacific Northwest. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1394136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khound, R.; Santra, D.K. Omics for proso millet genetic improvement. Nucleus 2020, 63, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, R.; Francis, N. Genetic and genomic resources for improving proso millet (Panicum miliaceum L.): A potential crop for food and nutritional security. Nucleus 2021, 64, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Huang, L.; Fu, C.; Zhang, T.; Ding, W.; Yang, C. Genotype-environment interaction of crocin in Gardenia jasminoides by AMMI and GGE biplot analysis. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 4080–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholizadeh, A.; Khodadadi, M.; Sharifi-Zagheh, A. Modeling the final fruit yield of coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) using multiple linear regression and artificial neural network models. Arch. Agron. Soil. Sci. 2021, 68, 1398–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladosu, Y.; Rafii, M.Y.; Abdullah, N.; Magaji, U.; Miah, G.; Hussin, G.; Ramli, A. Genotype × Environment interaction and stability analyses of yield and yield components of established and mutant rice genotypes tested in multiple locations in Malaysia*. Acta Agric. Scandinavica Sect. B-Soil. Plant Sci. 2017, 67, 590–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea-Gilabert, C.; Pagnotta, M.A.; Tripodi, P. Genotype × Environment Interactions in Crop Breeding. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W. Analysis and handling of G× E in a practical breeding program. Crop Sci. 2016, 56, 2106–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kona, P.; Ajay, B.C.; Gangadhara, K.; Kumar, N.; Choudhary, R.R.; Mahatma, M.K.; Singh, S.; Reddy, K.K.; Bera, S.K.; Sangh, C.; et al. AMMI and GGE biplot analysis of genotype by environment interaction for yield and yield contributing traits in confectionery groundnut. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhart, S.A.; Russell, W.A. Stability Parameters for Comparing Varieties. Crop Sci. 1966, 6, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauch, H.G.; Zobel, R.W. AMMI Analysis of Yield Trials in Genotype-by Environment Interactio; Kang, M.S., Gauch, H.G., Eds.; CRE CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; pp. 85–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zobel, R.W.; Wright, M.J.; Gauch, H.G. Statistical Analysis of a Yield Trial. Agron. J. 1988, 80, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purchase, J.L.; Hatting, H.; Van Deventer, C.S. Genotype x environment interaction of wheat in South Africa: Stability analysis of yield performance. S Afr. J. Plant Soil. 2000, 17, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Hunt, L.A.; Sheng, Q.; Szlavnics, Z. Cultivar Evaluation and Mega-Environment Investigation Based on the GGE Biplot. Crop Sci. 2000, 40, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, N.S.; Rao, P.J.; Saritha, A.; Neelima, G.; Sandeep, S.; Rao, P.M.; Chouhan, S.; Lingaiah, N. Phenotypic stability in elite pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Mill.) genotypes using biplot models. Bangladesh J. Bot. 2022, 51, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrani, A.; Omrani, S.; Khodarahmi, M.; Shojaei, S.H.; Illés, Á.; Bojtor, C.; Mousavi, S.M.N.; Nagy, J. Evaluation of Grain Yield Stability in Some Selected Wheat Genotypes Using AMMI and GGE Biplot Methods. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.J.; Kulsum, M.U.; Sarker, U.; Matin, M.Q.I.; Shahin, N.H.; Kabir, M.S.; Ercisli, S.; Marc, R.A. Assessment of GGE.; AMMI.; Regression.; and Its Deviation Model to Identify Stable Rice Hybrids in Bangladesh. Plants 2022, 11, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bao, H.; Xu, Z.; Hu, S.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Yu, X.; Gao, J. AMMI an GGE biplot analysis of grain yield for drought-tolerant maize hybrid selection in Inner Mongolia. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Liu, C.; Ye, Z. Influence of Genotype × Environment Interaction on Yield Stability of Maize Hybrids with AMMI Model and GGE Biplot. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daba, S.D.; Kiszonas, A.M.; McGee, R.J. Selecting High-Performing and Stable Pea Genotypes in Multi-Environmental Trial (MET): Applying AMMI.; GGE-Biplot.; and BLUP Procedures. Plants 2023, 12, 2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Soliman, A.A.; Hu, C.; Yang, F.; Lv, M.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, A.; Dai, Z.; Li, Q.; et al. Yield Adaptability and Stability in Field Pea Genotypes Using AMMI.; GGE.; and GYT Biplot Analyses. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, H.; Huang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, E.; Li, F.; Qin, L.; Yang, Y.; Guan, Y.; Liu, B.; et al. Assessment of yield performances for grain sorghum varieties by AMMI and GGE biplot analyses. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1261323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehareb, E.M.; Osman, M.A.M.; Attia, A.E.; Bekheet, M.A.; Abo Elenen, F.F.M. Stability assessment for selection of elite sugarcane clones across multi-environment based on AMMI and GGE-biplot models. Euphytica 2022, 218, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinu, V.; Alarmelu, S.; Elayaraja, K.; Appunu, C.; Hemaprabha, G.; Parthiban, S.; Shanmugasundaram, K.; Rajamadhan, R.; Saravanan, K.G.; Kathiravan, S.; et al. Multi-environment Analysis of Yield and Quality Traits in Sugarcane (Saccharum sp.) through AMMI and GGE Biplot Analysis. Sugar Tech. 2025, 27, 540–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Frégeau-Reid, J. Genotype by Yield*Trait (GYT) Biplot: A Novel Approach for Genotype Selection based on Multiple Traits. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfanah, A.M.S.; Darwish, M.A.; Selim, A.I.; Shabana, M.M.A.; Elmoselhy, O.M.A.; Khedr, R.A.; Ali, A.M.; Abdelhamid, M.T. Spectral Reflectance Indices’ Performance to Identify Seawater Salinity Tolerance in Bread Wheat Genotypes Using Genotype by Yield*Trait Biplot Approach. Agronomy 2023, 13, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, P.J.; Mayes, S.; Hui, C.H.; Jahanshiri, E.; Julkifle, A.; Kuppusamy, G.; Kuan, H.W.; Lin, T.X.; Massawe, F.; Suhairi, T.A.S.T.M.; et al. Crops For the Future (CFF): An overview of research efforts in the adoption of underutilised species. Planta 2019, 250, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Jiang, Y.M.; Li, H.Q.; Geng, L.L.; Liu, J.Y.; Qiao, Z.H.; Liu, G.Q. Effects of photoperiod changes on morphological characters and young panicle development in proso millet (Panicum miliaceum L.). Sci. Agric. Sin. 2020, 53, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar]
- Greveniotis, V.; Bouloumpasi, E.; Zotis, S.; Korkovelos, A.; Kantas, D.; Ipsilandis, C.G. Genotype-by-Environment Interaction Analysis for Quantity and Quality Traits in Faba Beans Using AMMI.; GGE Models.; and Stability Indices. Plants 2023, 12, 3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, B.; Rezaizad, A.; Hamedani, M.Y.; Shiresmaeili, G.; Nasserghadimi, F.; Khademhamzeh, H.R.; Gholizadeh, A. Genotype × Environment Interactions and Simultaneous Selection for High Seed Yield and Stability in Winter Rapeseed (Brassica napus) Multi-Environment Trials. Agric. Res. 2022, 11, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singamsetti, A.; Shahi, J.P.; Zaidi, P.H.; Seetharam, K.; Vinayan, M.T.; Kumar, M.; Singla, S.; Shikha, K.; Madankar, K. Genotype× environment interaction and selection of maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids across moisture regimes. Field Crops Res. 2021, 270, 108224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomma, N.; Shruthi, H.B.; Soregaon, C.D.; Gaddameedi, A.; Suma, K.; Pranati, J.; Chandappa, L.H.; Patil, D.K.; Kumar, N.; Sandeep, S.; et al. Multi-environment testing for G×E interactions and identification of high-yielding.; stable.; medium-duration pigeonpea genotypes employing AMMI.; GGE biplot.; and YREM analyses. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1396826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daemo, B.B.; Ashango, Z. Application of AMMI and GGE Biplot for Genotype by Environment Interaction and Yield Stability Analysis in Potato Genotypes Grown in Dawuro Zone.; Ethiopia. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 18, 101287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esan, V.I.; Oke, G.O.; Ogunbode, T.O.; Obisesan, I.A. AMMI and GGE biplot analyses of Bambara groundnut [Vigna subterranea (L.) Verdc.] for agronomic performances under three environmental conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 997429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefabadi, V.A.; Mehdikhani, P.; Nadali, F.; Sharifi, M.; Azizi, H.; Ahmadi, M.; Fasahat, P. Evaluation of yield and stability of sugar beet (beta vulgaris L.) genotypes using GGE biplot and AMMI analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailemariam Habtegebriel, M. Adaptability and stability for soybean yield by AMMI and GGE models in Ethiopia. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 950992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljubičić, N.; Popović, V.; Kostić, M.; Pajić, M.; Buđen, M.; Gligorević, K.; Dražić, M.; Bižić, M.; Crnojević, V. Multivariate interaction analysis of Zea mays L. genotypes growth productivity in different environmental conditions. Plants 2023, 12, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramitha, J.L.; Jeeva, G.; Ravikesavan, R.; Joel, A.J.; Vinothana, N.K.; Meenakumari, B.; Raveendran, M.; Uma, D.; Hossain, F.; Kumar, B.; et al. Environmental impact of phytic acid in Maize (Zea mays. L) genotypes for the identification of stable inbreds for low phytic acid. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2020, 26, 1477–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, A.; Adhikari, S.; Singh, N.K.; Kumar, A.; Jaiswal, J.P.; Pant, U.; Singh, R.P. Responses of maize× teosinte derived backcross inbred lines (BILs) to maydis leaf blight (MLB) disease. Euphytica 2021, 217, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagesh Kumar, M.V.; Ramya, V.; Govindaraj, M.; Sameer Kumar, C.V.; Maheshwaramma, S.; Gokenpally, S.; Prabhakar, M.; Krishna, H.; Sridhar, M.; Venkata Ramana, M.; et al. Harnessing Sorghum Landraces to Breed High-Yielding.; Grain Mold-Tolerant Cultivars With High Protein for Drought-Prone Environments. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 659874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Feng, Z.; Wang, J.; Yun, X.; Qu, F.; Sun, C.; Qian, W. Genotype by environment interaction for grain yield in foxtail millet (Setarai italica) using AMMI model and GGE Biplot. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 99, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, K.B.; Shin, S.H.; Shon, J.Y.; Kang, S.G.; Yang, W.H.; Heu, S.G. Interpretation of Genotype × Environment Interaction of Sesame Yield Using GGE Biplot Analysis. Korean J. Crop Sci. 2015, 60, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Kang, M.S. GGE Biplot Analysis: A Graphical Tool for Breeders, Geneticists, and Ggronomists; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mekonnen, T.W.; Mekbib, F.; Amsalu, B.; Gedil, M.; Labuschagne, M. Genotype by environment interaction and grain yield stability of drought tolerant cowpea landraces in Ethiopia. Euphytica 2022, 218, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faheem, M.; Arain, S.M.; Sial, M.A.; Laghari, K.A.; Oayyum, A. Genotype by yield*trait (GYT) biplot analysis: A novel approach for evaluating advance lines of durum wheat. Cereal Res. Commun. 2023, 51, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, R.W.; Harding, S.A.; Murray, D.A.; Soutar, D.M.; Baird, D.B.; Glaser, A.I.; Welham, S.J.; Gilmour, A.R.; Thompson, R.; Webster, R. GenStat Release 17: Statistical Software for Windows; VSN Int.: Hemel Hempstead, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Naroui Rad, M.R.; Bakhshi, B.; Ghasemi, A.; Ghasemi, M.M.; Kohpalekani, J.A. Identification of High-Yielding and Drought-Tolerant Melon Genotypes Based on Yield–Trait Combinations: A Comparison of Pcor Index and GYT Biplot Approaches. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e70048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, X.; Lin, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, Y. Comprehensive evaluation of sugar beet varieties based on genotype × yield × trait (GYT) in different environments. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Source | d.f. | s.s. | m.s. | v.r. | F pr | %GE | %SS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 107 | 20,389,988 | 190,561 | ||||
| Treatments | 53 | 19,477,392 | 367,498 | 32.19 | <0.001 | 95.52 | |
| Genotypes | 8 | 4,027,798 | 503,475 | 44.1 | <0.001 | 19.75 | |
| Environments | 5 | 12,923,233 | 2,584,647 | 42.54 | <0.001 | 63.38 | |
| Block | 6 | 364,561 | 60,760 | 5.32 | <0.001 | 1.79 | |
| Interactions | 40 | 2,526,361 | 63,159 | 5.53 | <0.001 | 12.39 | |
| IPCA 1 | 12 | 2,018,257 | 168,188 | 14.73 | <0.001 | 79.89 | |
| IPCA 2 | 10 | 312,356 | 31,236 | 2.74 | 0.0095 | 12.36 | |
| IPCA 3 | 8 | 141,735 | 17,717 | 1.55 | 0.1648 | 5.61 | |
| Residuals | 10 | 54,013 | 5401 | 0.47 | 0.8992 | 2.14 | |
| Error | 48 | 548,036 | 11,417 |
| Genotype | Number | Stability (ASV) | Stability Rank | Yield (kg ha−1) | Yield Rank | IPCAg1 | IPCAg2 | IPCAg3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JS15 | 1 | 99.45 | 8 | 3568 | 2 | 15.35012 | −7.27391 | −3.11981 |
| JS8 | 2 | 40.63 | 3 | 3248 | 8 | 6.28441 | 1.50112 | −0.47202 |
| PM3 | 3 | 77.98 | 7 | 3563 | 3 | −12.00416 | −8.07218 | 6.20031 |
| PM4 | 4 | 71.81 | 6 | 3871 | 1 | −11.01911 | −9.35572 | 1.32932 |
| PS3 | 5 | 49.65 | 4 | 3501 | 6 | 7.64295 | 5.13867 | 1.11319 |
| PS4 | 6 | 107.78 | 9 | 3303 | 7 | −16.65642 | 5.78785 | −11.24808 |
| PS5 | 7 | 27.25 | 1 | 3207 | 9 | −3.90099 | 10.36699 | 7.37735 |
| PS6 | 8 | 61.09 | 5 | 3547 | 4 | 9.44874 | −2.05827 | −4.66214 |
| YS13 | 9 | 31.62 | 2 | 3536 | 5 | 4.85447 | 3.96544 | 3.48188 |
| Sites | Altitude (m.a.s.l.) | Longitude | Latitude | 2019 | 2020 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Type | Soil PH | Organic Matter (g·kg−1) | Annual Rainfall (mm) | Mean Temperature (°C) | Annual Rainfall (mm) | Mean Temperature (°C) | ||||
| Datong | 1050 | 113.349863° E | 40.184444° N | Sandy loam | 7.8 | 12.5 | 256.9 | 6.5 | 247 | 6.5 |
| Huairen | 1150 | 113.154957° E | 39.838817° N | Loam | 7.2 | 18.3 | 365 | 6 | 333.5 | 6.8 |
| Shuozhou | 1147 | 112.457984° E | 39.407646° N | Loam | 7.5 | 15.7 | 371.9 | 7 | 423 | 7 |
| Xinzhou | 790 | 112.712176° E | 38.445148° N | Sandy loam | 8.1 | 13.2 | 529.7 | 8.5 | 458.9 | 8.5 |
| Yuxian | 1079 | 113.423528° E | 38.053179° N | Loam | 7.6 | 16.5 | 563 | 8.5 | 547.1 | 10.5 |
| Yuci | 795 | 112.792022° E | 37.712020° N | Sandy loam | 7.4 | 14.8 | 495 | 10 | 472 | 9.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Peng, C.; Chen, H.; Cao, X. Adaptability and Stability of Proso Millet Grain Yield: A Multi-Environment Evaluation Using AMMI, GGE, and GYT Biplots. Plants 2025, 14, 2719. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172719
Zhang J, Wang M, Peng C, Chen H, Cao X. Adaptability and Stability of Proso Millet Grain Yield: A Multi-Environment Evaluation Using AMMI, GGE, and GYT Biplots. Plants. 2025; 14(17):2719. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172719
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jin, Mengyao Wang, Chengyu Peng, Hong Chen, and Xiaoning Cao. 2025. "Adaptability and Stability of Proso Millet Grain Yield: A Multi-Environment Evaluation Using AMMI, GGE, and GYT Biplots" Plants 14, no. 17: 2719. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172719
APA StyleZhang, J., Wang, M., Peng, C., Chen, H., & Cao, X. (2025). Adaptability and Stability of Proso Millet Grain Yield: A Multi-Environment Evaluation Using AMMI, GGE, and GYT Biplots. Plants, 14(17), 2719. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172719





