Effects of Cadmium Stress on Root Exudates and Soil Rhizosphere Microorganisms of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) and Its Ecological Regulatory Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
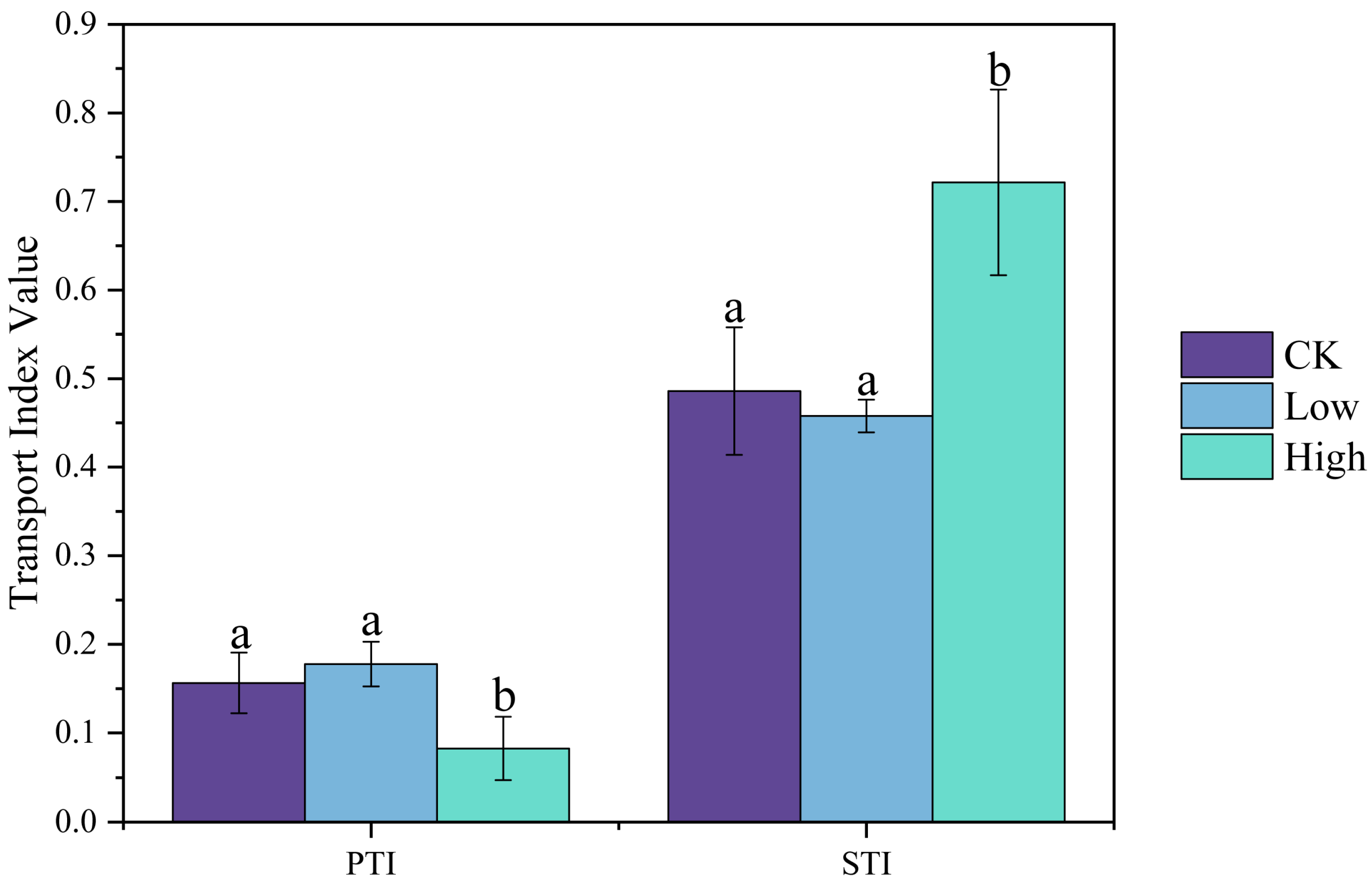
2.1. Changes in the Cadmium Content of Rice Tissues Under Cd Stress
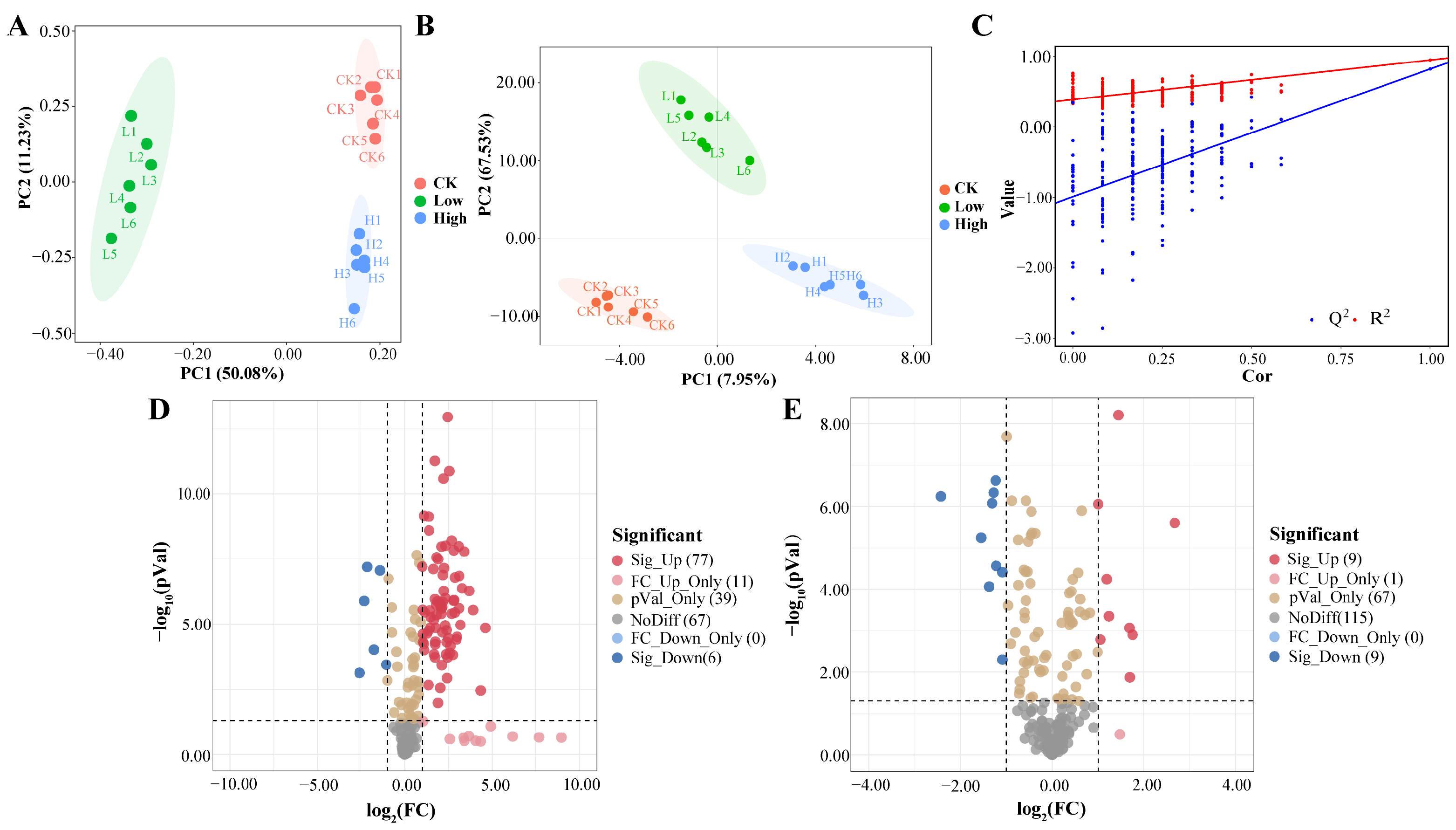
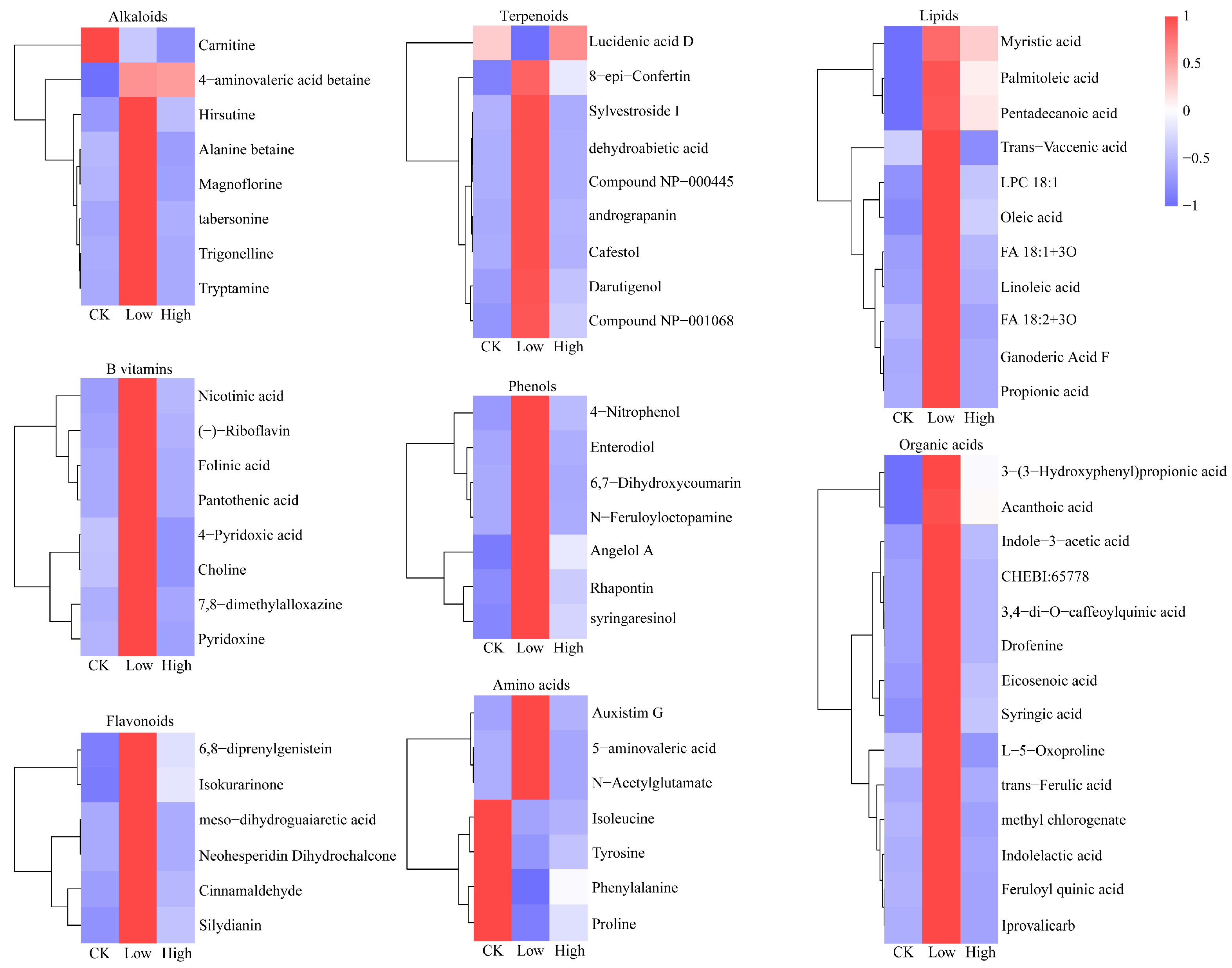
2.2. Effect of Cd Stress on Root Exudates of Rice
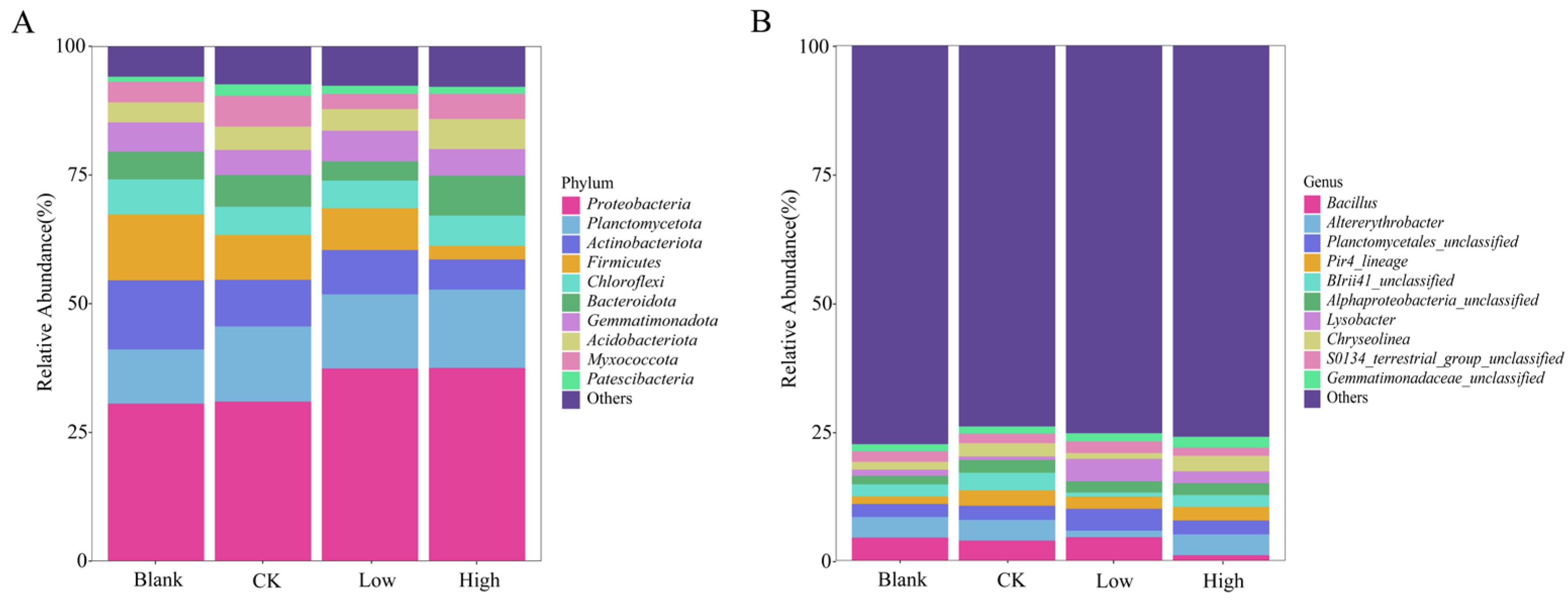
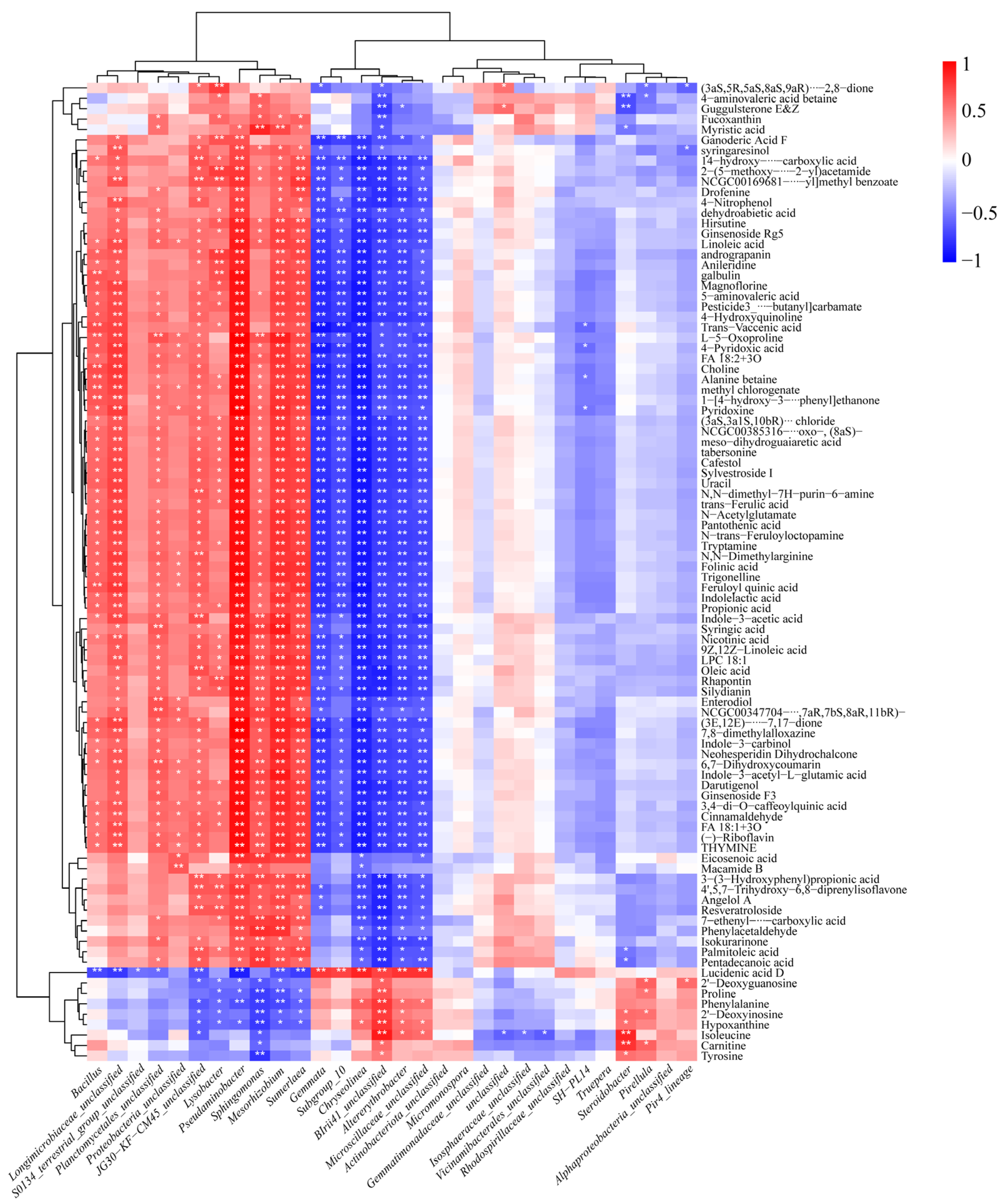
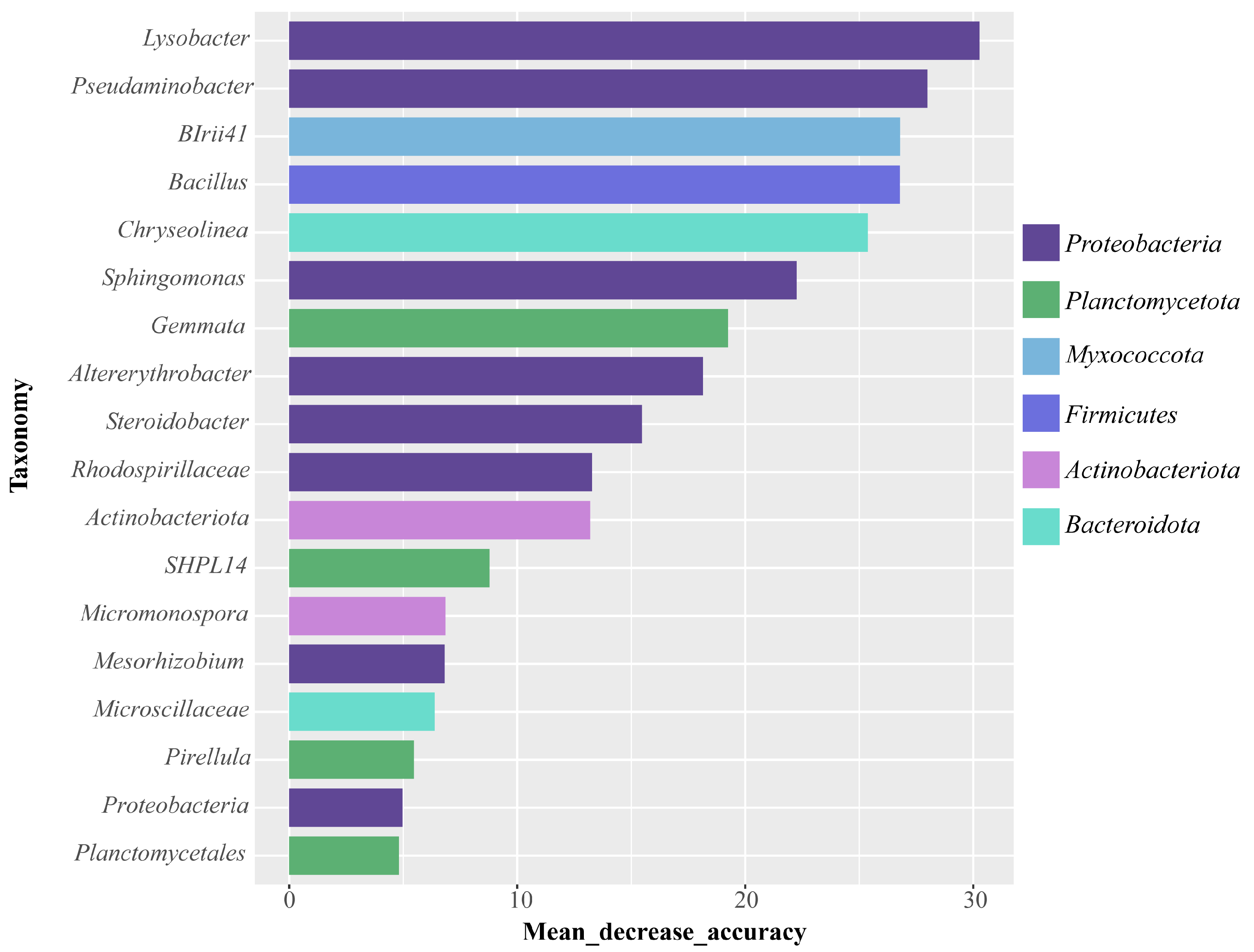
2.3. Effect of Cd Stress on Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Communities
3. Discussion
3.1. Changes in Rice Root Exudate Patterns: Impacts on Cd Uptake and Translocation as Well as Self-Repair
3.2. Effects of Cd Stress on the Rhizosphere Microbial Communities
3.3. Ecological Regulatory Mechanisms of Microbial Communities Recruited by Rice Root Exudates Under Cd Stress
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design
4.2. Analysis of Root Exudates
4.3. DNA Extraction and Bacterial Sequencing
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, F.; Gu, F.; Yan, H.; He, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Yang, T.; Wang, F. Effects of soaking process on arsenic and other mineral elements in brown rice. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2020, 9, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Deng, M.; Japenga, J.; Li, T.; Yang, X.; He, Z. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of agricultural soils in a typical peri-urban area in southeast China. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 207, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Ma, J.; Wei, H.; Wu, X.; Zhao, L.; Hou, H. Status of cadmium accumulation in agricultural soils across China (1975–2016): From temporal and spatial variations to risk assessment. Chemosphere 2019, 230, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, K.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, W. Cadmium Absorption in Various Genotypes of Rice under Cadmium Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, B.; Huang, R.; Li, H.; Tao, Q.; Li, Q.; Tang, X.; Xu, Q.; et al. Integrated morphological, physiological and transcriptomic analyses reveal response mechanisms of rice under different cadmium exposure routes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, A.S.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Kumar, V. Root exudates ameliorate cadmium tolerance in plants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1243–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, R.; Srivastava, S.; Prakash, S.; Srivastava, M.M. Cadmium mobilisation and plant availability—The impact of organic acids commonly exuded from roots. Plant Soil 2001, 230, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UdDin, I.; Bano, A.; Masood, S. Chromium toxicity tolerance of Solanum nigrum L. and Parthenium hysterophorus L. plants with reference to ion pattern, antioxidation activity and root exudation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 113, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallverdú-Queralt, A.; Regueiro, J.; Martínez-Huélamo, M.; Rinaldi Alvarenga, J.F.; Leal, L.N.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M. A comprehensive study on the phenolic profile of widely used culinary herbs and spices: Rosemary, thyme, oregano, cinnamon, cumin and bay. Food Chem. 2014, 154, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjitha, K.S.; Sameena, P.P.; Puthur, J.T. Functional aspects of plant secondary metabolites in metal stress tolerance and their importance in pharmacology. Plant Stress 2021, 2, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manquián-Cerda, K.; Escudey, M.; Zúñiga, G.; Arancibia-Miranda, N.; Molina, M.; Cruces, E. Effect of cadmium on phenolic compounds, antioxidant enzyme activity and oxidative stress in blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) plantlets grown in vitro. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 133, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeeshma, E.; Rajan, V.K.; Puthur, J.T. Spectral variations associated with anthocyanin accumulation; an apt tool to evaluate zinc stress in Zea mays L. Chem. Ecol. 2021, 37, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, S.; Jamwal, V.L.; Kohli, S.K.; Kaur, P.; Tejpal, R.; Bhalla, V.; Ohri, P.; Gandhi, S.G.; Bhardwaj, R.; Al-Huqail, A.A.; et al. Jasmonic acid application triggers detoxification of lead (Pb) toxicity in tomato through the modifications of secondary metabolites and gene expression. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 734–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, V.; Schiavon, M.; Celi, L. Role of soil abiotic processes on phosphorus availability and plant responses with a focus on strigolactones in tomato plants. Plant Soil 2024, 494, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, M.; Ghorbanpour, M.; Kariman, K. Physiological and antioxidative responses of medicinal plants exposed to heavy metals stress. Plant Gene 2017, 11, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Vibhandik, R.; Agrahari, R.; Daverey, A.; Rani, R. Role of Root Exudates on the Soil Microbial Diversity and Biogeochemistry of Heavy Metals. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 196, 2673–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Jiang, S.; Jiang, C.; Wu, C.; Gao, M.; Wang, Q. A review of root exudates and rhizosphere microbiome for crop production. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 54497–54510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Wang, Q.; Lv, M.; Chen, L. Microorganism remediation strategies towards heavy metals. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, A.; Dennis, P.G.; Forstner, C.; Raghavendra, A.K.H.; Mathesius, U.; Richardson, A.E.; Delhaize, E.; Gilliham, M.; Watt, M.; Ryan, P.R. Manipulating exudate composition from root apices shapes the microbiome throughout the root system. Plant Physiol. 2021, 187, 2279–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, A.; Okada, S.; Zhang, C.; Delhaize, E.; Mathesius, U.; Richardson, A.E.; Watt, M.; Gilliham, M.; Ryan, P.R. A sterile hydroponic system for characterising root exudates from specific root types and whole-root systems of large crop plants. Plant Methods 2018, 14, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalhais, L.C.; Dennis, P.G.; Badri, D.V.; Kidd, B.N.; Vivanco, J.M.; Schenk, P.M. Linking Jasmonic Acid Signaling, Root Exudates, and Rhizosphere Microbiomes. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2015, 28, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulgarelli, D.; Schlaeppi, K.; Spaepen, S.; van Themaat, E.V.L.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Structure and Functions of the Bacterial Microbiota of Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2013, 64, 807–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhao, J.; Ding, Z.; Xiong, F.; Liu, X.; Tian, J.; Wu, N. Cadmium-absorptive Bacillus vietnamensis 151–6 reduces the grain cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.): Potential for cadmium bioremediation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 254, 114760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, L.; Tian, J.; Wu, N. Cadmium Pollution Impact on the Bacterial Community Structure of Arable Soil and the Isolation of the Cadmium Resistant Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 698834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, S.A.; Farooq, M.; Afzal, A.; West, H. Integrated phytobial heavy metal remediation strategies for a sustainable clean environment—A review. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 925–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, S.P.; Zhao, F.-J. Phytoextraction of metals and metalloids from contaminated soils. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 14, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonell-Barrachina, A.A.; Burló-Carbonell, F.; Mataix-Beneyto, J. Arsenic uptake, distribution, and accumulation in bean plants: Effect of Arsenite and salinity on plant growth and yield. J. Plant Nutr. 1997, 20, 1419–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, N.; Wu, X.; Geng, W.; Xu, X. Effect of insect feces (Hermetia illucens) on rice growth and heavy metal migration from polluted soil to rice plant. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 14695–14704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, X. Cadmium absorption and transportation pathways in plants. Int. J. Phytorem. 2017, 19, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getzke, F.; Hassani, M.A.; Crüsemann, M.; Malisic, M.; Zhang, P.; Ishigaki, Y.; Böhringer, N.; Jiménez Fernández, A.; Wang, L.; Ordon, J.; et al. Cofunctioning of bacterial exometabolites drives root microbiota establishment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2221508120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaashikaa, P.R.; Kumar, P.S.; Jeevanantham, S.; Saravanan, R. A review on bioremediation approach for heavy metal detoxification and accumulation in plants. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 301, 119035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezapour, S.; Atashpaz, B.; Moghaddam, S.S.; Kalavrouziotis, I.K.; Damalas, C.A. Cadmium accumulation, translocation factor, and health risk potential in a wastewater-irrigated soil-wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) system. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Z.; He, Q.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Fang, L.; Nie, J. Assessing the Effects of Cadmium Stress on the Growth, Physiological Characteristics, and Metabolic Profiling of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Using HPLC-QTOF/MS. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Yu, H.; Li, T.; Zhang, X. Influence of cadmium stress on root exudates of high cadmium accumulating rice line (Oryza sativa L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 150, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z. Rice organs concentrate cadmium by chelation of amino acids containing dicarboxyl groups and enhance risks to human and environmental health in Cd-contaminated areas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 128130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Nie, Z.; Jia, H.; Yan, C.; Hong, H.; Wang, X.; Du, D. Phenolic root exudates enhance Avicennia marina tolerance to cadmium under the mediation of functional bacteria in mangrove sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 185, 114227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, X.; Lv, J. Dynamics of fungal and bacterial communities in different types of soil ageing with different dosages of cadmium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 242, 113860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, W.; Lu, X. Shifts in bacterial diversity, interactions and microbial elemental cycling genes under cadmium contamination in paddy soil: Implications for altered ecological function. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, T.; Krohn, C.; Jin, J.; Chathurika, J.B.A.J.; Franks, A.; Xu, J.; Potter, I.D.; Tang, C. The effects of biochar aging on rhizosphere microbial communities in cadmium-contaminated acid soil. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fang, L.; Beiyuan, J.; Cui, Y.; Peng, Q.; Zhu, S.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X. Improvement of alfalfa resistance against Cd stress through rhizobia and arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi co-inoculation in Cd-contaminated soil. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.M.; Yang, H.J.; Huang, J.G.; Yuan, L. Lysobacter enzymogenes LE16 autolysates have potential as biocontrol agents—Lysobacter sp. autolysates as biofungicide. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1684–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Qiao, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, Z.; Yu, C. Microbial community succession in soils under long-term heavy metal stress from community diversity-structure to KEGG function pathways. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.; Mishra, S.; Bisen, K.; Singh, S.; Sarma, B.K.; Singh, H.B. Modulation in phenolic root exudate profile of Abelmoschus esculentus expressing activation of defense pathway. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 207, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whipps, J.M. Microbial interactions and biocontrol in the rhizosphere. J. Exp. Bot. 2001, 52, 487–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, B.S.; Ritz, K.; Ebblewhite, N.; Dobson, G. Soil microbial community structure: Effects of substrate loading rates. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yu, G.; Wu, F. Soil phenolics in a continuously mono-cropped cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) system and their effects on cucumber seedling growth and soil microbial communities. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2012, 63, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, H.; Mou, L.; Ru, J.; Zhao, J.; Xiao, S. Long-term and high-concentration heavy-metal contamination strongly influences the microbiome and functional genes in Yellow River sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-G.; Ding, C.-F.; Hua, K.; Zhang, T.-L.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Y.-R.; Liu, J.-G.; Wang, X.-X. Soil sickness of peanuts is attributable to modifications in soil microbes induced by peanut root exudates rather than to direct allelopathy. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankati, S.; Podile, A.R. Metabolites in the root exudates of groundnut change during interaction with plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in a strain-specific manner. J. Plant Physiol. 2019, 243, 153057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ge, C.; Xu, S.A.; Wu, Y.; Sahito, Z.A.; Ma, L.; Pan, F.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, L.; Feng, Y.; et al. The endophytic bacterium Sphingomonas SaMR12 alleviates Cd stress in oilseed rape through regulation of the GSH-AsA cycle and antioxidative enzymes. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logue, J.B.; Stedmon, C.A.; Kellerman, A.M.; Nielsen, N.J.; Andersson, A.F.; Laudon, H.; Lindström, E.S.; Kritzberg, E.S. Experimental insights into the importance of aquatic bacterial community composition to the degradation of dissolved organic matter. ISME J. 2016, 10, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, S.; He, Q.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H.; Mu, Q.; Wang, S.; Nie, J. Effects of Cadmium Stress on Root Exudates and Soil Rhizosphere Microorganisms of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) and Its Ecological Regulatory Mechanisms. Plants 2025, 14, 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111695
Lin S, He Q, Zhang M, Huang Y, Liu H, Mu Q, Wang S, Nie J. Effects of Cadmium Stress on Root Exudates and Soil Rhizosphere Microorganisms of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) and Its Ecological Regulatory Mechanisms. Plants. 2025; 14(11):1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111695
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Siqi, Qing He, Mingxia Zhang, Yingyi Huang, Huahong Liu, Qi’er Mu, Sheng Wang, and Jinfang Nie. 2025. "Effects of Cadmium Stress on Root Exudates and Soil Rhizosphere Microorganisms of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) and Its Ecological Regulatory Mechanisms" Plants 14, no. 11: 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111695
APA StyleLin, S., He, Q., Zhang, M., Huang, Y., Liu, H., Mu, Q., Wang, S., & Nie, J. (2025). Effects of Cadmium Stress on Root Exudates and Soil Rhizosphere Microorganisms of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) and Its Ecological Regulatory Mechanisms. Plants, 14(11), 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111695






