Mitigation of Cadmium and Copper Stress in Lettuce: The Role of Biochar on Metal Uptake, Oxidative Stress, and Yield
Abstract
1. Introduction
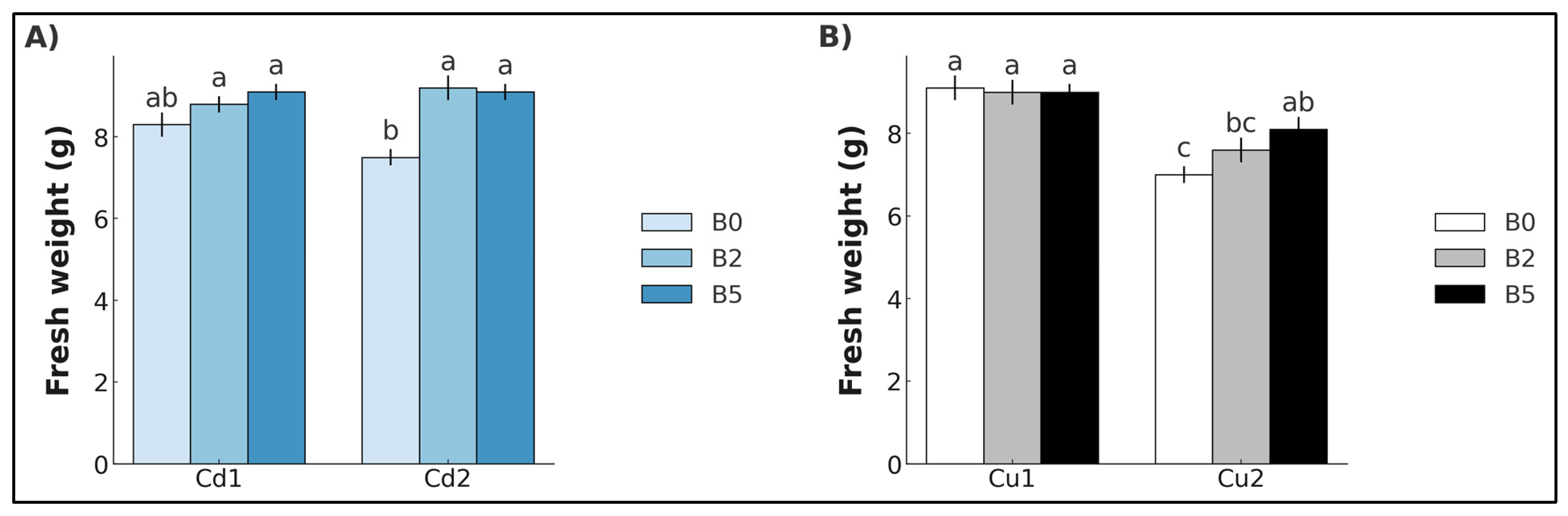
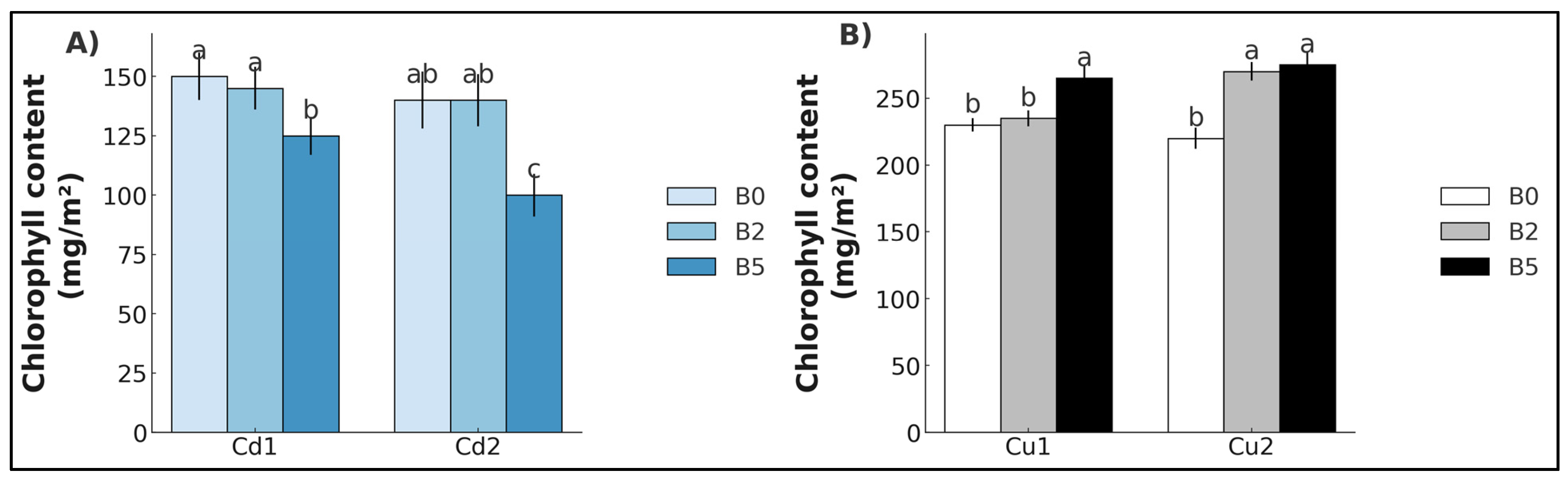
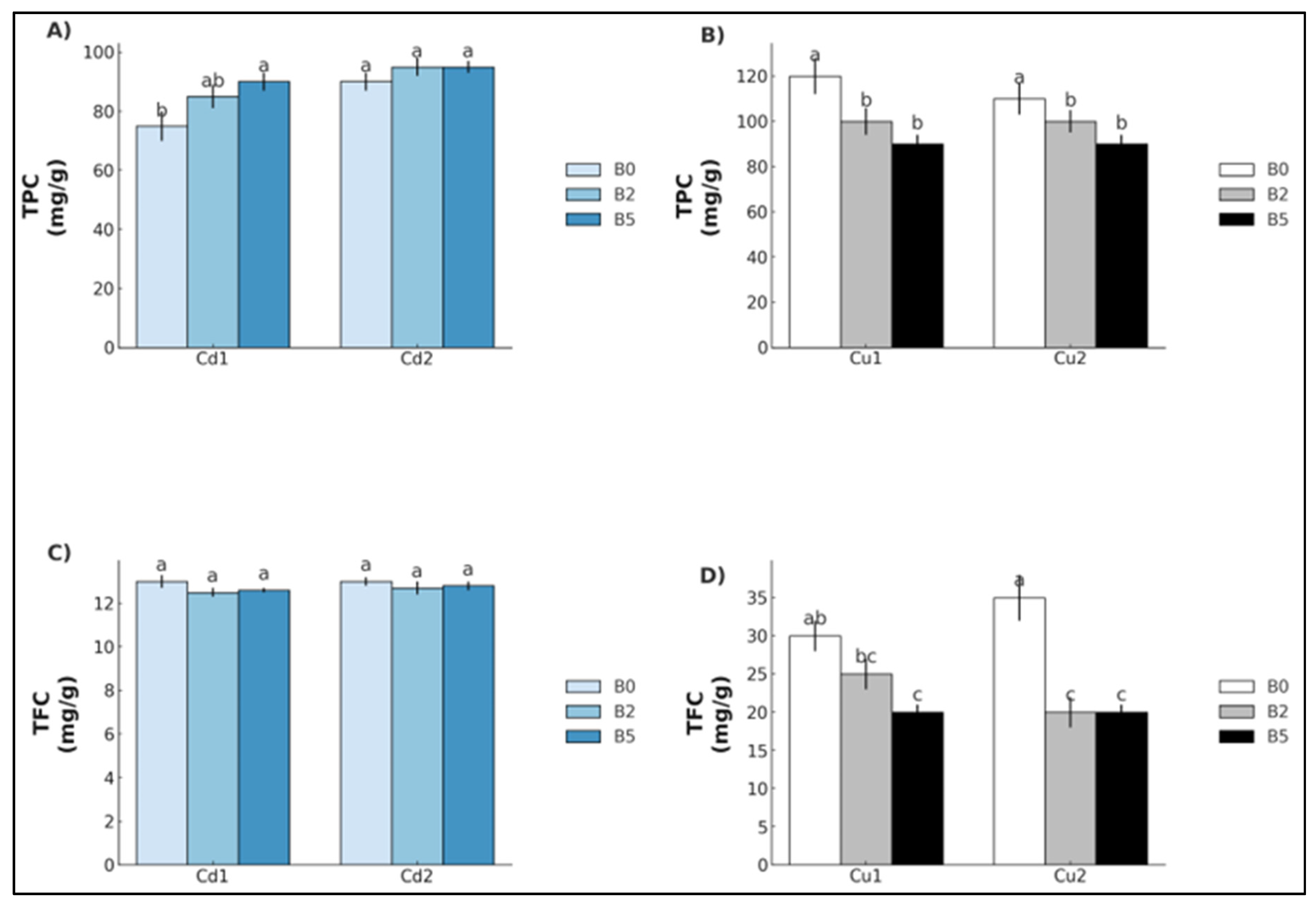
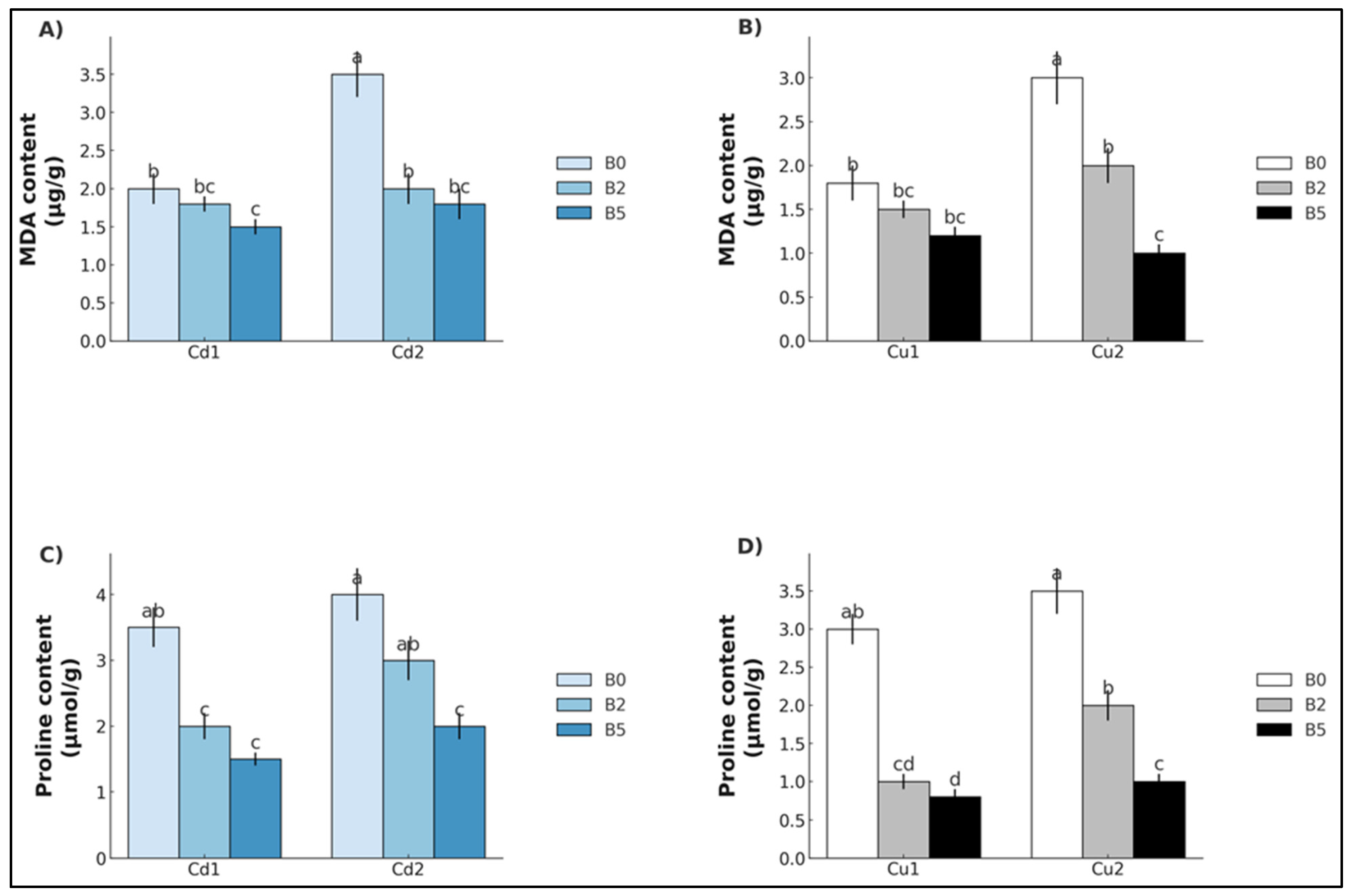
2. Results
3. Discussion
3.1. Cadmium
3.2. Copper
4. Materials and Methods
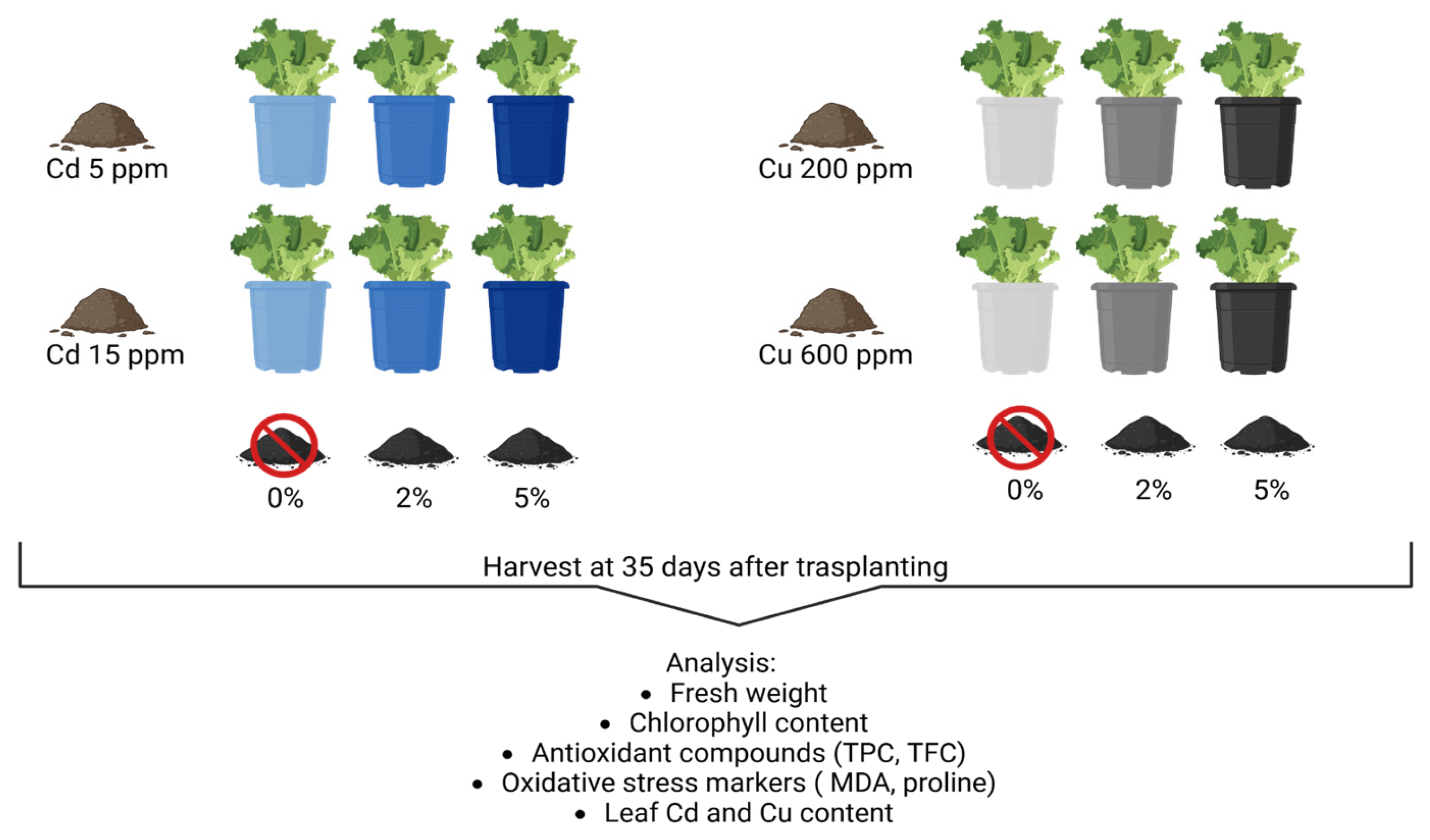
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Chlorophyll Content
4.3. Antioxidant Compounds
4.3.1. Total Phenolic Content
4.3.2. Total Flavonoid Content
4.4. Oxidative Stress Markers
4.4.1. Malondialdehyde
4.4.2. Proline
4.5. Cd and Cu Determination
4.5.1. Cadmium
4.5.2. Copper
4.6. Bioaccumulation Factor and Immobilization Index
- Leaf [M] = content (mg/kg) of Cd or Cu in lettuce leaves;
- Soil [M] = initial concentration (mg/kg) of Cd or Cu in the soil.
- [M]Control = content (mg/kg) of Cd or Cu in leaves from lettuce plants grown in unamended soil (B0);
- [M]Sample = content (mg/kg) of Cd or Cu in leaves from lettuce plants grown in biochar-amended soils (B2 and B5).
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mishra, S.; Bharagava, R.N.; More, N.; Yadav, A.; Zainith, S.; Mani, S.; Chowdhary, P. Heavy metal contamination: An alarming threat to environment and human health. In Environmental Biotechnology: For Sustainable Future; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2019; pp. 103–125. [Google Scholar]
- Alengebawy, A.; Abdelkhalek, S.T.; Qureshi, S.R.; Wang, M.Q. Heavy metals and pesticides toxicity in agricultural soil and plants: Ecological risks and human health implications. Toxics 2021, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, M.T.; Nauman, M.; Nazir, N.; Ali, S.; Bangash, N. Environmental hazards of cadmium: Past, present, and future. In Cadmium Toxicity and Tolerance in Plants; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 163–183. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, M.; Liu, L.; Wang, Q.; Saleem, M.H.; Bashir, S.; Ullah, S.; Peng, D. Copper environmental toxicology, recent advances, and future outlook: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 18003–18016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulfiqar, U.; Ayub, A.; Hussain, S.; Waraich, E.A.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Ishfaq, M.; Maqsood, M.F. Cadmium toxicity in plants: Recent progress on morpho-physiological effects and remediation strategies. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 212–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järup, L.; Åkesson, A. Current status of cadmium as an environmental health problem. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopoulos, G.; Roy, A.; Yonone-Lioy, M.J.; Opiekun, R.E.; Lioy, P.J. Environmental copper: Its dynamics and human exposure issues. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B 2001, 4, 341–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonthula, S.; Bonthula, S.R.; Pothu, R.; Srivastava, R.K.; Boddula, R.; Radwan, A.B.; Al-Qahtani, N. Recent advances in copper-based materials for sustainable environmental applications. Sustain. Chem. 2023, 4, 246–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, R.M.; Shuman, L. Micronutrient nutrition of plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1995, 14, 49–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, A.R.; Pichtel, J.; Hayat, S. Copper: Uptake, toxicity and tolerance in plants and management of Cu-contaminated soil. Biometals 2021, 34, 737–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Gu, J.; Gao, H.; Qin, Q.; Chen, Z.; Shao, L.; Liu, J. Effects of Cu on metabolisms and enzyme activities of microbial communities in the process of composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 108, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louekari, K.; Mäkelä-Kurtto, R.; Pasanen, J.; Virtanen, V.; Sippola, J.; Malm, J. Cadmium in fertilizers. Risk to human health and the environment. Maa-Ja Metsätalousministeriö 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Suhani, I.; Sahab, S.; Srivastava, V.; Singh, R.P. Impact of cadmium pollution on food safety and human health. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2021, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, A.; Abbey, L.; Gunupuru, L.R. Production, prospects and potential application of pyroligneous acid in agriculture. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 135, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Lu, L.; He, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, Y. Applications of biochar and modified biochar in heavy metal contaminated soil: A descriptive review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 14041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.M.; Panda, S.S.; Dhal, N.K. Biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for heavy metal removal: A review. Int. J. Res. Biosci. 2017, 6, 105081. [Google Scholar]
- Tomczyk, A.; Sokołowska, Z.; Boguta, P. Biochar physicochemical properties: Pyrolysis temperature and feedstock kind effects. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio Technol. 2020, 19, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Toor, G.S.; Zhang, X. Biochar increased immobilization of Cu in contaminated soils: Evidence from soil chemical properties and microbial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 784–793. [Google Scholar]
- Fedeli, R.; Celletti, S.; Alexandrov, D.; Nafikova, E.; Loppi, S. Biochar-mediated bioremediation: A sustainable strategy to increase Avena sativa L. tolerance to crude oil soil contamination. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 52774–52783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.P.; Li, Z.A.; Gasco, G.; Mendez, A.; Shen, Y.; Paz-Ferreiro, J. Use of magnetic biochars for the immobilization of heavy metals in a multi-contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.F.; Zhu, S.S.; Wang, R.P.; Chen, Y.D.; Show, P.L.; Zhang, F.F.; Ho, S.H. Role of biochar surface characteristics in the adsorption of aromatic compounds: Pore structure and functional groups. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 2939–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekiya, A.O.; Olayanju, T.M.A.; Ejue, S.W.; Alori, E.T.; Adegbite, K.A. Contribution of biochar in improving soil health. Soil Health 2020, 99, 99–113. [Google Scholar]
- Razzaghi, F.; Obour, P.B.; Arthur, E. Does biochar improve soil water retention? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Geoderma 2020, 361, 114055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, U.E.; Toluwase, A.O.; Kehinde, E.O.; Omasan, E.E.; Tolulope, A.Y.; George, O.O.; Hongyan, W. Effect of biochar on soil structure and storage of soil organic carbon and nitrogen in the aggregate fractions of an Albic soil. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2020, 66, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Fan, X.; Khan, M.N.; Khan, M.A.; Zhang, K.; Fu, Y.; Shen, H. The toxicity of heavy metals and plant signaling facilitated by biochar application: Implications for stress mitigation and crop production. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ippolito, J.A.; Cui, L.; Kammann, C.; Wrage-Mönnig, N.; Estavillo, J.M.; Fuertes-Mendizabal, T.; Borchard, N. Feedstock choice, pyrolysis temperature and type influence biochar characteristics: A comprehensive meta-data analysis review. Biochar 2020, 2, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decreto Legislativo. Available online: https://www.normattiva.it/uri-res/N2Ls?urn:nir:stato:decreto.legislativo:2006-04-03;152 (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Decreto Legislativo. Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/id/2019/06/07/19G00052/sg (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Lux, A.; Martinka, M.; Vaculík, M.; White, P.J. Root responses to cadmium in the rhizosphere: A review. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Rasafi, T.; Oukarroum, A.; Haddioui, A.; Song, H.; Kwon, E.E.; Bolan, N.; Rinklebe, J. Cadmium stress in plants: A critical review of the effects, mechanisms, and tolerance strategies. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 675–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, D.; Couder, E.; Sonnet, P. Leachability of cadmium, lead, and zinc in a long-term spontaneously revegetated slag heap: Implications for phytostabilization. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samartini Queiroz Alves, B.; Arnaldo Fernandes, L.; Southard, R.J. Evaluating cadmium uptake in spinach using unoxidized, oxidized biochars, zinc, compost or lime. Randal J. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3969709 (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, L.; Wu, H.; Li, J.; Kong, L.; Yang, H. Effects of applying biochar on soil cadmium immobilisation and cadmium pollution control in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Agriculture 2024, 14, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Zhang, R.H. Decreasing surface chlorophyll in the tropical ocean as an indicator of anthropogenic greenhouse effect during 1998–2020. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 084019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.S.; Dietz, K.J. The relationship between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ba, Q.; Chen, S.; Liu, F.; Li, G. Exogenous application of glycine betaine alleviates cadmium toxicity in super black waxy maize by improving photosynthesis, the antioxidant system and glutathione-ascorbic acid cycle metabolites. Cereal Res. Commun. 2020, 48, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Dong, X.; Park, J. Adsorption characteristics of cadmium ions from aqueous solution onto pine sawdust biomass and biochar. BioResources 2019, 14, 4270–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismael, M.A.; Elyamine, A.M.; Moussa, M.G.; Cai, M.; Zhao, X.; Hu, C. Cadmium in plants: Uptake, toxicity, and its interactions with selenium fertilizers. Metallomics 2019, 11, 255–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandara, T.; Franks, A.; Xu, J.; Chathurika, J.B.A.J.; Tang, C. Biochar aging alters the bioavailability of cadmium and microbial activity in acid contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wu, D.; Yang, J.; Shi, Y.; Abid, G.; Wang, L.; Li, Z. A biochar-based amendment improved cadmium (Cd) immobilization, reduced its bioaccumulation, and increased rice yield. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1487190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=LEGISSUM:4707404 (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, G. Comparative efficacies of iron oxide-modified biochar and pyrite-modified biochar for simultaneous passivation of cadmium and arsenic in aqueous solutions and lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) cultivation. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2025, 68, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ur Rehman, M.Z.; Waqar, M.; Bashir, S.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; El Baroudy, A.A.E.F.; Jahan, S. Effect of biochar and compost on cadmium bioavailability and its uptake by wheat–rice cropping system irrigated with untreated sewage water: A field study. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yruela, I. Copper in plants: Acquisition, transport and interactions. Funct. Plant Biol. 2009, 36, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wairich, A.; De Conti, L.; Lamb, T.I.; Keil, R.; Neves, L.O.; Brunetto, G.; Ricachenevsky, F.K. Throwing copper around: How plants control uptake, distribution, and accumulation of copper. Agronomy 2022, 12, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, W.; Mašek, O.; Graham, M. Inorganic carbon controls on the reactivity of biochar in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 53, 56–65. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, S.; Curaqueo, G.; Khan, N.; Cea, M.; Navia, R.; Diez, M.C. Chicken-manure-derived biochar reduced Cu bioavailability and enhanced plant growth in contaminated soils. Agronomy 2017, 11, 993. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.S.; Tang, C.S.; Gu, K.; Shi, B. Remediation of heavy-metal-contaminated soils by biochar: A review. Environ. Geotech. 2019, 9, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Nguy-Robertson, A.; Arkebauer, T.; Gitelson, A.A. Assessment of canopy chlorophyll content retrieval in maize and soybean: Implications of hysteresis on the development of generic algorithms. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zada, J.; Hazrat, A.; Ullah, S.; Nafees, M. Ameliorative effect of brassinosteroids and biochar on morpho-physiological attributes of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) under induced drought stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 128997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xie, G.; Qin, M. Copper stress-induced changes in biomass accumulation, antioxidant activity and flavonoid contents in Belamcanda chinensis calli. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2020, 142, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartacci, M.F.; Sgherri, C.; Frisenda, S. Biochar amendment affects phenolic composition and antioxidant capacity restoring the nutraceutical value of lettuce grown in a copper-contaminated soil. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 215, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Tanvir, B.; Xiukang, W.; Brtnicky, M.; Ditta, A.; Kucerik, J.; Mustafa, A. Co-composted biochar enhances growth, physiological, and phytostabilization efficiency of Brassica napus and reduces associated health risks under chromium stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 775785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, M.M.; Lee, J.; Thiele, D.J. A delicate balance: Homeostatic control of copper uptake and distribution. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Szteke, B. Trace Elements in Abiotic and Biotic Environments; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 2015; p. 468. [Google Scholar]
- Salmani, M.S.; Khorsandi, F.; Yasrebi, J.; Karimian, N. Effects of biochar on sunflower yield and some soil properties in a copper contaminated calcareous soil. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2014, 8, 2310–2314. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, F.; González, M.E.; Khan, N.; Curaqueo, G.; Sanchez-Monedero, M.; Rilling, J.; Meier, S. Copper immobilization by biochar and microbial community abundance in metal-contaminated soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umaira Shams, H.; Nazneen, S.; Khan, S.; Ali, N. Role of poultry manure and corn cob biochar in reducing ozone-induced damage to chili plant (Capsicum annuum L.). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2025, 236, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedeli, R.; Cruz, C.; Loppi, S.; Munzi, S. Hormetic effect of wood distillate on hydroponically grown lettuce. Plants 2024, 13, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedeli, R.; Celletti, S.; Loppi, S. Wood distillate promotes the tolerance of lettuce in extreme salt stress conditions. Plants 2024, 13, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakeel, A.; Jan, S.A.; Ullah, I.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Xu, M. Solvent polarity mediates phytochemical yield and antioxidant capacity of Isatis tinctoria. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedeli, R.; Mazza, I.; Perini, C.; Salerni, E.; Loppi, S. New frontiers in the cultivation of edible fungi: The application of biostimulants enhances the nutritional characteristics of Pleurotus eryngii (DC.) Quél. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedeli, R.; Loppi, S.; Cruz, C.; Munzi, S. Evaluating seawater and wood distillate for sustainable hydroponic cultivation: Implications for crop growth and nutritional quality. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarnejad, N.; Celletti, S.; Ghorbani, M.; Fedeli, R.; Loppi, S. Dose-dependent effects of a corn starch-based bioplastic on basil (Ocimum basilicum L.): Implications for growth, biochemical parameters, and nutrient content. Toxics 2024, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedeli, R.; Zhatkanbayeva, Z.; Loppi, S. Wood Distillate as a Solution for Growing Crops Under Water Deficiency. Crops 2025, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamaro, G.P.; Tsehaye, Y.; Girma, A.; Vannini, A.; Fedeli, R.; Loppi, S. Essential mineral elements and potentially toxic elements in orange-fleshed sweet potato cultivated in northern Ethiopia. Biology 2023, 12, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedeli, R.; Di Lella, L.A.; Loppi, S. Suitability of XRF for routine analysis of multi-elemental composition: A multi-standard verification. Methods Protoc. 2024, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedeli, R.; Zhatkanbayeva, Z.; Loppi, S. Soil amendment with biochar from slaughterhouse waste bones enhances soil quality and promotes the growth of crop plants. Plant Biosyst.-Int. J. Deal. All Asp. Plant Biol. 2025, 159, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Lim, J.E.; El-Azeem, S.A.A.; Choi, B.; Oh, S.E.; Moon, D.H.; Ok, Y.S. Heavy metal immobilization in soil near abandoned mines using eggshell waste and rapeseed residue. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifin, A.; Parisa, A.; Hazandy, A.H.; Mahmud, T.M.; Junejo, N.; Fatemeh, A.; Majid, N.M. Evaluation of cadmium bioaccumulation and translocation by Hopea odorata grown in a contaminated soil. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 7472–7482. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2025; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 12 January 2025).
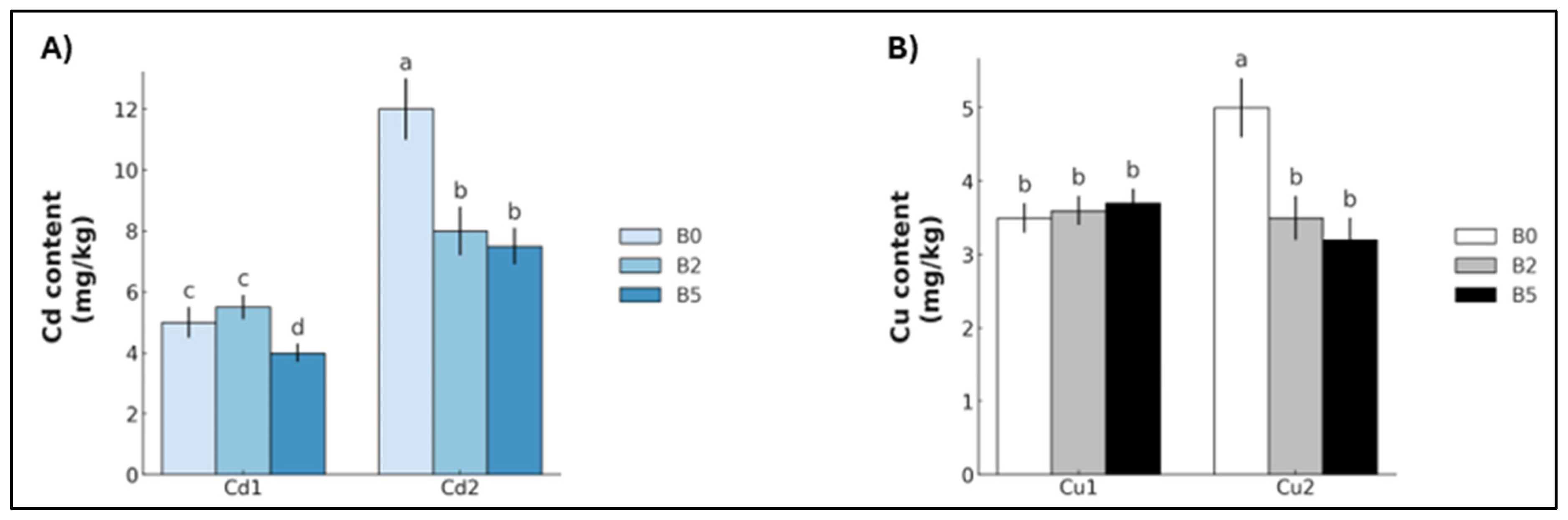
| BAF | ||||
| Cd1 | Cd2 | Cu1 | Cu2 | |
| B0 | 1.10 ± 0.10 a | 0.76 ± 0.07 b | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 0.008 ± 0.001 b |
| B2 | 1.04 ± 0.08 a | 0.54 ± 0.05 c | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 0.005 ± 0.001 c |
| B5 | 0.75 ± 0.06 b | 0.56 ± 0.05 c | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 0.005 ± 0.001 c |
| II (%) | ||||
| Cd1 | Cd2 | Cu1 | Cu2 | |
| B0 | - | - | - | - |
| B2 | 5.46 | 29.80 | 2.98 | 27.1 |
| B5 | 31.89 | 27.02 | 1.85 | 34.1 |
| Particle diameter (µm) | <200 |
| Total N (%) | <0.4 |
| Total K (mg kg−1) | 3020 |
| Total P (mg kg−1) | 340 |
| Total Ca (mg kg−1) | 9920 |
| Total Mg (mg kg−1) | 852 |
| Total Na (mg kg−1) | 291 |
| C from carbonate (%) | <0.1 |
| Total Cd (mg kg−1) | <1 |
| Total Cu (mg kg−1) | 30 |
| Total C (%) | 68.7 |
| WHC (%) | 23.5 |
| Salinity (mS m−1) | 110 |
| pH | 9.9 |
| Hash content (%) | 4.6 |
| H/C | 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fedeli, R.; Zhatkanbayeva, Z.; Marcelli, R.; Zhatkanbayev, Y.; Desideri, S.; Loppi, S. Mitigation of Cadmium and Copper Stress in Lettuce: The Role of Biochar on Metal Uptake, Oxidative Stress, and Yield. Plants 2025, 14, 2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152255
Fedeli R, Zhatkanbayeva Z, Marcelli R, Zhatkanbayev Y, Desideri S, Loppi S. Mitigation of Cadmium and Copper Stress in Lettuce: The Role of Biochar on Metal Uptake, Oxidative Stress, and Yield. Plants. 2025; 14(15):2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152255
Chicago/Turabian StyleFedeli, Riccardo, Zhanna Zhatkanbayeva, Rachele Marcelli, Yerlan Zhatkanbayev, Sara Desideri, and Stefano Loppi. 2025. "Mitigation of Cadmium and Copper Stress in Lettuce: The Role of Biochar on Metal Uptake, Oxidative Stress, and Yield" Plants 14, no. 15: 2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152255
APA StyleFedeli, R., Zhatkanbayeva, Z., Marcelli, R., Zhatkanbayev, Y., Desideri, S., & Loppi, S. (2025). Mitigation of Cadmium and Copper Stress in Lettuce: The Role of Biochar on Metal Uptake, Oxidative Stress, and Yield. Plants, 14(15), 2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152255








