Efficient Virus-Induced Gene Silencing (VIGS) Method for Discovery of Resistance Genes in Soybean
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
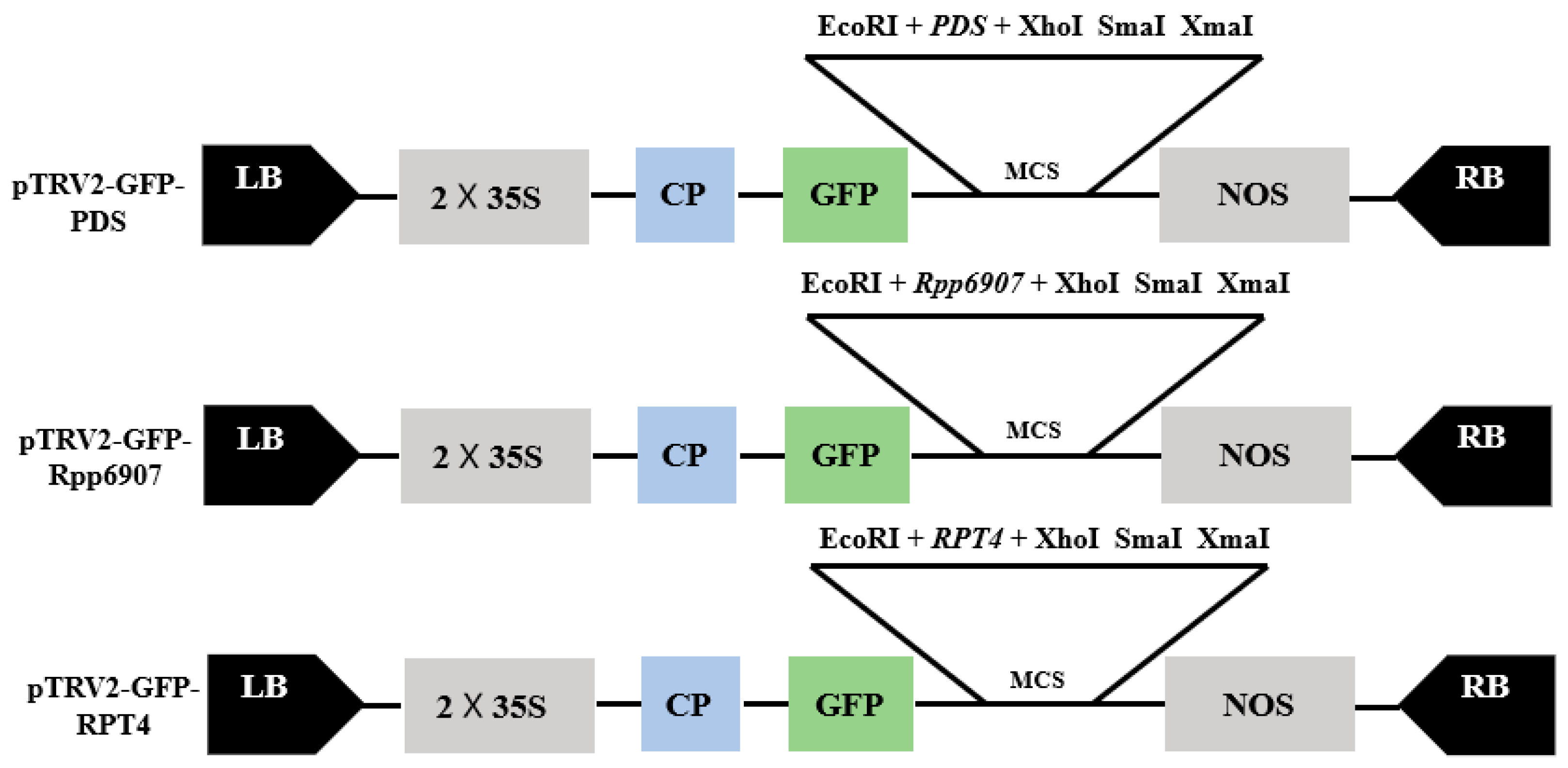
2.1. Construction of TRV–VIGS Vector
2.2. Agroinfiltration Methods
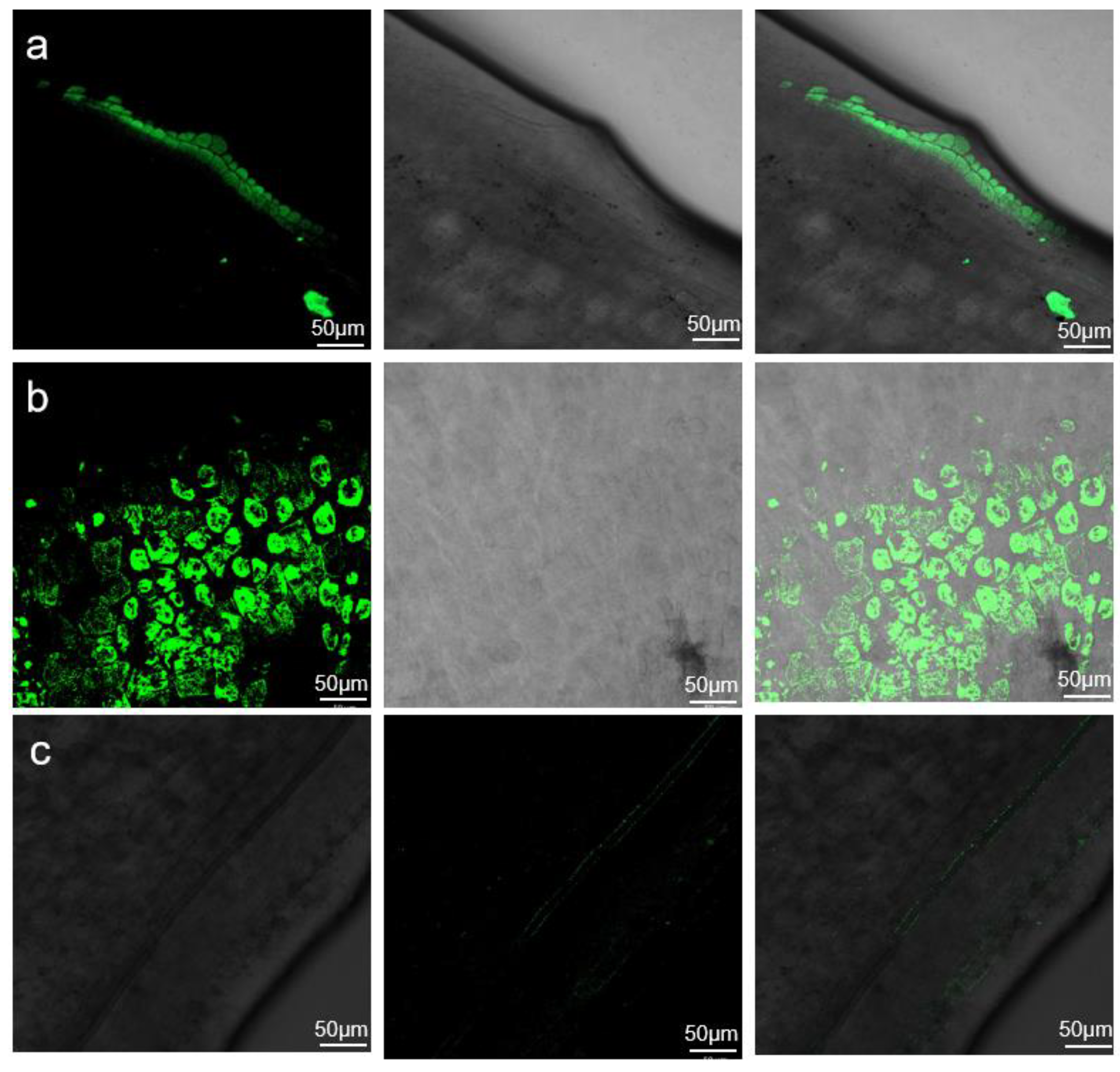
2.3. GFP Fluorescence Evaluation of Agrobacterium Infection Efficiency
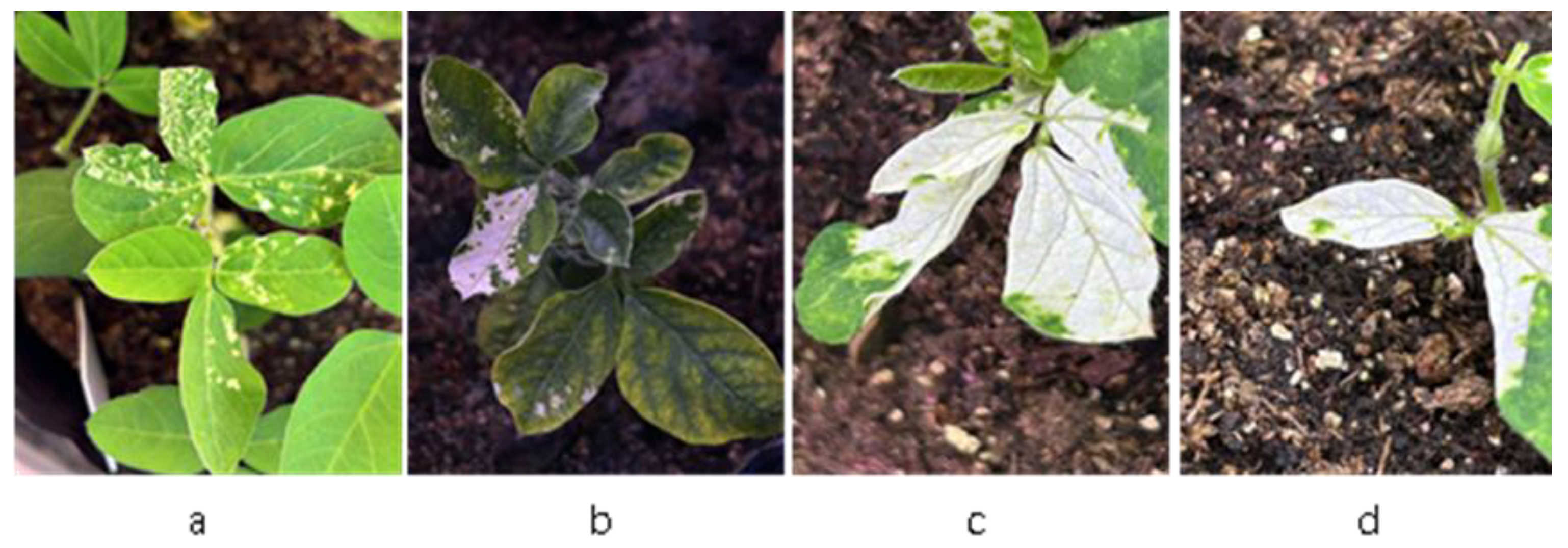
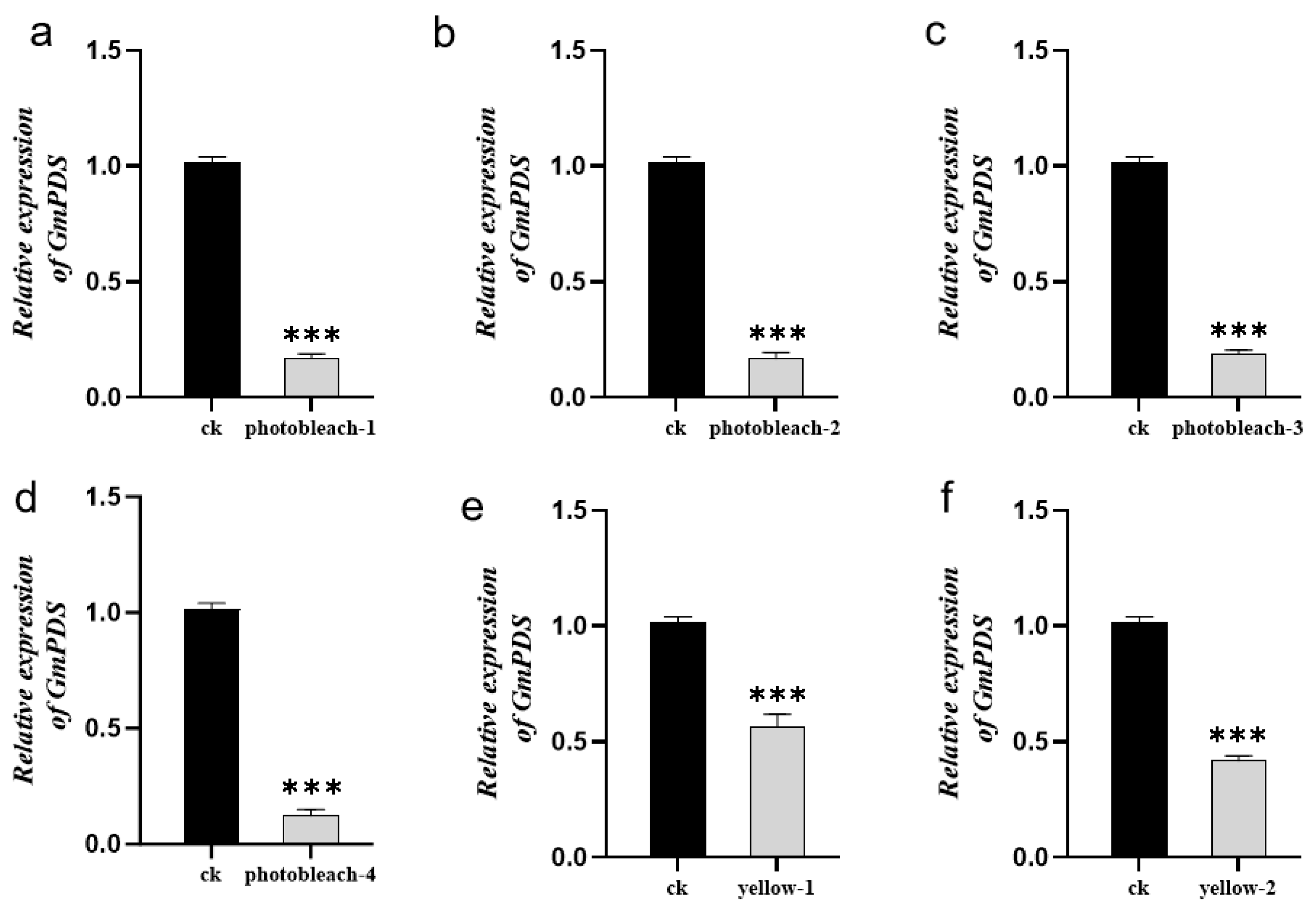
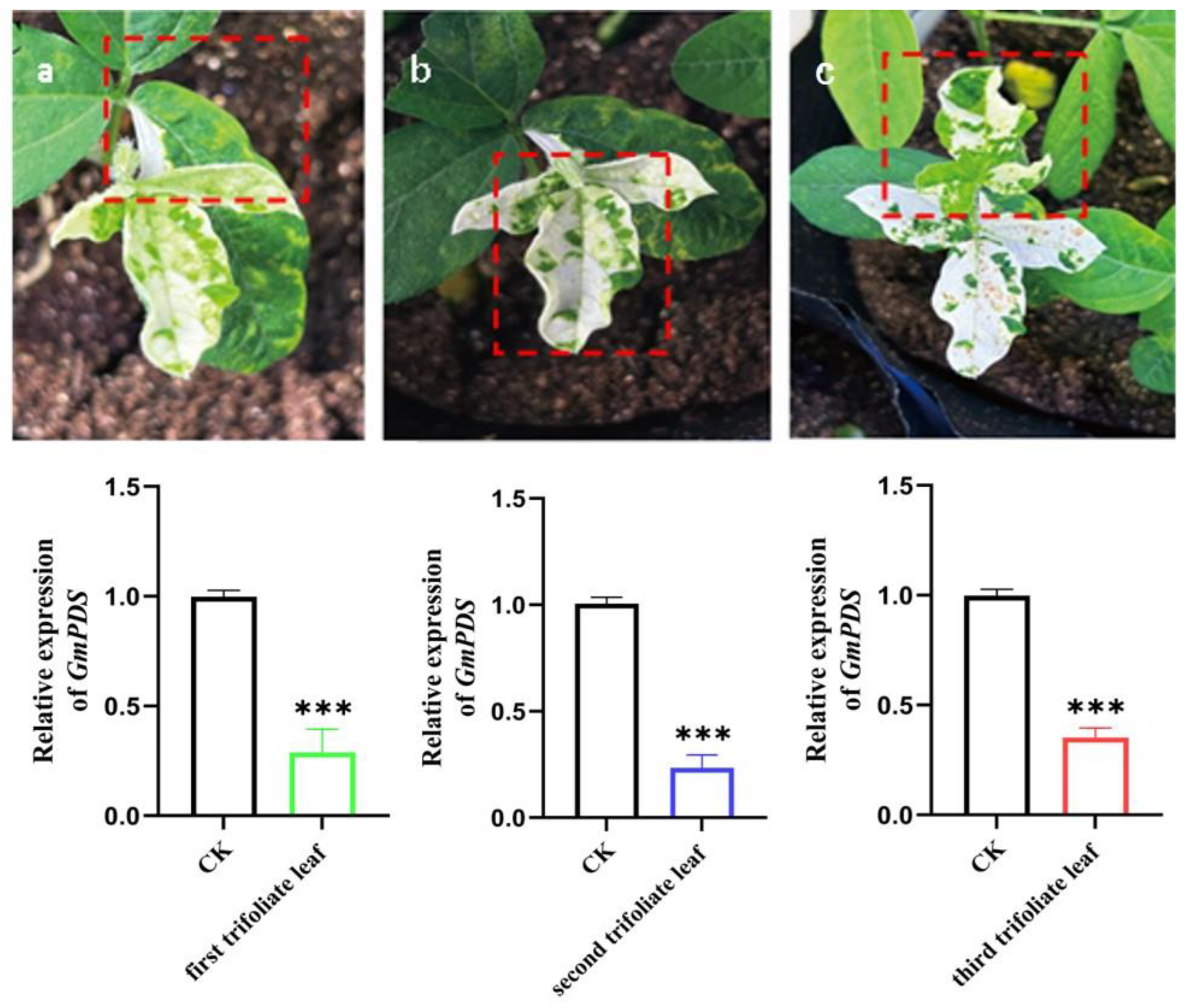
2.4. GmPDS Silencing in Soybean
2.5. Systematic Silencing of TRV–VIGS
2.6. Application of TRV–VIGS System
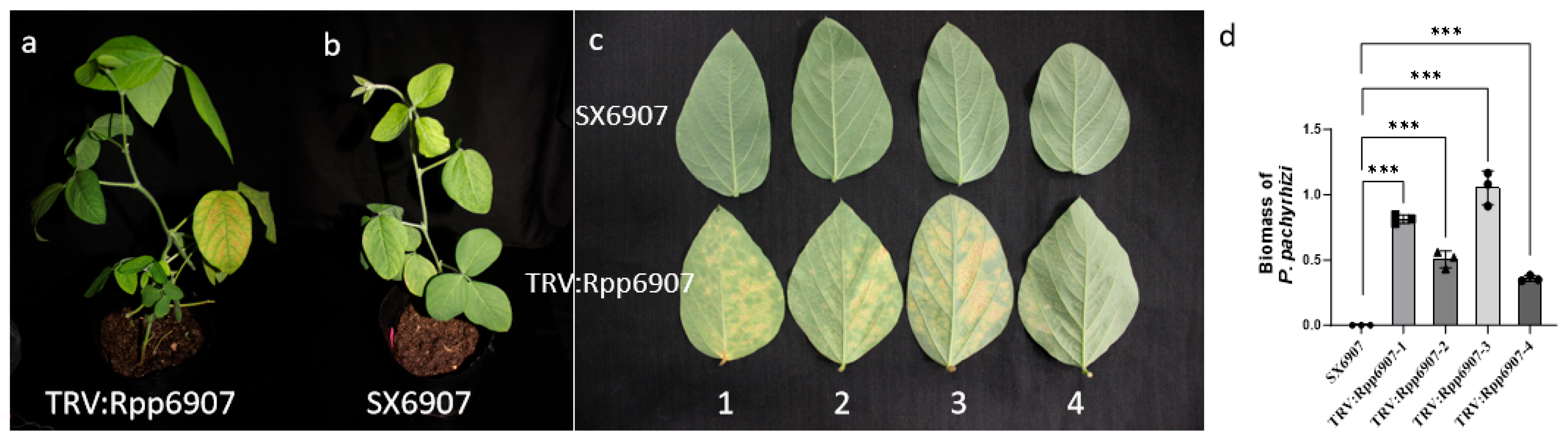
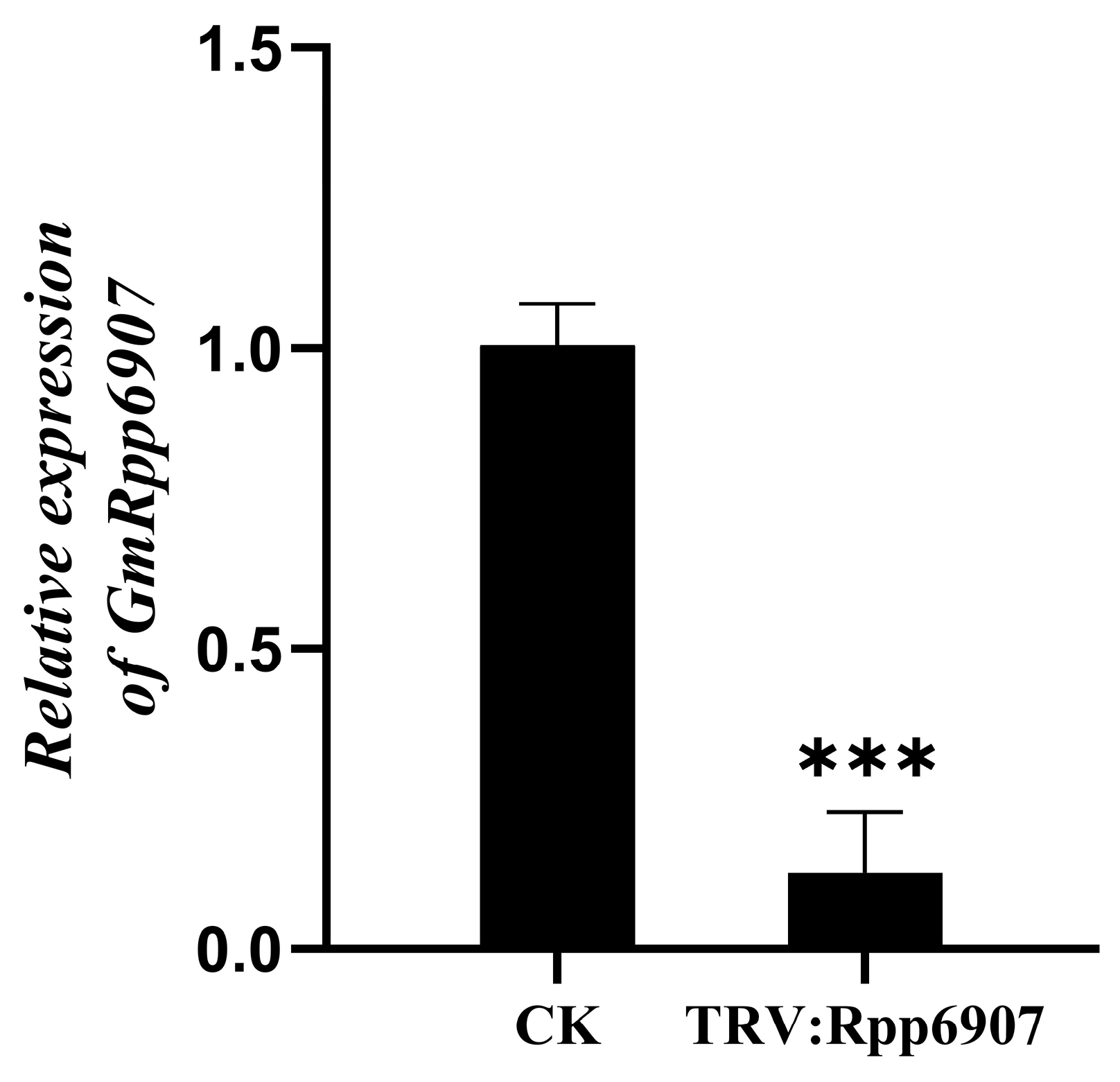
2.6.1. Functional Analysis of the GmRpp6907 Gene Using the TRV–VIGS System
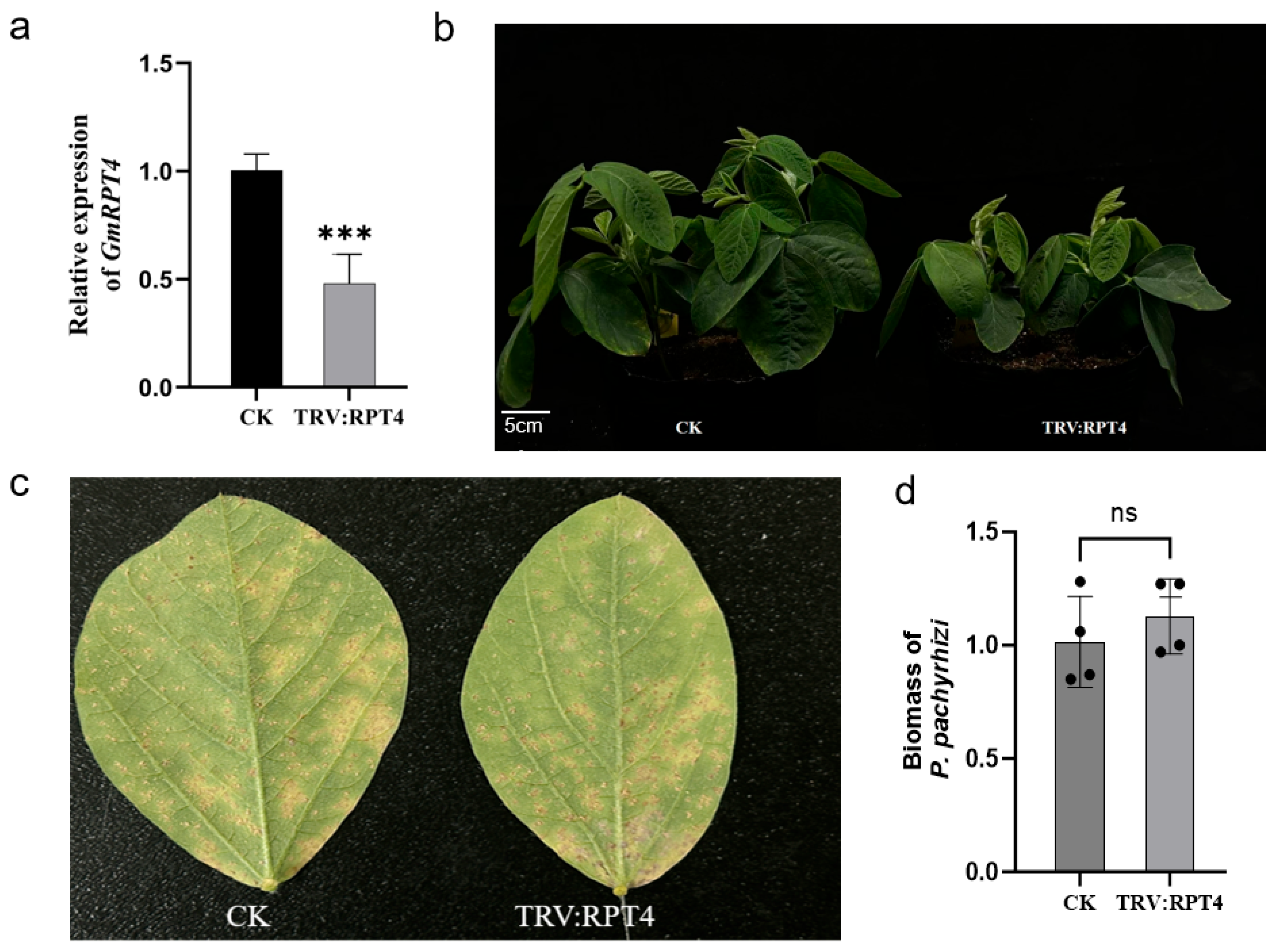
2.6.2. Functional Identification of GmRPT4
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Soybean Rust Pathogen
4.2. Developing TRV–VIGS Constructs
4.3. Preparation of Infection Solution
4.4. Explant Preparation and Infection
4.5. Explant Co-Cultivation
4.6. Fluorescence Observation
4.7. Total RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
4.8. P. pachyrhizi Infection and Phenotypic Analyses
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whitham, S.A.; Qi, M.; Innes, R.W.; Ma, W.; Lopes-Caitar, V.; Hewezi, T. Molecular soybean-pathogen interactions. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2016, 54, 443–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savary, S.; Willocquet, L.; Pethybridge, S.J.; Esker, P.; McRoberts, N.; Nelson, A. The global burden of pathogens and pests on major food crops. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Fang, C.; Li, Y.; Kong, F.; Liu, B. Understandings and future challenges in soybean functional genomics and molecular breeding. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2023, 65, 468–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rössner, C.; Lotz, D.; Becker, A. VIGS Goes Viral: How VIGS transforms our understanding of plant science. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2022, 73, 703–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, S.; Farooq, M.A.; Zhao, T.; Wang, P.; Tabusam, J.; Wang, Y.; Xuan, S.; Zhao, J.; Chen, X.; Shen, S.; et al. Virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS): A powerful tool for crop improvement and its advancement towards epigenetics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.; Yellina, A.L.; Orashakova, S.; Becker, A. Virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) in plants: An overview of target species and the virus-derived vector systems. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 975, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramegowda, V.; Mysore, K.S.; Senthil-Kumar, M. Virus-induced gene silencing is a versatile tool for unraveling the functional relevance of multiple abiotic-stress-responsive genes in crop plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin, G.D.; Krath, B.N.; MacFarlane, S.A.; Nicolaisen, M.; Johansen, I.E.; Lund, O.S. Virus-induced gene silencing as a tool for functional genomics in a legume species. Plant J. 2004, 40, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Lim, S.; Kang, Y.J.; Yoon, M.Y.; Nam, M.; Jun, T.H.; Seo, M.J.; Baek, S.B.; Lee, J.H.; Moon, J.K.; et al. Optimization of a virus-induced gene silencing system with soybean yellow common mosaic virus for gene function studies in soybeans. Plant Pathol. J. 2016, 32, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Camino, C.; Annamalai, P.; Sanchez, F.; Kachroo, A.; Ghabrial, S.A. An effective virus-based gene silencing method for functional genomics studies in common bean. Plant Methods 2011, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, N.; Yoshikawa, N. Virus-induced gene silencing in soybean seeds and the emergence stage of soybean plants with apple latent spherical virus vectors. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 71, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamatsu, A.; Masuta, C.; Senda, M.; Matsuura, H.; Kasai, A.; Hong, J.S.; Kitamura, K.; Abe, J.; Kanazawa, A. Functional analysis of soybean genes involved in flavonoid biosynthesis by virus-induced gene silencing. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2007, 5, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandoth, P.K.; Heinz, R.; Yeckel, G.; Gross, N.W.; Juvale, P.S.; Hill, J.; Whitham, S.A.; Baum, T.J.; Mitchum, M.G. A virus-induced gene silencing method to study soybean cyst nematode parasitism in Glycine max. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, B.; Campbell, K.B.; McMahon, M.B.; Luster, D.G. Disruption of Rpp1-mediated soybean rust immunity by virus-induced gene silencing. Plant Signal Behav. 2013, 8, e27543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Karthikeyan, A.; Wang, L.; Zong, T.; Wang, T.; Yin, J.; Hu, T.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Cui, Y.; et al. Digs out and characterization of the resistance gene accountable to soybean mosaic virus in soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 4217–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.D.; Lan, H.J.; Masoud, H.S.; Ye, M.Y.; Dai, X.Y.; Zhong, C.L.; Tian, S.N.; Liu, J.Z. Silencing GmBIR1 in soybean results in activated defense responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, C.E.; Lincoln, L.M.; O’Rourke, J.A.; Graham, M.A. Virus induced gene silencing confirms oligogenic inheritance of brown stem rot resistance in soybean. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1292605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Hao, M.; Tian, B.; Cao, G.; Wei, F.; Xie, Z. A methodological advance of tobacco rattle virus-induced gene silencing for functional genomics in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 671091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachan, S.; Dinesh-Kumar, S.P. Tobacco rattle virus (TRV)-based virus-induced gene silencing. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 894, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkostefanakis, S.; Sedeek, K.E.; Raad, M.; Zaki, M.S.; Kalaitzis, P. Virus induced gene silencing of three putative prolyl 4-hydroxylases enhances plant growth in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 85, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil-Kumar, M.; Mysore, K.S. Tobacco rattle virus-based virus-induced gene silencing in Nicotiana benthamiana. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, S.R.; Jones, M.L. An optimized protocol to increase virus-induced gene silencing efficiency and minimize viral symptoms in petunia. Plant Mol. Biol. Report 2014, 32, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.; Seong, E.; Kim, Y.C.; Chung, E.J.; Oh, S.K.; Lee, S.; Park, J.M.; Joung, Y.H.; Choi, D. A method of high frequency virus-induced gene silencing in chili pepper (Capsicum annuum L. cv. Bukang). Mol. Cells 2004, 17, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Baltanás, V.; De Jaeger-Braet, J.; Cher, W.Y.; Schönbeck, N.; Chae, E.; Schnittger, A.; Wijnker, E. Knock-down of gene expression throughout meiosis and pollen formation by virus-induced gene silencing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2022, 111, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wheeler, T.; Li, Z.; Kenerley, C.M.; He, P.; Shan, L. Silencing GhNDR1 and GhMKK2 compromises cotton resistance to verticillium wilt. Plant J. 2011, 66, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Geng, R.; Ren, M.; Cheng, L.; Liu, D.; Jiang, C.; Wen, L.; Xiao, Z.; Yang, A. Genome-wide identification of the TIFY gene family in tobacco and expression analysis in response to ralstonia solanacearum infection. Genomics 2024, 116, 110823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, F.; Fu, X.; Min, D.; Ali, M.; Zhao, X.; Song, Y.; Ding, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, X. SlMsrB5 contributes to the chilling tolerance induced by methyl jasmonate in postharvest tomato fruit. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 322, 112386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Qayyum, A.; Farooq, S.; Almutairi, S.M.; Rasheed, R.A.; Qadir, M.; Vyhnánek, T.; Sun, Y. Pepper immunity against ralstonia solanacearum is positively regulated by CaWRKY3 through modulation of different WRKY transcription factors. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.J.; Snoeren, T.A.; Hogewoning, S.W.; van Loon, J.J.; Dicke, M. Disruption of plant carotenoid biosynthesis through virus-induced gene silencing affects oviposition behaviour of the butterfly pieris rapae. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.Z.; Chen, J.C.; Reid, M. Virus-induced gene silencing in ornamental plants. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 744, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, K.; Xu, K.; Zhang, F.; Wang, J.; Tan, G.; Nie, X.; Ji, Q.; et al. Vacuum and co-cultivation agroinfiltration of (germinated) seeds results in tobacco rattle virus (TRV) mediated whole-plant virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) in wheat and maize. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Z.; Graham, M.A.; Pedley, K.F.; Whitham, S.A. Gaining insight into soybean defense responses using functional genomics approaches. Brief Funct. Genom. 2015, 14, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juvale, P.S.; Hewezi, T.; Zhang, C.; Kandoth, P.K.; Mitchum, M.G.; Hill, J.H.; Whitham, S.A.; Baum, T.J. Temporal and spatial bean pod mottle virus-induced gene silencing in soybean. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Sun, J.; Liu, N.; Sun, X.; Liu, C.; Wu, L.; Liu, G.; Zeng, F.; Hou, C.; Han, S.; et al. A novel cysteine-rich receptor-like kinase gene, TaCRK2, contributes to leaf rust resistance in wheat. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 21, 732–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cheng, P.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Hu, Z.; Xin, D.; Wu, X.; Yang, M.; Chen, Q. A highly efficient soybean transformation system using GRF3-GIF1 chimeric protein. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2025, 67, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Pei, H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, W.; Yang, R.; Meng, Y.; You, J.; Gao, J.; Ma, N. TRV-GFP: A modified tobacco rattle virus vector for efficient and visualizable analysis of gene function. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Xie, Y.; Liu, G.; Wei, Y.; Hu, W.; Shi, H. Agrobacterium-mediated gene transient overexpression and tobacco rattle virus (TRV)-based gene silencing in cassava. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Yuan, X.; Wu, Z.; Khan, M.A.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Gong, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, J.; Wu, C.; et al. Virus-induced gene silencing for comparative functional studies in Gladiolus hybridus. Plant Cell. Rep. 2014, 33, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragonés, V.; Aliaga, F.; Pasin, F.; Daròs, J.A. Simplifying plant gene silencing and genome editing logistics by a one-agrobacterium system for simultaneous delivery of multipartite virus vectors. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 17, e2100504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.D.G.; Staskawicz, B.J.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system: From discovery to deployment. Cell 2024, 187, 2095–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, N.; Li, F.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D. Establishment of TRV-mediated transient gene-silencing system in soybean. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2015, 48, 2479–2486. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Name | Sequence (5′→3′) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| PDS-F | taaggttaccGAATTCTCTCCGCGTCCTCTAAAAC | Vector construction |
| PDS-R | atgcccgggcCTCGAGTCCAGGCTTATTTGGCATAGC | |
| Rpp6907-F | taaggttaccGAATTCTCGGCAAAGTTGGTTTTCATCT | |
| Rpp6907-R | atgcccgggcCTCGAGCCATTCCTGGGCTCCACATT | |
| RPT4-F | taaggttaccGAATTCTTTTCCGCACTGATGGTATT | |
| RPT4-R | atgcccgggcCTCGAGAGAGCAGCCTCGTTCAAGTA |
| Name | Sequence (5′→3′) | Amplification Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Actin-F | ATTGGACTCTGGTGATGGTG | 104.2 |
| Actin-R | TCAGCAGAGGTGGTGAACAT | |
| qPDS-F | TCGCTTCTTCAGACGCCAC | 94.5 |
| qPDS-R | TATGCCCAGCATCAGCCAAA | |
| qRpp6907-F | TCGGCAAAGTTGGTTTTCATCT | 93.0 |
| qRpp6907-R | CCATTCCTGGGCTCCACATT | |
| qRPT4-F | TTTTCCGCACTGATGGTATT | 94.9 |
| qRPT4-R | AGCAGCCTCGTTCAAGTA | |
| RT-Pp-α-tubulin-F | CCAAGGCTTCTTCGTGTTTCA | 108.4 |
| RT-Pp-α-tubulin-R | CAAGAGAAGAGCGCCAAACC | |
| RT-GmUbiquitin-3-F | GTGTAATGTTGGATGTGTTCCC | 108.3 |
| RT-GmUbiquitin-3-R | ACACAATTGAGTTCAACACAAACCG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, K.; Lu, Z.; Yang, H.; Chen, S.; Li, C.; Cao, D.; Wang, H.; Hao, Q.; Chen, H.; Shan, Z. Efficient Virus-Induced Gene Silencing (VIGS) Method for Discovery of Resistance Genes in Soybean. Plants 2025, 14, 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101547
Deng K, Lu Z, Yang H, Chen S, Li C, Cao D, Wang H, Hao Q, Chen H, Shan Z. Efficient Virus-Induced Gene Silencing (VIGS) Method for Discovery of Resistance Genes in Soybean. Plants. 2025; 14(10):1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101547
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Kelin, Zihua Lu, Hongli Yang, Shuilian Chen, Chao Li, Dong Cao, Hongwei Wang, Qingnan Hao, Haifeng Chen, and Zhihui Shan. 2025. "Efficient Virus-Induced Gene Silencing (VIGS) Method for Discovery of Resistance Genes in Soybean" Plants 14, no. 10: 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101547
APA StyleDeng, K., Lu, Z., Yang, H., Chen, S., Li, C., Cao, D., Wang, H., Hao, Q., Chen, H., & Shan, Z. (2025). Efficient Virus-Induced Gene Silencing (VIGS) Method for Discovery of Resistance Genes in Soybean. Plants, 14(10), 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101547





