Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the mTERF Gene Family in Spinach and the Role of SomTERF5 in Response to Heat Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
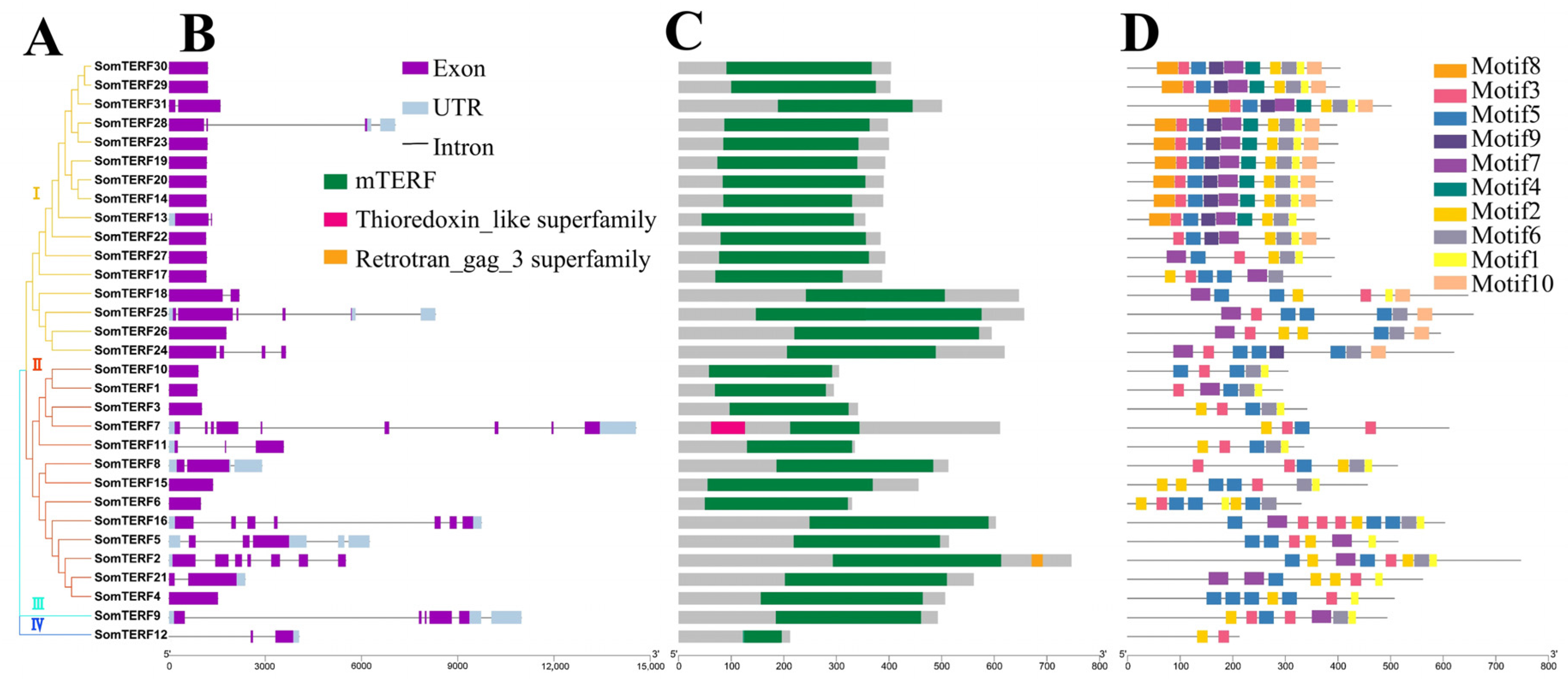
2.1. Phylogenetic Relationships Between Members of the Spinach mTERF Family and Other Species
2.2. Analysis of Gene Structure, Functional Structural Domains, and Conserved Motifs of SomTERF Family Genes
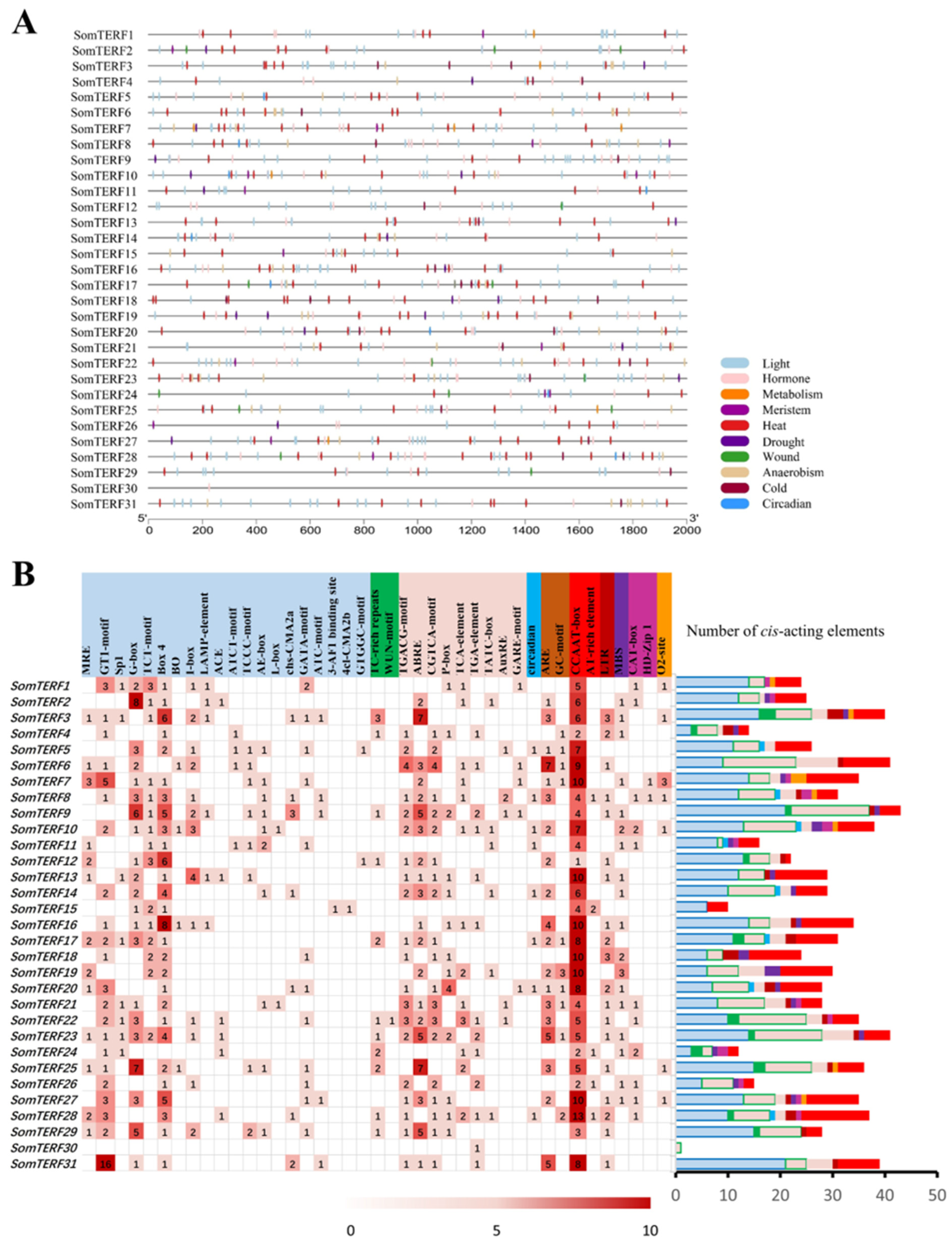
2.3. Analysis of Cis-Acting Elements of the Spinach mTERF Family
2.4. Expression Analysis of the SomTERF Family in Different Spinach Organs
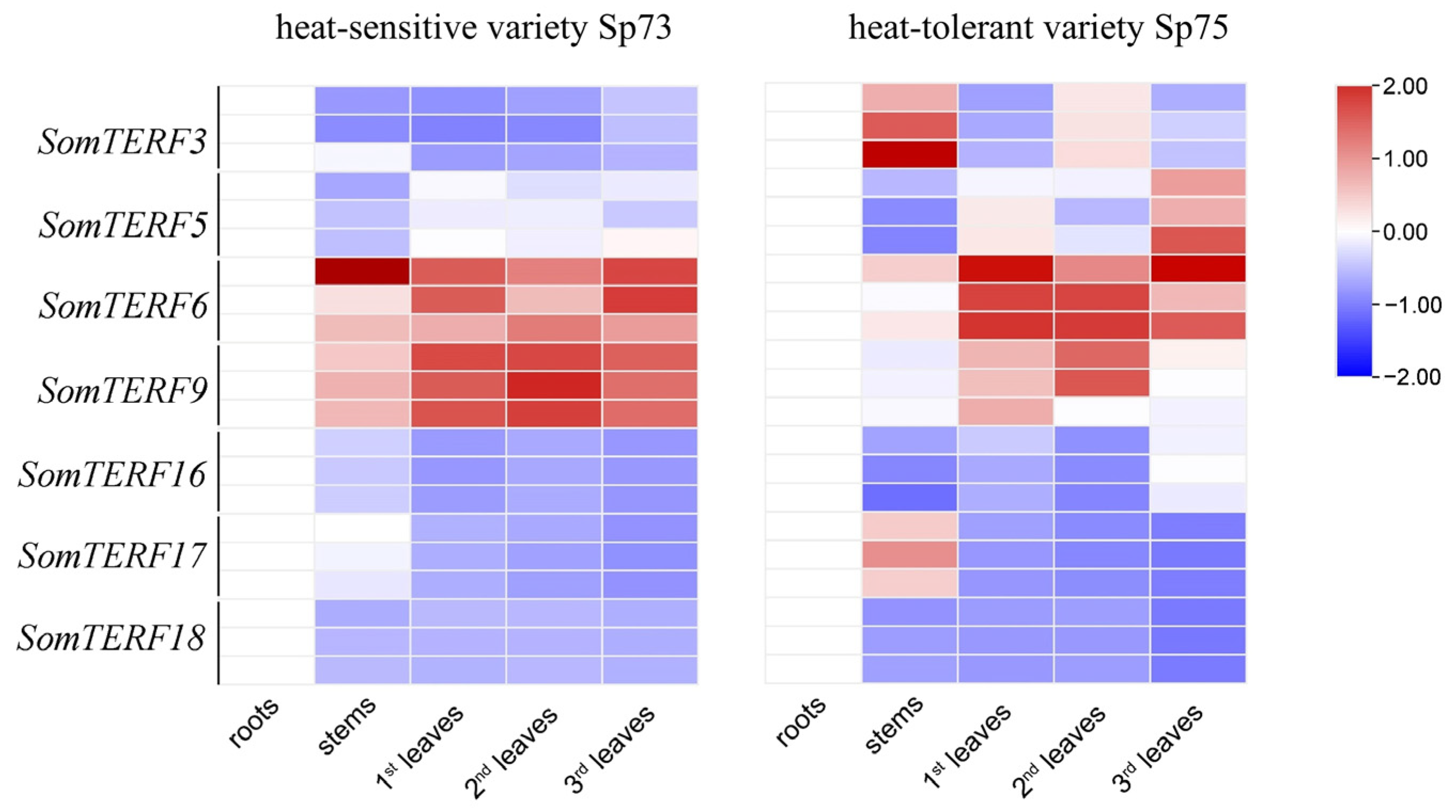
2.5. Expression Analysis of SomTERF Family Genes Under Heat Stress
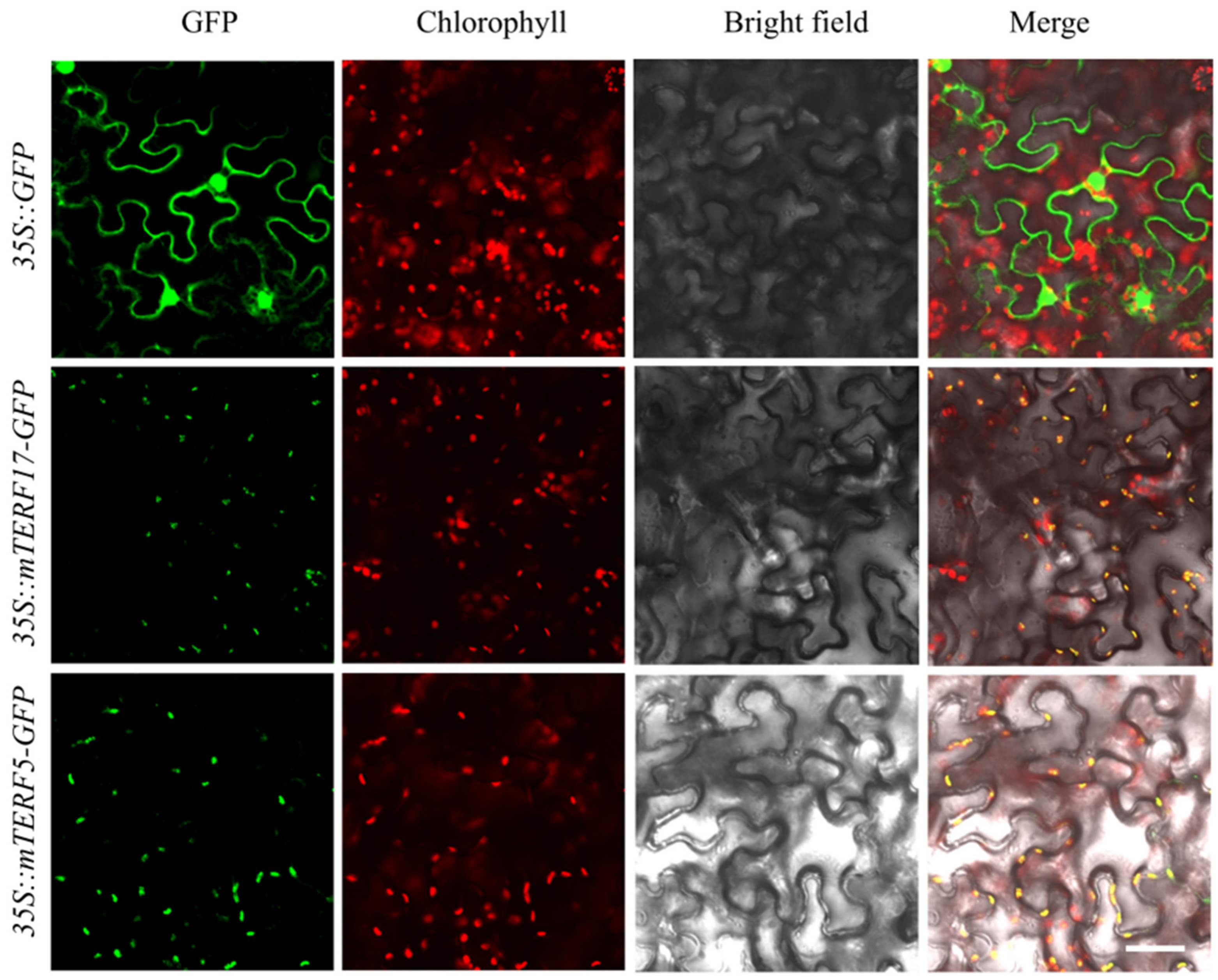
2.6. Subcellular Localization of SomTERF5 and SomTERF17
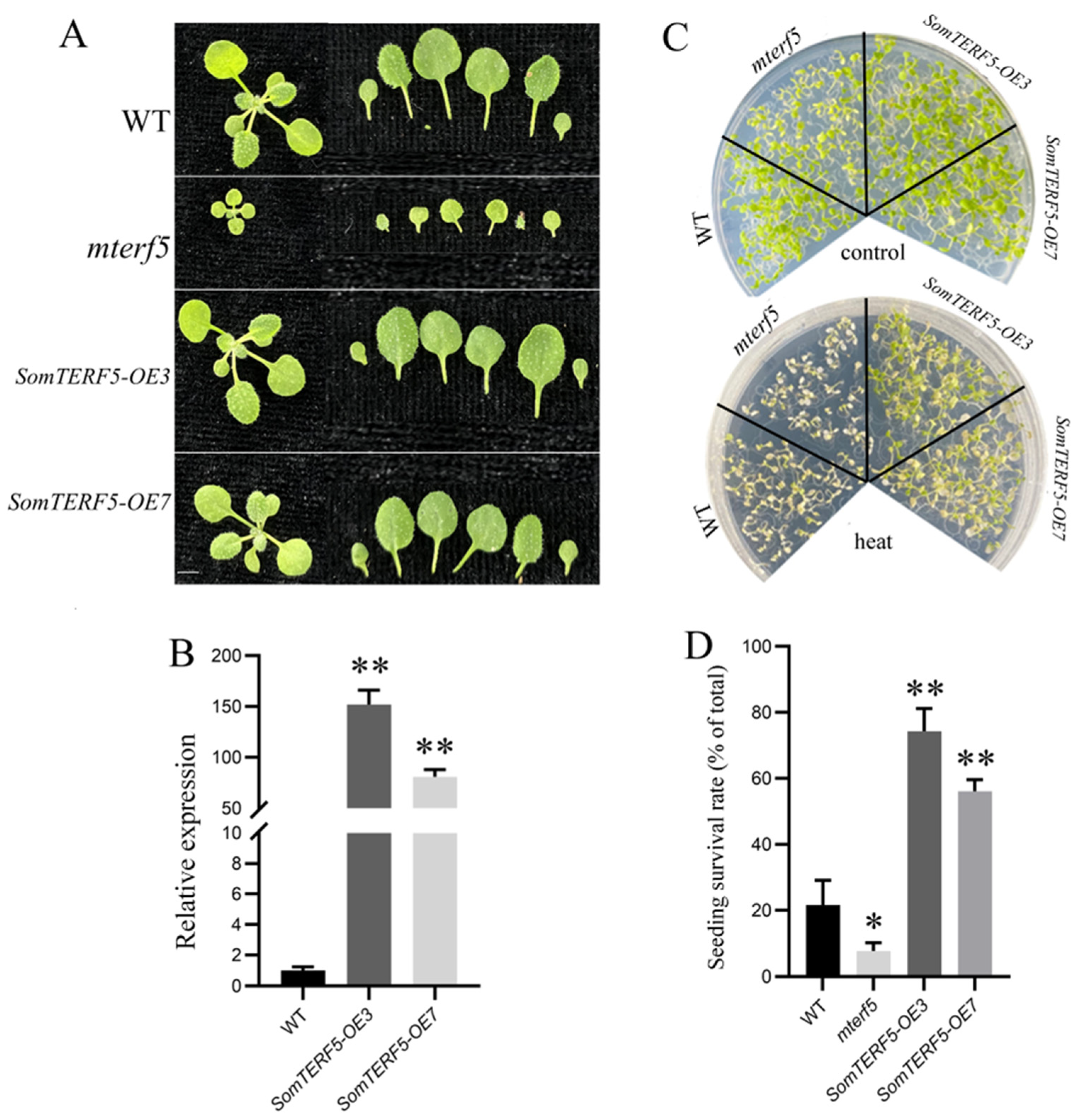
2.7. Thermotolerance Analysis of SomTERF5 in Arabidopsis
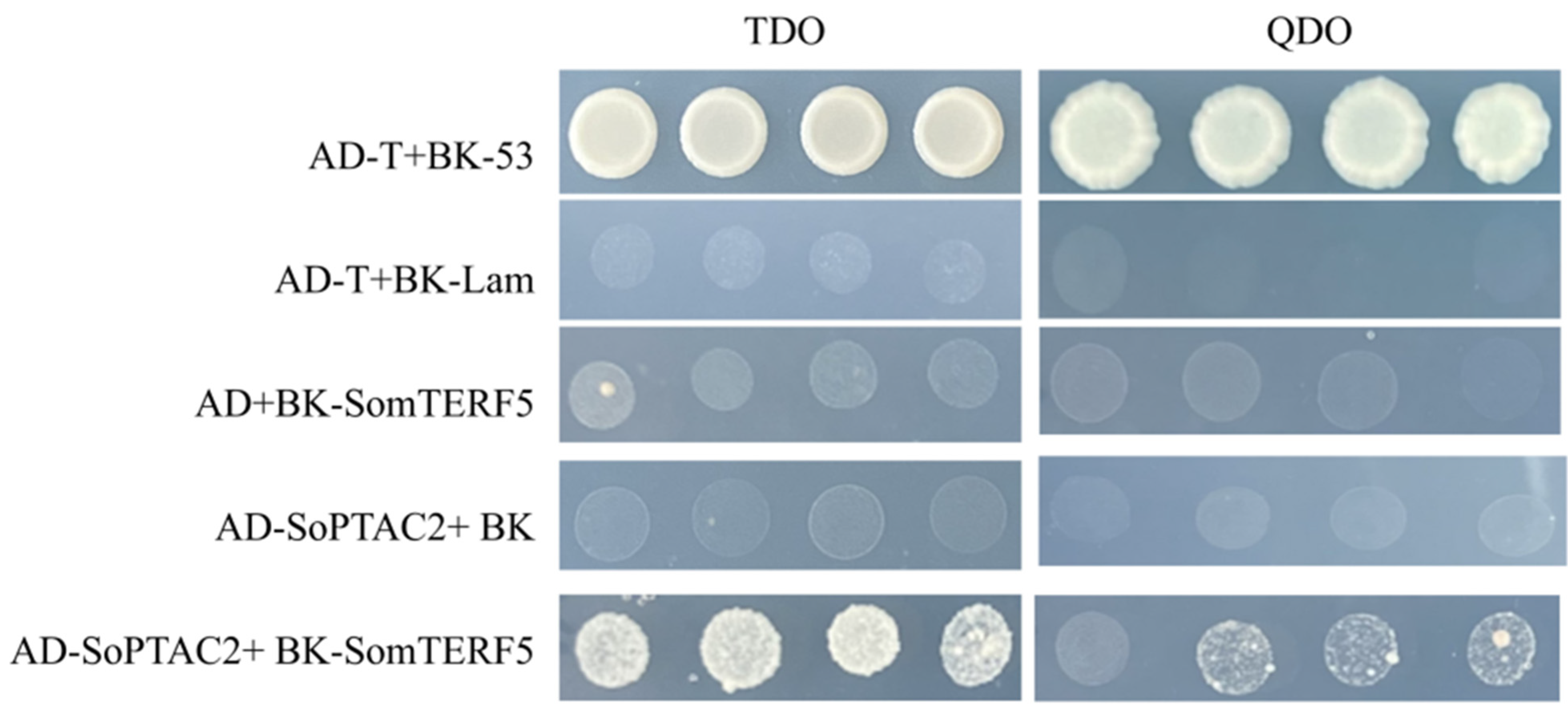
2.8. SomTERF5 Interacts with SopTAC2
3. Discussion
3.1. Higher Homology Between Spinach SomTERFs and Arabidopsis mTERFs
3.2. SomTERF5 Affects Plant Heat Tolerance
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification and Cloning of mTERFs Genes in Spinach
4.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of mTERFs in Different Species
4.3. Analysis of Gene Structure, Functional Structural Domains, and Conserved Motifs
4.4. Prediction of Promoter Cis-Acting Elements
4.5. Plant Materials, RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and RT-qPCR
4.6. Subcellular Localisation of SomTERF5 and SomTERF17
4.7. Thermotolerance Analysis of Transgenic Arabidopsis
4.8. Yeast Two-Hybrid Experiments
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, J.; Yu, L.; Xuan, J.; Lu, Y.; Lu, S.; Zhu, W. De novo transcriptome sequencing and gene expression profiling of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) leaves under heat stress. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Jiao, C.; Sun, H.; Cai, X.; Wang, X.; Ge, C.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, W.; Sun, X.; Xu, Y.; et al. Draft genome of spinach and transcriptome diversity of 120 Spinacia accessions. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Sun, X.; Xu, C.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Ge, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Fei, Z.; Jiao, C.; et al. Genomic analyses provide insights into spinach domestication and the genetic basis of agronomic traits. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thebud, R.; Santarius, K.A. Effects of high-temperature stress on various biomembranes of leaf cells in situ and in vitro. Plant Physiol. 1982, 70, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yu, W.; Gong, F.; Xu, H.; Lyu, J.; Zhou, X. Golden 2-like Transcription Factors Regulate Photosynthesis under UV-B Stress by Regulating the Calvin Cycle. Plants 2024, 13, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, M.A.; Du, H.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, G.; Huang, Y.; Ni, X.; Chen, F.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Tang, Q.; et al. A dominant role of transcriptional regulation during the evolution of C4 photosynthesis in Flaveria species. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Bao, X.; Bian, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Cai, X.; Wang, Q.; et al. Heat-Responsive Proteomics of a Heat-Sensitive Spinach Variety. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmis, J.N.; Ayliffe, M.A.; Huang, C.Y.; Martin, W. Endosymbiotic gene transfer: Organelle genomes forge eukaryotic chromosomes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, M.; Uchida, S.; Mori, H.; Komayama, K.; Ohira, S.; Morita, N.; Nakanishi, T.; Yamamoto, Y. Quality control of photosystem II. Cleavage of reaction center D1 protein in spinach thylakoids by FtsH protease under moderate heat stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 21660–21669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komayama, K.; Khatoon, M.; Takenaka, D.; Horie, J.; Yamashita, A.; Yoshioka, M.; Nakayama, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Ohira, S.; Morita, N.; et al. Quality control of Photosystem II: Cleavage and aggregation of heat-damaged D1 protein in spinach thylakoids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1767, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.L.; Yu, Q.B.; Sun, Y.; Lu, Y.; Cui, Y.L.; Yang, Z.N. A point mutation in the pentatricopeptide repeat motif of the AtECB2 protein causes delayed chloroplast development. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruse, B.; Narasimhan, N.; Attardi, G. Termination of transcription in human mitochondria: Identification and purification of a DNA binding protein factor that promotes termination. Cell 1989, 58, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asin-Cayuela, J.; Gustafsson, C.M. Mitochondrial transcription and its regulation in mammalian cells. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2007, 32, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberti, M.; Polosa, P.L.; Bruni, F.; Deceglie, S.; Gadaleta, M.N.; Cantatore, P. MTERF factors: A multifunction protein family. Biomol. Concepts 2010, 1, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meskauskiene, R.; Wursch, M.; Laloi, C.; Vidi, P.A.; Coll, N.S.; Kessler, F.; Baruah, A.; Kim, C.; Apel, K. A mutation in the Arabidopsis mTERF-related plastid protein SOLDAT10 activates retrograde signaling and suppresses 1O2-induced cell death. Plant J. 2009, 60, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wobbe, L.; Nixon, P.J. The mTERF protein MOC1 terminates mitochondrial DNA transcription in the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 6553–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powikrowska, M.; Oetke, S.; Jensen, P.E.; Krupinska, K. Dynamic composition, shaping and organization of plastid nucleoids. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammani, K.; Barkan, A. An mTERF domain protein functions in group II intron splicing in maize chloroplasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 5033–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, X.; Yang, C.; Li, L. Peanut AhmTERF1 Regulates Root Growth by Modulating Mitochondrial Abundance. Genes 2023, 14, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhou, F.; Wang, H.M.; Xue, X.; Liu, Y.G.; Zhang, Q.Y. A rice mTERF protein V14 sustains photosynthesis establishment and temperature acclimation in early seedling leaves. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, A.; Ge, S.; Zhou, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, H.; et al. Analysis of the Tomato mTERF Gene Family and Study of the Stress Resistance Function of SLmTERF-13. Plants 2023, 12, 2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terzioglu, M.; Ruzzenente, B.; Harmel, J.; Mourier, A.; Jemt, E.; Lopez, M.D.; Kukat, C.; Stewart, J.B.; Wibom, R.; Meharg, C.; et al. MTERF1 binds mtDNA to prevent transcriptional interference at the light-strand promoter but is dispensable for rRNA gene transcription regulation. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Silva, P.; Martinez-Azorin, F.; Micol, V.; Attardi, G. The human mitochondrial transcription termination factor (mTERF) is a multizipper protein but binds to DNA as a monomer, with evidence pointing to intramolecular leucine zipper interactions. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 1066–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wobbe, L. The Molecular Function of Plant mTERFs as Key Regulators of Organellar Gene Expression. Plant Cell Physiol. 2021, 61, 2004–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melonek, J.; Small, I. Triticeae genome sequences reveal huge expansions of gene families implicated in fertility restoration. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2022, 66, 102166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhang, B.; Lu, Q.; Wen, X.; Wang, Y.; Lu, C. mTERF5 Acts as a Transcriptional Pausing Factor to Positively Regulate Transcription of Chloroplast psbEFLJ. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 1259–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meteignier, L.V.; Ghandour, R.; Meierhoff, K.; Zimmerman, A.; Chicher, J.; Baumberger, N.; Alioua, A.; Meurer, J.; Zoschke, R.; Hammani, K. The Arabidopsis mTERF-repeat MDA1 protein plays a dual function in transcription and stabilization of specific chloroplast transcripts within the psbE and ndhH operons. New Phytol. 2020, 227, 1376–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y.L.; Zhang, X.L.; Yu, Q.B.; Wang, X.; Yuan, X.B.; Qin, X.M.; He, X.F.; Huang, C.; Yang, Z.N. A nuclear-encoded protein, mTERF6, mediates transcription termination of rpoA polycistron for plastid-encoded RNA polymerase-dependent chloroplast gene expression and chloroplast development. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.B.; Wang, J.; Huang, C.; Rochaix, J.D.; Lin, F.M.; Zhang, J.X.; Ye, L.S.; Shi, X.H.; Yu, Q.B.; Yang, Z.N. mTERF8, a Member of the Mitochondrial Transcription Termination Factor Family, Is Involved in the Transcription Termination of Chloroplast Gene psbJ. Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 408–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Tang, R.; Shi, Y.; Ke, X.; Wang, Y.; Che, Y.; Luan, S.; Hou, X. Arabidopsis Seedling Lethal 1 Interacting With Plastid-Encoded RNA Polymerase Complex Proteins Is Essential for Chloroplast Development. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 602782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada, V.; Sarmiento-Manus, R.; Gonzalez-Bayon, R.; Hricova, A.; Perez-Marcos, R.; Gracia-Martinez, E.; Medina-Ruiz, L.; Leyva-Diaz, E.; Ponce, M.R.; Micol, J.L. Arabidopsis RUGOSA2 encodes an mTERF family member required for mitochondrion, chloroplast and leaf development. Plant J. 2011, 68, 738–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michotey, C. Plant Bioinformatics Facility (PlantBioinfoPF) data management plan. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombauts, S.; Dehais, P.; Van Montagu, M.; Rouze, P. PlantCARE, a plant cis-acting regulatory element database. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 295–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, U.G.; Zauner, S.; Woehle, C.; Bolte, K.; Hempel, F.; Allen, J.F.; Martin, W.F. Massively convergent evolution for ribosomal protein gene content in plastid and mitochondrial genomes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 2318–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, N.; Lloyd, J.; Sweeney, C.; Myouga, F.; Meinke, D. Identification of nuclear genes encoding chloroplast-localized proteins required for embryo development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2011, 155, 1678–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkan, A.; Klipcan, L.; Ostersetzer, O.; Kawamura, T.; Asakura, Y.; Watkins, K.P. The CRM domain: An RNA binding module derived from an ancient ribosome-associated protein. RNA 2007, 13, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupinska, K.; Oetke, S.; Desel, C.; Mulisch, M.; Schafer, A.; Hollmann, J.; Kumlehn, J.; Hensel, G. WHIRLY1 is a major organizer of chloroplast nucleoids. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Yu, Q.; Sun, M.; Xu, X. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the mTERF Gene Family in Spinach and the Role of SomTERF5 in Response to Heat Stress. Plants 2025, 14, 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111570
Sun Z, Li L, Liu Y, Liu Y, Li G, Li Y, Yu Q, Sun M, Xu X. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the mTERF Gene Family in Spinach and the Role of SomTERF5 in Response to Heat Stress. Plants. 2025; 14(11):1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111570
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Ziyue, Li Li, Yaqi Liu, Yanshuang Liu, Gaojian Li, Yueyue Li, Qingbo Yu, Meihong Sun, and Xiaofeng Xu. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the mTERF Gene Family in Spinach and the Role of SomTERF5 in Response to Heat Stress" Plants 14, no. 11: 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111570
APA StyleSun, Z., Li, L., Liu, Y., Liu, Y., Li, G., Li, Y., Yu, Q., Sun, M., & Xu, X. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the mTERF Gene Family in Spinach and the Role of SomTERF5 in Response to Heat Stress. Plants, 14(11), 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111570






