OsEDS1 and OsPAD4 Are Involved in Brown Planthopper Resistance in Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
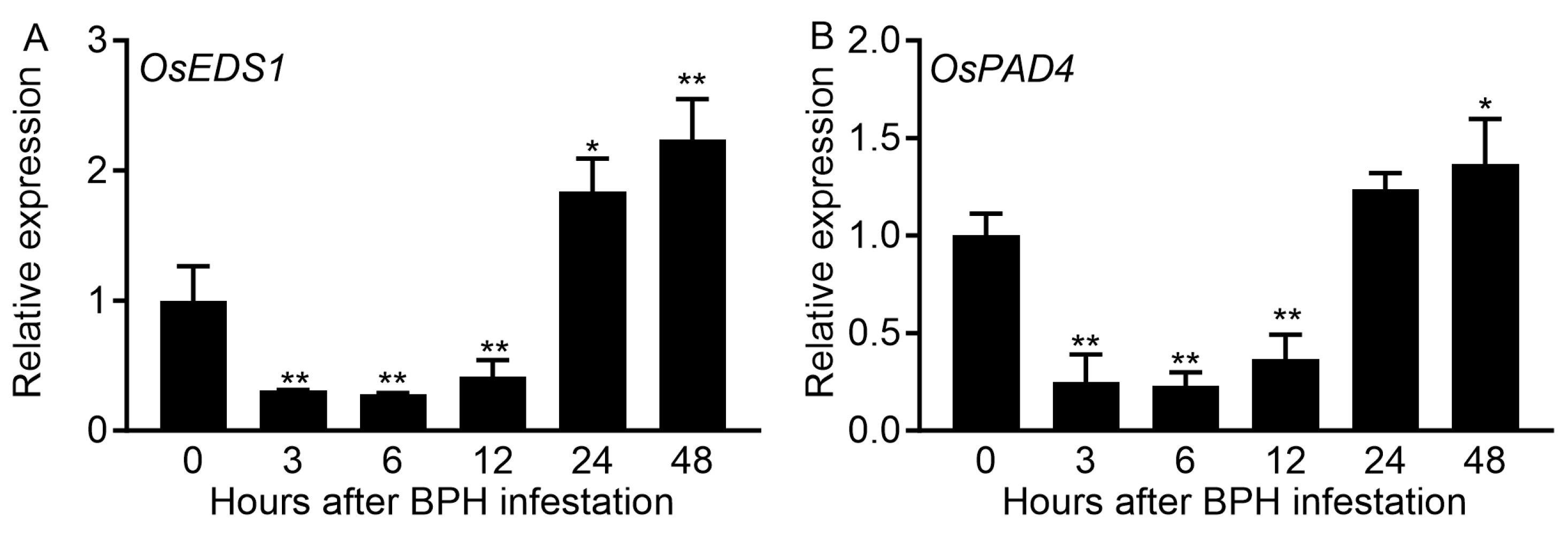
2.1. BPH Infestation Influences Expression Levels of OsEDS1 and OsPAD4
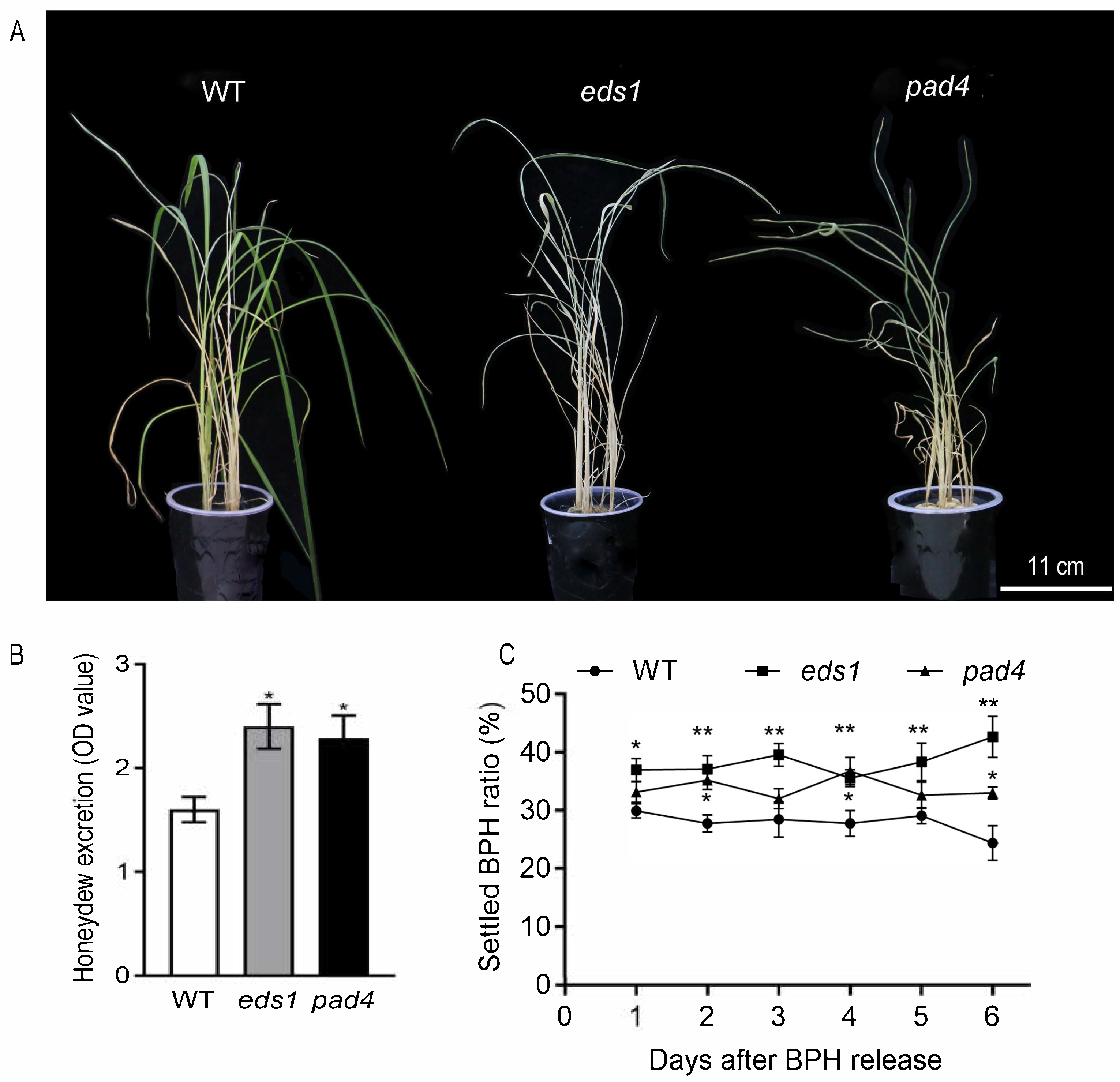
2.2. Mutations in OsPAD4 and OsEDS1 Decrease Rice Resistance to BPH
2.3. Mutations in OsEDS1 and OsPAD4 Alter the Expression of Defense-Responsive Genes
2.4. Mutations of OsEDS1 and OsPAD4 Impair BPH-Induced SA and JA Modulation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Plant Growth Conditions
4.3. BPH Rearing and Infestation
4.4. Gene Expression Analysis
4.5. Quantification of JA, JA-Ile and SA
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BPH | Nilaparvata lugens Stål |
| JA | Jasmonic acid |
| SA | Salicylic acid |
| EDS1 | Enhanced disease susceptibility 1 |
| PAD4 | Phytoalexin deficient 4 |
| OsPAL | Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase |
| OsICS1 | Isochorismate synthase 1 |
| OsPR1a | Basic pathogenesis-related gene 1a |
| OsLOX1 | Lipoxygenase 1 |
| OsAOS1 | Allene oxide synthase 1 |
| OsJAZ11 | Jasmonate-zim domain 11 |
References
- Cheng, X.; Zhu, L.; He, G. Towards understanding of molecular interactions between rice and the brown planthopper. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, B.; Chen, R.; Guo, J.; He, G. Current understanding of the genomic, genetic, and molecular control of insect resistance in rice. Mol. Breed. 2020, 40, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J.; Li, Q.; Luo, L.; Cui, F. Key role of exportin 6 in exosome-mediated viral transmission from insect vectors to plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2207848119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogawa, K. The rice brown planthopper: Feeding physiology and host plant interactions. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1982, 27, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erb, M.; Reymond, P. Molecular interactions between plants and insect herbivores. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2019, 70, 527–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigeard, J.; Colcombet, J.; Hirt, H. Signaling mechanisms in pattern-triggered immunity (PTI). Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieterse, C.; Van der Does, D.; Zamioudis, C.; Leon-Reyes, A.; Van Wees, S. Hormonal modulation of plant immunity. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 28, 489–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dicke, M.; Kroes, A.; Liu, W.; Gols, R. Interactive effects of cabbage aphid and caterpillar herbivory on transcription of plant genes associated with phytohormonal signalling in wild cabbage. J. Chem. Ecol. 2016, 42, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Zhang, W.; Liu, B.; Hu, J.; Wei, Z.; Shi, Z.; He, R.; Zhu, L.; Chen, R.; Han, B.; et al. Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22163–22168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.; Fu, J.; Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Jing, M.; Wang, L.; Yang, S.; Tian, T.; Wang, L.; Ju, J.; et al. Vitellogenin from planthopper oral secretion acts as a novel effector to impair plant defenses. New Phytol. 2021, 232, 802–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Luo, T.; Fu, H.; Wang, L.; Tan, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, Q.; Ye, G.; Gatehouse, A.; Lou, Y.; et al. Resistance of rice to insect pests mediated by suppression of serotonin biosynthesis. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, S.; Wan, P.; Yuan, S.; Lai, F.; Wang, W.; Fu, Q. Differential responses of OsMPKs in IR56 rice to two BPH populations of different virulence levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, D.; Duan, M.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Yang, C.; Qiu, Z.; Liu, D.; Wen, P.; et al. An R2R3 MYB transcription factor confers brown planthopper resistance by regulating the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase pathway in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 117, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, Z.; Jing, S.; Wang, Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Cai, B.; Xin, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; et al. Allelic diversity in an NLR gene BPH9 enables rice to combat planthopper variation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 12850–12855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wang, H.; Guan, W.; Guo, Q.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Peng, Y.; Shan, J.; Gao, M.; Shi, S.; et al. A tripartite rheostat controls self-regulated host plant resistance to insects. Nature 2023, 618, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, C.; Liu, F.; Huang, F.; Qiu, Y.; Li, R.; Luo, X. Map-based cloning and characterization of BPH29, a B3 domain-containing recessive gene conferring brown planthopper resistance in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 6035–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Qi, J.; Ren, N.; Cheng, J.; Erb, M.; Mao, B.; Lou, Y. Silencing OsHI-LOX makes rice more susceptible to chewing herbivores, but enhances resistance to a phloem feeder. Plant J. 2009, 60, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jin, G.; Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Lou, Y.; Baldwin, I.; Li, R. Multiomic analyses reveal key sectors of jasmonate-mediated defense responses in rice. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 3362–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidrich, K.; Wirthmueller, L.; Tasset, C.; Pouzet, C.; Deslandes, L.; Parker, J. Arabidopsis EDS1 connects pathogen effector recognition to cell compartment–specific immune responses. Science 2011, 334, 1401–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Qiu, J.; Zhao, C.; Bautor, J.; Parker, J. Antagonism of transcription factor MYC2 by EDS1/PAD4 complexes bolsters salicylic acid defense in Arabidopsis effector-triggered immunity. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Halane, M.; Kim, S.; Gassmann, W. Pathogen effectors target Arabidopsis EDS1 and alter its interactions with immune regulators. Science 2011, 334, 1405–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Y.; Kang, Y.; Wu, M.; Liu, H.; Hui, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S. Jasmonic acid-involved OsEDS1 signaling in rice-bacteria interactions. Rice 2019, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S. Rice OsPAD4 functions differently from Arabidopsis AtPAD4 in host-pathogen interactions. Plant J. 2014, 78, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Gobbato, E.; Kracher, B.; Qiu, J.; Bautor, J.; Parker, J. A core function of EDS1 with PAD4 is to protect the salicylic acid defense sector in Arabidopsis immunity. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 1802–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feys, B.; Moisan, L.; Newman, M.; Parker, J. Direct interaction between the Arabidopsis disease resistance signaling proteins, EDS1 and PAD4. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 5400–5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapin, D.; Bhandari, D.; Parker, J. Origins and immunity networking functions of EDS1 family proteins. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2020, 58, 253–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiermer, M.; Feys, B.; Parker, J. Plant immunity: The EDS1 regulatory node. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2005, 8, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, J.; Shah, J. Plant defence against aphids: The PAD4 signalling nexus. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 66, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegadaraju, V.; Louis, J.; Singh, V.; Reese, J.; Bautor, J.; Feys, B.; Cook, G.; Parker, J.; Shah, J. Phloem-based resistance to green peach aphid is controlled by Arabidopsis PHYTOALEXIN DEFICIENT4 without its signaling partner ENHANCED DISEASE SUSCEPTIBILITY1. Plant J. 2007, 52, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegadaraju, V.; Knepper, C.; Reese, J.; Shah, J. Premature leaf senescence modulated by the Arabidopsis PHYTOALEXIN DEFICIENT4 gene is associated with defense against the phloem-feeding green peach aphid. Plant Physiol. 2005, 139, 1927–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongus, J.; Bhandari, D.; Patel, M.; Archer, L.; Dijkgraaf, L.; Deslandes, L.; Shah, J.; Parker, J. The Arabidopsis PAD4 lipase-like domain is sufficient for resistance to green peach aphid. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2020, 33, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Xu, W.; Chen, S.; Wu, X.; Rao, W.; Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, J.; Nishimura, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Activation of a helper NLR by plant and bacterial TIR immune signaling. Science 2024, 386, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhao, G.; Lei, Z.; Li, K.; Liu, J.; Huang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhong, X.; Yin, X.; et al. A canonical protein complex controls immune homeostasis and multipathogen resistance. Science 2024, 386, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feys, B.; Wiermer, M.; Bhat, R.; Moisan, L.; Medina-Escobar, N.; Neu, C.; Cabral, A.; Parker, J. Arabidopsis SENESCENCE-ASSOCIATED GENE101 stabilizes and signals within an ENHANCED DISEASE SUSCEPTIBILITY1 complex in plant innate immunity. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 2601–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, S.; Stuttmann, J.; Rietz, S.; Guerois, R.; Brunstein, E.; Bautor, J.; Niefind, K.; Parker, J. Structural basis for signaling by exclusive EDS1 heteromeric complexes with SAG101 or PAD4 in plant innate immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Luo, S.; Xie, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, T.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhu-Salzman, K.; Zeng, R. Silencing COI1 in rice increases susceptibility to chewing insects and impairs inducible defense. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Ren, N.; Qi, J.; Lu, J.; Xiang, C.; Ju, H.; Cheng, J.; Lou, Y. The 9-lipoxygenase Osr9-LOX1 interacts with the 13-lipoxygenase-mediated pathway to regulate resistance to chewing and piercing-sucking herbivores in rice. Physiol. Plant. 2014, 152, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zhou, G.; Yang, L.; Erb, M.; Lu, Y.; Sun, X.; Cheng, J.; Lou, Y. The chloroplast-localized phospholipases D α4 and α5 regulate herbivore-induced direct and indirect defenses in rice. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 1987–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, D.; Xue, R.; Long, J.; Lin, X.; Lin, Y.; Jia, L.; Zeng, R.; Song, Y. Effects of boron, silicon and their interactions on cadmium accumulation and toxicity in rice plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 367, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Qi, J.; Hettenhausen, C.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, C.; Song, J.; Li, J.; Cao, G.; et al. Elevated CO2 differentially affects tobacco and rice defense against lepidopteran larvae via the jasmonic acid signaling pathway. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2018, 60, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, L.; Su, R.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Song, Y.; Zeng, R.; Wang, Q.; Cui, H.; Chen, D. OsEDS1 and OsPAD4 Are Involved in Brown Planthopper Resistance in Rice. Plants 2025, 14, 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111612
Fang L, Su R, Li C, Liu X, Song Y, Zeng R, Wang Q, Cui H, Chen D. OsEDS1 and OsPAD4 Are Involved in Brown Planthopper Resistance in Rice. Plants. 2025; 14(11):1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111612
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Linzhi, Rong Su, Cunyan Li, Xiaodong Liu, Yuanyuan Song, Rensen Zeng, Qiongli Wang, Haitao Cui, and Daoqian Chen. 2025. "OsEDS1 and OsPAD4 Are Involved in Brown Planthopper Resistance in Rice" Plants 14, no. 11: 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111612
APA StyleFang, L., Su, R., Li, C., Liu, X., Song, Y., Zeng, R., Wang, Q., Cui, H., & Chen, D. (2025). OsEDS1 and OsPAD4 Are Involved in Brown Planthopper Resistance in Rice. Plants, 14(11), 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111612







