Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics of Plant–Litter–Soil Among Different Forest Stands in a Limestone Region of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
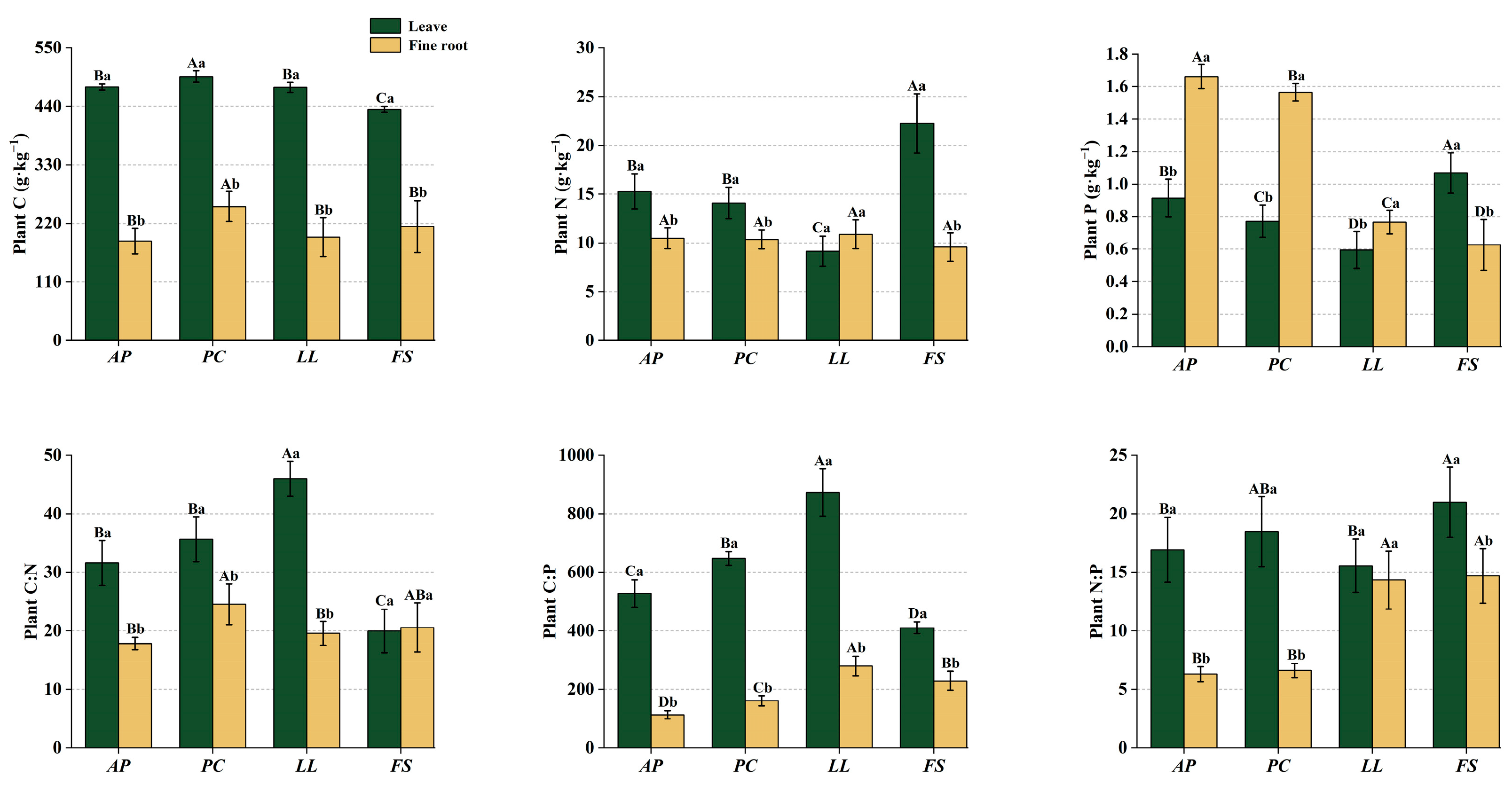
2.1. Ecological Stoichiometry in Plants
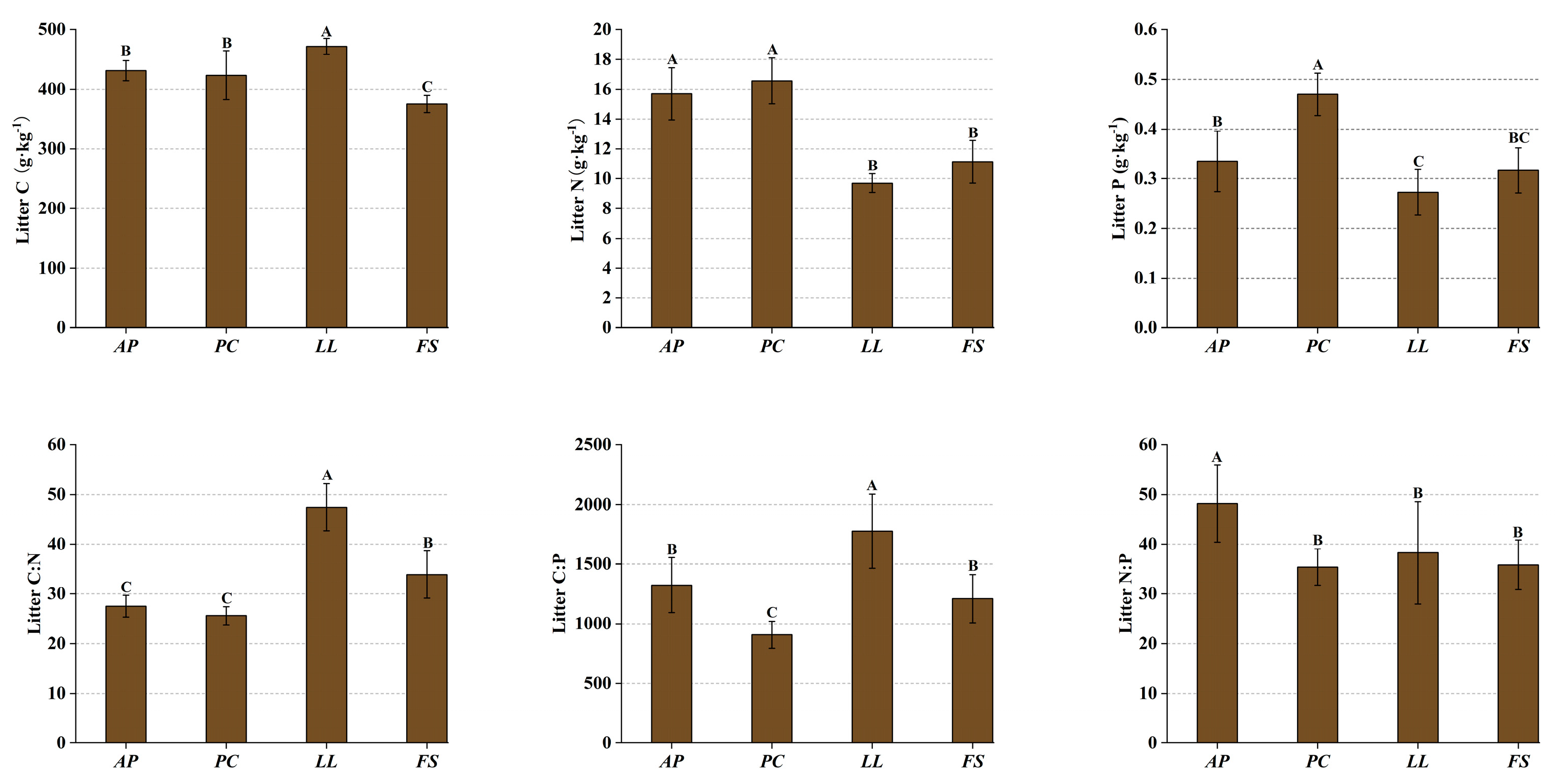
2.2. Ecological Stoichiometry in Litter
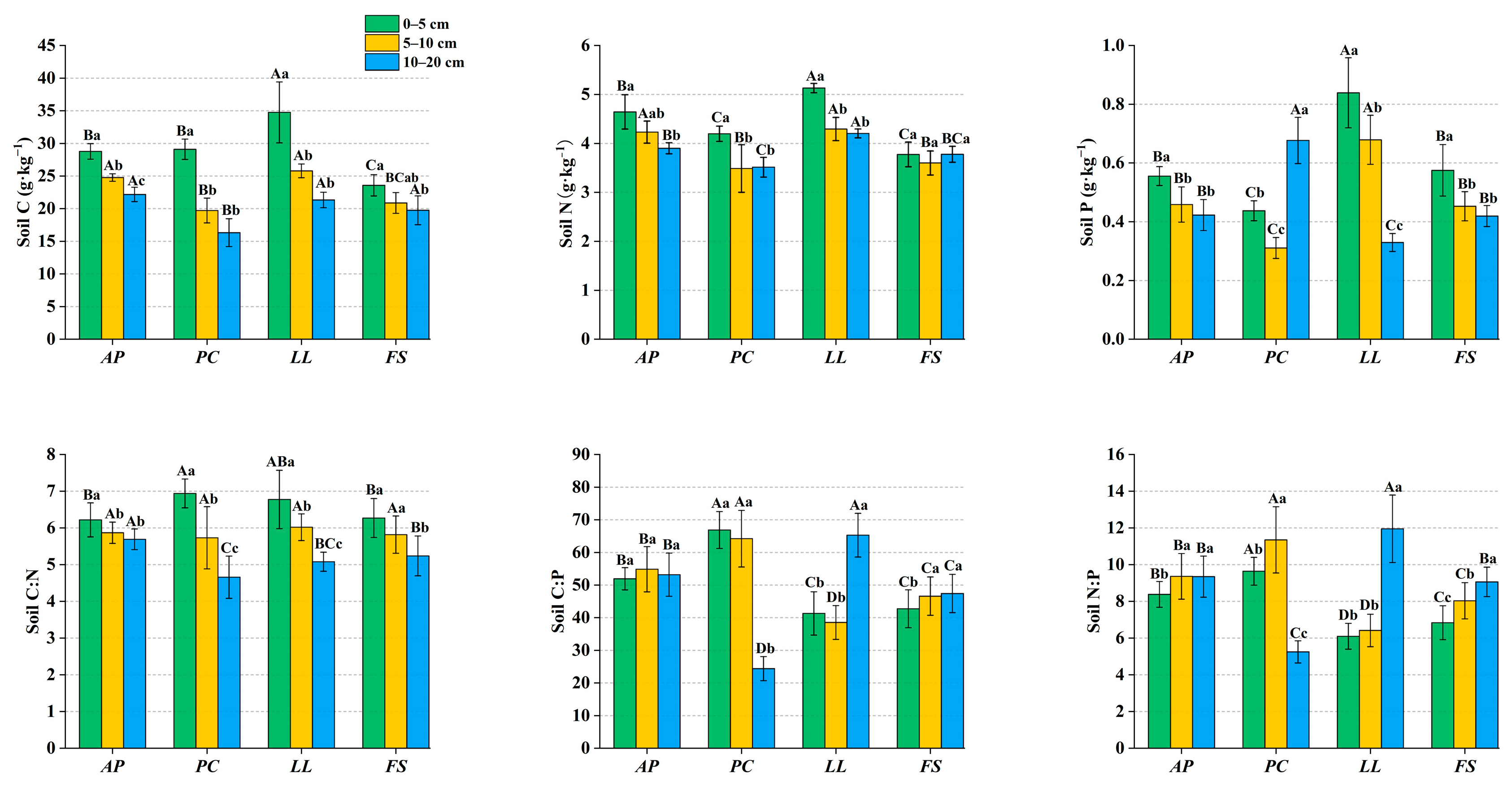
2.3. Ecological Stoichiometry in Soil
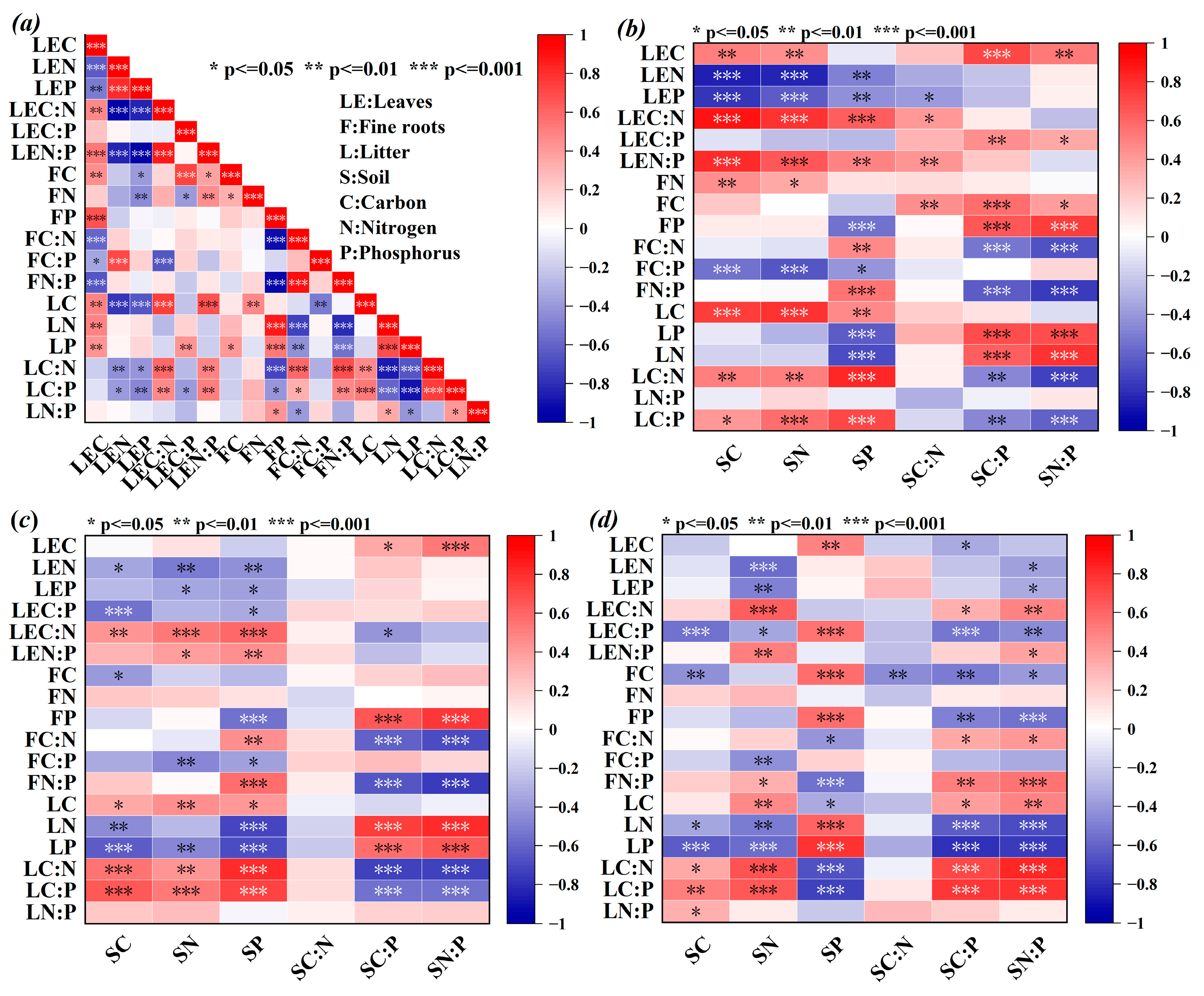
2.4. Relationship Among Plants, Litter, and Soil in Artificial Forests
2.4.1. Analysis of Stoichiometry Between Plants, Litter, and Soil
2.4.2. RDA of Aboveground Stoichiometry and Soil Properties
3. Discussion
3.1. Plant Stoichiometry of Different Forest Stands
3.2. Litter Stoichiometry of Different Forest Stands
3.3. Soil Stoichiometry of Different Forest Stands
3.4. Analysis of Stoichiometric Relationships Among Plants, Litter, and Soil
4. Materials and Methods
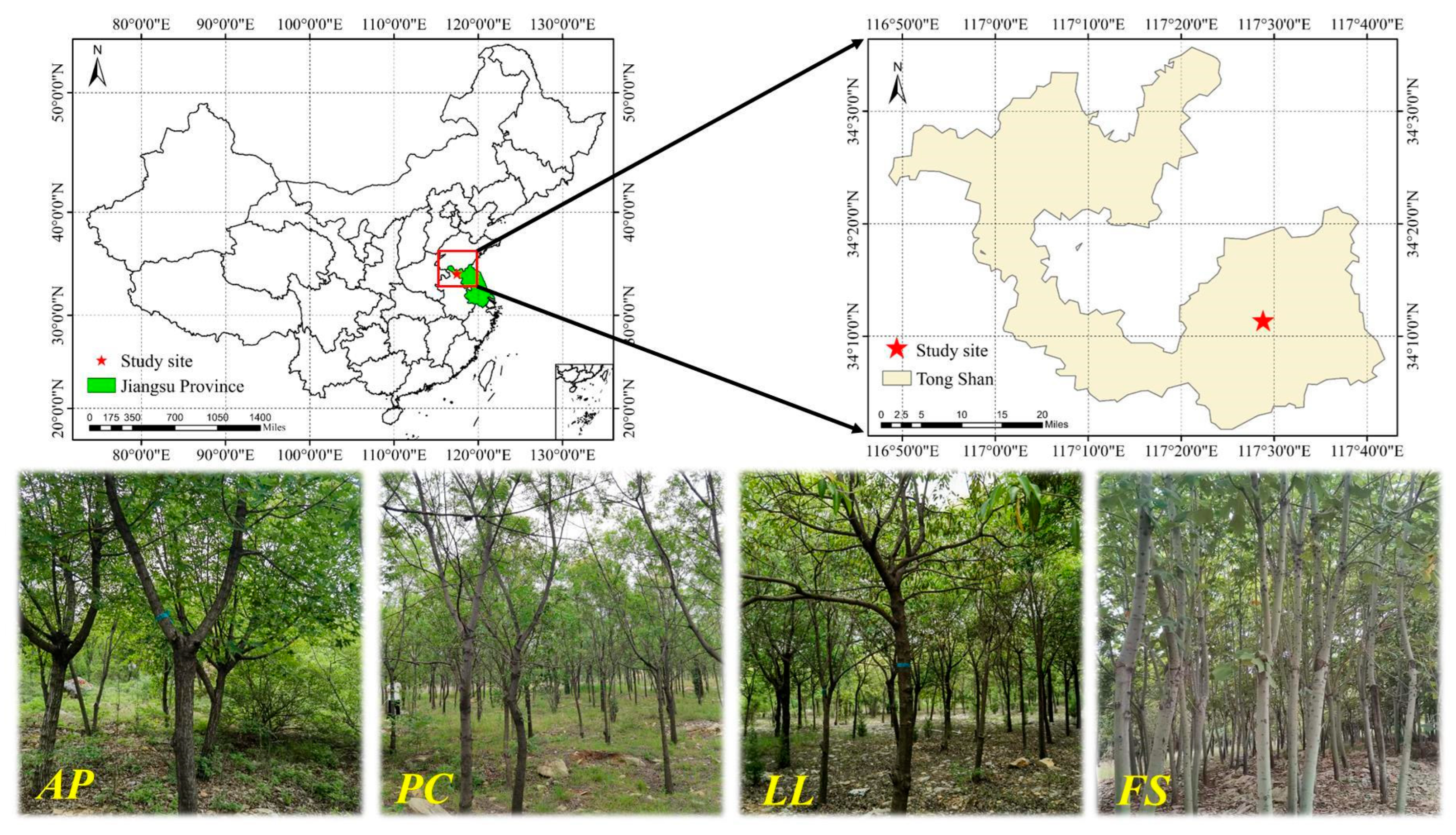
4.1. Study Site
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Data Collection
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, X.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; Chen, J.; Qi, L.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wu, C.; Dong, J.; et al. Forest Areas in China Are Recovering Since the 21st Century. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2024GL110312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S. Impact of China’s Large-Scale Ecological Restoration Program on the Environment and Society in Arid and Semiarid Areas of China: Achievements, Problems, Synthesis, and Applications. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, M.; Schwartz, C.; Macpherson, J.; Piorr, A. A Conceptual Model Framework for Mapping, Analyzing and Managing Supply–Demand Mismatches of Ecosystem Services in Agricultural Landscapes. Land 2021, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fan, Z.; Xiong, K.; Shen, H.; Guo, Q.; Dan, W.; Li, R. Current situation and prospects of the studies of ecological industries and ecological products in eco-fragile areas. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Chen, L.; Shankman, D.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H. Excessive reliance on afforestation in China’s arid and semi-arid regions: Lessons in ecological restoration. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2011, 104, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.; Sterner, R.; Gorokhova, E.; Fagan, W.; Markow, T.; Cotner, J.; Harrison, J.; Hobbie, S.; Odell, G.; Weider, L. Biological stoichiometry from genes to ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2000, 3, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Keiblinger, K.M.; Mooshammer, M.; Peñuelas, J.; Richter, A.; Sardans, J.; Wanek, W. The application of ecological stoichiometry to plant–microbial–soil organic matter transformations. Ecol. Monogr. 2015, 85, 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Shah, J.J.F. Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry and Ecological Theory. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 313–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, C.; Luo, Y. Meta-analysis of the impacts of global change factors on soil microbial diversity and functionality. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Barnes, A.D.; Potapov, A.; Yang, J.; Zhu, M.; Chen, X.; Hu, F.; Liu, M. Altered litter stoichiometry drives energy dynamics of food webs through changing multiple facets of soil biodiversity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 191, 109331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; LaZerte, S.E.; Waterway, M.J.; Lechowicz, M.J. Functional ecology of congeneric variation in the leaf economics spectrum. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Tian, D.; Han, W.; Tang, Z.; Fang, J. An assessment on the uncertainty of the nitrogen to phosphorus ratio as a threshold for nutrient limitation in plants. Ann. Bot. 2017, 120, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niklas, K.J.; Cobb, E.D. N, P, and C stoichiometry of Eranthis hyemalis (Ranunculaceae) and the allometry of plant growth. Am. J. Bot. 2005, 92, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Wu, H.; He, N.; Lü, X.; Wang, Z.; Elser, J.J.; Wu, J.; Han, X. Testing the Growth Rate Hypothesis in Vascular Plants with Above- and Below-Ground Biomass. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güsewell, S. N:P ratios in terrestrial plants: Variation and functional significance. New Phytol. 2004, 164, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Moorhead, D.L.; Guo, X.; Peng, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Fang, L. Stoichiometric models of microbial metabolic limitation in soil systems. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2021, 30, 2297–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Lal, R.; Chen, Y.; An, S. Soil, Leaf and Root Ecological Stoichiometry of Caragana korshinskii on the Loess Plateau of China in Relation to Plantation Age. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, L.-H.; Hu, H.-L.; Chen, G.; Peng, Y.; Xiao, Y.-L.; Hu, T.-X.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.-W.; Liu, L.; Tang, Y. Nitrogen Addition Significantly Affects Forest Litter Decomposition under High Levels of Ambient Nitrogen Deposition. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C.; Carrillo, Y.; Boot, C.M.; Rocca, J.D.; Pendall, E.; Wallenstein, M.D. Rhizosphere stoichiometry: Are C:N:P ratios of plants, soils, and enzymes conserved at the plant species-level? New Phytol. 2014, 201, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Cheng, X.; Kang, F.; Wang, J.; Yan, J.; Han, H. The patterns of N/P/K stoichiometry in the Quercus wutaishanica community among different life forms and organs and their responses to environmental factors in northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Harris, W.; Zhong, H. Stoichiometry of leaf nitrogen and phosphorus of grasslands of the Inner Mongolian and Qinghai-Tibet Plateaus in relation to climatic variables and vegetation organization levels. Ecol. Res. 2016, 31, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Fang, L.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, X. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and microbial nutrient limitation in rhizosphere soil in the arid area of the northern Loess Plateau, China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 116, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipping, E.; Somerville, C.J.; Luster, J. The C:N:P:S stoichiometry of soil organic matter. Biogeochemistry 2016, 130, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, D.; Digel, C.; Klarner, B.; Maraun, M.; Pollierer, M.; Rall, B.C.; Scheu, S.; Seelig, G.; Brose, U. Litter elemental stoichiometry and biomass densities of forest soil invertebrates. Oikos 2014, 123, 1212–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, B.-R.; An, S.-S. Ecological stoichiometry in leaves, roots, litters and soil among different plant communities in a desertified region of Northern China. CATENA 2018, 166, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, X.; Yao, W.; Han, C.; Sun, S.; Zhao, C. C, N, P, K stoichiometric characteristics of the “leaf-root-litter-soil” system in dryland plantations. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.A.; Durán, M.; Luquin, J.; Emeterio, L.S.; Yeste, A.; Canals, R.M. Soil C/N ratios cause opposing effects in forests compared to grasslands on decomposition rates and stabilization factors in southern European ecosystems. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 888, 164118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaźmierczak, M.; Błońska, E.; Lasota, J. Effect of litter decomposition and nutrient release from shrub litter on enzymatic activity and C/N/P stoichiometry of soils in a temperate pine forest. Acta Oecologica 2024, 124, 104020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Kang, D.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Yang, G.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Soil stoichiometry and carbon storage in long-term afforestation soil affected by understory vegetation diversity. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 74, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wu, J.; Liu, W.; Yuan, Y.; Hu, L.; Cai, Q. Linkages of plant and soil C:N:P stoichiometry and their relationships to forest growth in subtropical plantations. Plant Soil 2015, 392, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Q.; Liu, J.; Xu, D.; He, Z. C:N:P Stoichiometry of Plant, Litter and Soil along an Elevational Gradient in Subtropical Forests of China. Forests 2022, 13, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, P.; Sheng, M.; Tian, J. Ecological stoichiometry and environmental influencing factors of soil nutrients in the karst rocky desertification ecosystem, southwest China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2018, 16, e00449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Peng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lei, S.; Wang, X.; Farooq, T.H.; Liang, X.; Zhang, C.; Yan, W.; Chen, X. Ecological Stoichiometry and Stock Distribution of C, N, and P in Three Forest Types in a Karst Region of China. Plants 2023, 12, 2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zeng, F.; Zeng, Z.; Du, H.; Zhang, L.; Su, L.; Lu, M.; Zhang, H. Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Stoichiometry and Its Influencing Factors in Karst Primary Forest. Forests 2022, 13, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhou, G.; Bai, Y.; Li, J.; Tang, X.; Chen, D.; Liu, Q.; Ma, W.; Xiong, G.; et al. Patterns of plant carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus concentration in relation to productivity in China’s terrestrial ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4033–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, Q.; Tian, J.; Tang, X.; Tang, Z.; Xie, Z.; He, N.; Yu, G. Spatial patterns and environmental factors influencing leaf carbon content in the forests and shrublands of China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Yin, J.; Qi, J.; Jepsen, M.; Lü, X. Ecosystem carbon storage of tropical forests over limestone in Xishuang-banna, SW China. J. Trop. For. Sci. 2012, 24, 399–407. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/23617124 (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- Han, W.X.; Fang, J.Y.; Guo, D.L.; Zhang, Y. Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across 753 terrestrial plant species in China. New Phytol. 2005, 168, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, P.B.; Oleksyn, J. Global patterns of plant leaf N and P in relation to temperature and latitude. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11001–11006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Yang, H.; Xu, C.; Hua, W.; Li, B. Patterns and driving factors of leaf C, N, and P stoichiometry in two forest types with different stand ages in a mid-subtropical zone. For. Ecosyst. 2022, 9, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Sheng, M.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. Ecological stoichiometry of C, N, P and Si of Karst Masson pine forests: Insights for the forest management in southern China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 912, 169490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Sheng, M.; Bai, Y.; Jie, Y.; Xiao, H. Response of C, N, and P stoichiometry characteristics of Broussonetia papyrifera to altitude gradients and soil nutrients in the karst rocky ecosystem, SW China. Plant Soil 2022, 475, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, E.; Cuevas, E.; Lugo, A.E. Substrate Chemistry and Rainfall Regime Regulate Elemental Composition of Tree Leaves in Karst Forests. Forests 2017, 8, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedin, L.O. Global organization of terrestrial plant–nutrient interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10849–10850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Hu, J.; Chen, X.; Xu, X.; Yang, Y.; Ni, J. Adaptation strategy of karst forests: Evidence from the community-weighted mean of plant functional traits. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e8680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, X.; Song, Y.; Yu, D.; Qian, W.; He, M.; Lin, X.; Zhang, D.; Gao, S. Early Growth Characterization and C:N:P Stoichiometry in Firmiana simplex Seedlings in Response to Shade and Soil Types. Forests 2023, 14, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibar, D.T.; Zhang, K.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Ye, X. Ecological stoichiometric characteristics of Carbon (C), Nitrogen (N) and Phosphorus (P) in leaf, root, stem, and soil in four wetland plants communities in Shengjin Lake, China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Chen, H.Y.; Reich, P.B. Global-scale latitudinal patterns of plant fine-root nitrogen and phosphorus. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ågren, G.I. Stoichiometry and Nutrition of Plant Growth in Natural Communities. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2008, 39, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Gao, X.; Gui, D.; Liu, B.; Zhang, B.; Li, X. Stoichiometry in aboveground and fine roots of Seriphidium korovinii in desert grassland in response to artificial nitrogen addition. J. Plant Res. 2017, 130, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yan, Z.; Gheyret, G.; Zhou, G.; Xie, Z.; Tang, Z. The community-level scaling relationship between leaf nitrogen and phosphorus changes with plant growth, climate and nutrient limitation. J. Ecol. 2020, 108, 1276–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadelhoffer, K.J. The potential effects of nitrogen deposition on fine-root production in forest ecosystems. New Phytol. 2000, 147, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Rivas-Ubach, A.; Peñuelas, J. The C:N:P stoichiometry of organisms and ecosystems in a changing world: A review and perspectives. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 14, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, C.; Kautsky, U.; Kumblad, L. Ecological Stoichiometry and Multi-element Transfer in a Coastal Ecosystem. Ecosystems 2012, 15, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lu, J.; Yang, M.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Q. Stoichiometric Characteristics of Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus in Leaves of Differently Aged Lucerne (Medicago sativa) Stands. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lv, S.; Song, H.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, H.; Niklas, K.J. Plant type dominates fine-root C:N:P stoichiometry across China: A meta-analysis. J. Biogeogr. 2020, 47, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenovsky, R.; Richards, J. Critical N:P values: Predicting nutrient deficiencies in desert shrublands. Plant Soil 2004, 259, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, E.; Dossa, G.G.; Xu, J.; Harrison, R.D. Litterfall and nutrient return along a disturbance gradient in a tropical montane forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 353, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, R.D.; Wurzbacher, S.J.; Washko, S.E.; Wind, L.; Rice, A.M.; Coble, A.E.; Baldauf, N.; Johnson, B.; Wang, J.; Simpson, M.; et al. Long-term Nitrogen Addition Decreases Organic Matter Decomposition and Increases Forest Soil Carbon. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2019, 83, S82–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Lu, Z.; Xu, X.; Wan, F.; Liao, J.; Wang, J. Global distributions of foliar nitrogen and phosphorus resorption in forest ecosystems. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 871, 162075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killingbeck, K.T. Nutrients in Senesced Leaves: Keys to the Search for Potential Resorption and Resorption Proficiency. Ecology 1996, 77, 1716–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, D. C:N:P stoichiometric characteristics and seasonal dynamics of leaf-root-litter-soil in plantations on the loess plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrufo, M.F.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Boot, C.M.; Denef, K.; Paul, E. The Microbial Efficiency-Matrix Stabilization (MEMS) framework integrates plant litter decomposition with soil organic matter stabilization: Do labile plant inputs form stable soil organic matter? Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, R. Nutrient Resorption from Senescing Leaves of Perennials: Are there General Patterns? J. Ecol. 1996, 84, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Tan, T.; Wu, D.; Li, C.; Jing, H.; Wu, J. Seasonal variations in carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus of Pinus yunnanenis at different stand ages. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1107961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Melillo, J.M.; Hall, C.A.S. Pattern and variation of C:N:P ratios in China’s soils: A synthesis of observational data. Biogeochemistry 2010, 98, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Huang, K.; Yang, Q.; Lu, R.; Yan, L.; Wang, X.; Xia, J. Depth-dependent soil C-N-P stoichiometry in a mature subtropical broadleaf forest. Geoderma 2020, 370, 114357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, M.; Huang, Z.; Lin, T.; Vadeboncoeur, M.A.; Searle, E.B.; Chen, H.Y.H. Temporal changes in soil C-N-P stoichiometry over the past 60 years across subtropical China. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 1308–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, J.M.; McGoff, N.M.; Byrne, K.A.; Leahy, P.; Kiely, G. Land cover change and soil organic carbon stocks in the Republic of Ireland 1851–2000. Clim. Change 2008, 91, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Shao, M.; Wei, X.; Horton, R. Soil organic carbon and total nitrogen as affected by vegetation types in Northern Loess Plateau of China. Geoderma 2010, 155, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindhavani, P.M.; Chitdeshwari, T.; Selvi, D.; Sivakumar, U.; Jeyakumar, P. Solubilization of phosphorus by low molecular weight organic acids and amino acids in calcareous soils: LMWOA and amino acid on P solubilization. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2022, 14, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taalab, A.S.; Ageeb, G.W.; Siam, H.S.; Mahmoud, S.A. Some characteristics of calcareous soils. A review. Middle East J. Agric. Res. 2019, 8, 96–105. Available online: https://www.curresweb.com/mejar/mejar/2019/96-105.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Siswanto, D.; Widjajani, B.W.; Siswanto, S. Analisis Status dan Kelas Kemampuan Kesuburan Tanah pada Beberapa Lahan Tebu di Kecamatan Japah Kabupaten Blora. J. Agrotropika 2024, 23, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbie, S.E. Plant species effects on nutrient cycling: Revisiting litter feedbacks. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, Y.; An, S. How C:N:P stoichiometry in soils and plants responds to succession in Robinia pseudoacacia forests on the Loess Plateau, China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 475, 118394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, B. Effects of planting Caragana shrubs on soil nutrients and stoichiometries in desert steppe of Northwest China. CATENA 2019, 183, 104213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błońska, E.; Lasota, J.; Prażuch, W.; Ilek, A. Vertical variations in enzymatic activity and C:N:P stoichiometry in forest soils under the influence of different tree species. Eur. J. For. Res. 2024, 144, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Sun, J.; Ren, C.; Deng, J.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Land use change influences soil C, N and P stoichiometry under ‘Grain-to-Green Program’ in China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, srep10195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladanai, S.; Ågren, G.I.; Olsson, B.A. Relationships Between Tree and Soil Properties in Picea abies and Pinus sylvestris Forests in Sweden. Ecosystems 2010, 13, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, E.N.; Henderson, B.L. C:N:P stoichiometry in Australian soils with respect to vegetation and environmental factors. Plant Soil 2013, 373, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Li, X.; Dong, Y.; An, S.; Darboux, F. Soil and plant components ecological stoichiometry in four steppe communities in the Loess Plateau of China. CATENA 2016, 147, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Zhang, K.; Tan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X. Influence of life form, taxonomy, climate, and soil properties on shoot and root concentrations of 11 elements in herbaceous plants in a temperate desert. Plant Soil 2016, 398, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, C.J.; Matthaeus, W.J.; Cook, S.C.; Housley, L.M.; Robison, S.E.; Garbarino, M.A.; LeBrun, E.S.; Raut, S.; Tseng, C.; King, R.S. Leaf litter identity alters the timing of lotic nutrient dynamics. Freshw. Biol. 2019, 64, 2247–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordoñez, J.C.; Van Bodegom, P.M.; Witte, J.M.; Wright, I.J.; Reich, P.B.; Aerts, R. A global study of relationships between leaf traits, climate and soil measures of nutrient fertility. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2009, 18, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, N.; Liu, C.; Yang, H.; Li, M.; Yu, G.; Wilcox, K.; Yu, Q.; He, N. C:N:P stoichiometry in China’s forests: From organs to ecosystems. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripler, C.E.; Kaushal, S.S.; Likens, G.E.; Todd Walter, M. Patterns in potassium dynamics in forest ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Q.; Tan, Y.; Yan, P.; Arif, M. Examining the stoichiometry of C:N:P:K in the dynamics of foliar-litter-soil within dominant tree species across different altitudes in southern China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 51, e02885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J.; Coll, M.; Vayreda, J.; Rivas-Ubach, A. Stoichiometry of potassium is largely determined by water availability and growth in Catalonian forests. Funct. Ecol. 2012, 26, 1077–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G.; DeForest, J.L.; Marxsen, J.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Stromberger, M.E.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Weintraub, M.N.; Zoppini, A. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: Current knowledge and future directions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Lauber, C.L.; Weintraub, M.N.; Ahmed, B.; Allison, S.D.; Crenshaw, C.; Contosta, A.R.; Cusack, D.; Frey, S.; Gallo, M.E.; et al. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; Czimczik, C.I.; Treseder, K.K. Microbial activity and soil respiration under nitrogen addition in Alaskan boreal forest. Glob. Change Biol. 2008, 14, 1156–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiblinger, K.M.; Hall, E.K.; Wanek, W.; Szukics, U.; Hämmerle, I.; Ellersdorfer, G.; Böck, S.; Strauss, J.; Sterflinger, K.; Richter, A.; et al. The effect of resource quantity and resource stoichiometry on microbial carbon-use-efficiency. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 73, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Long, M.; He, X.; Guo, L.; Yang, J.; Yang, P.; Hu, T. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and water availability affect biomass and C:N:P ecological stoichiometry in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) during regrowth. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2017, 39, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhongaray, G.; Janssens, I.A.; King, J.S.; Ceulemans, R. Fine root biomass and turnover of two fast-growing poplar genotypes in a short-rotation coppice culture. Plant Soil 2013, 373, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Factor | F (p) Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | N | P | C:N | N:P | C:P | |
| Forest stand type | 61.571 (<0.001) | 108.526 (<0.001) | 37.665 (<0.001) | 0.937 (0.426) | 10.447 (<0.001) | 8.127 (<0.001) |
| Soil depth | 223.808 (<0.001) | 91.889 (<0.001) | 57.648 (<0.001) | 63.767 (<0.001) | 17.790 (<0.001) | 11.682 (<0.001) |
| Forest stand type × Soil depth | 16.493 (<0.001) | 7.919 (<0.001) | 74.984 (<0.001) | 4.965 (<0.001) | 85.012 (<0.001) | 84.003 (<0.001) |
| Forest Stand | Age (a) | Canopy Density (%) | Average DBH (cm) | Average H (m) | Density (Tree·Ha) | Altitude (m) | Slope (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP | 16 | 0.69 | 8.9 | 4.8 | 2600 | 130 | 18 |
| PC | 15 | 0.54 | 8.7 | 5.3 | 2600 | 113 | 14 |
| LL | 15 | 0.60 | 9.2 | 8.0 | 3200 | 115 | 11 |
| FS | 16 | 0.82 | 8.1 | 4.2 | 2700 | 98 | 13 |
| Forest Stand | Soil Depth | pH | SW (%) | AP (mg·kg−1) | AK (mg·kg−1) | MBC (mg·kg−1) | MBN (mg·kg−1) | MBP (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP | 0–5 cm | 7.26 ± 0.17 Aa | 23.63 ± 1.91 Aa | 2.77 ± 0.78 Aa | 281.26 ± 4.77 Ba | 451.99 ± 20.03 Cb | 341.66 ± 16.07 Ba | 10.55 ± 0.26 Ba |
| 5–10 cm | 7.41 ± 0.14 Aa | 23.16 ± 1.10 Aa | 2.56 ± 0.49 ABa | 268.59 ± 4.31 Ba | 490.51 ± 45.81 Ca | 352.28 ± 14.84 Ba | 4.61 ± 0.30 Bb | |
| 10–20 cm | 7.34 ± 0.15 Aa | 24.45 ± 1.18 Aa | 1.98 ± 0.33 Bb | 203.66 ± 9.19 Bb | 314.52 ± 28.23 Cc | 225.83 ± 24.40 Ab | 10.9 ± 0.42 Aa | |
| PC | 0–5 cm | 7.06 ± 0.22 Aa | 25.72 ± 2.22 Aa | 2.36 ± 0.28 Aa | 214.06 ± 6.83 Ca | 512.08 ± 58.65 Cab | 309.45 ± 13.01 Ba | 11.91 ± 0.99 Ba |
| 5–10 cm | 7.23 ± 0.09 Aa | 25.80 ± 1.80 Aa | 2.21 ± 0.17 Ba | 203.42 ± 6.08 Ca | 532.31 ± 24.73 Ca | 287.82 ± 8.28 Ca | 5.22 ± 0.24 Bb | |
| 10–20 cm | 7.29 ± 0.11 Aa | 26.83 ± 2.73 Aa | 1.92 ± 0.12 Bb | 186.16 ± 9.38 Ba | 506.25 ± 20.59 Bb | 198.08 ± 16.05 Bb | 3.65 ± 0.64 Dc | |
| LL | 0–5 cm | 7.26 ± 0.18 Aa | 23.96 ± 2.11 Aa | 3.48 ± 0.43 Aa | 352.14 ± 37.29 Aa | 1262.05 ± 141.57 Aa | 326.25 ± 34.09 Ba | 18.55 ± 3.05 Aa |
| 5–10 cm | 7.24 ± 0.17 Aa | 23.87 ± 1.95 Aa | 3.31 ± 0.24 Aa | 327.67 ± 18.49 Ab | 1389.52 ± 15.51 Aa | 337.61 ± 25.47 Ba | 13.49 ± 1.18 Ab | |
| 10–20 cm | 7.23 ± 0.13 Aa | 24.53 ± 2.19 Aa | 2.63 ± 0.29 Ab | 296.28 ± 9.84 Ac | 1062.82 ± 57.86 Ab | 111.22 ± 8.56 Cb | 7.98 ± 0.52 Bc | |
| FS | 0–5 cm | 7.20 ± 0.10 Aa | 25.12 ± 3.31 Aa | 2.82 ± 0.68 Aa | 336.07 ± 14.12 Aa | 955.51 ± 59.25 Bb | 963.77 ± 41.28 Aa | 19.76 ± 0.34 Aa |
| 5–10 cm | 7.28 ± 0.11 Aa | 24.81 ± 2.29 Aa | 2.68 ± 0.67 ABa | 311.28 ± 14.27 Ab | 1144.49 ± 62.74 Ba | 464.01 ± 39.09 Ab | 3.09 ± 0.24 Cc | |
| 10–20 cm | 7.25 ± 0.13 Aa | 25.96 ± 2.58 Aa | 1.89 ± 0.26 Bb | 277.93 ± 18.46 Ac | 980.85 ± 51.88 Ab | 237.16 ± 28.86 Ac | 6.02 ± 0.51 Cb |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Tu, H.; Zheng, J.; Li, X.; Wang, G.; Guo, J. Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics of Plant–Litter–Soil Among Different Forest Stands in a Limestone Region of China. Plants 2025, 14, 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121758
Wang Y, Tu H, Zheng J, Li X, Wang G, Guo J. Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics of Plant–Litter–Soil Among Different Forest Stands in a Limestone Region of China. Plants. 2025; 14(12):1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121758
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yeqiao, Haochuan Tu, Jingjing Zheng, Xiongjie Li, Guibin Wang, and Jing Guo. 2025. "Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics of Plant–Litter–Soil Among Different Forest Stands in a Limestone Region of China" Plants 14, no. 12: 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121758
APA StyleWang, Y., Tu, H., Zheng, J., Li, X., Wang, G., & Guo, J. (2025). Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics of Plant–Litter–Soil Among Different Forest Stands in a Limestone Region of China. Plants, 14(12), 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121758





