Successful Establishment of Somatic Embryogenesis and Shoot Organogenesis Systems in Catalpa bungei C.A.Mey
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
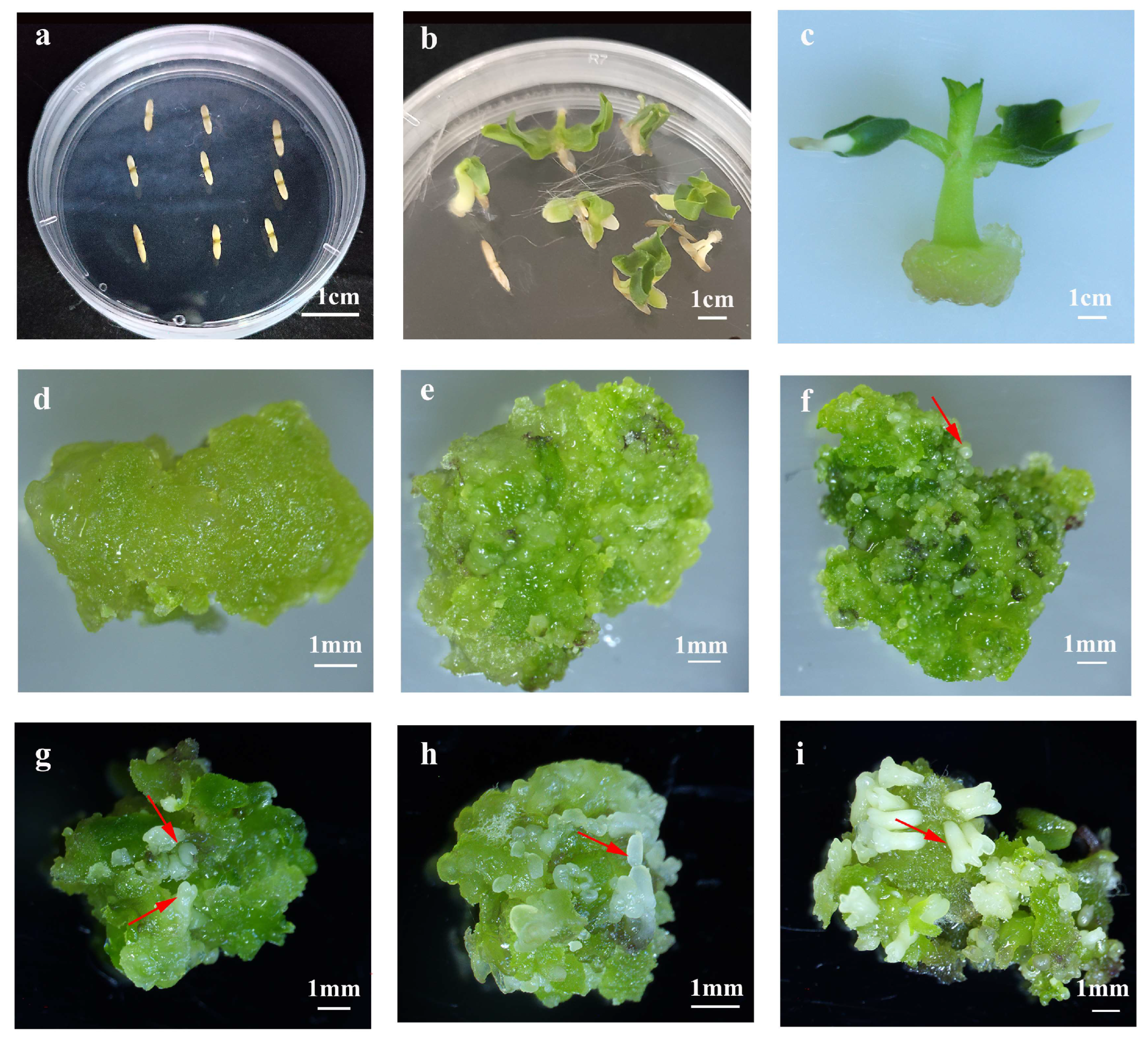
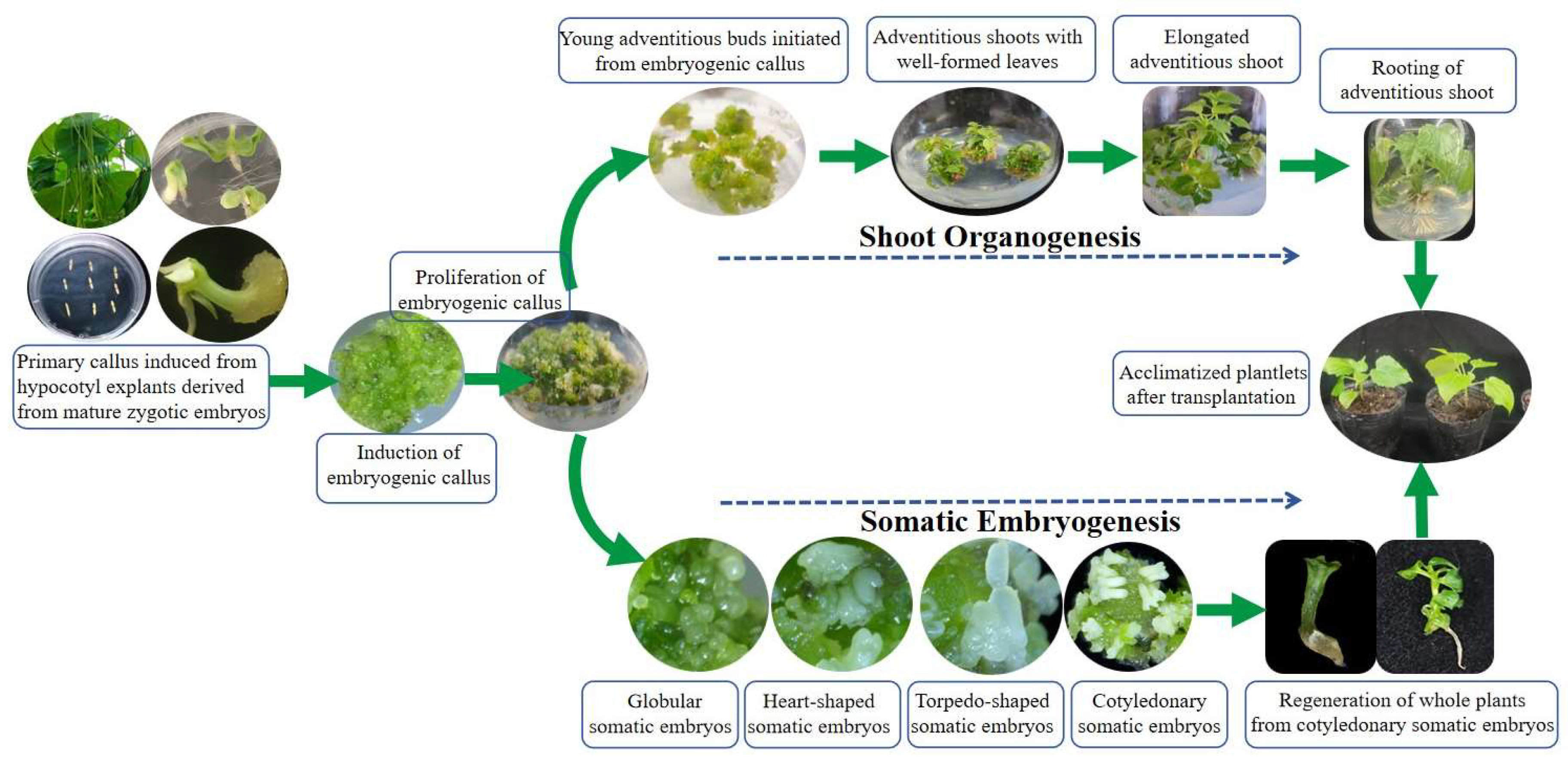
2.1. Establishment and Histological Characterization of Somatic Embryogenesis in C. bungei
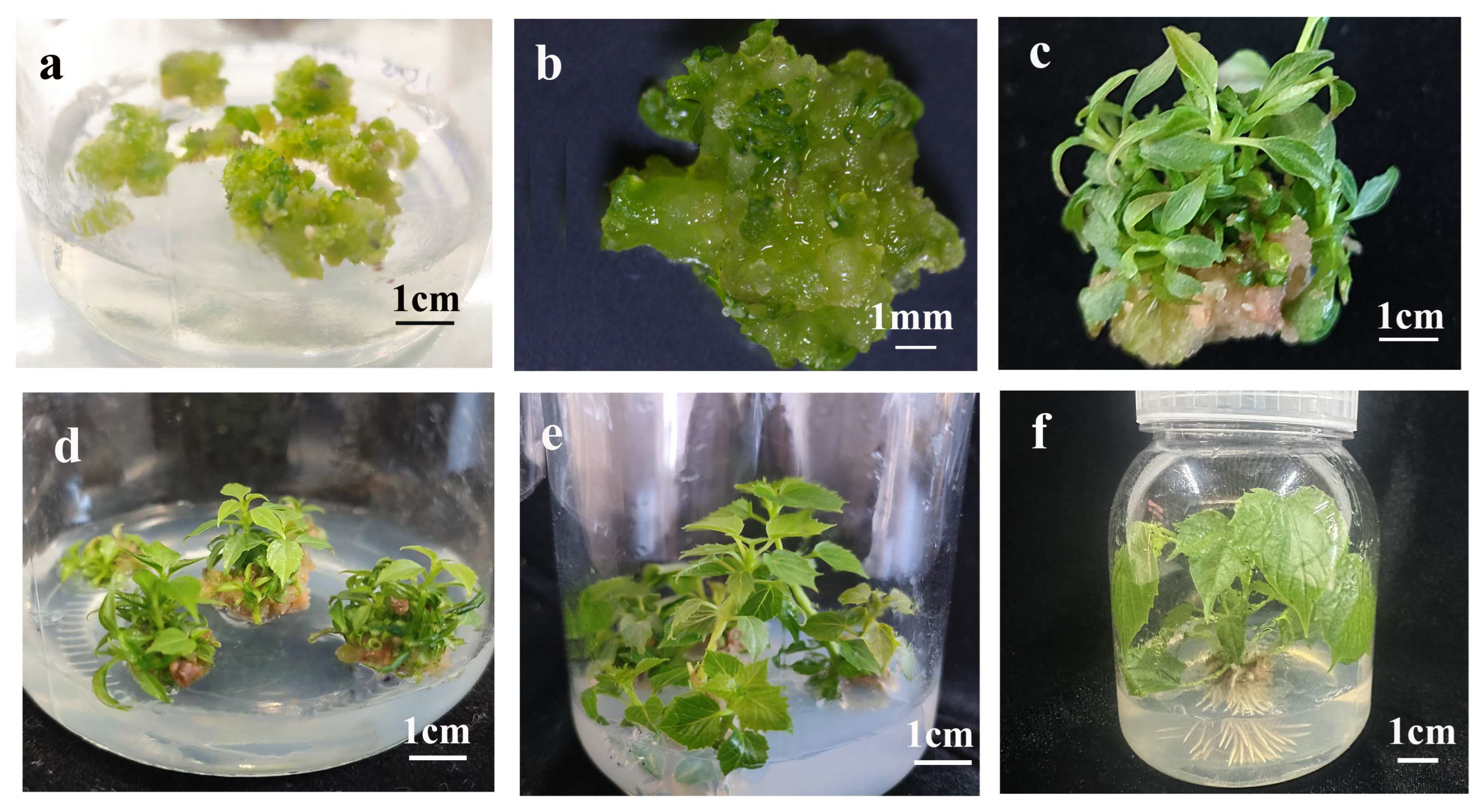
2.2. Establishment of Shoot Organogenesis in C. bungei
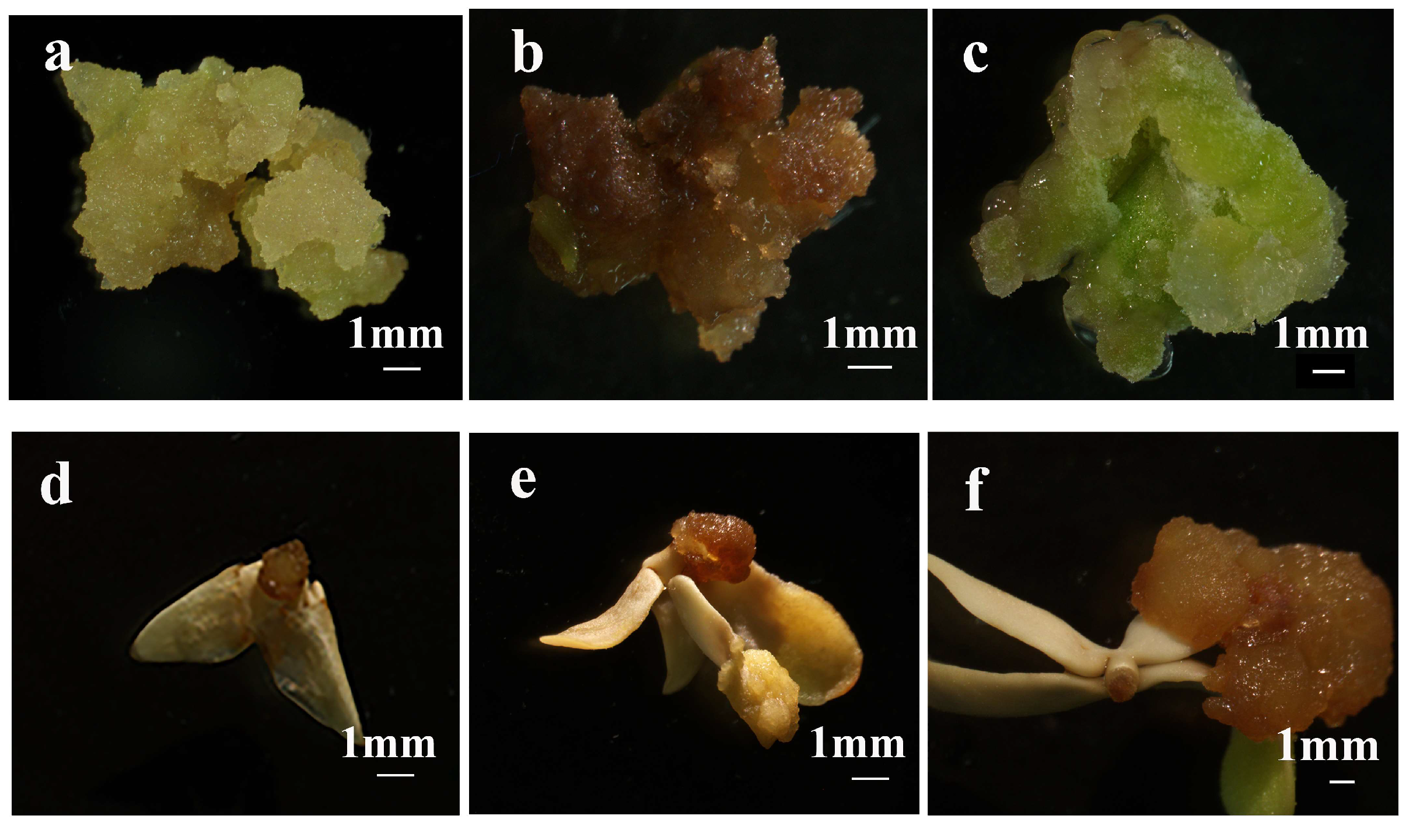
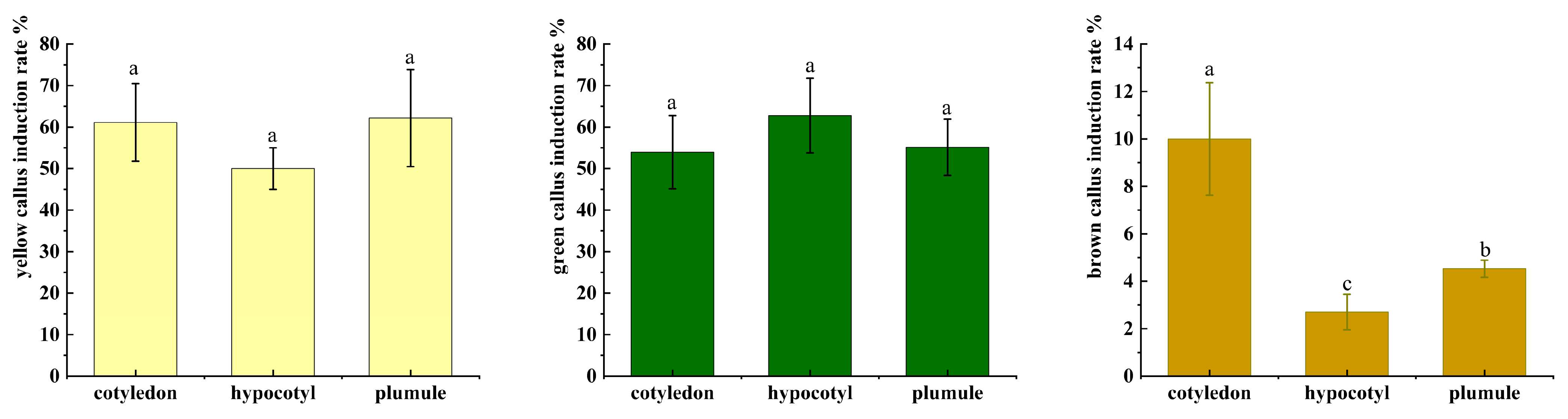
2.3. Effect of Plant Growth Regulators and Explants on Primary Callus Induction
2.4. Effect of Basal Media and Plant Growth Regulators on Yellow-Green Compact Callus Induction During Subculture
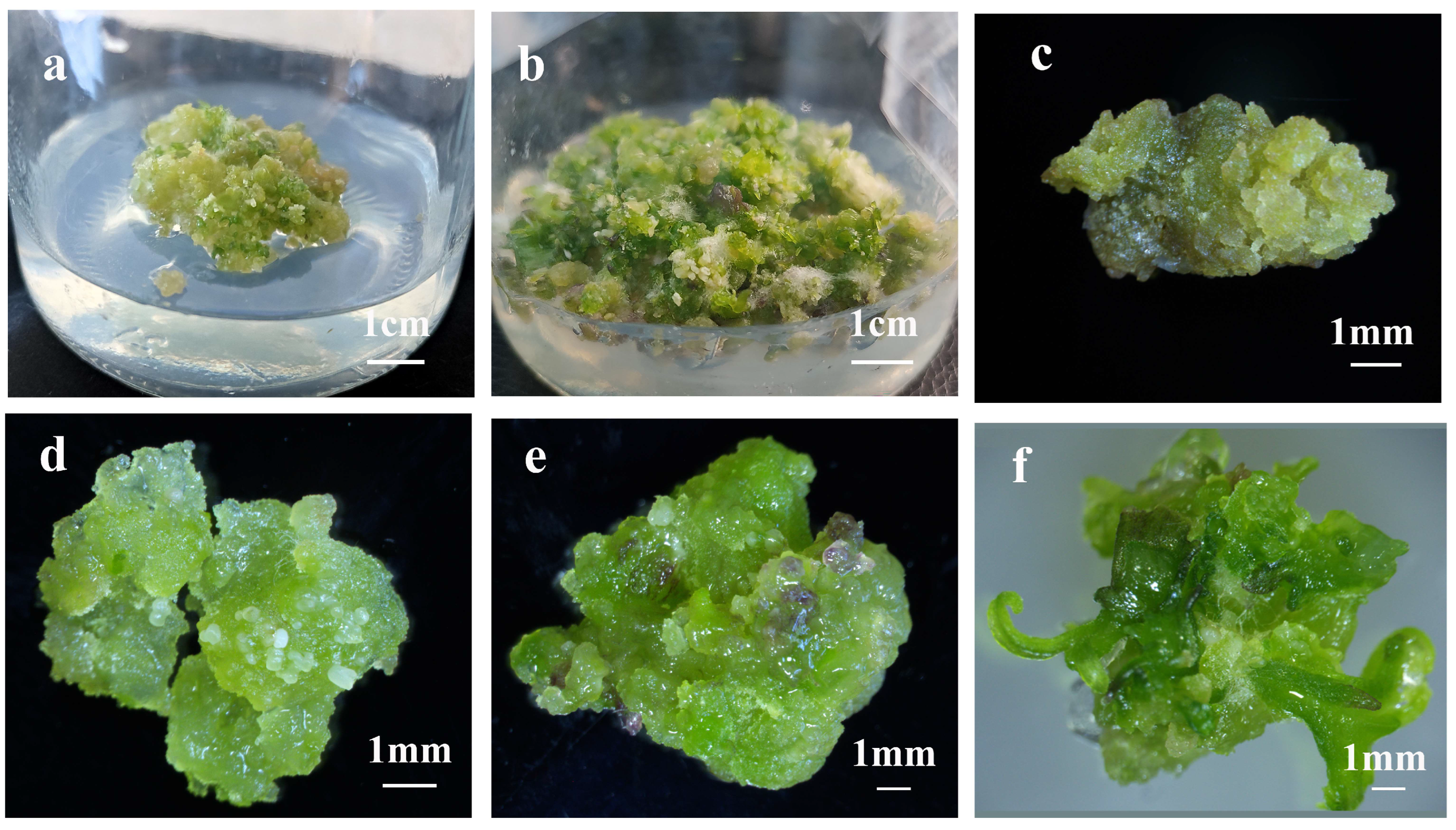
2.5. Effects of Basal Medium and Plant Growth Regulator Combinations for Inducing Embryogenic Callus from Yellow-Green Compact Callus
2.6. Effects of Plant Growth Regulator Combinations for Morphological Maintenance of Embryogenic Callus During Subculture
2.7. Effect of Plant Growth Regulator Combinations on Shoot Organogenesis
2.8. Additive Effects on Somatic Embryogenesis
2.9. Plantlet Regeneration from Somatic Embryos
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Explants Preparation
4.2. Primary Callus Induction
4.3. Subculture of Primary Callus
4.4. Embryogenic Callus Induction and Proliferation
4.5. Somatic Embryogenesis and Shoot Organogenesis
4.6. Histological Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olsen, R.T.; Kirkbride, J.H., Jr. Taxonomic revision of the genus Catalpa (Bignoniaceae). Brittonia 2017, 69, 387–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Ma, W.; Song, J.; Lu, M.; Rahman, S.U.; Bui, T.T.X.; Vu, D.D.; Zheng, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Physiological and transcriptional responses of Catalpa bungei to drought stress under sufficient-and deficient-nitrogen conditions. Tree Physiol. 2017, 37, 1457–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, S.; Zhu, T.; Wang, J.; Yan, D. The current and future potential geographical distribution and evolution process of Catalpa bungei in China. Forests 2022, 13, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Yun, H.; Ling, J.; Zhai, W.; Zhao, K.; Yu, X.; Ma, W. Growth adaptability and stability in Catalpa bungei clones: The role of genetics and environment. For. Res. 2025, 5, e002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, J.; Yun, H.; Yang, G.; Ma, J.; Ma, W.; Qu, G. Genetic evaluation and combined selection for the simultaneous improvement of growth and wood properties in Catalpa bungei clones. Forests 2021, 12, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Lan, Z.P.; Ma, K.; Hu, H.Z. Rooting response of Catalpa bungei softwood cutting to different hormone treatments and medium mixture. For. Res. 2011, 21, 749–753. [Google Scholar]
- Szczygiel, K.; Hazubska-Przybyl, T.; Bojarczuk, K. Somatic embryogenesis of selected coniferous tree species of the genera Picea, Abies and Larix. Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 2007, 76, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Y.; Li, S.-G.; Fan, X.-F.; Su, Z.-H. Application of somatic embryogenesis in woody plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, e1002014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isah, T. Induction of somatic embryogenesis in woody plants. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2016, 38, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degenhardt-Goldbach, J.; Quoirin, M.; Buss, S.; de Oliveira, Y.; Franciscon, L.; Gerhardt, I. In vitro shoot organogenesis from Eucalyptus sp. leaf explants. BMC Proc. 2011, 5, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duclercq, J.; Sangwan-Norreel, B.; Catterou, M.; Sangwan, R.S. De novo shoot organogenesis: From art to science. Trends Plant Sci. 2011, 16, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Liu, S.; Guo, W.; Yang, L.; Shen, H. Effects of a new plant growth regulator on callus induction from immature embryo explants of Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis). Forests 2023, 14, 2413–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, R.; Rahmah, M.; Trisnia, H.; Chaniago, I.; Syukriani, L.; Yunita, R.; Jamsari, J. Embryogenic callus induction of coffee [Coffea arabica L.] on several plant growth regulator concentration and incubation temperature. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 497, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathil, N.A.M.; Puad, N.I.M.; Amid, A.; Azmi, A.S.; Ibrahim, R. Optimization of plant growth regulators for Citrus suhuiensis callus induction. Asia Pac. J. Mol. Biol. Biotechnol. 2017, 25, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y.; Xiao, X.; Gong, W.; Liu, J. Effect of different plant growth regulators on micro-tuber induction and plant regeneration of pinellia ternate (thunb) briet. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2009, 15, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, M.G.; Gurumurthi, K. Effects of type of explant and age, plant growth regulators and medium strength on somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Eucalyptus camaldulensis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2010, 100, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, V. Role of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2, 4-D) in somatic embryogenesis on cultured zygotic embryos of Arabidopsis: Cell expansion, cell cycling, and morphogenesis during continuous exposure of embryos to 2, 4-D. Am. J. Bot. 2004, 91, 1743–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hamidi, A.; Al-Hadedy, S.; Bashi, A. Effect of 2, 4-D and NAA in callus induction and differentiation from different explants of Moringa oleifera Lam. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1252, 012091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyuni, D.K.; Andriani, P.; Ansori, A.N.M.; Utami, E.S.W. Callus induction of gendarussa (Justicia gendarussa) by various concentration of 2, 4-D, IBA, and BAP. Biosaintifika J. Biol. Biol. Educ. 2017, 9, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, M.; Luo, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Li, H. Effect of 6-BA on the plant regeneration via organogenesis from cotyledonary node of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp). J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashan, M.I.; Arshad, M.; Zafar, Y.; Asad, S. Optimization of zeatin and explant types for efficient embryogenesis and plant regeneration of diploid cotton (Gossypium arboreum L.). J. Agric. Res. 2008, 46, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Huetteman, C.A.; Preece, J.E. Thidiazuron: A potent cytokinin for woody plant tissue culture. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 1993, 33, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-M.; Liu, H.-M.; Wang, W.-J.; Zu, Y.-G. Effects of thidiazuron basal medium light quality on adventitious shoot regeneration from in vitro cultured stem of Populus alba ×, P. berolinensis. J. For. Res. 2008, 19, 257–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenath, H.; Shanta, H.; Babu, K.H.; Naidu, M. Somatic embryogenesis from integument (perisperm) cultures of coffee. Plant Cell Rep. 1995, 14, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, G.; Silva, S.; Park, Y.-S.; Neves, L.; Araújo, C.; Santos, C. Factors influencing somatic embryogenesis induction in Eucalyptus globulus Labill.: Basal medium and anti-browning agents. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2008, 95, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, T.b.; Mukherjee, P.; Datta, M.M. Somatic embryogenesis in Jatropha curcas Linn., an important biofuel plant. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2007, 1, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziee, S.; Sarmast, M.K.; Ghaderi-far, F.; Wang, C. Somatic embryogenesis induction in Rosa persica Michx ex Juss. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2024, 158, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-Victor, C.M.; Arjona-Suárez, E.d.J.; Iracheta-Donjuan, L.; Valdez-Carrasco, J.M.; Gómez-Merino, F.C.; Robledo-Paz, A. Callus type, growth regulators, and phytagel on indirect somatic embryogenesis of coffee (Coffea arabica L. var. Colombia). Plants 2023, 12, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Wang, P.; Zhang, E.; Ma, L.; Gao, L.; Yang, R.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y. Efficient transformation of Catalpa bungei shows Crystal genes conferring resistance to the shoot borer Omphisa plagialis. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 777411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Shen, X.; Liang, H.; Wang, Y.; He, Z.; Zhang, D.; Chen, F. Comparative transcriptome analysis highlights the hormone effects on somatic embryogenesis in Catalpa bungei. Plant Reprod. 2019, 32, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaller, G.E.; Street, I.H.; Kieber, J.J. Cytokinin and the cell cycle. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2014, 21, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, S.H.; Lall, S.; Che, P. Cytokinins and shoot development. Trends Plant Sci. 2003, 8, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uggla, C.; Moritz, T.; Sandberg, G.; Sundberg, B. Auxin as a positional signal in pattern formation in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 9282–9286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Leyser, O. Auxin, cytokinin and the control of shoot branching. Ann. Bot. 2011, 107, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodová, H.; Albrechtová, J.; Kumstýřová, L.; Lipavská, H.; Vágner, M.; Vondráková, Z. Somatic embryogenesis in Norway spruce: Anatomical study of embryo development and influence of polyethylene glycol on maturation process. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 1999, 37, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Arnold, S.; Hakman, I. Regulation of somatic embryo development in Picea abies by abscisic acid (ABA). J. Plant Physiol. 1988, 132, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Chen, S.; Wu, T.; Wu, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; da Silva, J.A.T.; Zeng, S.; Ma, G. Shoot organogenesis and somatic embryogenesis from leaf and petiole explants of endangered Euryodendron excelsum. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, E.Y.Y.; Biddle, J.; Kalaipandian, S.; Bazrafshan, A.; Mu, Z.; Adkins, S.W. Improvement of somatic embryo maturation and shoot formation in somatic embryogenesis of Asian coconut varieties. Sci. Hortic. 2025, 343, 114069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazubska-Przybył, T.; Ratajczak, E.; Obarska, A.; Pers-Kamczyc, E. Different roles of auxins in somatic embryogenesis efficiency in two Picea species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcikowska, B.; Wójcik, A.M.; Gaj, M.D. Epigenetic regulation of auxin-induced somatic embryogenesis in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LingPick, K.; LeongSok, W.; Hussein, S.; Ibrahim, R. Induction of somatic embryos from different explants of Citrus sinensis. J. Plant Sci. 2008, 3, 18–32. [Google Scholar]
- Anandan, R.; Sudhakar, D.; Balasubramanian, P.; Gutiérrez-Mora, A. In vitro somatic embryogenesis from suspension cultures of Carica papaya L. Sci.Hortic. 2012, 136, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.Y.; Shu, M.L.; Yang, F.; Wang, G.F.; Zhang, W.E.; Pan, X.J. Somatic Embryo Induction and Plantlet Regeneration of Canna × generalis from Immature Zygotic Embryo. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2023, 155, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.A.; Fraga, M.E.; Guerra, M.P.; Silva, M.C. Assessing the Effects of Basal Media on the Propagation and Nutritional Status of Eucalyptus dunnii Maiden. New For. 2016, 47, 153–170. [Google Scholar]
- Callado, A.M.; Guerra, M.P.; Silva, M.C. Plant Regeneration in Spanish Cedar (Cedrela odorata L.) Using Zygotic Embryo Explants from Mature Seed and Improvement of Embryogenic Nodule Initiation by Heat Shock. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2010, 46, 452–459. [Google Scholar]
- Callaham, D.; McDade, H.L.; Pooler, M.R. Multiple Shoot Formation from Cotyledonary Node Segments of Eastern Redbud (Cercis canadensis L.). Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2003, 39, 258–263. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, S. Direct and Indirect Somatic Embryogenesis Induction in Camellia oleifera Abel. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 644389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.M.; Chen, S.L. Tissue Culture of Taiwania cryptomerioides Hayata. J. For. Res. 1991, 2, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, H. In Vitro Regeneration of Camellia japonica L. and Relationship with Endogenous Hormones during Adventitious Bud Differentiation. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2023, 50, 1876–1888. [Google Scholar]
- Ewa, U.; Maigorzata, K.; Gaj, D. Histological analysis of direct somatic embryogenesis in Arabidopsis thaniana. Planta 2007, 226, 619–628. [Google Scholar]
- Chengalrayan, K.; Hazra, S.; Gallo-Meagher, M. Histological analysis of somatic embryogenesis and organogenesis induced from mature zygotic embryo-derived leaflets of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Plant Sci. 2001, 161, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, R.J. Somatic embryogenesis in the Medicago truncatula model: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- do Nascimento, A.M.M.; Polesi, L.G.; Back, F.P.; Steiner, N.; Guerra, M.P.; Castander-Olarieta, A.; Moncaleán, P.; Montalbán, I.A. The chemical environment at maturation stage in Pinus spp. somatic embryogenesis: Implications in the polyamine profile of somatic embryos and morphological characteristics of the developed plantlets. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 771464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awada, R.; Lepelley, M.; Breton, D.; Charpagne, A.; Campa, C.; Berry, V.; Georget, F.; Breitler, J.-C.; Léran, S.; Djerrab, D. Global transcriptome profiling reveals differential regulatory, metabolic and hormonal networks during somatic embryogenesis in Coffea arabica. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.-I.; Lee, C.-B.; Kwon, S.-H.; Park, J.-M.; Kang, K.-S.; Shim, D. Comparative transcriptome analysis during developmental stages of direct somatic embryogenesis in Tilia amurensis Rupr. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, A.-R.; Cui, H.-Y.; Lee, H.; Shin, H.; Kang, K.-S.; Park, S.-Y. Light quality affects shoot regeneration, cell division, and wood formation in elite clones of Populus euramericana. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2015, 37, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pałka, P.; Cioć, M.; Hura, K.; Szewczyk-Taranek, B.; Pawłowska, B. Adventitious organogenesis and phytochemical composition of Madonna lily (Lilium candidum L.) in vitro modeled by different light quality. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2023, 152, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Treatment | Cytokinin | Auxin | Yellow Callus Induction Rate % | Green Callus Induction Rate % | Brown Callus Induction Rate % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6-BA (mg/L) | NAA (mg/L) | 2,4-D (mg/L) | ||||
| CIM1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0 | 29.96 ± 7.76 c | 46.63 ± 10.42 b | 3.00 ± 0.29 e |
| CIM2 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0 | 41.88 ± 17.79 b | 43.16 ± 12.11 bc | 9.62 ± 2.26 c |
| CIM3 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0 | 31.86 ± 9.70 c | 57.04 ± 18.48 a | 6.54 ± 1.90 d |
| CIM4 | 2.0 | 0.2 | 0 | 18.64 ± 6.81 d | 58.30 ± 11.05 a | 20.33 ± 5.22 b |
| CIM5 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0 | 19.23 ± 0.31 d | 55.14 ± 0.14 a | 17.56 ± 0.16 b |
| CIM6 | 2.0 | 0.8 | 0 | 59.94 ± 13.90 a | 35.09 ± 7.25 c | 4.66 ± 1.91 e |
| CIM7 | 0.1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 48.50 ± 4.25 a |
| CIM8 | 0.1 | 0 | 1.0 | 0 | 0 | 9.85 ± 1.30 c |
| CIM9 | 0.1 | 0 | 2.0 | 0 | 0 | 7.95 ± 0.50 cd |
| Treatment | Basal Medium | Cytokinin | Auxin | Yellow-Green Callus Induction Rate % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6-BA (mg/L) | ZT (mg/L) | NAA (mg/L) | |||
| SCM1 | DKW | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 37.53 ± 5.59 ab |
| SCM2 | DKW | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 26.89 ± 9.33 c |
| SCM3 | DKW | 2.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 26.58 ± 3.78 c |
| SCM4 | DKW | 2.0 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 35.09 ± 2.64 b |
| SCM5 | DKW | 2.0 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 45.73 ± 6.17 a |
| SCM6 | DKW | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.01 | 7.69 ± 2.51 e |
| SCM7 | DKW | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 24.50 ± 1.93 cd |
| SCM8 | WPM | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 16.92 ± 5.36 d |
| SCM9 | WPM | 2.0 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 20.73 ± 7.01 d |
| SCM10 | MS | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 3.09 ± 2.01 f |
| SCM11 | MS | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 8.87 ± 2.23 e |
| Treatment | Basal Medium | Cytokinin | Auxin | Embryogenic Callus Induction Rate % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6-BA (mg/L) | ZT (mg/L) | NAA (mg/L) | |||
| ECM 1 | DKW | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0 c |
| ECM 2 | DKW | 2.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0 c |
| ECM 3 | DKW | 2.0 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 c |
| ECM 4 | MS | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 5.41 ± 0.67 b |
| ECM 5 | MS | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 12.67 ± 2.45 a |
| ECM 6 | MS | 2.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 5.80 ± 1.05 b |
| ECM 7 | 1.5 × MS | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 16.57 ± 3.02 a |
| Treatment | Cytokinin | Auxin | Status of Embryogenic Callus | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZT (mg/L) | 6-BA (mg/L) | NAA (mg/L) | ||
| EPM1 | 0 | 0.6 | 0.1 | Yellowish-brown, soft |
| EPM2 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.1 | Yellow-green, soft |
| EPM3 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.1 | Green, granular |
| EPM4 | 0.2 | 1.2 | 0.1 | Green callus, abnormal shoot |
| EPM5 | 0.2 | 1.5 | 0.1 | Green callus, abnormal shoot |
| Treatment | Cytokinin | Auxin | Shoot Organogenesis Rate % | Number of Adventitious Buds per Callus | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6-BA (mg/L) | KT (mg/L) | ZT (mg/L) | TDZ (mg/L) | NAA (mg/L) | |||
| SOM1 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 0.02 | 63.59 ± 20.49 c | 1.33 ± 0.24 c |
| SOM2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 0.02 | 61.11 ± 35.00 c | 2.80 ± 0.41 b |
| SOM3 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 0.02 | 85.64 ± 12.29 a | 2.79 ± 0.28 b |
| SOM4 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 0.15 | 88.89 ± 15.71 a | 4.07 ± 0.64 a |
| SOM5 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0.15 | 78.09 ± 14.29 a | 3.89 ± 0.43 ab |
| SOM6 | 0.6 | 0 | 0.2 | 0 | 0.15 | 72.29 ± 13.31 b | 4.06 ± 0.57 a |
| SOM7 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | 0.15 | 75.29 ± 13.35 b | 4.05 ± 0.24 a |
| Treatment | Additive | Concentration (g/L) | Somatic Embryogenesis Induction Rate % |
|---|---|---|---|
| SEM1 | ABA | 0.0005 | 67.22 ± 10.07 a |
| SEM2 | ABA | 0.002 | 40.34 ± 4.48 bcd |
| SEM3 | ABA | 0.005 | 28.58 ± 5.97 d |
| SEM4 | PEG4000 | 2.0 | 37.50 ± 8.84 cd |
| SEM5 | PEG4000 | 5.0 | 59.44 ± 8.58 bc |
| SEM6 | PEG4000 | 10.0 | 64.99 ± 8.18 ab |
| SEM7 | Phytagel | 3.0 | 45.15 ± 4.72 bc |
| SEM8 | Phytagel | 5.0 | 76.31 ± 5.28 a |
| SEM9 | Phytagel | 8.0 | 66.07 ± 2.24 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, J.; Di, B.; Ma, W.; Wang, J.; Hu, R. Successful Establishment of Somatic Embryogenesis and Shoot Organogenesis Systems in Catalpa bungei C.A.Mey. Plants 2025, 14, 2688. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172688
Sun J, Li J, Zhao M, Zheng G, Zhang J, Di B, Ma W, Wang J, Hu R. Successful Establishment of Somatic Embryogenesis and Shoot Organogenesis Systems in Catalpa bungei C.A.Mey. Plants. 2025; 14(17):2688. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172688
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jingshuang, Jiewen Li, Mengnan Zhao, Guangshun Zheng, Jing Zhang, Bao Di, Wenjun Ma, Junhui Wang, and Ruiyang Hu. 2025. "Successful Establishment of Somatic Embryogenesis and Shoot Organogenesis Systems in Catalpa bungei C.A.Mey" Plants 14, no. 17: 2688. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172688
APA StyleSun, J., Li, J., Zhao, M., Zheng, G., Zhang, J., Di, B., Ma, W., Wang, J., & Hu, R. (2025). Successful Establishment of Somatic Embryogenesis and Shoot Organogenesis Systems in Catalpa bungei C.A.Mey. Plants, 14(17), 2688. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172688






