Postharvest Preservation Strategies for Table Grapes: A Comprehensive Review from Practical Methods to Future Developments
Abstract
1. Introduction
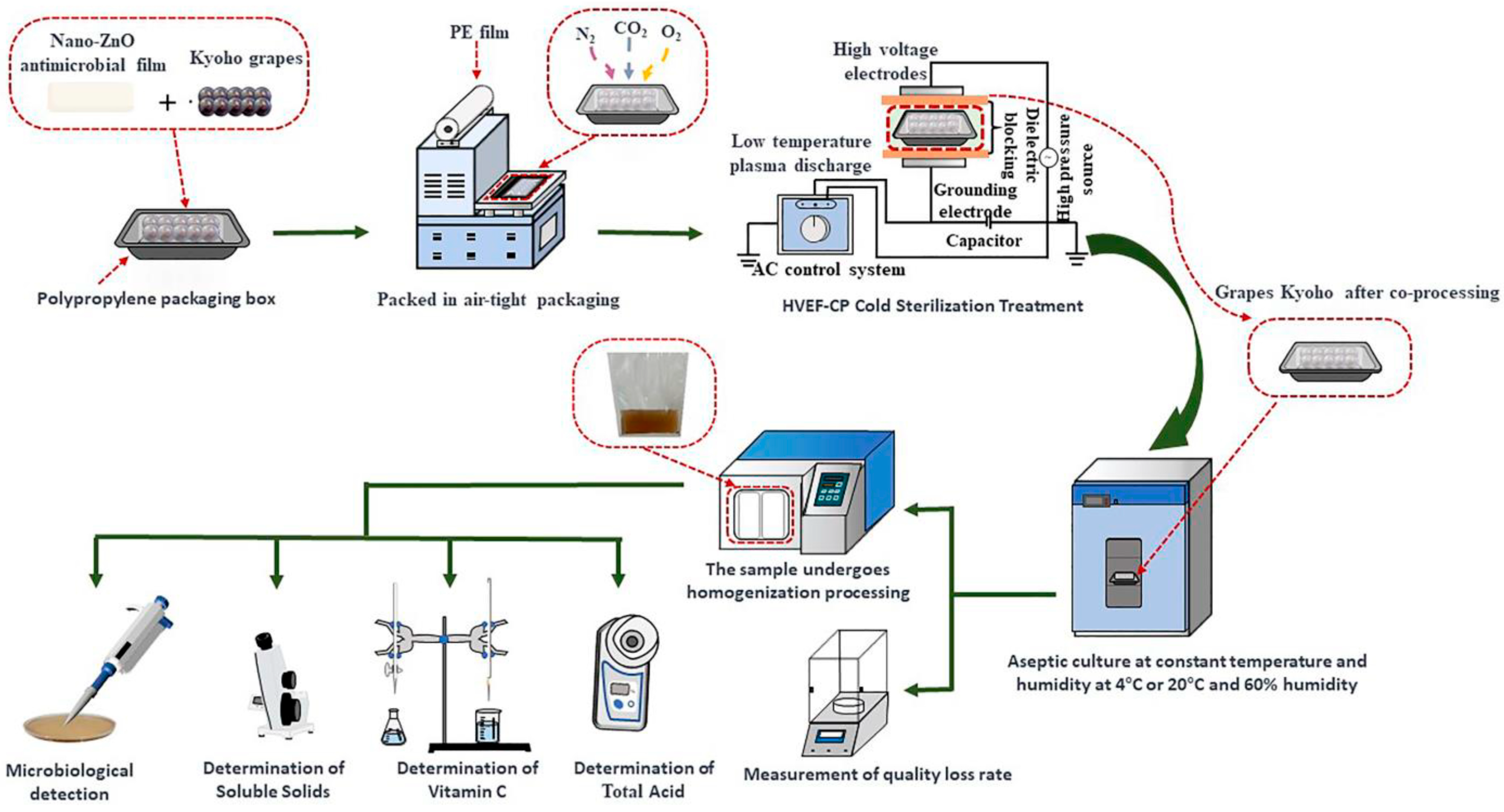
2. Postharvest Preservation Technologies
| Preservation Technologies | Mechanism | Key Parameters | Advantages | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
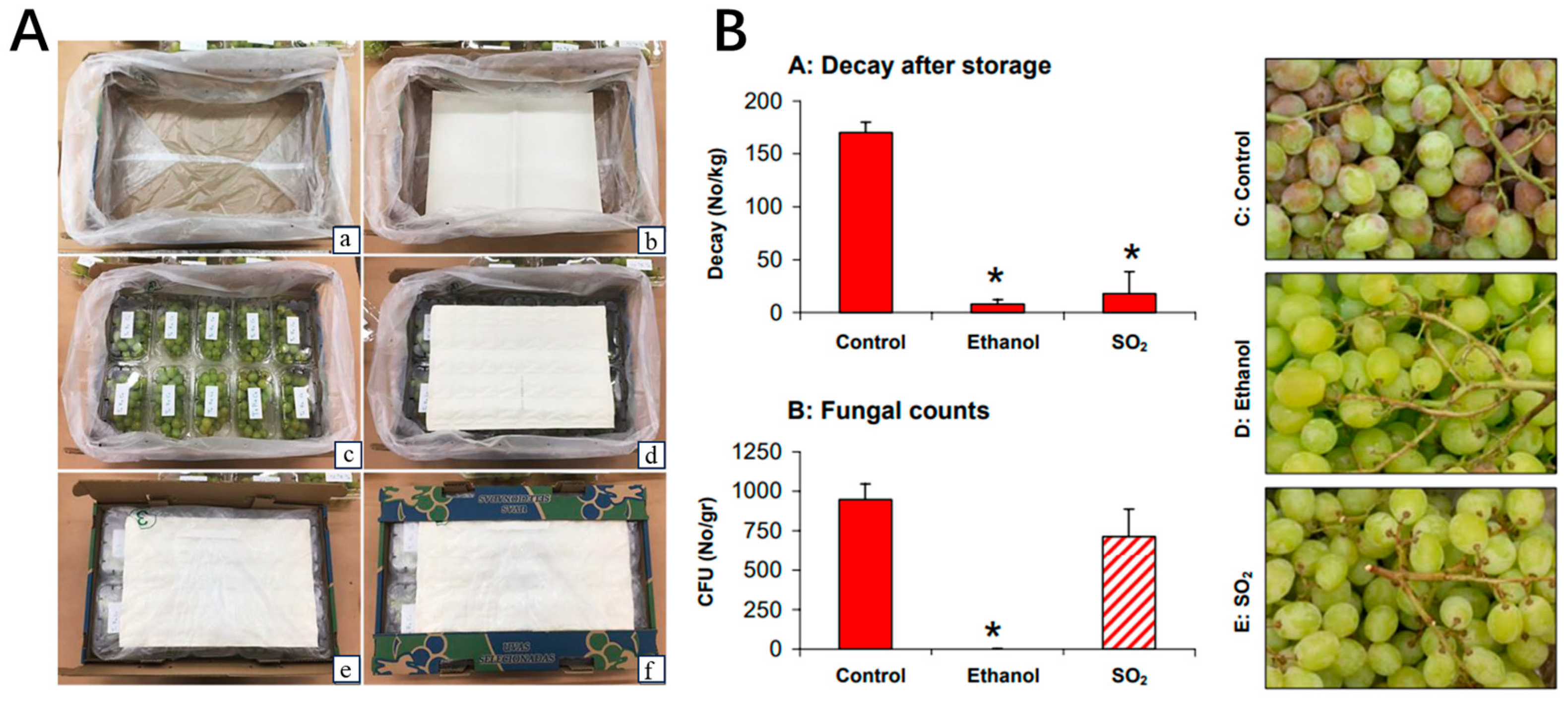
| SO2 fumigation | Inhibits microbial growth and oxidation via sulfur dioxide release | Fumigant concentration; exposure time; storage temperature | Highly effective against gray mold; low cost; long-standing commercial use | Potential residue issues; consumer sensitivity; regulatory restrictions | [17,18,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29] |
| Irradiation | Destroys microorganisms and pests with ionizing radiation | Radiation dose; exposure duration | Non-thermal; broad-spectrum efficacy; can replace chemical fumigants | Expensive equipment; possible changes in texture/flavor; consumer perception issues | [30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48] |
| Liquid treatments | Creates antimicrobial environment using agents like ethanol, chitosan, etc. | Type of liquid; concentration; application method; treatment duration; temperature | Simple application (spray/dip); low toxicity; some materials are natural and biodegradable | Shorter-lasting effect; requires direct contact; excess moisture may cause decay | [49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68] |
| Sealing and packaging | Blocks air, moisture, and contaminants | Packaging material type; barrier properties; sealing conditions, storage temperature | Prevents dehydration and mechanical damage; maintains appearance during transport | Passive protection; limited control over internal microenvironment | [69,70] |
| Modified atmosphere packaging | Alters O2/CO2 levels to reduce respiration and spoilage | Gas composition; permeability of packaging film; temperature; storage duration | Delays senescence; suppresses pathogens; prolongs shelf life; suitable for export | Requires precise gas composition control; potential flavor loss; cost of active systems | [71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82] |
| Biodegradable/Edible coatings | Forms a physical and biochemical barrier on grape surface | Film composition; coating thickness; bioactive additives; drying conditions; storage temperature | Environmentally friendly; reduces water loss; can incorporate functional agents (e.g., essential oils) | Mechanical fragility; inconsistent coating uniformity; short shelf life without cold chain | [83,84,85,86,87,88,89] |
| Synergistic technologies | Integrates multiple methods (e.g., MAP + ethanol; UV-C + chitosan) | Type and sequence of methods; compatibility; application timing; storage environment | Combines strengths of each technique; enhances efficacy and spectrum; lowers chemical dependency | May require optimization for specific cultivars; increased system complexity and cost | [90,91,92,93,94,95] |
2.1. SO2 Fumigation
2.2. Irradiation
2.3. Preservation Methods Using Liquids: Spraying, Vaporing, and Immersing
2.4. Sealing and Packaging
2.5. Modified Atmosphere Packaging
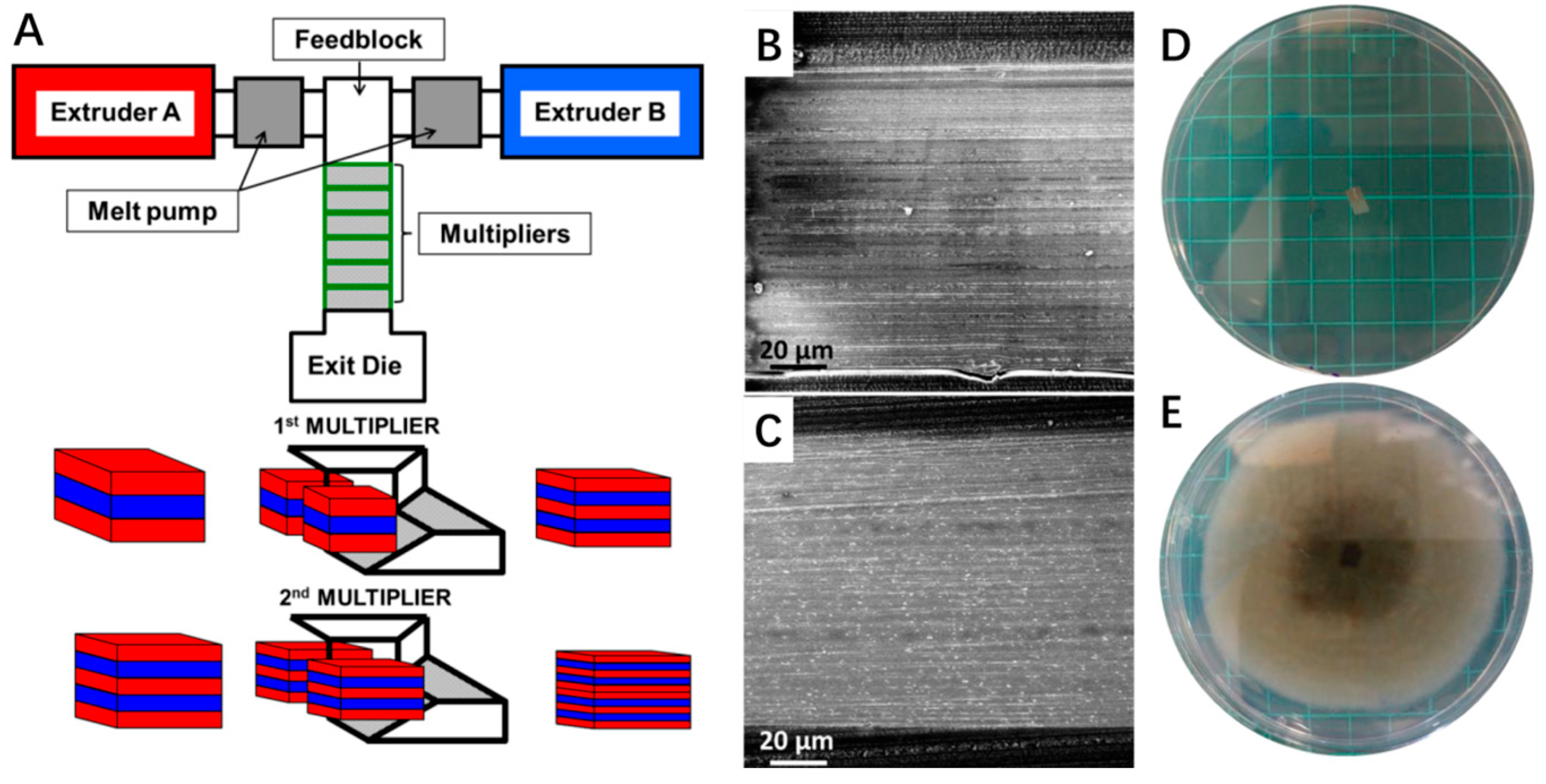
2.6. Biodegradable or Edible Coating
2.7. Synergistic Effects with Emerging Technologies
3. Toward Next-Generation Preservation Technologies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farbo, A.; Trombetta, N.G.; de Palma, L.; Borgogno-Mondino, E. Estimation of Intercepted Solar Radiation and Stem Water Potential in a Table Grape Vineyard Covered by Plastic Film Using Sentinel-2 Data: A Comparison of OLS-, MLR-, and ML-Based Methods. Plants 2024, 13, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisciotta, A.; Barone, E.; Di Lorenzo, R. Table-Grape Cultivation in Soil-Less Systems: A Review. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organisation of Vine and Wine. State of the World Vine and Wine Sector in 2023; International Organisation of Vine and Wine: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yahia, E.M. Postharvest Biology and Technology of Tropical and Subtropical Fruits. Volume 3: Cocona to Mango; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 179–214e. [Google Scholar]
- Ejsmentewicz, T.; Balic, I.; Sanhueza, D.; Barria, R.; Meneses, C.; Orellana, A.; Prieto, H.; Defilippi, B.G.; Campos-Vargas, R. Comparative Study of Two Table Grape Varieties with Contrasting Texture during Cold Storage. Molecules 2015, 20, 3667–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sortino, G.; Allegra, A.; Passafiume, R.; Gianguzzi, G.; Gullo, G.; Gallotta, A. Postharvest application of sulphur dioxide fumigation to improve quality and storage ability of “Red Globe” grape cultivar during long cold storage. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2017, 58, 403–408. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, I.; Vazquez-Hernandez, M.; Maestro-Gaitan, I.; Escribano, M.I.; Merodio, C.; Sanchez-Ballesta, M.T. Table Grapes during Postharvest Storage: A Review of the Mechanisms Implicated in the Beneficial Effects of Treatments Applied for Quality Retention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Jain, S.; Bhardwaj, A.; Nagpal, R.; Puniya, M.; Tomar, R.; Singh, V.; Parkash, O.; Prasad, G.B.K.S.; Marotta, F.; et al. Biological and Medicinal Properties of Grapes and Their Bioactive Constituents: An Update. J. Med. Food 2009, 12, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabra, A.; Netticadan, T.; Wijekoon, C. Grape bioactive molecules, and the potential health benefits in reducing the risk of heart diseases. Food Chem. X 2021, 12, 100149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solairaj, D.; Legrand, N.N.G.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, H. Isolation of pathogenic fungi causing postharvest decay in table grapes and in vivo biocontrol activity of selected yeasts against them. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 110, 101478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocco, A.F.; Diaz, M.E.; Romera, M.R.; Mercado, L.A.; Rivero, M.L.; Ponsone, M.L. Biocontrol of postharvest Alternaria decay in table grapes from Mendoza province. Biol. Control 2019, 134, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; He, F.; Wei, H.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y. Efficacy and Molecular Mechanisms of Nystatin Against Botrytis cinerea on Postharvest Table Grape. Foods 2024, 13, 3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkitasamy, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, R.; Pan, Z. Chapter 6—Grapes. In Integrated Processing Technologies for Food and Agricultural By-Products; Pan, Z., Zhang, R., Zicari, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 133–163. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, H.; Abdel-Samie, M.A.-S.; Lin, L. Novel packaging systems in grape storage—A review. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e13162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Huo, L.; Li, N.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Hu, J. Packaging performance evaluation and freshness intelligent prediction modeling in grape transportation. Food Control 2024, 165, 110684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanckenberg, A.; Opara, U.L.; Fawole, O.A. Postharvest Losses in Quantity and Quality of Table Grape (cv. Crimson Seedless) along the Supply Chain and Associated Economic, Environmental and Resource Impacts. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichter, A.; Gabler, F.M.; Smilanick, J.L. Control of spoilage in table grapes. Stewart Postharvest Rev. 2006, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonker, N.; Pandey, A.K.; Singh, P. Strategies to control post-harvest diseases of table grape: A review. J. Wine Res. 2016, 27, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, D.-I.; Manaila-Maximean, D.; Fierascu, I.; Baroi, A.M.; Matei, R.I.; Fistos, T.; Chican, I.E.; Fierascu, R.C. Applications of Natural Polymers in the Grapevine Industry: Plant Protection and Value-Added Utilization of Waste. Polymers 2025, 17, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D. Synergistic Microbial Inhibition and Quality Preservation for Grapes through High-Voltage Electric Field Cold Plasma and Nano-ZnO Antimicrobial Film Treatment. Foods 2023, 12, 4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Aguiar, A.C.; Caetano, B.E.B.; Roberto, S.R. Combination of Sulfur Dioxide-Generating Pads Reduces Gray Mold Disease Caused by Botrytis cinerea in ‘BRS Vitoria’ Hybrid Seedless Grapes during Cold Storage. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Wei, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, B.; Chen, J. Integrative Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analysis Provides Novel Insights into the Effects of SO2 on the Postharvest Quality of ‘Munage’ Table Grapes. Foods 2024, 13, 3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichter, A.; Zutahy, Y.; Kaplunov, T.; Lurie, S. Evaluation of Table Grape Storage in Boxes with Sulfur Dioxide-releasing Pads with Either an Internal Plastic Liner or External Wrap. HortTechnology 2008, 18, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Aguiar, A.C.; Higuchi, M.T.; Yamashita, F.; Roberto, S.R. SO2-Generating Pads and Packaging Materials for Postharvest Conservation of Table Grapes: A Review. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisosto, C.H.; Palou, L.s.; Garner, D.; Armson, D.A. Concentration by time product and gas penetration after marine container fumigation of table grapes with reduced doses of sulfur dioxide. HortTechnology 2002, 12, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luvisi, D.A. Sulfur Dioxide Fumigation of Table Grapes; UCANR Publications: Oakland, CA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Zoffoli, J.; Latorre, B. Table grape (Vitis vinifera L.). In Postharvest Biology and Technology of Tropical and Subtropical Fruits; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 179–214e. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Wei, J.; Xing, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, B.; Guan, J. Sulfur dioxide (SO2) accumulation in postharvest grape: The role of pedicels of four different varieties. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 190, 111953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoffoli, J.P.; Latorre, B.A.; Naranjo, P. Hairline, a postharvest cracking disorder in table grapes induced by sulfur dioxide. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2008, 47, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, H. Preservation Effect of High Energy Electron Beam on Kyoho Grape. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2010, 24, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, X.; Su, M.; Du, J.; Zhang, M. Effect of Electron Beam on Quality and Physiological Metabolism of Blueberry. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2013, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Kong, Q.; Yan, W.; Yue, L.; Ma, J.; Chen, Z.; Qi, R.; Bao, Y.; Qi, W. Effect of Electron Beam Irradiation on Ripening and Ethylene Production of Tomato Fruits Harvested at Different Mature Stages. J. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 617–623. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, L.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, H.; Kong, Q.; Yan, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, W. Application of Electron Beam Irradiation on Fresh-cut Apple During Cold Storage. Acta Agric. Shanghai 2022, 38, 106–113. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Q.; Huang, M.; Wu, L.; Mo, Y.; Du, X.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, P.; Kang, J. Effect Of Ion Beam Irradiation on Fresh-keeping of Strawberry. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2011, 25, 510–513. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Qiao, Y. Fresh-keeping Effect of High Energy Electron Beam Irradiation on Strawberry. Acta Agric. Shanghai 2010, 26, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Q.; Chen, Q.; Qi, W.; Yue, L.; Chen, Z.; Bao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Guo, K.; Yuan, Z.; Wu, Q. Effects of Quarantine Radiation Treatments on Quality of Imported Sweet Cherry in Shelf Life. Acta Agric. Shanghai 2010, 26, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S. Effects of Different Electron Beam Irradiation Doses on Sweet Cherry Preservation. Food Ferment. Ind. 2019, 45, 232–236. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S. Investigation of the Preservation Efficacy of Electron Beam Irradiation on Kiwifruit; Northwest A&F University: Yangling, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G. Study on the Preservation Effect of 60Co-γ Irradiation on Fresh Hazelnuts; Shenyang Agricultural University: Shenyang, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X. Effect of Electron Accelerator X-Ray Treatment on the Preservation of Winter Jujube and Development of a Shelf-Life Prediction Model; Northwest A&F University: Yangling, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Kong, Q.; Yue, L.; Yan, W.; Qi, W.; Bao, Y.; Dai, X. Effects of electronic beam irradiation on color and storage characteristics of table grape. J. Radiat. Res. Radiat. Process. 2013, 31, 060402. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Qiao, Y.; Qiao, X. Effects of High Energy Electron Beam on Physiological Quality of Kyoho Grape. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2010, 43, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, F.; Xu, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, B.; Ran, L.; Zhen, Z. Inhibitory Effect of 60Co-γ Irradiation on Three Pathogenic Fungi of Grapes. Nonwood For. Res. 2022, 40, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, K.; Zheng, H.; Shui, S.; Yan, L.; Liu, C.; Zheng, L. Comparison of postharvest UV-B and UV-C treatments on table grape: Changes in phenolic compounds and their transcription of biosynthetic genes during storage. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 138, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Tu, Q.; Xi, X.; Wu, X.; Bai, J.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Yuan, C. Effects of X-ray and electron beam irradiation on wine quality: Emphasizing phenolic compounds and aroma profiles. Food Chem. X 2025, 25, 102124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Long, M.; Li, Y.; He, Y.; Liang, Q.; Shi, B.; Luo, Q. Effects of 1-methylcyclopropene combined with 60Co-γ irradiation treatment on preservation of crystal grape. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2021, 12, 9124–9131. [Google Scholar]
- Bustos-Griffin, E.; Hallman, G.J.; Griffin, R.L. Current and potential trade in horticultural products irradiated for phytosanitary purposes. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2012, 81, 1203–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maherani, B.; Hossain, F.; Criado, P.; Ben-Fadhel, Y.; Salmieri, S.; Lacroix, M. World market development and consumer acceptance of irradiation technology. Foods 2016, 5, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Zhou, W.H.; Xu, Y.Y.; He, X.E.; He, F.Y.; Wang, Y. Effect of calcium spray at flowering combined with post-harvest 1-MCP treatment on the preservation of grapes. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, N.; Zhan, F.; Liu, F.; Wang, S.; Wu, L.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W. Mechanism of Acetophenone Fumigation to Inhibit Postharvest Botrytis cinerea in Grape. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2025, 46, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petriccione, M.; Pagano, L.; Forniti, R.; Zampella, L.; Mastrobuoni, F.; Scortichini, M.; Mencarelli, F. Postharvest treatment with chitosan affects the antioxidant metabolism and quality of wine grape during partial dehydration. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 137, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, S.; Navarro, D.; Zapata, P.; Guillén, F.; Valero, D.; Serrano, M.; Martínez-Romero, D. Antifungal efficacy of Aloe vera in vitro and its use as a preharvest treatment to maintain postharvest table grape quality. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2010, 57, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, B.; Liu, J.; Tian, S. Physiological responses and quality attributes of table grape fruit to chitosan preharvest spray and postharvest coating during storage. Food Chem. 2008, 106, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-H.; Qin, G.-Z.; Tian, S.-P. Influences of preharvest spraying Cryptococcus laurentii combined with postharvest chitosan coating on postharvest diseases and quality of table grapes in storage. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Tian, S. Effects of preharvest application of antagonistic yeast combined with chitosan on decay and quality of harvested table grape fruit. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2009, 89, 1838–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venditti, T.; Ladu, G.; Cubaiu, L.; Myronycheva, O.; D’hallewin, G. Repeated treatments with acetic acid vapors during storage preserve table grapes fruit quality. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2017, 125, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholberg, P.L.; Shephard, T.; Randall, P.; Moyls, L. Use of measured concentrations of acetic acid vapour to control postharvest decay in d’Anjou pears. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2004, 32, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chervin, C.; Westercamp, P.; Monteils, G. Ethanol vapours limit Botrytis development over the postharvest life of table grapes. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2005, 36, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.-T.; Huang, K.-L.; Guo, F.; Qu, W.; Yang, J.-J.; Liang, Z.-H.; Luo, Y.-B. Postharvest grapefruit seed extract and chitosan treatments of table grapes to control Botrytis cinerea. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2007, 46, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, O.A.; Gabler, F.M.; Mansour, M.; Smilanick, J.L. Postharvest ethanol and hot water treatments of table grapes to control gray mold. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2004, 34, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabler, F.M.; Smilanick, J.; Ghosoph, J.; Margosan, D. Impact of postharvest hot water or ethanol treatment of table grapes on gray mold incidence, quality, and ethanol content. Plant Dis. 2005, 89, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichter, A.; Zutahy, Y.; Kaplunov, T.; Aharoni, N.; Lurie, S. The effect of ethanol dip and modified atmosphere on prevention of Botrytis rot of table grapes. HortTechnology 2005, 15, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshi, V.; Ozturk, B.; Siddiqui, M.W.; Yousuf, B. Fresh-cut fruits and vegetables: Quality issues and safety concerns. In Fresh-Cut Fruits and Vegetables; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Pandey, A.K.; Tripathi, N. Essential oils: A renewable source for the management of stored product insects—A review. Agric. Rev. 2012, 33, 226–236. [Google Scholar]
- Kordali, S.; Cakir, A.; Ozer, H.; Cakmakci, R.; Kesdek, M.; Mete, E. Antifungal, phytotoxic and insecticidal properties of essential oil isolated from Turkish Origanum acutidens and its three components, carvacrol, thymol and p-cymene. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 8788–8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukatta, U.; Haruthaithanasan, V.; Chantarapanont, W.; Dilokkunanant, U.; Suppakul, P. Antifungal activity of clove and cinnamon oil and their synergistic against postharvest decay fungi of grape in vitro. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2008, 42, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.; Zheng, X. Essential oils to control Alternaria alternata in vitro and in vivo. Food Control 2007, 18, 1126–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Pandey, M.; Singh, U. Antifungal activity of an alkaloid allosecurinine against some fungi. Mycobiology 2007, 35, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiri, M.A.; Ghasemnezhad, M.; Bakhshi, D.; Dadi, M. Changes in phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of fresh-cut table grape (‘Vitis vinifera’) cultivar ‘Shahaneh’ as influence by fruit preparation methods and packagings. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2011, 5, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Kou, L.; Luo, Y.; Wu, D.; Liu, X. Effects of mild heat treatment on microbial growth and product quality of packaged fresh-cut table grapes. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, S567–S573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, J.; Golding, J.; McGlasson, W. Innovation in cold storage technologies. Stewart Postharvest Rev. 2005, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudry, R. Effect of O2 and CO2 partial pressure on selected phenomena affecting fruit and vegetable quality. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 1999, 15, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisosto, C.H.; Garner, D.; Crisosto, G. Carbon dioxide-enriched atmospheres during cold storage limit losses from Botrytis but accelerate rachis browning of ‘Redglobe’ table grapes. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2002, 26, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artés-Hernández, F.; Aguayo, E.; Artés, F. Alternative atmosphere treatments for keeping quality of ‘Autumn seedless’ table grapes during long-term cold storage. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2004, 31, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Lucera, A.; Conte, A.; Mastromatteo, M.; Speranza, B.; Antonacci, A.; Del Nobile, M.A. Effects of passive and active modified atmosphere packaging conditions on ready-to-eat table grape. J. Food Eng. 2011, 102, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Physiological responses and quality attributes of ‘Kyoho’ grapes to controlled atmosphere storage. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 39, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smilanick, J.L.; Crisosto, C.; Mlikota, F. Postharvest use of ozone on fresh fruit. Perish. Handl. Q. 1999, 99, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Skog, L.J.; Chu, C.L. Effect of ozone on qualities of fruits and vegetables in cold storage. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2001, 81, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palou, L.s.; Smilanick, J.L.; Crisosto, C.H.; Mansour, M.; Plaza, P. Ozone gas penetration and control of the sporulation of Penicillium digitatum and Penicillium italicum within commercial packages of oranges during cold storage. Crop Prot. 2003, 22, 1131–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayuela, J.A.; Vázquez, A.; Pérez, A.; García, J. Control of table grapes postharvest decay by ozone treatment and resveratrol induction. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2009, 15, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabler, F.M.; Smilanick, J. Postharvest control of table grape gray mold on detached berries with carbonate and bicarbonate salts and disinfectants. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2001, 52, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, K.; Maoz, I.; Vinokur, Y.; Rodov, V.; Lewinsohn, E.; Lichter, A. Enhancement of table grape flavor by postharvest application of monoterpenes in modified atmosphere. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 159, 111018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yang, X.; Liang, J.; Rong, Y.; Zhao, W.; Ding, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q. Preparation, characterization, antimicrobial evaluation, and grape preservation applications of polyvinyl alcohol/gelatin composite films containing zinc oxide@quaternized chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teymoorian, M.; Moghimi, R.; Hosseinzadeh, R.; Zandi, F.; Lakouraj, M.M. Fabrication the emulsion-based edible film containing Dracocephalum kotschyi Boiss essential oil using chitosan–gelatin composite for grape preservation. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2024, 7, 100444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanazzi, G.; Gabler, F.M.; Margosan, D.; Mackey, B.E.; Smilanick, J.L. Effect of chitosan dissolved in different acids on its ability to control postharvest gray mold of table grape. Phytopathology 2009, 99, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, M.; Valverde, J.M.; Guillén, F.; Castillo, S.; Martínez-Romero, D.; Valero, D. Use of Aloe vera gel coating preserves the functional properties of table grapes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3882–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Zong, Y.; Chen, Q.; Hua, D.; Tian, S. Inhibitory effect of boron against Botrytis cinerea on table grapes and its possible mechanisms of action. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 138, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolahi, A.; Hassani, A.; Ghosta, Y.; Bernousi, I.; Meshkatalsadat, M. Study on the potential use of essential oils for decay control and quality preservation of Tabarzeh table grape. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2010, 50, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, C.; Ma, W.; He, R.; Rong, Y.; Sarker, S.; Liu, Q.; Tian, F. A novel active packaging film containing citronella oil: Preparation, characterization, antimicrobial activity and application in grape preservation. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2023, 40, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, J.M.; Guillén, F.; Martínez-Romero, D.; Castillo, S.; Serrano, M.; Valero, D. Improvement of table grapes quality and safety by the combination of modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) and eugenol, menthol, or thymol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7458–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurie, S.; Zutahy, Y.; Kaplonov, T.; Lichter, A.; Saks, Y. The Effect of Ethanol Dip and Modified Atmosphere on Prevention of Botrytis Rot of Table Grapes. Acta Hortic. 2010, 857, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurie, S.; Pesis, E.; Gadiyeva, O.; Feygenberg, O.; Ben-Arie, R.; Kaplunov, T.; Zutahy, Y.; Lichter, A. Modified ethanol atmosphere to control decay of table grapes during storage. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2006, 42, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanazzi, G.; Gabler, F.M.; Smilanick, J. Preharvest chitosan and postharvest UV irradiation treatments suppress gray mold of table grapes. Plant Dis. 2006, 90, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanazzi, G.; Smilanick, J.L.; Lichter, A. Postharvest ethanol and potassium sorbate treatments of table grapes to control gray mold. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2005, 37, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imlak, M.; Randhawa, M.; Hassan, A.; Ahmad, N.; Nadeem, M. Post-harvest shelf life extension and nutritional profile of Thompson seedless table grapes under calcium chloride and modified atmospheric storage. J. Food Process. Technol. 2017, 8, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, D.; Subramani, D.; Kumaraguruparaswami, M. Eco-Friendly Active Packaging for Fresh and Minimally Processed Fruits and Vegetables. In Green Materials for Active Food Packaging; Islam, S.U., Shahid, M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2025; pp. 417–454. [Google Scholar]
- University of Kentucky. Postharvest Diseases of Fruits and Vegetables. Available online: https://plantpathology.ca.uky.edu/files/ppfs-gen-24.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- Chen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, L.; Zhao, L. Research Progress on Physical Preservation Technology of Fresh-Cut Fruits and Vegetables. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krepker, M.; Zhang, C.; Nitzan, N.; Prinz-Setter, O.; Massad-Ivanir, N.; Olah, A.; Baer, E.; Segal, E. Antimicrobial LDPE/EVOH layered films containing carvacrol fabricated by multiplication extrusion. Polymers 2018, 10, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, M.H.B.; Duarte-Sierra, A. An Overview of Low-Cost Approaches for the Postharvest Storage of Fruits and Vegetables for Smallholders, Retailers, and Consumers. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Liu, M.; Sun, Y. Overview of Food Preservation and Traceability Technology in the Smart Cold Chain System. Foods 2023, 12, 2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Wu, J.; Meng, X.; Wang, X.; Manzardo, A. Digital twin integration for dynamic quality loss control in fruit supply chains. J. Food Eng. 2025, 397, 112577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhu, H.; Chang, Q.; Mao, Q. A Comprehensive Review of Digital Twins Technology in Agriculture. Agriculture 2025, 15, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defraeye, T.; Shrivastava, C.; Berry, T.; Verboven, P.; Onwude, D.; Schudel, S.; Bühlmann, A.; Cronje, P.; Rossi, R.M. Digital twins are coming: Will we need them in supply chains of fresh horticultural produce? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Wang, Q.; He, H.; Wu, Y.; Shan, W.; Liu, H. Postharvest Preservation Strategies for Table Grapes: A Comprehensive Review from Practical Methods to Future Developments. Plants 2025, 14, 2462. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162462
Zhang C, Wang Q, He H, Wu Y, Shan W, Liu H. Postharvest Preservation Strategies for Table Grapes: A Comprehensive Review from Practical Methods to Future Developments. Plants. 2025; 14(16):2462. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162462
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ci, Qiankun Wang, Hui He, Yusen Wu, Wenpeng Shan, and Hongru Liu. 2025. "Postharvest Preservation Strategies for Table Grapes: A Comprehensive Review from Practical Methods to Future Developments" Plants 14, no. 16: 2462. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162462
APA StyleZhang, C., Wang, Q., He, H., Wu, Y., Shan, W., & Liu, H. (2025). Postharvest Preservation Strategies for Table Grapes: A Comprehensive Review from Practical Methods to Future Developments. Plants, 14(16), 2462. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162462






