Influence of Rice–Crayfish Co-Culture Systems on Soil Properties and Microbial Communities in Paddy Fields
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Rice–Crayfish Co-Culture Systems on Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.2. Effects of Rice–Crayfish Co-Culture on Soil Nutrient Contents
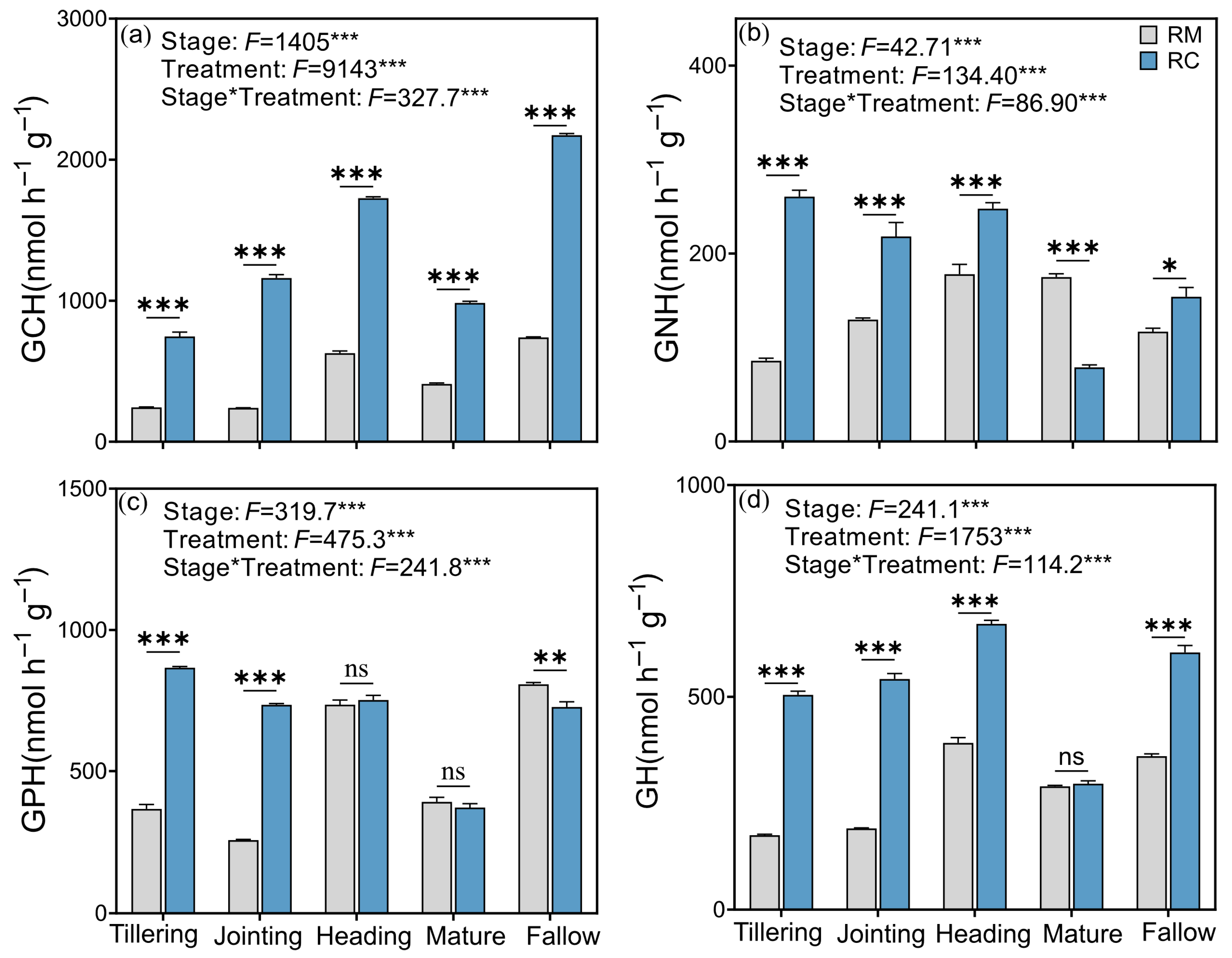
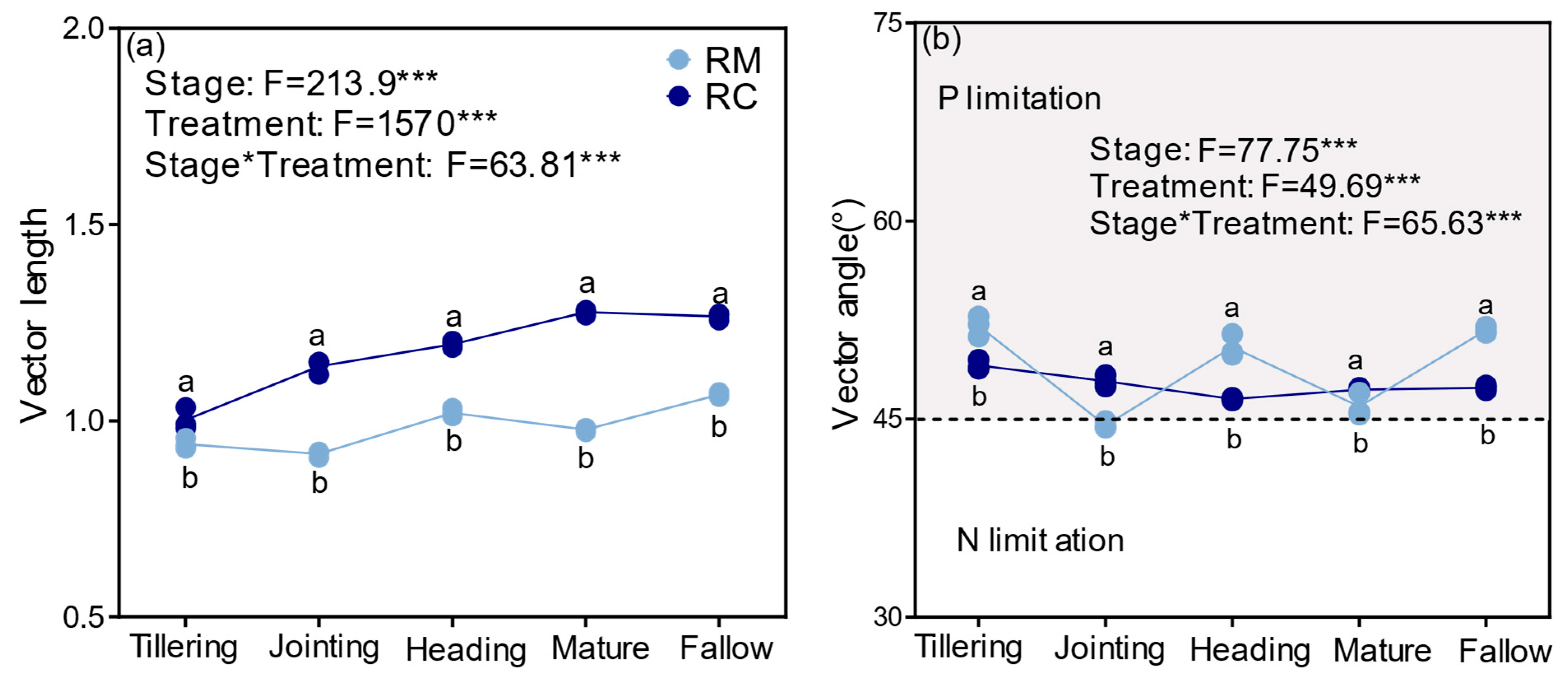
2.3. Effects of the Rice–Crayfish Co-Culture System on Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activities and Vector Characteristics
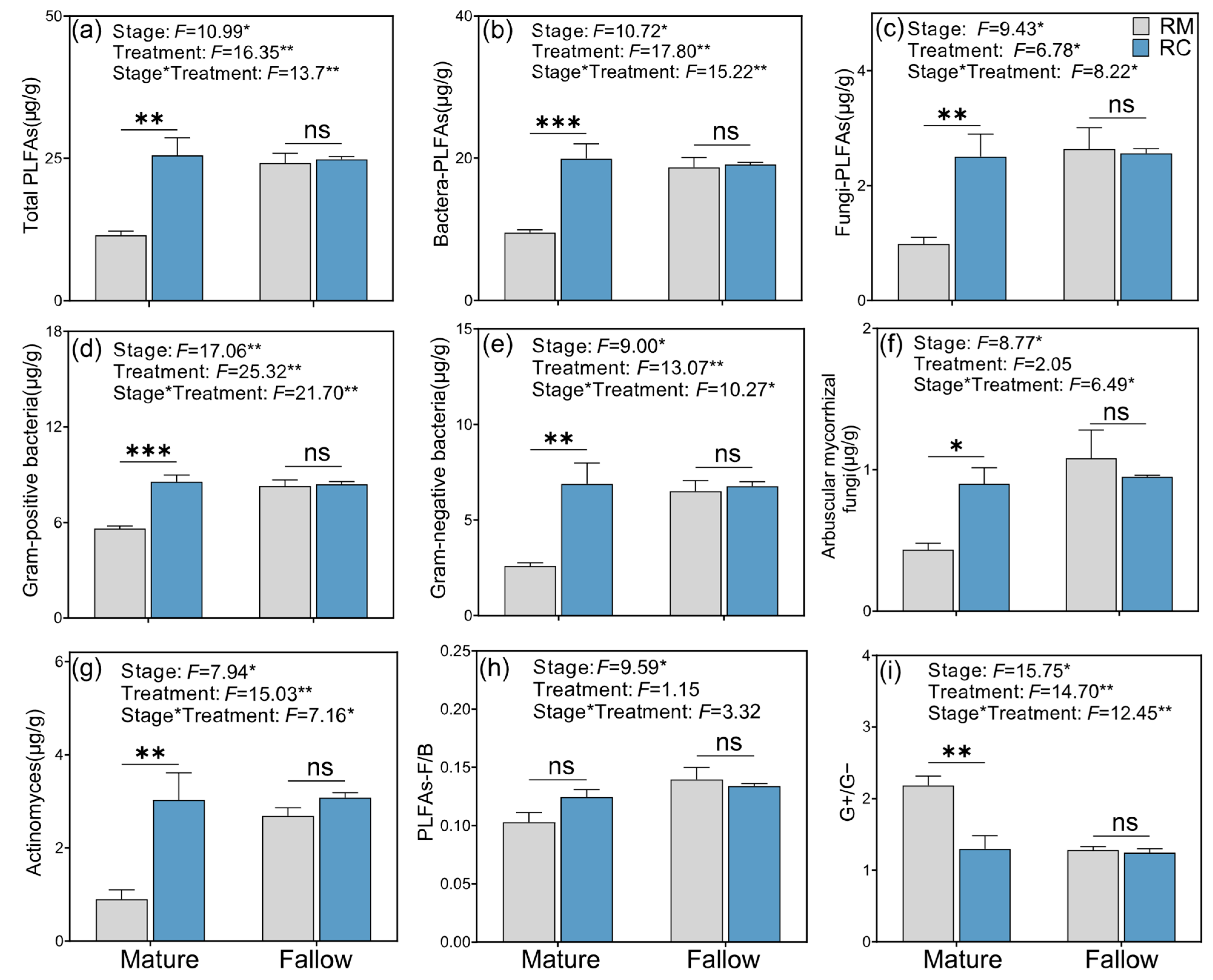
2.4. Effects of Rice–Crayfish Co-Culture System Models on Soil Microbial Phospholipid Fatty Acids (PLFAs)
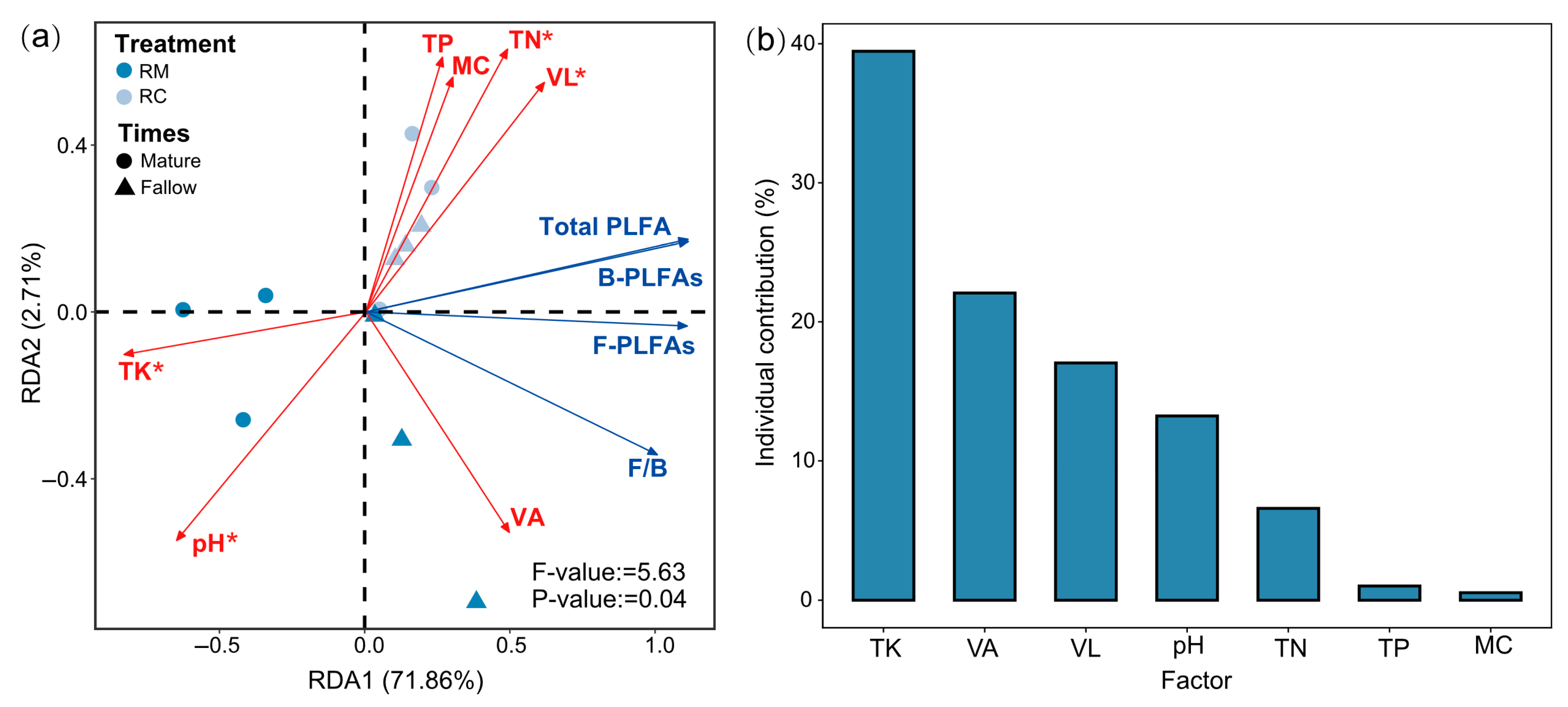
2.5. Effects of Soil Environmental Factors on Microbial Community Composition Under Rice–Crayfish Co-Culture Systems
3. Discussions
3.1. Changes in Soil Physicochemical Properties Under Rice–Crayfish Co-Culture Systems
3.2. Dynamic Changes in Soil Nutrient Availability and Stoichiometry in Rice–Crayfish Systems
3.3. Rice–Crayfish Co-Culture Enhances Soil Enzyme Activities and Alters Microbial Stoichiometric Constraints
3.4. Rice–Crayfish Co-Culture Reshapes Soil Microbial Community Composition and Enhances Biomass
3.5. Effects of Soil Environmental Factors on Microbial Community Composition
4. Materials and Methods
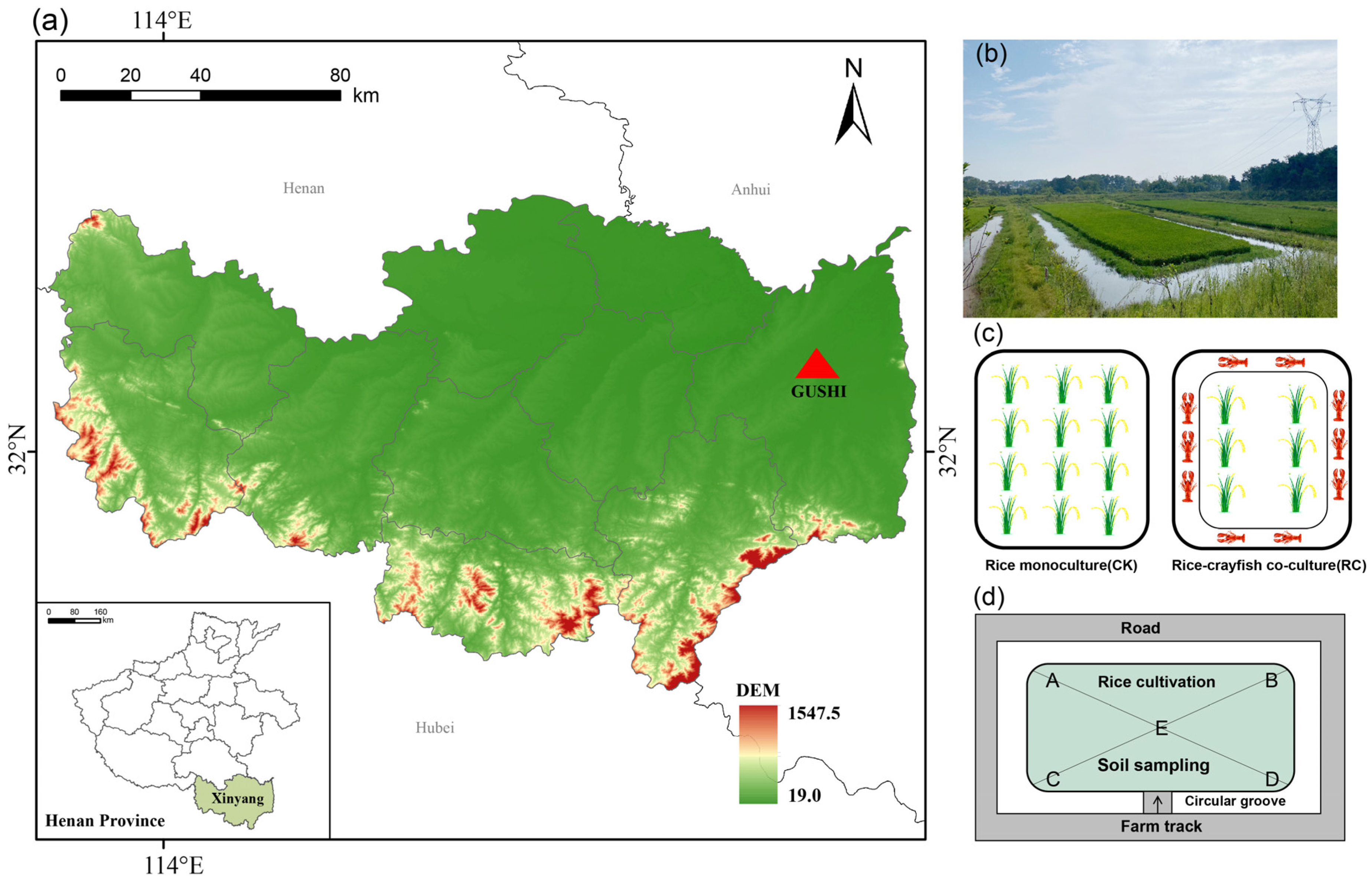
4.1. Site Description
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Sample Collection
4.4. Soil Measurement and Analysis
4.5. Soil Microbial Phospholipid Fatty Acid (PLFA) Analysis
4.6. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Sun, Q.; Khoshnevisan, B.; Zhu, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Pan, J.; Fan, X.; Zhang, D.; Wu, M.; Liu, H. Comprehensive assessment of integrated rice-crayfish farming system as a new paradigm to air-water-food nexus sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 377, 134247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Pan, R.; Hu, H.-W.; Huang, Q.; Zheng, J.; Tan, W.; Liu, Y.-R.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M. Effects of integrated rice-crayfish farming on soil biodiversity and functions. Sci. Bull 2023, 68, 2311–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, M.; Lu, J.; Zhang, H.; Héroux, P.; Wang, G.; Tang, L.; Liu, Y. Evaluating micro-nano bubbles coupled with rice-crayfish co-culture systems: A field study promoting sustainable rice production intensification. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 933, 173162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Schlaeppi, K.; Van Der Heijden, M.G. Keystone taxa as drivers of microbiome structure and functioning. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Hu, L.; Tang, J.; Wu, X.; Li, N. Ecological mechanisms underlying rice–crayfish integrated farming. Agric. Syst. 2020, 180, 102768. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Huang, L.; Zhao, X. Effects of rice–crayfish co-culture on soil health and crop yield: A review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2816. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; He, J. Crayfish activity improves soil quality and nutrient cycling in paddy fields. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 158, 103787. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Lin, X. Integrated rice–aquatic animal farming: A model for sustainable agriculture in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 479–489. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzayakov, Y.; Blagodatskaya, E. Microbial hotspots and hot moments in soil: Concept and review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 83, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Niu, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H. Nutrient status of integrated rice-crayfish system impacts the microbial nitrogen-transformation processes in paddy fields and rice yields. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhao, L.; Ye, J.; Ji, Z.; Tang, J.-J.; Bai, K.; Zheng, S.; Hu, L.; Chen, X. Using aquatic animals as partners to increase yield and maintain soil nitrogen in the paddy ecosystems. elife 2022, 11, 73869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, B.; Ma, M.; Guan, D.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Cao, F.; Shen, D. Thirty four years of nitrogen fertilization decreases fungal diversity and alters fungal community composition in black soil in northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 95, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Oliverio, A.M.; Brewer, T.E.; Benavent-González, A.; Eldridge, D.J.; Bardgett, R.D.; Maestre, F.T.; Singh, B.K.; Fierer, N. A global atlas of the dominant bacteria found in soil. Science 2018, 359, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, G.; Li, Y.; Hu, C.; Ge, L.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Bai, N. Long-term rice-crayfish-turtle co-culture maintains high crop yields by improving soil health and increasing soil microbial community stability. Geoderma 2022, 413, 115745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zheng, H.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jia, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhao, M.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Luo, M. Rice-Fish Co-Culture Promotes Soil Carbon Sequestration Through Alterations in Soil Microbial Community Structure. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.A.; Liu, J.; Geng, Y.; Wang, H.; Pan, J.; Zhang, D.; Rehim, A.; Aon, M.; Liu, H. Co-culture of rice and aquatic animals: An integrated system to achieve production and environmental sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 249, 119310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, P.; Xiong, G.; Wei, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Ning, K. Microbial biogeochemical cycling reveals the sustainability of the rice-crayfish co-culture model. Iscience 2023, 26, 106769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Peng, C.; Si, G.; Sha, A.; Yuan, J.; Zhao, S.; Xu, D.; Liu, W. Effects of straw returning on soil chemical properties and microbial community diversity under the rice-crayfish integrated system. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, J.; Xu, M.; Ma, T.; Lu, J.; Zhu, J.; Ren, T.; Cong, R.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Rice-crayfish farming increases soil organic carbon sequestration by promoting aggregate protection and microbial necromass accumulation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 383, 109519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Guo, P. Microbiome Analysis Reveals Microecological Balance in the Emerging Rice–Crayfish Integrated Breeding Mode. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 669570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, M.; Liu, Q. Effects of reduced nitrogen application rate with increased density on yield and quality of indica-japonica hybrid rice. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2023, 52, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Si, G.; Yuan, J.; Peng, C.; Zhao, S.; Xu, D.; Yu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, J. Mechanism of long-term integrated rice-crayfish farming increasing soil biological fertility of paddy fields. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2020, 26, 2168–2176. [Google Scholar]
- Si, G.; Yuan, J.; Peng, C.; Xia, X.; Cheng, J.; Xu, X.; Jia, P.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, J. Nitrogen and phosphorus cycling characteristics and balance of the integrated rice-crayfish system. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2019, 27, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Du, L.; Xiao, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, P.; Sun, G.; Ye, Y.; Hu, T.; Wang, H. Rice-crayfish farming increases soil organic carbon. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 329, 107857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Hao, X.; Chen, W.; Luo, X.; Huang, Q. Rice-crayfish co-culture increases microbial necromass’ contribution to the soil nitrogen pool. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunrat, N.; Sansupa, C.; Kongsurakan, P.; Sereenonchai, S.; Hatano, R. Soil microbial diversity and community composition in rice–fish co-culture and rice monoculture farming system. Biology 2022, 11, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, C.; Xu, R.; Yang, T.; Han, G.; Wu, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, Q.; Kou, X. Slow-release nitrogen fertilizer reduces input without yield loss in a rice-crayfish integrated system. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2024, 128, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, G.; Yuan, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, S.; Peng, C.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Z. Effects of an integrated rice-crayfish farming system on soil organic carbon, enzyme activity, and microbial diversity in waterlogged paddy soil. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Cao, C. Crayfish–rice integrated system of production: An agriculture success story in China. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 41, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.-F.; Li, B.; Yu, Z.-X.; Hou, Y.-R.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J. Effects of rice-crayfish integrated model on root exudates and microorganisms of rice during grain filling. J. Fish. China 2022, 46, 2122–2133. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Li, C.; Tan, W.; Wang, J.; Feng, J.; Hu, Q.; Cao, C. Rice-crayfish co-culture reduces ammonia volatilization and increases rice nitrogen uptake in central China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 330, 107869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, G.-H.; Peng, C.-L.; Yuan, J.-F.; Xia, X.-G.; Cheng, J.-P.; Xu, X.-Y.; Jia, P.-A.; Xie, Y.-Y.; Zhou, J.-X. Effect of rice straw returning to field on ammonia volatilization in paddy fields under the integrated rice-crayfish system. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2021, 37, 360–368. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Chen, T.; Liu, C.; Zhang, F.; Sun, Y.; Bai, Y.; Meng, J.; Chi, D.; Chen, W. Effects of acid modified biochar on potassium uptake, leaching and balance in an alternate wetting and drying paddy ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 166344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Cheng, M.; Kumar, U.; Maniruzzaman, M.; Nasreen, S.; Haque, M.; Jahiruddin, M.; Bell, R.; Jahangir, M. Conservation agriculture in intensive rice cropping reverses soil potassium depletion. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2023, 125, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ji, L.; Cheng, M.; Wei, H.; Wang, Z.; Ning, K. Sustainability of the rice-crayfish co-culture aquaculture model: Microbiome profiles based on multi-kingdom analyses. Environ. Microbiome 2022, 17, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Shaaban, M.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Sun, G.; Yu, Y.; Xiao, Z. Effects of long-term rice-crayfish farming on soil CNP storage and stoichiometry. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 235, 105882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Bradford, M.A. Soil-carbon response to warming dependent on microbial physiology. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Han, S.; Se, J.; Tang, S.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Wu, L. Crop rotation stage has a greater effect than fertilisation on soil microbiome assembly and enzymatic stoichiometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, G.; Peng, C.; Yuan, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, S.; Xu, D.; Wu, J. Changes in soil microbial community composition and organic carbon fractions in an integrated rice–crayfish farming system in subtropical China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Jia, Q.; Sun, D.; Huang, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X. Rice–fish coculture incorporating spent mushroom substrate substitution alleviated microbial metabolism limitation reflected by soil extracellular enzymatic stoichiometry. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 1434–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.; Huang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Wan, T.; Jiang, C.; Dai, Z.; Xiong, S.; Cao, M.; Tu, S. Silicone stressed response of crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) in antioxidant enzyme activity and related gene expression. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 115836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xu, L.; Xu, L.; Qian, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y. Influence of consecutive integrated rice–crayfish culture on phosphorus fertility of paddy soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3413–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, J. Nutrient accumulation from excessive nutrient surplus caused by shifting from rice monoculture to rice–crayfish rotation. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, H.; Chen, G.; Cheng, W.; Shen, Y. Effects of long-term rice–crayfish coculture systems on soil nutrients, carbon pools, and rice yields in Northern Zhejiang province, China. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Z. Cultivating crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) significantly enhances the quantity and diversity of soil microorganisms: Evidence from the comparison of rice-wheat and rice-crayfish rotation models. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1528883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, J.; Wan, W.; Xu, Z.; Hu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Gu, Z. The microbiome structure of a rice-crayfish integrated breeding model and its association with crayfish growth and water quality. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, 02204–02221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Mi, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Bi, Y. Long-term integrated rice-crayfish culture disrupts the microbial communities in paddy soil. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 29, 101515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jing, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Lu, H. Responses of soil microbial community structure changes and activities to biochar addition: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Du, X.; Qin, Z.; Liu, Q.; Pan, F. Integrated Rice-Snail-Crayfish Farming System Shapes Soil Microbial Community by Enhancing pH and Microbial Biomass in South Subtropical China. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, G.; Peng, C.; Xu, X.; Xu, D.; Yuan, J.; Li, J. Effect of integrated rice-crayfish farming system on soil physico-chemical properties in waterlogged paddy soils. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2017, 25, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liu, T.; Du, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Cao, C. Long-term rice–crayfish coculture increases plant lignin but not microbial necromass contribution to soil organic carbon. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 248, 106424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Hao, L.; Dai, L.; Tao, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, G.; Zhu, J. Rice-crayfish farming enhances soil organic carbon by increasing labile organic carbon and altering microbial functions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 206, 105901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Cao, C. Long-term rice–crayfish farming aggravates soil gleying and induced changes of soil iron morphology. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buresh, R.J.; Pampolino, M.F.; Witt, C. Field-specific potassium and phosphorus balances and fertilizer requirements for irrigated rice-based cropping systems. Plant Soil 2010, 335, 35–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Qin, H.; Wang, J.; Yao, D.; Zhang, L.; Guo, J.; Zhu, B. Immediate response of paddy soil microbial community and structure to moisture changes and nitrogen fertilizer application. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1130298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Zeng, Q.; Mei, T.; Zhang, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, M.; Tan, W. Disentangling drivers of soil microbial nutrient limitation in intensive agricultural and natural ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Wei, S.; Chen, H. Effects of different fertilization patterns on the dietary composition of Procambarus clarkii in a rice-crayfish coculture system. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 33, 101801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.C.; Landman, A.; Pruden, G.; Jenkinson, D.S. Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: A rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil—ScienceDirect. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1985, 17, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Dang, P.; Gao, X.; Xu, Y.; He, T.; Liu, Z.; Yan, W. Nitrogen availability and its related enzyme activities affect microbial residue nitrogen accumulation during Chinese fir plantation development. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 202, 105555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossio, D.A.; Scow, K.M. Impacts of Carbon and Flooding on Soil Microbial Communities: Phospholipid Fatty Acid Profiles and Substrate Utilization Patterns. Microb. Ecol. 1998, 35, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Stage | Treatment | MC | SP | BD | pH | SOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tillering | RM | 0.53 ± 0.02 b | 56.66 ± 0.43 b | 1.15 ± 0.01 a | 6.45 ± 0.24 a | 3.59 ± 0.17 b |
| RC | 0.69 ± 0.01 a | 62.08 ± 0.89 a | 1.01 ± 0.02 b | 6.62 ± 0.05 a | 7.03 ± 0.59 a | |
| Jointing | RM | 0.47 ± 0.01 b | 52.88 ± 1.32 b | 1.25 ± 0.03 a | 6.8 ± 0.07 a | 3.91 ± 0.06 b |
| RC | 0.55 ± 0.01 a | 61.08 ± 1.22 a | 0.99 ± 0.05 b | 5.87 ± 0.09 b | 11.72 ± 0.13 a | |
| Heading | RM | 0.47 ± 0.03 b | 54.23 ± 0.48 b | 1.21 ± 0.01 a | 6.92 ± 0.06 a | 4.09 ± 0.36 b |
| RC | 0.53 ± 0.01 a | 58.49 ± 0.87 a | 1.1 ± 0.02 a | 5.54 ± 0.28 b | 13.61 ± 0.45 a | |
| Mature | RM | 0.37 ± 0.01 b | 59.17 ± 1.1 b | 1.07 ± 0.04 a | 6.94 ± 0.02 a | 4.17 ± 0.42 b |
| RC | 0.52 ± 0.03 a | 64.27 ± 0.64 a | 0.91 ± 0.04 b | 6.04 ± 0.1 b | 12.19 ± 0.64 a | |
| Fallow | RM | 0.31 ± 0.01 b | 49.43 ± 0.77 b | 1.34 ± 0.02 a | 6.44 ± 0.15 a | 4.32 ± 0.23 b |
| RC | 0.43 ± 0.01 a | 56.16 ± 0.38 a | 1.16 ± 0.01 b | 6.03 ± 0.05 a | 11.26 ± 0.26 a | |
| ANOVA | ||||||
| Stage, S | *** | *** | *** | ns | *** | |
| Treatment, T | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| S × T | *** | ns | ns | *** | *** | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, D.; He, D.; Zhao, L.; Tan, C.; Yang, D.; Yan, W.; Wang, G.; Chen, X. Influence of Rice–Crayfish Co-Culture Systems on Soil Properties and Microbial Communities in Paddy Fields. Plants 2025, 14, 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152320
Duan D, He D, Zhao L, Tan C, Yang D, Yan W, Wang G, Chen X. Influence of Rice–Crayfish Co-Culture Systems on Soil Properties and Microbial Communities in Paddy Fields. Plants. 2025; 14(15):2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152320
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Dingyu, Dingxuan He, Liangjie Zhao, Chenxi Tan, Donghui Yang, Wende Yan, Guangjun Wang, and Xiaoyong Chen. 2025. "Influence of Rice–Crayfish Co-Culture Systems on Soil Properties and Microbial Communities in Paddy Fields" Plants 14, no. 15: 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152320
APA StyleDuan, D., He, D., Zhao, L., Tan, C., Yang, D., Yan, W., Wang, G., & Chen, X. (2025). Influence of Rice–Crayfish Co-Culture Systems on Soil Properties and Microbial Communities in Paddy Fields. Plants, 14(15), 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152320






