Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Wild Ancient Camellia tetracocca in Pu’an, Guizhou, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Evaluation of Genetic Parameters and the Degree of Diversity at ILP Loci
2.2. Evaluation of the Genetic Diversity Level of Wild Ancient Tea Populations in Pu’an
2.3. Genetic Relationship and Genetic Differentiation of Wild Ancient C. tetracocca Population in Pu’an
2.4. Genetic Structure of Wild Ancient C. tetracocca Population in Pu’an
3. Discussion
3.1. Genetic Diversity of Wild Ancient Tea Plants of C. tetracocca Using ILP Markers
3.2. Molecular Variation and Population Genetic Structure
3.3. Wild Ancient Tea Germplasm Conservation and Utilization
4. Materials and Methods
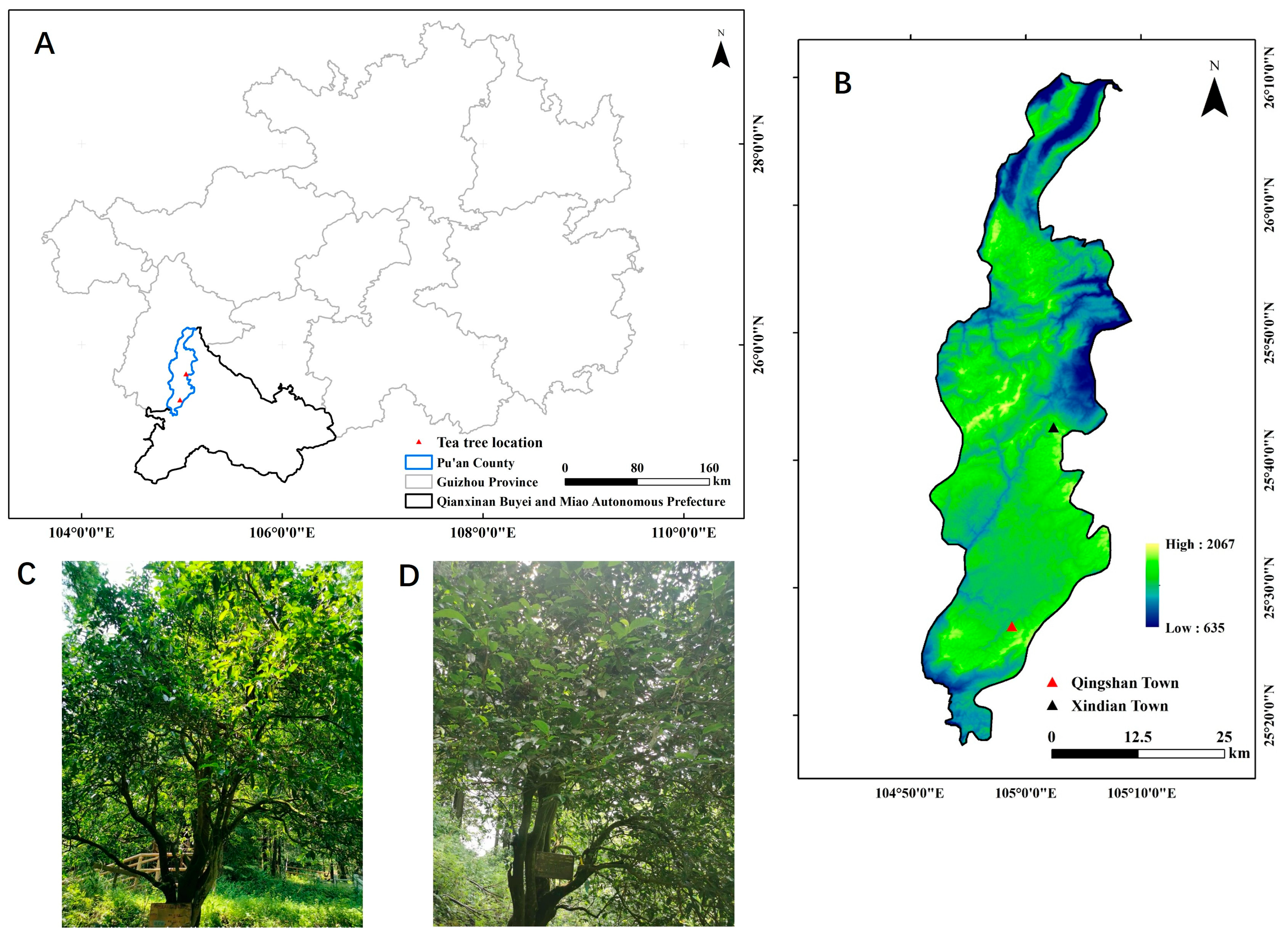
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. ILP Primer Sources
4.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Product Detection
4.4. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.D. Systematic classification of tea plants. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 1981, 1, 87–99. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, M.Q.; Qian, C.J. Study on endemic plant Camellia tetracocca in Pu’an county, Guizhou. Guizhou Sci. 2009, 2, 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, X.Y.; Hu, H.J.; Wang, J.L.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, H.F. Present situation, protection and utilization of big tea tree resources in southwest Guizhou. Agric. Technol. Serv. 2011, 28, 1736–1737. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yin, S.H.; Wang, L.F.; Huang, X.X.; Geng, F.; Chen, X.M. Genetic diversity of Camellia tetracocca Zhang germplasm resources in Pu’an, Guizhou Province. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2022, 44, 74–85. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, F.; Jiang, H.; Yang, F.; Yang, C.; Yu, Z. Comparative analysis of antioxidant activities and chemical compositions in the extracts of different edible parts from Camellia tetracocca Zhang (C. tetracocca) with two distinct color characteristics. Food Chem. 2024, 22, 101496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Ouyang, S.H.; Chang, Y.Q.; Wang, T.M.; Li, W.X.; Tian, H.Y.; Cao, H.; Kurihara, H.; He, R.R. A comparative analysis of chemical compositions in Camellia sinensis var. Pu’anensis Kurihara, a novel Chinese tea, by HPLC and UFLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2017, 216, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.J.; Zhao, G.F.; Li, X.; Shen, Q.; Wu, Q.; Zhuang, J.H.; Zhang, X.Q.; Xia, E.H.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Qian, Y.M.; et al. Comparative analysis of phenolic compound metabolism among tea plants in the section Thea of the genus Camellia. Food Res. Int. 2020, 135, 109276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Tan, W.; Luo, G.; Pu, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Song, Y. Untargeted metabolite profiling of camellia tetracocca’s response to an empoasca onukii attack using GC-MS and LC-MS. Agronomy 2023, 13, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, H.; Wu, Q.; Zha, Y.; Su, J.; Li, F.; Tong, W.; Zhang, L.; Xia, E. Natural variation in promoters of F3’5’H and ANS correlates with catechins diversification in thea species of genus Camellia. Plant J. 2025, 121, e70108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jlassi, I.; Bnejdi, F.; Saadoun, M.; Hajji, A.; Mansouri, D.; Ben-Attia, M.; El-Gazzah, M.; El-Bok, S. SSR markers and seed quality traits revealed genetic diversity in durum wheat (Triticum durum desf.). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 3185–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.C.; Jiang, W.X.; Liang, C.X.; Yao, Q.; Nie, H.Q.; Bai, T.D. Est-SSR-based analysis on genetic diversity of ancient Liupao tea trees and their progeny in Guangxi. Mol. Plant Breed. 2021, 19, 2410–2418. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.Y.; Zhao, C.M.; Sun, X.M.; Li, Y.Y.; Jiang, H.B.; Wang, Y.G.; Machtelinckx, L.; Duan, Z.F. Establishment of DNA fingerprinting in clonal tea improved cultivars from yunnan of china using ISSR markers. Pak. J. Bot. 2015, 47, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, P.Z.; Gao, J.; Liang, M.Z.; Huang, X.Q. AFLP analysis of genetic variation among cloned, seed produced and wild Camellia sinensis var. assamica tea plant in Yunnan, China. Pak. J. Bot. 2012, 44, 1989–1992. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.H.; Yang, P.X.; Peng, H.; Li, C.; Yue, C.N.; Li, W.J.; Jiang, X.F. Comprehensive evaluation of 47 tea [Camel-liasinensis (L.) O. Kuntze] germplasm based on entropy weight method and grey relational degree. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2021, 68, 3257–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.H.; Zhong, J.M.; He, Y.Y.; Fu, W.F.; Yang, J.; Wen, L.G. Genetic relationship and diversity of tea plant germplasm in Fu’an. J. Tea. Commun. 2022, 49, 173–180. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K.; Wang, X.C.; Hao, X.Y.; Qian, Y.H.; Li, X.; Xu, L.Y.; Ruan, L.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Bai, P.X.; et al. Development of a genome-wide 200K SNP array and its application for high-density genetic mapping and origin analysis of Camellia sinensis. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 414–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Fan, X.; Yu, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, P.; Wei, M.; Lu, M.J.; Lv, S.Y.; Cai, C.P.; Ye, N.X. Genetic variation of tea plant in Ningde and its adjacent regions revealed by single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping. Agron. J. 2023, 115, 2829–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Chen, C.; Xu, L.; Tao, L.; Tong, X.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, H.; Chen, L.; Wen, H.; Liu, S.; et al. Genetic diversity analysis and core collection construction of tea plant from the Yunnan Province of China using ddRAD sequencing. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Xie, S.; Zhou, C.; Tian, C.; Zhu, C.; You, X.; Chen, C.; Lai, Z.; Guo, Y. Analysis of the genetic diversity in tea plant germplasm in fujian province based on restriction site-associated DNA sequencing. Plants 2024, 13, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; He, S.; Zheng, X.; Shi, D.; Bai, P.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, J.; Niu, X. Simple sequence repeat marker-based genetic diversity and chemical composition analysis of ancient Camellia sinensis in jiulong county, Sichuan Province, China. Genes 2024, 15, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, E.; Tong, W.; Hou, Y.; An, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yu, J.; Li, F.; Li, R.; et al. The reference genome of tea plant and resequencing of 81 diverse accessions provide insights into its genome evolution and adaptation. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.W.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.W.; Wang, Y.X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, N.; Hu, Z.H.; Li, T.; Zhuang, J. Molecular markers in tea plant (Camellia sinensis): Applications to evolution, genetic identification, and molecular breeding. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2023, 198, 107704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Peng, H.; Yue, C.; Ye, C.; Li, W.; Yang, P. Molecular markers and phenotypic identification reveal the genetic diversity and structure of four local tea plant populations in China. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2024, 71, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Min, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W. Genome-wide development and utilization of novel intron-length polymorphic (ILP) markers in Medicago sativa. Mol. Breed. 2017, 37, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; He, X.; Zu, F.; Huang, X.; Yin, S.; Wang, L.; Geng, F.; Cheng, X. Development of genome-wide intron length polymorphism (ILP) markers in tea plant (Camellia sinensis) and related applications for genetics research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Luo, J.; Niu, S.; Bai, D.; Chen, Y. Population structure analysis to explore genetic diversity and geographical distribution characteristics of wild tea plant in Guizhou Plateau. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.Z.; Song, Q.F.; Koiwa, H.; Qiao, D.H.; Zhao, D.G.; Chen, Z.W.; Liu, X.; Wen, X.P. Genetic diversity, linkage disequilibrium, and population structure analysis of the tea plant (Camellia sinensis) from an origin center, Guizhou plateau, using genome-wide SNPs developed by genotyping-by-sequencing. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Qiu, H.J.; Guo, Y.F.; Wan, H.L.; Zhang, X.L.; Scossa, F.; Alseekh, S.; Zhang, Q.H.; Wang, P.; et al. Genome assembly of wild tea tree DASZ reveals pedigree and selection history of tea varieties. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinosio, S.; Marroni, F.; Zuccolo, A.; Vitulo, N.; Mariette, S.; Sonnante, G.; Aravanopoulos, F.A.; Ganopoulos, I.; Palasciano, M.; Vidotto, M.; et al. A draft genome of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) reveals genome-wide and local effects of domestication. Plant J. 2020, 103, 1420–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Zhai, F.; Su, J.; Wu, D.; Yi, L.; Gao, Q.; Wu, Q.; Xia, E. Genomic variation of 363 diverse tea accessions unveils the genetic diversity, domestication, and structural variations associated with tea adaptation. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2024, 66, 2175–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, E.H.; Zhang, H.B.; Sheng, J.; Li, K.; Zhang, Q.J.; Kim, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, T.; Li, W.; et al. The tea tree genome provides insights into tea flavor and independent evolution of caffeine biosynthesis. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 866–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, E.; Li, F.; Tong, W.; Yang, H.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Gao, L.; Tai, Y.; She, G.; et al. The tea plant reference genome and improved gene annotation using long-read and paired-end sequencing data. Sci. Data. 2019, 6, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.C.; Feng, H.; Chang, Y.X.; Ma, C.L.; Wang, L.Y.; Hao, X.Y.; Li, A.L.; Cheng, H.; Wang, L.; Cui, P.; et al. Population sequencing enhances understanding of tea plant evolution. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Shi, L.; Gong, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Zhan, D.; Vasseur, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; et al. Haplotype-resolved genome assembly provides insights into evolutionary history of the tea plant Camellia sinensis. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.J.; Li, W.; Li, K.; Nan, H.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Z.Y.; Lin, Y.L.; Yang, X.L.; Tong, Y.; et al. The chromosome-level reference genome of tea tree unveils recent bursts of non-autonomous LTR retrotransposons in driving genome size evolution. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yu, J.; Jin, S.; Chen, S.; Yue, C.; Wang, W.; Gao, S.; Cao, H.; Zheng, Y.; Gu, M.; et al. Genetic basis of high aroma and stress tolerance in the oolong tea cultivar genome. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, S.; Martins-Lopes, P.; Lopes, J.; Guedes-Pinto, H. Assessing genetic diversity in Olea europaea L. using ISSR and SSR markers. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2009, 27, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, A.; De la Rosa, R.; Martín, A.; Rallo, P. Development, characterization and inheritance of new microsatellites in olive (Olea europaea L.) and evaluation of their usefulness in cultivar identification and genetic relationship studies. Tree Genet. Genomes 2006, 2, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botstein, D.; White, R.L.; Skolnick, M.; Davis, R.W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1980, 32, 314. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, J.; Colowit, P.M.; Mackill, D.J. Evaluation of genetic diversity in rice subspecies using microsatellite markers. Crop Sci. 2002, 42, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.Z.; Ma, C.L.; Qiao, T.T.; Jin, J.Q.; Chen, L. Diversity distribution and population structure of tea germplasms in China revealed by EST-SSR markers. Tree Genet. Genomes 2012, 8, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Wu, A.; Hou, Y.; An, Y.; Wei, C. Construction of fingerprinting for tea plant (Camellia sinensis) accessions using new genomic SSR markers. Mol. Breed. 2017, 37, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, J.; Lafontaine, P. Life history traits and dispersal shape neutral genetic diversity in metapopulations. J. Math. Biol. 2022, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, M.K.; Huh, H.W. Patterns of genetic diversity and population structure of the clonal herb, Potentilla fragarioides var. sprengeliana (Rosaceae) in Korea. Acta. Bot. Sin. 2000, 42, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, S.C.H.; Kohn, J.K. Genetic and evolutionary consequences of small population size in plants: Implications for conservation. In Genetics & Conservation of Rare Plants; Falk, D.A., Holsinger, K.E., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 3–33. [Google Scholar]
- Tackett, M.; Berg, C.; Simmonds, T.; Lopez, O.; Brown, J.; Ruggiero, R.; Weber, J. Breeding system and geospatial variation shape the population genetics of Triodanis perfoliata. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Cheng, X.; Cheng, S.; Li, W.; Huang, X. Genetic diversity of the wild ancient tea tree (Camellia taliensis) populations at different altitudes in Qianjiazhai. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.W. Plant Allozyme Analysis; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1996; pp. 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, Q.; Dong, X.; Zhao, D.G. Genetic diversity of ancient camellia sinensis (L.) o. kuntze in sandu county of Guizhou Province in China. Diversity 2021, 13, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Lee, J.R.; Sebastin, R.; Shin, M.J.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, G.T.; Hyun, D.Y. Assessment of genetic diversity of tea germplasm for its management and sustainable use in Korea genebank. Forests 2019, 10, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bemmels, J.B.; Title, P.O.; Ortego, J.; Knowles, L.L. Tests of species-specific models reveal the importance of drought in postglacial range shifts of a Mediterranean-climate tree: Insights from integrative distributional, demographic and coalescent modelling and ABC model selection. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 4889–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.L.; Zhang, F.S. Plant Nutrition Genetics; Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1997; Volume 22, pp. 40–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, X.; Xu, Y.D.; Wu, Q.; Liu, D.D.; Shen, J.X.; Wang, L.G.; Wang, W.J. Genetic diversity analysis and fingerprinting of tea lines from tea regions in Anhui Province. Mol. Plant Breed. 2020, 18, 4692–4701. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Song, Q.; Bai, D.; Niu, S.; He, Y.; Qiao, D.; Chen, Z.; Li, C.; Luo, J.; Li, F. Population structure analysis to explore genetic diversity and geographical distribution characteristics of cultivated-type tea plant in Guizhou Plateau. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.M.; Meegahakumbura, M.K.; Wambulwa, M.C.; Burgess, K.S.; Möller, M.; Shen, Z.F.; Li, D.Z.; Gao, L.M. Genetic analyses of ancient tea trees provide insights into the breeding history and dissemination of Chinese Assam tea (Camellia sinensis var. assamica). Plant Divers. 2024, 46, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, P.Z.; Li, H.; Gao, L.Z.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Huang, X.Q. ISSR diversity and genetic differentiation of ancient tea (Camellia sinensis var. assamica) plantations from China: Implications for precious tea germplasm conservation. Pak. J. Bot. 2011, 43, 281–291. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.W.; Yang, J.B.; Yang, S.X.; Kato, K.; Luo, J.P. Genetic diversity and domestication origin of tea plant Camellia taliensis (Theaceae) as revealed by microsatellite markers. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Fan, W. The physiological responds of cutting seedlings of ancient tea plant to drought stress and the comprehensive evaluation on their drought resistance capacity in karst region. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2013, 40, 1541. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhang, M. A method for extracting genomic DNA of tea tree by modified CTAB method. J. Fujian Inst. Educ. 2007, 99–101. [Google Scholar]
- Jayaswall, K.; Sharma, H.; Bhandawat, A.; Sagar, R.; Yadav, V.K.; Sharma, V.; Mahajan, V.; Roy, J.; Singh, M. Development of intron length polymorphic (ILP) markers in onion (Allium cepa L.), and their cross-species transferability in garlic (A. sativum L.) and wild relatives. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2019, 66, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.Q.; Gai, H.M.; Sun, X.; Yang, A.G.; Zhang, Z.F.; Ren, M. SSR data format conversion software DataFormater. Mol. Plant Breed. 2016, 14, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, F.C.; Yang, R. POPGENE(Version 1.31): Population Genetic Analysis Software; University of Alberta and Tim Boyle Center for International Forestry Research: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinowski, S.T. HP-RARE 1.0: A computer program for performing rarefaction on measures of allelic richness. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2004, 5, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Smouse, P.E.; Quattro, J.M. Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distance among DNA haplotypes: Application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 1992, 131, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 8, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research—An update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primer | Na | Ne | I | Ho | He | H | PIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tea_ILP1116 | 6.00 | 3.99 | 1.51 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| Tea_ILP1418 | 4.00 | 2.50 | 1.01 | 0.89 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.60 |
| Tea_ILP1396 | 4.00 | 2.42 | 0.99 | 0.22 | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.59 |
| Tea_ILP1000 | 5.00 | 2.87 | 1.27 | 0.00 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.65 |
| Tea_ILP1589 | 3.00 | 2.21 | 0.93 | 0.39 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 |
| Tea_ILP900 | 3.00 | 1.68 | 0.73 | 0.28 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.41 |
| Tea_ILP1097 | 3.00 | 2.03 | 0.73 | 0.00 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.51 |
| Tea_ILP1023 | 6.00 | 4.36 | 1.58 | 0.04 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.77 |
| Tea_ILP1222 | 4.00 | 2.19 | 0.92 | 0.17 | 0.55 | 0.54 | 0.54 |
| Tea_ILP1192 | 4.00 | 1.61 | 0.77 | 0.18 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.38 |
| Tea_ILP1073 | 3.00 | 1.36 | 0.51 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 |
| Tea_ILP591 | 7.00 | 5.49 | 1.81 | 0.00 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.82 |
| Tea_ILP1158 | 5.00 | 4.26 | 1.51 | 0.48 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.77 |
| Tea_ILP072 | 3.00 | 1.79 | 0.70 | 0.58 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.44 |
| Tea_ILP015 | 4.00 | 3.50 | 1.31 | 0.00 | 0.72 | 0.71 | 0.71 |
| Tea_ILP290 | 2.00 | 1.75 | 0.62 | 0.00 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.43 |
| Tea_ILP380 | 6.00 | 4.35 | 1.59 | 0.39 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.77 |
| Tea_ILP450 | 3.00 | 1.83 | 0.78 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.45 | 0.45 |
| Tea_ILP202 | 4.00 | 2.62 | 1.07 | 0.00 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.62 |
| Tea_ILP284 | 4.00 | 3.19 | 1.23 | 0.00 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.69 |
| Tea_ILP1875 | 8.00 | 6.72 | 1.99 | 0.00 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.85 |
| Tea_ILP1946 | 4.00 | 3.20 | 1.23 | 0.00 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.69 |
| Tea_ILP1986 | 10.00 | 8.01 | 2.19 | 0.00 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 |
| Tea_ILP2114 | 7.00 | 2.89 | 1.32 | 0.00 | 0.66 | 0.65 | 0.65 |
| Tea_ILP2142 | 4.00 | 1.81 | 0.79 | 0.01 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 |
| Tea_ILP2171 | 5.00 | 3.50 | 1.37 | 0.00 | 0.72 | 0.71 | 0.71 |
| Tea_ILP1923 | 3.00 | 2.07 | 0.79 | 0.82 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.52 |
| Tea_ILP1924 | 6.00 | 1.47 | 0.70 | 0.00 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 |
| Tea_ILP1945 | 4.00 | 2.29 | 1.00 | 0.61 | 0.57 | 0.56 | 0.56 |
| Tea_ILP1951 | 4.00 | 2.04 | 0.94 | 0.38 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.51 |
| Tea_ILP1967 | 4.00 | 3.03 | 1.15 | 0.00 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.67 |
| Tea_ILP1982 | 5.00 | 1.93 | 0.94 | 0.00 | 0.48 | 0.48 | 0.48 |
| Tea_ILP1991 | 4.00 | 2.41 | 1.05 | 0.58 | 0.59 | 0.58 | 0.58 |
| Tea_ILP2017 | 6.00 | 3.96 | 1.56 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| Tea_ILP2551 | 3.00 | 1.55 | 0.57 | 0.44 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.35 |
| Tea_ILP3195 | 5.00 | 2.51 | 1.13 | 0.00 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.60 |
| Tea_ILP1959 | 3.00 | 2.02 | 0.79 | 0.72 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.51 |
| Tea_ILP3087 | 3.00 | 1.16 | 0.28 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 |
| Tea_ILP1953 | 4.00 | 2.86 | 1.14 | 0.00 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.65 |
| Tea_ILP2343 | 5.00 | 3.04 | 1.28 | 0.00 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.67 |
| Mean | 4.50 | 2.86 | 1.10 | 0.20 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.58 |
| Population | Sample Size | Na | Ne | I | Ho | He | H | AR | PA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qingshan town | 90 | 4.38 | 2.98 | 1.13 | 0.20 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 2.54 | 0.89 |
| Xindian town | 48 | 4.05 | 2.30 | 0.90 | 0.20 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 2.21 | 0.57 |
| p value | 0.04 * | 0.03 * | 0.02 * | 0.70 | 0.03 * | 0.03 * | 0.02 * | 0.00 * |
| POPGENE | AMOVA | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fis | Fit | Fst | Nm | Source of Variation | df | SS | var. Components | PMV% |
| 0.64 | 0.65 | 0.04 | 6.85 | Among population | 1 | 519.24 | 1.93 | 8.41 (p < 0.001) |
| Within populations | 136 | 4631.68 | 21.02 | 91.59 (p < 0.001) | ||||
| Population | Typology | Sample Size | Longitude | Latitude | Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qingshan town | Wild-type | 90 | 104.96–104.98 | 25.43–25.45 | 1691–1744 |
| Xindian town | Wild-type | 48 | 105.03–105.04 | 25.70–25.71 | 1822–1834 |
| Marker ID | Forward Primer 5′-3′ | Reverse Primer 5′-3′ |
|---|---|---|
| Tea_ILP1116 | AGTAGGGTTTTTGCCTCCGT | AAGTACCGTACCCGCACTTG |
| Tea_ILP1418 | ATTGCATTCTTCCTCGCACT | TCACAAATCAATTCCACCGA |
| Tea_ILP1396 | CATCTCTCTCCTCCCTGCTG | TGTTCTATGGGATCTTCGCC |
| Tea_ILP1000 | CCACCGGTTTCTGAAGATGT | CGCCTCCTTCTCTTTCCTCT |
| Tea_ILP1589 | TCTGCTGCTAGATGCAAATGA | AGGAGCAACATAATTTGGCG |
| Tea_ILP900 | GCTCGCACTCCAAGTAGGAT | TGACCTTGAAGCCAAAATTAAA |
| Tea_ILP1097 | GCAGGAGACCTACTGGATGC | AAAGCGACAGTAGCCAGGAA |
| Tea_ILP1023 | GGTGTAACCCAAGATCCCCT | TCCCACTGTCGATGTCTCAG |
| Tea_ILP1222 | GCTGAGTTTCCTTTGGCAAG | CAAATGCATAATGTGGTCGC |
| Tea_ILP1192 | GGCTGGGAATATGCTCTCAA | TTTGCAGAGCACTGAGGTTG |
| Tea_ILP1073 | AATTCAGCCATCTGTCCAGC | TGACAGGATGGGCTTAAAGG |
| Tea_ILP591 | TCATCGTTGTCGAGATTGGA | GACATGGCTGAGAGGAGAGG |
| Tea_ILP1158 | CTTCGACTGAACACCCTCGT | GGAGGTGCAAACCACCTTTA |
| Tea_ILP072 | TGCTTCATGTGCAGAACCAT | CTTGAACGACAACCCTCCAT |
| Tea_ILP015 | AGATGCAGACGGAGAGCAAT | GCTTGCTTGGTTCAGGTAGC |
| Tea_ILP290 | TTGAGATTCACTGCATAGCCA | AAATTCACTCAAACGGCCTG |
| Tea_ILP380 | CTCGATAGGTTTGGGGTCAA | AATTGTGGGTGGCTCGTTAC |
| Tea_ILP450 | TTGGGTTCGAAGAGTTGAGG | TAGCGAAAACGAAAGCCAGT |
| Tea_ILP202 | TGAATCCGCCTTAACCAAAC | GAGCAACAACAGTTGGCTGA |
| Tea_ILP284 | GAAATGAAACTGCCCATGCT | TAGGAGCAGGTGCTGGAACT |
| Tea_ILP1875 | ACGACTCCAAGGTGGTTTTG | AAGGAAGCCCTTTCTGGATG |
| Tea_ILP1946 | TTTCGCATTCTATCAAACATGG | TGATGGTATGACATGGTGCC |
| Tea_ILP1986 | TTTCTTCCTCCACAGCAAGC | CTTGCGCACTTCTTCCTTGT |
| Tea_ILP2114 | GATTTTGGCGCTCATCATTT | GCTTTTATCGTCCATCGGAA |
| Tea_ILP2142 | CAAATTCCAACAACAATGCG | TTCCCCACCAAATTCGTTT |
| Tea_ILP2171 | TGAAGTATGCCCACTTGGAA | TAAAGGATGCAGTTGGTCGG |
| Tea_ILP1923 | GCTTCAAAGCCTATGCAAGAA | GGGAAGATCAGAGGCATTCA |
| Tea_ILP1924 | GAGCACGGATTCAGTTGTCA | GAGCCACCCTTCCCAATTAT |
| Tea_ILP1945 | AAGGCCATTGAGCACAAAAC | GGGGCAATAAATGACAATGG |
| Tea_ILP1951 | AAGGCAATCAAGCAAGCACT | GAGGAAGCAGTTGCATCACA |
| Tea_ILP1967 | TCTCGTGTTGTGGGCAAATA | TTGTTCAGGGCTCTTGCTTT |
| Tea_ILP1982 | GCAAATGGAAAGCTTGTGCT | AATGCCATCCTCTCAAATGC |
| Tea_ILP1991 | AAAGCTGGCAGGGTCATCT | GGCAAGGATGACAAGGCTAA |
| Tea_ILP2017 | GATGTGCCGTGTTGTGAGAC | GCATTGCATATGAGGAGGGT |
| Tea_ILP2551 | GGATTCCTCCTCAAACTCTTCA | TGCCAGCCTTCTTCTCTTTC |
| Tea_ILP3195 | CATTACCAATGGCAAATCCC | CTCGAGTCCACCAAGGAAAC |
| Tea_ILP1959 | ACACTGTGTCAGTTGGCGAG | TTCGAGATCGAATGTTTAGGC |
| Tea_ILP3087 | GACCAGAAAATTGGGCATTG | AGCTGCATGTTCAGCAACAA |
| Tea_ILP1953 | TATGCTGAAGCCCACACATC | TGTGGACCATGCAAGGTTAG |
| Tea_ILP2343 | AAACCAGCGAGATGGAACAC | AGATCGACGGGATTGAGTTG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Li, L.; Chang, S.; Zhang, S.; Feng, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Hu, H.; Zu, F.; Cheng, X. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Wild Ancient Camellia tetracocca in Pu’an, Guizhou, China. Plants 2025, 14, 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111709
Li D, Li L, Chang S, Zhang S, Feng J, Wang L, Huang X, Hu H, Zu F, Cheng X. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Wild Ancient Camellia tetracocca in Pu’an, Guizhou, China. Plants. 2025; 14(11):1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111709
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Deqin, Lushan Li, Shukui Chang, Shunrong Zhang, Jian Feng, Lifei Wang, Xiaoxia Huang, Huizhen Hu, Feng Zu, and Xiaomao Cheng. 2025. "Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Wild Ancient Camellia tetracocca in Pu’an, Guizhou, China" Plants 14, no. 11: 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111709
APA StyleLi, D., Li, L., Chang, S., Zhang, S., Feng, J., Wang, L., Huang, X., Hu, H., Zu, F., & Cheng, X. (2025). Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Wild Ancient Camellia tetracocca in Pu’an, Guizhou, China. Plants, 14(11), 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111709







