A Comprehensive Screening of the Interactors of Areca Palm Necrotic Ringspot Virus (ANRSV) HCPro2 Highlights the Proviral Roles of eIF4A and PGK in Viral Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
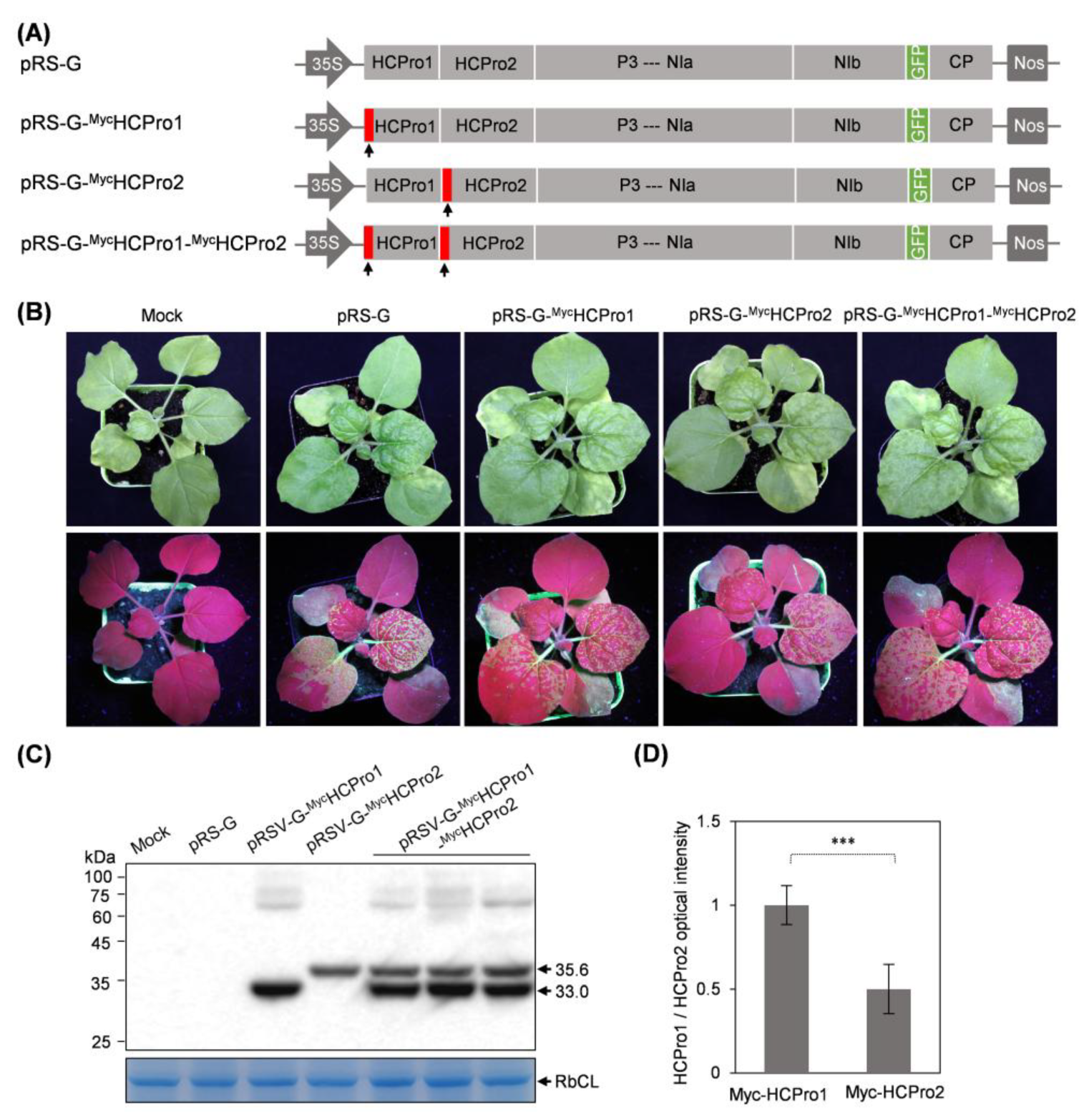
2.1. Both HCPro1 and HCPro2 Were Immuno-Detected in ANRSV-Infected Cells
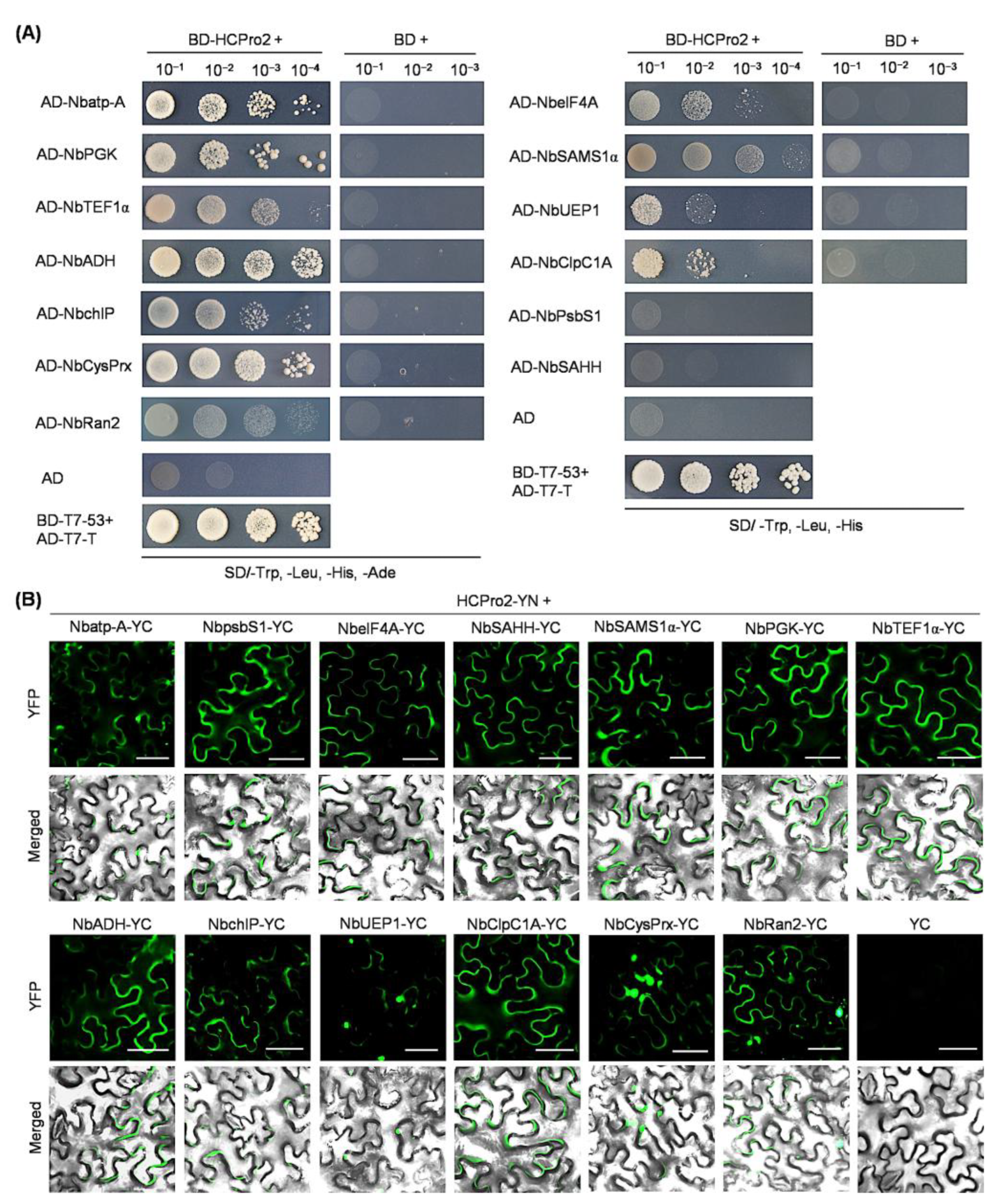
2.2. Thirteen Host Proteins Are Interactive with HCPro2
2.3. Five Viral Factors (HCPro1, 6K2, VPg, NIa-Pro, and NIb) Interact with HCPro2 in Planta
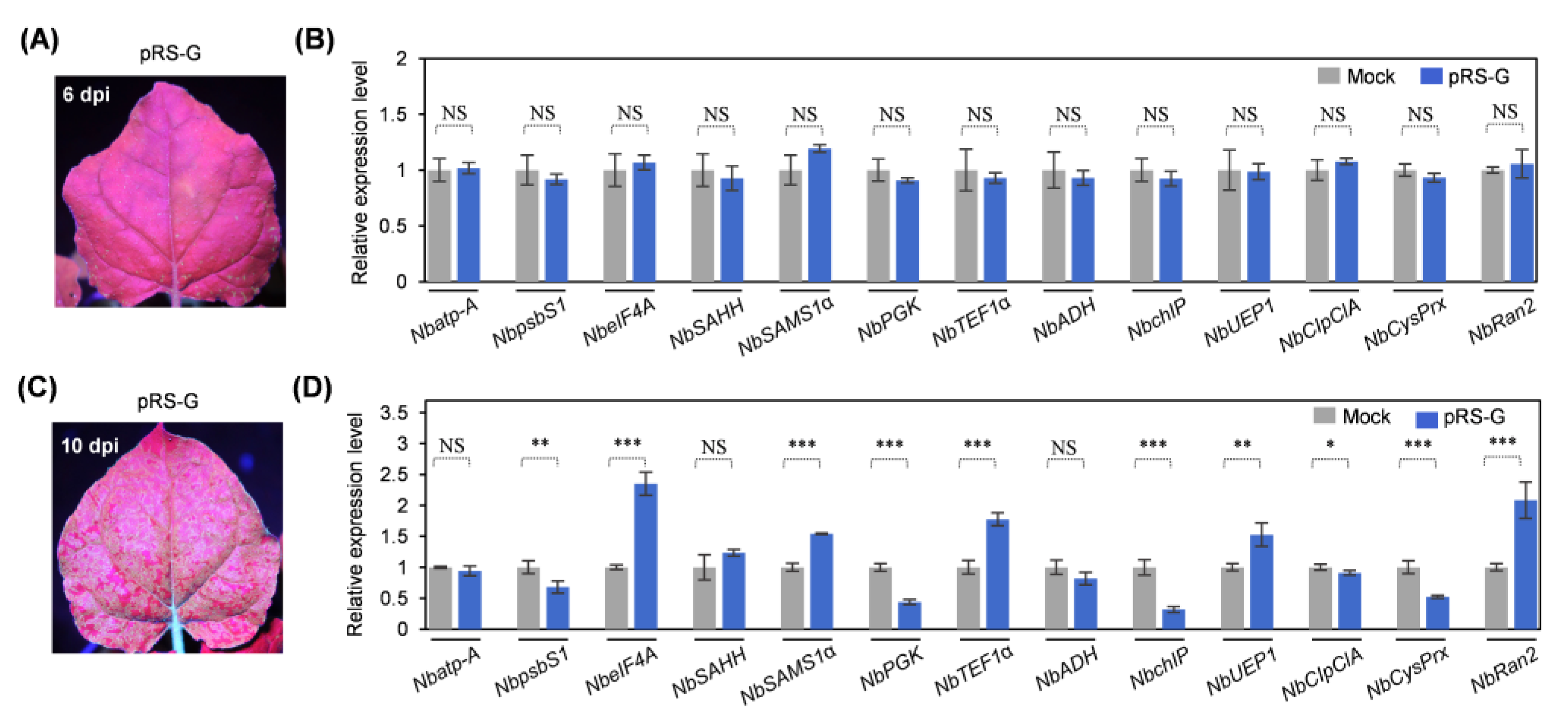
2.4. Expression of Ten Genes Encoding HCPro2-Interacting Proteins Is Changed upon Viral Infection
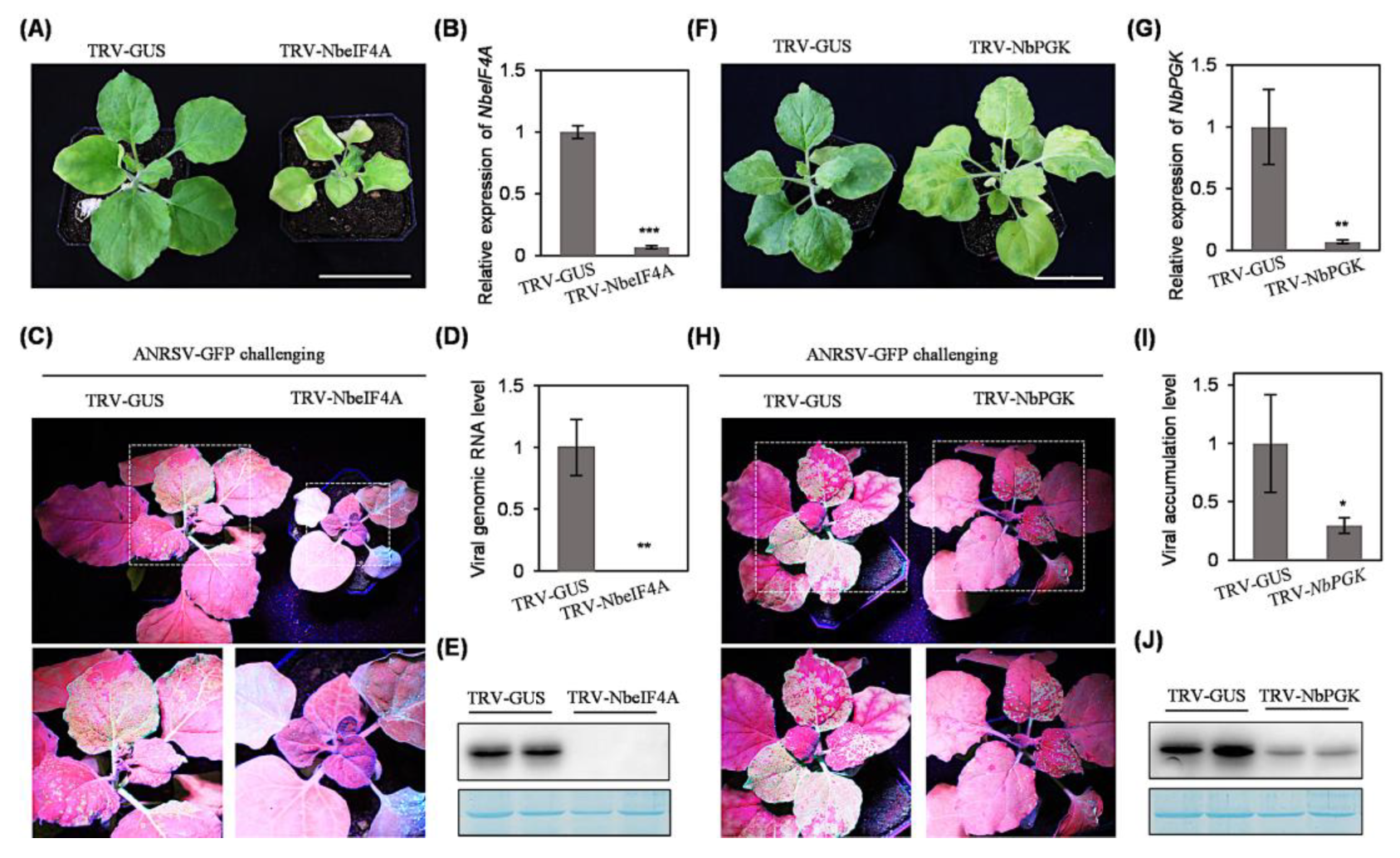
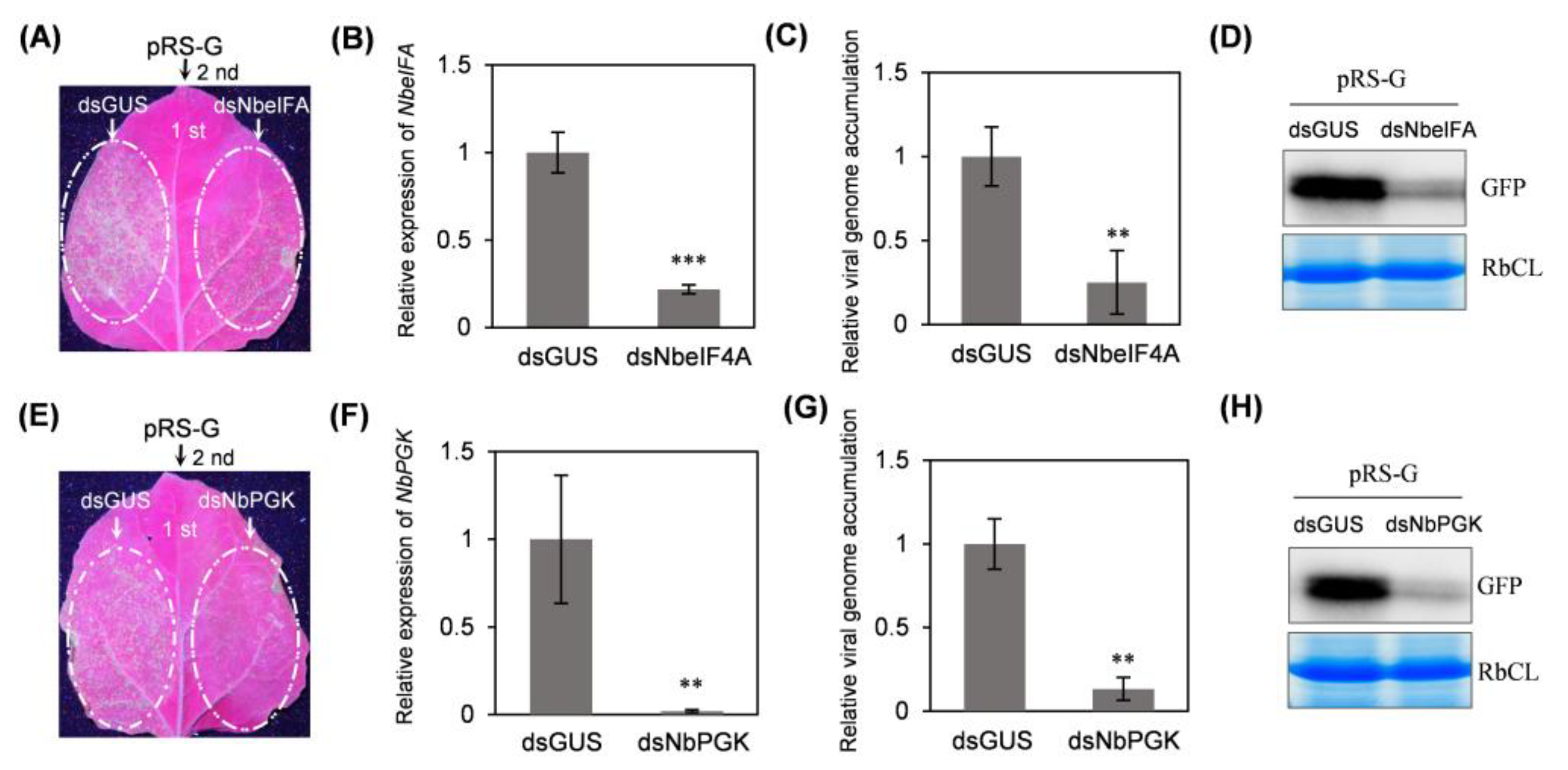
2.5. Silencing of NbeIF4A or NbPGK via TRV-Based VIGS Abolishes or Significantly Impairs Viral Systemic Infection
2.6. Transient Silencing of NbeIF4A or NbPGK in Local Leaves Through Expressing a Hairpin Structure Significantly Attenuates Viral Infectivity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Plasmid Construction
4.3. Agrobacterium-Mediated Inoculation and Sap Rub-Inoculation
4.4. Y2H
4.5. BiFC
4.6. Co-IP
4.7. Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) and Real-TIME RT Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADH | alcohol dehydrogenase |
| ANRSV | areca palm necrotic ringspot virus |
| ANSSV | areca palm necrotic spindle-spot virus |
| atp-A | ATP synthase F1 subunit 1 |
| BiFC | bimolecular fluorescence complementation |
| BMV | brome mosaic virus |
| chIP | geranylgeranyl reductase |
| ClpC1A | chloroplast ATP-dependent Clp protease chaperone protein |
| Co-IP | co-immunoprecipiation |
| CysPrs | 2-Cys peroxiredoxin |
| dpi | day post-inoculation |
| eIF4A | eukaryotic initiation factor 4A |
| HEN1 | HUA enhancer 1 |
| hpi | hours post-inoculation |
| LC-MS/MS | liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry |
| OD600 | optical density at 600 nm |
| ORFs | open reading frames |
| PGK | phosphoglycerate kinase |
| PPV | plum pox virus |
| psbS1 | chloroplast photosystem II 22 kDa componentry |
| PVA | potato virus A |
| Ran2 | small GTPase Ran2 |
| RbCS | Rubisco small unit |
| RT-PCR | reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| RT-qPCR | real-time RT quantitative PCR |
| RSS | RNA silencing suppression |
| SAHH | S-adenosyl homocysteine hydrolase |
| SAMS1α | S-adenosylmethionine synthetase |
| SD/-Leu/-Trp | synthetically defined medium, including leucine and tryptophan dropout medium |
| SD/-Leu/-Trp/-His | synthetically defined medium, including leucine, tryptophan, and histidine dropout medium |
| SD/-Leu/-Trp/-His/-Ade | synthetically defined medium, including leucine, tryptophan, histidine, and adenine dropout medium |
| ssRNA | single-stranded RNA |
| TEF1α | translation elongation factor 1 alpha |
| TRV | tobacco rattle virus |
| UEP1 | ubiquitin extension protein 1 |
| VIGS | virus-based virus-induced gene silencing |
| Y2H | yeast two-hybrid |
References
- Inoue-Nagata, A.K.; Jordan, R.; Kreuze, J.; Li, F.; López-Moya, J.J.; Mäkinen, K.; Ohshima, K.; Wylie, S.J.; Consortium, I.R. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Potyviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 001738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäkinen, K.; Aspelin, W.; Pollari, M.; Wang, L. How do they do it? The infection biology of potyviruses. Adv. Virus Res. 2023, 117, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollari, M.E.; Aspelin, W.W.; Wang, L.; Mäkinen, K.M. The molecular Maze of potyviral and host protein interactions. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2024, 11, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, B.Y.-W.; Miller, W.A.; Atkins, J.F.; Firth, A.E. An overlapping essential gene in the Potyviridae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5897–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olspert, A.; Chung, B.Y.W.; Atkins, J.F.; Carr, J.P.; Firth, A.E. Transcriptional slippage in the positive-sense RNA virus family Potyviridae. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodamilans, B.; Valli, A.; Mingot, A.; San León, D.; Baulcombe, D.; López-Moya, J.J.; García, J.A. RNA polymerase slippage as a mechanism for the production of frameshift gene products in plant viruses of the Potyviridae family. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6965–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Wang, A. The biological impact of the hypervariable N-terminal region of potyviral genomes. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2019, 6, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, A. Research advances in potyviruses: From the laboratory bench to the field. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2021, 59, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Shen, W.; Tang, Z.; Hu, W.; Shangguan, L.; Wang, Y.; Tuo, D.; Li, Z.; Miao, W.; Valli, A.A.; et al. A newly identified virus in the family Potyviridae encodes two leader cysteine proteases in tandem that evolved contrasting RNA silencing suppression functions. J. Virol. 2021, 95, 10.1128/jvi.01414-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Dai, Z.; Liu, P.; Deng, C.; Shen, W.; Li, Z.; Cui, H. The single distinct leader protease encoded by alpinia oxyphylla mosaic virus (genus Macluravirus) suppresses RNA silencing through interfering with double-stranded RNA synthesis. Phytopathology 2023, 113, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandalakshmi, R.; Pruss, G.J.; Ge, X.; Marathe, R.; Mallory, A.C.; Smith, T.H.; Vance, V.B. A viral suppressor of gene silencing in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13079–13084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasschau, K.D.; Carrington, J.C. A counterdefensive strategy of plant viruses: Suppression of posttranscriptional gene silencing. Cell 1998, 95, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valli, A.; Gallo, A.; Rodamilans, B.; López-Moya, J.J.; García, J.A. The HCPro from the Potyviridae family: An enviable multitasking Helper Component that every virus would like to have. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 744–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valli, A.; Gallo, A.; Calvo, M.; Pérez, J.d.J.; García, J.A. A novel role of the potyviral helper component proteinase contributes to enhance the yield of viral particles. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 9808–9818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafren, A.; Lohmus, A.; Mäkinen, K. Formation of Potato virus A-induced RNA granules and viral translation are interrelated processes required for optimal virus accumulation. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Pollari, M.; Varjosalo, M.; Mäkinen, K. Association of host protein VARICOSE with HCPro within a multiprotein complex is crucial for RNA silencing suppression, translation, encapsidation and systemic spread of potato virus A infection. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ruiz, H.; Carbonell, A.; Hoyer, J.S.; Fahlgren, N.; Gilbert, K.B.; Takeda, A.; Giampetruzzi, A.; Garcia Ruiz, M.T.; McGinn, M.G.; Lowery, N.; et al. Roles and programming of Arabidopsis ARGONAUTE proteins during Turnip mosaic virus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Toro, F.J.; Donaire, L.; Aguilar, E.; Chung, B.-N.; Tenllado, F.; Canto, T. Potato virus Y HCPro suppression of antiviral silencing in Nicotiana benthamiana plants correlates with its ability to bind in vivo to 21-and 22-nucleotide small RNAs of viral sequence. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00367-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Shirako, Y. Bymovirus reverse genetics: Requirements for RNA2-encoded proteins in systemic infection. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2010, 11, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, H.Y.; Hu, S.M.; Tian, M.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.Y.; Han, C.G. The P1 protein of wheat yellow mosaic virus exerts RNA silencing suppression activity to facilitate virus infection in wheat plants. Plant J. 2023, 116, 1717–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Shen, W.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Miao, W.; Wang, A.; Cui, H. Areca palm necrotic ringspot virus, classified within a recently proposed genus Arepavirus of the family Potyviridae, is associated with necrotic ringspot disease in areca palm. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Ran, M.; Li, Z.; Hu, M.; Zheng, L.; Liu, W.; Jin, P.; Miao, W.; Zhou, P.; Shen, W.; et al. Analysis of the complete genomic sequence of a novel virus, areca palm necrotic spindle-spot virus, reveals the existence of a new genus in the family Potyviridae. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 3471–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, R.T.P.; Sidharthan, V.K.; Rajesh, M.; Babu, M.; Sharma, S.K.; Kumar, B.N.; Chaithra, M.; Hegde, V. From the discovery of a novel arepavirus in diseased arecanut palms (Areca catechu L.) in India to the identification of known and novel arepaviruses in bee and plant transcriptomes through data-mining. Virology 2024, 600, 110256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Liu, H.; Liu, P.; Jiang, L.; Cheng, X.; Li, F.; Shen, W.; Qiu, W.; Dai, Z.; Cui, H. Rubisco small subunit (RbCS) is co-opted by potyvirids as the scaffold protein in assembling a complex for viral intercellular movement. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1012064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Schiff, M.; Marathe, R.; Dinesh-Kumar, S. Tobacco Rar1, EDS1 and NPR1/NIM1 like genes are required for N-mediated resistance to tobacco mosaic virus. Plant J. 2002, 30, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrick, W.C. eIF4F: A retrospective. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 24091–24099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanfaçon, H. Plant translation factors and virus resistance. Viruses 2015, 7, 3392–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yin, Y.; Su, Y.; Jia, Z.; Jiang, L.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Peng, J.; Rao, S.; Wu, G.; et al. eIF4A, a target of siRNA derived from rice stripe virus, negatively regulates antiviral autophagy by interacting with ATG5 in Nicotiana benthamiana. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Ismayil, A.; Gao, T.; Ye, Z.; Yue, N.; Wu, J.; Zheng, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hong, Y.; et al. Cotton leaf curl Multan virus C4 protein suppresses autophagy to facilitate viral infection. Plant Physiol. 2023, 193, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-Álvarez, D.; Leastro, M.O.; Pallas, V.; Sánchez-Navarro, J.Á. Identification of Host Factors Interacting with Movement Proteins of the 30K Family in Nicotiana tabacum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-W.; Ding, M.-P.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Tsai, C.-H. Chloroplast phosphoglycerate kinase, a gluconeogenetic enzyme, is required for efficient accumulation of Bamboo mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouibrahim, L.; Mazier, M.; Estevan, J.; Pagny, G.; Decroocq, V.; Desbiez, C.; Moretti, A.; Gallois, J.L.; Caranta, C. Cloning of the A rabidopsis rwm1 gene for resistance to Watermelon mosaic virus points to a new function for natural virus resistance genes. Plant J. 2014, 79, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poque, S.; Pagny, G.; Ouibrahim, L.; Chague, A.; Eyquard, J.-P.; Caballero, M.; Candresse, T.; Caranta, C.; Mariette, S.; Decroocq, V. Allelic variation at the rpv1 locus controls partial resistance to Plum pox virus infection in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakatos, L.; Csorba, T.; Pantaleo, V.; Chapman, E.J.; Carrington, J.C.; Liu, Y.P.; Dolja, V.V.; Calvino, L.F.; López-Moya, J.J.; Burgyán, J. Small RNA binding is a common strategy to suppress RNA silencing by several viral suppressors. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 2768–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revers, F.; García, J.A. Molecular biology of potyviruses. Adv. Virus Res. 2015, 92, 101–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, K.I.; Eskelin, K.; Bašić, M.; De, S.; Lohmus, A.; Varjosalo, M.; Mäkinen, K. Molecular insights into the function of the viral RNA silencing suppressor HCP ro. Plant J. 2016, 85, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamous, R.M.; Boonrod, K.; Fuellgrabe, M.W.; Ali-Shtayeh, M.S.; Krczal, G.; Wassenegger, M. The helper component-proteinase of the Zucchini yellow mosaic virus inhibits the Hua Enhancer 1 methyltransferase activity in vitro. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 2222–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanobar, N.; Lin, P.-C.; Pan, Z.-J.; Fang, R.-Y.; Tjita, V.; Chen, F.-F.; Wang, H.-C.; Tsai, H.-L.; Wu, S.-H.; Shen, T.-L.; et al. Investigating the viral suppressor HC-pro inhibiting small rna methylation through functional comparison of HEN1 in angiosperm and bryophyte. Viruses 2021, 13, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Várallyay, É.; Havelda, Z. Unrelated viral suppressors of RNA silencing mediate the control of ARGONAUTE1 level. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Du, P.; Lu, L.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, W.; Cao, X.; Ren, B.; Wei, C.; Li, Y. Contrasting effects of HC-Pro and 2b viral suppressors from Sugarcane mosaic virus and Tomato aspermy cucumovirus on the accumulation of siRNAs. Virology 2008, 374, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ala-Poikela, M.; Goytia, E.; Haikonen, T.; Rajamäki, M.-L.; Valkonen, J.P. Helper component proteinase of the genus Potyvirus is an interaction partner of translation initiation factors eIF (iso) 4E and eIF4E and contains a 4E binding motif. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 6784–6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Xie, H.; Wu, J.; Xie, L.; Yang, J.; Chi, Y. Translation initiation factor eIF4E and eIFiso4E are both required for peanut stripe virus infection in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hýsková, V.; Bělonožníková, K.; Chmelík, J.; Hoffmeisterová, H.; Čeřovská, N.; Moravec, T.; Ryšlavá, H. Potyviral Helper-Component Protease: Multifaced Functions and Interactions with Host Proteins. Plants 2024, 13, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.-Q.; Liu, Z.-M.; Xu, J.; Zhou, T.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.-T.; Li, H.-F.; Fan, Z.-F. HC-Pro protein of sugar cane mosaic virus interacts specifically with maize ferredoxin-5 in vitro and in planta. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 2046–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Ma, D.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, J.; Wang, T. Interaction between PVY HC-Pro and the NtCF1β-subunit reduces the amount of chloroplast ATP synthase in virus-infected tobacco. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Li, H.; Dong, J.; Wang, T. Potato virus Y HC-Pro reduces the ATPase activity of NtMinD, which results in enlarged chloroplasts in HC-Pro transgenic tobacco. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Karmakar, R.; Gupta, I.; Patel, A.K. Interaction of potyvirus helper component-proteinase (HcPro) with RuBisCO and nucleosome in viral infections of plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 151, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, S.; López-Moya, J.-J.; Wang, R.; García-Lampasona, S.; Thornbury, D.W.; Pirone, T.P. A specific interaction between coat protein and helper component correlates with aphid transmission of a potyvirus. Virology 1997, 231, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrejeva, J.; Puurand, Ü.; Merits, A.; Rabenstein, F.; Järvekülg, L.; Valkonen, J. Potyvirus helper component-proteinase and coat protein (CP) have coordinated functions in virus–host interactions and the same CP motif affects virus transmission and accumulation. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merits, A.; Guo, D.; Järvekülg, L.; Saarma, M. Biochemical and genetic evidence for interactions between potato A potyvirus-encoded proteins P1 and P3 and proteins of the putative replication complex. Virology 1999, 263, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.-R.; Stenger, D.C.; French, R. Multiple interactions among proteins encoded by the mite-transmitted wheat streak mosaic tritimovirus. Virology 2000, 267, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Guo, D.; Rajamäki, M.-L.; Saarma, M.; Valkonen, J.P. Towards a protein interaction map of potyviruses: Protein interaction matrixes of two potyviruses based on the yeast two-hybrid system. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilian, E.; Maiss, E. Detection of plum pox potyviral protein–protein interactions in planta using an optimized mRFP-based bimolecular fluorescence complementation system. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 2711–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roudet-Tavert, G.; German-Retana, S.; Delaunay, T.; Delécolle, B.; Candresse, T.; Le Gall, O. Interaction between potyvirus helper component-proteinase and capsid protein in infected plants. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 1765–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yambao, M.L.M.; Masuta, C.; Nakahara, K.; Uyeda, I. The central and C-terminal domains of VPg of Clover yellow vein virus are important for VPg–HCPro and VPg–VPg interactions. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 2861–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roudet-Tavert, G.; Michon, T.; Walter, J.; Delaunay, T.; Redondo, E.; Le Gall, O. Central domain of a potyvirus VPg is involved in the interaction with the host translation initiation factor eIF4E and the viral protein HcPro. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, W.; Dai, Z.; Gou, B.; Liu, H.; Hu, W.; Qin, L.; Li, Z.; Tuo, D.; Cui, H. Biological and molecular characterization of two closely related arepaviruses and their antagonistic interaction in Nicotiana benthamiana. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 755156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earley, K.W.; Haag, J.R.; Pontes, O.; Opper, K.; Juehne, T.; Song, K.; Pikaard, C.S. Gateway-compatible vectors for plant functional genomics and proteomics. Plant J. 2006, 45, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Tang, X.; Tian, G.; Wang, F.; Liu, K.; Nguyen, V.; Kohalmi, S.E.; Keller, W.A.; Tsang, E.W.; Harada, J.J.; et al. Arabidopsis homolog of the yeast TREX-2 mRNA export complex: Components and anchoring nucleoporin. Plant J. 2010, 61, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Hu, F.; Wang, R.; Zhou, X.; Sze, S.-H.; Liou, L.W.; Barefoot, A.; Dickman, M.; Zhang, X. Arabidopsis Argonaute10 specifically sequesters miR166/165 to regulate shoot apical meristem development. Cell 2011, 145, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, L.; Liu, P.; Shen, W.; Dai, Z.; Cui, H. A Comprehensive Screening of the Interactors of Areca Palm Necrotic Ringspot Virus (ANRSV) HCPro2 Highlights the Proviral Roles of eIF4A and PGK in Viral Infection. Plants 2025, 14, 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111673
Qin L, Liu P, Shen W, Dai Z, Cui H. A Comprehensive Screening of the Interactors of Areca Palm Necrotic Ringspot Virus (ANRSV) HCPro2 Highlights the Proviral Roles of eIF4A and PGK in Viral Infection. Plants. 2025; 14(11):1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111673
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Li, Peilan Liu, Wentao Shen, Zhaoji Dai, and Hongguang Cui. 2025. "A Comprehensive Screening of the Interactors of Areca Palm Necrotic Ringspot Virus (ANRSV) HCPro2 Highlights the Proviral Roles of eIF4A and PGK in Viral Infection" Plants 14, no. 11: 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111673
APA StyleQin, L., Liu, P., Shen, W., Dai, Z., & Cui, H. (2025). A Comprehensive Screening of the Interactors of Areca Palm Necrotic Ringspot Virus (ANRSV) HCPro2 Highlights the Proviral Roles of eIF4A and PGK in Viral Infection. Plants, 14(11), 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111673





