Co-Incorporation of Green Manure and Rice Straw Increases Rice Yield and Nutrient Utilization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design and Implementation
2.3. Sample Collection and Index Determination
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
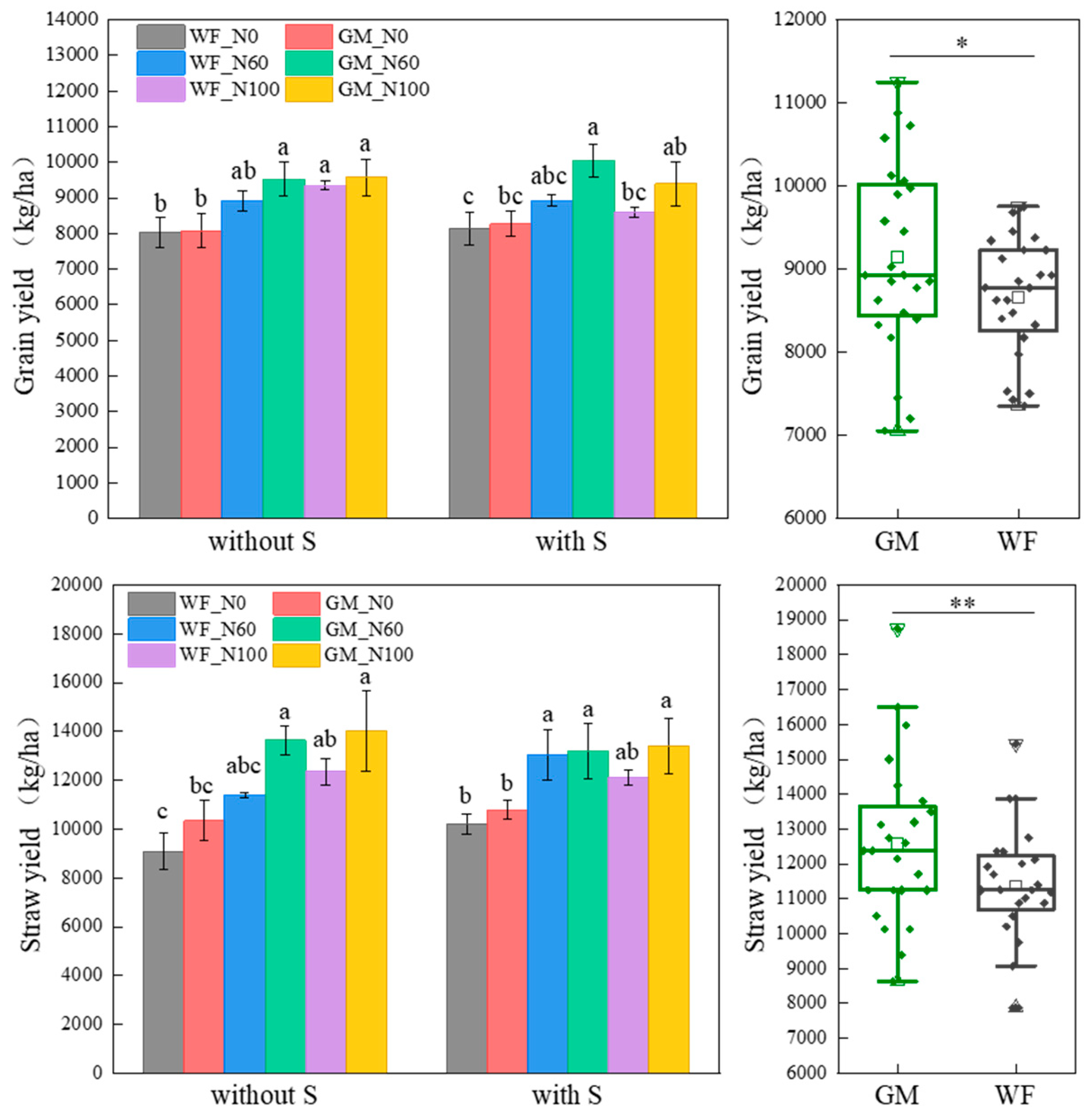
3.1. Rice and Straw Yield Under the Co-Utilization of Milk Vetch and Rice Straw
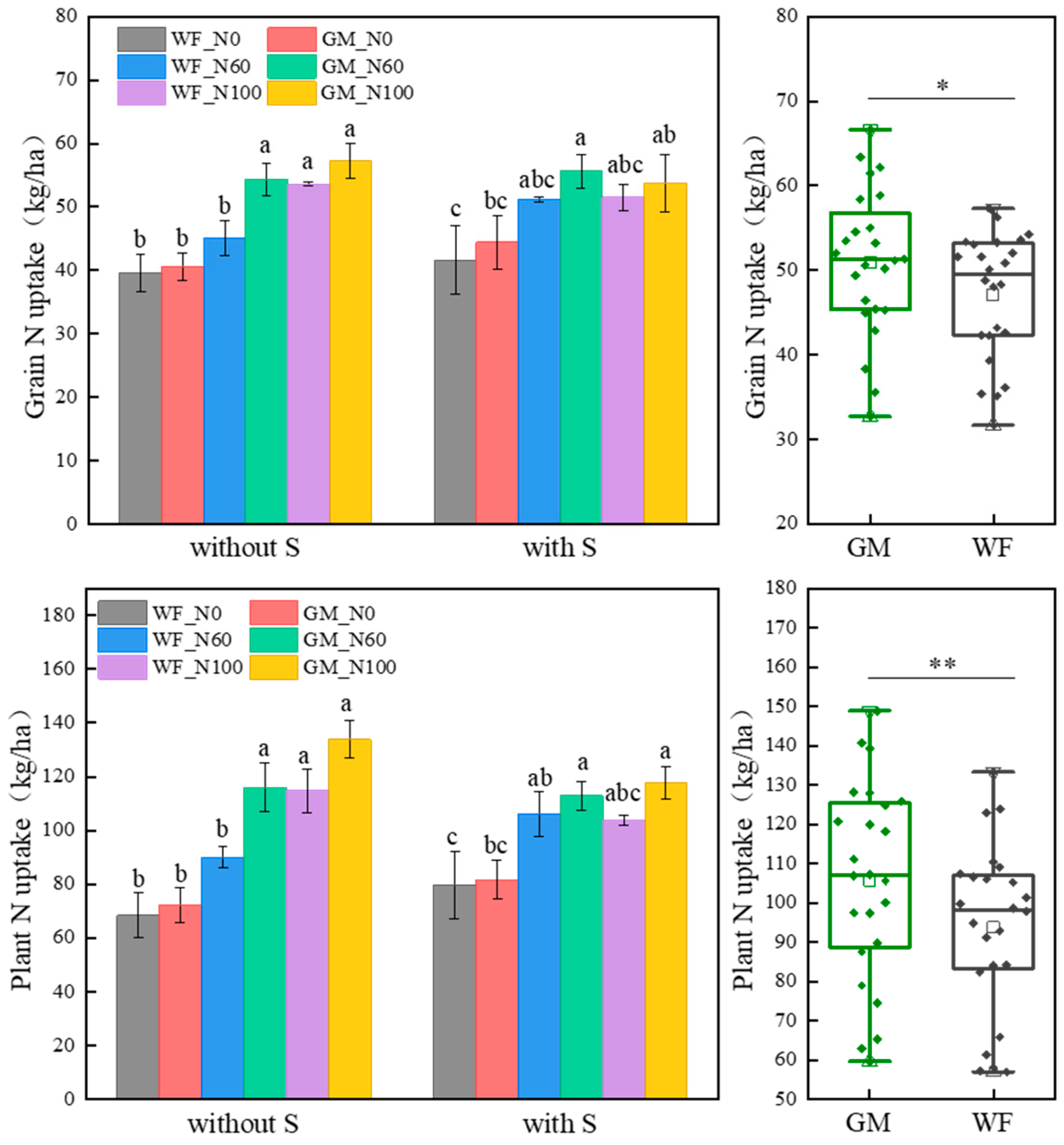
3.2. N Absorption and Utilization of the Co-Utilization of Milk Vetch and Rice Straw
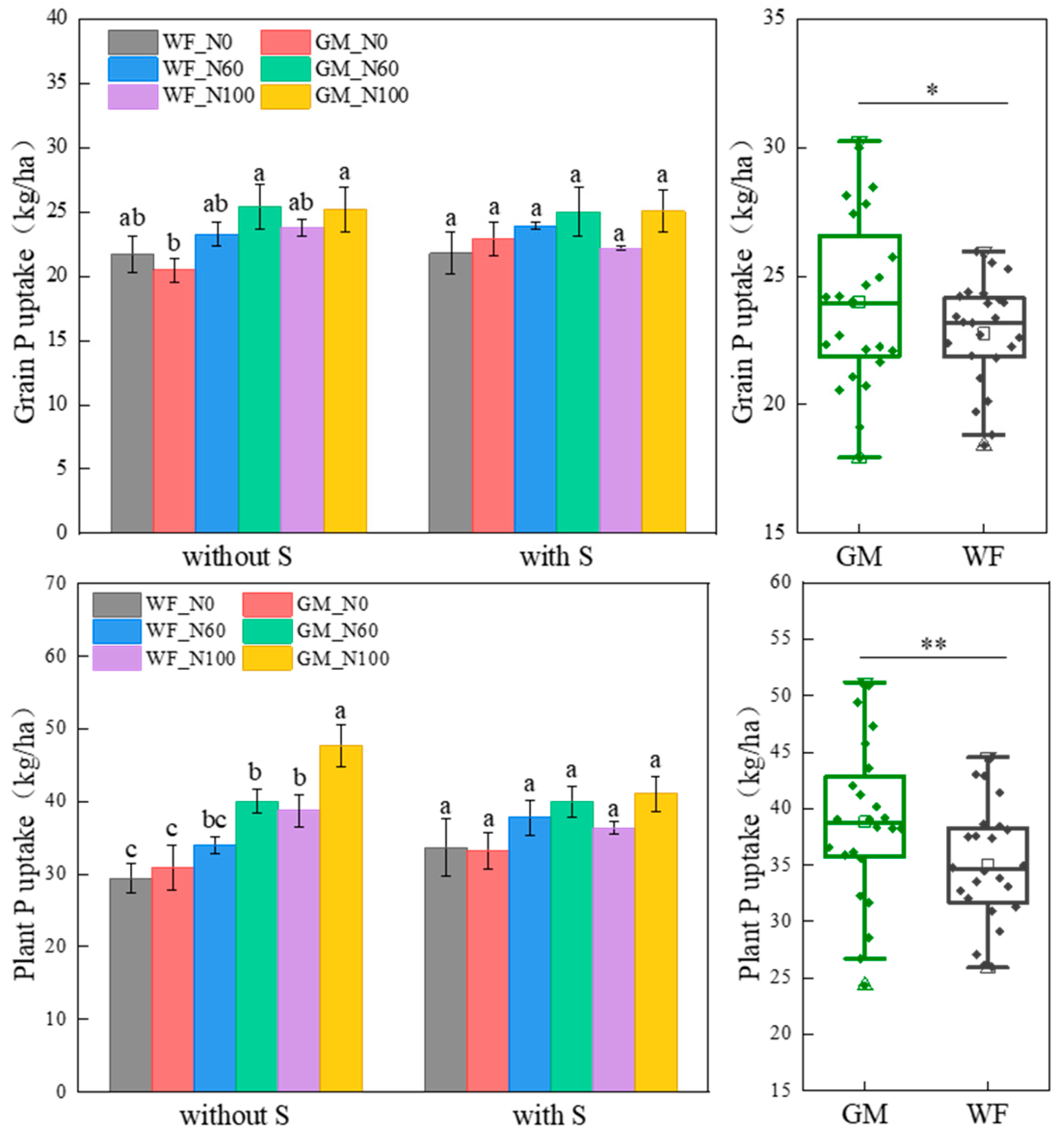
3.3. P Absorption and Utilization of Rice Under the Co-Utilization of Milk Vetch and Rice Straw
3.4. K Absorption and Utilization of Rice Under the Co-Utilization of Milk Vetch and Rice Straw
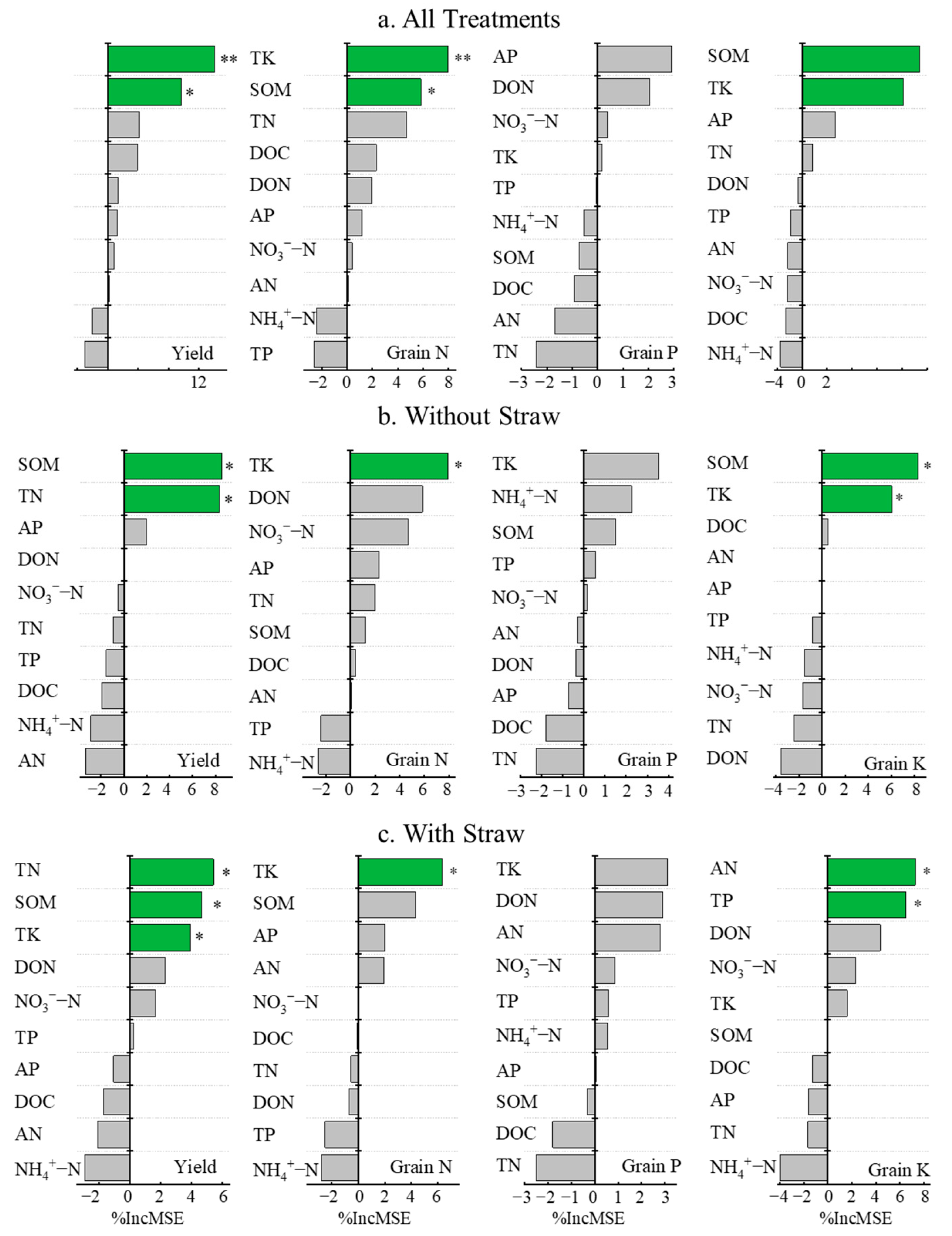
3.5. Impact of Co-Utilization of Milk Vetch and Rice Straw on Soil Fertility
3.6. Impact of Soil Fertility on Rice Yield and Nutrient Absorption Under Co-Utilization of Milk Vetch and Rice Straw
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Milk Vetch Combined with Rice Straw on Rice Yield and Nutrient Absorption
4.2. Effects of Soil Fertility Improvement by Combining Milk Vetch and Rice Straw Return on Rice Growth and Nutrient Absorption
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alengebawy, A.; Ran, Y.; Ghimire, N.; Osman, A.I.; Ai, P. Rice straw for energy and value-added products in China: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 2729–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Fan, M.; Vitousek, P.; Zhang, F.; Yan, X.; Yang, J. Producing more grain with lower environmental costs. Nature 2014, 514, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing nitrogen for sustainable development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, D.; Pyle, J.A.; Raven, J.A.; Sutton, M.A. The global nitrogen cycle in the twenty-first century: Introduction. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 2013, 368, 20130164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, A.F.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Billen, G. Human alteration of the global nitrogen and phosphorus soil balances for the period 1970–2050. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 2009, GB0A04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, W.; Kros, J.; Kroeze, C.; Seitzinger, S.P. Assessing planetary and regional nitrogen boundaries related to food security and adverse environmental impacts. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Xie, J.; Du, J.; Ge, H.; Wei, C.; Qian, H.; Liang, H.; Nie, J.; Hu, F.; Gao, S.; et al. Rice straw nitrogen can be utilized by rice more efficiently when co-incorporating with milk vetch. Eur. J. Agron. 2025, 164, 127495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.J.; Zhou, G.P.; Chang, D.N.; Liang, H.; Nie, J.; Liao, Y.Y.; Lu, Y.H.; Xu, C.C.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.; et al. Southern China can produce more high-quality rice with less N by green manuring. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 196, 107025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.P.; Xu, M.G.; Zheng, S.X.; Nie, J.; Gao, J.S.; Liao, Y.L.; Xie, J. Effects of Long-Term Winter Planted Green Manure on Physical Properties of Reddish Paddy Soil Under a Double-Rice Cropping System. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Nie, J.; Liang, H.; Zhou, G.P.; Zhang, J.L.; Liao, Y.L.; Lu, Y.H.; Tao, Y.Y.; Gao, S.J.; Cao, W.D. Paddy fields can gain high productivity with low net global warming potential by utilizing green manure. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 377, 124596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, G.D.; Zhou, G.P.; Nie, J.; Zhang, J.L.; Gao, S.J.; Cao, W.D. Rice straw returning under winter green manuring enhances soil carbon pool via stoichiometric regulation of extracellular enzymes. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 252, 106617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.Y.; Xu, C.X.; Zhang, L.; Xie, J.C.; Zhou, G.P.; Liu, J.; Hu, F.; Gao, S.J.; Cao, W.D. Application of milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) with reduced chemical fertilizer improves rice yield and nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium use efficiency in southern China. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 144, 126762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Nie, J.; Liang, H.; Wei, C.L.; Wang, Y.; Liao, Y.L.; Lu, Y.H.; Zhou, G.P.; Gao, S.J.; Cao, W.D. The effects of co-utilizing green manure and rice straw on soil aggregates and soil carbon stability in a paddy soil in South China. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 1529–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhou, G.P.; Gao, S.J.; Nie, J.; Xu, C.X.; Wu, J.; Liu, C.Z.; Lv, Y.H.; Huang, Y.B.; Geng, M.J.; et al. Exploring site-specific N application rate to reduce N footprint and increase crop production for green manure-rice rotation system in southern China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 237, 119033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Li, G.; Liang, H.; Liu, R.; Ma, Z.; Gao, S.; Chang, D.; Liu, J.; Chadwick, D.R.; Jones, D.L.; et al. Green manure coupled with straw returning increases soil organic carbon via decreased priming effect and enhanced microbial carbon pump. Glob. Change Biol. 2025, 31, e70232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Chang, D.; Gao, S.; Liang, T.; Liu, R.; Cao, W. Co-incorporating leguminous green manure and rice straw drives the synergistic release of carbon and nitrogen, increases hydrolase activities, and changes the composition of main microbial groups. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2021, 57, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Gao, S.; Chang, D.; Rees, R.M.; Cao, W. Using milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) to promote rice straw decomposition by regulating enzyme activity and bacterial community. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Gao, S.; Chang, D.; Shimizu, K.-Y.; Cao, W. Succession of fungal community and enzyme activity during the co-decomposition process of rice (Oryza sativa L.) straw and milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.). Waste Manag. 2021, 134, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.J.; Zhang, L.L.; Yu, C.X.; Li, D.P.; Gong, P.; Xue, Y.; Song, Y.C.; Cui, Y.L.; Doane, T.A.; Wu, Z.J. Nitrogen fertilizer and straw applications affect uptake of 13C, 15N-glycine by soil microorganisms in wheat growth stages. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.X.; Xiao, Q.; Shen, Y.F.; Li, S.Q. Effects of biochar and maize straw on the short-term carbon and nitrogen dynamics in a cultivated silty loam in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Cao, W.; Bai, J.S.; Xu, C.X.; Zeng, N.H.; Gao, S.J. Non-additive responses of soil C and N to rice straw and hairy vetch (Vicia villosa Roth L.) mixtures in a paddy soil. Plant Soil. 2019, 436, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, X.; Liao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Nie, J.; Cao, W. Co-incorporation of rice straw and green manure benefits rice yield and nutrient uptake. Crop Sci. 2019, 59, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewpradit, W.; Toomsan, B.; Cadisch, G.; Vityakon, P.; Limpinuntana, V.; Saenjan, P.; Jogloy, S.; Patanothai, A. Mixing groundnut residues and rice straw to improve rice yield and N use efficiency. Field Crops Res. 2009, 110, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blonska, E.; Piaszczyk, W.; Staszel, K.; Lasota, J. Enzymatic activity of soils and soil organic matter stabilization as an effect of components released from the decomposition of litter. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 157, 103723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoorens, B.; Aerts, R.; Stroetenga, M. Litter quality and interactive effects in litter mixtures: More negative interactions under elevated CO2? J. Ecol. 2002, 90, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, P.; Haque, M.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, P.J. C and N accumulations in soil aggregates determine nitrous oxide emissions from cover crop treated rice paddy soils during fallow season. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L. Effects of Astragalus sinicus L. and Rice Straw Co-Application on Fertilizer Reduction and Nitrogen Fixation Regulation Mechanism; Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agrochemical Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.J.; Zhou, G.P.; Cao, W.D. Increased Yield and Fertilizer-saving Effects of Astragalus sinicus L. as a Winter Green Manure in Southern Paddy Fields. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2020, 26, 2114–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.P.; Xie, Z.J.; Cao, W.D.; Xu, C.X.; Bai, J.S.; Zeng, N.H.; Gao, S.J.; Yang, L. Improving Soil Fertility and Crop Yield via Combined Incorporation of Rice Straw Stubble and Astragalus sinicus L. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Shi, H.; Pan, X.H.; Chen, Y.; Xu, T.; Wan, S.Y. Effects of Combined Green Manure and Rice Straw Return on Photosynthetic Characteristics, Nutrient Absorption, and Yield Quality of Machine-transplanted Rice. J. Jiangxi Agric. Univ. 2020, 42, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Shi, H.; Pan, X.H.; Xu, T.; Xie, H.W.; Liu, F.P.; Cao, N. Effects of Combined Green Manure and Rice Straw Return on Growth and Yield of Double-cropped Rice. J. Jiangxi Agric. Univ. 2019, 41, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, G.P.; Gao, S.J.; Cao, W.D. Responses of functional genes involved in nitrogen cycling to green manuring in different paddy soils in south China. Plant Soil 2022, 478, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Chang, D.N.; Zhou, G.P.; Gao, S.J.; Zeng, N.H.; Nie, L.P.; Lv, Y.H.; Cao, W.D. Effects of reducing nitrogen fertilizer application rates on nutrient uptake and translocation in rice in the south Henan alfalfa-rice rotation zone. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2022, 28, 1194–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Gao, J.S.; Liu, S.J.; Cao, W.D.; Zhang, Y.Z. Effects of Winter-sown Astragalus sinicus L. on Rice Yield and Nutrient Absorption. Chin. J. Soil Fertil. 2013, 1, 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.G.; Zhang, S.H.; Zhao, J.J.; Wu, G.C.; Li, Z.F.; Xia, J.F. Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer Management on Nitrogen Uptake and Utilization and Yield of Double-cropped Rice at the Northern Margin. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2007, 13, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.M.; Xiao, X.P.; Li, C.; Tang, W.G.; Guo, L.J.; Cheng, K.K.; Li, W.Y. Effects of Different Soil Tillage Systems on Nutrient Accumulation and Translocation in Double-cropped Rice. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2019, 42, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, S.; Mariotti, A.; Abbadie, L. The priming effect of organic matter: A question of microbial competition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil science and the carbon civilization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 71, 1425–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A. Annual crop residue production and nutrient replacement costs for bioenergy feedstock production in United States. Agron. J. 2013, 105, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J. Impacts of 9 years of a new conservational agricultural management on soil organic carbon fractions. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 143, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendener, C.M.; Lehmann, J.; de Camargo, P.B.; Luizão, R.C.C.; Fernandes, E.C.M. Nitrogen transfer between high- and low-quality leaves on a nutrient-poor Oxisol determined by 15N enrichment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Yi, L.; Xu, H.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Dijkstra, P.; Koch, G.W.; Hungate, B.A.; Zhu, B. Leguminous cover crop Astragalus sinicus enhances grain yields and nitrogen use efficiency through increased tillering in an intensive double-cropping rice system in southern China. Agronomy 2019, 9, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Z.; Chang, D.N.; Li, B.Y.; Cao, W.D.; Lü, Y.H.; Pan, Z.L. Effects of green manure and fertilizer application on active organic carbon and nitrogen in paddy soils. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2017, 54, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.T.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, H.Y. Green manure application improves rice growth and urea nitrogen use efficiency assessed using 15N labeling. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 65, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, C.X.; Lv, Y.H.; Gao, S.J.; Cao, W.D. Long-term green manuring enhances crop N uptake and reduces N losses in rice production system. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 220, 105369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenholtz, S.H.; Miegroet, H.V.; Burger, J.A. A review of chemical and physical properties as indicators of forest soil quality: Challenges and opportunities. For. Ecol. Manag. 2000, 138, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, H.H.; Su, Y.R.; Xiao, H.A.; Huang, D.Y.; Wu, J.S. Effects of Straw Return and Soil Relocation on Soil Organic Carbon and Its Active Fractions in Hilly Red Soil Farmland. Chin. J. Agric. Sci. 2009, 42, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Shi, X.J.; Song, G.Y. Long-term effect of rice straw return on soil fertility and productivity of purple paddy soil. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2005, 11, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.J.; Bai, Y.H.; Gao, H.W.; He, J.; Chen, H.; Chesney, R.C.; Kuhn, N.J.; Li, H.W. Soil chemical properties and microbial biomass after 16 years of no-tillage farming on the Loess Plateau, China. Geoderma 2008, 144, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Jalota, S.K.; Singh, Y. Manuring and residue management effects on physical properties of a soil under the rice–wheat system in Punjab, India. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 94, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Y. Release of potassium from K-bearing minerals: Effect of plant roots under P deficiency. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2000, 56, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelt, H.; Coleman, N.T.; Pratt, P.F. Interactions between organic compounds, minerals, and in volcanic-ash-derived soils: Effects of organic compounds on the adsorption of phosphate. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1975, 39, 628–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Ma, J.; Cao, Y. Phosphorus deficiency enhances root exudation of low-molecular weight organic acids and utilization of sparingly soluble inorganic phosphates by radish (Raphanus sativus L.) and rape (Brassica napus L.) plants. Plant Soil 1997, 196, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Liu, S.; Hussain, L.; Wu, Z.; Qin, X.; Li, X. Greenhouse gas emissions, soil quality, and crop productivity from a mono-rice cultivation system as influenced by fallow season straw management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.S.; Huang, J.; Yang, Z.C.; Cao, W.D.; Zhang, H.M.; Gao, P.; Gao, X.C. Combined application of green manure and rice straw increases soil organic matter and stabilizes nitrogen supply. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2020, 26, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlauskiene, A.; Slepetiene, A.; Liaudanskiene, I.; Sarunaite, L.; Amaleviciute, K.; Velykis, A. The influence of short-lived legume swards and straw on soil humic substances in a clay loam cambisol. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2015, 24, 1636–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Thorup-Kristensen, K.; Halberg, N.; Nicolaisen, M.; Olesen, J.E.; Crews, T.E.; Hinsinger, P.; Kirkegaard, J.; Pierret, A.; Dresboll, D.B. Digging Deeper for Agricultural Resources, the Value of Deep Rooting. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Zhang, S.N.; Gu, M.J.; Xu, G.H. Function, transport, and regulation of amino acids: What is missing in rice? Crop J. 2021, 9, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

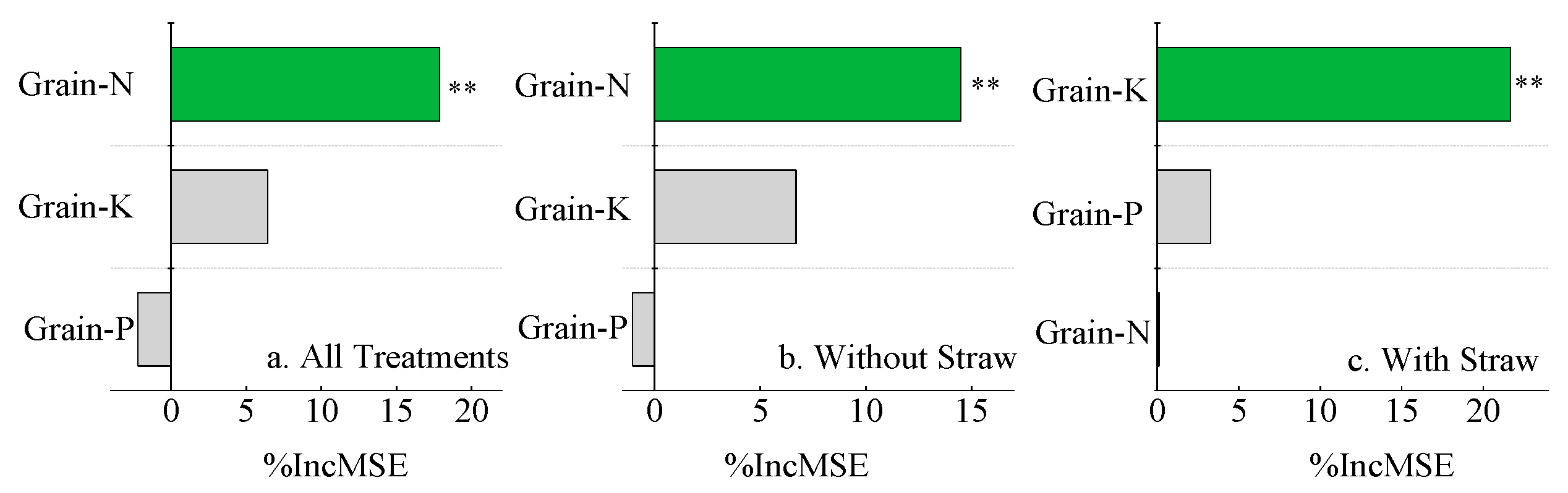
| Treatment | C Content (g/kg) | N Content (g/kg) | P Content (g/kg) | C/N Ratio | C/P Ratio | N/P Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GM | 445.1 ± 2.4 | 32.0 ± 1.3 | 3.4 ± 0.2 | 13.9 ± 0.6 | 131.3 ± 6.3 | 9.4 ± 0.4 |
| RS | 423.2 ± 6.4 | 8.9 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.2 | 47.3 ± 0.5 | 204.8 ± 18.2 | 4.3 ± 0.4 |
| GMS | 429.4 ± 10.8 | 14.2 ± 0.5 | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 30.4 ± 1.4 | 182.0 ± 10.0 | 6.0 ± 0.4 |
| Treament | Winter Crop | Rice Straw Return | N (kg/ha) | P2O5 (kg/ha) | K2O (kg/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WF_N0 | Winter fallow | no rice straw return | 0 | 75 | 100 |
| GM_N0 | Green manure (milk vetch) | no rice straw return | 0 | 75 | 100 |
| WFS_N0 | Winter fallow | rice straw return | 0 | 75 | 100 |
| GMS_N0 | Green manure (milk vetch) | rice straw return | 0 | 75 | 100 |
| WF_N60 | Winter fallow | no rice straw return | 120 | 75 | 100 |
| GM_N60 | Green manure (milk vetch) | no rice straw return | 120 | 75 | 100 |
| WFS_N60 | Winter fallow | rice straw return | 120 | 75 | 100 |
| GMS_N60 | Green manure (milk vetch) | rice straw return | 120 | 75 | 100 |
| WF_N100 | Winter fallow | no rice straw return | 200 | 75 | 100 |
| GM_N100 | Green manure (milk vetch) | no rice straw return | 200 | 75 | 100 |
| WFS_N100 | Winter fallow | rice straw return | 200 | 75 | 100 |
| GMS_N100 | Green manure (milk vetch) | rice straw return | 200 | 75 | 100 |
| Treatment | N Fertilizer Recovery Efficiency (%) | N Fertilizer Agronomic Efficiency (kg/kg) | N Fertilizer Partial Productivity (kg/kg) | N Fertilizer Harvest Index (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| without S | WF_N60 | 23.90 ± 3.32 b | 10.16 ± 2.38 a | 74.38 ± 2.38 a | 50.16 ± 1.90 a |
| GM_N60 | 45.52 ± 7.53 a | 15.16 ± 3.91 a | 79.38 ± 3.91 a | 47.81 ± 4.57 a | |
| WF_N100 | 26.74 ± 4.06 b | 8.18 ± 0.60 a | 46.71 ± 0.60 b | 47.35 ± 3.17 a | |
| GM_N100 | 36.32 ± 3.37 ab | 9.35 ± 2.55 a | 47.88 ± 2.55 b | 42.94 ± 2.49 a | |
| with S | WF_N60 | 37.32 ± 6.86 a | 10.16 ± 1.35 b | 74.38 ± 1.35 b | 49.13 ± 3.86 a |
| GM_N60 | 42.99 ± 4.31 a | 19.60 ± 3.81 a | 83.82 ± 3.81 a | 49.72 ± 3.93 a | |
| WF_N100 | 21.20 ± 0.94 b | 4.50 ± 0.72 b | 43.03 ± 0.72 c | 49.65 ± 1.40 a | |
| GM_N100 | 28.25 ± 3.02 ab | 8.44 ± 3.04 b | 46.97 ± 3.04 c | 45.54 ± 2.58 a | |
| GM | 38.27 ± 2.79 ** | 13.14 ± 1.91 ** | 64.51 ± 4.68 ** | 46.50 ± 1.70 n.s. | |
| WF | 27.29 ± 2.50 | 8.25 ± 0.88 | 59.62 ± 3.88 | 49.07 ± 1.26 | |
| Treatment | P Fertilizer Recovery Efficiency (%) | P Fertilizer Agronomic Efficiency (kg/kg) | P Fertilizer Partial Productivity (kg/kg) | P Fertilizer Harvest Index (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| without S | WF_N0 | 11.92 ± 6.24 d | 11.36 ± 5.64 b | 106.92 ± 5.64 b | 74.04 ± 2.22 a |
| GM_N0 | 23.29 ± 6.70 cd | 16.55 ± 4.52 ab | 112.11 ± 4.52 ab | 65.28 ± 3.27 ab | |
| WF_N60 | 26.18 ± 3.55 bcd | 23.44 ± 3.81 ab | 119.00 ± 3.81 ab | 68.42 ± 1.82 ab | |
| GM_N60 | 44.53 ± 4.83 b | 31.44 ± 6.26 a | 127.00 ± 6.26 a | 63.81 ± 4.88 abc | |
| WF_N100 | 40.43 ± 6.97 bc | 29.00 ± 1.59 a | 124.56 ± 1.59 a | 61.91 ± 2.62 bc | |
| GM_N100 | 67.74 ± 8.84 a | 32.11 ± 6.80 a | 127.67 ± 6.80 a | 53.27 ± 4.23 c | |
| with S | WF_N0 | 31.75 ± 9.86 a | 15.77 ± 5.57 b | 111.33 ± 5.57 b | 64.32 ± 2.16 a |
| GM_N0 | 30.36 ± 3.78 a | 19.44 ± 0.82 b | 115.00 ± 0.82 b | 68.62 ± 2.13 a | |
| WF_N60 | 37.67 ± 7.35 a | 23.44 ± 2.16 b | 119.00 ± 2.16 b | 64.14 ± 4.80 a | |
| GM_N60 | 44.46 ± 6.44 a | 38.55 ± 6.10 a | 134.11 ± 6.10 a | 63.14 ± 6.00 a | |
| WF_N100 | 33.24 ± 2.61 a | 19.19 ± 1.93 b | 114.75 ± 1.93 b | 61.09 ± 0.92 a | |
| GM_N100 | 47.57 ± 7.29 a | 29.69 ± 8.11 ab | 125.25 ± 8.11 ab | 61.12 ± 2.31 a | |
| GM | 51.08 ± 4.01 ** | 32.95 ± 3.19 ** | 128.51 ± 3.19 ** | 60.33 ± 2.30 * | |
| WF | 34.38 ± 2.84 | 23.77 ± 1.44 | 119.33 ± 1.44 | 63.89 ± 1.50 | |
| Treatment | K Fertilizer Recovery Efficiency (%) | K Fertilizer Agronomic Efficiency (kg/kg) | K Fertilizer Partial Productivity (kg/kg) | K Fertilizer Harvest Index (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| without S | WF_N0 | 30.53 ± 11.66 b | 8.52 ± 4.23 b | 80.19 ± 4.23 a | 11.00 ± 1.60 a |
| GM_N0 | 57.37 ± 3.09 a | 12.41 ± 3.39 ab | 80.69 ± 4.80 b | 8.93 ± 1.12 a | |
| WF_N60 | 73.93 ± 8.80 a | 17.58 ± 2.86 ab | 89.25 ± 2.86 ab | 8.98 ± 0.51 a | |
| GM_N60 | 82.37 ± 5.29 a | 23.58 ± 4.69 a | 95.25 ± 4.69 a | 8.47 ± 1.19 a | |
| WF_N100 | 64.17 ± 5.26 a | 21.75 ± 1.20 a | 93.42 ± 1.20 a | 7.98 ± 0.49 a | |
| GM_N100 | 67.47 ± 6.16 a | 24.08 ± 5.10 a | 95.75 ± 5.10 a | 8.49 ± 0.73 a | |
| with S | WF_N0 | 49.13 ± 4.50 b | 9.71 ± 4.69 c | 81.38 ± 4.69 c | 9.21 ± 1.04 a |
| GM_N0 | 69.10 ± 6.35 ab | 14.58 ± 0.61 bc | 82.69 ± 3.61 bc | 8.78 ± 0.45 a | |
| WF_N60 | 71.25 ± 10.62 a | 17.58 ± 1.62 bc | 89.25 ± 1.62 bc | 8.72 ± 1.27 a | |
| GM_N60 | 71.82 ± 7.01 a | 28.91 ± 4.58 a | 100.58 ± 4.58 a | 9.85 ± 0.70 a | |
| WF_N100 | 70.24 ± 5.13 a | 14.39 ± 1.45 bc | 86.06 ± 1.45 bc | 7.63 ± 0.26 a | |
| GM_N100 | 68.53 ± 5.24 ab | 22.27 ± 6.08 ab | 93.94 ± 6.08 ab | 9.18 ± 0.82 a | |
| GM | 72.55 ± 3.07 * | 24.71 ± 2.39 ** | 96.38 ± 2.39 * | 9.00 ± 0.42 n.s. | |
| WF | 69.90 ± 3.61 | 17.82 ± 1.08 | 89.49 ± 1.085 | 8.33 ± 0.36 | |
| Treatment | SOM (g/kg) | TN (g/kg) | TP (g/kg) | TK (g/kg) | NH4+-N (mg/kg) | NO3−N (mg/kg) | AP (mg/kg) | AK (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WF_N0 | 20.26 ± 1.97 a | 1.42 ± 0.08 a | 0.44 ± 0.01 ab | 6.96 ± 0.1 c | 1.9 ± 0.5 b | 3.1 ± 0.6 a | 18 ± 2 a | 79 ± 3 a |
| GM_N0 | 20.97 ± 1.42 a | 1.21 ± 0.04 ab | 0.45 ± 0.02 ab | 9.70 ± 1.04 b | 2.0 ± 0.2 b | 4.7 ± 0.6 a | 19 ± 1 a | 84 ± 5 a |
| WFS_N0 | 21.96 ± 1.69 a | 1.22 ± 0.05 ab | 0.44 ± 0.01 ab | 10.28 ± 0.26 ab | 1.4 ± 0.1 b | 3.8 ± 0.8 a | 22 ± 3 a | 83 ± 2 a |
| GMS_N0 | 22.61 ± 1.57 a | 1.30 ± 0.05 ab | 0.48 ± 0.01 a | 10.88 ± 0.12 a | 1.9 ± 0.1 b | 4.3 ± 1.0 a | 22 ± 2 a | 83 ± 2 a |
| WF_N60 | 22.05 ± 0.56 a | 1.15 ± 0.03 b | 0.45 ± 0.01 ab | 6.65 ± 0.19 c | 2.1 ± 0.2 b | 3.3 ± 0.7 a | 22 ± 3 a | 77 ± 2 a |
| GM_N60 | 21.63 ± 1.19 a | 1.17 ± 0.11 b | 0.41 ± 0.01 b | 6.60 ± 0.07 c | 1.9 ± 0.2 b | 3.1 ± 0.6 a | 19 ± 2 a | 74 ± 2 a |
| WFS_N60 | 21.63 ± 0.35 a | 1.24 ± 0.04 ab | 0.44 ± 0.007 ab | 6.70 ± 0.17 c | 2.2 ± 0.2 b | 2.6 ± 0.7 a | 21 ± 1 a | 79 ± 4 a |
| GMS_N60 | 23.16 ± 1.62 a | 1.29 ± 0.11 ab | 0.44 ± 0.01 ab | 6.68 ± 0.06 c | 1.7 ± 0.1 b | 3.3 ± 0.7 a | 17 ± 1 a | 79 ± 4 a |
| WF_N100 | 21.53 ± 1.61 a | 1.12 ± 0.08 b | 0.44 ± 0.02 ab | 6.63 ± 0.13 c | 1.9 ± 0.4 b | 2.9 ± 0.6 a | 19 ± 2 a | 81 ± 4 a |
| GM_N100 | 21.48 ± 0.54 a | 1.15 ± 0.05 b | 0.44 ± 0.02 ab | 6.49 ± 0.19 c | 4.4 ± 1.4 a | 3.2 ± 0.4 a | 18 ± 2 a | 82 ± 4 a |
| WFS_N100 | 23.16 ± 1.51 a | 1.17 ± 0.05 b | 0.43 ± 0.02 ab | 6.61 ± 0.04 c | 1.4 ± 0.2 b | 2.8 ± 0.6 a | 18 ± 2 a | 86 ± 8 a |
| GMS_N100 | 23.57 ± 0.74 a | 1.23 ± 0.05 ab | 0.43 ± 0.02 ab | 6.53 ± 0.06 c | 2.4 ± 0.5 b | 3.0 ± 0.4 a | 17 ± 2 a | 81 ± 3 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, C.; Cao, B.; Gao, S.; Liang, H. Co-Incorporation of Green Manure and Rice Straw Increases Rice Yield and Nutrient Utilization. Plants 2025, 14, 1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111678
Wei C, Cao B, Gao S, Liang H. Co-Incorporation of Green Manure and Rice Straw Increases Rice Yield and Nutrient Utilization. Plants. 2025; 14(11):1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111678
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Cuilan, Bingshuai Cao, Songjuan Gao, and Hao Liang. 2025. "Co-Incorporation of Green Manure and Rice Straw Increases Rice Yield and Nutrient Utilization" Plants 14, no. 11: 1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111678
APA StyleWei, C., Cao, B., Gao, S., & Liang, H. (2025). Co-Incorporation of Green Manure and Rice Straw Increases Rice Yield and Nutrient Utilization. Plants, 14(11), 1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111678







