Modeling the Combined Effects of Straw Returning, Urease Inhibitors, and Nitrogen Split Application on Rice Yield and Ammonia Volatilization in Purple Soil Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Model Calibration and Evaluation
2.2. Rice Yield and Crop N Uptake
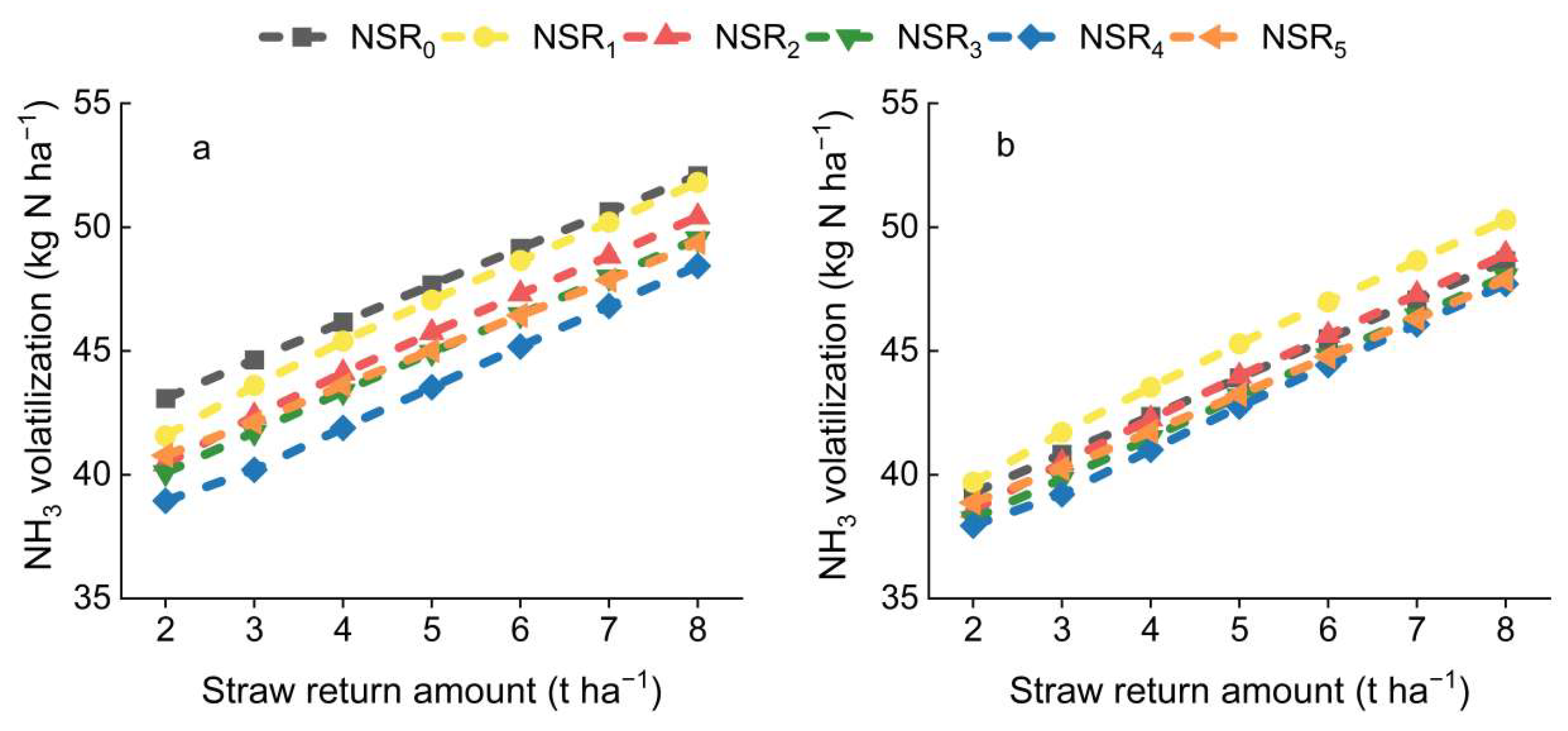
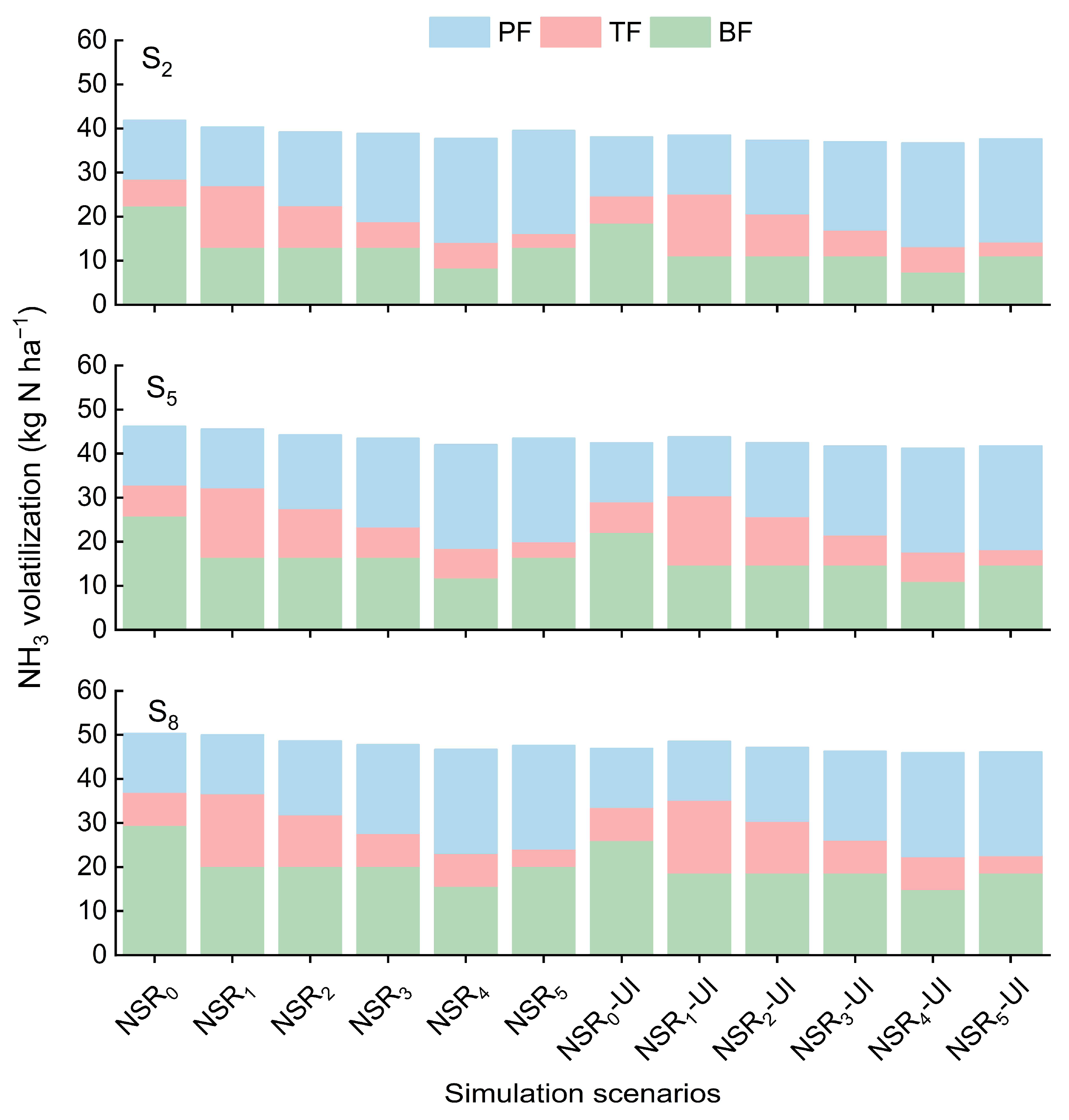
2.3. NH3 Volatilization
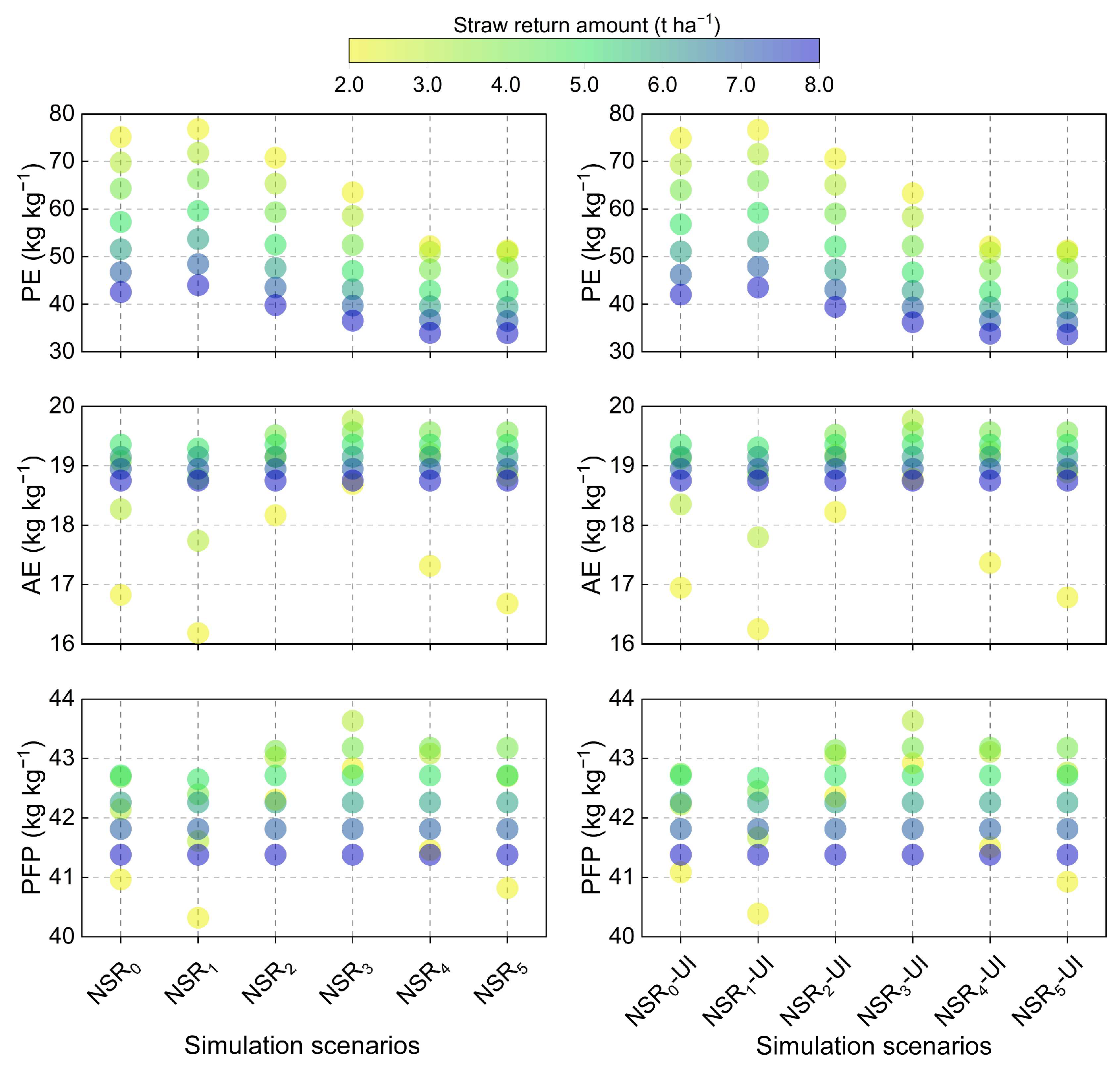
2.4. N Use Efficiency
3. Discussion
3.1. Effects of Straw Returning on Rice Yield and NH3 Volatilization
3.2. Effects of Urease Inhibitor on Rice Yield and NH3 Volatilization
3.3. Effects of N Split Application Ratio on Rice Yield and NH3 Volatilization
3.4. Limitations of the Model Simulation
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. The Study Site
4.2. Experimental Design and Field Management
4.3. Observations and Measurement Methods
4.4. WHCNS Model
4.5. Model Calibration, Validation, and Evaluation
4.6. Simulation Scenarios
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muthayya, S.; Sugimoto, J.D.; Montgomery, S.; Maberly, G.F. An overview of global rice production, supply, trade, and consumption. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1324, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Linquist, B.A.; Wilson, L.T.; Cassman, K.G.; Stuart, A.M.; Pede, V.; Miro, B.; Saito, K.; Agustiani, N.; Aristya, V.E.; et al. Sustainable intensification for a larger global rice bowl. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S. Contemporary Global Rice Economies: Structural Changes of Rice Production/Consumption and Trade. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2019, 65, S23–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodirsky, B.L.; Popp, A.; Lotze-Campen, H.; Dietrich, J.P.; Rolinski, S.; Weindl, I.; Schmitz, C.; Müller, C.; Bonsch, M.; Humpenöder, F.; et al. Reactive nitrogen requirements to feed the world in 2050 and potential to mitigate nitrogen pollution. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Zhao, X.; Pittelkow, C.M.; Fan, M.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X. Optimal nitrogen rate strategy for sustainable rice production in China. Nature 2023, 615, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Li, X.; Guo, C.; Feng, P.; Hu, K. Modeling ammonia volatilization following urea and controlled-release urea application to paddy fields. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 196, 106888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Li, G.; Zheng, Y.; Fung, J.C.H.; Chen, A.; Zeng, Z.; Shen, H.; Hu, M.; Mao, J.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Fertilizer management for global ammonia emission reduction. Nature 2024, 626, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Hu, K.; Batchelor, W.D.; Liang, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Fu, J.; Cui, X.; Zhou, F. Exploring optimal nitrogen management strategies to mitigate nitrogen losses from paddy soil in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 228, 105877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Gu, J.; Yang, J. Effects of long-term straw returning on rice yield and soil properties and bacterial community in a rice-wheat rotation system. Field Crops Res. 2023, 291, 108800. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Hu, K.; Yao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, C.; Liu, H.; Luo, F.; Chen, H. Effects of the Combining Straw Return with Urease Inhibitor on Ammonia Volatilization, Nitrogen Use Efficiency, and Rice Yield in Purple Soil Areas. Plants 2023, 12, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Hu, S.; Wang, R.; Jiu, A.; Kan, Z.; Yang, H.; Palta, J.A.; Li, F. Straw return under deep tillage increases grain yield in the rice-rotated wheat cropping system. Field Crops Res. 2024, 317, 109559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Huang, G.; Jiang, X.; Liang, Y.; Yang, C.; Huang, L. Comparison of yield prediction models and estimation of the relative importance of main agronomic traits affecting rice yield formation in saline-sodic paddy fields. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 148, 126870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunrat, N.; Kongsurakan, P.; Sereenonchai, S.; Hatano, R. Soil Organic Carbon in Sandy Paddy Fields of Northeast Thailand: A Review. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, W.; Piao, J.; Gao, Q.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Jin, F. Response of soil physicochemical properties, soil nutrients, enzyme activity and rice yield to rice straw returning in highly saline-alkali paddy soils. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 4396–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Nie, H.; Yi, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Ren, Q.; Li, S.; Fei, Y.; Hu, K.; Nan, X.; et al. Characteristics of Soil Moisture Response to Rainfall under Different Land Use Patterns at Red Soil Region in Southern China. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 6813–6826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Sheng, F.; Cao, C.; Li, C. Effects of long-term no tillage and straw return on greenhouse gas emissions and crop yields from a rice-wheat system in central China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 322, 107650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, G.; Wang, C. Effect of wheat straw application on ammonia volatilization from urea applied to a paddy field. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2012, 94, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Ma, X.; Yang, G.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G.; Li, N.; Xie, C.; Xu, H. Effect of straw returning on ammonia emissions from soil in a wheat-maize multiple cropping system in the Guanzhong region, China. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2020, 28, 513–522. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, B.; Huang, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J. Urea ammonium nitrate solution combined with urease and nitrification inhibitors jointly mitigate NH3 and N2O emissions and improves nitrogen efficiency of summer maize under fertigation. Field Crops Res. 2023, 296, 108909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; He, W.; Smith, W.N.; Drury, C.F.; Jiang, R.; Grant, B.B.; Shi, Y.; Song, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Global evaluation of inhibitor impacts on ammonia and nitrous oxide emissions from agricultural soils: A meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 5121–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.R.; Sant Anna, S.A.C.; Zaman, M.; Santos, R.C.; Monteiro, R.C.; Alves, B.J.R.; Jantalia, C.P.; Boddey, R.M.; Urquiaga, S. Strategies for the use of urease and nitrification inhibitors with urea: Impact on N2O and NH3 emissions, fertilizer-15N recovery and maize yield in a tropical soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 247, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishfaq, M.; Akbar, N.; Zulfiqar, U.; Ali, N.; Jabran, K.; Nawaz, M.; Farooq, M. Influence of Nitrogen Fertilization Pattern on Productivity, Nitrogen Use Efficiencies, and Profitability in Different Rice Production Systems. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Lu, S.; Jiang, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F. Triangular Transplanting Pattern and Split Nitrogen Fertilizer Application Increase Rice Yield and Nitrogen Fertilizer Recovery. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Zhao, Q.; Cao, L. Quantifying nitrogen loading from a paddy field in Shanghai, China with modified DNDC model. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 197, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Shao, D.; Gu, W.; Liu, H. Field analysis of water and nitrogen fate in lowland paddy fields under different water managements using HYDRUS-1D. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 150, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Yu, K.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Shan, J. Adaptability evaluation of ORYZA (v3) for single-cropped rice under different establishment techniques in eastern China. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 2741–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyang’Au, W.O.; Mati, B.M.; Kalamwa, K.; Wanjogu, R.K.; Kiplagat, L.K. Estimating Rice Yield under Changing Weather Conditions in Kenya Using CERES Rice Model. Int. J. Agron. 2014, 2014, 849496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liang, H.; Hu, K.; Batchelor, W.D.; Qi, Z.; Li, B. An integrated soil-crop system model for water and nitrogen management in North China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Yang, S.; Xu, J.; Hu, K. Modeling water consumption, N fates, and rice yield for water-saving and conventional rice production systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 209, 104944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.U.; Guo, Z.; Jiang, F.; Peng, X. Does straw return increase crop yield in the wheat-maize cropping system in China? A meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2022, 279, 108447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Song, D.; Pu, X.; Dang, P.; Qin, X.; Siddique, K.H.M. Effect of different straw returning measures on resource use efficiency and spring maize yield under a plastic film mulch system. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 134, 126461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qiu, T.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Tan, W.; Wei, X.; Cui, Y.; Cui, Q.; Wu, C.; Liu, L.; et al. Crop residue return sustains global soil ecological stoichiometry balance. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 2203–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimczyk, M.; Siczek, A.; Schimmelpfennig, L. Improving the efficiency of urea-based fertilization leading to reduction in ammonia emission. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 145483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, P.; Bell, S.M.; Chen, L.; Huang, S.; Wang, H.; Miao, J.; Qi, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liao, B.; Zeng, Y.; et al. Improving rice grain yield and reducing lodging risk simultaneously: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 143, 126709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Huang, G.; Xiao, W.; Han, L. The composition characteristics of different crop straw types and their multivariate analysis and comparison. Waste Manag. 2020, 110, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Huang, S.; Zhai, J.; Wang, J.; Cao, C.; Cai, M.; Zhan, M.; Tang, X. Effects of N Management on Yield and N Uptake of Rice in Central China. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 1993–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Ciampitti, I.A.; He, P.; Xu, X.; Qiu, S.; Zhao, S. Response of soil denitrification potential and community composition of denitrifying bacterial to different rates of straw return in north-central China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 170, 104312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Lam, S.K.; Mosier, A.; Luo, Y.; Chen, D. Ammonia volatilization from synthetic fertilizers and its mitigation strategies: A global synthesis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 232, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Lu, L.; Shi, L.; Zhou, S. Effects of different fertilization methods on ammonia volatilization from rice paddies. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Zhou, C.; Wang, L. Reducing Ammonia Volatilization from Maize Fields with Separation of Nitrogen Fertilizer and Water in an Alternating Furrow Irrigation System. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Che, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, C.; Li, L.; Liu, Y. Effects of Straw Return and Nitrogen Application Rates on Soil Ammonia Volatilization and Yield of Winter Wheat. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, H.; Hu, H. Responses of Rice Yield, N Uptake, NH3 and N2O Losses from Reclaimed Saline Soils to Varied N Inputs. Plants 2023, 12, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, X.T.; Xing, G.X.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, X.J.; Cui, Z.L.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z.L.; et al. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Castillo, A.G.; Giraldo-Sanclemente, W.; Monge-Muñoz, M.; Chinchilla-Soto, C.; Alpízar-Marín, M.; Zaman, M. Rice yield in Costa Rican Central Pacific did not improve with a urease inhibitor. Front. Agron. 2024, 6, 1394143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Z.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Lv, T.; Li, Q.; Misselbrook, T.; Liu, X. Effect of N stabilizers on fertilizer-N fate in the soil-crop system: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 290, 106763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.G.B.; Sequeira, C.H.; Sermarini, R.A.; Otto, R. Urease Inhibitor NBPT on Ammonia Volatilization and Crop Productivity: A Meta-Analysis. Agron. J. 2017, 109, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulesza, S.B.; Woodley, A.L.; Heather, K.; Kilroy, G. Cover crops can increase ammonia volatilization and reduce the efficacy of urease inhibitors. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2022, 86, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phongpan, S.; Freney, J.R.; Keerthisinghe, D.G.; Chaiwanakup, R. Use of phenylphosphorodiamidate and N-(n-butyl)thiophosphorictriamide to reduce ammonia loss and increase grain yield following application of urea to flooded rice. Fertil Res. 1995, 41, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, H.U.; Basra, S.M.A.; Wahid, A. Optimizing Nitrogen-split Application Time to Improve Dry Matter Accumulation and Yield in Dry Direct Seeded Rice. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2013, 15, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Freney, J.R.; Leuning, R.; Simpson, J.R.; Denmead, O.T.; Muirhead, W.A. Estimating ammonia volatilization from flooded rice fields by simplified techniques. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1985, 49, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoninger, E.L.; González-Villalba, H.A.; Bendassolli, J.A.; Ocheuze Trivelin, P.C. Fertilizer nitrogen and corn plants: Not all volatilized ammonia is lost. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xu, Y.; Shen, Q. Progress in Research on Ammonia Volatilization from Plant Leaves. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2006, 22, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Scotto Di Perta, E.; Fiorentino, N.; Carozzi, M.; Cervelli, E.; Pindozzi, S. A Review of Chamber and Micrometeorological Methods to Quantify NH3 Emissions from Fertilisers Field Application. Int. J. Agron. 2020, 2020, 8909784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Yin, B.; Zhu, Z. Assessment of ammonia volatilization from paddy fields under crop management practices aimed to increase grain yield and N efficiency. Field Crops Res. 2013, 147, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, Y.K.; Kalra, Y.P. A comparison of plant tissue digestion methods for nitrogen and phosphorus analyses. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1995, 75, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yin, X.; Raza, S.; Tong, Y.A. Optimising nitrogen fertilisation: A key to improving nitrogen-use efficiency and minimising nitrate leaching losses in an intensive wheat/maize rotation (2008–2014). Field Crops Res. 2017, 206, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaughton, K.G.; Jarvis, P.G. Using the Penman-Monteith equation predictively. Agric. Water Manag. 1984, 8, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachum, A.Y.; Alfaro, J.F. Rain Infiltration into Layered Soils: Prediction. J. Irrig. Drain. Div. 1980, 106, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driessen, P.M.; Konijn, N.T. Land-Use Systems Analysis, 1st ed.; Wageningen Agricultural University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 41–175. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, S.; Abrahamsen, P.; Petersen, C.T.; Styczen, M. Daisy: Model Use, Calibration, and Validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1315–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Hu, K.; Feng, P.; Batchelor, W.D.; Liu, H.; Lü, S. Simulating the Responses of Rice Yield and Nitrogen Fates to the Ground Cover Rice Production System under Different Types of Precipitation Years. Rice Sci. 2024, 31, 725–739. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.M.; Yang, J.Y.; Liu, S.; Hoogenboom, G. An evaluation of the statistical methods for testing the performance of crop models with observed data. Agric. Syst. 2014, 127, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Indicators | 2018 | 2019 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nRMSE (%) | IA (−) | NSE (−) | nRMSE (%) | IA (−) | NSE (−) | |
| Rice yield | 7.3 | 0.96 | 0.74 | 6.3 | 0.94 | 0.60 |
| ADM | 7.2 | 0.93 | 0.57 | 1.9 | 0.99 | 0.96 |
| Nupt | 10.0 | 0.93 | 0.57 | 12.8 | 0.87 | 0.29 |
| NH3 volatilization | 7.2 | 0.99 | 0.94 | 15.1 | 0.95 | 0.72 |
| Parameters | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Soil hydraulic parameters | Saturated hydraulic conductivity: Ks1, Ks2, and Ks3 (cm d−1) | 1, 0.6, 0.7 |
| Saturated water content: θs1, θs2, and θs3 (cm3 cm−3) | 0.65, 0.50, 0.43 | |
| Field capacity: FC1, FC2, and FC3 (cm3 cm−3) | 0.35, 0.25, 0.24 | |
| Wilting point water content: WP1, WP2, and WP3 (cm3 cm−3) | 0.17, 0.15, 0.13 | |
| Crop parameters | Base temperature: Tb (°C) | 10 |
| Accumulated temperature: Ts (°C) | 1630 | |
| Extinction coefficient: Ke (−) | 0.5 | |
| Crop coefficient in the initial stage: Kini (−) | 0.8 | |
| Crop coefficient in the middle stage: Kmid (−) | 1.4 | |
| Crop coefficient in the end stage: Kend (−) | 0.7 | |
| Maximum specific leaf area: SLAmax (m2 kg−1) | 22 | |
| Minimum specific leaf area: SLAmin (m2 kg−1) | 10 | |
| Maximum root depth: Rmax (m) | 0.5 | |
| Crop maximum critical N concentration: Ncrit (%) | 2.5 | |
| N transformation parameters | Maximum nitrification rate: Vn (mg L−1 d−1) | 70 |
| Nitrification half saturation constant: Kn (mg L−1) | 70 | |
| Denitrification empirical proportionality factor: Kd (−) | 0.5 | |
| Denitrification empirical constant: Ad (mg mg−1) | 0.02 | |
| Ammonia volatilization first-order kinetic constant: Kv (d−1) | 0.095 | |
| Hydrolysis coefficient of urea: Kh (d−1) | 0.05 | |
| Hydrolysis coefficient of urea in treatment with 1% urease inhibitors: Kh (d−1) | 0.007 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, T.; Wang, H.; Hao, H.; Lin, C.; Hu, K. Modeling the Combined Effects of Straw Returning, Urease Inhibitors, and Nitrogen Split Application on Rice Yield and Ammonia Volatilization in Purple Soil Area. Plants 2025, 14, 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121744
Xu T, Wang H, Hao H, Lin C, Hu K. Modeling the Combined Effects of Straw Returning, Urease Inhibitors, and Nitrogen Split Application on Rice Yield and Ammonia Volatilization in Purple Soil Area. Plants. 2025; 14(12):1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121744
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Tianxiang, Hong Wang, Huirong Hao, Chaowen Lin, and Kelin Hu. 2025. "Modeling the Combined Effects of Straw Returning, Urease Inhibitors, and Nitrogen Split Application on Rice Yield and Ammonia Volatilization in Purple Soil Area" Plants 14, no. 12: 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121744
APA StyleXu, T., Wang, H., Hao, H., Lin, C., & Hu, K. (2025). Modeling the Combined Effects of Straw Returning, Urease Inhibitors, and Nitrogen Split Application on Rice Yield and Ammonia Volatilization in Purple Soil Area. Plants, 14(12), 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121744






