Combined Effects of Flood Disturbances and Nutrient Enrichment Prompt Aquatic Vegetation Expansion: Sediment Evidence from a Floodplain Lake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
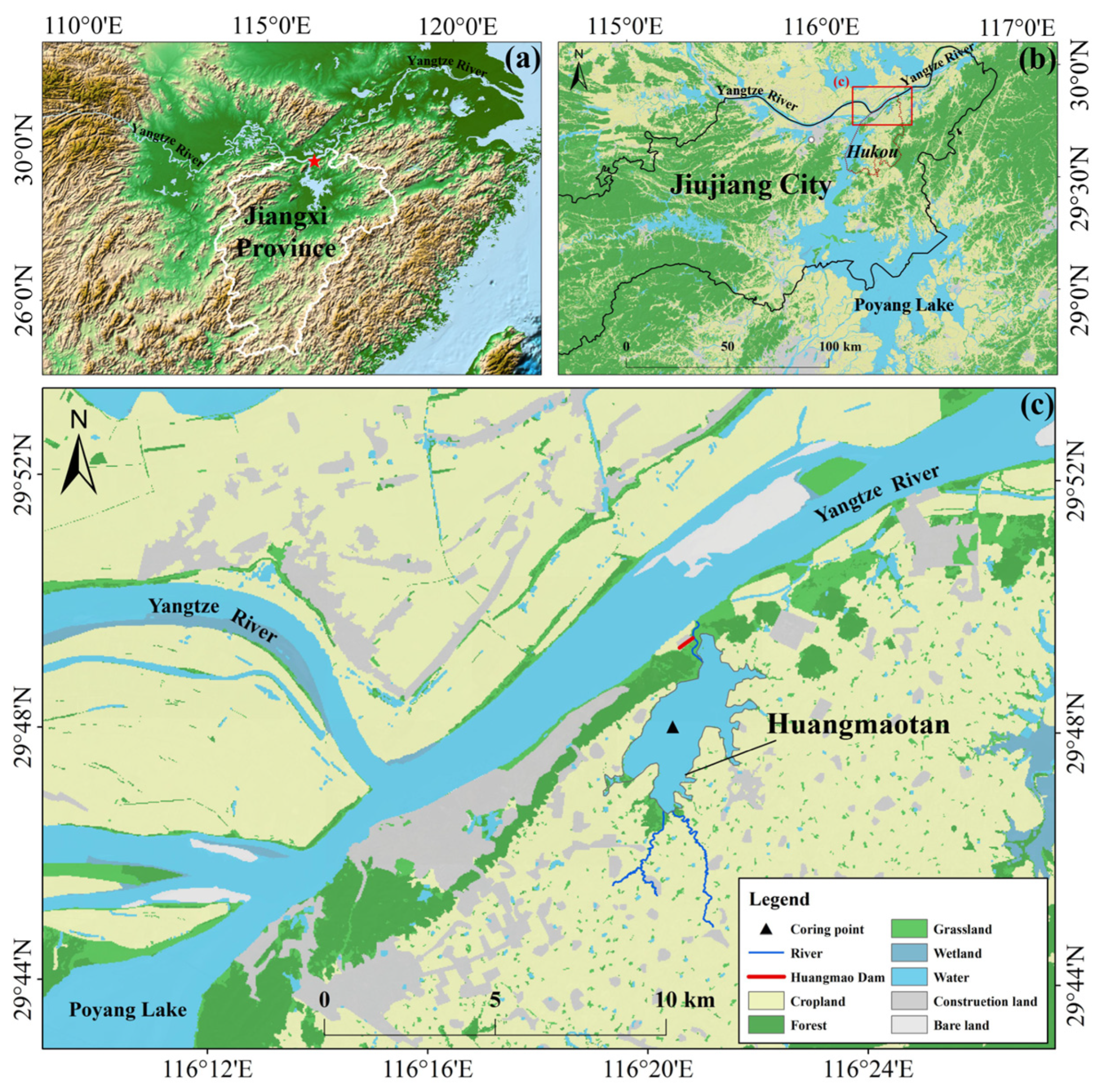
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Historical Records on Droughts and Floods
2.3. Historical Lake Area and Shoreline Changes Extracted from Remote Sensing Images
2.4. Sampling and Laboratory Analysis
2.5. Numerical Analyses
3. Results
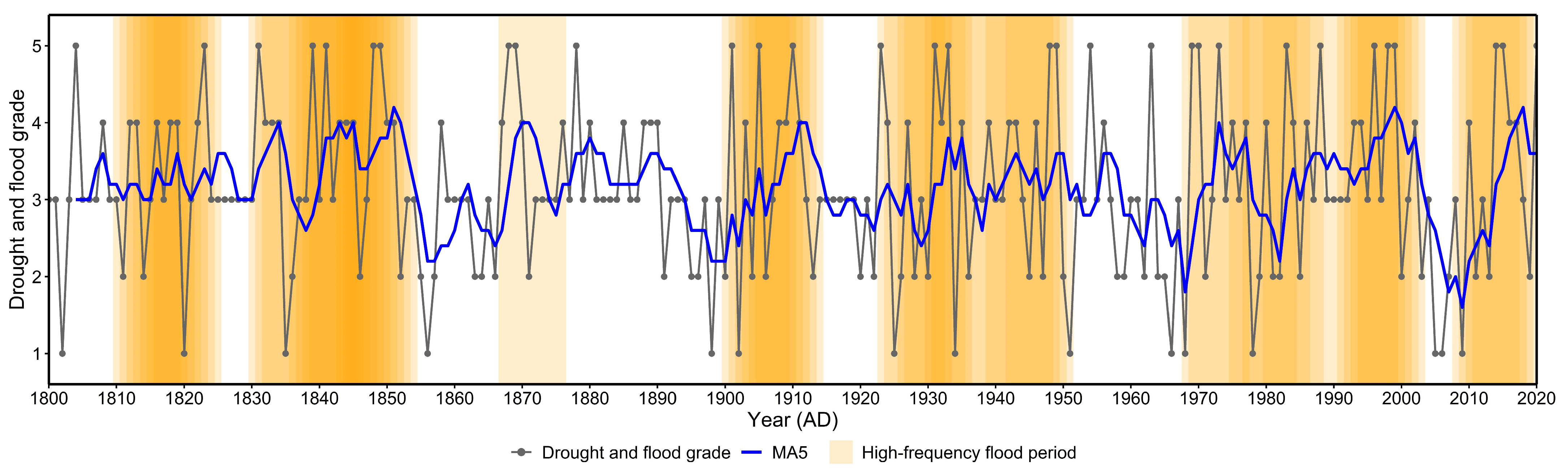
3.1. Historical Drought–Flood Variability in the Huangmaotan Watershed
3.2. Historical Changes in Lake Morphology
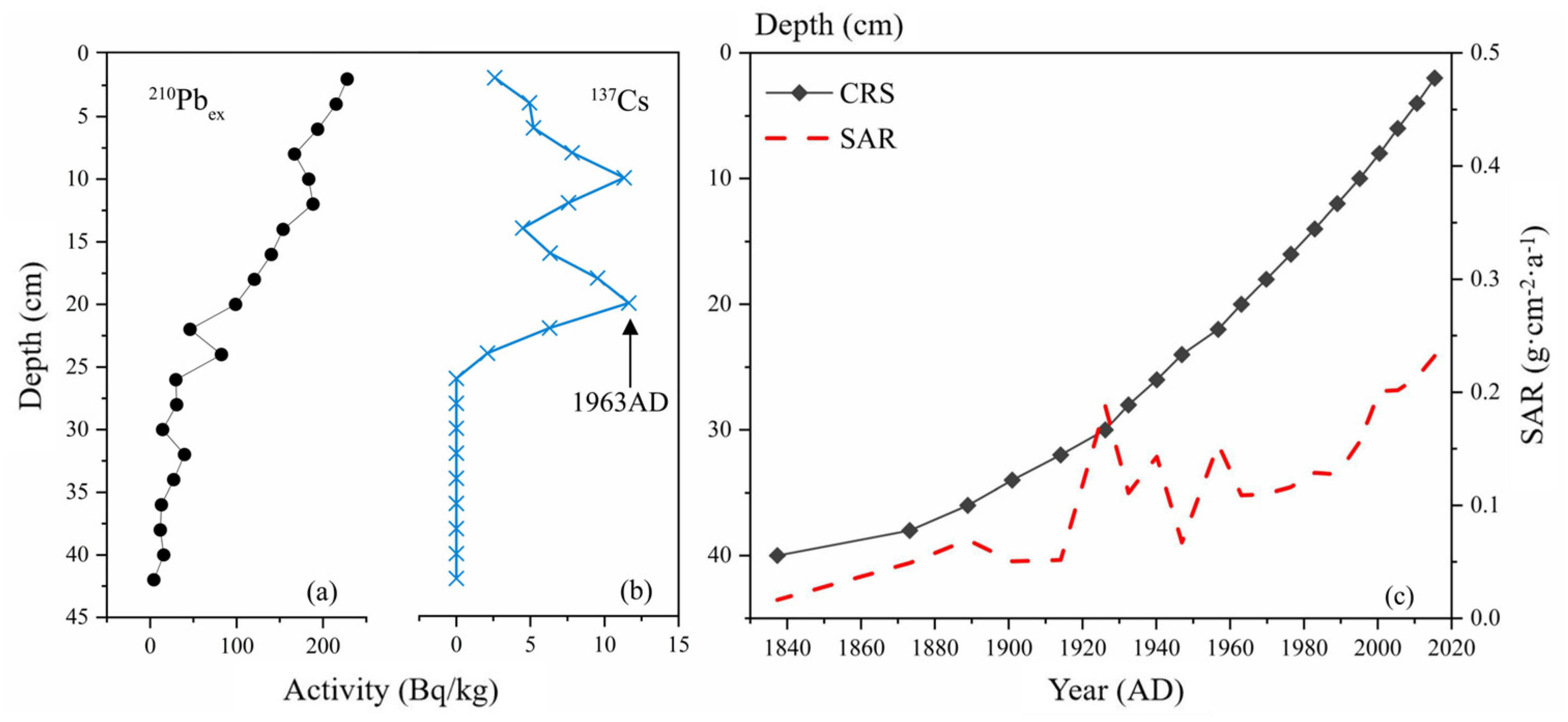
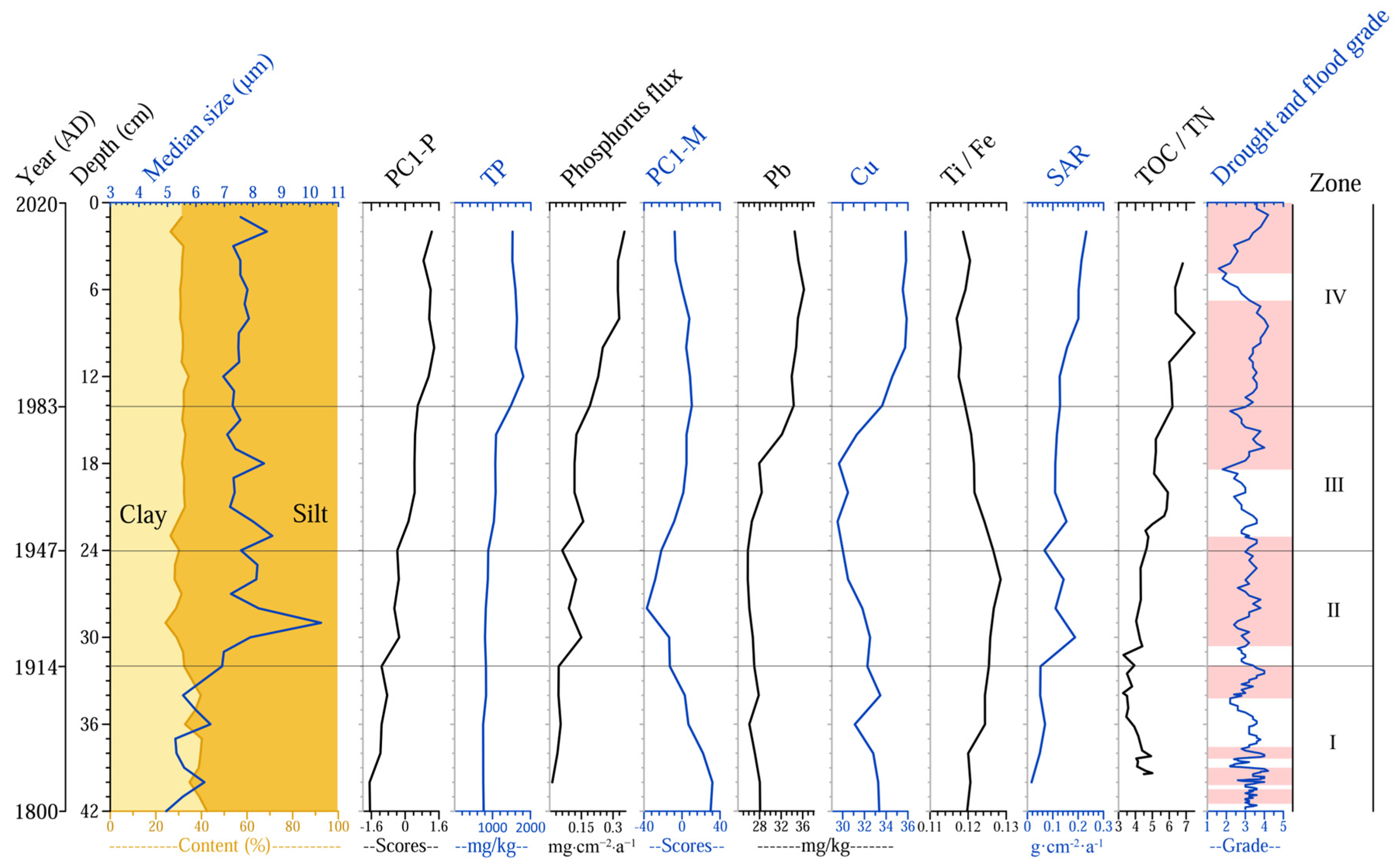
3.3. Sediment Chronology
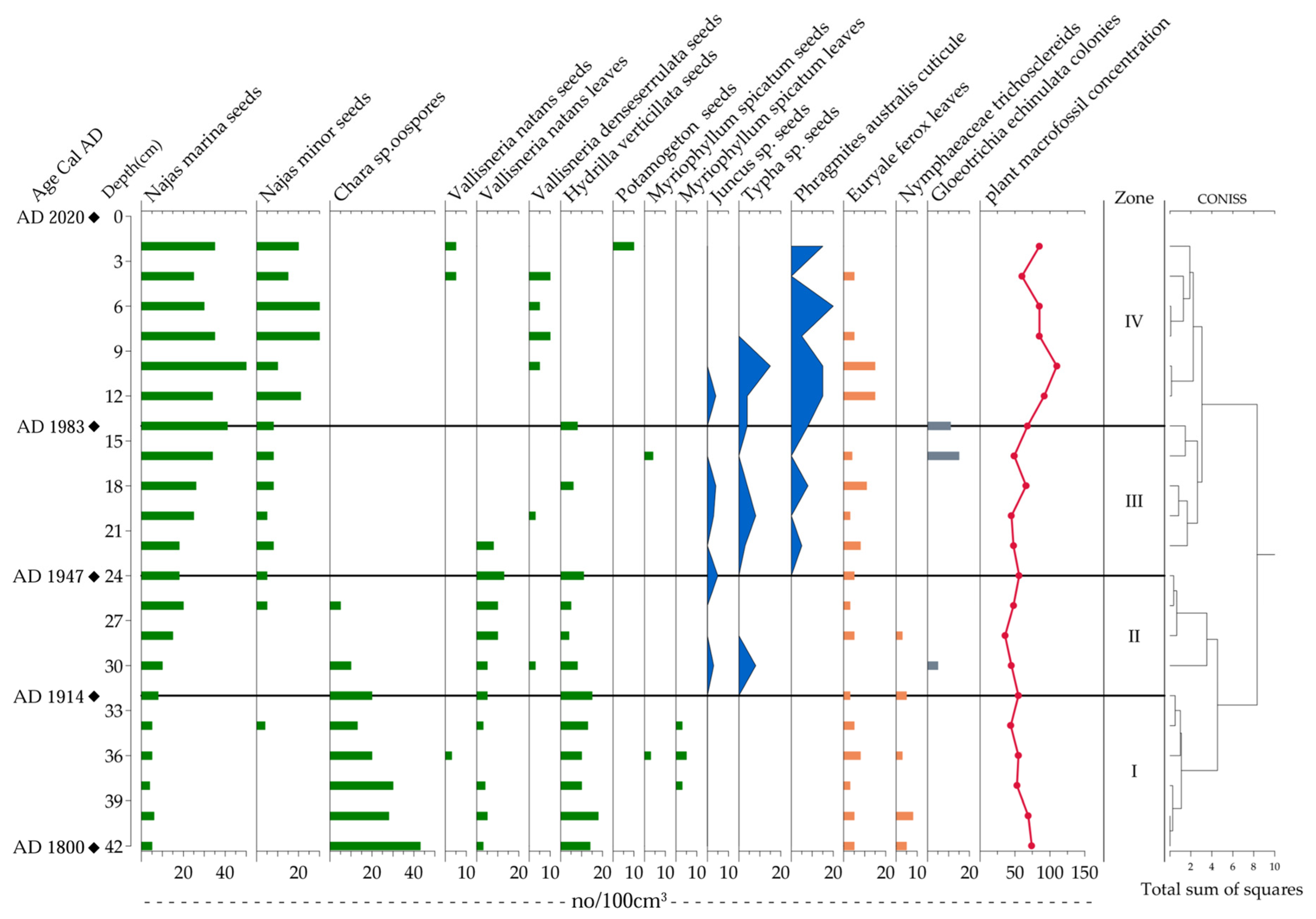
3.4. Aquatic Plant Vegetation Assemblage in Huangmaotan Lake
3.5. Multi-Indicator Analysis Results
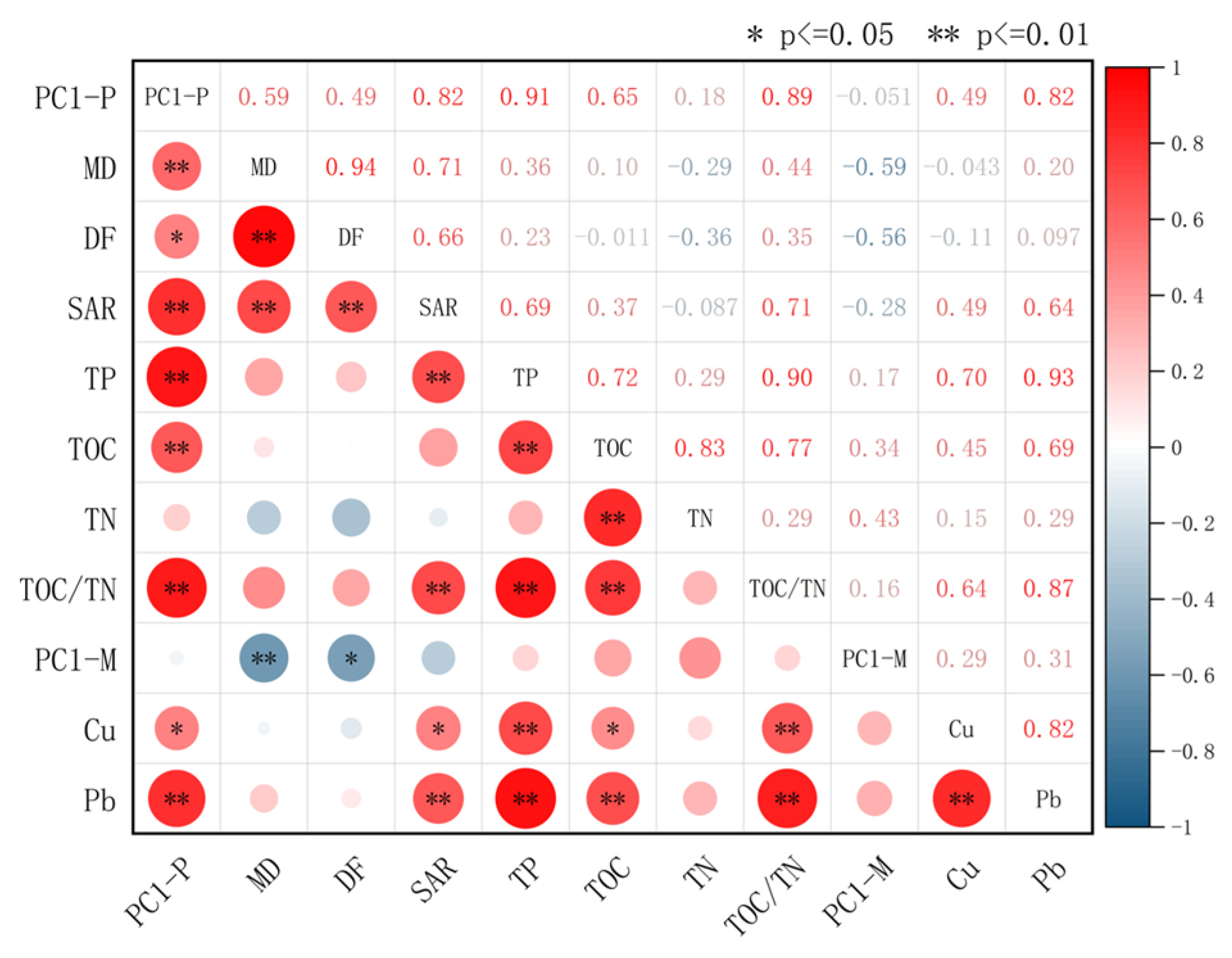
3.6. Multivariate Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Low Human Disturbance on Aquatic Communities During 1800–1947
4.2. Intensifying Anthropogenic Pressures (1947–2020)
4.3. Flood-Induced Macrophyte Inhibition in Huangmaotan Lake During Historical Periods
4.4. Inhibitory Effects of Nutrient Enrichment on Aquatic Macrophytes
4.5. Combined Effects of Flood Disturbances and Nutrient Enrichment Prompt Aquatic Vegetation Expansion
4.6. Dam Effects
4.7. Implications for Lake Management
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, R.; Han, Y.; Fan, F.; García Molinos, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, K.; Wang, D.; Mei, Z. Need to shift in river-lake connection scheme under the “ten-year fishing ban” in the Yangtze River, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Søndergaard, M.; Christoffersen, K. The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 131. [Google Scholar]
- Essien, A.I.; Udoinim, M.M.; Akpan, G.D.; Effiong, J.O. Aquatic macrophytes and Limnological implications on fisheries resources: A case study of Obio Akpa Stream in Akwa Ibom State, Nigeria. Int. J. Water Soil Res. 2012, 3, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, P.; Yan, W.; Kong, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, B.; Ma, J.; et al. Spatial and seasonal variation of water parameters, sediment properties, and submerged macrophytes after ecological restoration in a long-term (6 year) study in Hangzhou west lake in China: Submerged macrophyte distribution influenced by environmental variables. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezbrytska, I.; Usenko, O.; Konovets, I.; Leontieva, T.; Abramiuk, I.; Goncharova, M.; Bilous, O. Potential Use of Aquatic Vascular Plants to Control Cyanobacterial Blooms: A Review. Water 2022, 14, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilt, S.; Brothers, S.; Jeppesen, E.; Veraart, A.J.; Kosten, S. Translating regime shifts in shallow lakes into changes in ecosystem functions and services. BioScience 2017, 67, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moi, D.A.; Alves, D.C.; Antiqueira, P.A.P.; Thomaz, S.M.; de Mello, F.T.; Bonecker, C.C.; Rodrigues, L.C.; García-Ríos, R.; Mormul, R.P. Ecosystem shift from submerged to floating plants simplifying the food web in a tropical shallow lake. Ecosystems 2021, 24, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Hu, W.; Liu, Z.; Gao, G.; Xiao, H.; Hu, H.; Song, Y.; Chen, Z. An experimental study on water quality purification through ecological restoration in Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake. China Water Resour. 2006, 17, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Junk, W.J.; Bayley, P.B.; Sparks, R.E. The flood pulse concept in river-floodplain systems. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 106, 110–127. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Jiang, T.; Yang, G.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Y. The spatial-temporal variation of water clarity and its influencing factors in Jiaozhou Bay from 1986 to 2017. Mar. Sci. 2020, 44, 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, X.; Yan, Z.; Tian, D.; Fang, J.; Xie, P. Morphological traits of submerged macrophytes reveal specific positive feedbacks to water clarity in freshwater ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Liang, T.; Wang, L.; Li, K. Simulation on phosphorus release characteristics of Poyang Lake sediments under variable water levels and velocities. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinçon-Leite, B.; Bassin, H.; Baytex, J. Impact of a flood event on the biogeochemical behaviour of a mesotrophic alpine lake: Lake Bourget (Savoy). Hydrobiologia 1998, 373, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, M.C. Oxygen deficiency and root metabolism: Injury and acclimation under hypoxia and anoxia. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1997, 48, 223–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Yin, W.; Li, W.; Han, Q. Two negatives make an affirmative: Can extreme flooding reduce the expansion of invasive submerged macrophyte in a large river? J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 346, 118964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, G.; Lei, H.; Zhu, D. Mechanisms of the Photochemical Release of Phosphate from Resuspended Sediments under Solar Irradiation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Pang, Y.; Ma, X. Research progress on influencing of environmental factors on the growth of submersed macrophytes. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 3958–3968. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Liu, X.; Qin, B.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Thomaz, S.M.; Deng, J. Global loss of aquatic vegetation in lakes. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 173, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilarranz, L.J.; Narwani, A.; Odermatt, D.; Dakos, V. Regime shifts, trends, and variability of lake productivity at a global scale. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2116413119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörtner, H.-O.; Roberts, D.C.; Adams, H.; Adler, C.; Aldunce, P.; Ali, E.; Begum, R.A.; Betts, R.; Kerr, R.B.; Biesbroek, R. Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.; Feng, L.; Dai, Y.; Hu, C.; Gibson, L.; Tang, J.; Lee, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cai, X.; Liu, J.; et al. Global mapping reveals increase in lacustrine algal blooms over the past decade. Nat. Geosci. 2022, 15, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Dai, Y.; Hou, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zheng, C. Concerns about phytoplankton bloom trends in global lakes. Nature 2021, 590, E35–E47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zhang, K.; Huang, S.; Lin, Q. Patterns and trajectories of macrophyte change in East China’s shallow lakes over the past one century. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 1735–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Yu, X.; Xia, S.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, X.; Yu, D. Effects of water depth on the biomass of two dominant submerged macrophyte species in floodplain lakes during flood and dry seasons. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Dong, X.; Yang, X.; Odgaard, B.V.; Jeppesen, E. Hydrologic and anthropogenic influences on aquatic macrophyte development in a large, shallow lake in China. Freshw. Biol. 2019, 64, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, T.A.; Sayer, C.D.; Bennion, H.; David, C.; Rose, N.; Wade, M.P. A 250 year comparison of historical, macrofossil and pollen records of aquatic plants in a shallow lake. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1671–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hukou County Annals Compilation Committee of Jiangxi Province. Hukou County Annals; Hukǒu County Government Press: Hukou, China, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Academy of Meteorological Science of China Central Meteorological Administration. Yearly Charts of Dryness/Wetness in China for the Last 500-Year Period; Cartographic Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.E.; Liu, C.Z. Supplement to the Atlas of Drought and Flood Distribution in China over the Past 500 Years (1980–1992). Meteorol. Mon. 1993, 19, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, K.G. China Meteorological Disaster Encyclopedia: Jiangxi Volume; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- EarthExplorer. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Liu, E.; Xue, B.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; Xia, W. Dating method for modern sediments based on the distribution of 210Pb and 137Cs: A case study of Chaohu Lake and Taibai Lake. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2009, 29, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleby, P. Chronostratigraphic techniques in recent sediments. In Tracking Environmental Change Using Lake Sediments; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 171–203. [Google Scholar]
- Shepard, F.P. Nomenclature based on sand-silt-clay ratios. J. Sediment. Res. 1954, 24, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Birks, H.H.; Birks, H.J.B.; Flower, R.J.; Peglar, S.M.; Ramdani, M. Recent ecosystem dynamics in nine North African lakes in the CASSARINA Project. Aquat. Ecol. 2001, 35, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berggren, G. Atlas of seeds and small fruits of northwest European plant species with morphological descriptions. Part 2: Cyperaceae. Oikos 1969, 20, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, J.N. First identification key for charophyte oospores from central Europe. Eur. J. Phycol. 1994, 29, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauquoy, D.; van Geel, B. Mire and peat macrofossils. Encycl. Quat. Sci. 2007, 3, 2315–2336. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S. Regional Climate Change and Human Activities Recorded by Lake Sediments in Huangmaotan Since the Little Ice Age. Master’s Thesis, Jiangxi Normal University, Nanchang, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ashley, G.M. Interpretation of polymodal sediments. J. Geol. 1978, 86, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blindow, I. Decline of charophytes during eutrophication: Comparison with angiosperms. Freshw. Biol. 1992, 28, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gao, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, K.; Lin, Q.; Jia, J.; Lu, Y. Lake pigment characteristics and their applicability in reconstructing phytoplankton communities under irregular hydrological regulation in a floodplain lake system. J. Hydrol. 2022, 614, 128575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.W. Advances in Modern Climatology Research; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Yang, Q.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, J. Aquatic vegetation in Liangzi Lake. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 1994, 13, 281–290. [Google Scholar]
- Küpper, H.; Andresen, E. Mechanisms of Metal Toxicity in Plants. Metallomics 2016, 8, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danlu, S.; Kai, Z.; Yan, X.; Changhua, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhubing, H.; Zhenguo, S. Hydrilla verticillata Employs Two Different Ways to Affect DNA Methylation under Excess Copper Stress. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 193, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Zhuang, K.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Z.; Shen, Z. Phytotoxicity and Accumulation of Cu in Mature and Young Leaves of Submerged Macrophyte Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babanazarova, O.V.; Lyashenko, O.A. Inferring long-term changes in the physical-chemical environment of the shallow, enriched Lake Nero from statistical and functional analyses of its phytoplankton. J. Plankton Res. 2007, 29, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Borics, G.; Várbíró, G.; Grigorszky, I.; Krasznai, E.; Szabó, S.; Kiss, K.T. A new evaluation technique of potamo-plankton for the assessment of the ecological status of rivers. River Syst. 2007, 17, 465–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Ma, J.; Qiu, D.; Wu, Z. Succession and species replacement of aquatic plant community in East Lake. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 1997, 21, 319–327. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Gao, X.; Shan, H.; Zhang, X.; Ni, L.; Cao, T. The measurement of photosynthetic parameters of submerged macrophytes to explore plant distribution depth in Lake Erhai. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2023, 47, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, J.L.; Kingsford, R.T.; Brock, M.A. Seed Banks in Arid Wetlands with Contrasting Flooding, Salinity and Turbidity Regimes. Plant Ecol. 2007, 188, 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, A.E.S.; Florentine, S. Factors affecting the global distribution of Hydrilla verticillata (L. fil.) Royle: A review. Weed Res. 2021, 61, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Hosper, S.H.; Meijer, M.-L.; Moss, B.; Jeppesen, E. Alternative Equilibria in Shallow Lakes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1993, 8, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blindow, I.; Hargeby, A.; Andersson, G. Seasonal Changes of Mechanisms Maintaining Clear Water in a Shallow Lake with Abundant Chara Vegetation. Aquat. Bot. 2002, 72, 315–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seadler, A.W.; Aldridge, N. The Translocation of Radioactive Phosphorus by the Aquatic Vascular Plant Najas minor. Ohio J. Sci. 1977, 77, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffer, M.; Carpenter, S.; Foley, J.A.; Folke, C.; Walker, B. Catastrophic Shifts in Ecosystems. Nature 2001, 413, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, Q.; Yao, M.; Wang, R.; Xu, M. Using sedimentary diatoms to identify reference conditions and historical variability in shallow lake ecosystems in the Yangtze floodplain. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2016, 67, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Anderson, N.J.; Dong, X.; Shen, J. Surface Sediment Diatom Assemblages and Epilimnetic Total Phosphorus in Large, Shallow Lakes of the Yangtze Floodplain: Their Relationships and Implications for Assessing Long-Term Eutrophication. Freshw. Biol. 2008, 53, 1273–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shen, J.; Dong, X.; Liu, E. Evolution of Nutrient Status and Ecological Response of Shallow Lakes in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River during Historical Periods: A Case Study of Longgan Lake and Taibai Lake. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2006, 49 (Suppl. S1), 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, B.D. Water and plants in freshwater wetlands. In Eco-Hydrology: Plants and Water in Terrestrial and Aquatic Environments; Baird, A.J., Wilby, R., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 1999; pp. 128–157. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yu, D. Influence of sediment fertility on morphological variability of Vallisneria spiralis L. Aquat. Bot. 2007, 87, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Kautsky, L. Life strategies of aquatic soft bottom macrophytes. Oikos 1988, 53, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.B.; Drew, M. Effects of flooding on growth and metabolism of herbaceous plants. In Flooding and Plant Growth; Kozlowski, T.T., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1984; pp. 47–128. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Ren, B.; Li, F. Increased nutrient supply facilitates acclimation to high-water level in the marsh plant Deyeuxia angustifolia: The response of root morphology. Aquat. Bot. 2009, 91, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Yu, D. Size-related auto-fragment production and carbohydrate storage in auto-fragment of Myriophyllum spicatum L. in response to sediment nutrient and plant density. Hydrobiologia 2011, 658, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Yu, D. Turion Production and Nutrient Reserves in Potamogeton crispus Are Influenced by Sediment Nutrient Level. Aquat. Biol. 2011, 14, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brewer, C.A.; Parker, M. Adaptations of macrophytes to life in moving water: Upslope limits and mechanical properties of stems. Hydrobiologia 1990, 194, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Yu, D.; Wang, J. Habitat selection in spatially heterogeneous environments: A test of foraging behaviour in the clonal submerged macrophyte Vallisneria spiralis. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 1552–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, Y.; Cao, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, W.; Jeppesen, E. Indirect effects of extreme precipitation on the growth of Vallisneria denseserrulata Makino. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 153, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mal, T.K.; Narine, L. The biology of Canadian weeds. 129. Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steud. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2004, 84, 365–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostendorp, W.; Dienst, M.; Schmieder, K. Disturbance and rehabilitation of lakeside Phragmites reeds following an extreme flood in Lake Constance (Germany). Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmer, T.D.; Voesenek, L.A.C.J. Flooding Tolerance: Suites of Plant Traits in Variable Environments. Funct. Plant Biol. 2009, 36, 665–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Liu, Y.; Lou, Y.; Yu, D.; Zhou, M.; Lu, X.; Jiang, M. Nitrogen availability affects the responses of marsh grass and sedge plants (Phragmites australis and Bolboschoenus planiculmis) to flooding time. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 908, 168008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiedrzyńska, E.; Kiedrzyński, M.; Zalewski, M. Flood sediment deposition and phosphorus retention in a lowland river floodplain: Impact on water quality of a reservoir, Sulejów, Poland. Ecol. Hydrol. Hydrobiol. 2008, 8, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, B.; Shi, W. Phosphorus Buffering by Suspended Particulate Matter under the Pressure of Extreme Storm Floods in the Lake Erhai Basin, Southwest China. Water Res. 2022, 219, 118540. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Yang, L.; Lin, Z.; Yao, S.; He, H.; Huang, X.; Liu, Z.; Jeppesen, E.; Yu, J. Nutrient-rich sediment promotes, while fertile water inhibits the growth of the submerged macrophyte Vallisneria denseserrulata: Implications for shallow lake restoration. Hydrobiologia 2024, 851, 4821–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.; Smith, J.P.; Dai, S.B.; Gao, A.; Li, P. Impact of dams on Yangtze River sediment supply to the sea and delta intertidal wetland response. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, F03006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Ma, C.; Yu, S.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, M. Palynological evidence of natural and anthropogenic impacts on aquatic environmental changes over the last 150 years in Dongping Lake, North China. Quat. Int. 2014, 349, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Si, Q.; Niu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wen, X.; Lv, Z.; Wang, H.; He, J.; Lv, G.; et al. A quantitative method to infer lake area changes based on an extensive survey of lake surface sediment grain size across the Inner Mongolia Plateau, and its application to understanding the evolution of Lake Wulanhushao in northern China since 18.59 cal. kyr BP. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2024, 641, 112114. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G. Eutrophication control of large shallow lakes in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Dong, X.; Li, Y.; Hong, Q.; Flower, R. Optimizing safe and just operating spaces at sub-watershed scales to guide local environmental management. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 398, 136530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
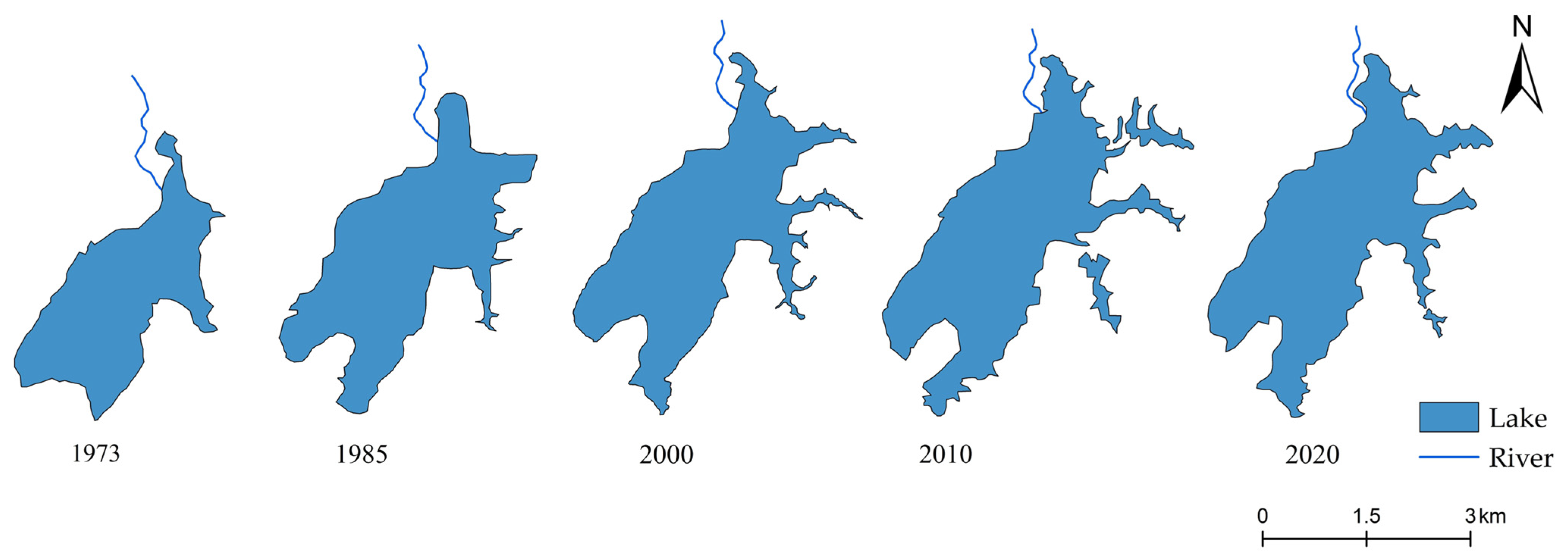
| Date | Lake Area (km2) | Shorelines (km) |
|---|---|---|
| November 2020 | 7.485 | 25.414 |
| November 2010 | 7.551 | 31.979 |
| November 2000 | 6.977 | 25.271 |
| December 1985 | 6.590 | 19.209 |
| December 1973 | 4.812 | 13.749 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Dong, X. Combined Effects of Flood Disturbances and Nutrient Enrichment Prompt Aquatic Vegetation Expansion: Sediment Evidence from a Floodplain Lake. Plants 2025, 14, 2381. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152381
Gu Z, Li Y, Li J, Liu Z, Chen Y, Wang Y, Jeppesen E, Dong X. Combined Effects of Flood Disturbances and Nutrient Enrichment Prompt Aquatic Vegetation Expansion: Sediment Evidence from a Floodplain Lake. Plants. 2025; 14(15):2381. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152381
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Zhuoxuan, Yan Li, Jingxiang Li, Zixin Liu, Yingying Chen, Yajing Wang, Erik Jeppesen, and Xuhui Dong. 2025. "Combined Effects of Flood Disturbances and Nutrient Enrichment Prompt Aquatic Vegetation Expansion: Sediment Evidence from a Floodplain Lake" Plants 14, no. 15: 2381. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152381
APA StyleGu, Z., Li, Y., Li, J., Liu, Z., Chen, Y., Wang, Y., Jeppesen, E., & Dong, X. (2025). Combined Effects of Flood Disturbances and Nutrient Enrichment Prompt Aquatic Vegetation Expansion: Sediment Evidence from a Floodplain Lake. Plants, 14(15), 2381. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152381







