Suitable Planting Area Prediction for Two Arnebia Species: An Analysis Based on Habitat and Phytochemical Suitability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Model Performance and Key Environmental Variables
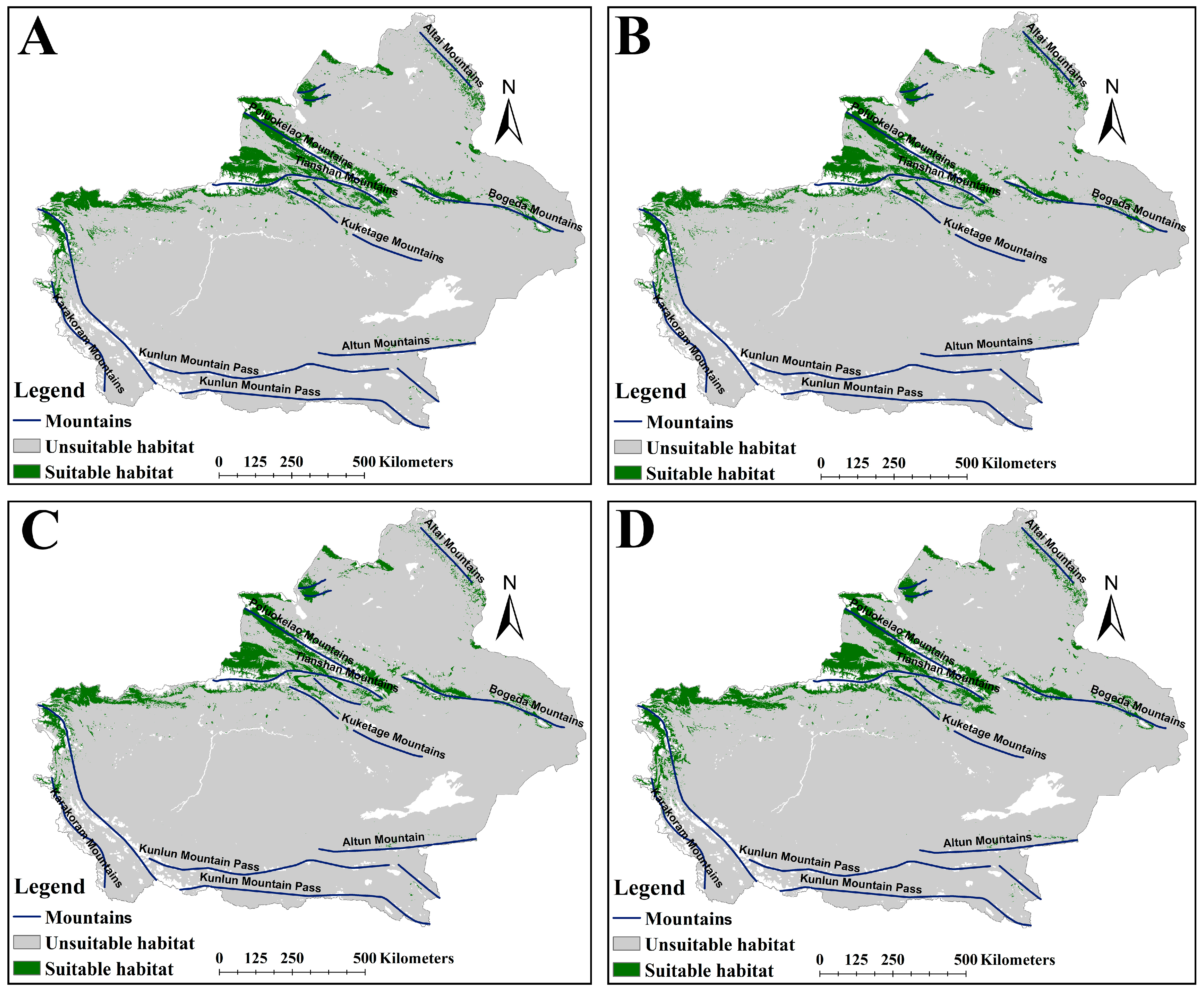
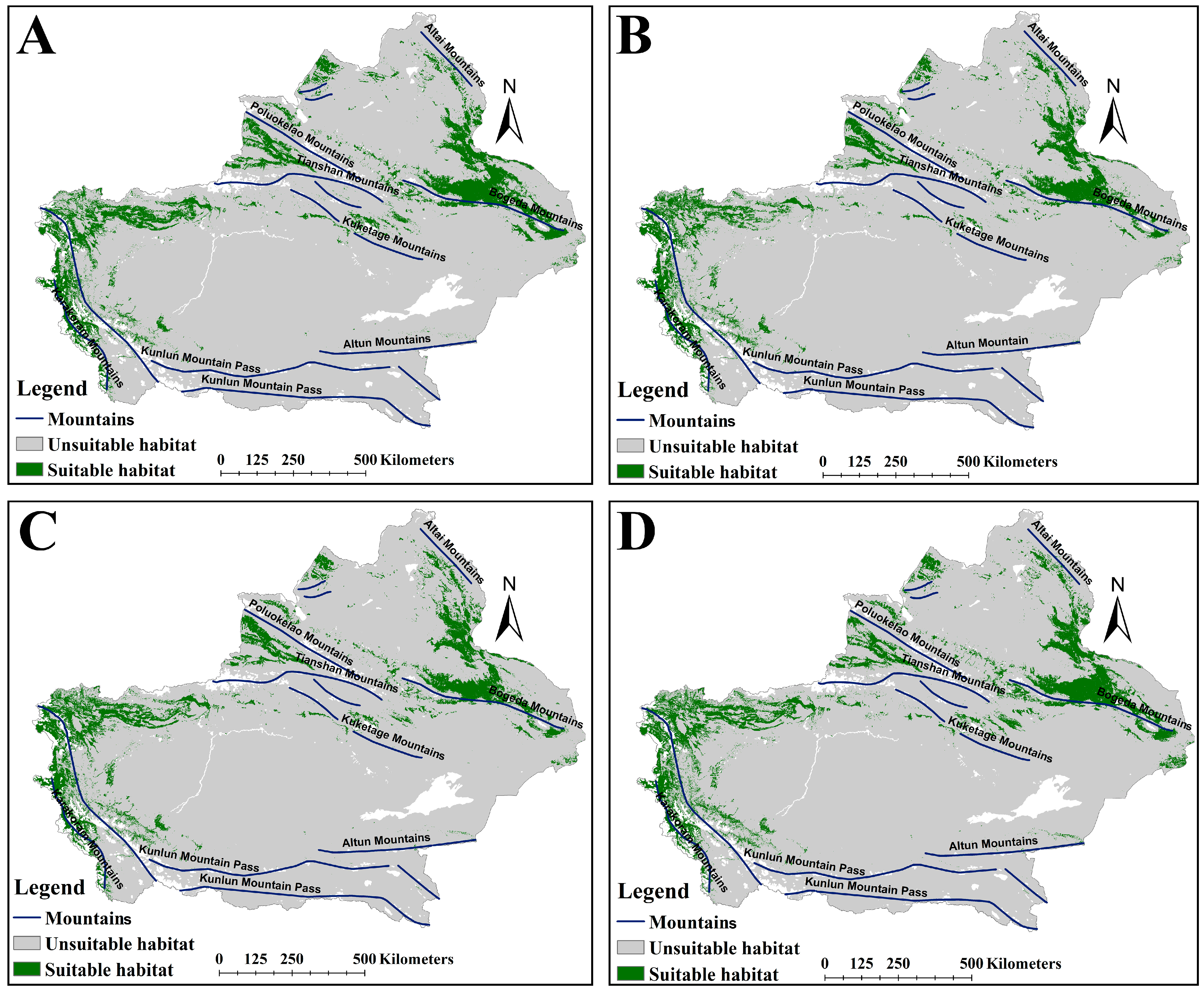
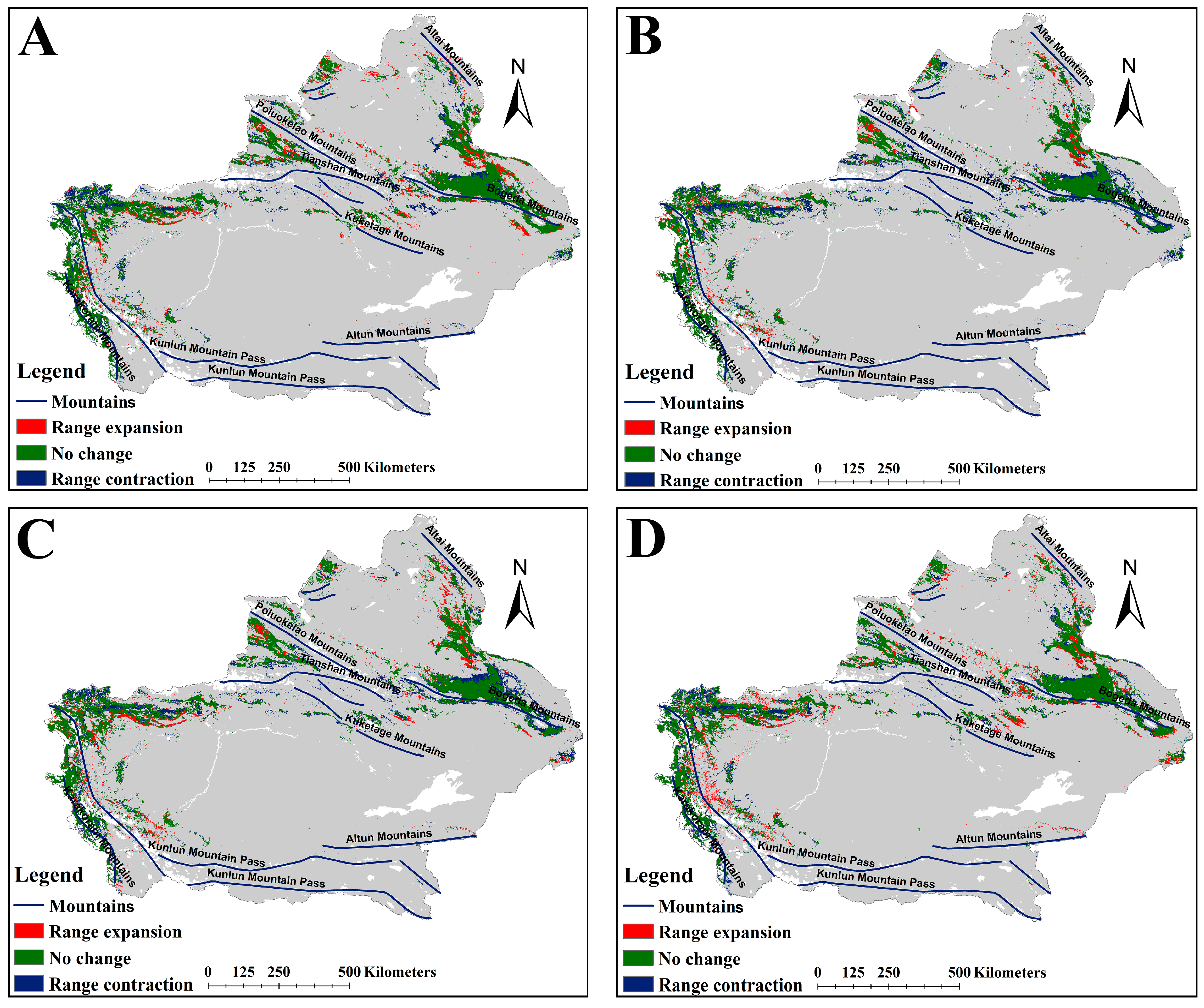
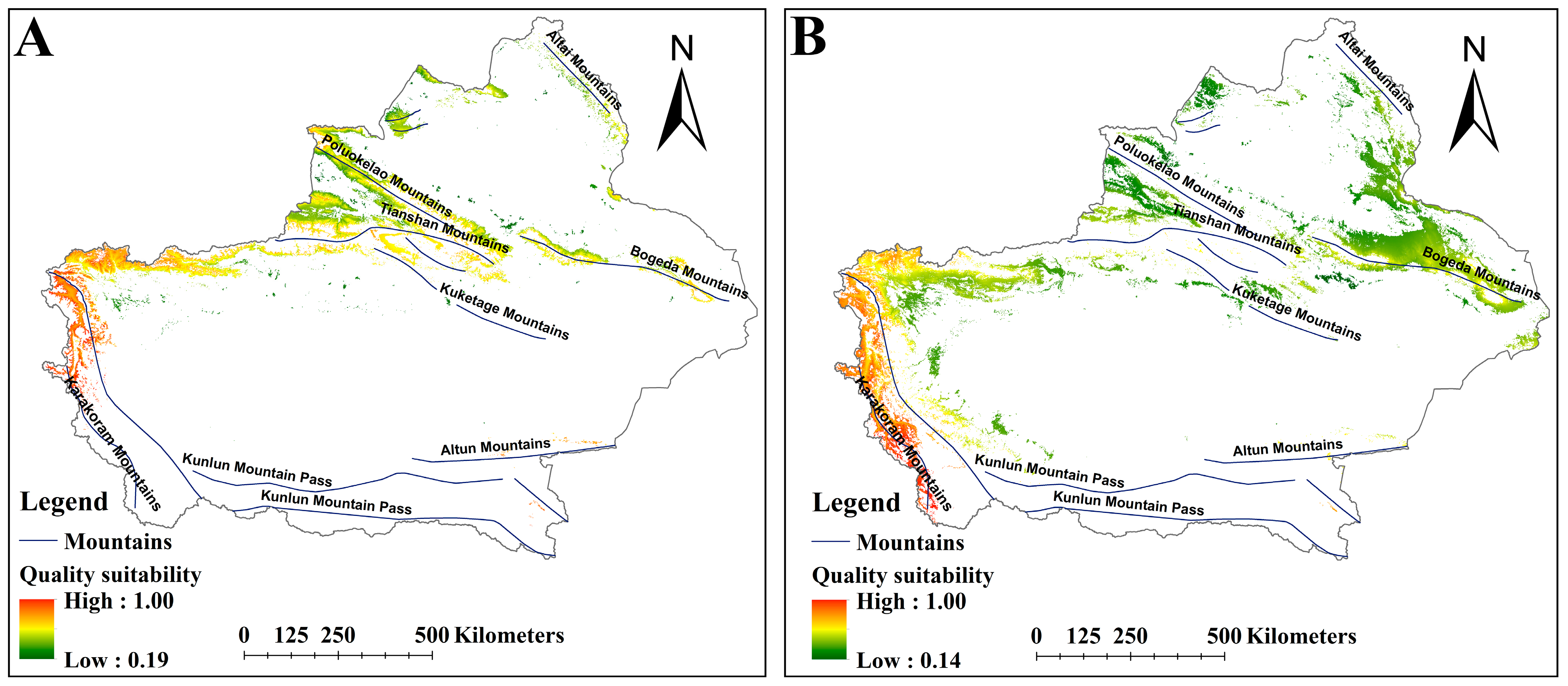
2.2. The Suitable Habitat Distribution of Two Medicinal Plants Under the Current Scenario
2.3. The Suitable Habitat Distribution of Two Medicinal Plants Under the Current Scenario
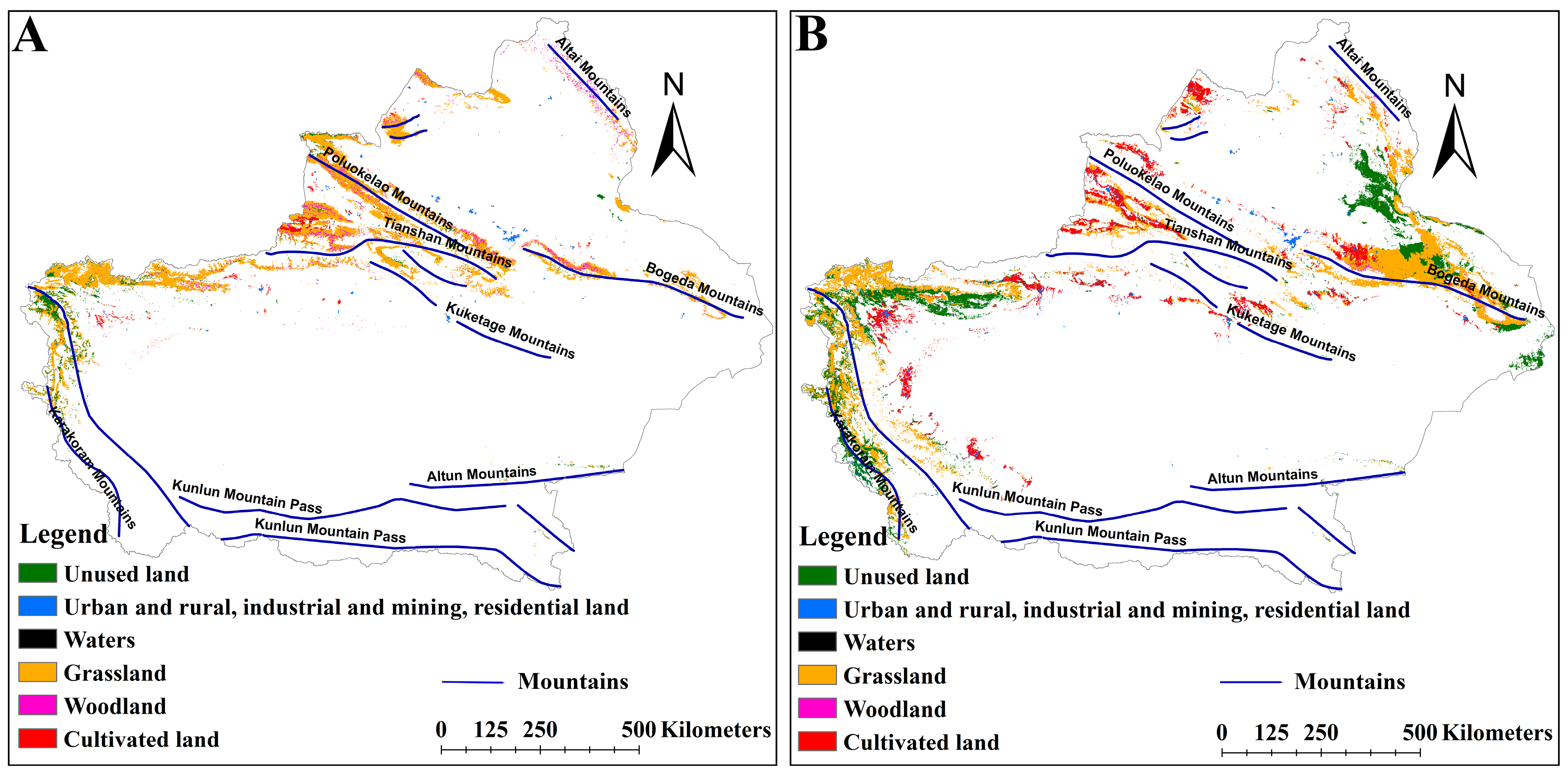
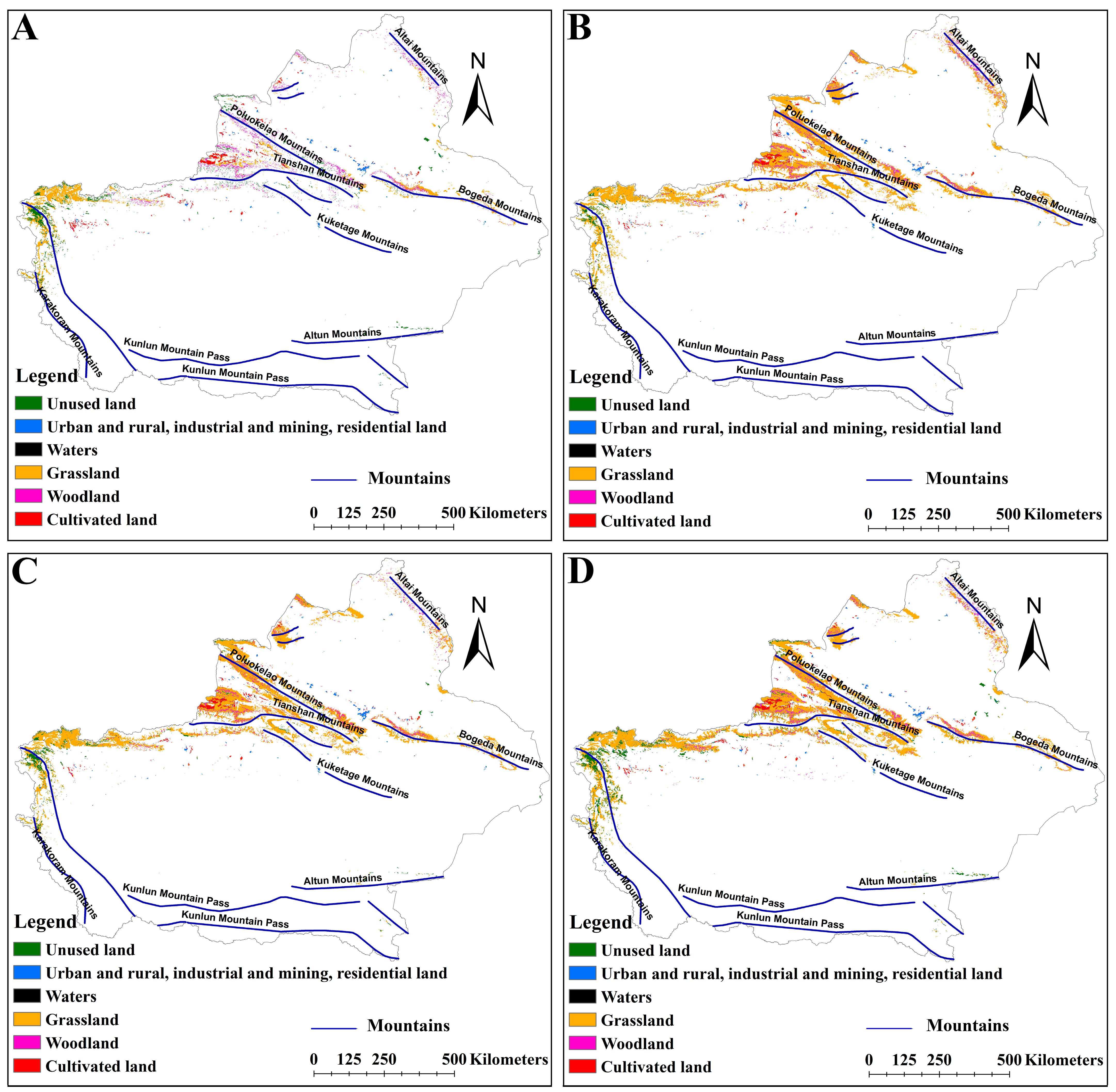
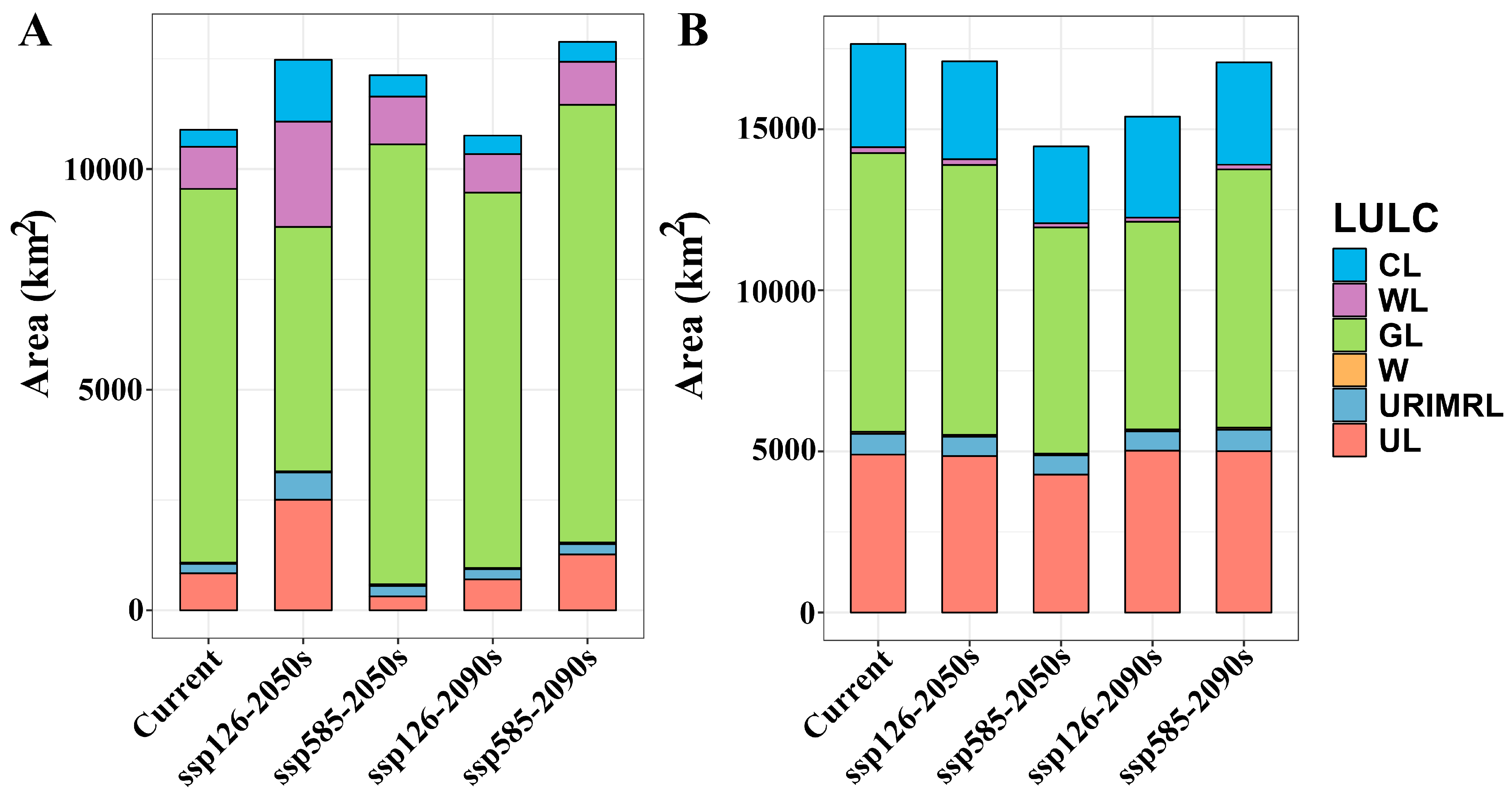
2.4. Effects of LULC on the Distribution of Suitable Habitats for Two Medicinal Plants
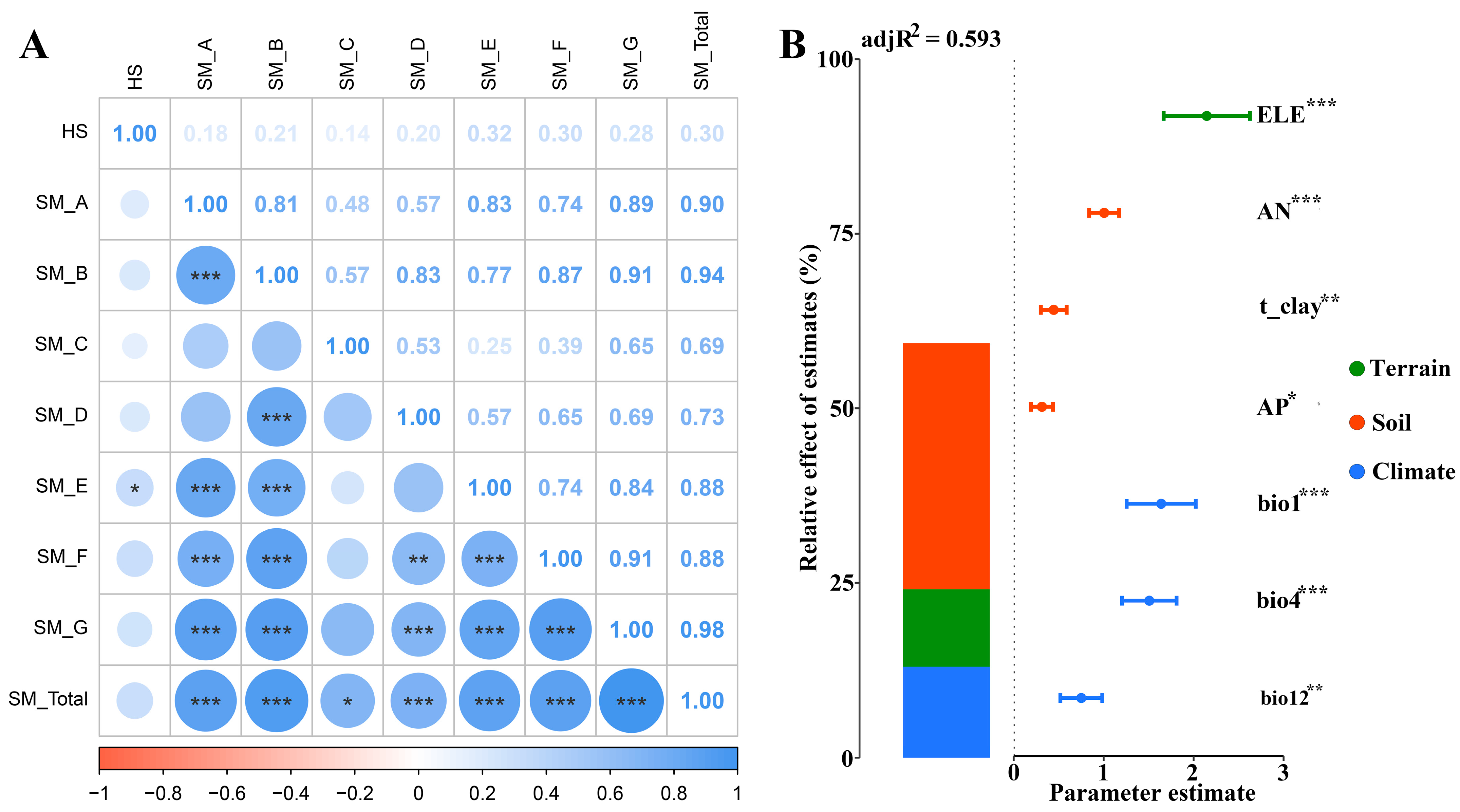
2.5. Relationship Between Secondary Metabolite Contents of Two Medicinal Plants and Habitat Suitability and Environmental Variables
3. Discussion
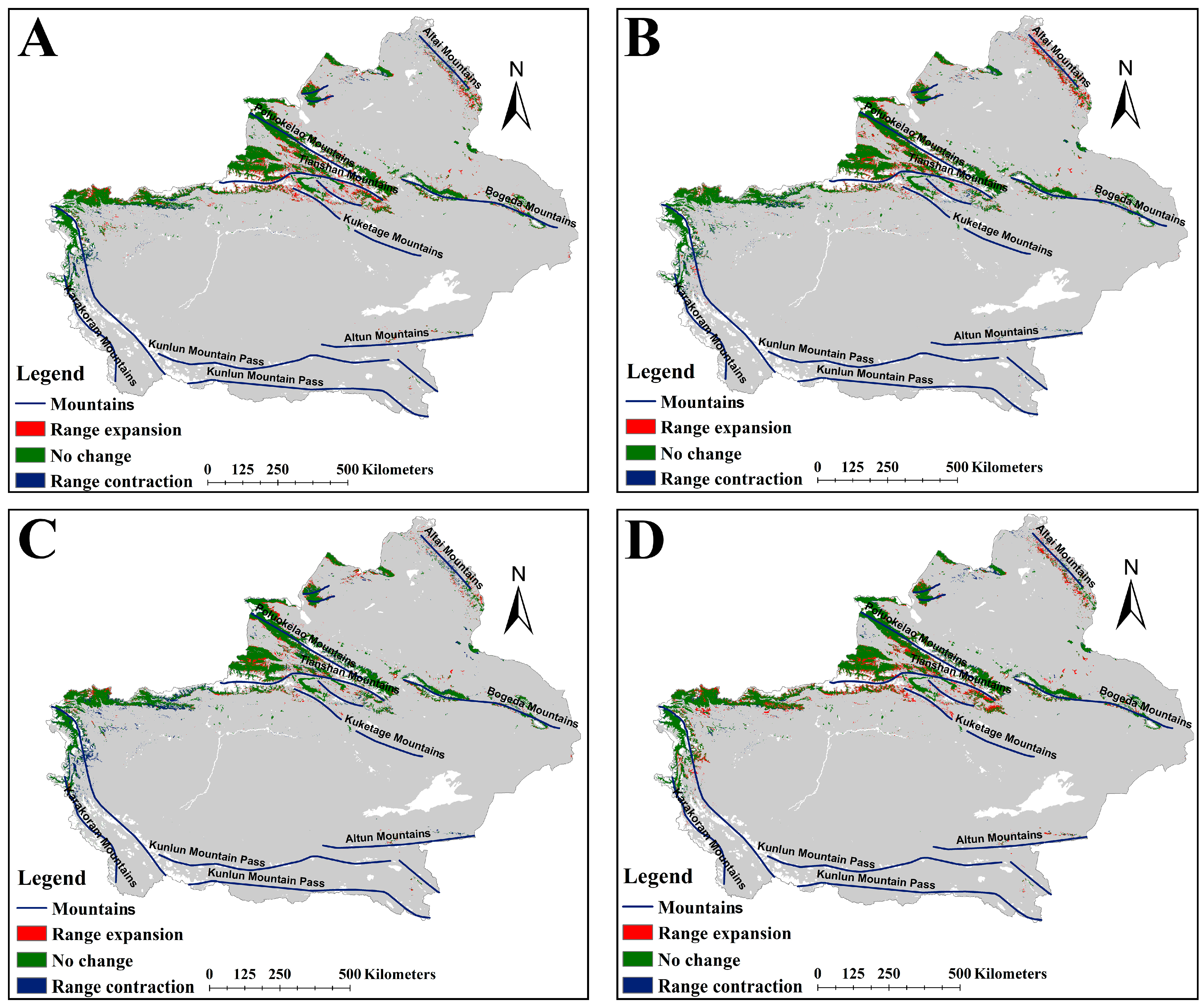
3.1. Changes in Suitable Habitats of the Two Medicinal Plants
3.2. Environmental Factors Affecting the Distribution of Suitable Habitats and Secondary Metabolites of Two Medicinal Plants
3.3. Impact of LULC on the Distribution of Suitable Habitats
3.4. Suggestions on the Protection and Utilization of Two Medicinal Plants Combined with Habitat Suitability and Quality
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Area
4.2. Materials
4.2.1. Species Occurrence Records
4.2.2. Environmental Variables
4.3. Methods
4.3.1. Model Construction
4.3.2. Analysis of Suitable Habitat Distribution Under Different LULCs
4.3.3. Analysis of the Relationship Between Secondary Metabolite Content and Habitat Suitability
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chi, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.; et al. Threatened medicinal plants in China: Distributions and conservation priorities. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 210, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yuan, R.; Ye, Y. Research progress of medicinal plant resource diversity. Hortic. Seed 2022, 42, 51–53. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Chen, B.; Liu, C.; Lai, J.; Zhang, J.; Ma, K. Identifying hotspots of endemic woody seed plant diversity in China. Divers. Distrib. 2012, 18, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzoieva, T.; Tomashevska, O.; Gerasymchuk, N. Analysis of medicinal plants cultivation in Ukraine on sustainable development principles. Grassroots J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 4, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.-Z.; Wang, L.; Jin, L.; Chen, J. Evaluation of environmental factors affecting the quality of Codonopsis pilosula based on chromatographic fingerprint and MaxEnt model. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 170, 113783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Cui, X. Studies on the resources survey methods of Panax notogingseng based on remote sensing. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2005, 30, 1902–1905. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Huang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, C.; Pan, Y.; Lv, D.; Zhang, Q. Key influencing factors on essential oil components of Atractylodes lancea and study on its division of climate adaptability. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2007, 32, 888–893. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Guo, L.; Cui, Y.; Xiao, R.; Yu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Fu, R.; Zhang, J.; Xu, T.; Chen, J.; et al. Quality suitability modeling of volatile oil in Chinese Materia Medica-Based on maximum entropy and independent weight coefficient method: Case studies of Atractylodes lancea, Angelica sinensis, Curcuma longa and Atractylodes macrocephala. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 142, 111807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amindin, A.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Safaeian, R.; Rahmanian, S.; Tiefenbacher, J.P.; Naimi, B. Predicting current and future habitat suitability of an endemic species using data-fusion approach: Responses to climate change. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2024, 94, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulighe, G.; Lupia, F.; Manente, V. Climate-driven invasion risks of Japanese beetle (Popillia japonica Newman) in Europe predicted through species distribution modelling. Agriculture 2025, 15, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Shi, Z.; Yang, X.; Yahdjian, L. Plant invasion risk assessment in Argentina’s arid and semi-arid rangelands. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 377, 124648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedin, I.; Singha, H.; Singh, S.; Mukherjee, T.; Kim, H.-W.; Kundu, S. Riverine realities: Evaluating climate change impacts on habitat dynamics of the critically endangered gharial (Gavialis gangeticus) in the Indian landscape. Animals 2025, 15, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvajal-Hernandez, C.I.; Gomez-Diaz, J.A. Distribution and conservation of Mexican tepezmaite cycads. Biodivers. Conserv. 2024, 33, 3727–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahat, E.A.; Tashani, A.F.; Mahmoud, A.R. The sensitivity and response of the threatened endemic shrub Arbutus pavarii to current and future climate change. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2025, 25, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.; Bai, X.; Zhao, L.; Dong, H.; Liu, C. Comparative analysis of climate-induced habitat shift of economically significant species with diverse ecological preferences in the Northwest Pacific. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1476097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, Z.; He, J.; Guo, C.; Zhou, Q.; Song, L. Simulating the impact of climate change on the suitable area for cotton in Xinjiang based on SDMs model. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 227, 120750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidoo, O.F.; Amaro, G.C.; Souza, P.G.C.; Picanco, M.C.; Awuah-Mensah, K.A.; da Silva, R.S. Climate change impacts on worldwide ecological niche and invasive potential of Sternochetus mangiferae. Pest Manag. Sci. 2025, 81, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, R.R.; Morrison Iii, W.R.; Gerken, A.R. Projected range overlap between the predator Teretrius nigrescens and the invasive stored product pest Prostephanus truncatus expands under climate change. Biol. Control 2025, 200, 105682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, J. Predicting the potential distribution of Paeonia veitchii (Paeoniaceae) in China by incorporating climate change into a Maxent model. Forests 2019, 10, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S.; Zhao, A.; Ning, X.; Fan, G.; Wu, N.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z. Prediction of the potentially suitable areas of Litsea cubeba in China based on future climate change using the optimized MaxEnt model. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fan, G.; He, Y. Predicting the current and future distribution of three Coptis herbs in China under climate change conditions, using the MaxEnt model and chemical analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Wang, H.; Lv, Z. Evaluating the performance of species distribution models Biomod2 and MaxEnt using the giant panda distribution data. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 4001–4006. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, W.; Huang, X.; Hu, S.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, P.; Niu, P.; Su, J.; Wang, M.; Chu, G. Impacts of climate change on the habitat suitability and natural product accumulation of the medicinal plant Sophora alopecuroides L. based on the MaxEnt model. Plants 2024, 13, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.-Z. Assessing the impacts of climate change and habitat suitability on the distribution and quality of medicinal plant using multiple information integration: Take Gentiana rigescens as an example. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 123, 107376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, L.; He, Y. Analysis of the impact of climate change on the distribution and active compound content of the plateau medicinal plant Nardostachys jatamansi (D. Don) DC. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 187, 115438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.; Wang, F.; Xia, P.; Zhao, G.; Wei, M.; Wei, F.; Han, R. Assessment of suitable cultivation region for Panax notoginseng under different climatic conditions using MaxEnt model and high-performance liquid chromatography in China. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 176, 114416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Bai, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, G.; Mao, M. Modeling habitat distribution of Cornus officinalis with Maxent modeling and fuzzy logics in China. J. Plant Ecol. 2016, 9, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Zhang, B.; Chen, B.; Duan, D.; Zhou, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X. A multi-dimensional “climate-land-quality” approach to conservation planning for medicinal plants: Take Gentiana scabra Bunge in China as an example. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 211, 18222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, H.; Song, J.; Li, X.; Xie, C. Climatic features and geographical distribution of medicinal plants in Xinjiang. Arid Land Geogr. 2015, 38, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, X.; Li, H.; Zeng, W.; Shi, X.; Zhang, F.; Chen, B.; Ge, L.; Huang, X.; ZHou, Q. Research progress on chemical constituents, pharmacological effects and product application of gromwell root. Chin. Wild Plant Resour. 2021, 40, 52–56+69. [Google Scholar]
- Huhezhula; Alatanchaolumen; Liao, C.; Caijihula. Research progress of Arnebiae Radix and prediction of its quality markers. Acta Chin. Med. Pharmacol. 2024, 52, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, G. The market demand of Arnebia euchroma increased. N. Rural Technol. 2011, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Geng, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhu, L. Advances in studies on medicinal Arnebiae Radix. Mod. Chin. Med. 2021, 23, 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X. Moderate warming will expand the suitable habitat of Ophiocordyceps sinensis and expand the area of O. sinensis with high adenosine content. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, I.I.; Shah, M.A.A.; Ganie, A.H. Integrating human footprint with ensemble modelling identifies priority habitats for conservation: A case study in the distributional range of Arnebia euchroma, a vulnerable species. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Fan, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, G.; Shi, S.; Li, X. Ecological suitability of Arnebia euchroma producing area based on MaxEnt and GIS. Mod. Chin. Med. 2022, 24, 770–775. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Xu, J.; Yu, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Chen, W. Prediction of suitable planting areas of Rubia cordifolia in China based on a species distribution model and analysis of specific secondary metabolites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 206, 117651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Study on the Resources and Quality Evaluation of Arnebia Species in Xinjiang. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, S.; Samant, S.S. Population ecology and habitat suitability modelling of an endangered and endemic medicinal plant Meconopsis aculeata Royle under projected climate change in the Himalaya. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2024, 225, 105837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Fan, C. Correlation between rhizosphere environment and content of medicinal components of Arnebia euchroma. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2023, 48, 6030–6038. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; He, X.; Chen, W. Effects of geographical, soil and climatic factors on the two marker secondary metabolites contents in the roots of Rubia cordifolia L. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1419392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Hao, Z.; Yu, M.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, A.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, B. Improved phosphorus nutrition by arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis as a key factor facilitating glycyrrhizin and liquiritin accumulation in Glycyrrhiza uralensis. Plant Soil 2019, 439, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, E.; Anand, G.; Kapoor, R. Terpenoids in plant and arbuscular mycorrhiza-reinforced defence against herbivorous insects. Ann. Bot. 2017, 119, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, R.; Anand, G.; Gupta, P.; Mandal, S. Insight into the mechanisms of enhanced production of valuable terpenoids by arbuscular mycorrhiza. Phytochem. Rev. 2017, 16, 677–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, X.; Jiang, C.; Guo, L. Advances in studies on genes related to shikonin and its derivatives biosynthesis and signal transduction. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2012, 43, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar]
- Zamora-Gutierrez, V.; Pearson, R.G.; Green, R.E.; Jones, K.E. Forecasting the combined effects of climate and land use change on Mexican bats. Divers. Distrib. 2018, 24, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Chen, C.; Xiao, F.; Yi, J.; Zhou, W.; She, J. Distribution of suitable habitat of Firmiana danxiaensis H.H.Hsue and H.S.Kiu in China: An integrated analysis based on changes in climate and high forest thematic resolution land use. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhu, T.; Shi, T.; Chen, J.; Jin, L. Quality suitability regionalization analysis of Angelica sinensis in Gansu, China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Xiang, L. Protection and application of genetic resources of medicinal plants. Mod. Chin. Med. 2019, 21, 1456–1463. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, C.C.; Choisy, P. Medicinal plants meet modern biodiversity science. Curr. Biol. 2024, 34, R158–R173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Jing, C.; Chen, C. Temporal and spatial variation of Xinjiang natural grassland and their responses to climate factors. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2023, 25, 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Y.; Cao, Z.; Li, M.L.; Xu, S.Y.; Huang, J.H.; Ding, Y.; Zang, R.G. The diversity composition and distribution characteristics of resource plants in Xinjiang. Terr. Ecosyst. Conserv. 2024, 4, 11–22+34. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Li, P.; Ren, G.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Liu, C. Authentication of three source spices of Arnebiae Radix using DNA barcoding and HPLC. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 677014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y. Effects of Ecological Factors on Biological Characteristics and Quality of Arnebia euchroma. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Ürümqi, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, E.; Liu, W.; Song, H.; Xu, H.; Tian, S. Resource investigation of Arnebia guttata Bge.in Hami district of Xinjiang. Mod. Chin. Med. 2016, 18, 1479–1483. [Google Scholar]
- Aiello-Lammens, M.E.; Boria, R.A.; Radosavljevic, A.; Vilela, B.; Anderson, R.P. spThin: An R package for spatial thinning of species occurrence records for use in ecological niche models. Ecography 2015, 38, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, S.E.; Hijmans, R.J. WorldClim 2: New 1-km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Shangguan, W. Dataset of Soil Properties for Land Surface Modeling over China; National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center: Beijing, China, 2019; Available online: https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/zh-hans/data/8ba0a731-5b0b-4e2f-8b95-8b29cc3c0f3a (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Meng, X.; Wang, H. Soil Map Based Harmonized World Soil Database (v1.2); National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center: Beijing, China, 2018; Available online: https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/zh-hans/data/844010ba-d359-4020-bf76-2b58806f9205 (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; Wu, S. China Multi-Period Land Use Remote Sensing Monitoring Data Set (CNLUCC), Resource and Environmental Science Data Registration and Publishing System. 2018. Available online: https://www.resdc.cn/DOI/doi.aspx?DOIid=54 (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Brown, J.L.; Bennett, J.R.; French, C.M. SDMtoolbox 2.0: The next generation Python-based GIS toolkit for landscape genetic, biogeographic and species distribution model analyses. PeerJ 2017, 5, e4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, S.J.; Anderson, R.P.; Schapire, R.E. Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecol. Model. 2006, 190, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anibaba, Q.A.; Dyderski, M.K.; Jagodzinski, A.M. Predicted range shifts of invasive giant hogweed (Heracleum mantegazzianum) in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 154053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.R.; Berry, P.M.; Dawson, T.P.; Pearson, R.G. Selecting thresholds of occurrence in the prediction of species distributions. Ecography 2005, 28, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Fu, Y.; Sussman, M.R.; Wu, H. The effect of developmental and environmental factors on secondary metabolites in medicinal plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ncube, B.; Finnie, J.F.; Van Staden, J. Quality from the field: The impact of environmental factors as quality determinants in medicinal plants. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2012, 82, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Palacios, P.; Gross, N.; Gaitán, J.; Maestre, F.T. Climate mediates the biodiversity–ecosystem stability relationship globally. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 8400–8405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Morrissey, E.; Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Qu, L.; Sang, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, G.; et al. Integrating microbial community properties, biomass and necromass to predict cropland soil organic carbon. ISME Commun. 2023, 3, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Indicator | A. euchroma | A. guttata |
|---|---|---|
| AUC | 0.977 | 0.952 |
| TSS | 0.829 | 0.725 |
| Scenario | A. euchroma | A. guttata | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unsuitable Habitat (km2) | Suitable Habitat (km2) | Unsuitable Habitat (km2) | Suitable Habitat (km2) | |
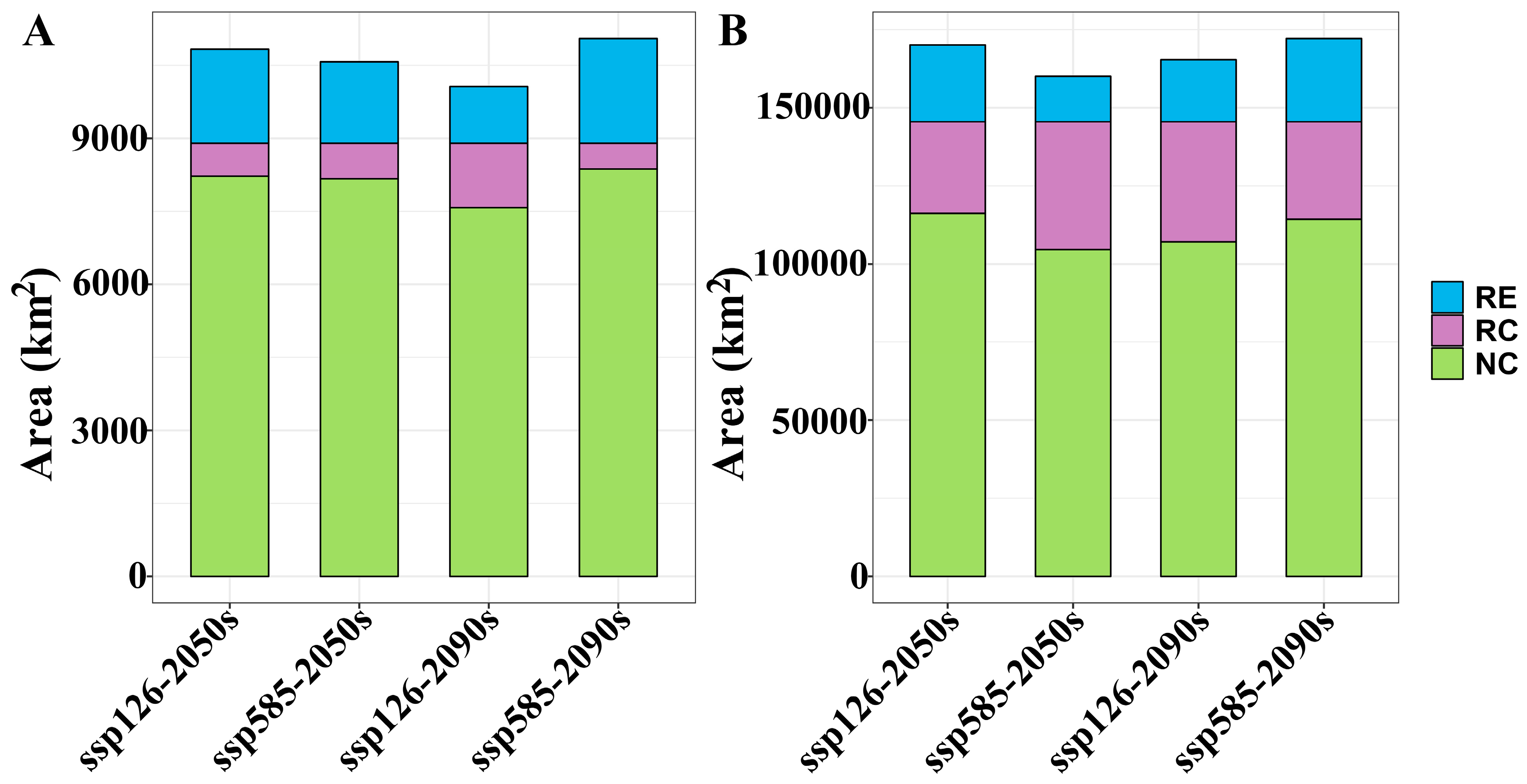
| Current | 1,522,816 | 108,914 | 1,455,285 | 176,445 |
| ssp126-2050s | 1,506,950 | 124,780 | 1,460,649 | 171,081 |
| ssp585-2050s | 1,510,447 | 121,283 | 1,487,060 | 144,670 |
| ssp126-2090s | 1,524,163 | 107,568 | 1,477,810 | 153,920 |
| ssp585-2090s | 1,502,891 | 128,839 | 1,460,973 | 170,757 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Yan, S.; Gao, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, Q. Suitable Planting Area Prediction for Two Arnebia Species: An Analysis Based on Habitat and Phytochemical Suitability. Plants 2025, 14, 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111669
Wang Y, Yan S, Gao S, Liu H, Wang Q. Suitable Planting Area Prediction for Two Arnebia Species: An Analysis Based on Habitat and Phytochemical Suitability. Plants. 2025; 14(11):1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111669
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yanlin, Shuo Yan, Shanshan Gao, Huanchu Liu, and Qi Wang. 2025. "Suitable Planting Area Prediction for Two Arnebia Species: An Analysis Based on Habitat and Phytochemical Suitability" Plants 14, no. 11: 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111669
APA StyleWang, Y., Yan, S., Gao, S., Liu, H., & Wang, Q. (2025). Suitable Planting Area Prediction for Two Arnebia Species: An Analysis Based on Habitat and Phytochemical Suitability. Plants, 14(11), 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111669






