Effects of Potassium Fulvic Acid on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Soil Microenvironment of Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) Under Salt Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Potassium Fulvic Acid (PFA) on Physical and Chemical Properties and Enzyme Activities of Blueberry Rhizosphere Soil
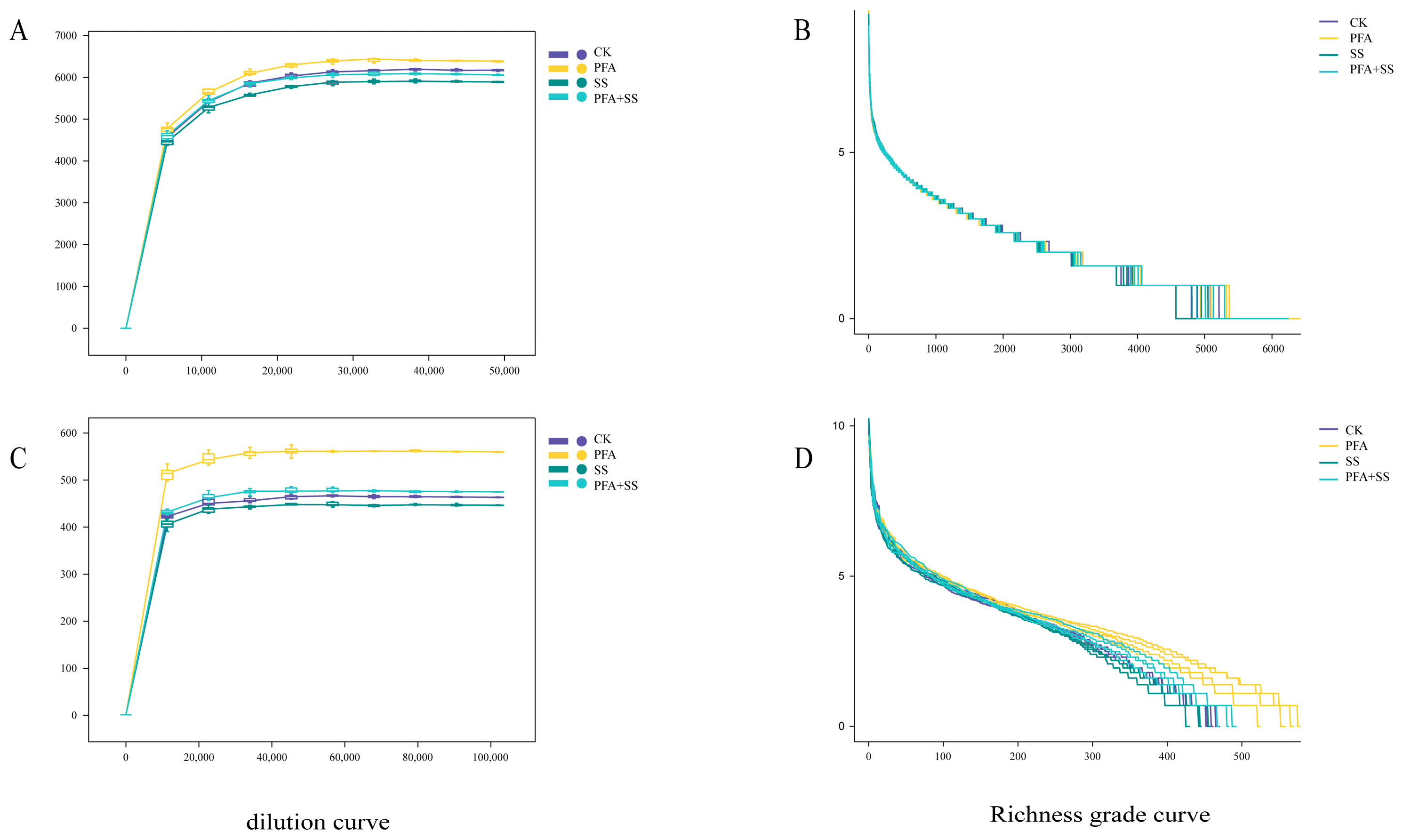
2.2. Comparison of Potassium Fulvic Acid on the Composition and Richness of Bacteria and Fungi in the Rhizosphere Soil of Blueberry
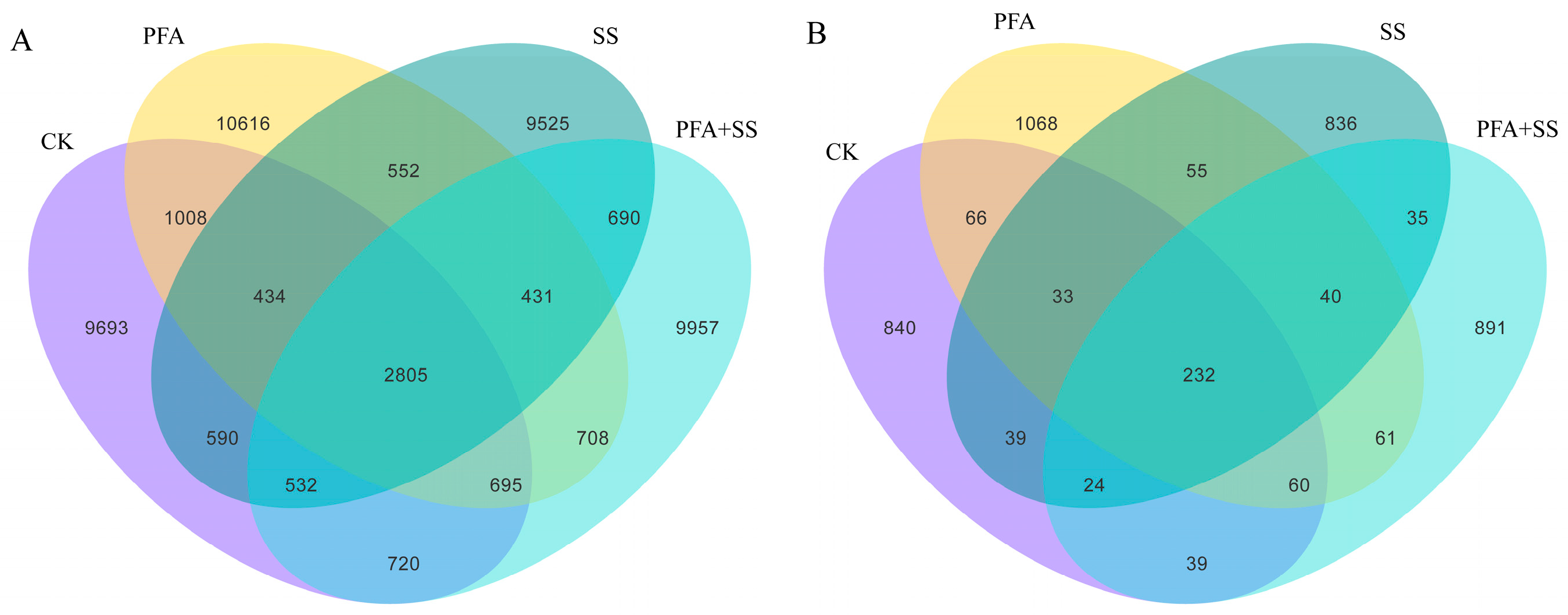
2.3. Effect of Potassium Fulvic Acid on the Distribution of Bacterial ASVs in the Inter-Root Soil of Blueberry
2.4. Analysis of Microorganisms in Rhizosphere Soil of Blueberry (Alpha Diversity)
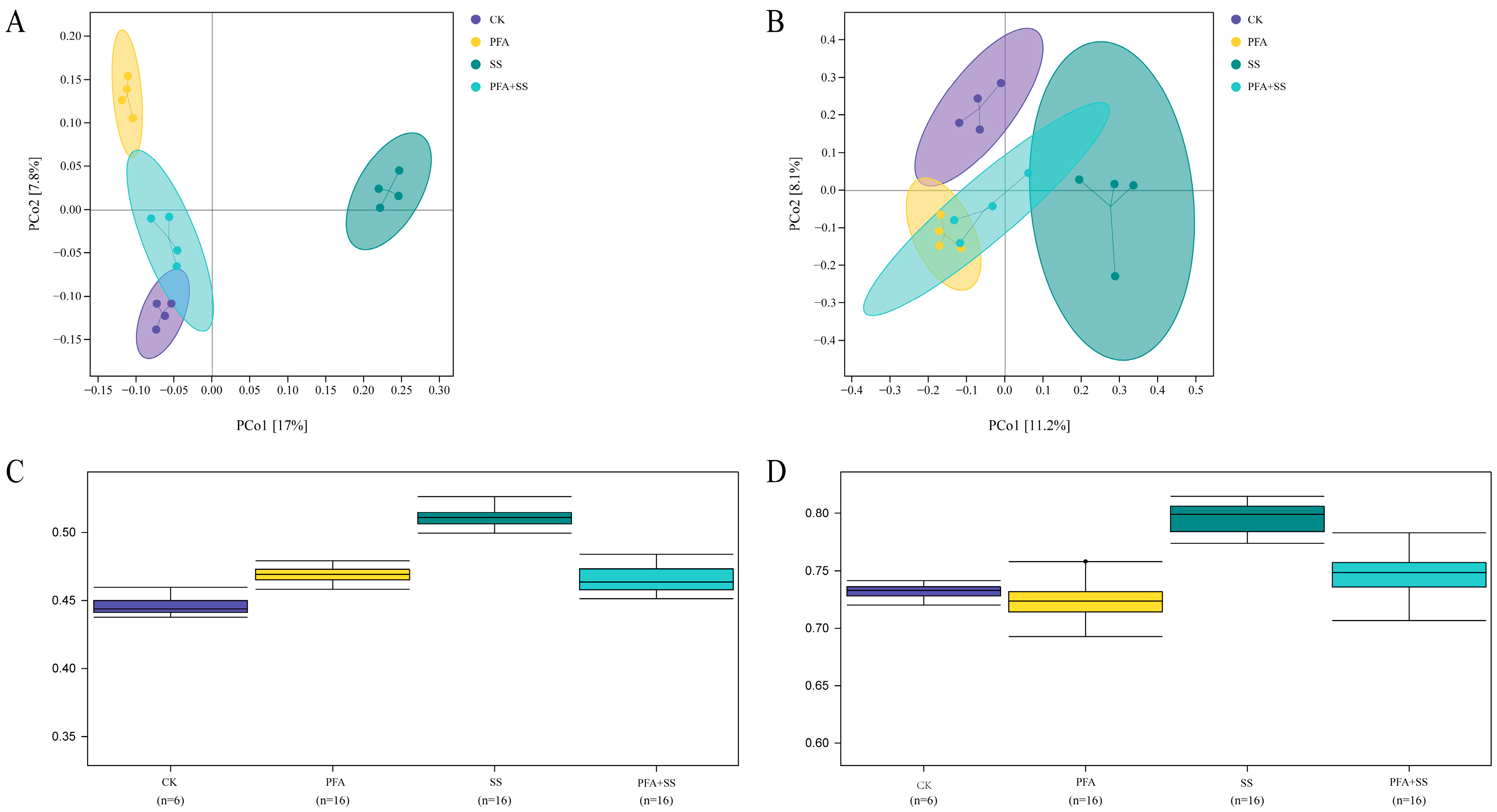
2.5. Effects of Potassium Fulvic Acid on PCoA of Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Rhizosphere Soil of Blueberry and Analysis of Differences Between Groups
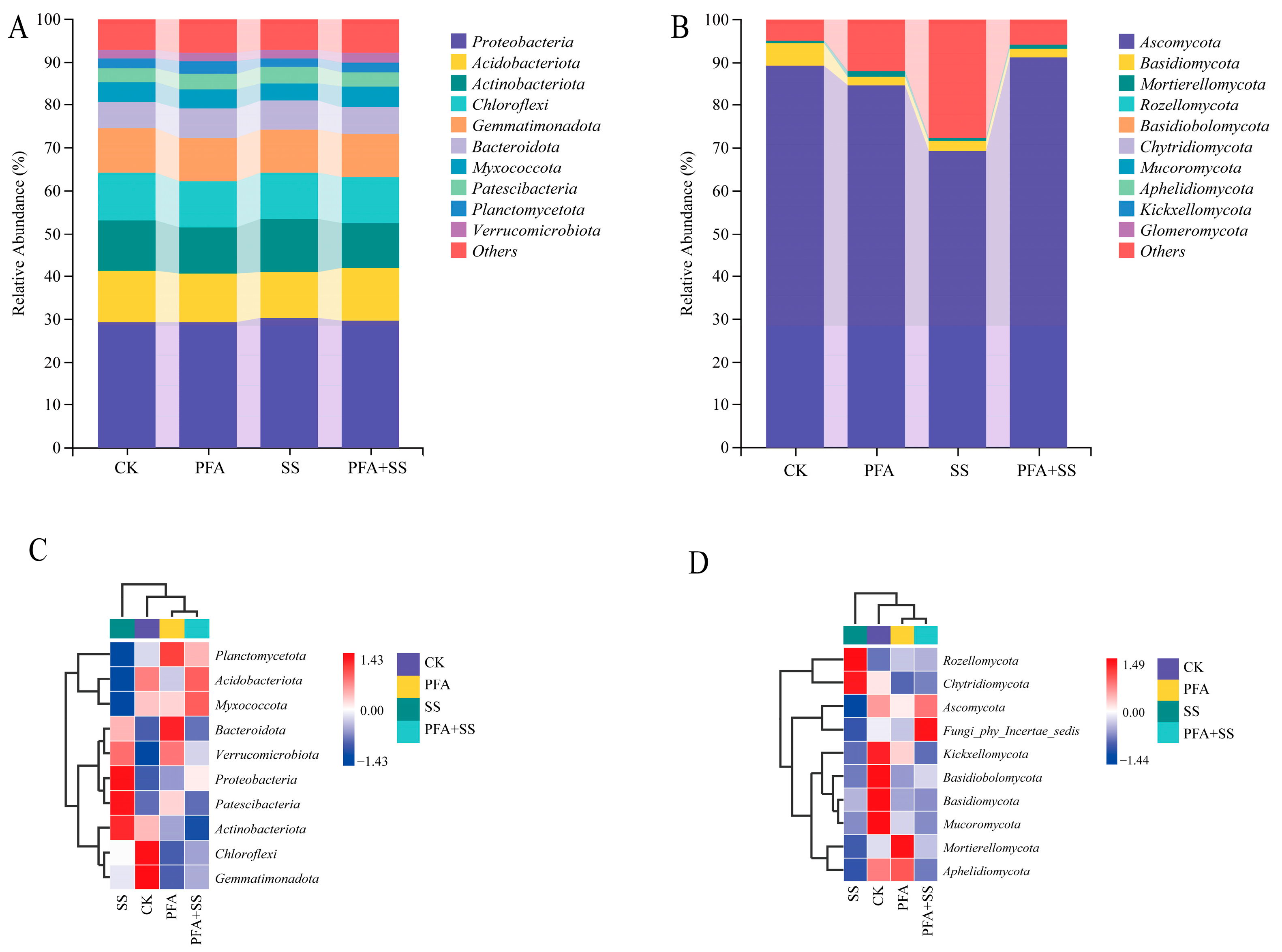
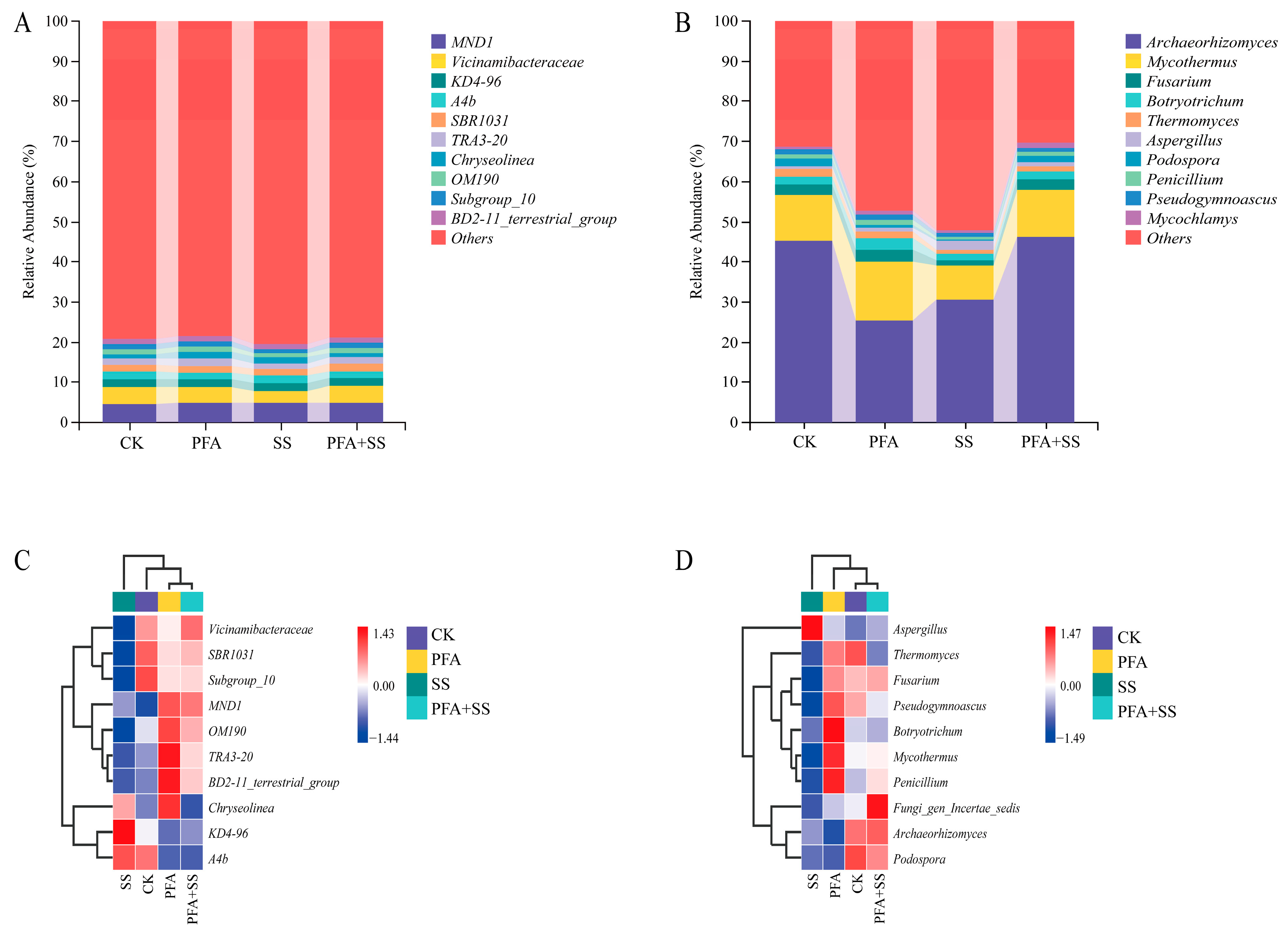
2.6. Effect of Potassium Fulvic Acis on Bacterial Community Composition in Blueberry Rhizosphere Soil
2.6.1. Analysis of Microbial Community at the Phylum Level
2.6.2. Composition of Bacterial Community at Genus Level
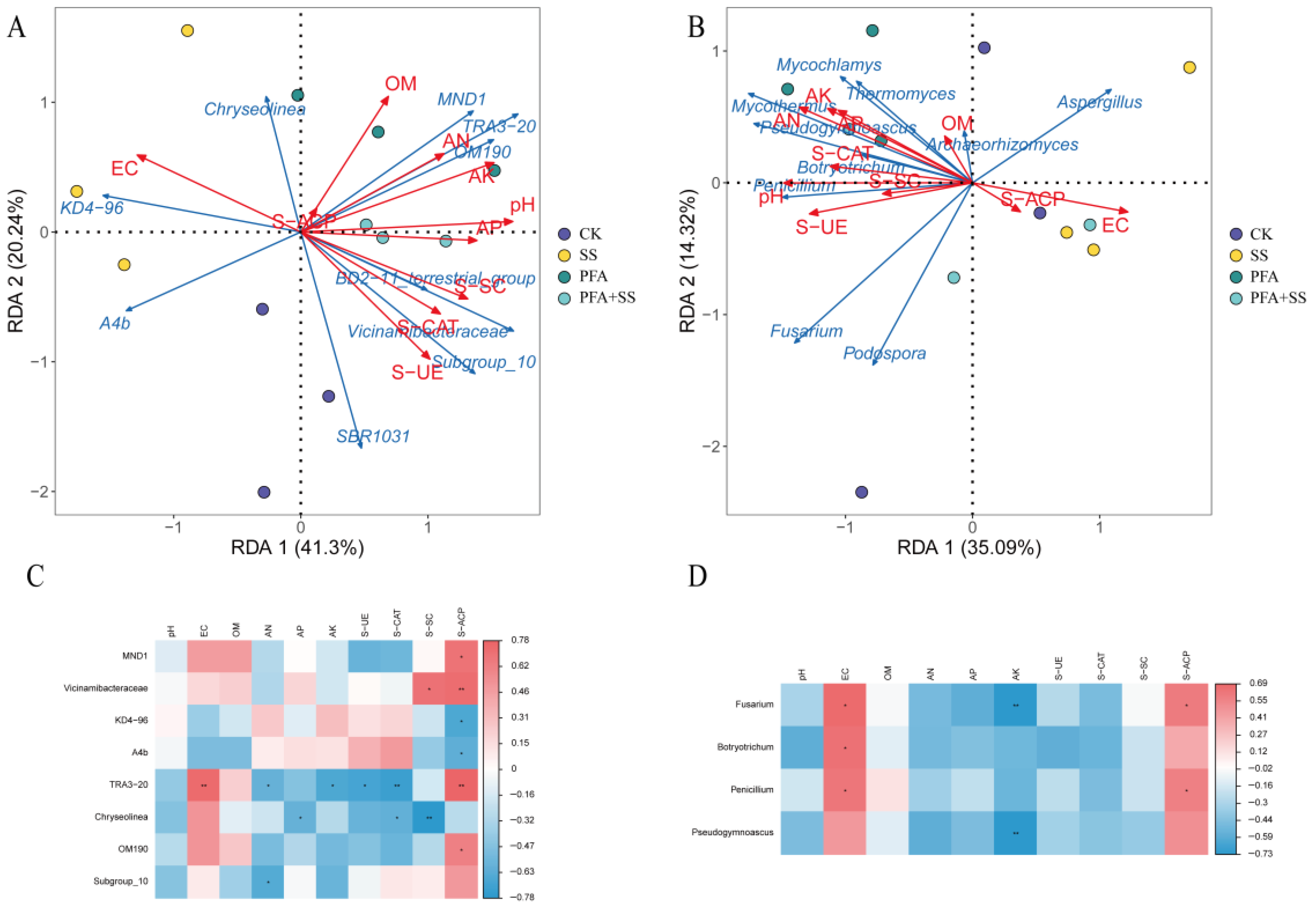
2.7. Correlation Analysis Between Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Rhizosphere Soil of Potassium Fulvic Acids Blueberry and Soil Environmental Factors
2.8. Effects of Potassium Fulvic Acid on the Growth and Physiology of Blueberry
3. Discussion
3.1. Effects of Potassium Fulvic Acid on Physical and Chemical Properties and Soil Enzyme Content of Blueberry Rhizosphere Soil
3.2. Effects of Potassium Fulvic Acid Treatment on Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Diversity and Composition in Blueberry
3.3. Effects of Potassium Fulvic Acid on the Growth and Physiological Activity of Blueberry
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Overview of Test Site
4.2. Experimental Design and Sample Collection
4.3. Determination of Plant Growth and Physiological Indices
4.4. Determination of the Physicochemical Indices and Enzyme Activities of Rhizosphere Soil
4.5. Microbial Community Analysis of Rhizosphere Soil Samples
- (1)
- Using an OMEGA Soil DNA Kit (D5635-02) (Omega Bio-Tek, Norcross, GA, USA), the total microbial DNA was extracted.
- (2)
- PCR amplification was performed using qualified soil DNA as a template. The target fragments were the V3–V4 region of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene and fungal ITS1. The ITS1 was selected. The upstream and downstream primers were 338F, 806R, ITS5, and ITS2. The same amplification system (25 μL) for bacteria and fungi: Q5 high-fidelity DNA polymerase 0.25 μL, 5 × reaction buffer 5 μL, 5 × GC buffer 5 μL, dNTP (10 mM) 2 μL, forward primer (10 μM) 1 μL, reverse primer (10 μM) 1 μL, DNA template 2 μL.
- (3)
- The amplification conditions were as follows: 98 °C for 5 min, 98 °C for 30 s, 55 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 45 s, a total of 30 cycles; the reaction was extended at 72 °C for 5 min, and the reaction was terminated at 12 °C.
- (4)
- The PCR amplification products were detected using 0.8% agarose gel electrophoresis, and the qualified products were entrusted to Shanghai Pasenuo Biotechnology Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China) for sequencing and microbial diversity analysis using the Illumina NovaSeq platform (Shanghai, China).
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, W.; Song, X.; He, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J. Distribution of Soil Organic Carbon Density Fractions in Aggregates as Influenced by Salts and Microbial Community. Land 2023, 12, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pascale, S.; Orsini, F.; Caputo, R.; Palermo, M.A.; Barbieri, G.; Maggio, A. Seasonal and multiannual effects of salinisation on tomato yield and fruit quality. Funct. Plant Biol. 2012, 39, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y.; Huo, A.; Liu, L. Soil salinity accumulation and groundwater degradation due to overexploitation over recent 40-year period in Yaoba Oasis, China. Soil Till. Res. 2025, 248, 106398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihandoust, M.; Ghabchi, R. Multiscale evaluation of asphalt binder-aggregate interface exposed to sodium chloride deicer. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2024, 25, 2370555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Cai, J.; Yang, X.; Qiu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Integrated assessment of soil quality and contaminant risks in salinized farmland adjacent to an oil-exploitation zone: Insights from the Yellow River Delta. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litalien, A.; Zeeb, B. Curing the earth: A review of anthropogenic soil salinization and plant-based strategies for sustainable mitigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Yao, R.; Yang, J. Regulation of Nitrogen and Fulvic Acid on Soil Organic Carbon and Aggregates in Saline Soil. Soils 2020, 52, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas, J.; Daliakopoulos, I.N.; del Moral, F.; Hueso, J.J.; Tsanis, I.K. A Review of Soil-Improving Cropping Systems for Soil Salinization. Agronomy 2019, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Global Status of Salt-Affected Soils—Main Report; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, W.-B.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Zhou, H.-T.; Wu, B. Identification and evaluation of salt-alkali tolerance and screening of salt-alkali tolerant germplasm of oat (Avena sativa L.). Acta Agron. Sin. 2023, 49, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Fan, Y.; Ning, Y.; Wei, J.; Yong, C. Analysis and Prospects of Saline-alkali Land in China from the Perspective of Utilization. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2023, 54, 489–494. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Song, M.; Han, M.; Li, Z. Evaluation of Saline-Alkali Adaptability and Soil Improvement Effect of Different Crops in Eastern Agricultural Area of Qinghai Province. J. Sichuan Agric. Univ. 2025, 43, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-Z.; Chen, J.-S.; Peng, E.-R.; Li, R.-L.; Wu, D.-Z. Research Progress on Soil Salinization and Management. China Rural Water Hydropower 2023, 6, 202–208. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Song, G.; Peng, E. Effects of Salt-isolating Materials on Water-salt Distribution and Evaporation Characteristic of Salinized Soil. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2024, 39, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L. Thirty-five Years of Research and Industry Development of Blueberry in China. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2016, 38, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L. Review on Cultivation Physiology of Blueberry in China. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2013, 35, 379–383+388. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, C.; Yang, C.; Chen, C. Research Progress of Blueberry Cultivation Technology. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2021, 27, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Wei, X.; Liu, J. Development Report of 2024 China Blueberry Industry. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2025, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.T.; Liang, H.W.; Sun, S.G. Research Progress in Extraction of Humic Acid from Lignite. Chem. Bioeng. 2024, 41, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Q. Effects of Potassium Fulvic Acid on Physiological Characteristics of Salt Tolerance in Pear Tissue Culture Seedlings; SDAU: Taian, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Wu, W.L.; Lv, L.F.; Li, W.L.; Wu, Y.Q. Effects of soil pH value on growth and physiological characteristics of blueberry and its regulation methods: A review. J. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2022, 50, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yildirim, E.; Ekinci, M.; Turan, M.; Ağar, G.; Dursun, A.; Kul, R.; Alim, Z.; Argin, S. Humic + Fulvic acid mitigated Cd adverse effects on plant growth, physiology and biochemical properties of garden cress. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8040. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Sun, H.; Liu, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Effects of potassium fulvic acid and potassium humate on microbial biodiversity in bulk soil and rhizosphere soil of Panax ginseng. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 254, 126914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Jin, Q.; Lu, G.; Wang, X. Effect of the Soil Modifier of Biochemical Fulvic Acid on Saline Land. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2010, 38, 1931–1932. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, G.; Xu, H.; Yuan, F. Effect of fulvic acid on plant growth. Appl. Chem. Ind. 2021, 50, 1069–1072+1076. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Wang, D.; Gao, Z.; Du, C. Effects of fulvic acid potassium on N transformation in and N2O emission from tobacco plantation soil. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Zhu, S. Potassium fulvic acid alleviates salt stress of citrus by regulating rhizosphere microbial community, osmotic substances and enzyme activities. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1161469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, R.; Garbeva, P.; Raaijmakers, J.M. The rhizosphere microbiome: Significance of plant beneficial, plant pathogenic, and human pathogenic microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 634–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Gao, Y. The Effects of Localized Plant–Soil–Microbe Interactions on Soil Nitrogen Cycle in Maize Rhizosphere Soil under Long-Term Fertilizers. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Lang, M.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Chen, X. Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria rather than ammonia-oxidizing archaea dominate nitrification in a nitrogen-fertilized calcareous soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 151402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Sun, H.; Dai, H.; Xu, Z. Characterization of Plant-Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria for Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis) Development and Soil Nutrient Enrichment. Plants 2024, 13, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, X.; Lu, X.; Hou, D.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L. Study on the Changes in the Microbial Community in Rhizosphere Soil of Blueberry Plants at Different Growth Stages. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Vancov, T.; Si, H.; Yang, W.; Tong, K.; Chen, W.; Fang, Y. Isolation and Characterization of Endomycorrhizal Fungi Associated with Growth Promotion of Blueberry Plants. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Dong, H.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, H.; Yang, H.; Li, L. Isolation and identification of mycorrhizal helper bacteria of Vaccinium uliginosum and their interaction with mycorrhizal fungi. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1180319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Zheng, H.; Yin, S.; Zhang, X.; You, X.; Wu, H.; Suo, F.; Han, K.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. Comparative study of pyrochar and hydrochar on peanut seedling growth in a coastal salt-affected soil of Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Lin, Y. Research on the Effects of Salt Stress in Plant Rhizosphere Environments. Grass Forage Sci. 2023, 2, 1–4+10. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, D.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Wu, L. Comparative Study on the Effects of Different Soil Improvement Methods in Blueberry Soil. Agronomy 2024, 14, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Andom, O.; Fang, W.; Yan, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jin, X.; Cao, A. Effects of Soil Amendments on Soil Properties, Soil-Borne Pathogens, and Strawberry Growth after Dazomet Fumigation. Agriculture 2024, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Mao, W.; Sun, Y.; Qu, Y. Effect of Potassium Humate on Adsorption and Leaching of Main Salt Ions in Coastal Clay Saline Soil. Water Sav. Irrig. 2022, 4, 77–82+93. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar Sootahar, M.; Zeng, X.; Su, S.; Wang, Y.; Bai, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, X. The Effect of Fulvic Acids Derived from Different Materials on Changing Properties of Albic Black Soil in the Northeast Plain of China. Molecules 2019, 24, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyung, J.L.; Jun, H.P.; Ju, S.C. Effect of pyroligneous acid on soil urease, amidase, and nitrogen use efficiency by Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris var. Pekinensis). Environ. Pollut. 2021, 29, 1118132. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Mao, S.; Conkle, J.L.; Chen, Y.; Kim, Y.M. Effects of interaction between enrofloxacin and copper on soil enzyme activity and evaluation of comprehensive toxicity. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 129208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; George, T.S.; Feng, G. Hyphosphere core taxa link plant-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi combinations to soil organic phosphorus mineralization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 201, 109647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.X.; Wang, Y.; Lyu, H.; Chen, X.D. Effects of a compoundTrichodermaagent onCoptis chinensisgrowth, nutrients, enzyme activity, and microbial community of rhizosphere soil. Peerj 2023, 11, e15652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q. Effects of Weathered Coal Humic Acid Char-Based Nitrogen on Wheat Soil Nutrients and Bacterial Communities; NWAFU: Yangling, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Han, D.; Zhao, M.; Li, X.; Guan, C. Effects of application of microbial agents along with humic acid potassium on tobacco-planted soil and economic benefit of flue-cured tobacco. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2017, 29, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, T.; Wang, M. Diversity and Differences of Rhizosphere Microbial Community Structure in Different Blueberries. North. Hortic. 2022, 14, 76–86. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, F.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Jeyakumar, P.; Sarkar, B.; Luo, Z.; Bolan, N. Pristine and Fe-functionalized biochar for the simultaneous immobilization of arsenic and antimony in a contaminated mining soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 133937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; He, Z.L.; Lin, Q.; Lin, Y.; Long, K.; Xie, Z.; Hu, W. Salt stress affects the bacterial communities in rhizosphere soil of rice. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1505368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H.; Cheng, J.; Miao, L. Community composition and cellulase activity of cellulolytic bacteria from forest soils planted with broad-leaved deciduous and evergreen trees. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 98, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wang, W.; Xi, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, K.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, F. Impact of Aerated Irrigation Duration on the Growth of Greenhouse Grape Seedlings and Rhizosphere Soil Microorganisms. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhao, X.; Ren, J.; Dong, J.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Q.; Jiang, C.; Zhong, C. Influence of Peanut, Sorghum, and Soil Salinity on Microbial Community Composition in Interspecific Interaction Zone. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 678250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manici, L.M.; Caputo, F.; Fornasier, F.; Paletto, A.; Ceotto, E.; Demeo, I. Ascomycota and Basidiomycota fungal phyla as indicators of land use efficiency for soil organic carbon accrual with woody plantations. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Feng, L.; Zhang, J. Effects of potassium fulvic acid on the germination and seedling growth of Pak Choi (Brassica chinensis L.)under salt stress. China Cucurb. Veget. 2020, 12, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z. Experimental Techniques of Plant Physiology; Jilin University Press: Changchun, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S. Agrochemical Analysis of Soil; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]

| Treatment | pH | EC (uS/cm) | OM (g/kg) | AN (mg/kg) | AP (mg/kg) | AK (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 4.84 ± 0.04 b | 697 ± 59 c | 16.80 ± 0.29 c | 150 ± 5 b | 33.87 ± 1.12 a | 305 ± 7 c |
| SS | 4.72 ± 0.04 c | 1824 ± 159 a | 17.80 ± 0.31 b | 145 ± 5 b | 29.37 ± 1.70 b | 268 ± 4 d |
| PFA | 4.96 ± 0.04 a | 698 ± 15 c | 18.34 ± 0.51 b | 169 ± 4 a | 35.40 ± 1.43 a | 425 ± 10 a |
| PFA + SS | 4.93 ± 0.05 a | 1028 ± 7 b | 19.55 ± 0.19 a | 160 ± 5 a | 35.67 ± 1.23 a | 399 ± 17 b |
| Treatment | S-UE Activity (U/g) | S-CAT Activity (U/g) | S-SC Activity (U/g) | S-ACP Activity (U/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 1585 ± 64 a | 34 ± 1 a | 183 ± 17 ab | 798 ± 18 c |
| SS | 1104 ± 76 b | 26 ± 1 c | 107 ± 25 c | 904 ± 21 b |
| PFA | 1470 ± 141 a | 33 ± 0 a | 161 ± 12 b | 773 ± 6 c |
| PFA + SS | 1406 ± 79 a | 30 ± 0 b | 201 ± 12 a | 1023 ± 84 a |
| Treatment | Plant Height (mm) | Stem Thick (mm) | Total Chlorophyll Content (mg/g) | Root Activity [ug/(g·h)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 351 ± 12 a | 2.63 ± 0.17 b | 1.82 ± 0.05 a | 235 ± 5 a |
| SS | 256 ± 5 c | 2.47 ± 0.09 b | 1.35 ± 0.04 c | 149 ± 7 c |
| PFA | 351 ± 14 a | 2.65 ± 0.46 b | 1.78 ± 0.03 a | 226 ± 5 a |
| PFA + SS | 324 ± 3 b | 3.21 ± 0.03 a | 1.67 ± 0.05 b | 184 ± 2 b |
| Measured Parameters | Determination Method [56] |
|---|---|
| Electrical conductivity (EC) and pH | Measured at a water/soil mass ratio of 5:1. |
| Organic matter (OM) content | Used the high-temperature external thermal potassium dichromate oxidation-volumetric method. |
| Alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen (AN) content | Used the alkali solution diffusion absorption method. |
| Content of available phosphorus (AP) | The 0.5 mol/L NaHCO3 extraction-molybdenum antimony colorimetric method. |
| Content of available potassium (AK) | Used a 1 mol/L NH4OAc extraction-flame photometric method. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Hou, D.; Ma, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, L.; Liu, H.; Zuo, Y.; Guo, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Effects of Potassium Fulvic Acid on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Soil Microenvironment of Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) Under Salt Stress. Plants 2025, 14, 1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111654
Wu X, Hou D, Ma J, Li Y, Wu L, Liu H, Zuo Y, Guo X, Li J, Wang Y. Effects of Potassium Fulvic Acid on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Soil Microenvironment of Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) Under Salt Stress. Plants. 2025; 14(11):1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111654
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xuanrong, Dekang Hou, Jing Ma, Yanan Li, Lin Wu, Haiguang Liu, Yi Zuo, Xinxin Guo, Jinying Li, and Ying Wang. 2025. "Effects of Potassium Fulvic Acid on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Soil Microenvironment of Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) Under Salt Stress" Plants 14, no. 11: 1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111654
APA StyleWu, X., Hou, D., Ma, J., Li, Y., Wu, L., Liu, H., Zuo, Y., Guo, X., Li, J., & Wang, Y. (2025). Effects of Potassium Fulvic Acid on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Soil Microenvironment of Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) Under Salt Stress. Plants, 14(11), 1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111654






